
Video-Super-Resolution-Library
Native C and C++ implementation of RAISR (Rapid and Accurate Image Super-Resolution). Intel Video Super Resolution Library
Stars: 67
Intel® Library for Video Super Resolution (Intel® Library for VSR) is a project that offers a variety of algorithms, including machine learning and deep learning implementations, to convert low-resolution videos to high resolution. It enhances the RAISR algorithm to provide better visual quality and real-time performance for upscaling on Intel® Xeon® platforms and Intel® GPUs. The project is developed in C++ and utilizes Intel® AVX-512 on Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processor family and OpenCL support on Intel® GPUs. It includes an FFmpeg plugin inside a Docker container for ease of testing and deployment.
README:
Video Super Resolution converts video from low resolution to high resolution using traditional image processing or AI-based methods. Intel Library for Video Super Resolution consist of a few different algorithms including machine learning and deep learning implementations to offer a balance between quality and performance.
We have enhanced the public RAISR (Rapid and Accurate Image Super Resolution), an AI based Super Resolution algorithm https://arxiv.org/pdf/1606.01299.pdf, to achieve better visual quality and beyond real-time performance for 2x and 1.5x upscaling on Intel® Xeon® platforms and Intel® GPUs. Enhanced RAISR provides better quality results than standard (bicubic) algorithms and a good performance vs quality trade-off as compared to compute intensive DL-based algorithms.
Enhanced RAISR is provided as an FFmpeg plugin inside of a Docker container(Docker container only for CPU) to help ease testing and deployment burdens. This project is developed using C++ and takes advantage of Intel® Advanced Vector Extension 512 (Intel® AVX-512) on Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processor family and OpenCL support on Intel® GPUs.
-
July 2024 : Release performance of the alogorithm and pipeline on Intel® Xeon® Scalable processor as well as EC2 Intel instances deployed on AWS Cloud. See details at performance.md.
-
April 2024: Intel Library for Video Super Resolution algorithm now available on AWS. See the repository for details on how video super resolution works on the AWS service at https://github.com/aws-samples/video-super-resolution-tool. Technical details including video quality comparisons and performance information are available in a joint Intel / AWS white paper available at https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/content-details/820769/aws-compute-video-super-resolution-powered-by-the-intel-library-for-video-super-resolution.html
-
Feb 2024 : AWS and Intel announced collaboration to release Intel Library for VSR on AWS Cloud at the Mile High Video 2024 conference, technical details available at https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3638036.3640290
We have enhanced the public RAISR algorithm to achieve better visual quality and beyond real-time performance for 2x and 1.5x upscaling on Intel® Xeon® platforms and Intel® GPUs. The Intel Library for VSR is provided as an FFmpeg plugin inside of a Docker container to help ease testing and deployment burdens. This project is developed using C++ and takes advantage of Intel® Advanced Vector Extension 512 (Intel® AVX-512) where available and newly added Intel® AVX-512FP16 support on Intel® Xeon® 4th Generation (Sapphire Rapids) and added OpenCL support on Intel® GPUs.
Please see "How to build.md" to build via scripts or manually.
One should be able to test with video files:
./ffmpeg -y -i /input_files/input.mp4 -vf raisr=threadcount=20 -pix_fmt yuv420p /output_files/out.yuv
Or folders of images:
./ffmpeg -y -start_number 000 -i '/input_files/img_%03d.png' -vf scale=out_range=full,raisr=threadcount=20 -start_number 000 '/output_files/img_%03d.png'
Because saving raw uncompressed (.yuv) video can take up a lot of disk space, one could consider using the lossless (-crf 0) setting in x264/x265 to reduce the output file size by a substantial amount.
x264 lossless encoding
./ffmpeg -y -i /input_files/input.mp4 -vf raisr=threadcount=20 -pix_fmt yuv420p -c:v libx264 -crf 0 /output_files/out.mp4
x265 lossless encoding
./ffmpeg -y -i /input_files/input.mp4 -vf raisr=threadcount=20 -pix_fmt yuv420p -c:v libx265 -crf 0 /output_files/out_hevc.mp4
Evaluating the quality of the RAISR can be done in different ways.
