
VLM-R1
Solve Visual Understanding with Reinforced VLMs
Stars: 4429
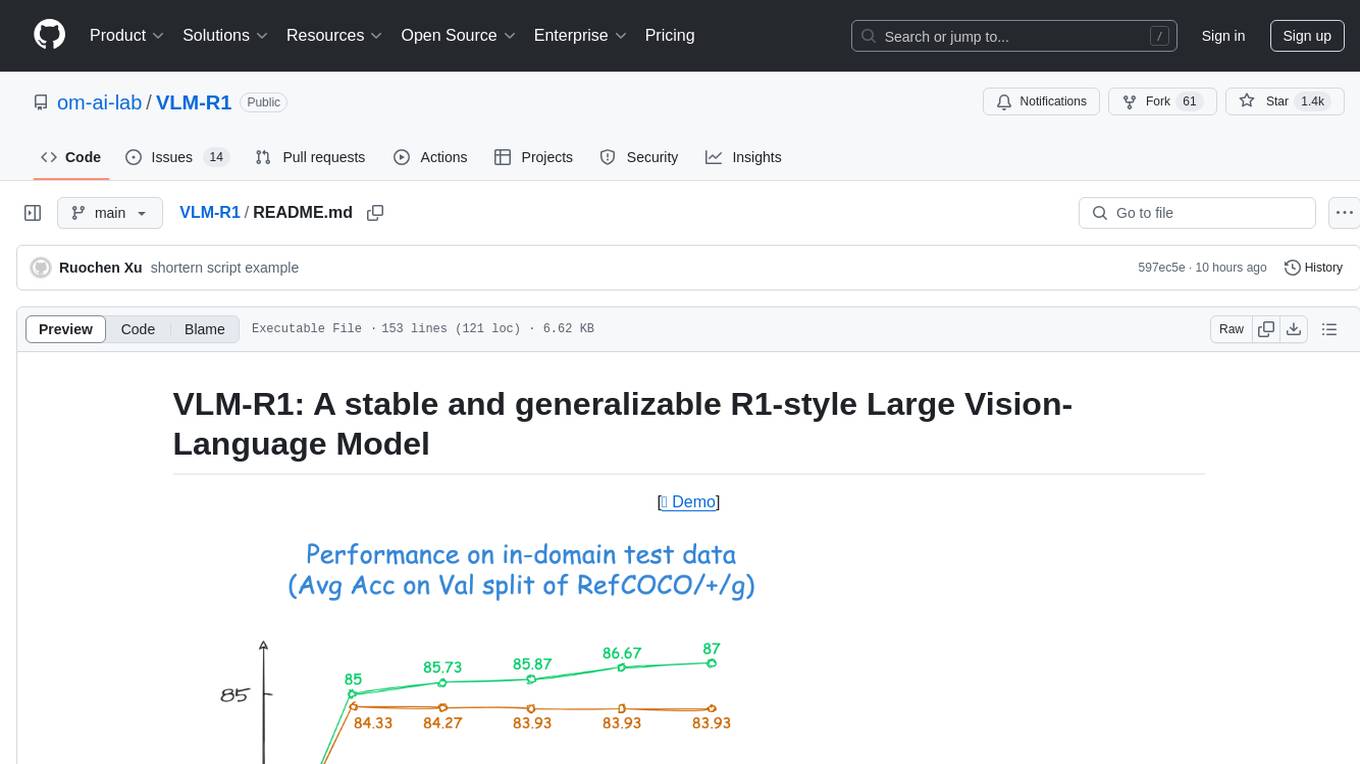
VLM-R1 is a stable and generalizable R1-style Large Vision-Language Model proposed for Referring Expression Comprehension (REC) task. It compares R1 and SFT approaches, showing R1 model's steady improvement on out-of-domain test data. The project includes setup instructions, training steps for GRPO and SFT models, support for user data loading, and evaluation process. Acknowledgements to various open-source projects and resources are mentioned. The project aims to provide a reliable and versatile solution for vision-language tasks.
README:

🎉 Our VLM-R1 Math model reaches the top of the Open-Compass Math Leaderboard (under 4B parameters) and OVD model achieves the state-of-the-art performance on OVDEval.
Since the introduction of Deepseek-R1, numerous works have emerged focusing on reproducing and improving upon it. In this project, we propose VLM-R1, a stable and generalizable R1-style Large Vision-Language Model.
