Awesome-LLM-Reasoning
Reasoning in Large Language Models: Papers and Resources, including Chain-of-Thought and OpenAI o1 🍓
Stars: 2283
**Curated collection of papers and resources on how to unlock the reasoning ability of LLMs and MLLMs.** **Description in less than 400 words, no line breaks and quotation marks.** Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized the NLP landscape, showing improved performance and sample efficiency over smaller models. However, increasing model size alone has not proved sufficient for high performance on challenging reasoning tasks, such as solving arithmetic or commonsense problems. This curated collection of papers and resources presents the latest advancements in unlocking the reasoning abilities of LLMs and Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs). It covers various techniques, benchmarks, and applications, providing a comprehensive overview of the field. **5 jobs suitable for this tool, in lowercase letters.** - content writer - researcher - data analyst - software engineer - product manager **Keywords of the tool, in lowercase letters.** - llm - reasoning - multimodal - chain-of-thought - prompt engineering **5 specific tasks user can use this tool to do, in less than 3 words, Verb + noun form, in daily spoken language.** - write a story - answer a question - translate a language - generate code - summarize a document
README:
Curated collection of papers and resources on how to unlock the reasoning ability of LLMs and MLLMs.
🗂️ Table of Contents
Also check out Awesome-Controllable-Diffusion.
-
Attention Heads of Large Language Models: A Survey. [code]
Zifan Zheng, Yezhaohui Wang, Yuxin Huang, Shichao Song, Bo Tang, Feiyu Xiong, Zhiyu Li. Preprint'24
-
Internal Consistency and Self-Feedback in Large Language Models: A Survey. [code]
Xun Liang, Shichao Song, Zifan Zheng, Hanyu Wang, Qingchen Yu, Xunkai Li, Rong-Hua Li, Feiyu Xiong, Zhiyu Li. Preprint'24
-
Puzzle Solving using Reasoning of Large Language Models: A Survey. [code]
Panagiotis Giadikiaroglou, Maria Lymperaiou, Giorgos Filandrianos, Giorgos Stamou. Preprint'24
-
Large Language Models for Mathematical Reasoning: Progresses and Challenges.
Janice Ahn, Rishu Verma, Renze Lou, Di Liu, Rui Zhang, Wenpeng Yin. ACL'24
-
Towards Reasoning in Large Language Models: A Survey. [code]
Jie Huang, Kevin Chen-Chuan Chang. ACL'23 Findings
-
Reasoning with Language Model Prompting: A Survey. [code]
Shuofei Qiao, Yixin Ou, Ningyu Zhang, Xiang Chen, Yunzhi Yao, Shumin Deng, Chuanqi Tan, Fei Huang, Huajun Chen. ACL'23
-
From Medprompt to o1: Exploration of Run-Time Strategies for Medical Challenge Problems and Beyond.
Harsha Nori, Naoto Usuyama, Nicholas King, Scott Mayer McKinney, Xavier Fernandes, Sheng Zhang, Eric Horvitz. Preprint'24
-
To CoT or not to CoT? Chain-of-thought helps mainly on math and symbolic reasoning.
Zayne Sprague, Fangcong Yin, Juan Diego Rodriguez, Dongwei Jiang, Manya Wadhwa, Prasann Singhal, Xinyu Zhao, Xi Ye, Kyle Mahowald, Greg Durrett. Preprint'24
-
Can LLMs Generate Novel Research Ideas? A Large-Scale Human Study with 100+ NLP Researchers.
Chenglei Si, Diyi Yang, Tatsunori Hashimoto. Preprint'24
-
A Peek into Token Bias: Large Language Models Are Not Yet Genuine Reasoners. [code]
Bowen Jiang, Yangxinyu Xie, Zhuoqun Hao, Xiaomeng Wang, Tanwi Mallick, Weijie J. Su, Camillo J. Taylor, Dan Roth. EMNLP'24
-
Iteration Head: A Mechanistic Study of Chain-of-Thought
Vivien Cabannes, Charles Arnal, Wassim Bouaziz, Alice Yang, Francois Charton, Julia Kempe. NeurIPS'24
-
Do Large Language Models Latently Perform Multi-Hop Reasoning?
Sohee Yang, Elena Gribovskaya, Nora Kassner, Mor Geva, Sebastian Riedel. ACL'24
-
Premise Order Matters in Reasoning with Large Language Models.
Xinyun Chen, Ryan A. Chi, Xuezhi Wang, Denny Zhou. ICML'24
-
The Impact of Reasoning Step Length on Large Language Models.
Mingyu Jin, Qinkai Yu, Dong Shu, Haiyan Zhao, Wenyue Hua, Yanda Meng, Yongfeng Zhang, Mengnan Du. ACL'24 Findings
-
Large Language Models Cannot Self-Correct Reasoning Yet.
Jie Huang, Xinyun Chen, Swaroop Mishra, Huaixiu Steven Zheng, Adams Wei Yu, Xinying Song, Denny Zhou. ICLR'24
-
At Which Training Stage Does Code Data Help LLM Reasoning?
Yingwei Ma, Yue Liu, Yue Yu, Yuanliang Zhang, Yu Jiang, Changjian Wang, Shanshan Li. ICLR'24
-
Measuring Faithfulness in Chain-of-Thought Reasoning.
Tamera Lanham, Anna Chen, Ansh Radhakrishnan, Benoit Steiner, Carson Denison, Danny Hernandez, Dustin Li, Esin Durmus, Evan Hubinger, Jackson Kernion, Kamilė Lukošiūtė, Karina Nguyen, Newton Cheng, Nicholas Joseph, Nicholas Schiefer, Oliver Rausch, Robin Larson, Sam McCandlish, Sandipan Kundu, Saurav Kadavath, Shannon Yang, Thomas Henighan, Timothy Maxwell, Timothy Telleen-Lawton, Tristan Hume, Zac Hatfield-Dodds, Jared Kaplan, Jan Brauner, Samuel R. Bowman, Ethan Perez. Preprint'23
-
Faith and Fate: Limits of Transformers on Compositionality.
Nouha Dziri, Ximing Lu, Melanie Sclar, Xiang Lorraine Li, Liwei Jiang, Bill Yuchen Lin, Peter West, Chandra Bhagavatula, Ronan Le Bras, Jena D. Hwang, Soumya Sanyal, Sean Welleck, Xiang Ren, Allyson Ettinger, Zaid Harchaoui, Yejin Choi. NeurIPS'23
-
Language Models Don't Always Say What They Think: Unfaithful Explanations in Chain-of-Thought Prompting. [code]
Miles Turpin, Julian Michael, Ethan Perez, Samuel R. Bowman. NeurIPS'23
-
Yejin Bang, Samuel Cahyawijaya, Nayeon Lee, Wenliang Dai, Dan Su, Bryan Wilie, Holy Lovenia, Ziwei Ji, Tiezheng Yu, Willy Chung, Quyet V. Do, Yan Xu, Pascale Fung. AACL'23
-
Large Language Models Can Be Easily Distracted by Irrelevant Context.
Freda Shi, Xinyun Chen, Kanishka Misra, Nathan Scales, David Dohan, Ed Chi, Nathanael Schärli, Denny Zhou. ICML'23
-
On Second Thought, Let's Not Think Step by Step! Bias and Toxicity in Zero-Shot Reasoning.
Omar Shaikh, Hongxin Zhang, William Held, Michael Bernstein, Diyi Yang. ACL'23
-
Towards Understanding Chain-of-Thought Prompting: An Empirical Study of What Matters. [code]
Boshi Wang, Sewon Min, Xiang Deng, Jiaming Shen, You Wu, Luke Zettlemoyer, Huan Sun. ACL'23
-
Challenging BIG-Bench Tasks and Whether Chain-of-Thought Can Solve Them. [code]
Mirac Suzgun, Nathan Scales, Nathanael Schärli, Sebastian Gehrmann, Yi Tay, Hyung Won Chung, Aakanksha Chowdhery, Quoc V. Le, Ed H. Chi, Denny Zhou, Jason Wei. ACL'23 Findings
-
Emergent Abilities of Large Language Models. [blog]
Jason Wei, Yi Tay, Rishi Bommasani, Colin Raffel, Barret Zoph, Sebastian Borgeaud, Dani Yogatama, Maarten Bosma, Denny Zhou, Donald Metzler, Ed H. Chi, Tatsunori Hashimoto, Oriol Vinyals, Percy Liang, Jeff Dean, William Fedus. TMLR'22
-
Can language models learn from explanations in context?