- A source video or image can be upscaled by 2x using different filter configurations. We suggest trying these 3 command lines based upon preference:
Sharpest output
./ffmpeg -i /input_files/input.mp4 -vf "raisr=threadcount=20:passes=2:filterfolder=filters_2x/filters_highres" -pix_fmt yuv420p /output_files/out.yuv
Fastest Performance ( second pass disabled )
./ffmpeg -i /input_files/input.mp4 -vf "raisr=threadcount=20:filterfolder=filters_2x/filters_lowres" -pix_fmt yuv420p /output_files/out.yuv
Denoised output
./ffmpeg -i /input_files/input.mp4 -vf "raisr=threadcount=20:passes=2:mode=2:filterfolder=filters_2x/filters_denoise" -pix_fmt yuv420p /output_files/out.yuv
- A source video or image can be downscaled by 2x, then passed through the RAISR filter which upscales by 2x
./ffmpeg -y -i /input_files/input.mp4 -vf scale=iw/2:ih/2,raisr=threadcount=20 -pix_fmt yuv420p /output_files/out.yuv
At this point the source content is the same resolution as the output and the two can be compared to understand how well the super resolution is working. RAISR can be compared against existing DL super resolution algorithms as well. It is recommended to enable second pass in Intel Library for VSR to produce sharper images. Please see the Advanced Usage section for guidance on enabling second pass as a feature.
OpenCL acceleration
./ffmpeg -y -i /input_files/input.mp4 -vf raisr=asm=opencl -pix_fmt yuv420p /output_files/out.yuv
or user can use filter "raisr_opencl" to build full gpu pipeline.
ffmpeg-qsv
ffmpeg-vaapi
ffmpeg -init_hw_device vaapi=va -init_hw_device qsv=qs@va -init_hw_device opencl=ocl@va -hwaccel qsv -c:v h264_qsv -i input.264 -vf "hwmap=derive_device=opencl,format=opencl,raisr_opencl,hwmap=derive_device=qsv:reverse=1:extra_hw_frames=16" -c:v hevc_qsv output.mp4
ffmpeg -init_hw_device vaapi=va -init_hw_device opencl=ocl@va -hwaccel vaapi -hwaccel_output_format vaapi -i input.264 -vf "hwmap=derive_device=opencl,format=opencl,raisr_opencl,hwmap=derive_device=vaapi:reverse=1:extra_hw_frames=16" -c:v hevc_vaapi output.mp4
Even output
There are certain codecs that support only even resolution, the evenoutput parameter will support users to choose whether to make the output an even number
Set evenoutput=1 to make output size as even number, the following command will get 632x632 output.
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -an -vf scale=422x422,raisr=ratio=1.5:filterfolder=filters_1.5x/filters_highres:threadcount=1:evenoutput=1 output.mp4
It will keep the output resolution as the input resolution multiply by the upscaling ratio if set evenoutput=0 or not set the parameter, will get 633x633 output with 422x422 input.
./ffmpeg -h filter=raisr
raisr AVOptions:
ratio <float> ..FV....... ratio of the upscaling, between 1 and 2 (default 2)
bits <int> ..FV....... bit depth (from 8 to 10) (default 8)
range <string> ..FV....... color range of the input. If you are working with images, you may want to set range to full (video/full) (default video)
threadcount <int> ..FV....... thread count (from 1 to 120) (default 20)
filterfolder <string> ..FV....... absolute filter folder path (default "filters_2x/filters_lowres")
blending <int> ..FV....... CT blending mode (1: Randomness, 2: CountOfBitsChanged) (from 1 to 2) (default 2)
passes <int> ..FV....... passes to run (1: one pass, 2: two pass) (from 1 to 2) (default 1)
mode <int> ..FV....... mode for two pass (1: upscale in 1st pass, 2: upscale in 2nd pass) (from 1 to 2) (default 1)
asm <string> ..FV....... x86 asm type: (avx512fp16, avx512, avx2 or opencl) (default "avx512fp16")
platform <int> ..FV....... select the platform (from 0 to INT_MAX) (default 0)
device <int> ..FV....... select the device (from 0 to INT_MAX) (default 0)
evenoutput <int> ..FV....... make output size as even number (0: ignore, 1: subtract 1px if needed) (from 0 to 1) (default 0)
We welcome community contributions to the Open Visual Cloud repositories. If you have any idea how to improve the project, please share it with us.
