
Time-LLM
[ICLR 2024] Official implementation of " 🦙 Time-LLM: Time Series Forecasting by Reprogramming Large Language Models"
Stars: 764
Time-LLM is a reprogramming framework that repurposes large language models (LLMs) for time series forecasting. It allows users to treat time series analysis as a 'language task' and effectively leverage pre-trained LLMs for forecasting. The framework involves reprogramming time series data into text representations and providing declarative prompts to guide the LLM reasoning process. Time-LLM supports various backbone models such as Llama-7B, GPT-2, and BERT, offering flexibility in model selection. The tool provides a general framework for repurposing language models for time series forecasting tasks.
README:
[Paper Page] [YouTube Talk 1] [YouTube Talk 2] [Medium Blog]
[机器之心中文解读] [时序人中文解读] [AI算法厨房中文解读] [知乎中文解读]
🙋 Please let us know if you find out a mistake or have any suggestions!
🌟 If you find this resource helpful, please consider to star this repository and cite our research:
@inproceedings{jin2023time,
title={{Time-LLM}: Time series forecasting by reprogramming large language models},
author={Jin, Ming and Wang, Shiyu and Ma, Lintao and Chu, Zhixuan and Zhang, James Y and Shi, Xiaoming and Chen, Pin-Yu and Liang, Yuxuan and Li, Yuan-Fang and Pan, Shirui and Wen, Qingsong},
booktitle={International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR)},
year={2024}
}
🚩 News (March 2024): Time-LLM has been upgraded to serve as a general framework for repurposing a wide range of language models to time series forecasting. It now defaults to supporting Llama-7B and includes compatibility with two additional smaller PLMs (GPT-2 and BERT). Simply adjust --llm_model and --llm_dim to switch backbones.
Time-LLM is a reprogramming framework to repurpose LLMs for general time series forecasting with the backbone language models kept intact. Notably, we show that time series analysis (e.g., forecasting) can be cast as yet another "language task" that can be effectively tackled by an off-the-shelf LLM.
- Time-LLM comprises two key components: (1) reprogramming the input time series into text prototype representations that are more natural for the LLM, and (2) augmenting the input context with declarative prompts (e.g., domain expert knowledge and task instructions) to guide LLM reasoning.
Use python 3.11 from MiniConda
- torch==2.2.2
- accelerate==0.28.0
- einops==0.7.0
- matplotlib==3.7.0
- numpy==1.23.5
- pandas==1.5.3
- scikit_learn==1.2.2
- scipy==1.12.0
- tqdm==4.65.0
- peft==0.4.0
- transformers==4.31.0
- deepspeed==0.14.0
- sentencepiece==0.2.0
To install all dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
You can access the well pre-processed datasets from [Google Drive], then place the downloaded contents under ./dataset
- Download datasets and place them under
./dataset - Tune the model. We provide five experiment scripts for demonstration purpose under the folder
./scripts. For example, you can evaluate on ETT datasets by:
bash ./scripts/TimeLLM_ETTh1.sh bash ./scripts/TimeLLM_ETTh2.sh bash ./scripts/TimeLLM_ETTm1.sh bash ./scripts/TimeLLM_ETTm2.shPlease refer to run_main.py, run_m4.py and run_pretrain.py for the detailed description of each hyperparameter.
1, Position Paper: What Can Large Language Models Tell Us about Time Series Analysis, in ICML 2024.