Andrew K. Lampinen, Ishita Dasgupta, Stephanie C. Y. Chan, Kory Matthewson, Michael Henry Tessler, Antonia Creswell, James L. McClelland, Jane X. Wang, Felix Hill. EMNLP'22
-
SmartAgent: Chain-of-User-Thought for Embodied Personalized Agent in Cyber World.
Jiaqi Zhang, Chen Gao, Liyuan Zhang, Yong Li, Hongzhi Yin. Preprint'24
-
Marco-o1: Towards Open Reasoning Models for Open-Ended Solutions. [code] [model]
Yu Zhao, Huifeng Yin, Bo Zeng, Hao Wang, Tianqi Shi, Chenyang Lyu, Longyue Wang, Weihua Luo, Kaifu Zhang. Preprint'24
-
Kuofeng Gao, Huanqia Cai, Qingyao Shuai, Dihong Gong, Zhifeng Li. Preprint'24
-
Training Language Models to Self-Correct via Reinforcement Learning.
Aviral Kumar, Vincent Zhuang, Rishabh Agarwal, Yi Su, JD Co-Reyes, Avi Singh, Kate Baumli, Shariq Iqbal, Colton Bishop, Rebecca Roelofs, Lei M. Zhang, Kay McKinney, Disha Shrivastava, Cosmin Paduraru, George Tucker, Doina Precup, Feryal Behbahani, Aleksandra Faust. Preprint'24
-
Open AI Team. Technical Report'24
-
Agent Q: Advanced Reasoning and Learning for Autonomous AI Agents.
Pranav Putta, Edmund Mills, Naman Garg, Sumeet Motwani, Chelsea Finn, Divyansh Garg, Rafael Rafailov. Preprint'24
-
DotaMath: Decomposition of Thought with Code Assistance and Self-correction for Mathematical Reasoning. [code]
Chengpeng Li, Guanting Dong, Mingfeng Xue, Ru Peng, Xiang Wang, Dayiheng Liu. Preprint'24
-
LLM-ARC: Enhancing LLMs with an Automated Reasoning Critic.
Aditya Kalyanpur, Kailash Saravanakumar, Victor Barres, Jennifer Chu-Carroll, David Melville, David Ferrucci. Preprint'24
-
Q*: Improving Multi-step Reasoning for LLMs with Deliberative Planning.
Chaojie Wang, Yanchen Deng, Zhiyi Lv, Shuicheng Yan, An Bo. Preprint'24
-
Buffer of Thoughts: Thought-Augmented Reasoning with Large Language Models. [code]
Ling Yang, Zhaochen Yu, Tianjun Zhang, Shiyi Cao, Minkai Xu, Wentao Zhang, Joseph E. Gonzalez, Bin Cui. Preprint'24
-
Toward Self-Improvement of LLMs via Imagination, Searching, and Criticizing.
Ye Tian, Baolin Peng, Linfeng Song, Lifeng Jin, Dian Yu, Haitao Mi, Dong Yu. Preprint'24
-
Self-playing Adversarial Language Game Enhances LLM Reasoning.
Pengyu Cheng, Tianhao Hu, Han Xu, Zhisong Zhang, Yong Dai, Lei Han, Nan Du. Preprint'24
-
Evaluating Mathematical Reasoning Beyond Accuracy.
Shijie Xia, Xuefeng Li, Yixin Liu, Tongshuang Wu, Pengfei Liu. Preprint'24
-
Advancing LLM Reasoning Generalists with Preference Trees.
Lifan Yuan, Ganqu Cui, Hanbin Wang, Ning Ding, Xingyao Wang, Jia Deng, Boji Shan, Huimin Chen, Ruobing Xie, Yankai Lin, Zhenghao Liu, Bowen Zhou, Hao Peng, Zhiyuan Liu, Maosong Sun. Preprint'24
-
LLM3: Large Language Model-based Task and Motion Planning with Motion Failure Reasoning. [code]
Shu Wang, Muzhi Han, Ziyuan Jiao, Zeyu Zhang, Ying Nian Wu, Song-Chun Zhu, Hangxin Liu. IROS'24
-
Quiet-STaR: Language Models Can Teach Themselves to Think Before Speaking.
Eric Zelikman, Georges Harik, Yijia Shao, Varuna Jayasiri, Nick Haber, Noah D. Goodman. Preprint'24
-
GLoRe: When, Where, and How to Improve LLM Reasoning via Global and Local Refinements.
Alex Havrilla, Sharath Raparthy, Christoforus Nalmpantis, Jane Dwivedi-Yu, Maksym Zhuravinskyi, Eric Hambro, Roberta Railneau. ICML'24
-
Chain-of-Thought Reasoning Without Prompting.
Xuezhi Wang, Denny Zhou. Preprint'24
-
V-STaR: Training Verifiers for Self-Taught Reasoners.
Arian Hosseini, Xingdi Yuan, Nikolay Malkin, Aaron Courville, Alessandro Sordoni, Rishabh Agarwal. Preprint'24
-
InternLM-Math: Open Math Large Language Models Toward Verifiable Reasoning.
Huaiyuan Ying, Shuo Zhang, Linyang Li, Zhejian Zhou, Yunfan Shao, Zhaoye Fei, Yichuan Ma, Jiawei Hong, Kuikun Liu, Ziyi Wang, Yudong Wang, Zijian Wu, Shuaibin Li, Fengzhe Zhou, Hongwei Liu, Songyang Zhang, Wenwei Zhang, Hang Yan, Xipeng Qiu, Jiayu Wang, Kai Chen, Dahua Lin. Preprint'24
-
Self-Discover: Large Language Models Self-Compose Reasoning Structures.
Pei Zhou, Jay Pujara, Xiang Ren, Xinyun Chen, Heng-Tze Cheng, Quoc V. Le, Ed H. Chi, Denny Zhou, Swaroop Mishra, Huaixiu Steven Zheng. Preprint'24
-
DeepSeekMath: Pushing the Limits of Mathematical Reasoning in Open Language Models.
Zhihong Shao, Peiyi Wang, Qihao Zhu, Runxin Xu, Junxiao Song, Xiao Bi, Haowei Zhang, Mingchuan Zhang, Y.K. Li, Y. Wu, Daya Guo. Preprint'24
-
K-Level Reasoning with Large Language Models.
Yadong Zhang, Shaoguang Mao, Tao Ge, Xun Wang, Yan Xia, Man Lan, Furu Wei. Preprint'24
-
Efficient Tool Use with Chain-of-Abstraction Reasoning.
Silin Gao, Jane Dwivedi-Yu, Ping Yu, Xiaoqing Ellen Tan, Ramakanth Pasunuru, Olga Golovneva, Koustuv Sinha, Asli Celikyilmaz, Antoine Bosselut, Tianlu Wang. Preprint'24
-
Teaching Language Models to Self-Improve through Interactive Demonstrations.
Xiao Yu, Baolin Peng, Michel Galley, Jianfeng Gao, Zhou Yu. NAACL'24
-
Enhancing Zero-Shot Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in Large Language Models through Logic. [code]
Xufeng Zhao, Mengdi Li, Wenhao Lu, Cornelius Weber, Jae Hee Lee, Kun Chu, Stefan Wermter. COLING'24
-
Chain-of-Verification Reduces Hallucination in Large Language Models.
Shehzaad Dhuliawala, Mojtaba Komeili, Jing Xu, Roberta Raileanu, Xian Li, Asli Celikyilmaz, Jason Weston. ACL'24 Findings
-
Skeleton-of-Thought: Large Language Models Can Do Parallel Decoding.
