
llm.rb
Ruby toolkit for multiple Large Language Models (LLMs)
Stars: 104
llm.rb is a zero-dependency Ruby toolkit for Large Language Models that includes various providers like OpenAI, Gemini, Anthropic, xAI (Grok), zAI, DeepSeek, Ollama, and LlamaCpp. It provides full support for chat, streaming, tool calling, audio, images, files, and structured outputs. The toolkit offers features like unified API across providers, pluggable JSON adapters, tool calling, JSON Schema structured output, streaming responses, TTS, transcription, translation, image generation, files API, multimodal prompts, embeddings, models API, OpenAI vector stores, and more.
README:
llm.rb is a zero-dependency Ruby toolkit for Large Language Models that includes OpenAI, Gemini, Anthropic, xAI (Grok), zAI, DeepSeek, Ollama, and LlamaCpp. The toolkit includes full support for chat, streaming, tool calling, audio, images, files, and structured outputs.
The LLM::Bot class provides a session with an LLM provider that maintains conversation history and context across multiple requests. The following example implements a simple REPL loop:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
llm = LLM.openai(key: ENV["KEY"])
bot = LLM::Bot.new(llm, stream: $stdout)
loop do
print "> "
bot.chat(STDIN.gets)
puts
endThe LLM::Schema class provides a simple DSL for describing the structure of a response that an LLM emits according to a JSON schema. The schema lets a client describe what JSON object an LLM should emit, and the LLM will abide by the schema to the best of its ability:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
require "pp"
class Report < LLM::Schema
property :category, String, "Report category", required: true
property :summary, String, "Short summary", required: true
property :impact, String, "Impact", required: true
property :timestamp, String, "When it happened", optional: true
end
llm = LLM.openai(key: ENV["KEY"])
bot = LLM::Bot.new(llm, schema: Report)
res = bot.chat("Structure this report: 'Database latency spiked at 10:42 UTC, causing 5% request timeouts for 12 minutes.'")
pp res.messages.first(&:assistant?).content!The LLM::Tool class lets you define callable tools for the model. Each tool is described to the LLM as a function it can invoke to fetch information or perform an action. The model decides when to call tools based on the conversation; when it does, llm.rb runs the tool and sends the result back on the next request. The following example implements a simple tool that runs shell commands:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
class System < LLM::Tool
name "system"
description "Run a shell command"
param :command, String, "Command to execute", required: true
def call(command:)
{success: system(command)}
end
end
llm = LLM.openai(key: ENV["KEY"])
bot = LLM::Bot.new(llm, tools: [System])
bot.chat("Run `date`.")
bot.chat(bot.functions.map(&:call)) # report return value to the LLMThe LLM::Agent class provides a class-level DSL for defining reusable, preconfigured assistants with defaults for model, tools, schema, and instructions. Instructions are injected only on the first request, and unlike LLM::Bot, an LLM::Agent will automatically call tools when needed:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
class SystemAdmin < LLM::Agent
model "gpt-4.1"
instructions "You are a Linux system admin"
tools Shell
schema Result
end
llm = LLM.openai(key: ENV["KEY"])
agent = SystemAdmin.new(llm)
res = agent.chat("Run 'date'")The LLM::Bot#build_prompt method provides a simple DSL for building a chain of messages that can be sent in a single request. A conversation with an LLM consists of messages that have a role (eg system, user), and content:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
llm = LLM.openai(key: ENV["KEY"])
bot = LLM::Bot.new(llm)
prompt = bot.build_prompt do
it.system "Be concise and show your reasoning briefly."
it.user "If a train goes 60 mph for 1.5 hours, how far does it travel?"
it.user "Now double the speed for the same time."
