
YuLan-Mini
A highly capable 2.4B lightweight LLM using only 1T pre-training data with all details.
Stars: 168
YuLan-Mini is a lightweight language model with 2.4 billion parameters that achieves performance comparable to industry-leading models despite being pre-trained on only 1.08T tokens. It excels in mathematics and code domains. The repository provides pre-training resources, including data pipeline, optimization methods, and annealing approaches. Users can pre-train their own language models, perform learning rate annealing, fine-tune the model, research training dynamics, and synthesize data. The team behind YuLan-Mini is AI Box at Renmin University of China. The code is released under the MIT License with future updates on model weights usage policies. Users are advised on potential safety concerns and ethical use of the model.
README:
YuLan-Mini is a lightweight language model with 2.4 billion parameters. It achieves performance comparable to industry-leading models trained on significantly more data, despite being pre-trained on only 1.08T tokens. The model excels particularly in the domains of mathematics and code. To facilitate reproducibility, we open-source the relevant pre-training resources and post-training technical report.
- [2025.03.16] Math, code, & reasoninig classifiers released
- [2025.03.07] W&B Logs for ablation studies released
- [2025.02.28] YuLan-Mini-Instruct released
- [2025.01.29] YuLan-Mini-Instruct-v1 released
- [2024.12.23] YuLan-Mini & pre-training resources released
YuLan-Mini is part of the YuLan family, which includes models with larger sizes and different training strategies.
| Model | Context Length | SFT | 🤗 Hugging Face | ModelScope | Wise Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YuLan-Mini | 28K | ❎ | Base |
Base |
Base |
| YuLan-Mini-Instruct | 28K | ✅ | Instruct |
The intermediate checkpoint can be found here
Our pre-training methodology improves training efficiency through three key innovations:
- an elaborately designed data pipeline that combines data cleaning with data schedule strategies;
- a systematic optimization method that can effectively mitigate training instability;
- an effective annealing approach that integrate targeted data selection and long context training.
| Models | MMLU | CEVAL | GSM8K | ARC_CHALLENGE | GPQA | MATH | HUMANEVAL@1 | MBPP@10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen-2.5-1.5B-Instruct | 57.5 | 65.4 | 73.2 | 47.8 | 29.8 | 55.2 | 61.6 | 88.1 |
| Llama3.2-3B-Instruct | 60 | 45.9 | 43.4 | 78.6 | 38.6 | 48 | 51.5 | 80.4 |
| YuLan-Mini-Instruct | 53.6 | 50.5 | 82.3 | 51.8 | 30.1 | 55.2 | 67.7 | 85.7 |
Note: The model size calculation includes the embedding size.
| Models | Model Size | # Train Tokens | Context Length | MATH 500 | GSM 8K | Human Eval | MBPP | RACE Middle | RACE High | RULER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MiniCPM | 2.71B | 1.06T | 4K | 15.00 | 53.83 | 50.00* | 47.31 | 56.61 | 44.27 | N/A |
| Qwen-2 | 1.54B | 7T | 128K | 22.60 | 46.90* | 34.80* | 46.90* | 55.77 | 43.69 | 60.16 |
| Qwen2.5 | 0.49B | 18T | 128K | 23.60 | 41.60* | 30.50* | 39.30* | 52.36 | 40.31 | 49.23 |
| Qwen2.5 | 1.54B | 18T | 128K | 45.40 | 68.50* | 37.20* | 60.20* | 58.77 | 44.33 | 68.26 |
| Gemma2 | 2.61B | 2T | 8K | 18.30* | 30.30* | 19.50* | 42.10* | - | - | N/A |
| StableLM2 | 1.64B | 2T | 4K | - | 20.62 | 8.50* | 17.50 | 56.33 | 45.06 | N/A |
| SmolLM2 | 1.71B | 11T | 8K | 11.80 | - | 23.35 | 45.00 | 55.77 | 43.06 | N/A |
| Llama3.2 | 3.21B | 9T | 128K | 7.40 | - | 29.30 | 49.70 | 55.29 | 43.34 | 77.06 |
| YuLan-Mini | 2.42B | 1.04T | 4K | 32.60 | 66.65 | 61.60 | 66.70 | 55.71 | 43.58 | N/A |
| YuLan-Mini | 2.42B | 1.08T | 28K | 37.80 | 68.46 | 64.00 | 65.90 | 57.18 | 44.57 | 51.48 |