Xuefei Ning, Zinan Lin, Zixuan Zhou, Huazhong Yang, Yu Wang. ICLR'24
-
Question Decomposition Improves the Faithfulness of Model-Generated Reasoning. [code]
Ansh Radhakrishnan, Karina Nguyen, Anna Chen, Carol Chen, Carson Denison, Danny Hernandez, Esin Durmus, Evan Hubinger, Jackson Kernion, Kamilė Lukošiūtė, Newton Cheng, Nicholas Joseph, Nicholas Schiefer, Oliver Rausch, Sam McCandlish, Sheer El Showk, Tamera Lanham, Tim Maxwell, Venkatesa Chandrasekaran, Zac Hatfield-Dodds, Jared Kaplan, Jan Brauner, Samuel R. Bowman, Ethan Perez. Preprint'23
-
Hunter Lightman, Vineet Kosaraju, Yura Burda, Harri Edwards, Bowen Baker, Teddy Lee, Jan Leike, John Schulman, Ilya Sutskever, Karl Cobbe. ICLR'24
-
REFINER: Reasoning Feedback on Intermediate Representations. [project] [code]
Debjit Paul, Mete Ismayilzada, Maxime Peyrard, Beatriz Borges, Antoine Bosselut, Robert West, Boi Faltings. EACL'24
-
Active Prompting with Chain-of-Thought for Large Language Models. [code]
Shizhe Diao, Pengcheng Wang, Yong Lin, Tong Zhang. ACL'24
-
Language Models as Inductive Reasoners.
Zonglin Yang, Li Dong, Xinya Du, Hao Cheng, Erik Cambria, Xiaodong Liu, Jianfeng Gao, Furu Wei. EACL'24
-
Boosting LLM Reasoning: Push the Limits of Few-shot Learning with Reinforced In-Context Pruning.
Xijie Huang, Li Lyna Zhang, Kwang-Ting Cheng, Mao Yang. Preprint'23
-
Logic-LM: Empowering Large Language Models with Symbolic Solvers for Faithful Logical Reasoning. [code]
Liangming Pan, Alon Albalak, Xinyi Wang, William Yang Wang. EMNLP'23 Findings
-
Recursion of Thought: A Divide and Conquer Approach to Multi-Context Reasoning with Language Models. [code] [poster]
Soochan Lee, Gunhee Kim. ACL'23 Findings
-
Reasoning with Language Model is Planning with World Model.
Shibo Hao, Yi Gu, Haodi Ma, Joshua Jiahua Hong, Zhen Wang, Daisy Zhe Wang, Zhiting Hu. EMNLP'23
-
Reasoning Implicit Sentiment with Chain-of-Thought Prompting. [code]
Hao Fei, Bobo Li, Qian Liu, Lidong Bing, Fei Li, Tat-Seng Chua. ACL'23
-
Tree of Thoughts: Deliberate Problem Solving with Large Language Models. [code]
Shunyu Yao, Dian Yu, Jeffrey Zhao, Izhak Shafran, Thomas L. Griffiths, Yuan Cao, Karthik Narasimhan. NeurIPS'23
-
SatLM: Satisfiability-Aided Language Models Using Declarative Prompting. [code]
Xi Ye, Qiaochu Chen, Isil Dillig, Greg Durrett. NeurIPS'23
-
ART: Automatic multi-step reasoning and tool-use for large language models.
Bhargavi Paranjape, Scott Lundberg, Sameer Singh, Hannaneh Hajishirzi, Luke Zettlemoyer, Marco Tulio Ribeiro. Preprint'23
-
Automatic Prompt Augmentation and Selection with Chain-of-Thought from Labeled Data. [code]
KaShun Shum, Shizhe Diao, Tong Zhang. EMNLP'23 Findings
-
Synthetic Prompting: Generating Chain-of-Thought Demonstrations for Large Language Models.
Zhihong Shao, Yeyun Gong, Yelong Shen, Minlie Huang, Nan Duan, Weizhu Chen. ICML'23
-
Faithful Chain-of-Thought Reasoning.
Qing Lyu, Shreya Havaldar, Adam Stein, Li Zhang, Delip Rao, Eric Wong, Marianna Apidianaki, Chris Callison-Burch. IJCNLP-AACL'23
-
Rethinking with Retrieval: Faithful Large Language Model Inference.
Hangfeng He, Hongming Zhang, Dan Roth. Preprint'23
-
LAMBADA: Backward Chaining for Automated Reasoning in Natural Language.
Seyed Mehran Kazemi, Najoung Kim, Deepti Bhatia, Xin Xu, Deepak Ramachandran. ACL'23
-
Interleaving Retrieval with Chain-of-Thought Reasoning for Knowledge-Intensive Multi-Step Questions. [code]
Harsh Trivedi, Niranjan Balasubramanian, Tushar Khot, Ashish Sabharwal. ACL'23
-
Large Language Models are Reasoners with Self-Verification. [code]
Yixuan Weng, Minjun Zhu, Shizhu He, Kang Liu, Jun Zhao. EMNLP'23 Findings
-
Can Retriever-Augmented Language Models Reason? The Blame Game Between the Retriever and the Language Model. [code]
Parishad BehnamGhader, Santiago Miret, Siva Reddy. EMNLP'23 Findings
-
Complementary Explanations for Effective In-Context Learning.
Xi Ye, Srinivasan Iyer, Asli Celikyilmaz, Ves Stoyanov, Greg Durrett, Ramakanth Pasunuru. ACL'23 Findings
-
Program of Thoughts Prompting: Disentangling Computation from Reasoning for Numerical Reasoning Tasks. [code]
Wenhu Chen, Xueguang Ma, Xinyi Wang, William W. Cohen. TMLR'23
-
Unsupervised Explanation Generation via Correct Instantiations.
Sijie Cheng, Zhiyong Wu, Jiangjie Chen, Zhixing Li, Yang Liu, Lingpeng Kong. AAAI'23
-
PAL: Program-aided Language Models. [project] [code]
Luyu Gao, Aman Madaan, Shuyan Zhou, Uri Alon, Pengfei Liu, Yiming Yang, Jamie Callan, Graham Neubig. ICML'23
-
Solving Math Word Problems via Cooperative Reasoning induced Language Models. [code]
Xinyu Zhu, Junjie Wang, Lin Zhang, Yuxiang Zhang, Ruyi Gan, Jiaxing Zhang, Yujiu Yang. ACL'23
-
Large Language Models Can Self-Improve.
Jiaxin Huang, Shixiang Shane Gu, Le Hou, Yuexin Wu, Xuezhi Wang, Hongkun Yu, Jiawei Han. EMNLP'23
-
Mind's Eye: Grounded language model reasoning through simulation.
Ruibo Liu, Jason Wei, Shixiang Shane Gu, Te-Yen Wu, Soroush Vosoughi, Claire Cui, Denny Zhou, Andrew M. Dai. ICLR'23
-
Automatic Chain of Thought Prompting in Large Language Models. [code]
Zhuosheng Zhang, Aston Zhang, Mu Li, Alex Smola. ICLR'23
-
Language Models are Multilingual Chain-of-Thought Reasoners.
Freda Shi, Mirac Suzgun, Markus Freitag, Xuezhi Wang, Suraj Srivats, Soroush Vosoughi, Hyung Won Chung, Yi Tay, Sebastian Ruder, Denny Zhou, Dipanjan Das, Jason Wei. ICLR'23
-
Ask Me Anything: A simple strategy for prompting language models. [code]
Simran Arora, Avanika Narayan, Mayee F. Chen, Laurel Orr, Neel Guha, Kush Bhatia, Ines Chami, Frederic Sala, Christopher Ré. ICLR'23
-
Dynamic Prompt Learning via Policy Gradient for Semi-structured Mathematical Reasoning. [project] [code]
Pan Lu, Liang Qiu, Kai-Wei Chang, Ying Nian Wu, Song-Chun Zhu, Tanmay Rajpurohit, Peter Clark, Ashwin Kalyan. ICLR'23
-
Making Large Language Models Better Reasoners with Step-Aware Verifier.