end
bot.chat(prompt)- ✅ Unified API across providers
- 📦 Zero runtime deps (stdlib-only)
- 🧩 Pluggable JSON adapters (JSON, Oj, Yajl, etc)
- 🧱 Builtin tracer API (LLM::Tracer)
- ♻️ Optional persistent HTTP pool (net-http-persistent)
- 📈 Optional telemetry support via OpenTelemetry (opentelemetry-sdk)
- 🪵 Optional logging support via Ruby's standard library (ruby/logger)
- 🧠 Stateless + stateful chat (completions + responses)
- 🤖 Tool calling / function execution
- 🔁 Agent tool-call auto-execution (bounded)
- 🗂️ JSON Schema structured output
- 📡 Streaming responses
- 🗣️ TTS, transcription, translation
- 🖼️ Image generation + editing
- 📎 Files API + prompt-aware file inputs
- 📦 Streaming multipart uploads (no full buffering)
- 💡 Multimodal prompts (text, documents, audio, images, video, URLs)
- 🧮 Embeddings
- 🧱 OpenAI vector stores (RAG)
- 📜 Models API
- 🔧 OpenAI responses + moderations
| Feature / Provider | OpenAI | Anthropic | Gemini | DeepSeek | xAI (Grok) | zAI | Ollama | LlamaCpp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chat Completions | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Streaming | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Tool Calling | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| JSON Schema / Structured Output | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅* | ✅* |
| Embeddings | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Multimodal Prompts (text, documents, audio, images, videos, URLs, etc) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Files API | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Models API | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Audio (TTS / Transcribe / Translate) | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Image Generation & Editing | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Local Model Support | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Vector Stores (RAG) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Responses | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Moderations | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
* JSON Schema support in Ollama/LlamaCpp depends on the model, not the API.
All providers inherit from LLM::Provider – they share a common interface and set of functionality. Each provider can be instantiated using an API key (if required) and an optional set of configuration options via the singleton methods of LLM. For example:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
##
# remote providers
llm = LLM.openai(key: "yourapikey")
llm = LLM.gemini(key: "yourapikey")
llm = LLM.anthropic(key: "yourapikey")
llm = LLM.xai(key: "yourapikey")
llm = LLM.zai(key: "yourapikey")
llm = LLM.deepseek(key: "yourapikey")
##
# local providers
llm = LLM.ollama(key: nil)
llm = LLM.llamacpp(key: nil)All provider methods that perform requests return an
LLM::Response.
If the HTTP response is JSON (content-type: application/json),
response.body is parsed into an
LLM::Object for
dot-access. For non-JSON responses, response.body is a raw string.
It is also possible to access top-level keys directly on the response
(eg: res.object instead of res.body.object):
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
llm = LLM.openai(key: ENV["KEY"])
res = llm.models.all
puts res.object
puts res.data.first.idThe llm.rb library can maintain a process-wide connection pool for each provider that is instantiated. This feature can improve performance but it is optional, the implementation depends on net-http-persistent, and the gem should be installed separately:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
llm = LLM.openai(key: ENV["KEY"], persistent: true)
res1 = llm.responses.create "message 1"
res2 = llm.responses.create "message 2", previous_response_id: res1.response_id
res3 = llm.responses.create "message 3", previous_response_id: res2.response_id
puts res3.output_textThe llm.rb library includes telemetry support through its tracer API, and it can be used to trace LLM requests. It can be useful for debugging, monitoring, and observability. The primary use case in mind is integration with tools like LangSmith.
The telemetry implementation uses the opentelemetry-sdk and is based on the gen-ai telemetry spec(s). This feature is optional, disabled by default, and the opentelemetry-sdk gem should be installed separately. Please also note that llm.rb will take care of loading and configuring the opentelemetry-sdk library for you, and llm.rb configures an in-memory exporter that doesn't have external dependencies by default:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
require "pp"
llm = LLM.openai(key: ENV["KEY"])
llm.tracer = LLM::Tracer::Telemetry.new(llm)
bot = LLM::Bot.new(llm)
bot.chat "Hello world!"
bot.chat "Adios."
bot.tracer.spans.each { |span| pp span }The llm.rb library includes simple logging support through its
tracer API, and Ruby's standard library (ruby/logger).
