
gollm
Unified Go interface for Language Model (LLM) providers. Simplifies LLM integration with flexible prompt management and common task functions.
Stars: 414
gollm is a Go package designed to simplify interactions with Large Language Models (LLMs) for AI engineers and developers. It offers a unified API for multiple LLM providers, easy provider and model switching, flexible configuration options, advanced prompt engineering, prompt optimization, memory retention, structured output and validation, provider comparison tools, high-level AI functions, robust error handling and retries, and extensible architecture. The package enables users to create AI-powered golems for tasks like content creation workflows, complex reasoning tasks, structured data generation, model performance analysis, prompt optimization, and creating a mixture of agents.
README:
gollm is a Go package designed to help you build your own AI golems. Just as the mystical golem of legend was brought to life with sacred words, gollm empowers you to breathe life into your AI creations using the power of Large Language Models (LLMs). This package simplifies and streamlines interactions with various LLM providers, offering a unified, flexible, and powerful interface for AI engineers and developers to craft their own digital servants.
- Key Features
- Real-World Applications
- Installation
- Quick Start
- Quick Reference
- Advanced Usage
- Best Practices
- Examples and Tutorials
- Project Status
- Philosophy
- Contributing
- License
- Unified API for Multiple LLM Providers: Interact seamlessly with various providers, including OpenAI, Anthropic, Groq, and Ollama. Easily switch between models like GPT-4, Claude, and Llama-3.1.
- Easy Provider and Model Switching: Configure preferred providers and models with simple options.
- Flexible Configuration Options: Customize using environment variables, code-based configuration, or configuration files.
- Advanced Prompt Engineering: Craft sophisticated instructions to guide your AI's responses effectively.
- Prompt Optimizer: Automatically refine and improve your prompts for better results, with support for custom metrics and different rating systems.
- Memory Retention: Maintain context across multiple interactions for more coherent conversations.
- Structured Output and Validation: Ensure outputs are consistent and reliable with JSON schema generation and validation.
- Provider Comparison Tools: Test performance across different LLM providers and models for the same task.
-
High-Level AI Functions: Use pre-built functions like
ChainOfThoughtfor complex reasoning tasks. - Robust Error Handling and Retries: Built-in retry mechanisms to handle API rate limits and transient errors.
- Extensible Architecture: Easily expand support for new LLM providers and features.
gollm can handle a wide range of AI-powered tasks, including:
- Content Creation Workflows: Generate research summaries, article ideas, and refined paragraphs.
-
Complex Reasoning Tasks: Use the
ChainOfThoughtfunction to analyze complex problems step-by-step. - Structured Data Generation: Create and validate complex data structures with customizable JSON schemas.
- Model Performance Analysis: Compare different models' performance for specific tasks.
- Prompt Optimization: Automatically improve prompts for various tasks.
- Mixture of Agents: Combine responses from multiple LLM providers.
go get github.com/teilomillet/gollmpackage main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"github.com/teilomillet/gollm"
)
func main() {
// Load API key from environment variable
apiKey := os.Getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
if apiKey == "" {
log.Fatalf("OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable is not set")
}
// Create a new LLM instance with custom configuration
llm, err := gollm.NewLLM(
gollm.SetProvider("openai"),
gollm.SetModel("gpt-4o-mini"),
gollm.SetAPIKey(apiKey),
gollm.SetMaxTokens(200),
gollm.SetMaxRetries(3),
gollm.SetRetryDelay(time.Second*2),
gollm.SetLogLevel(gollm.LogLevelInfo),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create LLM: %v", err)
}
ctx := context.Background()
// Create a basic prompt
prompt := gollm.NewPrompt("Explain the concept of 'recursion' in programming.")