Make sure you can build the project and run tests with your patch. Submit a pull request at https://github.com/OpenVisualCloud/Video-Super-Resolution-Library/pulls. The Intel Library for VSR is licensed under the BSD 3-Clause "New" or "Revised" license. By contributing to the project, you agree to the license and copyright terms therein and release your contribution under these terms.
Use the Issues tab on Github.
Intel, the Intel logo and Xeon are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries.
Intel Library for VSR is licensed under the BSD 3-clause license.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Video-Super-Resolution-Library
Similar Open Source Tools

Video-Super-Resolution-Library
Intel® Library for Video Super Resolution (Intel® Library for VSR) is a project that offers a variety of algorithms, including machine learning and deep learning implementations, to convert low-resolution videos to high resolution. It enhances the RAISR algorithm to provide better visual quality and real-time performance for upscaling on Intel® Xeon® platforms and Intel® GPUs. The project is developed in C++ and utilizes Intel® AVX-512 on Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processor family and OpenCL support on Intel® GPUs. It includes an FFmpeg plugin inside a Docker container for ease of testing and deployment.
Easy-Translate
Easy-Translate is a script designed for translating large text files with a single command. It supports various models like M2M100, NLLB200, SeamlessM4T, LLaMA, and Bloom. The tool is beginner-friendly and offers seamless and customizable features for advanced users. It allows acceleration on CPU, multi-CPU, GPU, multi-GPU, and TPU, with support for different precisions and decoding strategies. Easy-Translate also provides an evaluation script for translations. Built on HuggingFace's Transformers and Accelerate library, it supports prompt usage and loading huge models efficiently.
FlexFlow
FlexFlow Serve is an open-source compiler and distributed system for **low latency**, **high performance** LLM serving. FlexFlow Serve outperforms existing systems by 1.3-2.0x for single-node, multi-GPU inference and by 1.4-2.4x for multi-node, multi-GPU inference.
Upscaler
Holloway's Upscaler is a consolidation of various compiled open-source AI image/video upscaling products for a CLI-friendly image and video upscaling program. It provides low-cost AI upscaling software that can run locally on a laptop, programmable for albums and videos, reliable for large video files, and works without GUI overheads. The repository supports hardware testing on various systems and provides important notes on GPU compatibility, video types, and image decoding bugs. Dependencies include ffmpeg and ffprobe for video processing. The user manual covers installation, setup pathing, calling for help, upscaling images and videos, and contributing back to the project. Benchmarks are provided for performance evaluation on different hardware setups.
RTL-Coder
RTL-Coder is a tool designed to outperform GPT-3.5 in RTL code generation by providing a fully open-source dataset and a lightweight solution. It targets Verilog code generation and offers an automated flow to generate a large labeled dataset with over 27,000 diverse Verilog design problems and answers. The tool addresses the data availability challenge in IC design-related tasks and can be used for various applications beyond LLMs. The tool includes four RTL code generation models available on the HuggingFace platform, each with specific features and performance characteristics. Additionally, RTL-Coder introduces a new LLM training scheme based on code quality feedback to further enhance model performance and reduce GPU memory consumption.