This feature is optional, disabled by default, and it can be useful for debugging and/or
monitoring requests to LLM providers. The path or io options can be used to choose
where logs are written to, and by default it is set to $stdout:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
llm = LLM.openai(key: ENV["KEY"])
llm.tracer = LLM::Tracer::Logger.new(llm, io: $stdout)
bot = LLM::Bot.new(llm)
bot.chat "Hello world!"
bot.chat "Adios."The llm.rb library is thread-safe and can be used in a multi-threaded environments but it is important to keep in mind that the LLM::Provider and LLM::Bot classes should be instantiated once per thread, and not shared between threads. Generally the library tries to avoid global or shared state but where it exists reentrant locks are used to ensure thread-safety.
The following example demonstrates LLM::Function and how it can define a local function (which happens to be a tool), and how a provider (such as OpenAI) can then detect when we should call the function. Its most notable feature is that it can act as a closure and has access to its surrounding scope, which can be useful in some situations:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
llm = LLM.openai(key: ENV["KEY"])
tool = LLM.function(:system) do |fn|
fn.description "Run a shell command"
fn.params do |schema|
schema.object(command: schema.string.required)
end
fn.define do |command:|
ro, wo = IO.pipe
re, we = IO.pipe
Process.wait Process.spawn(command, out: wo, err: we)
[wo,we].each(&:close)
{stderr: re.read, stdout: ro.read}
end
end
bot = LLM::Bot.new(llm, tools: [tool])
bot.chat "Your task is to run shell commands via a tool.", role: :user
bot.chat "What is the current date?", role: :user
bot.chat bot.functions.map(&:call) # report return value to the LLM
bot.chat "What operating system am I running?", role: :user
bot.chat bot.functions.map(&:call) # report return value to the LLM
##
# {stderr: "", stdout: "Thu May 1 10:01:02 UTC 2025"}
# {stderr: "", stdout: "FreeBSD"}The LLM::Tool class can be used to implement a LLM::Function as a class. Under the hood, a subclass of LLM::Tool wraps an instance of LLM::Function and delegates to it.
The choice between LLM::Function and LLM::Tool is often a matter of preference but each carry their own benefits. For example, LLM::Function has the benefit of being a closure that has access to its surrounding context and sometimes that is useful:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
class System < LLM::Tool
name "system"
description "Run a shell command"
param :command, String, "The command to execute", required: true
def call(command:)
ro, wo = IO.pipe
re, we = IO.pipe
Process.wait Process.spawn(command, out: wo, err: we)
[wo,we].each(&:close)
{stderr: re.read, stdout: ro.read}
end
end
llm = LLM.openai(key: ENV["KEY"])
bot = LLM::Bot.new(llm, tools: [System])
bot.chat "Your task is to run shell commands via a tool.", role: :user
bot.chat "What is the current date?", role: :user
bot.chat bot.functions.map(&:call) # report return value to the LLM
bot.chat "What operating system am I running?", role: :user
bot.chat bot.functions.map(&:call) # report return value to the LLM
##
# {stderr: "", stdout: "Thu May 1 10:01:02 UTC 2025"}
# {stderr: "", stdout: "FreeBSD"}The OpenAI and Gemini providers provide a Files API where a client can upload files that can be referenced from a prompt, and with other APIs as well. The following example uses the OpenAI provider to describe the contents of a PDF file after it has been uploaded. The file (a specialized instance of LLM::Response ) is given as part of a prompt that is understood by llm.rb:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
llm = LLM.openai(key: ENV["KEY"])
bot = LLM::Bot.new(llm)
file = llm.files.create(file: "/tmp/llm-book.pdf")
res = bot.chat ["Tell me about this file", file]
res.messages.each { |m| puts "[#{m.role}] #{m.content}" }LLMs are great with text, but many can also handle images, audio, video, and URLs. With llm.rb you pass those inputs by tagging them with one of the following methods. And for multipart prompts, we can pass an array where each element is a part of the input. See the example below for details, in the meantime here are the methods to know for multimodal inputs:
-
bot.image_urlfor an image URL -
bot.local_filefor a local file -
bot.remote_filefor a file already uploaded via the provider's Files API
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
llm = LLM.openai(key: ENV["KEY"])
bot = LLM::Bot.new(llm)
res = bot.chat ["Tell me about this image URL", bot.image_url(url)]
res = bot.chat ["Tell me about this PDF", bot.remote_file(file)]
res = bot.chat ["Tell me about this image", bot.local_file(path)]}Some but not all providers implement audio generation capabilities that
can create speech from text, transcribe audio to text, or translate