Specifically, for the task of Referring Expression Comprehension (REC), we trained Qwen2.5-VL using both R1 and SFT approaches. The results reveal that, on the in-domain test data, the performance of the SFT model shows little change compared to that of the R1 model base model when the number of training steps is relatively small (100–600 steps), while the R1 model shows a steady improvement (as shown at the left of the figure below). More importantly, on the out-of-domain test data, the SFT model’s performance deteriorates slightly as the number of steps increases. Nevertheless, the RL model generalizes its reasoning ability to the out-of-domain data (as shown at the right of the figure below).
 * We found previous REC SFT exps used a mismatch pixel config. Therefore, we re-run the study with the correct config on a more complex out-of-domain data. See our findings for details.
* We found previous REC SFT exps used a mismatch pixel config. Therefore, we re-run the study with the correct config on a more complex out-of-domain data. See our findings for details.
This repository supports:
-
Full Fine-tuning for GRPO: see run_grpo_rec.sh -
Freeze Vision Modules: setfreeze_vision_modulesastruein the script. -
LoRA Fine-tuning for GRPO: see run_grpo_rec_lora.sh -
Multi-node Training: see multinode_training_demo.sh -
Multi-image Input Training: see run_grpo_gui.sh -
For your own data: see here -
Support various VLMs: see How to add a new model, now we support QwenVL and InternVL
-
2025-03-24: 🔥 We release the findings of VLM-R1-OVD. -
2025-03-23: 🔥 We release the VLM-R1-OVD model weights and demo, which shows the state-of-the-art performance on OVDEval. Welcome to use it. -
2025-03-20: 🔥 We achieved SOTA results on OVDEval with our RL-based model, outperforming SFT baselines and specialized object detection models. Read our blog post for details on how reinforcement learning enhances object detection performance. -
2025-03-17: Our VLM-R1 Math model reaches the top of the Open-Compass Math Leaderboard (under 4B parameters). We have released the checkpoint. -
2025-03-15: We support multi-image input data. Check the format of multi-image input here. We also provide an example of multi-image script run_grpo_gui.sh, see here for details. -
2025-03-13: We support InternVL for GRPO. See run_grpo_rec_internvl.sh for details. The annotation json files used in InternVL are here. If you want to add your new model, please refer to How to add a new model. -
2025-03-02: We support LoRA Fine-tuning for GRPO. See run_grpo_rec_lora.sh for details. -
2025-02-27: We support thenumber of iterations per batchandepsilon value for clippingin the original GRPO algorithm with args:--num_iterationsand--epsilon. -
2025-02-25: We support multi-node training for GRPO. See multinode_training_demo.sh for details. -
2025-02-21: We release the checkpoint of the VLM-R1 REC model. -
2025-02-20: We release the script for general data loading. -
2025-02-19: We incorporate an explanation of the SFT method. -
2025-02-17: We release the VLM-R1 REC Demo on Hugging Face Spaces. -
2025-02-15: We release the VLM-R1 repository and GRPO training script.
-
OVD: Trained with VLM-R1, our Open-Vocabulary Detection (OVD) model achieves the state-of-the-art performance on OVDEval. -
Math: Through VLM-R1 training, our math model focuses on multimodal reasoning tasks and has achieved Top1 on the OpenCompass Multi-modal Reasoning Leaderboard among models < 4B. -
REC: Trained with VLM-R1, our Referring Expression Comprehension (REC) model showcases the superior performance on out-of-domain data and a series of reasoning-grounding tasks.
| Version | Base VLM | Checkpoint | Task Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| VLM-R1-Qwen2.5VL-3B-OVD-0321 | Qwen2.5VL-3B | omlab/VLM-R1-Qwen2.5VL-3B-OVD-0321 | Open-Vocabulary Detection |
| VLM-R1-Qwen2.5VL-3B-Math-0305 | Qwen2.5VL-3B | omlab/VLM-R1-Qwen2.5VL-3B-Math-0305 | Multi-Modal Math |
| VLM-R1-Qwen2.5VL-3B-REC-500steps | Qwen2.5VL-3B | omlab/Qwen2.5VL-3B-VLM-R1-REC-500steps | REC/Reasoning-Grounding |
- [x] Implement multi-node training.
- [x] Implement LoRA Fine-tuning.
- [x] Support more Multimodal LLMs.
