
AdaSociety
AdaSociety is a customizable multi-agent environment featuring expanding state and action spaces, alongside explicit and alterable social structures. AdaSociety is friendly to tensor-based and LLM-based methods.
Stars: 51
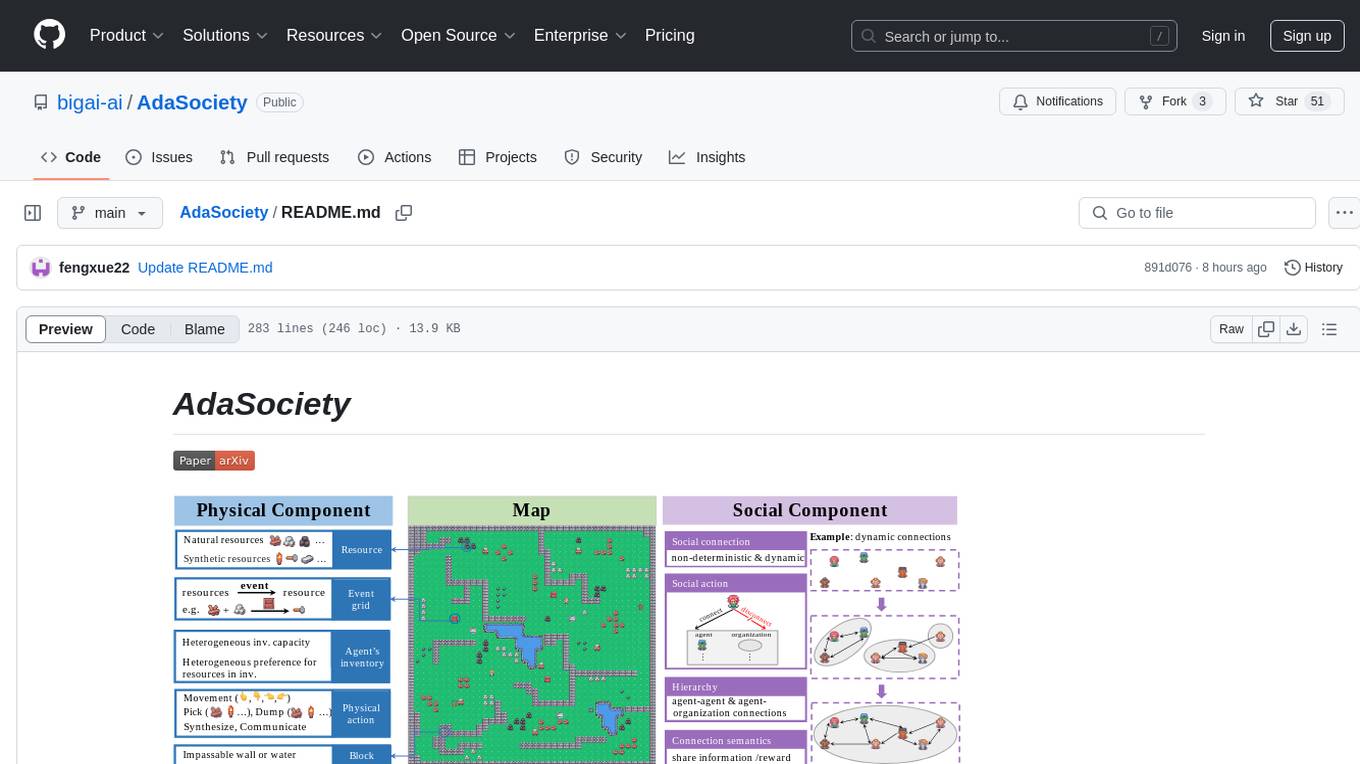
AdaSociety is a multi-agent environment designed for simulating social structures and decision-making processes. It offers built-in resources, events, and player interactions. Users can customize the environment through JSON configuration or custom Python code. The environment supports training agents using RLlib and LLM frameworks. It provides a platform for studying multi-agent systems and social dynamics.