audio to text (usually English). The following example uses the OpenAI provider
to create an audio file from a text prompt. The audio is then moved to
${HOME}/hello.mp3 as the final step:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
llm = LLM.openai(key: ENV["KEY"])
res = llm.audio.create_speech(input: "Hello world")
IO.copy_stream res.audio, File.join(Dir.home, "hello.mp3")The following example transcribes an audio file to text. The audio file
(${HOME}/hello.mp3) was theoretically created in the previous example,
and the result is printed to the console. The example uses the OpenAI
provider to transcribe the audio file:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
llm = LLM.openai(key: ENV["KEY"])
res = llm.audio.create_transcription(
file: File.join(Dir.home, "hello.mp3")
)
puts res.text # => "Hello world."The following example translates an audio file to text. In this example
the audio file (${HOME}/bomdia.mp3) is theoretically in Portuguese,
and it is translated to English. The example uses the OpenAI provider,
and at the time of writing, it can only translate to English:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
llm = LLM.openai(key: ENV["KEY"])
res = llm.audio.create_translation(
file: File.join(Dir.home, "bomdia.mp3")
)
puts res.text # => "Good morning."Some but not all LLM providers implement image generation capabilities that
can create new images from a prompt, or edit an existing image with a
prompt. The following example uses the OpenAI provider to create an
image of a dog on a rocket to the moon. The image is then moved to
${HOME}/dogonrocket.png as the final step:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
require "open-uri"
require "fileutils"
llm = LLM.openai(key: ENV["KEY"])
res = llm.images.create(prompt: "a dog on a rocket to the moon")
res.urls.each do |url|
FileUtils.mv OpenURI.open_uri(url).path,
File.join(Dir.home, "dogonrocket.png")
endThe following example is focused on editing a local image with the aid
of a prompt. The image (/tmp/llm-logo.png) is returned to us with a hat.
The image is then moved to ${HOME}/logo-with-hat.png as
the final step:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
require "open-uri"
require "fileutils"
llm = LLM.openai(key: ENV["KEY"])
res = llm.images.edit(
image: "/tmp/llm-logo.png",
prompt: "add a hat to the logo",
)
res.urls.each do |url|
FileUtils.mv OpenURI.open_uri(url).path,
File.join(Dir.home, "logo-with-hat.png")
endThe following example is focused on creating variations of a local image.
The image (/tmp/llm-logo.png) is returned to us with five different variations.
The images are then moved to ${HOME}/logo-variation0.png, ${HOME}/logo-variation1.png
and so on as the final step:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
require "open-uri"
require "fileutils"
llm = LLM.openai(key: ENV["KEY"])
res = llm.images.create_variation(
image: "/tmp/llm-logo.png",
n: 5
)
res.urls.each.with_index do |url, index|
FileUtils.mv OpenURI.open_uri(url).path,
File.join(Dir.home, "logo-variation#{index}.png")
endThe
LLM::Provider#embed
method returns vector embeddings for one or more text inputs. A common
use is semantic search (store vectors, then query for similar text):
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
llm = LLM.openai(key: ENV["KEY"])
res = llm.embed(["programming is fun", "ruby is a programming language", "sushi is art"])
puts res.class
puts res.embeddings.size
puts res.embeddings[0].size
##
# LLM::Response
# 3
# 1536Almost all LLM providers provide a models endpoint that allows a client to query the list of models that are available to use. The list is dynamic, maintained by LLM providers, and it is independent of a specific llm.rb release:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require "llm"
##
# List all models
llm = LLM.openai(key: ENV["KEY"])
llm.models.all.each do |model|
puts "model: #{model.id}"
end
##
# Select a model
model = llm.models.all.find { |m| m.id == "gpt-3.5-turbo" }
bot = LLM::Bot.new(llm, model: model.id)
res = bot.chat "Hello #{model.id} :)"
res.messages.each { |m| puts "[#{m.role}] #{m.content}" }llm.rb can be installed via rubygems.org:
gem install llm.rb
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for llm.rb
Similar Open Source Tools

llm.rb
llm.rb is a zero-dependency Ruby toolkit for Large Language Models that includes various providers like OpenAI, Gemini, Anthropic, xAI (Grok), zAI, DeepSeek, Ollama, and LlamaCpp. It provides full support for chat, streaming, tool calling, audio, images, files, and structured outputs. The toolkit offers features like unified API across providers, pluggable JSON adapters, tool calling, JSON Schema structured output, streaming responses, TTS, transcription, translation, image generation, files API, multimodal prompts, embeddings, models API, OpenAI vector stores, and more.