// Generate a response
response, err := llm.Generate(ctx, prompt)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to generate text: %v", err)
}
fmt.Printf("Response:\n%s\n", response)
}Here's a quick reference guide for the most commonly used functions and options in the gollm package:
llm, err := gollm.NewLLM(
gollm.SetProvider("openai"),
gollm.SetModel("gpt-4"),
gollm.SetAPIKey("your-api-key"),
gollm.SetMaxTokens(100),
gollm.SetTemperature(0.7),
gollm.SetMemory(4096),
)prompt := gollm.NewPrompt("Your prompt text here",
gollm.WithContext("Additional context"),
gollm.WithDirectives("Be concise", "Use examples"),
gollm.WithOutput("Expected output format"),
gollm.WithMaxLength(300),
)response, err := llm.Generate(ctx, prompt)response, err := tools.ChainOfThought(ctx, llm, "Your question here")optimizer := optimizer.NewPromptOptimizer(llm, initialPrompt, taskDescription,
optimizer.WithCustomMetrics(/* custom metrics */),
optimizer.WithRatingSystem("numerical"),
optimizer.WithThreshold(0.8),
)
optimizedPrompt, err := optimizer.OptimizePrompt(ctx)results, err := tools.CompareModels(ctx, promptText, validateFunc, configs...)The gollm package offers a range of advanced features to enhance your AI applications:
Create sophisticated prompts with multiple components:
prompt := gollm.NewPrompt("Explain the concept of recursion in programming.",
gollm.WithContext("The audience is beginner programmers."),
gollm.WithDirectives(
"Use simple language and avoid jargon.",
"Provide a practical example.",
"Explain potential pitfalls and how to avoid them.",
),
gollm.WithOutput("Structure your response with sections: Definition, Example, Pitfalls, Best Practices."),
gollm.WithMaxLength(300),
)
response, err := llm.Generate(ctx, prompt)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to generate explanation: %v", err)
}
fmt.Printf("Explanation of Recursion:\n%s\n", response)Use the ChainOfThought function for step-by-step reasoning:
question := "What is the result of 15 * 7 + 22?"
response, err := tools.ChainOfThought(ctx, llm, question)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to perform chain of thought: %v", err)
}
fmt.Printf("Chain of Thought:\n%s\n", response)Load examples directly from files:
examples, err := utils.ReadExamplesFromFile("examples.txt")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to read examples: %v", err)
}
prompt := gollm.NewPrompt("Generate a similar example:",
gollm.WithExamples(examples...),
)
response, err := llm.Generate(ctx, prompt)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to generate example: %v", err)
}
fmt.Printf("Generated Example:\n%s\n", response)Create reusable prompt templates for consistent prompt generation:
// Create a new prompt template
template := gollm.NewPromptTemplate(
"AnalysisTemplate",
"A template for analyzing topics",
"Provide a comprehensive analysis of {{.Topic}}. Consider the following aspects:\n" +
"1. Historical context\n" +
"2. Current relevance\n" +
"3. Future implications",
gollm.WithPromptOptions(
gollm.WithDirectives(
"Use clear and concise language",
"Provide specific examples where appropriate",
),
gollm.WithOutput("Structure your analysis with clear headings for each aspect."),
),
)
// Use the template to create a prompt
data := map[string]interface{}{
"Topic": "artificial intelligence in healthcare",
}
prompt, err := template.Execute(data)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to execute template: %v", err)
}
// Generate a response using the created prompt
response, err := llm.Generate(ctx, prompt)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to generate response: %v", err)
}
fmt.Printf("Analysis:\n%s\n", response)Ensure your LLM outputs are in a valid JSON format:
prompt := gollm.NewPrompt("Analyze the pros and cons of remote work.",
gollm.WithOutput("Respond in JSON format with 'topic', 'pros', 'cons', and 'conclusion' fields."),
)
response, err := llm.Generate(ctx, prompt, gollm.WithJSONSchemaValidation())
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to generate valid analysis: %v", err)
}
var result AnalysisResult
if err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(response), &result); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to parse response: %v", err)
}
fmt.Printf("Analysis: %+v\n", result)Use the PromptOptimizer to automatically refine and improve your prompts:
initialPrompt := gollm.NewPrompt("Write a short story about a robot learning to love.")
taskDescription := "Generate a compelling short story that explores the theme of artificial intelligence developing emotions."