| Models | LAMBADA | MMLU | CMMLU | CEval | HellaSwag | WinoGrande | StoryCloze | ARC-e | ARC-c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MiniCPM-2.71B | 61.91 | 53.37 | 48.97 | 48.24 | 67.92 | 65.74 | 78.51 | 55.51 | 43.86 |
| Qwen2-1.54B | 64.68 | 55.90 | 70.76 | 71.94 | 66.11 | 66.14 | 77.60 | 62.21 | 42.92 |
| Qwen2.5-0.49B | 52.00 | 47.50 | 52.17 | 54.27 | 50.54 | 55.88 | 71.67 | 56.10 | 39.51 |
| Qwen2.5-1.54B | 62.12 | 60.71 | 67.82 | 69.05 | 67.18 | 64.48 | 76.80 | 71.51 | 53.41 |
| Gemma2-2.61B | - | 52.20* | - | 28.00* | 74.60* | 71.50* | - | - | 55.70* |
| StableLM2-1.64B | 66.15 | 40.37 | 29.29 | 26.99 | 69.79 | 64.64 | 78.56 | 54.00 | 40.78 |
| SmolLM2-1.71B | 67.42 | 51.91 | 33.46 | 35.10 | 72.96 | 67.40 | 79.32 | 44.82 | 35.49 |
| Llama3.2-3.21B | 69.08 | 63.40 | 44.44 | 44.49 | 75.62 | 67.48 | 76.80 | 70.12 | 48.81 |
| YuLan-Mini-2.42B-4K | 64.72 | 51.79 | 48.35 | 51.47 | 68.65 | 67.09 | 76.37 | 69.87 | 50.51 |
| YuLan-Mini-2.42B-28K | 65.67 | 49.10 | 45.45 | 48.23 | 67.22 | 67.24 | 75.89 | 67.47 | 49.32 |
To enhance research transparency and reproducibility, we are open-sourcing relevant pre-training resources:
1. Pre-training and Evaluation Code
The pre-training code can be found here. Note that due to subsequent code modifications, this code may not run directly and may require some adjustments.
Due to the implementation of Hugging Face Trainer, certain parameters are stored in the config.json file and cannot be modified through the Trainer's command-line arguments. Therefore, you need to update these parameters in the config.json file first, particularly:
-
save_steps: The frequency of saving intermediate checkpoints. -
train_batch_size: The batch size per GPU (equivalent toper_device_train_batch_sizein the Trainer). We used a batch size of 1008 (approximately 4M tokens) during the stable training stage. Maintaining this same batch size is equally important for training effectiveness.
Below is an example of a properly configured config.json file:
{
"best_metric": null,
"best_model_checkpoint": null,
"epoch": 0.0,
"eval_steps": 500,
"global_step": 0,
"is_hyper_param_search": false,
"is_local_process_zero": true,
"is_world_process_zero": true,
"log_history": [],
"logging_steps": 3,
"max_steps": 0,
"num_input_tokens_seen": 0,
"num_train_epochs": 0,
"save_steps": 250,
"stateful_callbacks": {
"TrainerControl": {
"args": {
"should_epoch_stop": false,
"should_evaluate": false,
"should_log": false,
"should_save": true,
"should_training_stop": true
},
"attributes": {}
}
},
"total_flos": 0,
"train_batch_size": 3,
"trial_name": null,
"trial_params": null
}
To ensure DeepSpeed Integration loads the Universal Checkpoint, you need to enable this feature in the DeepSpeed configuration JSON file.
Here is an example of a ZeRO2 configuration with Universal Checkpointing enabled:
{
"bf16": {
"enabled": "auto"
},
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 2,
"allgather_partitions": true,
"allgather_bucket_size": 8e8,
"overlap_comm": true,
"reduce_scatter": true,
"reduce_bucket_size": 8e8,
"contiguous_gradients": true
},
"gradient_accumulation_steps": "auto",
"gradient_clipping": "auto",
"steps_per_print": 16,
"train_batch_size": "auto",
"train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu": "auto",
"wall_clock_breakdown": false,
"dump_state": true,
"optimizer": {
"type": "AdamW",
"params": {
"lr": "auto",
"betas": "auto",
"eps": "auto",
"weight_decay": "auto"
}
},
"checkpoint": {
"load_universal": true
}
}
When calling trainer.train, include the resume_from_checkpoint argument to load the distributed optimizer state from the Universal Checkpoint and resume training.
trainer.train(resume_from_checkpoint=training_args.resume_from_checkpoint)
We provide an internal training framework for your reference, but you are free to choose other frameworks.