PowerInfer
PowerInfer is a high-speed Large Language Model (LLM) inference engine designed for local deployment on consumer-grade hardware, leveraging activation locality to optimize efficiency. It features a locality-centric design, hybrid CPU/GPU utilization, easy integration with popular ReLU-sparse models, and support for various platforms. PowerInfer achieves high speed with lower resource demands and is flexible for easy deployment and compatibility with existing models like Falcon-40B, Llama2 family, ProSparse Llama2 family, and Bamboo-7B.

onnxruntime-genai
ONNX Runtime Generative AI is a library that provides the generative AI loop for ONNX models, including inference with ONNX Runtime, logits processing, search and sampling, and KV cache management. Users can call a high level `generate()` method, or run each iteration of the model in a loop. It supports greedy/beam search and TopP, TopK sampling to generate token sequences, has built in logits processing like repetition penalties, and allows for easy custom scoring.
exllamav2
ExLlamaV2 is an inference library designed for running local LLMs on modern consumer GPUs. The library supports paged attention via Flash Attention 2.5.7+, offers a new dynamic generator with features like dynamic batching, smart prompt caching, and K/V cache deduplication. It also provides an API for local or remote inference using TabbyAPI, with extended features like HF model downloading and support for HF Jinja2 chat templates. ExLlamaV2 aims to optimize performance and speed across different GPU models, with potential future optimizations and variations in speeds. The tool can be integrated with TabbyAPI for OpenAI-style web API compatibility and supports a standalone web UI called ExUI for single-user interaction with chat and notebook modes. ExLlamaV2 also offers support for text-generation-webui and lollms-webui through specific loaders and bindings.
torchtitan
Torchtitan is a PyTorch native platform designed for rapid experimentation and large-scale training of generative AI models. It provides a flexible foundation for developers to build upon with extension points for creating custom extensions. The tool showcases PyTorch's latest distributed training features and supports pretraining Llama 3.1 LLMs of various sizes. It offers key features like multi-dimensional parallelisms, FSDP2 with per-parameter sharding, Tensor Parallel, Pipeline Parallel, and more. Users can contribute to the tool through the experiments folder and core contributions guidelines. Installation can be done from source, nightly builds, or stable releases. The tool also supports training Llama 3.1 models and provides guidance on starting a training run and multi-node training. Citation information is available for referencing the tool in academic work, and the source code is under a BSD 3 license.
exllamav2
ExLlamaV2 is an inference library for running local LLMs on modern consumer GPUs. It is a faster, better, and more versatile codebase than its predecessor, ExLlamaV1, with support for a new quant format called EXL2. EXL2 is based on the same optimization method as GPTQ and supports 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 8-bit quantization. It allows for mixing quantization levels within a model to achieve any average bitrate between 2 and 8 bits per weight. ExLlamaV2 can be installed from source, from a release with prebuilt extension, or from PyPI. It supports integration with TabbyAPI, ExUI, text-generation-webui, and lollms-webui. Key features of ExLlamaV2 include: - Faster and better kernels - Cleaner and more versatile codebase - Support for EXL2 quantization format - Integration with various web UIs and APIs - Community support on Discord

djl
Deep Java Library (DJL) is an open-source, high-level, engine-agnostic Java framework for deep learning. It is designed to be easy to get started with and simple to use for Java developers. DJL provides a native Java development experience and allows users to integrate machine learning and deep learning models with their Java applications. The framework is deep learning engine agnostic, enabling users to switch engines at any point for optimal performance. DJL's ergonomic API interface guides users with best practices to accomplish deep learning tasks, such as running inference and training neural networks.

CogVideo
CogVideo is an open-source repository that provides pretrained text-to-video models for generating videos based on input text. It includes models like CogVideoX-2B and CogVideo, offering powerful video generation capabilities. The repository offers tools for inference, fine-tuning, and model conversion, along with demos showcasing the model's capabilities through CLI, web UI, and online experiences. CogVideo aims to facilitate the creation of high-quality videos from textual descriptions, catering to a wide range of applications.