optimizerInstance := optimizer.NewPromptOptimizer(
llm,
initialPrompt,
taskDescription,
optimizer.WithCustomMetrics(
optimizer.Metric{Name: "Creativity", Description: "How original and imaginative the story is"},
optimizer.Metric{Name: "Emotional Impact", Description: "How well the story evokes feelings in the reader"},
),
optimizer.WithRatingSystem("numerical"),
optimizer.WithThreshold(0.8),
optimizer.WithVerbose(),
)
optimizedPrompt, err := optimizerInstance.OptimizePrompt(ctx)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Optimization failed: %v", err)
}
fmt.Printf("Optimized Prompt: %s\n", optimizedPrompt.Input)Compare responses from different LLM providers or models:
configs := []*gollm.Config{
{
Provider: "openai",
Model: "gpt-4o-mini",
APIKey: os.Getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"),
MaxTokens: 500,
},
{
Provider: "anthropic",
Model: "claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620",
APIKey: os.Getenv("ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"),
MaxTokens: 500,
},
{
Provider: "groq",
Model: "llama-3.1-70b-versatile",
APIKey: os.Getenv("GROQ_API_KEY"),
MaxTokens: 500,
},
}
promptText := "Tell me a joke about programming. Respond in JSON format with 'setup' and 'punchline' fields."
validateJoke := func(joke map[string]interface{}) error {
if joke["setup"] == "" || joke["punchline"] == "" {
return fmt.Errorf("joke must have both a setup and a punchline")
}
return nil
}
results, err := tools.CompareModels(context.Background(), promptText, validateJoke, configs...)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Error comparing models: %v", err)
}
fmt.Println(tools.AnalyzeComparisonResults(results))Enable memory to maintain context across multiple interactions:
llm, err := gollm.NewLLM(
gollm.SetProvider("openai"),
gollm.SetModel("gpt-3.5-turbo"),
gollm.SetAPIKey(os.Getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")),
gollm.SetMemory(4096), // Enable memory with a 4096 token limit
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create LLM: %v", err)
}
ctx := context.Background()
// First interaction
prompt1 := gollm.NewPrompt("What's the capital of France?")
response1, err := llm.Generate(ctx, prompt1)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to generate response: %v", err)
}
fmt.Printf("Response 1: %s\n", response1)
// Second interaction, referencing the first
prompt2 := gollm.NewPrompt("What's the population of that city?")
response2, err := llm.Generate(ctx, prompt2)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to generate response: %v", err)
}
fmt.Printf("Response 2: %s\n", response2)-
Prompt Engineering:
- Use
NewPrompt()with options likeWithContext(),WithDirectives(), andWithOutput()to create well-structured prompts. - Example:
prompt := gollm.NewPrompt("Your main prompt here", gollm.WithContext("Provide relevant context"), gollm.WithDirectives("Be concise", "Use examples"), gollm.WithOutput("Specify expected output format"), )
- Use
-
Utilize Prompt Templates:
- For consistent prompt generation, create and use
PromptTemplateobjects. - Example:
template := gollm.NewPromptTemplate( "CustomTemplate", "A template for custom prompts", "Generate a {{.Type}} about {{.Topic}}", gollm.WithPromptOptions( gollm.WithDirectives("Be creative", "Use vivid language"), gollm.WithOutput("Your {{.Type}}:"), ), )
- For consistent prompt generation, create and use
-
Leverage Pre-built Functions:
- Use provided functions like
ChainOfThought()for complex reasoning tasks. - Example:
response, err := tools.ChainOfThought(ctx, llm, "Your complex question here")
- Use provided functions like
-
Work with Examples:
- Use
ReadExamplesFromFile()to load examples from files for consistent outputs. - Example:
examples, err := utils.ReadExamplesFromFile("examples.txt") if err != nil { log.Fatalf("Failed to read examples: %v", err) }
- Use
-
Implement Structured Output:
- Use
WithJSONSchemaValidation()to ensure valid JSON outputs. - Example:
response, err := llm.Generate(ctx, prompt, gollm.WithJSONSchemaValidation())
- Use
-
Optimize Prompts:
- Utilize
PromptOptimizerto refine prompts automatically. - Example:
optimizer := optimizer.NewPromptOptimizer(llm, initialPrompt, taskDescription, optimizer.WithCustomMetrics( optimizer.Metric{Name: "Relevance", Description: "How relevant the response is to the task"}, ), optimizer.WithRatingSystem("numerical"), optimizer.WithThreshold(0.8), )
- Utilize
-
Compare Model Performances:
- Use
CompareModels()to evaluate different models or providers. - Example:
results, err := tools.CompareModels(ctx, promptText, validateFunc, configs...)
- Use
-
Implement Memory for Contextual Interactions:
- Enable memory retention for maintaining context across interactions.
- Example:
llm, err := gollm.NewLLM( gollm.SetProvider("openai"), gollm.SetModel("gpt-3.5-turbo"), gollm.SetMemory(4096), )
-
Error Handling and Retries:
- Always check for errors and configure retry mechanisms.