2. Intermediate Stage Checkpoints
The intermediate stage checkpoints are released in YuLan-Mini.| Stage | Curriculum Phase | 4K Context | 28K Context | Optimizer | Inference Architecture | LAMBADA Acc
|
GSM8K Acc
|
HumanEval pass@1
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stable | 5 | YuLan-Mini-Phase5 | yulanmini |
53.85 | 3.41 | 12.26 | ||
| Stable | 10 | YuLan-Mini-Phase10 | yulanmini |
55.00 | 9.57 | 15.95 | ||
| Stable | 15 | YuLan-Mini-Phase15 | yulanmini |
55.81 | 13.81 | 16.99 | ||
| Stable | 20 | YuLan-Mini-Phase20 | ✅ | yulanmini |
55.81 | 21.39 | 20.79 | |
| Stable | 25 (1T tokens) | YuLan-Mini-Before-Annealing | ✅ | yulanmini |
55.67 | 29.94 | 34.06 | |
| Annealing | 26 | YuLan-Mini-4K |
llama* |
64.72 | 66.65 | 61.60 | ||
| Annealing | 27 | YuLan-Mini |
llama* |
65.67 | 68.46 | 64.00 |
*: For easier inference and deployment, we merged the re-parameterized added parameters and scaling factors into the final released models (YuLan-Mini and YuLan-Mini-Intermediate-4K), enabling it to run on the Llama architecture. However, these parameters are still retained in the intermediate checkpoints from the training process.
3. Optimizer States Before Annealing
4. Logs of Ablation Studies
We provide W&B logs, including the intermediate hidden states and weights of each module, for ablation studies:
- WeSaR Re-Param
- Cerebras muP
- Embedding LayerNorm
- Tie Embedding
- QK LayerNorm
- Weight Decay
5. The Used Open-Source Datasets
7. Synthetic Data
Data cleaning and synthesis pipeline:
The synthetic data we are using is released in 🤗 YuLan-Mini-Datasets
Classifiers: 🤗 Yulan-Mini Resources
- Pre-train your own LLM. You can use our data and curriculum to train a model that's just as powerful as YuLan-Mini.
- Perform your own learning rate annealing. During the annealing phase, YuLan-Mini's learning ability is at its peak. You can resume training from the checkpoint before annealing and use your own dataset for learning rate annealing.
- Fine-tune the Instruct version of the LLM. You can use the YuLan-Mini base model to train your own Instruct version.
- Training dynamics research. You can use YuLan-Mini's intermediate checkpoints to explore internal changes during the pre-training process.
- Synthesize your own data. You can use YuLan-Mini's data pipeline to clean and generate your own dataset.
Below is a simple example for inference using Huggingface:
Huggingface Inference Example
import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
# Load model and tokenizer
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("yulan-team/YuLan-Mini-Instruct")
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("yulan-team/YuLan-Mini-Instruct", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16)
# Input text
chat = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are YuLan-Mini, created by RUC AI Box. You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "What is Renmin University of China?"}
]
formatted_chat = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(chat, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)
inputs = tokenizer(formatted_chat, return_tensors="pt", add_special_tokens=False)
# Completion
output = model.generate(inputs["input_ids"], max_new_tokens=100, temperature=0.5)
print(tokenizer.decode(output[0][inputs['input_ids'].size(1):], skip_special_tokens=True))vLLM Serve Example
vllm serve yulan-team/YuLan-Mini-Instruct --dtype bfloat16SGLang Serve Example
python -m sglang.launch_server --model-path yulan-team/YuLan-Mini-Instruct --port 30000 --host 0.0.0.0Ollama
ollama run hf.co/mradermacher/YuLan-Mini-Instruct-GGUF:IQ4_XSWe welcome any form of contribution, including feedback on model bad cases, feature suggestions, and example contributions. You can do so by submitting an issue.
YuLan-Mini is developed and maintained by AI Box, Renmin University of China.
- The code in this repository, the model weights, and optimizer states are released under the MIT License.
- Policies regarding the use of model weights, intermediate optimizer states, and training data will be announced in future updates.
- Limitations: Despite our efforts to mitigate safety concerns and encourage the generation of ethical and lawful text, the probabilistic nature of language models may still lead to unexpected outputs. For instance, responses might contain bias, discrimination, or other harmful content. Please refrain from disseminating such content. We are not liable for any consequences arising from the spread of harmful information.