Authors: Ming Jin, Yifan Zhang, Wei Chen, Kexin Zhang, Yuxuan Liang*, Bin Yang, Jindong Wang, Shirui Pan, Qingsong Wen*
@inproceedings{jin2024position,
title={Position Paper: What Can Large Language Models Tell Us about Time Series Analysis},
author={Ming Jin and Yifan Zhang and Wei Chen and Kexin Zhang and Yuxuan Liang and Bin Yang and Jindong Wang and Shirui Pan and Qingsong Wen},
booktitle={International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2024)},
year={2024}
}2, Large Models for Time Series and Spatio-Temporal Data: A Survey and Outlook, in arXiv 2023. [GitHub Repo]
Authors: Ming Jin, Qingsong Wen*, Yuxuan Liang, Chaoli Zhang, Siqiao Xue, Xue Wang, James Zhang, Yi Wang, Haifeng Chen, Xiaoli Li (IEEE Fellow), Shirui Pan*, Vincent S. Tseng (IEEE Fellow), Yu Zheng (IEEE Fellow), Lei Chen (IEEE Fellow), Hui Xiong (IEEE Fellow)
@article{jin2023lm4ts,
title={Large Models for Time Series and Spatio-Temporal Data: A Survey and Outlook},
author={Ming Jin and Qingsong Wen and Yuxuan Liang and Chaoli Zhang and Siqiao Xue and Xue Wang and James Zhang and Yi Wang and Haifeng Chen and Xiaoli Li and Shirui Pan and Vincent S. Tseng and Yu Zheng and Lei Chen and Hui Xiong},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.10196},
year={2023}
}3, Transformers in Time Series: A Survey, in IJCAI 2023. [GitHub Repo]
Authors: Qingsong Wen, Tian Zhou, Chaoli Zhang, Weiqi Chen, Ziqing Ma, Junchi Yan, Liang Sun
@inproceedings{wen2023transformers,
title={Transformers in time series: A survey},
author={Wen, Qingsong and Zhou, Tian and Zhang, Chaoli and Chen, Weiqi and Ma, Ziqing and Yan, Junchi and Sun, Liang},
booktitle={International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence(IJCAI)},
year={2023}
}4, TimeMixer: Decomposable Multiscale Mixing for Time Series Forecasting, in ICLR 2024. [GitHub Repo]
Authors: Shiyu Wang, Haixu Wu, Xiaoming Shi, Tengge Hu, Huakun Luo, Lintao Ma, James Y. Zhang, Jun Zhou
@inproceedings{wang2023timemixer,
title={TimeMixer: Decomposable Multiscale Mixing for Time Series Forecasting},
author={Wang, Shiyu and Wu, Haixu and Shi, Xiaoming and Hu, Tengge and Luo, Huakun and Ma, Lintao and Zhang, James Y and ZHOU, JUN},
booktitle={International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR)},
year={2024}
}Our implementation adapts Time-Series-Library and OFA (GPT4TS) as the code base and have extensively modified it to our purposes. We thank the authors for sharing their implementations and related resources.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Time-LLM
Similar Open Source Tools

Time-LLM
Time-LLM is a reprogramming framework that repurposes large language models (LLMs) for time series forecasting. It allows users to treat time series analysis as a 'language task' and effectively leverage pre-trained LLMs for forecasting. The framework involves reprogramming time series data into text representations and providing declarative prompts to guide the LLM reasoning process. Time-LLM supports various backbone models such as Llama-7B, GPT-2, and BERT, offering flexibility in model selection. The tool provides a general framework for repurposing language models for time series forecasting tasks.
AI-PhD-S24
AI-PhD-S24 is a mono-repo for the PhD course 'AI for Business Research' at CUHK Business School in Spring 2024. The course aims to provide a basic understanding of machine learning and artificial intelligence concepts/methods used in business research, showcase how ML/AI is utilized in business research, and introduce state-of-the-art AI/ML technologies. The course includes scribed lecture notes, class recordings, and covers topics like AI/ML fundamentals, DL, NLP, CV, unsupervised learning, and diffusion models.
llm-self-correction-papers
This repository contains a curated list of papers focusing on the self-correction of large language models (LLMs) during inference. It covers various frameworks for self-correction, including intrinsic self-correction, self-correction with external tools, self-correction with information retrieval, and self-correction with training designed specifically for self-correction. The list includes survey papers, negative results, and frameworks utilizing reinforcement learning and OpenAI o1-like approaches. Contributions are welcome through pull requests following a specific format.