- Example:
llm, err := gollm.NewLLM( gollm.SetMaxRetries(3), gollm.SetRetryDelay(time.Second * 2), )
-
Secure API Key Handling:
- Use environment variables for API keys.
- Example:
llm, err := gollm.NewLLM( gollm.SetAPIKey(os.Getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")), )
Check out our examples directory for more usage examples, including:
- Basic usage
- Different prompt types
- Comparing providers
- Advanced prompt templates
- Prompt optimization
- JSON output validation
- Mixture of Agents
gollm is actively maintained and under continuous development. With the recent refactoring, we've streamlined the codebase to make it simpler and more accessible for new contributors. We welcome contributions and feedback from the community.
gollm is built on a philosophy of pragmatic minimalism and forward-thinking simplicity:
-
Build what's necessary: We add features as they become needed, avoiding speculative development.
-
Simplicity first: Additions should be straightforward while fulfilling their purpose.
-
Future-compatible: We consider how current changes might impact future development.
-
Readability counts: Code should be clear and self-explanatory.
-
Modular design: Each component should do one thing well.
We welcome contributions that align with our philosophy! Whether you're fixing a bug, improving documentation, or proposing new features, your efforts are appreciated.
To get started:
- Familiarize yourself with our philosophy.
- Check out our CONTRIBUTING.md.
- Look through our issues.
- Fork the repository, make your changes, and submit a pull request.
Thank you for helping make gollm better!
This project is licensed under the Apache License 2.0 - see the LICENSE file for details.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for gollm
Similar Open Source Tools

gollm
gollm is a Go package designed to simplify interactions with Large Language Models (LLMs) for AI engineers and developers. It offers a unified API for multiple LLM providers, easy provider and model switching, flexible configuration options, advanced prompt engineering, prompt optimization, memory retention, structured output and validation, provider comparison tools, high-level AI functions, robust error handling and retries, and extensible architecture. The package enables users to create AI-powered golems for tasks like content creation workflows, complex reasoning tasks, structured data generation, model performance analysis, prompt optimization, and creating a mixture of agents.
instructor-go
Instructor Go is a library that simplifies working with structured outputs from large language models (LLMs). Built on top of `invopop/jsonschema` and utilizing `jsonschema` Go struct tags, it provides a user-friendly API for managing validation, retries, and streaming responses without changing code logic. The library supports LLM provider APIs such as OpenAI, Anthropic, Cohere, and Google, capturing and returning usage data in responses. Users can easily add metadata to struct fields using `jsonschema` tags to enhance model awareness and streamline workflows.

req_llm
ReqLLM is a Req-based library for LLM interactions, offering a unified interface to AI providers through a plugin-based architecture. It brings composability and middleware advantages to LLM interactions, with features like auto-synced providers/models, typed data structures, ergonomic helpers, streaming capabilities, usage & cost extraction, and a plugin-based provider system. Users can easily generate text, structured data, embeddings, and track usage costs. The tool supports various AI providers like Anthropic, OpenAI, Groq, Google, and xAI, and allows for easy addition of new providers. ReqLLM also provides API key management, detailed documentation, and a roadmap for future enhancements.
go-utcp
The Universal Tool Calling Protocol (UTCP) is a modern, flexible, and scalable standard for defining and interacting with tools across various communication protocols. It emphasizes scalability, interoperability, and ease of use. It provides built-in transports for HTTP, CLI, Server-Sent Events, streaming HTTP, GraphQL, MCP, and UDP. Users can use the library to construct a client and call tools using the available transports. The library also includes utilities for variable substitution, in-memory repository for storing providers and tools, and OpenAPI conversion to UTCP manuals.
FlashLearn
FlashLearn is a tool that provides a simple interface and orchestration for incorporating Agent LLMs into workflows and ETL pipelines. It allows data transformations, classifications, summarizations, rewriting, and custom multi-step tasks using LLMs. Each step and task has a compact JSON definition, making pipelines easy to understand and maintain. FlashLearn supports LiteLLM, Ollama, OpenAI, DeepSeek, and other OpenAI-compatible clients.