If you find YuLan-Mini helpful for your research or development, please cite our technical report and blog:
@article{hu2024yulan,
title={YuLan-Mini: An Open Data-efficient Language Model},
author={Hu, Yiwen and Song, Huatong and Deng, Jia and Wang, Jiapeng and Chen, Jie and Zhou, Kun and Zhu, Yutao and Jiang, Jinhao and Dong, Zican and Zhao, Wayne Xin and others},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.17743},
year={2024}
}
@article{YuLan-Mini-Instruct,
title={YuLan-Mini-Instruct Technical Report},
author={RUCAIBox YuLan-Mini-Instruct Team},
url={https://github.com/RUC-GSAI/YuLan-Mini},
year={2025}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for YuLan-Mini
Similar Open Source Tools

YuLan-Mini
YuLan-Mini is a lightweight language model with 2.4 billion parameters that achieves performance comparable to industry-leading models despite being pre-trained on only 1.08T tokens. It excels in mathematics and code domains. The repository provides pre-training resources, including data pipeline, optimization methods, and annealing approaches. Users can pre-train their own language models, perform learning rate annealing, fine-tune the model, research training dynamics, and synthesize data. The team behind YuLan-Mini is AI Box at Renmin University of China. The code is released under the MIT License with future updates on model weights usage policies. Users are advised on potential safety concerns and ethical use of the model.
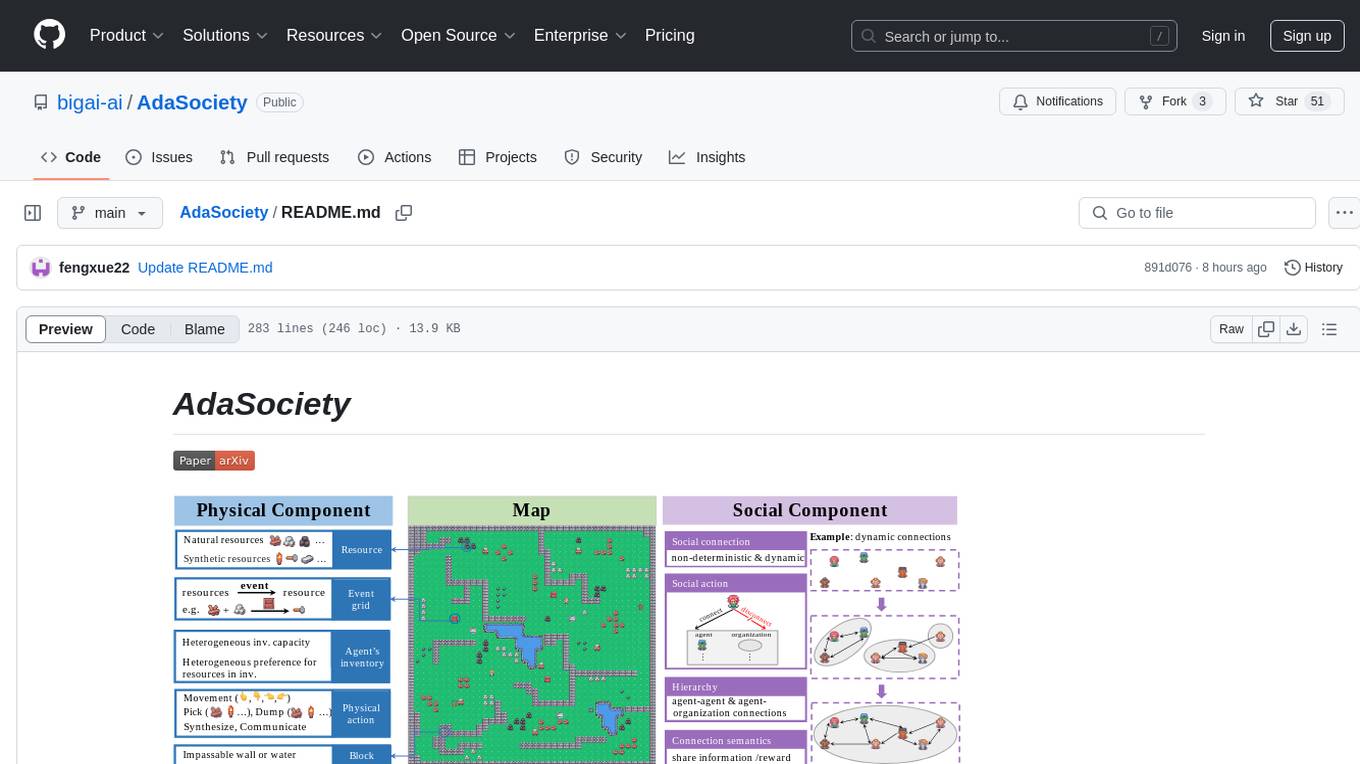
AdaSociety
AdaSociety is a multi-agent environment designed for simulating social structures and decision-making processes. It offers built-in resources, events, and player interactions. Users can customize the environment through JSON configuration or custom Python code. The environment supports training agents using RLlib and LLM frameworks. It provides a platform for studying multi-agent systems and social dynamics.