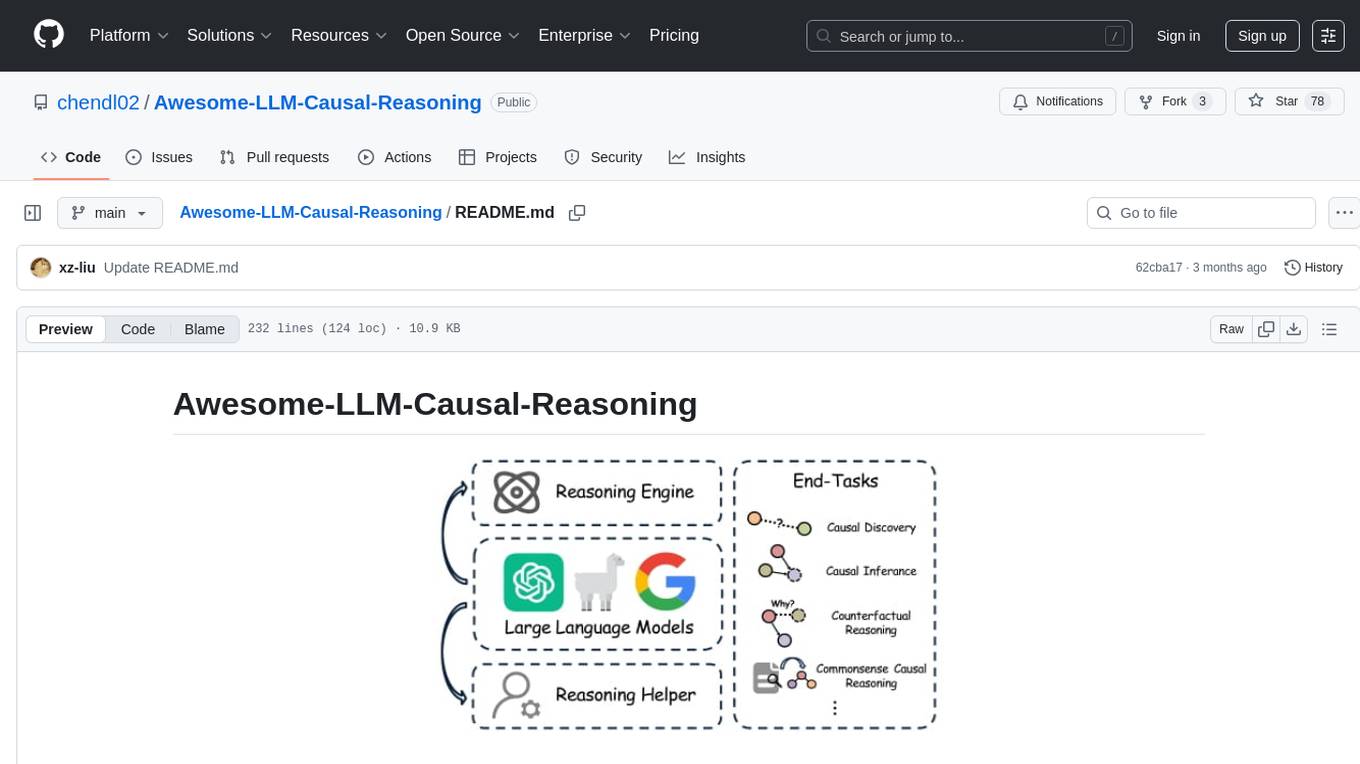
Awesome-LLM-Causal-Reasoning
The Awesome-LLM-Causal-Reasoning repository provides a comprehensive review of research focused on enhancing Large Language Models (LLMs) for causal reasoning (CR). It categorizes existing methods based on the role of LLMs as reasoning engines or helpers, evaluates LLMs' performance on various causal reasoning tasks, and discusses methodologies and insights for future research. The repository includes papers, datasets, and benchmarks related to causal reasoning in LLMs.
AI-PhD-S25
AI-PhD-S25 is a mono-repo for the DOTE 6635 course on AI for Business Research at CUHK Business School. The course aims to provide a fundamental understanding of ML/AI concepts and methods relevant to business research, explore applications of ML/AI in business research, and discover cutting-edge AI/ML technologies. The course resources include Google CoLab for code distribution, Jupyter Notebooks, Google Sheets for group tasks, Overleaf template for lecture notes, replication projects, and access to HPC Server compute resource. The course covers topics like AI/ML in business research, deep learning basics, attention mechanisms, transformer models, LLM pretraining, posttraining, causal inference fundamentals, and more.
OmniGibson
OmniGibson is a platform for accelerating Embodied AI research built upon NVIDIA's Omniverse platform. It features photorealistic visuals, physical realism, fluid and soft body support, large-scale high-quality scenes and objects, dynamic kinematic and semantic object states, mobile manipulator robots with modular controllers, and an OpenAI Gym interface. The platform provides a comprehensive environment for researchers to conduct experiments and simulations in the field of Embodied AI.