Yifei Li, Zeqi Lin, Shizhuo Zhang, Qiang Fu, Bei Chen, Jian-Guang Lou, Weizhu Chen. ACL'23
-
Least-to-most prompting enables complex reasoning in large language models.
Denny Zhou, Nathanael Schärli, Le Hou, Jason Wei, Nathan Scales, Xuezhi Wang, Dale Schuurmans, Claire Cui, Olivier Bousquet, Quoc Le, Ed Chi. ICLR'23
-
Self-consistency improves chain of thought reasoning in language models.
Xuezhi Wang, Jason Wei, Dale Schuurmans, Quoc Le, Ed Chi, Sharan Narang, Aakanksha Chowdhery, Denny Zhou. ICLR'23
-
Retrieval Augmentation for Commonsense Reasoning: A Unified Approach. [code]
Wenhao Yu, Chenguang Zhu, Zhihan Zhang, Shuohang Wang, Zhuosheng Zhang, Yuwei Fang, Meng Jiang. EMNLP'22
-
Language Models of Code are Few-Shot Commonsense Learners. [code]
Aman Madaan, Shuyan Zhou, Uri Alon, Yiming Yang, Graham Neubig. EMNLP'22
-
Solving Quantitative Reasoning Problems with Language Models. [blog]
Aitor Lewkowycz, Anders Andreassen, David Dohan, Ethan Dyer, Henryk Michalewski, Vinay Ramasesh, Ambrose Slone, Cem Anil, Imanol Schlag, Theo Gutman-Solo, Yuhuai Wu, Behnam Neyshabur, Guy Gur-Ari, Vedant Misra. NeurIPS'22
-
Large Language Models Still Can't Plan. [code]
Karthik Valmeekam, Alberto Olmo, Sarath Sreedharan, Subbarao Kambhampati. NeurIPS'22
-
Large Language Models are Zero-Shot Reasoners.
Takeshi Kojima, Shixiang Shane Gu, Machel Reid, Yutaka Matsuo, Yusuke Iwasawa. NeurIPS'22
-
Iteratively Prompt Pre-trained Language Models for Chain of Thought. [code]
Boshi Wang, Xiang Deng, Huan Sun. EMNLP'22
-
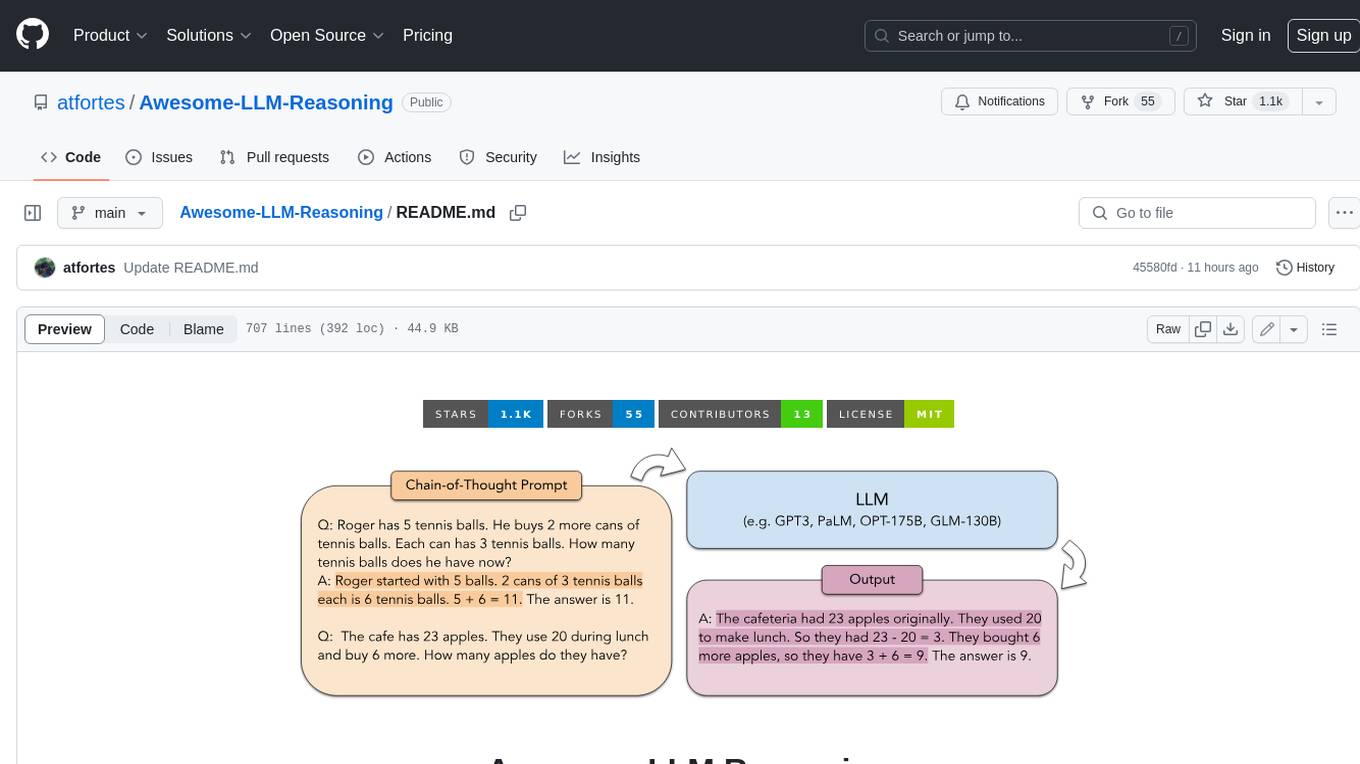
Chain of Thought Prompting Elicits Reasoning in Large Language Models. [blog]
Jason Wei, Xuezhi Wang, Dale Schuurmans, Maarten Bosma, Brian Ichter, Fei Xia, Ed Chi, Quoc Le, Denny Zhou. NeurIPS'22
-
LlamaV-o1: Rethinking Step-by-step Visual Reasoning in LLMs. [project] [code] [model]
Omkar Thawakar, Dinura Dissanayake, Ketan More, Ritesh Thawkar, Ahmed Heakl, Noor Ahsan, Yuhao Li, Mohammed Zumri, Jean Lahoud, Rao Muhammad Anwer, Hisham Cholakkal, Ivan Laptev, Mubarak Shah, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Salman Khan. Preprint'25
-
Insight-V: Exploring Long-Chain Visual Reasoning with Multimodal Large Language Models. [code] [model]
Yuhao Dong, Zuyan Liu, Hai-Long Sun, Jingkang Yang, Winston Hu, Yongming Rao, Ziwei Liu. Preprint'24
-
LLaVA-CoT: Let Vision Language Models Reason Step-by-Step code model
Guowei Xu, Peng Jin, Hao Li, Yibing Song, Lichao Sun, Li Yuan. Preprint'24
-
Visual Sketchpad: Sketching as a Visual Chain of Thought for Multimodal Language Models. [project] [code]
Yushi Hu, Weijia Shi, Xingyu Fu, Dan Roth, Mari Ostendorf, Luke Zettlemoyer, Noah A Smith, Ranjay Krishna. Preprint'24
-
Chart-based Reasoning: Transferring Capabilities from LLMs to VLMs.
Victor Carbune, Hassan Mansoor, Fangyu Liu, Rahul Aralikatte, Gilles Baechler, Jindong Chen, Abhanshu Sharma. NAACL'24 Findings
-
SpatialVLM: Endowing Vision-Language Models with Spatial Reasoning Capabilities. [project]
Boyuan Chen, Zhuo Xu, Sean Kirmani, Brian Ichter, Danny Driess, Pete Florence, Dorsa Sadigh, Leonidas Guibas, Fei Xia. CVPR'24
-
Chain-of-Table: Evolving Tables in the Reasoning Chain for Table Understanding.