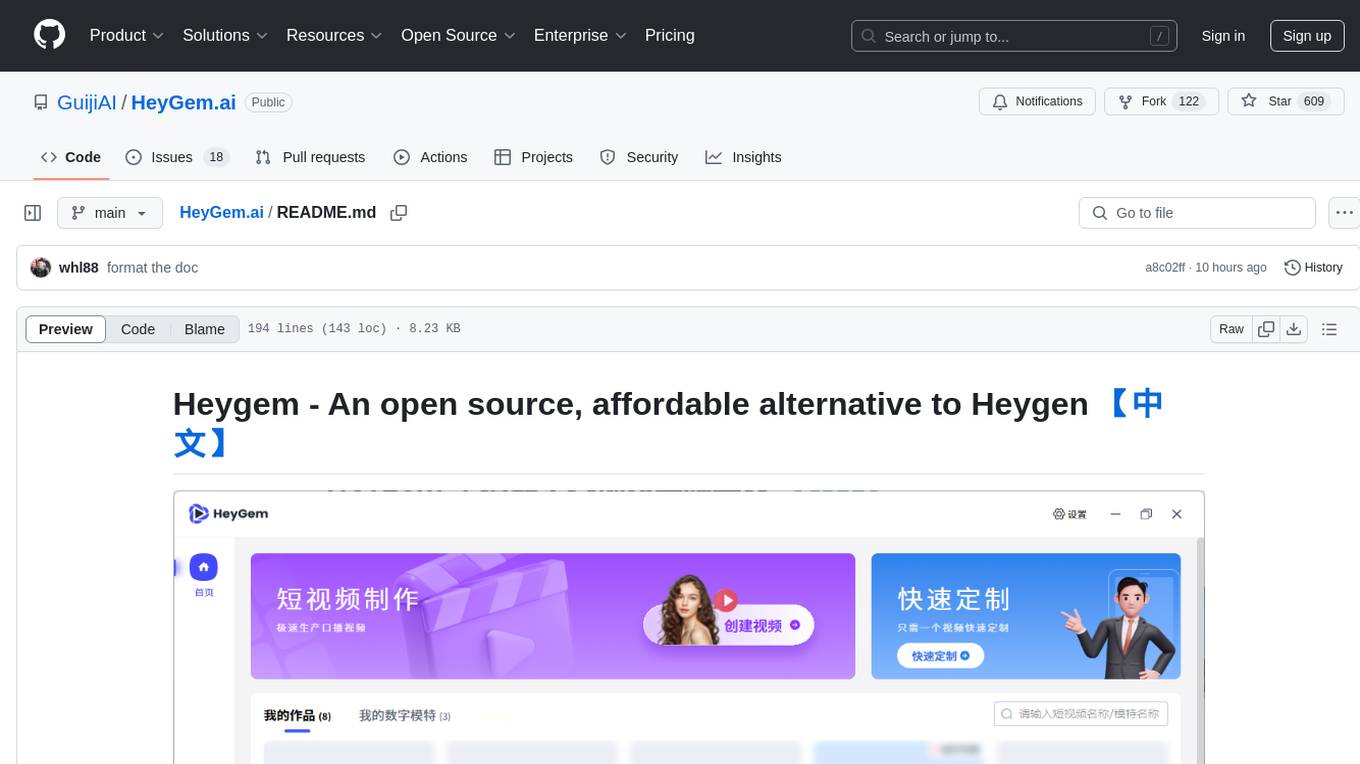
HeyGem.ai
Heygem is an open-source, affordable alternative to Heygen, offering a fully offline video synthesis tool for Windows systems. It enables precise appearance and voice cloning, allowing users to digitalize their image and drive virtual avatars through text and voice for video production. With core features like efficient video synthesis and multi-language support, Heygem ensures a user-friendly experience with fully offline operation and support for multiple models. The tool leverages advanced AI algorithms for voice cloning, automatic speech recognition, and computer vision technology to enhance the virtual avatar's performance and synchronization.