llm
llm.rb is a zero-dependency Ruby toolkit for Large Language Models that includes OpenAI, Gemini, Anthropic, xAI (Grok), DeepSeek, Ollama, and LlamaCpp. The toolkit provides full support for chat, streaming, tool calling, audio, images, files, and structured outputs (JSON Schema). It offers a single unified interface for multiple providers, zero dependencies outside Ruby's standard library, smart API design, and optional per-provider process-wide connection pool. Features include chat, agents, media support (text-to-speech, transcription, translation, image generation, editing), embeddings, model management, and more.
langchainrb
Langchain.rb is a Ruby library that makes it easy to build LLM-powered applications. It provides a unified interface to a variety of LLMs, vector search databases, and other tools, making it easy to build and deploy RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) systems and assistants. Langchain.rb is open source and available under the MIT License.
parrot.nvim
Parrot.nvim is a Neovim plugin that prioritizes a seamless out-of-the-box experience for text generation. It simplifies functionality and focuses solely on text generation, excluding integration of DALLE and Whisper. It supports persistent conversations as markdown files, custom hooks for inline text editing, multiple providers like Anthropic API, perplexity.ai API, OpenAI API, Mistral API, and local/offline serving via ollama. It allows custom agent definitions, flexible API credential support, and repository-specific instructions with a `.parrot.md` file. It does not have autocompletion or hidden requests in the background to analyze files.
ruby_llm-monitoring
RubyLLM::Monitoring is a tool designed to monitor the LLM (Live-Link Monitoring) usage within a Rails application. It provides a dashboard to display metrics such as Throughput, Cost, Response Time, and Error Rate. Users can customize the displayed metrics and add their own custom metrics. The tool also supports setting up alerts based on predefined conditions, such as monitoring cost and errors. Authentication and authorization are left to the user, allowing for flexibility in securing the monitoring dashboard. Overall, RubyLLM::Monitoring aims to provide a comprehensive solution for monitoring and analyzing the performance of a Rails application.
UnrealGenAISupport
The Unreal Engine Generative AI Support Plugin is a tool designed to integrate various cutting-edge LLM/GenAI models into Unreal Engine for game development. It aims to simplify the process of using AI models for game development tasks, such as controlling scene objects, generating blueprints, running Python scripts, and more. The plugin currently supports models from organizations like OpenAI, Anthropic, XAI, Google Gemini, Meta AI, Deepseek, and Baidu. It provides features like API support, model control, generative AI capabilities, UI generation, project file management, and more. The plugin is still under development but offers a promising solution for integrating AI models into game development workflows.