Zilong Wang, Hao Zhang, Chun-Liang Li, Julian Martin Eisenschlos, Vincent Perot, Zifeng Wang, Lesly Miculicich, Yasuhisa Fujii, Jingbo Shang, Chen-Yu Lee, Tomas Pfister. ICLR'24
-
Link-Context Learning for Multimodal LLMs. [code]
Yan Tai, Weichen Fan, Zhao Zhang, Feng Zhu, Rui Zhao, Ziwei Liu. CVPR'24
-
Gemini in Reasoning: Unveiling Commonsense in Multimodal Large Language Models.
Yuqing Wang, Yun Zhao. Preprint'23
-
G-LLaVA: Solving Geometric Problems with Multi-Modal Large Language Model.
Jiahui Gao, Renjie Pi, Jipeng Zhang, Jiacheng Ye, Wanjun Zhong, Yufei Wang, Lanqing Hong, Jianhua Han, Hang Xu, Zhenguo Li, Lingpeng Kong. Preprint'23
-
Chameleon: Plug-and-Play Compositional Reasoning with Large Language Models. [project] [code]
Pan Lu, Baolin Peng, Hao Cheng, Michel Galley, Kai-Wei Chang, Ying Nian Wu, Song-Chun Zhu, Jianfeng Gao. NeurIPS'23
-
MM-REACT: Prompting ChatGPT for Multimodal Reasoning and Action. [project] [code] [demo]
Zhengyuan Yang, Linjie Li, Jianfeng Wang, Kevin Lin, Ehsan Azarnasab, Faisal Ahmed, Zicheng Liu, Ce Liu, Michael Zeng, Lijuan Wang. Preprint'23
-
ViperGPT: Visual Inference via Python Execution for Reasoning. [project] [code]
Dídac Surís, Sachit Menon, Carl Vondrick. ICCV'23
-
Visual ChatGPT: Talking, Drawing and Editing with Visual Foundation Models. [code]
Chenfei Wu, Shengming Yin, Weizhen Qi, Xiaodong Wang, Zecheng Tang, Nan Duan. Preprint'23
-
Multimodal Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in Language Models. [code]
Zhuosheng Zhang, Aston Zhang, Mu Li, Hai Zhao, George Karypis, Alex Smola. Preprint'23
-
Visual Programming: Compositional Visual Reasoning without Training. [project] [code]
Tanmay Gupta, Aniruddha Kembhavi. CPVR'23
-
Socratic Models: Composing Zero-Shot Multimodal Reasoning with Language. [project] [code]
Andy Zeng, Maria Attarian, Brian Ichter, Krzysztof Choromanski, Adrian Wong, Stefan Welker, Federico Tombari, Aveek Purohit, Michael Ryoo, Vikas Sindhwani, Johnny Lee, Vincent Vanhoucke, Pete Florence. ICLR'23
-
MathScale: Scaling Instruction Tuning for Mathematical Reasoning.
Zhengyang Tang, Xingxing Zhang, Benyou Wang, Furu Wei. Preprint'24
-
Learning Deductive Reasoning from Synthetic Corpus based on Formal Logic. [code]
Terufumi Morishita, Gaku Morio, Atsuki Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro Sogawa. ICML'23
-
Symbolic Chain-of-Thought Distillation: Small Models Can Also "Think" Step-by-Step. [code]
Liunian Harold Li, Jack Hessel, Youngjae Yu, Xiang Ren, Kai-Wei Chang, Yejin Choi. ACL'23
-
Specializing Smaller Language Models towards Multi-Step Reasoning.
Yao Fu, Hao Peng, Litu Ou, Ashish Sabharwal, Tushar Khot. ICML'23
-
Large Language Models Are Reasoning Teachers. [code]
Namgyu Ho, Laura Schmid, Se-Young Yun. ACL'23
-
Teaching Small Language Models to Reason.
Lucie Charlotte Magister, Jonathan Mallinson, Jakub Adamek, Eric Malmi, Aliaksei Severyn. ACL'23 Short
-
Kumar Shridhar, Alessandro Stolfo, Mrinmaya Sachan. ACL'23 Findings
-
Scaling Instruction-Finetuned Language Models.
Hyung Won Chung, Le Hou, Shayne Longpre, Barret Zoph, Yi Tay, William Fedus, Eric Li, Xuezhi Wang, Mostafa Dehghani, Siddhartha Brahma, Albert Webson, Shixiang Shane Gu, Zhuyun Dai, Mirac Suzgun, Xinyun Chen, Aakanksha Chowdhery, Sharan Narang, Gaurav Mishra, Adams Yu, Vincent Zhao, Yanping Huang, Andrew Dai, Hongkun Yu, Slav Petrov, Ed H. Chi, Jeff Dean, Jacob Devlin, Adam Roberts, Denny Zhou, Quoc V. Le, Jason Wei. JMLR'22
- LLM Reasoners A library for advanced large language model reasoning.
- Chain-of-Thought Hub Benchmarking LLM reasoning performance with chain-of-thought prompting.
- ThoughtSource Central and open resource for data and tools related to chain-of-thought reasoning in large language models.
- AgentChain Chain together LLMs for reasoning & orchestrate multiple large models for accomplishing complex tasks.
- google/Cascades Python library which enables complex compositions of language models such as scratchpads, chain of thought, tool use, selection-inference, and more.
- LogiTorch PyTorch-based library for logical reasoning on natural language.
- salesforce/LAVIS One-stop Library for Language-Vision Intelligence.
- facebookresearch/RAM A framework to study AI models in Reasoning, Alignment, and use of Memory (RAM).
- Awesome-Controllable-Generation Collection of papers and resources on Controllable Generation using Diffusion Models.
- Chain-of-ThoughtsPapers A trend starts from "Chain-of-Thought Prompting Elicits Reasoning in Large Language Models".
- LM-reasoning Collection of papers and resources on Reasoning in Large Language Models.
- Prompt4ReasoningPapers Repository for the paper "Reasoning with Language Model Prompting: A Survey".
- ReasoningNLP Paper list on reasoning in NLP
- Awesome-LLM Curated list of Large Language Model.
- Awesome LLM Self-Consistency Curated list of Self-consistency in Large Language Models.
- Deep-Reasoning-Papers Recent Papers including Neural-Symbolic Reasoning, Logical Reasoning, and Visual Reasoning.
- Add a new paper or update an existing paper, thinking about which category the work should belong to.
- Use the same format as existing entries to describe the work.
- Add the abstract link of the paper (
/abs/format if it is an arXiv publication).
Don't worry if you do something wrong, it will be fixed for you!
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Awesome-LLM-Reasoning
Similar Open Source Tools

Awesome-LLM-Reasoning
**Curated collection of papers and resources on how to unlock the reasoning ability of LLMs and MLLMs.** **Description in less than 400 words, no line breaks and quotation marks.** Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized the NLP landscape, showing improved performance and sample efficiency over smaller models. However, increasing model size alone has not proved sufficient for high performance on challenging reasoning tasks, such as solving arithmetic or commonsense problems. This curated collection of papers and resources presents the latest advancements in unlocking the reasoning abilities of LLMs and Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs). It covers various techniques, benchmarks, and applications, providing a comprehensive overview of the field. **5 jobs suitable for this tool, in lowercase letters.** - content writer - researcher - data analyst - software engineer - product manager **Keywords of the tool, in lowercase letters.** - llm - reasoning - multimodal - chain-of-thought - prompt engineering **5 specific tasks user can use this tool to do, in less than 3 words, Verb + noun form, in daily spoken language.** - write a story - answer a question - translate a language - generate code - summarize a document
Prompt4ReasoningPapers
Prompt4ReasoningPapers is a repository dedicated to reasoning with language model prompting. It provides a comprehensive survey of cutting-edge research on reasoning abilities with language models. The repository includes papers, methods, analysis, resources, and tools related to reasoning tasks. It aims to support various real-world applications such as medical diagnosis, negotiation, etc.