README:
There are 15 kinds of built-in resources in AdaSociety, which can be divided into Natural Resources and Synthesized Resources based on whether they can be produced through events. Some of the natural resources can only be discovered and gathered by agents with certain resources (denoted by Requirement) in their inventories.
| Resource | Wood | Stone | Hammer | Coal | Torch | Iron | Steel | Shovel | Pickaxe | GemMine | Clay | Pottery | Cutter | Gem | Totem |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synthesized | ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ | ❌ | ✔️ | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Requirement | - | - | - | Hammer | - | Torch | - | - | - | Pickaxe | Shovel | - | - | - | - |
| Objective reward | 1 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 20 | 3 | 30 | 100 | 150 | 4 | 4 | 40 | 100 | 200 | 1000 |
There are 9 built-in events in AdaSociety. Each event takes 2 to 3 kinds of resources as input and outputs 1 kind of product. Events can only be observed and executed by agents whose inventories meet the event requirements.
| Event | Input1 | Input2 | Input3 | Output | Requirement1 | Requirement2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HammerCraft | 1Wood | 1Stone | - | 1Hammer | - | - |
| TorchCraft | 1Wood | 1Coal | - | 1Torch | Coal | - |
| SteelMaking | 1Iron | 1Coal | - | 1Steel | Iron | - |
| Potting | 2Clay | 1Coal | - | 1Pottery | Clay | - |
| ShovelCraft | 2Steel | 2Wood | - | 1Shovel | Steel | - |
| PickaxeCraft | 3Steel | 2Wood | - | 1Pickaxe | Steel | - |
| CutterCraft | 2Steel | 3Stone | - | 1Cutter | Steel | - |
| GemCutting | 1GemMine | - | - | 1Gem | Cutter | GemMine |
| TotemMaking | 2Gem | 1Pottery | 1Steel | 1Totem | Gem | - |
Every agent has an inventory with maximal capacities of every resource, implying skill diversity. For example, an agent with a $0$ capacity for hammers cannot possess hammers and observe coal. Agents can collect resources from the map into their inventories and dump resources on the map. Agents' rewards are attached to the resources in their inventories, while they exhibit heterogeneity in resource preferences. Specifically, for agent $i$, the reward of resource $\rho$ is $R_i(\rho) = m_i^{\rho} \cdot h_i(\rho) \cdot \overline{r}^{\rho}$, where $m_i^{\rho}$ is the amount of resource $\rho$ in the inventory of agent $i$, $h_i(\rho) \in \mathbb{R}$ represents the preference of agent $i$ for $\rho$, $\overline{r}^{\rho}$ is the objective reward of a unit of $\rho$.
| Name | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| episode_id | Current episode id. | int |
| step_id | Current step id. | int |
| Resource | ||
| name | Resource name. | str |
| position | Resource absolute coordinate the position of resources in inventory is None. |
[x: int, y: int] |
| amount | Resource number. | int |
| Event | ||
| name | Event name. | str |
| position | Event absolute coordinate. | [x: int, y: int] |
| Player | ||
| id | Player ID. | int |
| name | Player name. | str |
| position | Player's absolute coordinate. | [x: int, y: int] |
| inventory | Player's inventory, every player can only observe her own inventory. | [resource_1, resource_2, ...] |
| Map | ||
| block_grids | An agent-centered observable map of blocks. 1 stands for block, and 0 stands for blank. |
2D-array |
| resources | Observable resources list. | [resource_1, resource_2, ...] |
| events | Observable events list. | [event_1, event_2, ...] |
| players | Observable players list (exclude self). | [player_1, player_2, ...] |
| Sharing | ||
| Map | shared vision, same structure as Map. | Map |
| Node | ||
| type | Node type, player or group. | player or group |
| player | Player node attribute. | {'id': xxx} |
| group | Group node attribute. | {'id': xxx, 'member': [xxx, ...]} |
| name | Node name. | str |
| Edge | ||
| name | Edge name. | str |