- [x] Support multi-image input.
- [x] Release the VLM-R1 Math model.
- [x] Release the blog of VLM-R1.
- [x] Release the VLM-R1-OVD model.
- [ ] Release the technical report of VLM-R1.
- [ ] Study cross task generalization.
- [ ] Enhance VLM for other tasks [welcome issue].
conda create -n vlm-r1 python=3.10
conda activate vlm-r1
bash setup.sh-
Download the COCO Train2014 image and unzip it, and we refer to the image dir as
<your_image_root>. -
Download the RefCOCO/+/g and LISA-Grounding Annotation files and unzip it (LISA-Grounding is used for out-of-domain evaluation).
-
Write the path of the annotation files in the
src/open-r1-multimodal/data_config/rec.yamlfile.
datasets:
- json_path: /path/to/refcoco_train.json
- json_path: /path/to/refcocop_train.json
- json_path: /path/to/refcocog_train.jsonbash src/open-r1-multimodal/run_scripts/run_grpo_rec.sh
[!NOTE] If you encounter 'CUDA out of memory' error, you can try to (1) set
gradient_checkpointingastrue, (2) reduce theper_device_train_batch_size, or (3) use lora.
cd src/open-r1-multimodal
torchrun --nproc_per_node="8" \
--nnodes="1" \
--node_rank="0" \
--master_addr="127.0.0.1" \
--master_port="12346" \
src/open_r1/grpo_rec.py \
--deepspeed local_scripts/zero3.json \
--output_dir output/$RUN_NAME \
--model_name_or_path Qwen/Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct \
--dataset_name data_config/rec.yaml \
--image_root <your_image_root> \
--max_prompt_length 1024 \
--num_generations 8 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 8 \
--gradient_accumulation_steps 2 \
--logging_steps 1 \
--bf16 \
--torch_dtype bfloat16 \
--data_seed 42 \
--report_to wandb \
--gradient_checkpointing false \
--attn_implementation flash_attention_2 \
--num_train_epochs 2 \
--run_name $RUN_NAME \
--save_steps 100 \
--save_only_model true \
--freeze_vision_modules false # If you want to only finetune the language model, set this to true.For multi-node training, please refers to multinode_training_demo.sh.
We use LLaMA-Factory to train the SFT model.
- Clone the LLaMA-Factory repository and install the dependencies.
git clone https://github.com/hiyouga/LLaMA-Factory.git
cd LLaMA-Factory
pip install -e ".[torch,metrics]"-
Download the dataset_info.json, mllm_rec_json.json, and qwen2_5_vl_full_sft.yaml we provided here. Put the json files in the
LLaMA-Factory/datadirectory and the yaml file in theLLaMA-Factory/examples/train_fulldirectory. -
Run the following command to train the SFT model.
llamafactory-cli train examples/train_full/qwen2_5_vl_full_sft.yamlWe also support data loading the jsonl data of this format in src/open-r1-multimodal/src/open_r1/grpo_jsonl.py. Please note that you may need to use different reward functions for your specialized tasks. Welcome to PR to add your own reward functions or share any other interesting findings!
The jsonl has the format as follows:
{
"id": 1,
"image": "Clevr_CoGenT_TrainA_R1/data/images/CLEVR_trainA_000001_16885.png",
"conversations": [
{"from": "human", "value": "<image>What number of purple metallic balls are there?"},
{"from": "gpt", "value": "0"}
]
}If you want to use multi-image input, you can use the following format:
{
"id": 1,
"image": ["Clevr_CoGenT_TrainA_R1/data/images/CLEVR_trainA_000001_16885.png", "Clevr_CoGenT_TrainA_R1/data/images/CLEVR_trainA_000001_16886.png"],
"conversations": [
{"from": "human", "value": "<image><image>What number of purple metallic balls in total within the two images?"},
{"from": "gpt", "value": "3"}
]
}[!NOTE] The image path in the jsonl file should be relative to the image folder specified in
--image_folders. The absolute path of the input image is constructed asos.path.join(image_folder, data['image']). For example:
- If your jsonl has
"image": "folder1/image1.jpg" - And you specify
--image_folders "/path/to/images/" - The full image path will be
/path/to/images/folder1/image1.jpg
Multiple data files and image folders can be specified using ":" as a separator:
--data_file_paths /path/to/data1.jsonl:/path/to/data2.jsonl \
--image_folders /path/to/images1/:/path/to/images2/The script can be run like this:
torchrun --nproc_per_node="8" \
--nnodes="1" \
--node_rank="0" \
--master_addr="127.0.0.1" \
--master_port="12345" \
src/open_r1/grpo_jsonl.py \
--output_dir output/$RUN_NAME \
--model_name_or_path Qwen/Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct \
--deepspeed local_scripts/zero3.json \
--dataset_name <your_dataset_name> \
--data_file_paths /path/to/your/data.jsonl \ # can be multiple, separated by ":"
--image_folders /path/to/your/image/folder/ \ # can be multiple, separated by ":"
...We provide an example of multi-image script run_grpo_gui.sh. This task requires the model to analyze two GUI screenshots, taken before and after a user action, to determine if any UI interaction defects are present, which is from GUI-Testing-Arena. Download the image and unzip it into the /path/to/images/. Then modify the image_folders parameter in the script and run it.