AIRS
AIRS is a collection of open-source software tools, datasets, and benchmarks focused on Artificial Intelligence for Science in Quantum, Atomistic, and Continuum Systems. The goal is to develop and maintain an integrated, open, reproducible, and sustainable set of resources to advance the field of AI for Science. The current resources include tools for Quantum Mechanics, Density Functional Theory, Small Molecules, Protein Science, Materials Science, Molecular Interactions, and Partial Differential Equations.
rllm
rLLM (relationLLM) is a Pytorch library for Relational Table Learning (RTL) with LLMs. It breaks down state-of-the-art GNNs, LLMs, and TNNs as standardized modules and facilitates novel model building in a 'combine, align, and co-train' way using these modules. The library is LLM-friendly, processes various graphs as multiple tables linked by foreign keys, introduces new relational table datasets, and is supported by students and teachers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University and Tsinghua University.
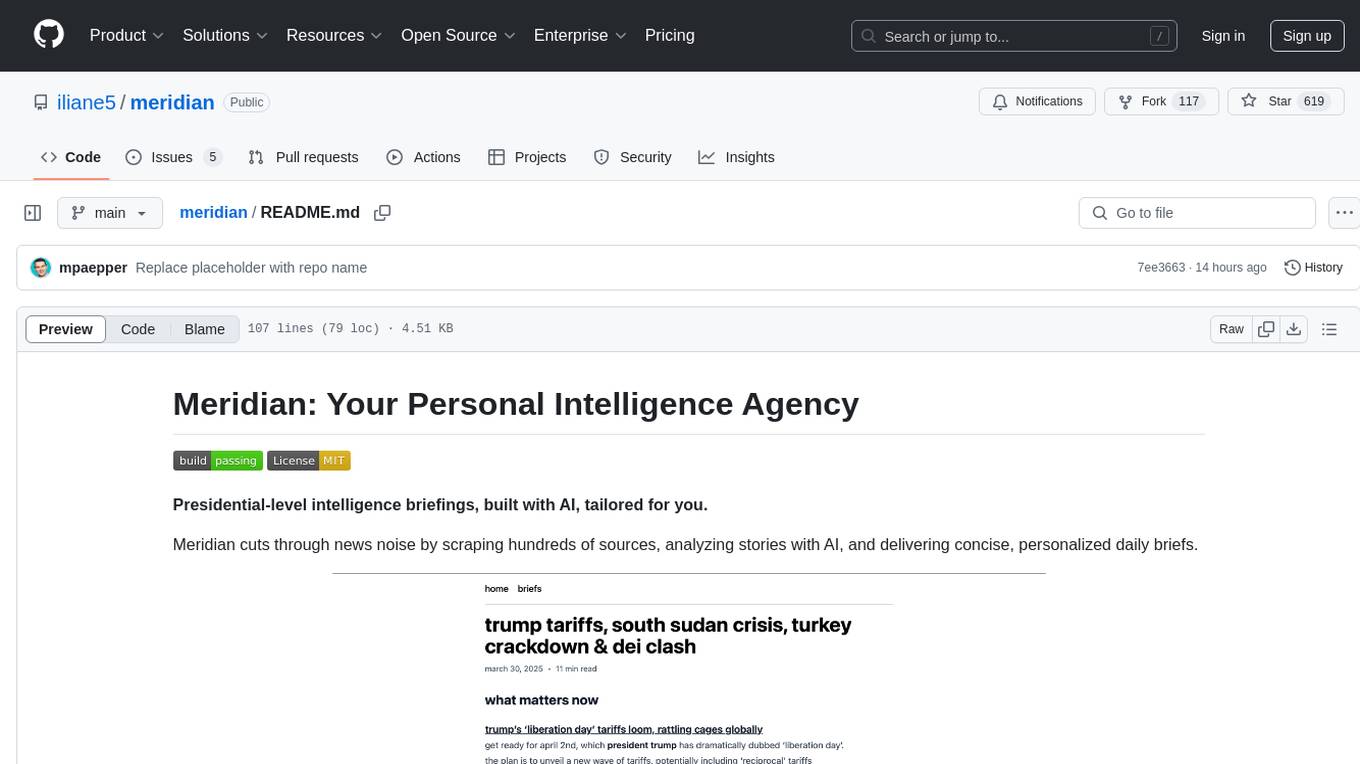
meridian
Meridian is a tool that provides personalized daily intelligence briefings by scraping news from hundreds of sources, analyzing stories with AI, and delivering concise briefs. It offers key global events, context, implications analysis, and open-source transparency. Built for the curious who seek in-depth news beyond headlines without spending too much time. The tool uses multi-stage LLM processing for article and cluster analysis, smart clustering techniques to group related articles, and a web interface powered by Nuxt 3. The workflow involves scraping RSS feeds, processing articles with Gemini for relevance, clustering articles, and generating a final brief. The project leverages AI models like Gemini, multilingual embeddings, UMAP, and HDBSCAN for analysis. The tech stack includes Turborepo, Cloudflare services, TypeScript, PostgreSQL, and Nuxt 3 with Vue 3 and Tailwind for the frontend.