LightRAG
LightRAG is a repository hosting the code for LightRAG, a system that supports seamless integration of custom knowledge graphs, Oracle Database 23ai, Neo4J for storage, and multiple file types. It includes features like entity deletion, batch insert, incremental insert, and graph visualization. LightRAG provides an API server implementation for RESTful API access to RAG operations, allowing users to interact with it through HTTP requests. The repository also includes evaluation scripts, code for reproducing results, and a comprehensive code structure.
trpc-agent-go
A powerful Go framework for building intelligent agent systems with large language models (LLMs), hierarchical planners, memory, telemetry, and a rich tool ecosystem. tRPC-Agent-Go enables the creation of autonomous or semi-autonomous agents that reason, call tools, collaborate with sub-agents, and maintain long-term state. The framework provides detailed documentation, examples, and tools for accelerating the development of AI applications.
UniChat
UniChat is a pipeline tool for creating online and offline chat-bots in Unity. It leverages Unity.Sentis and text vector embedding technology to enable offline mode text content search based on vector databases. The tool includes a chain toolkit for embedding LLM and Agent in games, along with middleware components for Text to Speech, Speech to Text, and Sub-classifier functionalities. UniChat also offers a tool for invoking tools based on ReActAgent workflow, allowing users to create personalized chat scenarios and character cards. The tool provides a comprehensive solution for designing flexible conversations in games while maintaining developer's ideas.
modelfusion
ModelFusion is an abstraction layer for integrating AI models into JavaScript and TypeScript applications, unifying the API for common operations such as text streaming, object generation, and tool usage. It provides features to support production environments, including observability hooks, logging, and automatic retries. You can use ModelFusion to build AI applications, chatbots, and agents. ModelFusion is a non-commercial open source project that is community-driven. You can use it with any supported provider. ModelFusion supports a wide range of models including text generation, image generation, vision, text-to-speech, speech-to-text, and embedding models. ModelFusion infers TypeScript types wherever possible and validates model responses. ModelFusion provides an observer framework and logging support. ModelFusion ensures seamless operation through automatic retries, throttling, and error handling mechanisms. ModelFusion is fully tree-shakeable, can be used in serverless environments, and only uses a minimal set of dependencies.
instructor
Instructor is a tool that provides structured outputs from Large Language Models (LLMs) in a reliable manner. It simplifies the process of extracting structured data by utilizing Pydantic for validation, type safety, and IDE support. With Instructor, users can define models and easily obtain structured data without the need for complex JSON parsing, error handling, or retries. The tool supports automatic retries, streaming support, and extraction of nested objects, making it production-ready for various AI applications. Trusted by a large community of developers and companies, Instructor is used by teams at OpenAI, Google, Microsoft, AWS, and YC startups.
bellman
Bellman is a unified interface to interact with language and embedding models, supporting various vendors like VertexAI/Gemini, OpenAI, Anthropic, VoyageAI, and Ollama. It consists of a library for direct interaction with models and a service 'bellmand' for proxying requests with one API key. Bellman simplifies switching between models, vendors, and common tasks like chat, structured data, tools, and binary input. It addresses the lack of official SDKs for major players and differences in APIs, providing a single proxy for handling different models. The library offers clients for different vendors implementing common interfaces for generating and embedding text, enabling easy interchangeability between models.
whetstone.chatgpt
Whetstone.ChatGPT is a simple light-weight library that wraps the Open AI API with support for dependency injection. It supports features like GPT 4, GPT 3.5 Turbo, chat completions, audio transcription and translation, vision completions, files, fine tunes, images, embeddings, moderations, and response streaming. The library provides a video walkthrough of a Blazor web app built on it and includes examples such as a command line bot. It offers quickstarts for dependency injection, chat completions, completions, file handling, fine tuning, image generation, and audio transcription.
pocketgroq
PocketGroq is a tool that provides advanced functionalities for text generation, web scraping, web search, and AI response evaluation. It includes features like an Autonomous Agent for answering questions, web crawling and scraping capabilities, enhanced web search functionality, and flexible integration with Ollama server. Users can customize the agent's behavior, evaluate responses using AI, and utilize various methods for text generation, conversation management, and Chain of Thought reasoning. The tool offers comprehensive methods for different tasks, such as initializing RAG, error handling, and tool management. PocketGroq is designed to enhance development processes and enable the creation of AI-powered applications with ease.