ruby-openai
Use the OpenAI API with Ruby! 🤖🩵 Stream text with GPT-4, transcribe and translate audio with Whisper, or create images with DALL·E... Hire me | 🎮 Ruby AI Builders Discord | 🐦 Twitter | 🧠 Anthropic Gem | 🚂 Midjourney Gem ## Table of Contents * Ruby OpenAI * Table of Contents * Installation * Bundler * Gem install * Usage * Quickstart * With Config * Custom timeout or base URI * Extra Headers per Client * Logging * Errors * Faraday middleware * Azure * Ollama * Counting Tokens * Models * Examples * Chat * Streaming Chat * Vision * JSON Mode * Functions * Edits * Embeddings * Batches * Files * Finetunes * Assistants * Threads and Messages * Runs * Runs involving function tools * Image Generation * DALL·E 2 * DALL·E 3 * Image Edit * Image Variations * Moderations * Whisper * Translate * Transcribe * Speech * Errors * Development * Release * Contributing * License * Code of Conduct
dspy.rb
DSPy.rb is a Ruby framework for building reliable LLM applications using composable, type-safe modules. It enables developers to define typed signatures and compose them into pipelines, offering a more structured approach compared to traditional prompting. The framework embraces Ruby conventions and adds innovations like CodeAct agents and enhanced production instrumentation, resulting in scalable LLM applications that are robust and efficient. DSPy.rb is actively developed, with a focus on stability and real-world feedback through the 0.x series before reaching a stable v1.0 API.
LocalAGI
LocalAGI is a powerful, self-hostable AI Agent platform that allows you to design AI automations without writing code. It provides a complete drop-in replacement for OpenAI's Responses APIs with advanced agentic capabilities. With LocalAGI, you can create customizable AI assistants, automations, chat bots, and agents that run 100% locally, without the need for cloud services or API keys. The platform offers features like no-code agents, web-based interface, advanced agent teaming, connectors for various platforms, comprehensive REST API, short & long-term memory capabilities, planning & reasoning, periodic tasks scheduling, memory management, multimodal support, extensible custom actions, fully customizable models, observability, and more.
promptic
Promptic is a tool designed for LLM app development, providing a productive and pythonic way to build LLM applications. It leverages LiteLLM, allowing flexibility to switch LLM providers easily. Promptic focuses on building features by providing type-safe structured outputs, easy-to-build agents, streaming support, automatic prompt caching, and built-in conversation memory.
LTEngine
LTEngine is a free and open-source local AI machine translation API written in Rust. It is self-hosted and compatible with LibreTranslate. LTEngine utilizes large language models (LLMs) via llama.cpp, offering high-quality translations that rival or surpass DeepL for certain languages. It supports various accelerators like CUDA, Metal, and Vulkan, with the largest model 'gemma3-27b' fitting on a single consumer RTX 3090. LTEngine is actively developed, with a roadmap outlining future enhancements and features.
quantalogic
QuantaLogic is a ReAct framework for building advanced AI agents that seamlessly integrates large language models with a robust tool system. It aims to bridge the gap between advanced AI models and practical implementation in business processes by enabling agents to understand, reason about, and execute complex tasks through natural language interaction. The framework includes features such as ReAct Framework, Universal LLM Support, Secure Tool System, Real-time Monitoring, Memory Management, and Enterprise Ready components.
sparkle
Sparkle is a tool that streamlines the process of building AI-driven features in applications using Large Language Models (LLMs). It guides users through creating and managing agents, defining tools, and interacting with LLM providers like OpenAI. Sparkle allows customization of LLM provider settings, model configurations, and provides a seamless integration with Sparkle Server for exposing agents via an OpenAI-compatible chat API endpoint.
client-python
The Mistral Python Client is a tool inspired by cohere-python that allows users to interact with the Mistral AI API. It provides functionalities to access and utilize the AI capabilities offered by Mistral. Users can easily install the client using pip and manage dependencies using poetry. The client includes examples demonstrating how to use the API for various tasks, such as chat interactions. To get started, users need to obtain a Mistral API Key and set it as an environment variable. Overall, the Mistral Python Client simplifies the integration of Mistral AI services into Python applications.