| from | Out-degree node type: 'player' or 'group'. id: node_id. |
{'type': xxx, 'id': xxx} |
| to | In-degree node type: 'player' or 'group'. id: node_id. |
{'type': xxx, 'id': xxx} |
| attribute | Attributes on the edge. | {'attribute_name': attribute_value} |
| Social | ||
| sharings | The shared information among agents. | {player_id: sharing, player_id: sharing, ...} |
| global | The gloabl social graph information list of nodes and edges. |
{'nodes': [node_1, ...], 'edges': [edge_1, ...] } |
{
"episode_id": 123,
"step_id": 456,
"Map": {
"block_grids": [
[1, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 1]
],
"resources": [
{"name": "wood", "position": [1, 1], "num": 3}
],
"events": [
{"name": "hammer_craft", "position": [2, 1]}
],
"players": [
{"id": 0, "name": "Adam", "position": [1, 2]}
]
},
"Player": {
"id": 1,
"name": "Eva",
"position": [3, 0],
"inventory": [
{"name": "stone", "num": 10}
]
},
"Social": {
"sharings": {
"player_id":{
"map": {
"block_grids": [
[1, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 1]
],
"resources": [
{"name": "stone", "position": [1, 1], "num": 2}
],
"events": [
{"name": "torch_craft", "position": [3, 1]}
],
"players": [
{"id": 3, "name": "Bob", "position": [3, 2]}
],
}
}
},
"global":{
"nodes":[
{"type": "player", "player": {"id": 0}},
{"type": "player", "player": {"id": 1}},
{"type": "group", "group": {"id": 0}},
],
"edges":[
{
"name": "sharing_obs",
"from": {"type": "player", "id": 0},
"to": {"type": "player", "id": 1},
"attribute": {"sharing": {"Map": true}}
}
]
}
}
}
| Name | Description | Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| no_act | Do nothing. | - |
| Move | ||
| move_up | Move up. | - |
| move_down | Move down. | - |
| move_left | Move left. | - |
| move_right | Move right. | - |
| Resource | ||
| pick_by_name | Pick up one unit of resource from the map. | resource_name: Resource name. |
| dump_by_name | Dump one unit of resource from the inventory. | resource_name: Resource name. |
| Event | ||
| produce | Perform a produce action on an event grid on the map, consuming the required items from the inventory and obtaining the produced resource. | - |
| Social | ||
| add_relation | Establish a relation with a player. |
to_player_id: The id of the target player; (attributes_dict): The attributes of the relation. |
| remove_relation | Deletes the specified attribute relation with one player. | (to_player_id): The id of the target player; (attribute_name): The attributes of the relation. |
| join_group | Join a group and add attributes. | (group_id): The group want to join; (attribute_dict): The group's attributes. |
| quit_group | Quit a group that has a specified attribute. | (group_id): The group want to quit; (attribute_name): The group's attribute. |
[
{
"action": "move_up",
},
{
"action": "pick_by_name",
"kwargs":{
"resource_name": "wood"
}
},
{
"action": "add_relation",
"kwargs":{
"player": 1,
"attributes_dict": {
"matching_request_step": 0
}
}
},
{
"action": "quit_group",
"kwargs":{
"group_id": 2,
"attribute_name": "score"
}
}
]| Element | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mapsize | $h, w$ | Map height and map width. |
| Terrain | $B$ | Terrain set $B=\lbrace b_1, \cdots, b_{|B|} \rbrace$. $b_i$ represents a block. |
| $b_i^{pos}$: the position of block $b_i$ on the map which can be assigned or randomly generated. | ||
| Resource | $\varrho$ | Set of resources $\varrho = \lbrace \rho_1, \cdots,\rho_{|\varrho|} \rbrace$. Each resource $\rho_i$ has an attribute $\rho_i^{req}$. |
| $\rho_i^{req}$: Necessary resources in agents' inventories to observe & collect $\rho_i$. | ||
| $\rho_{temp}$ | Temporary resources (Defined by specifying $\rho_{temp}^{req}$) | |
| Event | $\mathcal{E}$ | Set of events $\mathcal{E}=\lbrace \epsilon_1, \cdots, \epsilon_{|\mathcal{E}|} \rbrace$. Each event $\epsilon_i$ has attributes $\epsilon_i^{in}, \epsilon_i^{out}, \epsilon_i^{req}$. |