agent-sdk-go
Agent Go SDK is a powerful Go framework for building production-ready AI agents that seamlessly integrates memory management, tool execution, multi-LLM support, and enterprise features into a flexible, extensible architecture. It offers core capabilities like multi-model intelligence, modular tool ecosystem, advanced memory management, and MCP integration. The SDK is enterprise-ready with built-in guardrails, complete observability, and support for enterprise multi-tenancy. It provides a structured task framework, declarative configuration, and zero-effort bootstrapping for development experience. The SDK supports environment variables for configuration and includes features like creating agents with YAML configuration, auto-generating agent configurations, using MCP servers with an agent, and CLI tool for headless usage.
agentpress
AgentPress is a collection of simple but powerful utilities that serve as building blocks for creating AI agents. It includes core components for managing threads, registering tools, processing responses, state management, and utilizing LLMs. The tool provides a modular architecture for handling messages, LLM API calls, response processing, tool execution, and results management. Users can easily set up the environment, create custom tools with OpenAPI or XML schema, and manage conversation threads with real-time interaction. AgentPress aims to be agnostic, simple, and flexible, allowing users to customize and extend functionalities as needed.

KULLM
KULLM (구름) is a Korean Large Language Model developed by Korea University NLP & AI Lab and HIAI Research Institute. It is based on the upstage/SOLAR-10.7B-v1.0 model and has been fine-tuned for instruction. The model has been trained on 8×A100 GPUs and is capable of generating responses in Korean language. KULLM exhibits hallucination and repetition phenomena due to its decoding strategy. Users should be cautious as the model may produce inaccurate or harmful results. Performance may vary in benchmarks without a fixed system prompt.
For similar tasks

choco-builder
ChocoBuilder (aka Chocolate Factory) is an open-source LLM application development framework designed to help you easily create powerful software development SDLC + LLM generation assistants. It provides modules for integration into JVM projects, usage with RAGScript, and local deployment examples. ChocoBuilder follows a Domain Driven Problem-Solving design philosophy with key concepts like ProblemClarifier, ProblemAnalyzer, SolutionDesigner, SolutionReviewer, and SolutionExecutor. It offers use cases for desktop/IDE, server, and Android applications, with examples for frontend design, semantic code search, testcase generation, and code interpretation.

gollm
gollm is a Go package designed to simplify interactions with Large Language Models (LLMs) for AI engineers and developers. It offers a unified API for multiple LLM providers, easy provider and model switching, flexible configuration options, advanced prompt engineering, prompt optimization, memory retention, structured output and validation, provider comparison tools, high-level AI functions, robust error handling and retries, and extensible architecture. The package enables users to create AI-powered golems for tasks like content creation workflows, complex reasoning tasks, structured data generation, model performance analysis, prompt optimization, and creating a mixture of agents.