EVE
EVE is an official PyTorch implementation of Unveiling Encoder-Free Vision-Language Models. The project aims to explore the removal of vision encoders from Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and transfer LLMs to encoder-free VLMs efficiently. It also focuses on bridging the performance gap between encoder-free and encoder-based VLMs. EVE offers a superior capability with arbitrary image aspect ratio, data efficiency by utilizing publicly available data for pre-training, and training efficiency with a transparent and practical strategy for developing a pure decoder-only architecture across modalities.

MOSS-TTS
MOSS-TTS Family is an open-source speech and sound generation model family designed for high-fidelity, high-expressiveness, and complex real-world scenarios. It includes five production-ready models: MOSS-TTS, MOSS-TTSD, MOSS-VoiceGenerator, MOSS-TTS-Realtime, and MOSS-SoundEffect, each serving specific purposes in speech generation, dialogue, voice design, real-time interactions, and sound effect generation. The models offer features like long-speech generation, fine-grained control over phonemes and duration, multilingual synthesis, voice cloning, and real-time voice agents.
FlipAttack
FlipAttack is a jailbreak attack tool designed to exploit black-box Language Model Models (LLMs) by manipulating text inputs. It leverages insights into LLMs' autoregressive nature to construct noise on the left side of the input text, deceiving the model and enabling harmful behaviors. The tool offers four flipping modes to guide LLMs in denoising and executing malicious prompts effectively. FlipAttack is characterized by its universality, stealthiness, and simplicity, allowing users to compromise black-box LLMs with just one query. Experimental results demonstrate its high success rates against various LLMs, including GPT-4o and guardrail models.
IDvs.MoRec
This repository contains the source code for the SIGIR 2023 paper 'Where to Go Next for Recommender Systems? ID- vs. Modality-based Recommender Models Revisited'. It provides resources for evaluating foundation, transferable, multi-modal, and LLM recommendation models, along with datasets, pre-trained models, and training strategies for IDRec and MoRec using in-batch debiased cross-entropy loss. The repository also offers large-scale datasets, code for SASRec with in-batch debias cross-entropy loss, and information on joining the lab for research opportunities.
hcaptcha-challenger
hCaptcha Challenger is a tool designed to gracefully face hCaptcha challenges using a multimodal large language model. It does not rely on Tampermonkey scripts or third-party anti-captcha services, instead implementing interfaces for 'AI vs AI' scenarios. The tool supports various challenge types such as image labeling, drag and drop, and advanced tasks like self-supervised challenges and Agentic Workflow. Users can access documentation in multiple languages and leverage resources for tasks like model training, dataset annotation, and model upgrading. The tool aims to enhance user experience in handling hCaptcha challenges with innovative AI capabilities.
flute
FLUTE (Flexible Lookup Table Engine for LUT-quantized LLMs) is a tool designed for uniform quantization and lookup table quantization of weights in lower-precision intervals. It offers flexibility in mapping intervals to arbitrary values through a lookup table. FLUTE supports various quantization formats such as int4, int3, int2, fp4, fp3, fp2, nf4, nf3, nf2, and even custom tables. The tool also introduces new quantization algorithms like Learned Normal Float (NFL) for improved performance and calibration data learning. FLUTE provides benchmarks, model zoo, and integration with frameworks like vLLM and HuggingFace for easy deployment and usage.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.
KwaiAgents
KwaiAgents is a series of Agent-related works open-sourced by the [KwaiKEG](https://github.com/KwaiKEG) from [Kuaishou Technology](https://www.kuaishou.com/en). The open-sourced content includes: 1. **KAgentSys-Lite**: a lite version of the KAgentSys in the paper. While retaining some of the original system's functionality, KAgentSys-Lite has certain differences and limitations when compared to its full-featured counterpart, such as: (1) a more limited set of tools; (2) a lack of memory mechanisms; (3) slightly reduced performance capabilities; and (4) a different codebase, as it evolves from open-source projects like BabyAGI and Auto-GPT. Despite these modifications, KAgentSys-Lite still delivers comparable performance among numerous open-source Agent systems available. 2. **KAgentLMs**: a series of large language models with agent capabilities such as planning, reflection, and tool-use, acquired through the Meta-agent tuning proposed in the paper. 3. **KAgentInstruct**: over 200k Agent-related instructions finetuning data (partially human-edited) proposed in the paper. 4. **KAgentBench**: over 3,000 human-edited, automated evaluation data for testing Agent capabilities, with evaluation dimensions including planning, tool-use, reflection, concluding, and profiling.