| $\epsilon_i^{in}$ | Resources consumed by event $\epsilon_i$. | |
| $\epsilon_i^{out}$ | Resources produced by event $\epsilon_i$. | |
| $\epsilon_i^{req}$ | Necessary resources in agents' inventories to observe & execute $\epsilon_i$. | |
| $\mathcal{E}^{pos}$ | Event positions $\mathcal{E}^{pos} = \lbrace \epsilon_1^{pos}, \cdots, \epsilon_{|\mathcal{E}|^{pos}} \rbrace$. Each $\epsilon_i^{pos}$ represents a list of positions of $\epsilon_i$. | |
| $\epsilon_{temp}$ | Temporary events (Defined by specifying $\epsilon_{temp}^{in}, \epsilon_{temp}^{out}, \epsilon_{temp}^{req}$) | |
| Agent | $P$ | Set of agents $P=\lbrace 1, \cdots, |P| \rbrace$ |
| $m_i(0)$ | Initial inventories. $m^{\rho}_i(0)$ denotes the initial number of resource $\rho$ in inventories. | |
| $i^{cap}$ | Inventory capacity. $i^{cap}$: $\varrho\to\mathbb{R}$ denotes maximum quantities of resources $i$ can carry. | |
| $h_i$ | $h_i$: $\varrho\to\mathbb{R}$ denotes quantities of credits $i$ gets by acquiring resources. The actual reward obtained by $i$ is $h_i$ multiplied by the objective reward of the resource. | |
| $i^{pos}(0)$ | Initial positions of agents which can be predefined or generated randomly. |
To get started with the project, clone the repository and run the following command to install the required dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txtWe plan to publish this repository as a Python package in the future.
AdaSociety offers two primary methods for customizing the multi-agent environment:
-
JSON Configuration: Users can easily adjust environment parameters by passing settings in JSON format. Customizable configurations include:
- Map size
- Number, location and generation method of blocks
- Types and quantities of resources
- Event types and their respective quantities and generation methods
- Initial social structure and its evolution
- Specification of pre-update and post-update functions for each environment step
- Number of agents, their inventory capacity, and preferences
Additionally, users can customize non-built-in resources, events, and agent types. For a detailed description, please refer to JSON Configuration File Documentation.
-
Custom Python Code: Users can gain greater flexibility and control by crafting custom
env_handlerandagentclasses through Python code. This allows for:-
Implementation of custom observation processing functions and reward functions
-
Action translations for agents
-
Application of meta control within the environment, such as defining the rotation order of agents.
For a detailed description, please refer to Agent and Environment Handler Implementation.
-
For detailed instructions on each mini-game, consult the following documents:
Here are some key files and folders to run the environment and train the agents:
-
Environment running:
project/env/is the main folder in which AdaSociety runs. It contains the important components, such as event, resource, player. -
Agents training: AdaSociety is a general environment that supports implementing arbitrary algorithms on top of it and is compatible with all popular RL libraries.
We implemented an adaptation of AdaSociety for the well-known library RLlib. project/RLlib/ contains the modules needed to train agents using the RLlib framework, like network and policy. train/train.py in this folder is the main script which creates the environment instance and runs the RL algorithm.rllib_train.py serves as the entry point for executing the training process. It reads and processes command-line arguments and passes the parsed arguments to RLlib/train.py to configure the training run.
Please check further details and examples for using RLlib for AdaSociety in Training agents via RLlib in AdaSociety.
AdaSociety also supports using LLM to control agents. We provide an implementation, and please see LLM for details.