LLMAgentPapers
LLM Agents Papers is a repository containing must-read papers on Large Language Model Agents. It covers a wide range of topics related to language model agents, including interactive natural language processing, large language model-based autonomous agents, personality traits in large language models, memory enhancements, planning capabilities, tool use, multi-agent communication, and more. The repository also provides resources such as benchmarks, types of tools, and a tool list for building and evaluating language model agents. Contributors are encouraged to add important works to the repository.
awesome-llm-role-playing-with-persona
Awesome-llm-role-playing-with-persona is a curated list of resources for large language models for role-playing with assigned personas. It includes papers and resources related to persona-based dialogue systems, personalized response generation, psychology of LLMs, biases in LLMs, and more. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive collection of research papers and tools for exploring role-playing abilities of large language models in various contexts.
llm-self-correction-papers
This repository contains a curated list of papers focusing on the self-correction of large language models (LLMs) during inference. It covers various frameworks for self-correction, including intrinsic self-correction, self-correction with external tools, self-correction with information retrieval, and self-correction with training designed specifically for self-correction. The list includes survey papers, negative results, and frameworks utilizing reinforcement learning and OpenAI o1-like approaches. Contributions are welcome through pull requests following a specific format.
Awesome-LLM-Preference-Learning
The repository 'Awesome-LLM-Preference-Learning' is the official repository of a survey paper titled 'Towards a Unified View of Preference Learning for Large Language Models: A Survey'. It contains a curated list of papers related to preference learning for Large Language Models (LLMs). The repository covers various aspects of preference learning, including on-policy and off-policy methods, feedback mechanisms, reward models, algorithms, evaluation techniques, and more. The papers included in the repository explore different approaches to aligning LLMs with human preferences, improving mathematical reasoning in LLMs, enhancing code generation, and optimizing language model performance.
awesome-ai-llm4education
The 'awesome-ai-llm4education' repository is a curated list of papers related to artificial intelligence (AI) and large language models (LLM) for education. It collects papers from top conferences, journals, and specialized domain-specific conferences, categorizing them based on specific tasks for better organization. The repository covers a wide range of topics including tutoring, personalized learning, assessment, material preparation, specific scenarios like computer science, language, math, and medicine, aided teaching, as well as datasets and benchmarks for educational research.
LLM-Synthetic-Data
LLM-Synthetic-Data is a repository focused on real-time, fine-grained LLM-Synthetic-Data generation. It includes methods, surveys, and application areas related to synthetic data for language models. The repository covers topics like pre-training, instruction tuning, model collapse, LLM benchmarking, evaluation, and distillation. It also explores application areas such as mathematical reasoning, code generation, text-to-SQL, alignment, reward modeling, long context, weak-to-strong generalization, agent and tool use, vision and language, factuality, federated learning, generative design, and safety.
Awesome-Multimodal-LLM-for-Code
This repository contains papers, methods, benchmarks, and evaluations for code generation under multimodal scenarios. It covers UI code generation, scientific code generation, slide code generation, visually rich programming, logo generation, program repair, UML code generation, and general benchmarks.
LLM4DB
LLM4DB is a repository focused on the intersection of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Database technologies. It covers various aspects such as data processing, data analysis, database optimization, and data management for LLMs. The repository includes research papers, tools, and techniques related to leveraging LLMs for tasks like data cleaning, entity matching, schema matching, data discovery, NL2SQL, data exploration, data visualization, knob tuning, query optimization, and database diagnosis.

LLM4DB
LLM4DB is a repository focused on the intersection of Large Language Models (LLM) and Database technologies. It covers various aspects such as data processing, data analysis, database optimization, and data management for LLM. The repository includes works on data cleaning, entity matching, schema matching, data discovery, NL2SQL, data exploration, data visualization, configuration tuning, query optimization, and anomaly diagnosis using LLMs. It aims to provide insights and advancements in leveraging LLMs for improving data processing, analysis, and database management tasks.
Awesome-LLM-Reasoning-Openai-o1-Survey
The repository 'Awesome LLM Reasoning Openai-o1 Survey' provides a collection of survey papers and related works on OpenAI o1, focusing on topics such as LLM reasoning, self-play reinforcement learning, complex logic reasoning, and scaling law. It includes papers from various institutions and researchers, showcasing advancements in reasoning bootstrapping, reasoning scaling law, self-play learning, step-wise and process-based optimization, and applications beyond math. The repository serves as a valuable resource for researchers interested in exploring the intersection of language models and reasoning techniques.