bash src/open-r1-multimodal/run_scripts/run_grpo_gui.sh- Download the provided LISA-Grounding images.
cd ./src/eval
# Remember to change the model path, image root, and annotation path in the script
torchrun --nproc_per_node="X" test_rec_r1.py # for GRPO. 'X' is the number of GPUs you have.
torchrun --nproc_per_node="X" test_rec_baseline.py # for SFT.We would like to express our sincere gratitude to DeepSeek, Open-R1, QwenVL, Open-R1-Multimodal, R1-V, RefCOCO, RefGTA, LLaMA-Factory, OVDEval, GUI-Testing-Arena, and LISA for providing open-source resources that contributed to the development of this project.
If you find this project useful, welcome to cite us.
@misc{shen2025vlmr1,
author = {Shen, Haozhan and Zhang, Zilun and Zhao, Kangjia and Zhang, Qianqian and Xu, Ruochen and Zhao, Tiancheng},
title = {VLM-R1: A stable and generalizable R1-style Large Vision-Language Model},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/om-ai-lab/VLM-R1}},
note = {Accessed: 2025-02-15},
year = {2025}
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for VLM-R1
Similar Open Source Tools

VLM-R1
VLM-R1 is a stable and generalizable R1-style Large Vision-Language Model proposed for Referring Expression Comprehension (REC) task. It compares R1 and SFT approaches, showing R1 model's steady improvement on out-of-domain test data. The project includes setup instructions, training steps for GRPO and SFT models, support for user data loading, and evaluation process. Acknowledgements to various open-source projects and resources are mentioned. The project aims to provide a reliable and versatile solution for vision-language tasks.

VITA
VITA is an open-source interactive omni multimodal Large Language Model (LLM) capable of processing video, image, text, and audio inputs simultaneously. It stands out with features like Omni Multimodal Understanding, Non-awakening Interaction, and Audio Interrupt Interaction. VITA can respond to user queries without a wake-up word, track and filter external queries in real-time, and handle various query inputs effectively. The model utilizes state tokens and a duplex scheme to enhance the multimodal interactive experience.
TheoremExplainAgent
TheoremExplainAgent is an AI system that generates long-form Manim videos to visually explain theorems, proving its deep understanding while uncovering reasoning flaws that text alone often hides. The codebase for the paper 'TheoremExplainAgent: Towards Multimodal Explanations for LLM Theorem Understanding' is available in this repository. It provides a tool for creating multimodal explanations for theorem understanding using AI technology.
DeepResearch
Tongyi DeepResearch is an agentic large language model with 30.5 billion total parameters, designed for long-horizon, deep information-seeking tasks. It demonstrates state-of-the-art performance across various search benchmarks. The model features a fully automated synthetic data generation pipeline, large-scale continual pre-training on agentic data, end-to-end reinforcement learning, and compatibility with two inference paradigms. Users can download the model directly from HuggingFace or ModelScope. The repository also provides benchmark evaluation scripts and information on the Deep Research Agent Family.
understand-r1-zero
The 'understand-r1-zero' repository focuses on understanding R1-Zero-like training from a critical perspective. It provides insights into base models and reinforcement learning components, highlighting findings and proposing solutions for biased optimization. The repository offers a minimalist recipe for R1-Zero training, detailing the RL-tuning process and achieving state-of-the-art performance with minimal compute resources. It includes codebase, models, and paper related to R1-Zero training implemented with the Oat framework, emphasizing research-friendly and efficient LLM RL techniques.