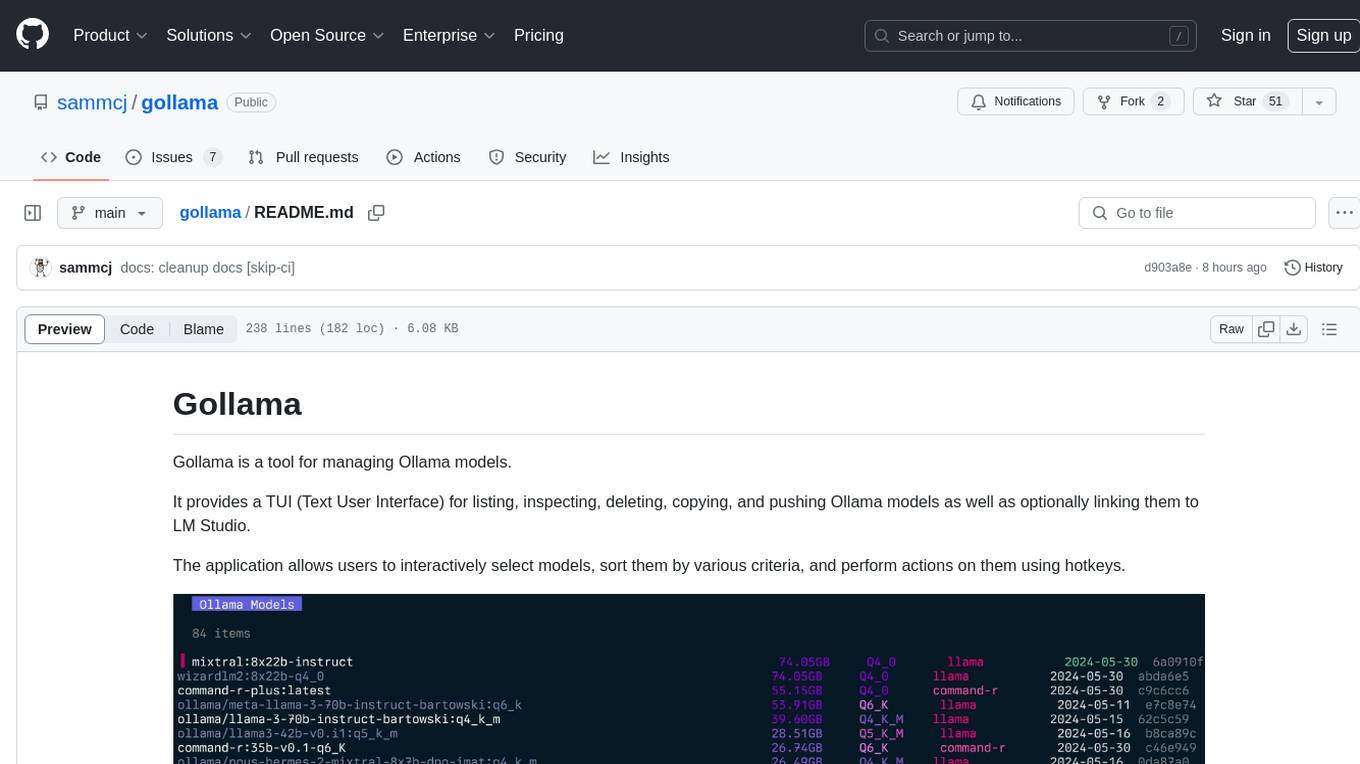
gollama
Gollama is a tool designed for managing Ollama models through a Text User Interface (TUI). Users can list, inspect, delete, copy, and push Ollama models, as well as link them to LM Studio. The application offers interactive model selection, sorting by various criteria, and actions using hotkeys. It provides features like sorting and filtering capabilities, displaying model metadata, model linking, copying, pushing, and more. Gollama aims to be user-friendly and useful for managing models, especially for cleaning up old models.
InternVL
InternVL scales up the ViT to _**6B parameters**_ and aligns it with LLM. It is a vision-language foundation model that can perform various tasks, including: **Visual Perception** - Linear-Probe Image Classification - Semantic Segmentation - Zero-Shot Image Classification - Multilingual Zero-Shot Image Classification - Zero-Shot Video Classification **Cross-Modal Retrieval** - English Zero-Shot Image-Text Retrieval - Chinese Zero-Shot Image-Text Retrieval - Multilingual Zero-Shot Image-Text Retrieval on XTD **Multimodal Dialogue** - Zero-Shot Image Captioning - Multimodal Benchmarks with Frozen LLM - Multimodal Benchmarks with Trainable LLM - Tiny LVLM InternVL has been shown to achieve state-of-the-art results on a variety of benchmarks. For example, on the MMMU image classification benchmark, InternVL achieves a top-1 accuracy of 51.6%, which is higher than GPT-4V and Gemini Pro. On the DocVQA question answering benchmark, InternVL achieves a score of 82.2%, which is also higher than GPT-4V and Gemini Pro. InternVL is open-sourced and available on Hugging Face. It can be used for a variety of applications, including image classification, object detection, semantic segmentation, image captioning, and question answering.