deep-research
Deep Research is a lightning-fast tool that uses powerful AI models to generate comprehensive research reports in just a few minutes. It leverages advanced 'Thinking' and 'Task' models, combined with an internet connection, to provide fast and insightful analysis on various topics. The tool ensures privacy by processing and storing all data locally. It supports multi-platform deployment, offers support for various large language models, web search functionality, knowledge graph generation, research history preservation, local and server API support, PWA technology, multi-key payload support, multi-language support, and is built with modern technologies like Next.js and Shadcn UI. Deep Research is open-source under the MIT License.
lm.rs
lm.rs is a tool that allows users to run inference on Language Models locally on the CPU using Rust. It supports LLama3.2 1B and 3B models, with a WebUI also available. The tool provides benchmarks and download links for models and tokenizers, with recommendations for quantization options. Users can convert models from Google/Meta on huggingface using provided scripts. The tool can be compiled with cargo and run with various arguments for model weights, tokenizer, temperature, and more. Additionally, a backend for the WebUI can be compiled and run to connect via the web interface.
kaito
KAITO is an operator that automates the AI/ML model inference or tuning workload in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, provides preset configurations to avoid adjusting workload parameters based on GPU hardware, supports popular open-sourced inference runtimes, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry. Using KAITO simplifies the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes.
For similar tasks

Video-Super-Resolution-Library
Intel® Library for Video Super Resolution (Intel® Library for VSR) is a project that offers a variety of algorithms, including machine learning and deep learning implementations, to convert low-resolution videos to high resolution. It enhances the RAISR algorithm to provide better visual quality and real-time performance for upscaling on Intel® Xeon® platforms and Intel® GPUs. The project is developed in C++ and utilizes Intel® AVX-512 on Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processor family and OpenCL support on Intel® GPUs. It includes an FFmpeg plugin inside a Docker container for ease of testing and deployment.
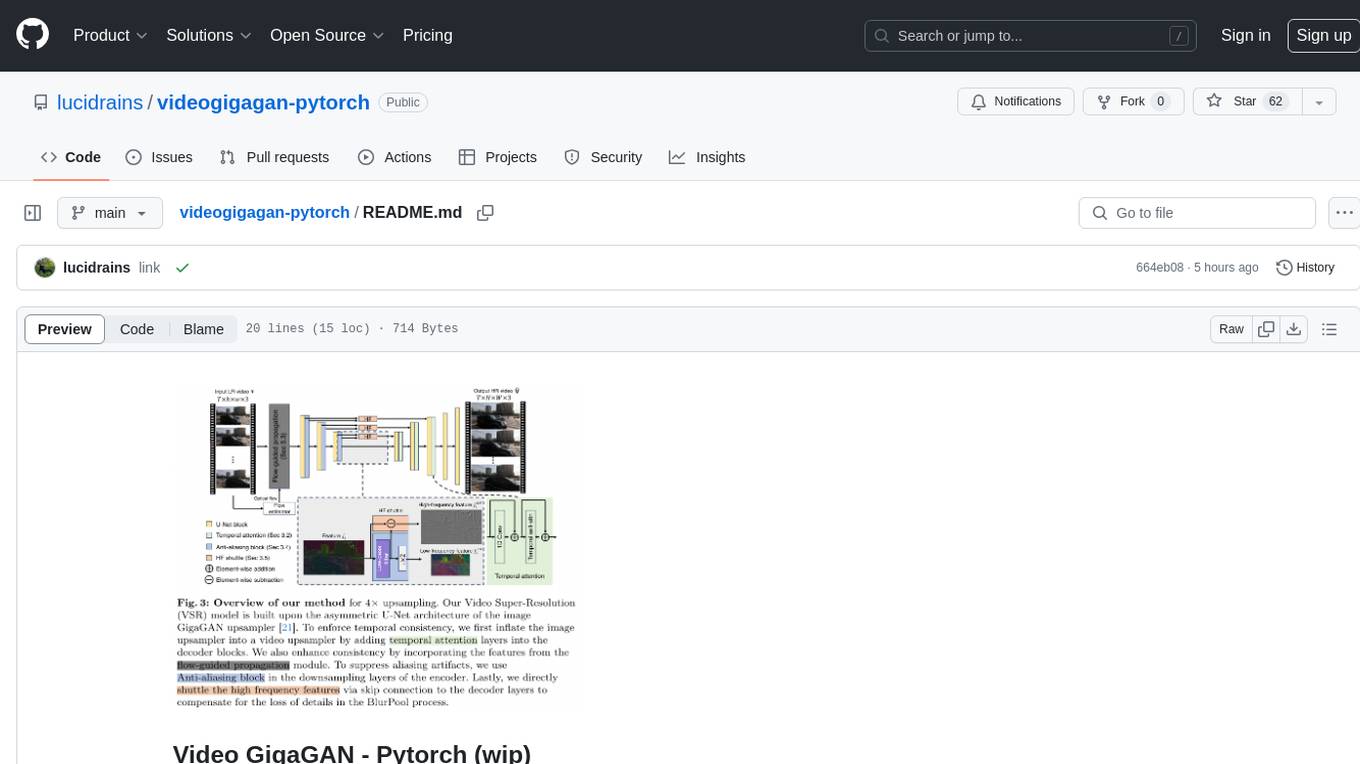
videogigagan-pytorch
Video GigaGAN - Pytorch is an implementation of Video GigaGAN, a state-of-the-art video upsampling technique developed by Adobe AI labs. The project aims to provide a Pytorch implementation for researchers and developers interested in video super-resolution. The codebase allows users to replicate the results of the original research paper and experiment with video upscaling techniques. The repository includes the necessary code and resources to train and test the GigaGAN model on video datasets. Researchers can leverage this implementation to enhance the visual quality of low-resolution videos and explore advancements in video super-resolution technology.