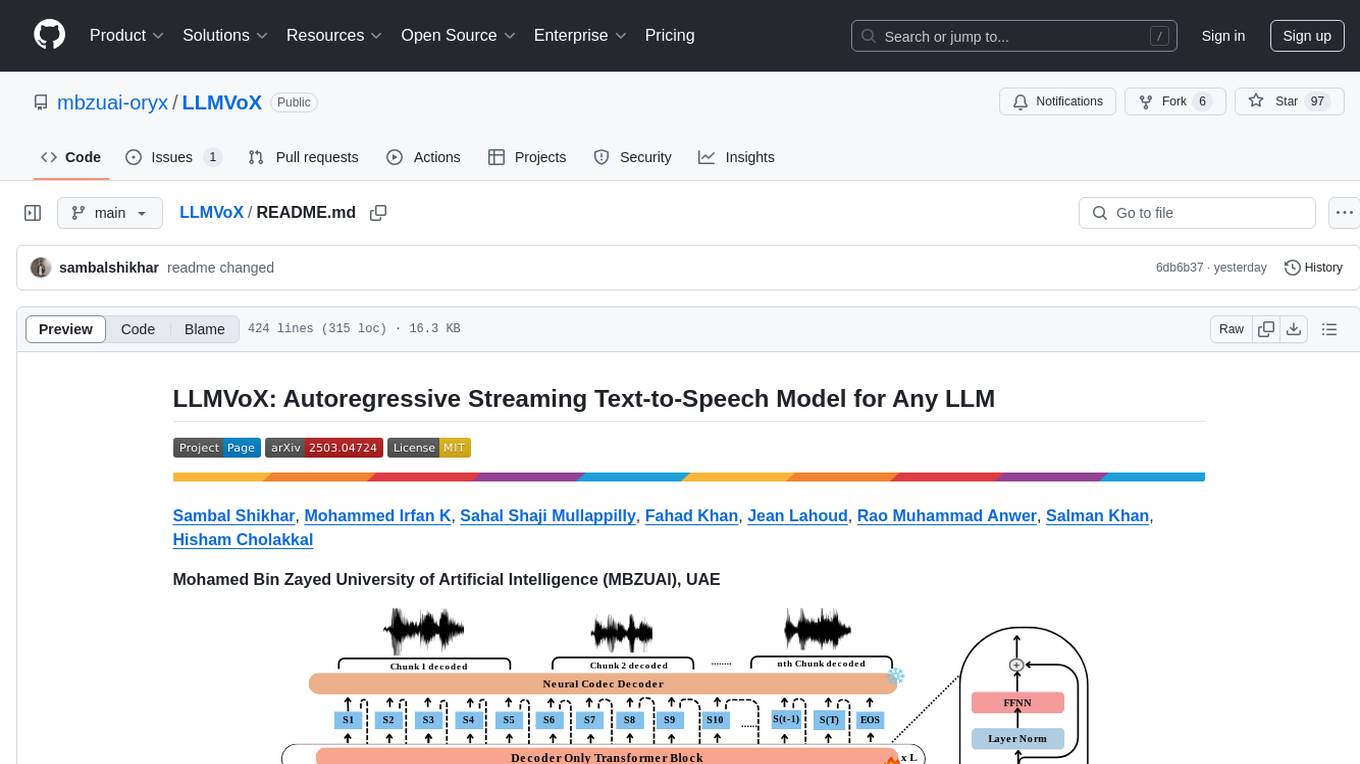
LLMVoX
LLMVoX is a lightweight 30M-parameter, LLM-agnostic, autoregressive streaming Text-to-Speech (TTS) system designed to convert text outputs from Large Language Models into high-fidelity streaming speech with low latency. It achieves significantly lower Word Error Rate compared to speech-enabled LLMs while operating at comparable latency and speech quality. Key features include being lightweight & fast with only 30M parameters, LLM-agnostic for easy integration with existing models, multi-queue streaming for continuous speech generation, and multilingual support for easy adaptation to new languages.
wtf.nvim
wtf.nvim is a Neovim plugin that enhances diagnostic debugging by providing explanations and solutions for code issues using ChatGPT. It allows users to search the web for answers directly from Neovim, making the debugging process faster and more efficient. The plugin works with any language that has LSP support in Neovim, offering AI-powered diagnostic assistance and seamless integration with various resources for resolving coding problems.