MHA2MLA
This repository contains the code for the paper 'Towards Economical Inference: Enabling DeepSeek's Multi-Head Latent Attention in Any Transformer-based LLMs'. It provides tools for fine-tuning and evaluating Llama models, converting models between different frameworks, processing datasets, and performing specific model training tasks like Partial-RoPE Fine-Tuning and Multiple-Head Latent Attention Fine-Tuning. The repository also includes commands for model evaluation using Lighteval and LongBench, along with necessary environment setup instructions.

starcoder2-self-align
StarCoder2-Instruct is an open-source pipeline that introduces StarCoder2-15B-Instruct-v0.1, a self-aligned code Large Language Model (LLM) trained with a fully permissive and transparent pipeline. It generates instruction-response pairs to fine-tune StarCoder-15B without human annotations or data from proprietary LLMs. The tool is primarily finetuned for Python code generation tasks that can be verified through execution, with potential biases and limitations. Users can provide response prefixes or one-shot examples to guide the model's output. The model may have limitations with other programming languages and out-of-domain coding tasks.
candle-vllm
Candle-vllm is an efficient and easy-to-use platform designed for inference and serving local LLMs, featuring an OpenAI compatible API server. It offers a highly extensible trait-based system for rapid implementation of new module pipelines, streaming support in generation, efficient management of key-value cache with PagedAttention, and continuous batching. The tool supports chat serving for various models and provides a seamless experience for users to interact with LLMs through different interfaces.
infinity
Infinity is a high-throughput, low-latency REST API for serving vector embeddings, supporting all sentence-transformer models and frameworks. It is developed under the MIT License and powers inference behind Gradient.ai. The API allows users to deploy models from SentenceTransformers, offers fast inference backends utilizing various accelerators, dynamic batching for efficient processing, correct and tested implementation, and easy-to-use API built on FastAPI with Swagger documentation. Users can embed text, rerank documents, and perform text classification tasks using the tool. Infinity supports various models from Huggingface and provides flexibility in deployment via CLI, Docker, Python API, and cloud services like dstack. The tool is suitable for tasks like embedding, reranking, and text classification.
LLMTSCS
LLMLight is a novel framework that employs Large Language Models (LLMs) as decision-making agents for Traffic Signal Control (TSC). The framework leverages the advanced generalization capabilities of LLMs to engage in a reasoning and decision-making process akin to human intuition for effective traffic control. LLMLight has been demonstrated to be remarkably effective, generalizable, and interpretable against various transportation-based and RL-based baselines on nine real-world and synthetic datasets.
chatllm.cpp
ChatLLM.cpp is a pure C++ implementation tool for real-time chatting with RAG on your computer. It supports inference of various models ranging from less than 1B to more than 300B. The tool provides accelerated memory-efficient CPU inference with quantization, optimized KV cache, and parallel computing. It allows streaming generation with a typewriter effect and continuous chatting with virtually unlimited content length. ChatLLM.cpp also offers features like Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), LoRA, Python/JavaScript/C bindings, web demo, and more possibilities. Users can clone the repository, quantize models, build the project using make or CMake, and run quantized models for interactive chatting.
LL3DA
LL3DA is a Large Language 3D Assistant that responds to both visual and textual interactions within complex 3D environments. It aims to help Large Multimodal Models (LMM) comprehend, reason, and plan in diverse 3D scenes by directly taking point cloud input and responding to textual instructions and visual prompts. LL3DA achieves remarkable results in 3D Dense Captioning and 3D Question Answering, surpassing various 3D vision-language models. The code is fully released, allowing users to train customized models and work with pre-trained weights. The tool supports training with different LLM backends and provides scripts for tuning and evaluating models on various tasks.
evalchemy
Evalchemy is a unified and easy-to-use toolkit for evaluating language models, focusing on post-trained models. It integrates multiple existing benchmarks such as RepoBench, AlpacaEval, and ZeroEval. Key features include unified installation, parallel evaluation, simplified usage, and results management. Users can run various benchmarks with a consistent command-line interface and track results locally or integrate with a database for systematic tracking and leaderboard submission.