video-subtitle-remover
Video-subtitle-remover (VSR) is a software based on AI technology that removes hard subtitles from videos. It achieves the following functions: - Lossless resolution: Remove hard subtitles from videos, generate files with subtitles removed - Fill the region of removed subtitles using a powerful AI algorithm model (non-adjacent pixel filling and mosaic removal) - Support custom subtitle positions, only remove subtitles in defined positions (input position) - Support automatic removal of all text in the entire video (no input position required) - Support batch removal of watermark text from multiple images.
VisionDepth3D
VisionDepth3D is an all-in-one 3D suite for creators, combining AI depth and custom stereo logic for cinema in VR. The suite includes features like real-time 3D stereo composer with CUDA + PyTorch acceleration, AI-powered depth estimation supporting 25+ models, AI upscaling & interpolation, depth blender for blending depth maps, audio to video sync, smart GUI workflow, and various output formats & aspect ratios. The tool is production-ready, offering advanced parallax controls, streamlined export for cinema, VR, or streaming, and real-time preview overlays.
For similar jobs
stable-diffusion.cpp
The stable-diffusion.cpp repository provides an implementation for inferring stable diffusion in pure C/C++. It offers features such as support for different versions of stable diffusion, lightweight and dependency-free implementation, various quantization support, memory-efficient CPU inference, GPU acceleration, and more. Users can download the built executable program or build it manually. The repository also includes instructions for downloading weights, building from scratch, using different acceleration methods, running the tool, converting weights, and utilizing various features like Flash Attention, ESRGAN upscaling, PhotoMaker support, and more. Additionally, it mentions future TODOs and provides information on memory requirements, bindings, UIs, contributors, and references.
joliGEN
JoliGEN is an integrated framework for training custom generative AI image-to-image models. It implements GAN, Diffusion, and Consistency models for various image translation tasks, including domain and style adaptation with conservation of semantics. The tool is designed for real-world applications such as Controlled Image Generation, Augmented Reality, Dataset Smart Augmentation, and Synthetic to Real transforms. JoliGEN allows for fast and stable training with a REST API server for simplified deployment. It offers a wide range of options and parameters with detailed documentation available for models, dataset formats, and data augmentation.