awesome-generative-information-retrieval
This repository contains a curated list of resources on generative information retrieval, including research papers, datasets, tools, and applications. Generative information retrieval is a subfield of information retrieval that uses generative models to generate new documents or passages of text that are relevant to a given query. This can be useful for a variety of tasks, such as question answering, summarization, and document generation. The resources in this repository are intended to help researchers and practitioners stay up-to-date on the latest advances in generative information retrieval.
LLM-as-a-Judge
LLM-as-a-Judge is a repository that includes papers discussed in a survey paper titled 'A Survey on LLM-as-a-Judge'. The repository covers various aspects of using Large Language Models (LLMs) as judges for tasks such as evaluation, reasoning, and decision-making. It provides insights into evaluation pipelines, improvement strategies, and specific tasks related to LLMs. The papers included in the repository explore different methodologies, applications, and future research directions for leveraging LLMs as evaluators in various domains.
For similar tasks
blog
这是一个程序员关于 ChatGPT 学习过程的记录,其中包括了 ChatGPT 的使用技巧、相关工具和资源的整理,以及一些个人见解和思考。 **使用技巧** * **充值 OpenAI API**:可以通过 https://beta.openai.com/account/api-keys 进行充值,支持信用卡和 PayPal。 * **使用专梯**:推荐使用稳定的专梯,可以有效提高 ChatGPT 的访问速度和稳定性。 * **使用魔法**:可以通过 https://my.x-air.app:666/#/register?aff=32853 访问 ChatGPT,无需魔法即可访问。 * **下载各种 apk**:可以通过 https://apkcombo.com 下载各种安卓应用的 apk 文件。 * **ChatGPT 官网**:ChatGPT 的官方网站是 https://ai.com。 * **Midjourney**:Midjourney 是一个生成式 AI 图像平台,可以通过 https://midjourney.com 访问。 * **文本转视频**:可以通过 https://www.d-id.com 将文本转换为视频。 * **国内大模型**:国内也有很多大模型,如阿里巴巴的通义千问、百度文心一言、讯飞星火、阿里巴巴通义听悟等。 * **查看 OpenAI 状态**:可以通过 https://status.openai.com/ 查看 OpenAI 的服务状态。 * **Canva 画图**:Canva 是一个在线平面设计平台,可以通过 https://www.canva.cn 进行画图。 **相关工具和资源** * **文字转语音**:可以通过 https://modelscope.cn/models?page=1&tasks=text-to-speech&type=audio 找到文字转语音的模型。 * **可好好玩玩的项目**: * https://github.com/sunner/ChatALL * https://github.com/labring/FastGPT * https://github.com/songquanpeng/one-api * **个人博客**: * https://baoyu.io/ * https://gorden-sun.notion.site/527689cd2b294e60912f040095e803c5?v=4f6cc12006c94f47aee4dc909511aeb5 * **srt 2 lrc 歌词**:可以通过 https://gotranscript.com/subtitle-converter 将 srt 格式的字幕转换为 lrc 格式的歌词。 * **5 种速率限制**:OpenAI API 有 5 种速率限制:RPM(每分钟请求数)、RPD(每天请求数)、TPM(每分钟 tokens 数量)、TPD(每天 tokens 数量)、IPM(每分钟图像数量)。 * **扣子平台**:coze.cn 是一个扣子平台,可以提供各种扣子。 * **通过云函数免费使用 GPT-3.5**:可以通过 https://juejin.cn/post/7353849549540589587 免费使用 GPT-3.5。 * **不蒜子 统计网页基数**:可以通过 https://busuanzi.ibruce.info/ 统计网页的基数。 * **视频总结和翻译网页**:可以通过 https://glarity.app/zh-CN 总结和翻译视频。 * **视频翻译和配音工具**:可以通过 https://github.com/jianchang512/pyvideotrans 翻译和配音视频。 * **文字生成音频**:可以通过 https://www.cnblogs.com/jijunjian/p/18118366 将文字生成音频。 * **memo ai**:memo.ac 是一个多模态 AI 平台,可以将视频链接、播客链接、本地音视频转换为文字,支持多语言转录后翻译,还可以将文字转换为新的音频。 * **视频总结工具**:可以通过 https://summarize.ing/ 总结视频。 * **可每天免费玩玩**:可以通过 https://www.perplexity.ai/ 每天免费玩玩。 * **Suno.ai**:Suno.ai 是一个 AI 语言模型,可以通过 https://bibigpt.co/ 访问。 * **CapCut**:CapCut 是一个视频编辑软件,可以通过 https://www.capcut.cn/ 下载。 * **Valla.ai**:Valla.ai 是一个多模态 AI 模型,可以通过 https://www.valla.ai/ 访问。 * **Viggle.ai**:Viggle.ai 是一个 AI 视频生成平台,可以通过 https://viggle.ai 访问。 * **使用免费的 GPU 部署文生图大模型**:可以通过 https://www.cnblogs.com/xuxiaona/p/18088404 部署文生图大模型。 * **语音转文字**:可以通过 https://speech.microsoft.com/portal 将语音转换为文字。 * **投资界的 ai**:可以通过 https://reportify.cc/ 了解投资界的 ai。 * **抓取小视频 app 的各种信息**:可以通过 https://github.com/NanmiCoder/MediaCrawler 抓取小视频 app 的各种信息。 * **马斯克 Grok1 开源**:马斯克的 Grok1 模型已经开源,可以通过 https://github.com/xai-org/grok-1 访问。 * **ChatALL**:ChatALL 是一个跨端支持的聊天机器人,可以通过 https://github.com/sunner/ChatALL 访问。 * **零一万物**:零一万物是一个 AI 平台,可以通过 https://www.01.ai/cn 访问。 * **智普**:智普是一个 AI 语言模型,可以通过 https://chatglm.cn/ 访问。 * **memo ai 下载**:可以通过 https://memo.ac/ 下载 memo ai。 * **ffmpeg 学习**:可以通过 https://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2020/01/ffmpeg.html 学习 ffmpeg。 * **自动生成文章小工具**:可以通过 https://www.cognition-labs.com/blog 生成文章。 * **简易商城**:可以通过 https://www.cnblogs.com/whuanle/p/18086537 搭建简易商城。 * **物联网**:可以通过 https://www.cnblogs.com/xuxiaona/p/18088404 学习物联网。 * **自定义表单、自定义列表、自定义上传和下载、自定义流程、自定义报表**:可以通过 https://www.cnblogs.com/whuanle/p/18086537 实现自定义表单、自定义列表、自定义上传和下载、自定义流程、自定义报表。 **个人见解和思考** * ChatGPT 是一个强大的工具,可以用来提高工作效率和创造力。 * ChatGPT 的使用门槛较低,即使是非技术人员也可以轻松上手。 * ChatGPT 的发展速度非常快,未来可能会对各个行业产生深远的影响。 * 我们应该理性看待 ChatGPT,既要看到它的优点,也要意识到它的局限性。 * 我们应该积极探索 ChatGPT 的应用场景,为社会创造价值。
chat-ui
A chat interface using open source models, eg OpenAssistant or Llama. It is a SvelteKit app and it powers the HuggingChat app on hf.co/chat.
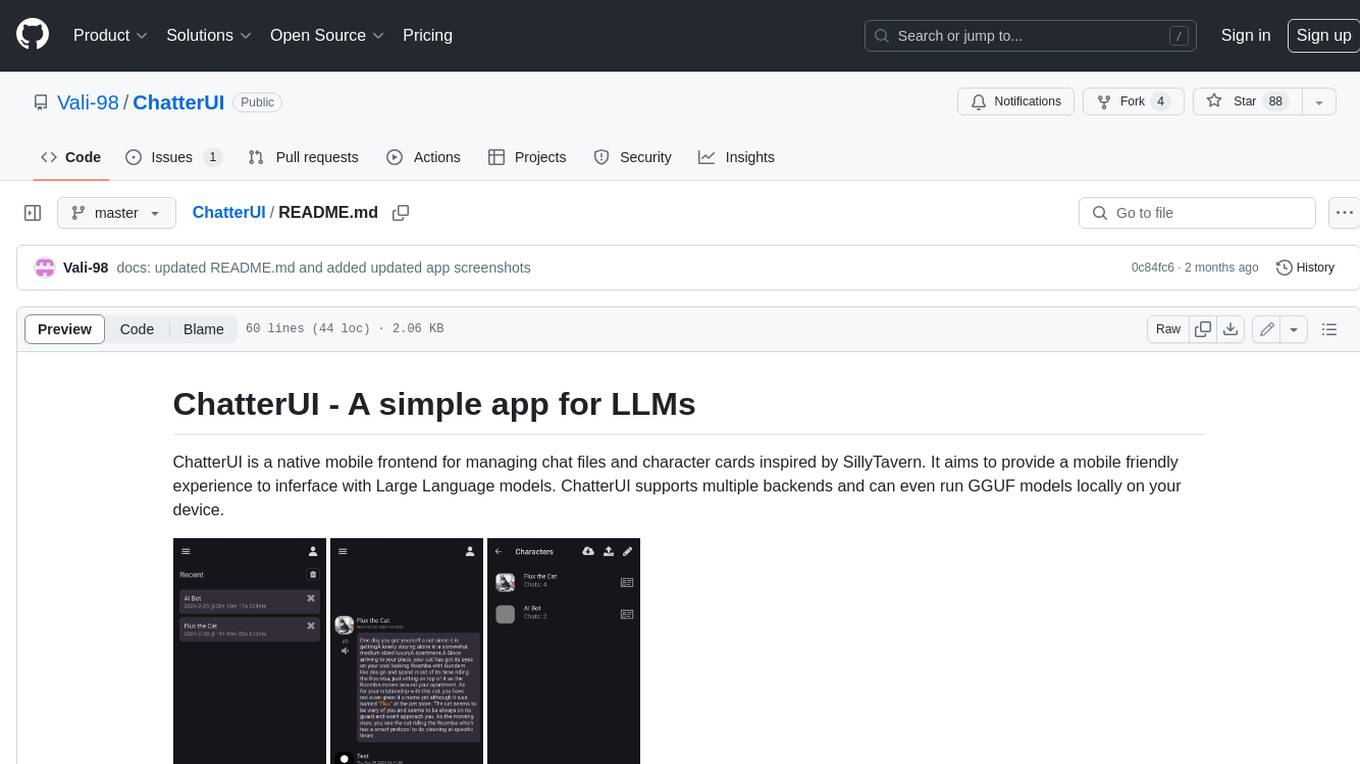
ChatterUI
ChatterUI is a mobile app that allows users to manage chat files and character cards, and to interact with Large Language Models (LLMs). It supports multiple backends, including local, koboldcpp, text-generation-webui, Generic Text Completions, AI Horde, Mancer, Open Router, and OpenAI. ChatterUI provides a mobile-friendly interface for interacting with LLMs, making it easy to use them for a variety of tasks, such as generating text, translating languages, writing code, and answering questions.