ichigo
Ichigo is a local real-time voice AI tool that uses an early fusion technique to extend a text-based LLM to have native 'listening' ability. It is an open research experiment with improved multiturn capabilities and the ability to refuse processing inaudible queries. The tool is designed for open data, open weight, on-device Siri-like functionality, inspired by Meta's Chameleon paper. Ichigo offers a web UI demo and Gradio web UI for users to interact with the tool. It has achieved enhanced MMLU scores, stronger context handling, advanced noise management, and improved multi-turn capabilities for a robust user experience.
evalscope
Eval-Scope is a framework designed to support the evaluation of large language models (LLMs) by providing pre-configured benchmark datasets, common evaluation metrics, model integration, automatic evaluation for objective questions, complex task evaluation using expert models, reports generation, visualization tools, and model inference performance evaluation. It is lightweight, easy to customize, supports new dataset integration, model hosting on ModelScope, deployment of locally hosted models, and rich evaluation metrics. Eval-Scope also supports various evaluation modes like single mode, pairwise-baseline mode, and pairwise (all) mode, making it suitable for assessing and improving LLMs.
rank_llm
RankLLM is a suite of prompt-decoders compatible with open source LLMs like Vicuna and Zephyr. It allows users to create custom ranking models for various NLP tasks, such as document reranking, question answering, and summarization. The tool offers a variety of features, including the ability to fine-tune models on custom datasets, use different retrieval methods, and control the context size and variable passages. RankLLM is easy to use and can be integrated into existing NLP pipelines.
For similar tasks

VLM-R1
VLM-R1 is a stable and generalizable R1-style Large Vision-Language Model proposed for Referring Expression Comprehension (REC) task. It compares R1 and SFT approaches, showing R1 model's steady improvement on out-of-domain test data. The project includes setup instructions, training steps for GRPO and SFT models, support for user data loading, and evaluation process. Acknowledgements to various open-source projects and resources are mentioned. The project aims to provide a reliable and versatile solution for vision-language tasks.
Co-LLM-Agents
This repository contains code for building cooperative embodied agents modularly with large language models. The agents are trained to perform tasks in two different environments: ThreeDWorld Multi-Agent Transport (TDW-MAT) and Communicative Watch-And-Help (C-WAH). TDW-MAT is a multi-agent environment where agents must transport objects to a goal position using containers. C-WAH is an extension of the Watch-And-Help challenge, which enables agents to send messages to each other. The code in this repository can be used to train agents to perform tasks in both of these environments.
GPT4Point
GPT4Point is a unified framework for point-language understanding and generation. It aligns 3D point clouds with language, providing a comprehensive solution for tasks such as 3D captioning and controlled 3D generation. The project includes an automated point-language dataset annotation engine, a novel object-level point cloud benchmark, and a 3D multi-modality model. Users can train and evaluate models using the provided code and datasets, with a focus on improving models' understanding capabilities and facilitating the generation of 3D objects.

asreview
The ASReview project implements active learning for systematic reviews, utilizing AI-aided pipelines to assist in finding relevant texts for search tasks. It accelerates the screening of textual data with minimal human input, saving time and increasing output quality. The software offers three modes: Oracle for interactive screening, Exploration for teaching purposes, and Simulation for evaluating active learning models. ASReview LAB is designed to support decision-making in any discipline or industry by improving efficiency and transparency in screening large amounts of textual data.