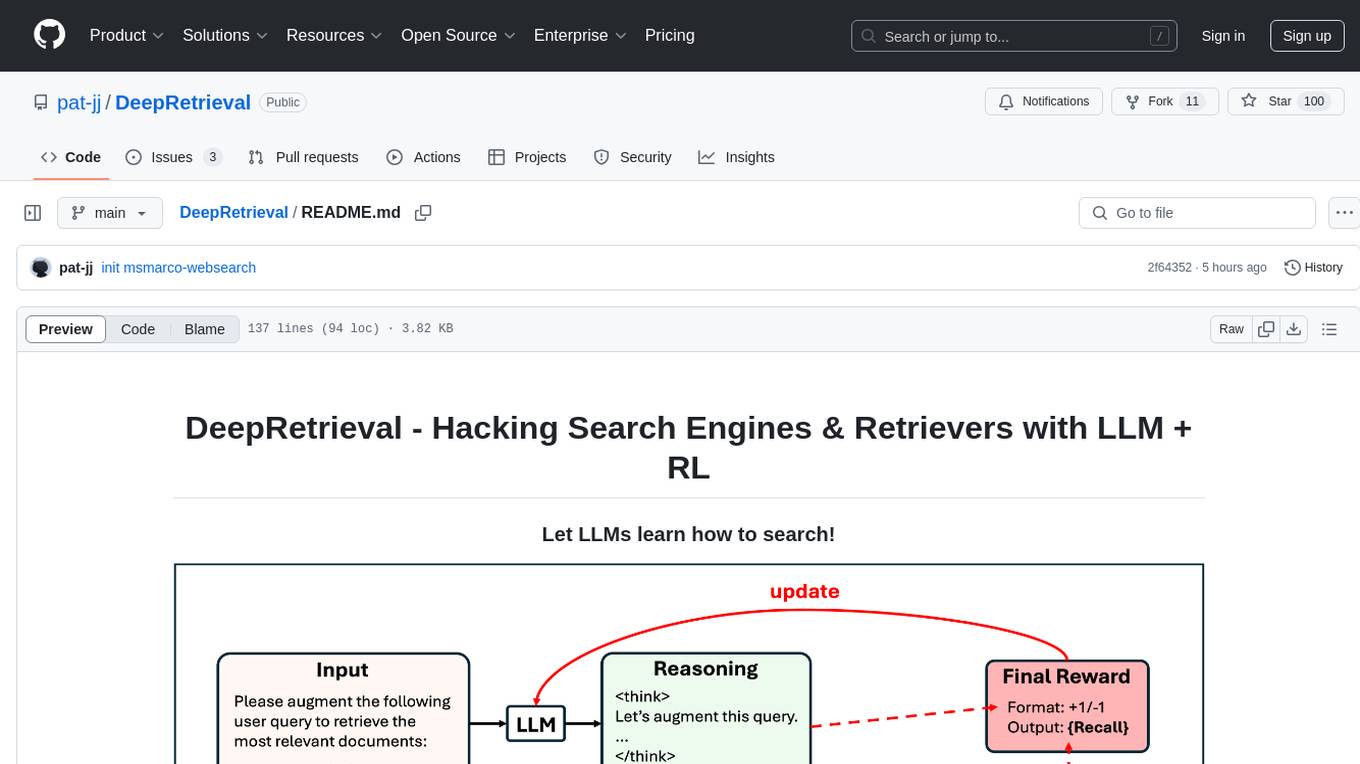
DeepRetrieval
DeepRetrieval is a tool designed to enhance search engines and retrievers using Large Language Models (LLMs) and Reinforcement Learning (RL). It allows LLMs to learn how to search effectively by integrating with search engine APIs and customizing reward functions. The tool provides functionalities for data preparation, training, evaluation, and monitoring search performance. DeepRetrieval aims to improve information retrieval tasks by leveraging advanced AI techniques.
jailbreak_llms
This is the official repository for the ACM CCS 2024 paper 'Do Anything Now': Characterizing and Evaluating In-The-Wild Jailbreak Prompts on Large Language Models. The project employs a new framework called JailbreakHub to conduct the first measurement study on jailbreak prompts in the wild, collecting 15,140 prompts from December 2022 to December 2023, including 1,405 jailbreak prompts. The dataset serves as the largest collection of in-the-wild jailbreak prompts. The repository contains examples of harmful language and is intended for research purposes only.