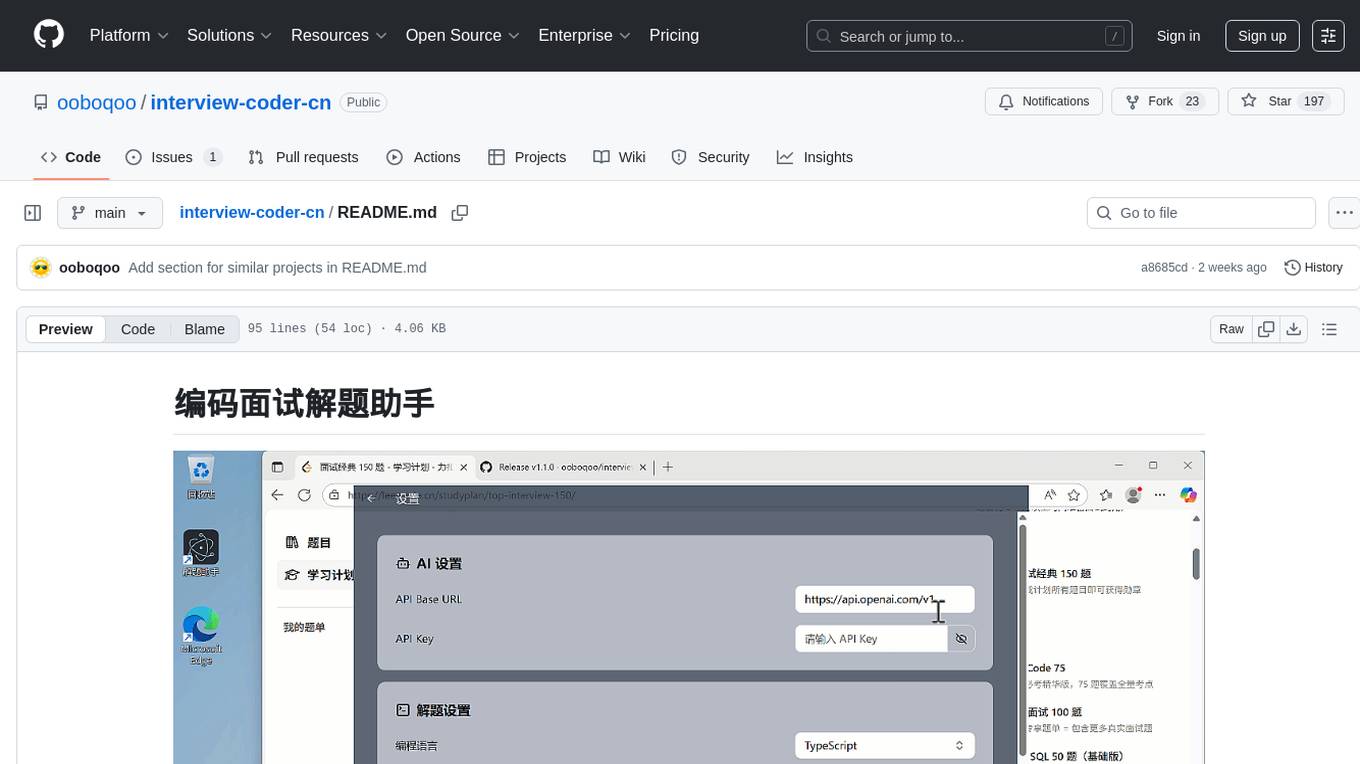
interview-coder-cn
This is a coding problem-solving assistant for Chinese users, tailored to the domestic AI ecosystem, simple and easy to use. It provides real-time problem-solving ideas and code analysis for coding interviews, avoiding detection during screen sharing. Users can also extend its functionality for other scenarios by customizing prompt words. The tool supports various programming languages and has stealth capabilities to hide its interface from interviewers even when screen sharing.
skyrim
Skyrim is a weather forecasting tool that enables users to run large weather models using consumer-grade GPUs. It provides access to state-of-the-art foundational weather models through a well-maintained infrastructure. Users can forecast weather conditions, such as wind speed and direction, by running simulations on their own GPUs or using modal volume or cloud services like s3 buckets. Skyrim supports various large weather models like Graphcast, Pangu, Fourcastnet, and DLWP, with plans for future enhancements like ensemble prediction and model quantization.
chinese-llm-benchmark
The Chinese LLM Benchmark is a continuous evaluation list of large models in CLiB, covering a wide range of commercial and open-source models from various companies and research institutions. It supports multidimensional evaluation of capabilities including classification, information extraction, reading comprehension, data analysis, Chinese encoding efficiency, and Chinese instruction compliance. The benchmark not only provides capability score rankings but also offers the original output results of all models for interested individuals to score and rank themselves.

LMeterX
LMeterX is a professional large language model performance testing platform that supports model inference services based on large model inference frameworks and cloud services. It provides an intuitive Web interface for creating and managing test tasks, monitoring testing processes, and obtaining detailed performance analysis reports to support model deployment and optimization.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.
zep
Zep is a long-term memory service for AI Assistant apps. With Zep, you can provide AI assistants with the ability to recall past conversations, no matter how distant, while also reducing hallucinations, latency, and cost. Zep persists and recalls chat histories, and automatically generates summaries and other artifacts from these chat histories. It also embeds messages and summaries, enabling you to search Zep for relevant context from past conversations. Zep does all of this asyncronously, ensuring these operations don't impact your user's chat experience. Data is persisted to database, allowing you to scale out when growth demands. Zep also provides a simple, easy to use abstraction for document vector search called Document Collections. This is designed to complement Zep's core memory features, but is not designed to be a general purpose vector database. Zep allows you to be more intentional about constructing your prompt: 1. automatically adding a few recent messages, with the number customized for your app; 2. a summary of recent conversations prior to the messages above; 3. and/or contextually relevant summaries or messages surfaced from the entire chat session. 4. and/or relevant Business data from Zep Document Collections.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.