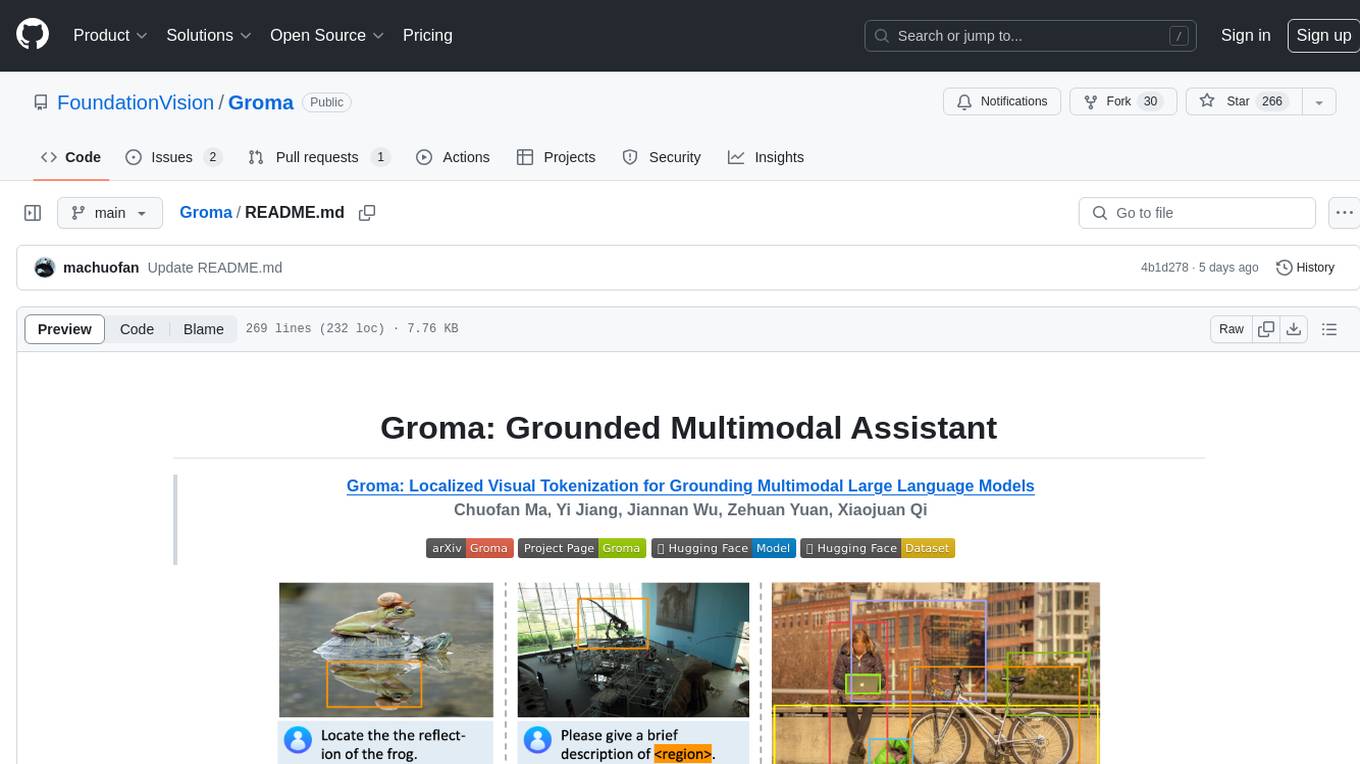
Groma
Groma is a grounded multimodal assistant that excels in region understanding and visual grounding. It can process user-defined region inputs and generate contextually grounded long-form responses. The tool presents a unique paradigm for multimodal large language models, focusing on visual tokenization for localization. Groma achieves state-of-the-art performance in referring expression comprehension benchmarks. The tool provides pretrained model weights and instructions for data preparation, training, inference, and evaluation. Users can customize training by starting from intermediate checkpoints. Groma is designed to handle tasks related to detection pretraining, alignment pretraining, instruction finetuning, instruction following, and more.
amber-train
Amber is the first model in the LLM360 family, an initiative for comprehensive and fully open-sourced LLMs. It is a 7B English language model with the LLaMA architecture. The model type is a language model with the same architecture as LLaMA-7B. It is licensed under Apache 2.0. The resources available include training code, data preparation, metrics, and fully processed Amber pretraining data. The model has been trained on various datasets like Arxiv, Book, C4, Refined-Web, StarCoder, StackExchange, and Wikipedia. The hyperparameters include a total of 6.7B parameters, hidden size of 4096, intermediate size of 11008, 32 attention heads, 32 hidden layers, RMSNorm ε of 1e^-6, max sequence length of 2048, and a vocabulary size of 32000.
kan-gpt
The KAN-GPT repository is a PyTorch implementation of Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPTs) using Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) for language modeling. It provides a model for generating text based on prompts, with a focus on improving performance compared to traditional MLP-GPT models. The repository includes scripts for training the model, downloading datasets, and evaluating model performance. Development tasks include integrating with other libraries, testing, and documentation.
LLM-SFT
LLM-SFT is a Chinese large model fine-tuning tool that supports models such as ChatGLM, LlaMA, Bloom, Baichuan-7B, and frameworks like LoRA, QLoRA, DeepSpeed, UI, and TensorboardX. It facilitates tasks like fine-tuning, inference, evaluation, and API integration. The tool provides pre-trained weights for various models and datasets for Chinese language processing. It requires specific versions of libraries like transformers and torch for different functionalities.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.