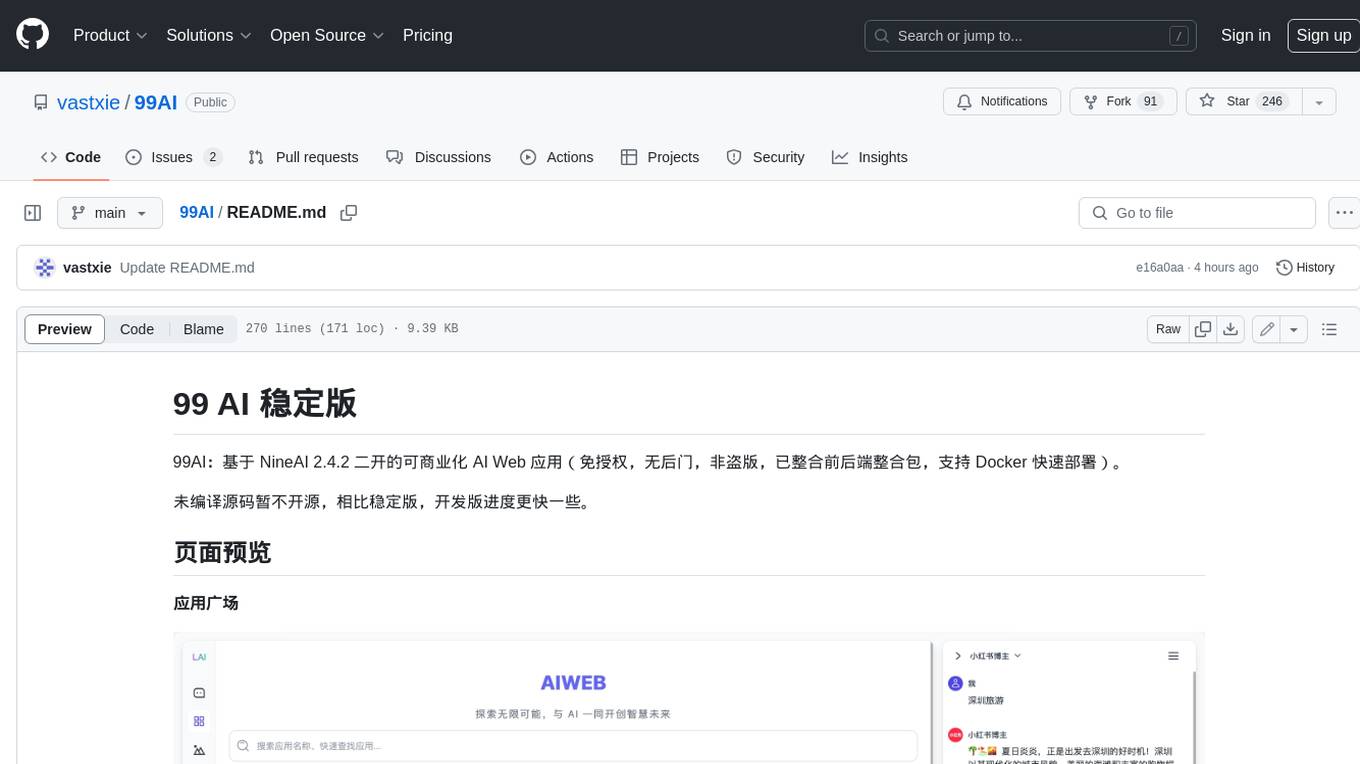
99AI
99AI is a commercializable AI web application based on NineAI 2.4.2 (no authorization, no backdoors, no piracy, integrated front-end and back-end integration packages, supports Docker rapid deployment). The uncompiled source code is temporarily closed. Compared with the stable version, the development version is faster.
chatnio
Chat Nio is a next-generation AI one-stop solution that provides a rich and user-friendly interface for interacting with various AI models. It offers features such as AI chat conversation, rich format compatibility, markdown support, message menu support, multi-platform adaptation, dialogue memory, full-model file parsing, full-model DuckDuckGo online search, full-screen large text editing, model marketplace, preset support, site announcements, preference settings, internationalization support, and a rich admin system. Chat Nio also boasts a powerful channel management system that utilizes a self-developed channel distribution algorithm, supports multi-channel management, is compatible with multiple formats, allows for custom models, supports channel retries, enables balanced load within the same channel, and provides channel model mapping and user grouping. Additionally, Chat Nio offers forwarding API services that are compatible with multiple formats in the OpenAI universal format and support multiple model compatible layers. It also provides a custom build and install option for highly customizable deployments. Chat Nio is an open-source project licensed under the Apache License 2.0 and welcomes contributions from the community.

Awesome-LLM-Reasoning
**Curated collection of papers and resources on how to unlock the reasoning ability of LLMs and MLLMs.** **Description in less than 400 words, no line breaks and quotation marks.** Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized the NLP landscape, showing improved performance and sample efficiency over smaller models. However, increasing model size alone has not proved sufficient for high performance on challenging reasoning tasks, such as solving arithmetic or commonsense problems. This curated collection of papers and resources presents the latest advancements in unlocking the reasoning abilities of LLMs and Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs). It covers various techniques, benchmarks, and applications, providing a comprehensive overview of the field. **5 jobs suitable for this tool, in lowercase letters.** - content writer - researcher - data analyst - software engineer - product manager **Keywords of the tool, in lowercase letters.** - llm - reasoning - multimodal - chain-of-thought - prompt engineering **5 specific tasks user can use this tool to do, in less than 3 words, Verb + noun form, in daily spoken language.** - write a story - answer a question - translate a language - generate code - summarize a document

Chinese-LLaMA-Alpaca-2
Chinese-LLaMA-Alpaca-2 is a large Chinese language model developed by Meta AI. It is based on the Llama-2 model and has been further trained on a large dataset of Chinese text. Chinese-LLaMA-Alpaca-2 can be used for a variety of natural language processing tasks, including text generation, question answering, and machine translation. Here are some of the key features of Chinese-LLaMA-Alpaca-2: * It is the largest Chinese language model ever trained, with 13 billion parameters. * It is trained on a massive dataset of Chinese text, including books, news articles, and social media posts. * It can be used for a variety of natural language processing tasks, including text generation, question answering, and machine translation. * It is open-source and available for anyone to use. Chinese-LLaMA-Alpaca-2 is a powerful tool that can be used to improve the performance of a wide range of natural language processing tasks. It is a valuable resource for researchers and developers working in the field of artificial intelligence.
Linly-Talker
Linly-Talker is an innovative digital human conversation system that integrates the latest artificial intelligence technologies, including Large Language Models (LLM) 🤖, Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) 🎙️, Text-to-Speech (TTS) 🗣️, and voice cloning technology 🎤. This system offers an interactive web interface through the Gradio platform 🌐, allowing users to upload images 📷 and engage in personalized dialogues with AI 💬.
For similar jobs
ChatFAQ
ChatFAQ is an open-source comprehensive platform for creating a wide variety of chatbots: generic ones, business-trained, or even capable of redirecting requests to human operators. It includes a specialized NLP/NLG engine based on a RAG architecture and customized chat widgets, ensuring a tailored experience for users and avoiding vendor lock-in.
anything-llm
AnythingLLM is a full-stack application that enables you to turn any document, resource, or piece of content into context that any LLM can use as references during chatting. This application allows you to pick and choose which LLM or Vector Database you want to use as well as supporting multi-user management and permissions.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.
mikupad
mikupad is a lightweight and efficient language model front-end powered by ReactJS, all packed into a single HTML file. Inspired by the likes of NovelAI, it provides a simple yet powerful interface for generating text with the help of various backends.

glide
Glide is a cloud-native LLM gateway that provides a unified REST API for accessing various large language models (LLMs) from different providers. It handles LLMOps tasks such as model failover, caching, key management, and more, making it easy to integrate LLMs into applications. Glide supports popular LLM providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI, AWS Bedrock (Titan), Cohere, Google Gemini, OctoML, and Ollama. It offers high availability, performance, and observability, and provides SDKs for Python and NodeJS to simplify integration.

onnxruntime-genai
ONNX Runtime Generative AI is a library that provides the generative AI loop for ONNX models, including inference with ONNX Runtime, logits processing, search and sampling, and KV cache management. Users can call a high level `generate()` method, or run each iteration of the model in a loop. It supports greedy/beam search and TopP, TopK sampling to generate token sequences, has built in logits processing like repetition penalties, and allows for easy custom scoring.
firecrawl
Firecrawl is an API service that takes a URL, crawls it, and converts it into clean markdown. It crawls all accessible subpages and provides clean markdown for each, without requiring a sitemap. The API is easy to use and can be self-hosted. It also integrates with Langchain and Llama Index. The Python SDK makes it easy to crawl and scrape websites in Python code.