For similar tasks

embedJs
EmbedJs is a NodeJS framework that simplifies RAG application development by efficiently processing unstructured data. It segments data, creates relevant embeddings, and stores them in a vector database for quick retrieval.
mistral-ai-kmp
Mistral AI SDK for Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP) allows communication with Mistral API to get AI models, start a chat with the assistant, and create embeddings. The library is based on Mistral API documentation and built with Kotlin Multiplatform and Ktor client library. Sample projects like ZeChat showcase the capabilities of Mistral AI SDK. Users can interact with different Mistral AI models through ZeChat apps on Android, Desktop, and Web platforms. The library is not yet published on Maven, but users can fork the project and use it as a module dependency in their apps.
pgai
pgai simplifies the process of building search and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) AI applications with PostgreSQL. It brings embedding and generation AI models closer to the database, allowing users to create embeddings, retrieve LLM chat completions, reason over data for classification, summarization, and data enrichment directly from within PostgreSQL in a SQL query. The tool requires an OpenAI API key and a PostgreSQL client to enable AI functionality in the database. Users can install pgai from source, run it in a pre-built Docker container, or enable it in a Timescale Cloud service. The tool provides functions to handle API keys using psql or Python, and offers various AI functionalities like tokenizing, detokenizing, embedding, chat completion, and content moderation.
azure-functions-openai-extension
Azure Functions OpenAI Extension is a project that adds support for OpenAI LLM (GPT-3.5-turbo, GPT-4) bindings in Azure Functions. It provides NuGet packages for various functionalities like text completions, chat completions, assistants, embeddings generators, and semantic search. The project requires .NET 6 SDK or greater, Azure Functions Core Tools v4.x, and specific settings in Azure Function or local settings for development. It offers features like text completions, chat completion, assistants with custom skills, embeddings generators for text relatedness, and semantic search using vector databases. The project also includes examples in C# and Python for different functionalities.
openai-kit
OpenAIKit is a Swift package designed to facilitate communication with the OpenAI API. It provides methods to interact with various OpenAI services such as chat, models, completions, edits, images, embeddings, files, moderations, and speech to text. The package encourages the use of environment variables to securely inject the OpenAI API key and organization details. It also offers error handling for API requests through the `OpenAIKit.APIErrorResponse`.
VectorETL
VectorETL is a lightweight ETL framework designed to assist Data & AI engineers in processing data for AI applications quickly. It streamlines the conversion of diverse data sources into vector embeddings and storage in various vector databases. The framework supports multiple data sources, embedding models, and vector database targets, simplifying the creation and management of vector search systems for semantic search, recommendation systems, and other vector-based operations.

LLamaWorker
LLamaWorker is a HTTP API server developed to provide an OpenAI-compatible API for integrating Large Language Models (LLM) into applications. It supports multi-model configuration, streaming responses, text embedding, chat templates, automatic model release, function calls, API key authentication, and test UI. Users can switch models, complete chats and prompts, manage chat history, and generate tokens through the test UI. Additionally, LLamaWorker offers a Vulkan compiled version for download and provides function call templates for testing. The tool supports various backends and provides API endpoints for chat completion, prompt completion, embeddings, model information, model configuration, and model switching. A Gradio UI demo is also available for testing.
openai-scala-client
This is a no-nonsense async Scala client for OpenAI API supporting all the available endpoints and params including streaming, chat completion, vision, and voice routines. It provides a single service called OpenAIService that supports various calls such as Models, Completions, Chat Completions, Edits, Images, Embeddings, Batches, Audio, Files, Fine-tunes, Moderations, Assistants, Threads, Thread Messages, Runs, Run Steps, Vector Stores, Vector Store Files, and Vector Store File Batches. The library aims to be self-contained with minimal dependencies and supports API-compatible providers like Azure OpenAI, Azure AI, Anthropic, Google Vertex AI, Groq, Grok, Fireworks AI, OctoAI, TogetherAI, Cerebras, Mistral, Deepseek, Ollama, FastChat, and more.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.