Our paper is available on ArXiv. If you find our work or code useful, we would greatly appreciate it if you could give us a star and consider citing our paper:
@inproceedings{
huang2024adasociety,
title={AdaSociety: An Adaptive Environment with Social Structures for Multi-Agent Decision-Making},
author={Yizhe Huang and Xingbo Wang and Hao Liu and Fanqi Kong and Aoyang Qin and Min Tang and Song-Chun Zhu and Mingjie Bi and Siyuan Qi and Xue Feng},
booktitle={The Thirty-eight Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems Datasets and Benchmarks Track},
year={2024}
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for AdaSociety
Similar Open Source Tools

AdaSociety
AdaSociety is a multi-agent environment designed for simulating social structures and decision-making processes. It offers built-in resources, events, and player interactions. Users can customize the environment through JSON configuration or custom Python code. The environment supports training agents using RLlib and LLM frameworks. It provides a platform for studying multi-agent systems and social dynamics.
YuLan-Mini
YuLan-Mini is a lightweight language model with 2.4 billion parameters that achieves performance comparable to industry-leading models despite being pre-trained on only 1.08T tokens. It excels in mathematics and code domains. The repository provides pre-training resources, including data pipeline, optimization methods, and annealing approaches. Users can pre-train their own language models, perform learning rate annealing, fine-tune the model, research training dynamics, and synthesize data. The team behind YuLan-Mini is AI Box at Renmin University of China. The code is released under the MIT License with future updates on model weights usage policies. Users are advised on potential safety concerns and ethical use of the model.
llm.nvim
llm.nvim is a universal plugin for a large language model (LLM) designed to enable users to interact with LLM within neovim. Users can customize various LLMs such as gpt, glm, kimi, and local LLM. The plugin provides tools for optimizing code, comparing code, translating text, and more. It also supports integration with free models from Cloudflare, Github models, siliconflow, and others. Users can customize tools, chat with LLM, quickly translate text, and explain code snippets. The plugin offers a flexible window interface for easy interaction and customization.
gollama
Gollama is a tool designed for managing Ollama models through a Text User Interface (TUI). Users can list, inspect, delete, copy, and push Ollama models, as well as link them to LM Studio. The application offers interactive model selection, sorting by various criteria, and actions using hotkeys. It provides features like sorting and filtering capabilities, displaying model metadata, model linking, copying, pushing, and more. Gollama aims to be user-friendly and useful for managing models, especially for cleaning up old models.
EVE
EVE is an official PyTorch implementation of Unveiling Encoder-Free Vision-Language Models. The project aims to explore the removal of vision encoders from Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and transfer LLMs to encoder-free VLMs efficiently. It also focuses on bridging the performance gap between encoder-free and encoder-based VLMs. EVE offers a superior capability with arbitrary image aspect ratio, data efficiency by utilizing publicly available data for pre-training, and training efficiency with a transparent and practical strategy for developing a pure decoder-only architecture across modalities.
KwaiAgents
KwaiAgents is a series of Agent-related works open-sourced by the [KwaiKEG](https://github.com/KwaiKEG) from [Kuaishou Technology](https://www.kuaishou.com/en). The open-sourced content includes: 1. **KAgentSys-Lite**: a lite version of the KAgentSys in the paper. While retaining some of the original system's functionality, KAgentSys-Lite has certain differences and limitations when compared to its full-featured counterpart, such as: (1) a more limited set of tools; (2) a lack of memory mechanisms; (3) slightly reduced performance capabilities; and (4) a different codebase, as it evolves from open-source projects like BabyAGI and Auto-GPT. Despite these modifications, KAgentSys-Lite still delivers comparable performance among numerous open-source Agent systems available. 2. **KAgentLMs**: a series of large language models with agent capabilities such as planning, reflection, and tool-use, acquired through the Meta-agent tuning proposed in the paper. 3. **KAgentInstruct**: over 200k Agent-related instructions finetuning data (partially human-edited) proposed in the paper. 4. **KAgentBench**: over 3,000 human-edited, automated evaluation data for testing Agent capabilities, with evaluation dimensions including planning, tool-use, reflection, concluding, and profiling.
flute
FLUTE (Flexible Lookup Table Engine for LUT-quantized LLMs) is a tool designed for uniform quantization and lookup table quantization of weights in lower-precision intervals. It offers flexibility in mapping intervals to arbitrary values through a lookup table. FLUTE supports various quantization formats such as int4, int3, int2, fp4, fp3, fp2, nf4, nf3, nf2, and even custom tables. The tool also introduces new quantization algorithms like Learned Normal Float (NFL) for improved performance and calibration data learning. FLUTE provides benchmarks, model zoo, and integration with frameworks like vLLM and HuggingFace for easy deployment and usage.