ShapeLLM
ShapeLLM is the first 3D Multimodal Large Language Model designed for embodied interaction, exploring a universal 3D object understanding with 3D point clouds and languages. It supports single-view colored point cloud input and introduces a robust 3D QA benchmark, 3D MM-Vet, encompassing various variants. The model extends the powerful point encoder architecture, ReCon++, achieving state-of-the-art performance across a range of representation learning tasks. ShapeLLM can be used for tasks such as training, zero-shot understanding, visual grounding, few-shot learning, and zero-shot learning on 3D MM-Vet.
gpupixel
GPUPixel is a real-time, high-performance image and video filter library written in C++11 and based on OpenGL/ES. It incorporates a built-in beauty face filter that achieves commercial-grade beauty effects. The library is extremely easy to compile and integrate with a small size, supporting platforms including iOS, Android, Mac, Windows, and Linux. GPUPixel provides various filters like skin smoothing, whitening, face slimming, big eyes, lipstick, and blush. It supports input formats like YUV420P, RGBA, JPEG, PNG, and output formats like RGBA and YUV420P. The library's performance on devices like iPhone and Android is optimized, with low CPU usage and fast processing times. GPUPixel's lib size is compact, making it suitable for mobile and desktop applications.
mediapipe-rs
MediaPipe-rs is a Rust library designed for MediaPipe tasks on WasmEdge WASI-NN. It offers easy-to-use low-code APIs similar to mediapipe-python, with low overhead and flexibility for custom media input. The library supports various tasks like object detection, image classification, gesture recognition, and more, including TfLite models, TF Hub models, and custom models. Users can create task instances, run sessions for pre-processing, inference, and post-processing, and speed up processing by reusing sessions. The library also provides support for audio tasks using audio data from symphonia, ffmpeg, or raw audio. Users can choose between CPU, GPU, or TPU devices for processing.
hold
This repository contains the code for HOLD, a method that jointly reconstructs hands and objects from monocular videos without assuming a pre-scanned object template. It can reconstruct 3D geometries of novel objects and hands, enabling template-free bimanual hand-object reconstruction, textureless object interaction with hands, and multiple objects interaction with hands. The repository provides instructions to download in-the-wild videos from HOLD, preprocess and train on custom videos, a volumetric rendering framework, a generalized codebase for single and two hand interaction with objects, a viewer to interact with predictions, and code to evaluate and compare with HOLD in HO3D. The repository also includes documentation for setup, training, evaluation, visualization, preprocessing custom sequences, and using HOLD on ARCTIC.
LL3DA
LL3DA is a Large Language 3D Assistant that responds to both visual and textual interactions within complex 3D environments. It aims to help Large Multimodal Models (LMM) comprehend, reason, and plan in diverse 3D scenes by directly taking point cloud input and responding to textual instructions and visual prompts. LL3DA achieves remarkable results in 3D Dense Captioning and 3D Question Answering, surpassing various 3D vision-language models. The code is fully released, allowing users to train customized models and work with pre-trained weights. The tool supports training with different LLM backends and provides scripts for tuning and evaluating models on various tasks.
generative-models
Generative Models by Stability AI is a repository that provides various generative models for research purposes. It includes models like Stable Video 4D (SV4D) for video synthesis, Stable Video 3D (SV3D) for multi-view synthesis, SDXL-Turbo for text-to-image generation, and more. The repository focuses on modularity and implements a config-driven approach for building and combining submodules. It supports training with PyTorch Lightning and offers inference demos for different models. Users can access pre-trained models like SDXL-base-1.0 and SDXL-refiner-1.0 under a CreativeML Open RAIL++-M license. The codebase also includes tools for invisible watermark detection in generated images.