EasyEdit
EasyEdit is a Python package for edit Large Language Models (LLM) like `GPT-J`, `Llama`, `GPT-NEO`, `GPT2`, `T5`(support models from **1B** to **65B**), the objective of which is to alter the behavior of LLMs efficiently within a specific domain without negatively impacting performance across other inputs. It is designed to be easy to use and easy to extend.
llm4regression
This project explores the capability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to perform regression tasks using in-context examples. It compares the performance of LLMs like GPT-4 and Claude 3 Opus with traditional supervised methods such as Linear Regression and Gradient Boosting. The project provides preprints and results demonstrating the strong performance of LLMs in regression tasks. It includes datasets, models used, and experiments on adaptation and contamination. The code and data for the experiments are available for interaction and analysis.
For similar tasks

dstack
Dstack is an open-source orchestration engine for running AI workloads in any cloud. It supports a wide range of cloud providers (such as AWS, GCP, Azure, Lambda, TensorDock, Vast.ai, CUDO, RunPod, etc.) as well as on-premises infrastructure. With Dstack, you can easily set up and manage dev environments, tasks, services, and pools for your AI workloads.
one-click-llms
The one-click-llms repository provides templates for quickly setting up an API for language models. It includes advanced inferencing scripts for function calling and offers various models for text generation and fine-tuning tasks. Users can choose between Runpod and Vast.AI for different GPU configurations, with recommendations for optimal performance. The repository also supports Trelis Research and offers templates for different model sizes and types, including multi-modal APIs and chat models.

starcoder2-self-align
StarCoder2-Instruct is an open-source pipeline that introduces StarCoder2-15B-Instruct-v0.1, a self-aligned code Large Language Model (LLM) trained with a fully permissive and transparent pipeline. It generates instruction-response pairs to fine-tune StarCoder-15B without human annotations or data from proprietary LLMs. The tool is primarily finetuned for Python code generation tasks that can be verified through execution, with potential biases and limitations. Users can provide response prefixes or one-shot examples to guide the model's output. The model may have limitations with other programming languages and out-of-domain coding tasks.
enhance_llm
The enhance_llm repository contains three main parts: 1. Vector model domain fine-tuning based on llama_index and qwen fine-tuning BGE vector model. 2. Large model domain fine-tuning based on PEFT fine-tuning qwen1.5-7b-chat, with sft and dpo. 3. High-order retrieval enhanced generation (RAG) system based on the above domain work, implementing a two-stage RAG system. It includes query rewriting, recall reordering, retrieval reordering, multi-turn dialogue, and more. The repository also provides hardware and environment configurations along with star history and licensing information.
fms-fsdp
The 'fms-fsdp' repository is a companion to the Foundation Model Stack, providing a (pre)training example to efficiently train FMS models, specifically Llama2, using native PyTorch features like FSDP for training and SDPA implementation of Flash attention v2. It focuses on leveraging FSDP for training efficiently, not as an end-to-end framework. The repo benchmarks training throughput on different GPUs, shares strategies, and provides installation and training instructions. It trained a model on IBM curated data achieving high efficiency and performance metrics.

CogVLM2
CogVLM2 is a new generation of open source models that offer significant improvements in benchmarks such as TextVQA and DocVQA. It supports 8K content length, image resolution up to 1344 * 1344, and both Chinese and English languages. The project provides basic calling methods, fine-tuning examples, and OpenAI API format calling examples to help developers quickly get started with the model.
liboai
liboai is a simple C++17 library for the OpenAI API, providing developers with access to OpenAI endpoints through a collection of methods and classes. It serves as a spiritual port of OpenAI's Python library, 'openai', with similar structure and features. The library supports various functionalities such as ChatGPT, Audio, Azure, Functions, Image DALL·E, Models, Completions, Edit, Embeddings, Files, Fine-tunes, Moderation, and Asynchronous Support. Users can easily integrate the library into their C++ projects to interact with OpenAI services.
extension-gen-ai
The Looker GenAI Extension provides code examples and resources for building a Looker Extension that integrates with Vertex AI Large Language Models (LLMs). Users can leverage the power of LLMs to enhance data exploration and analysis within Looker. The extension offers generative explore functionality to ask natural language questions about data and generative insights on dashboards to analyze data by asking questions. It leverages components like BQML Remote Models, BQML Remote UDF with Vertex AI, and Custom Fine Tune Model for different integration options. Deployment involves setting up infrastructure with Terraform and deploying the Looker Extension by creating a Looker project, copying extension files, configuring BigQuery connection, connecting to Git, and testing the extension. Users can save example prompts and configure user settings for the extension. Development of the Looker Extension environment includes installing dependencies, starting the development server, and building for production.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.