awesome-tool-llm
This repository focuses on exploring tools that enhance the performance of language models for various tasks. It provides a structured list of literature relevant to tool-augmented language models, covering topics such as tool basics, tool use paradigm, scenarios, advanced methods, and evaluation. The repository includes papers, preprints, and books that discuss the use of tools in conjunction with language models for tasks like reasoning, question answering, mathematical calculations, accessing knowledge, interacting with the world, and handling non-textual modalities.
LLM101n
LLM101n is a course focused on building a Storyteller AI Large Language Model (LLM) from scratch in Python, C, and CUDA. The course covers various topics such as language modeling, machine learning, attention mechanisms, tokenization, optimization, device usage, precision training, distributed optimization, datasets, inference, finetuning, deployment, and multimodal applications. Participants will gain a deep understanding of AI, LLMs, and deep learning through hands-on projects and practical examples.
flower
Flower is a framework for building federated learning systems. It is designed to be customizable, extensible, framework-agnostic, and understandable. Flower can be used with any machine learning framework, for example, PyTorch, TensorFlow, Hugging Face Transformers, PyTorch Lightning, scikit-learn, JAX, TFLite, MONAI, fastai, MLX, XGBoost, Pandas for federated analytics, or even raw NumPy for users who enjoy computing gradients by hand.
DataDreamer
DataDreamer is a powerful open-source Python library designed for prompting, synthetic data generation, and training workflows. It is simple, efficient, and research-grade, allowing users to create prompting workflows, generate synthetic datasets, and train models with ease. The library is built for researchers, by researchers, focusing on correctness, best practices, and reproducibility. It offers features like aggressive caching, resumability, support for bleeding-edge techniques, and easy sharing of datasets and models. DataDreamer enables users to run multi-step prompting workflows, generate synthetic datasets for various tasks, and train models by aligning, fine-tuning, instruction-tuning, and distilling them using existing or synthetic data.
FuseAI
FuseAI is a repository that focuses on knowledge fusion of large language models. It includes FuseChat, a state-of-the-art 7B LLM on MT-Bench, and FuseLLM, which surpasses Llama-2-7B by fusing three open-source foundation LLMs. The repository provides tech reports, releases, and datasets for FuseChat and FuseLLM, showcasing their performance and advancements in the field of chat models and large language models.
Agent-R1
Agent-R1 is an open-source framework designed to accelerate research and development at the critical intersection of RL and Agent. It employs End-to-End reinforcement learning to train agents in specific environments. Developers define domain-specific tools and reward functions to extend Agent-R1 to unique use cases, eliminating the need for complex workflow engineering. Key features include multi-turn tool calling, multi-tool coordination, process rewards, custom tools and environments, support for multiple RL algorithms, and multi-modal support. It aims to make it easier for researchers and developers to create and explore agents in their own domains, collectively advancing the development of autonomous agents.
xgen
XGen is a research release for the family of XGen models (7B) by Salesforce AI Research. It includes models with support for different sequence lengths and tokenization using the OpenAI Tiktoken package. The models can be used for auto-regressive sampling in natural language generation tasks.