IDvs.MoRec
This repository contains the source code for the SIGIR 2023 paper 'Where to Go Next for Recommender Systems? ID- vs. Modality-based Recommender Models Revisited'. It provides resources for evaluating foundation, transferable, multi-modal, and LLM recommendation models, along with datasets, pre-trained models, and training strategies for IDRec and MoRec using in-batch debiased cross-entropy loss. The repository also offers large-scale datasets, code for SASRec with in-batch debias cross-entropy loss, and information on joining the lab for research opportunities.
SuperAdapters
SuperAdapters is a tool designed to finetune Large Language Models (LLMs) with various adapters on different platforms. It supports models like Bloom, LLaMA, ChatGLM, Qwen, Baichuan, Mixtral, Phi, and more. Users can finetune LLMs on Windows, Linux, and Mac M1/2, handle train/test data with Terminal, File, or DataBase, and perform tasks like CausalLM and SequenceClassification. The tool provides detailed instructions on how to use different models with specific adapters for tasks like finetuning and inference. It also includes requirements for CentOS, Ubuntu, and MacOS, along with information on LLM downloads and data formats. Additionally, it offers parameters for finetuning and inference, as well as options for web and API-based inference.
hcaptcha-challenger
hCaptcha Challenger is a tool designed to gracefully face hCaptcha challenges using a multimodal large language model. It does not rely on Tampermonkey scripts or third-party anti-captcha services, instead implementing interfaces for 'AI vs AI' scenarios. The tool supports various challenge types such as image labeling, drag and drop, and advanced tasks like self-supervised challenges and Agentic Workflow. Users can access documentation in multiple languages and leverage resources for tasks like model training, dataset annotation, and model upgrading. The tool aims to enhance user experience in handling hCaptcha challenges with innovative AI capabilities.
optillm
optillm is an OpenAI API compatible optimizing inference proxy implementing state-of-the-art techniques to enhance accuracy and performance of LLMs, focusing on reasoning over coding, logical, and mathematical queries. By leveraging additional compute at inference time, it surpasses frontier models across diverse tasks.

EasyEdit
EasyEdit is a Python package for edit Large Language Models (LLM) like `GPT-J`, `Llama`, `GPT-NEO`, `GPT2`, `T5`(support models from **1B** to **65B**), the objective of which is to alter the behavior of LLMs efficiently within a specific domain without negatively impacting performance across other inputs. It is designed to be easy to use and easy to extend.
AnyCrawl
AnyCrawl is a high-performance crawling and scraping toolkit designed for SERP crawling, web scraping, site crawling, and batch tasks. It offers multi-threading and multi-process capabilities for high performance. The tool also provides AI extraction for structured data extraction from pages, making it LLM-friendly and easy to integrate and use.
llm4regression
This project explores the capability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to perform regression tasks using in-context examples. It compares the performance of LLMs like GPT-4 and Claude 3 Opus with traditional supervised methods such as Linear Regression and Gradient Boosting. The project provides preprints and results demonstrating the strong performance of LLMs in regression tasks. It includes datasets, models used, and experiments on adaptation and contamination. The code and data for the experiments are available for interaction and analysis.
jailbreak_llms
This is the official repository for the ACM CCS 2024 paper 'Do Anything Now': Characterizing and Evaluating In-The-Wild Jailbreak Prompts on Large Language Models. The project employs a new framework called JailbreakHub to conduct the first measurement study on jailbreak prompts in the wild, collecting 15,140 prompts from December 2022 to December 2023, including 1,405 jailbreak prompts. The dataset serves as the largest collection of in-the-wild jailbreak prompts. The repository contains examples of harmful language and is intended for research purposes only.