For similar tasks
Awesome-Segment-Anything
Awesome-Segment-Anything is a powerful tool for segmenting and extracting information from various types of data. It provides a user-friendly interface to easily define segmentation rules and apply them to text, images, and other data formats. The tool supports both supervised and unsupervised segmentation methods, allowing users to customize the segmentation process based on their specific needs. With its versatile functionality and intuitive design, Awesome-Segment-Anything is ideal for data analysts, researchers, content creators, and anyone looking to efficiently extract valuable insights from complex datasets.

Time-LLM
Time-LLM is a reprogramming framework that repurposes large language models (LLMs) for time series forecasting. It allows users to treat time series analysis as a 'language task' and effectively leverage pre-trained LLMs for forecasting. The framework involves reprogramming time series data into text representations and providing declarative prompts to guide the LLM reasoning process. Time-LLM supports various backbone models such as Llama-7B, GPT-2, and BERT, offering flexibility in model selection. The tool provides a general framework for repurposing language models for time series forecasting tasks.

crewAI
CrewAI is a cutting-edge framework designed to orchestrate role-playing autonomous AI agents. By fostering collaborative intelligence, CrewAI empowers agents to work together seamlessly, tackling complex tasks. It enables AI agents to assume roles, share goals, and operate in a cohesive unit, much like a well-oiled crew. Whether you're building a smart assistant platform, an automated customer service ensemble, or a multi-agent research team, CrewAI provides the backbone for sophisticated multi-agent interactions. With features like role-based agent design, autonomous inter-agent delegation, flexible task management, and support for various LLMs, CrewAI offers a dynamic and adaptable solution for both development and production workflows.
Transformers_And_LLM_Are_What_You_Dont_Need
Transformers_And_LLM_Are_What_You_Dont_Need is a repository that explores the limitations of transformers in time series forecasting. It contains a collection of papers, articles, and theses discussing the effectiveness of transformers and LLMs in this domain. The repository aims to provide insights into why transformers may not be the best choice for time series forecasting tasks.
pytorch-forecasting
PyTorch Forecasting is a PyTorch-based package for time series forecasting with state-of-the-art network architectures. It offers a high-level API for training networks on pandas data frames and utilizes PyTorch Lightning for scalable training on GPUs and CPUs. The package aims to simplify time series forecasting with neural networks by providing a flexible API for professionals and default settings for beginners. It includes a timeseries dataset class, base model class, multiple neural network architectures, multi-horizon timeseries metrics, and hyperparameter tuning with optuna. PyTorch Forecasting is built on pytorch-lightning for easy training on various hardware configurations.
spider
Spider is a high-performance web crawler and indexer designed to handle data curation workloads efficiently. It offers features such as concurrency, streaming, decentralization, headless Chrome rendering, HTTP proxies, cron jobs, subscriptions, smart mode, blacklisting, whitelisting, budgeting depth, dynamic AI prompt scripting, CSS scraping, and more. Users can easily get started with the Spider Cloud hosted service or set up local installations with spider-cli. The tool supports integration with Node.js and Python for additional flexibility. With a focus on speed and scalability, Spider is ideal for extracting and organizing data from the web.
AI_for_Science_paper_collection
AI for Science paper collection is an initiative by AI for Science Community to collect and categorize papers in AI for Science areas by subjects, years, venues, and keywords. The repository contains `.csv` files with paper lists labeled by keys such as `Title`, `Conference`, `Type`, `Application`, `MLTech`, `OpenReviewLink`. It covers top conferences like ICML, NeurIPS, and ICLR. Volunteers can contribute by updating existing `.csv` files or adding new ones for uncovered conferences/years. The initiative aims to track the increasing trend of AI for Science papers and analyze trends in different applications.
pytorch-forecasting
PyTorch Forecasting is a PyTorch-based package designed for state-of-the-art timeseries forecasting using deep learning architectures. It offers a high-level API and leverages PyTorch Lightning for efficient training on GPU or CPU with automatic logging. The package aims to simplify timeseries forecasting tasks by providing a flexible API for professionals and user-friendly defaults for beginners. It includes features such as a timeseries dataset class for handling data transformations, missing values, and subsampling, various neural network architectures optimized for real-world deployment, multi-horizon timeseries metrics, and hyperparameter tuning with optuna. Built on pytorch-lightning, it supports training on CPUs, single GPUs, and multiple GPUs out-of-the-box.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.