EAGLE
Eagle is a family of Vision-Centric High-Resolution Multimodal LLMs that enhance multimodal LLM perception using a mix of vision encoders and various input resolutions. The model features a channel-concatenation-based fusion for vision experts with different architectures and knowledge, supporting up to over 1K input resolution. It excels in resolution-sensitive tasks like optical character recognition and document understanding.
For similar tasks

AdaSociety
AdaSociety is a multi-agent environment designed for simulating social structures and decision-making processes. It offers built-in resources, events, and player interactions. Users can customize the environment through JSON configuration or custom Python code. The environment supports training agents using RLlib and LLM frameworks. It provides a platform for studying multi-agent systems and social dynamics.
Awesome-LLM-in-Social-Science
This repository compiles a list of academic papers that evaluate, align, simulate, and provide surveys or perspectives on the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the field of Social Science. The papers cover various aspects of LLM research, including assessing their alignment with human values, evaluating their capabilities in tasks such as opinion formation and moral reasoning, and exploring their potential for simulating social interactions and addressing issues in diverse fields of Social Science. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive resource for researchers and practitioners interested in the intersection of LLMs and Social Science.
agentic
Agentic is a lightweight and flexible Python library for building multi-agent systems. It provides a simple and intuitive API for creating and managing agents, defining their behaviors, and simulating interactions in a multi-agent environment. With Agentic, users can easily design and implement complex agent-based models to study emergent behaviors, social dynamics, and decentralized decision-making processes. The library supports various agent architectures, communication protocols, and simulation scenarios, making it suitable for a wide range of research and educational applications in the fields of artificial intelligence, machine learning, social sciences, and robotics.
AI4U
AI4U is a tool that provides a framework for modeling virtual reality and game environments. It offers an alternative approach to modeling Non-Player Characters (NPCs) in Godot Game Engine. AI4U defines an agent living in an environment and interacting with it through sensors and actuators. Sensors provide data to the agent's brain, while actuators send actions from the agent to the environment. The brain processes the sensor data and makes decisions (selects an action by time). AI4U can also be used in other situations, such as modeling environments for artificial intelligence experiments.
Co-LLM-Agents
This repository contains code for building cooperative embodied agents modularly with large language models. The agents are trained to perform tasks in two different environments: ThreeDWorld Multi-Agent Transport (TDW-MAT) and Communicative Watch-And-Help (C-WAH). TDW-MAT is a multi-agent environment where agents must transport objects to a goal position using containers. C-WAH is an extension of the Watch-And-Help challenge, which enables agents to send messages to each other. The code in this repository can be used to train agents to perform tasks in both of these environments.
godot_rl_agents
Godot RL Agents is an open-source package that facilitates the integration of Machine Learning algorithms with games created in the Godot Engine. It provides interfaces for popular RL frameworks, support for memory-based agents, 2D and 3D games, AI sensors, and is licensed under MIT. Users can train agents in the Godot editor, create custom environments, export trained agents in ONNX format, and utilize advanced features like different RL training frameworks.
agents
Agents 2.0 is a framework for training language agents using symbolic learning, inspired by connectionist learning for neural nets. It implements main components of connectionist learning like back-propagation and gradient-based weight update in the context of agent training using language-based loss, gradients, and weights. The framework supports optimizing multi-agent systems and allows multiple agents to take actions in one node.
foyle
Foyle is a project focused on building agents to assist software developers in deploying and operating software. It aims to improve agent performance by collecting human feedback on agent suggestions and human examples of reasoning traces. Foyle utilizes a literate environment using vscode notebooks to interact with infrastructure, capturing prompts, AI-provided answers, and user corrections. The goal is to continuously retrain AI to enhance performance. Additionally, Foyle emphasizes the importance of reasoning traces for training agents to work with internal systems, providing a self-documenting process for operations and troubleshooting.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.
