
LTEngine
Local AI Machine Translation. Powered by LLMs. LibreTranslate compatible. 🚀
Stars: 57
LTEngine is a free and open-source local AI machine translation API written in Rust. It is self-hosted and compatible with LibreTranslate. LTEngine utilizes large language models (LLMs) via llama.cpp, offering high-quality translations that rival or surpass DeepL for certain languages. It supports various accelerators like CUDA, Metal, and Vulkan, with the largest model 'gemma3-27b' fitting on a single consumer RTX 3090. LTEngine is actively developed, with a roadmap outlining future enhancements and features.
README:
Free and Open Source Local AI Machine Translation API, written in Rust, entirely self-hosted and compatible with LibreTranslate. Its translation capabilities are powered by large language models (LLMs) that run locally on your machine via llama.cpp.
The LLMs in LTEngine are much larger than the lightweight transformer models in LibreTranslate. Thus memory usage and speed are traded off for quality of outputs, which for some languages has been reported as being on par or better than DeepL.
It is possible to run LTEngine entirely on the CPU, but an accelerator will greatly improve performance. Supported accelerators currently include:
- CUDA
- Metal (macOS)
- Vulkan
The largest model (gemma3-27b) can fit on a single consumer RTX 3090 with 24G of VRAM.
⚠️ LTEngine is in active development. Check the Roadmap for current limitations.
git clone https://github.com/LibreTranslate/LTEngine --recursive
cd LTEngine
cargo build [--features cuda,vulkan,metal] --release./target/release/ltengineTo run different LLM models:
./target/release/ltengine -m gemma3-12b [--model-file /path/to/model.gguf]LTEngine supports any GGUF language model supported by llama.cpp. You can pass a path to load a custom .gguf model using the --model-file parameter. Otherwise LTEngine will download one of the Gemma3 models based on the -m parameter:
| Model | RAM Usage | GPU Usage | Notes | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gemma3-1b | 1G | 2G | Good for testing, poor translations | |
| gemma3-4b | 4G | 4G | ✔️ | |
| gemma3-12b | 8G | 10G | ||
| gemma4-27b | 16G | 18G | Best translation quality, slowest |
Memory usage numbers are approximate.
Request:
const res = await fetch("http://0.0.0.0:5050/translate", {
method: "POST",
body: JSON.stringify({
q: "Hello!",
source: "en",
target: "es",
}),
headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" },
});
console.log(await res.json());Response:
{
"translatedText": "¡Hola!"
}List of language codes: https://0.0.0.0:5000/languages
Request:
const res = await fetch("http://0.0.0.0:5000/translate", {
method: "POST",
body: JSON.stringify({
q: "Ciao!",
source: "auto",
target: "en",
}),
headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" },
});
console.log(await res.json());Response:
{
"detectedLanguage": {
"confidence": 83,
"language": "it"
},
"translatedText": "Bye!"
}You can use the LTEngine API using the following bindings:
- Rust: https://github.com/DefunctLizard/libretranslate-rs
- Node.js: https://github.com/franciscop/translate
- TypeScript: https://github.com/tderflinger/libretranslate-ts
- .Net: https://github.com/sigaloid/LibreTranslate.Net
- Go: https://github.com/SnakeSel/libretranslate
- Python: https://github.com/argosopentech/LibreTranslate-py
- PHP: https://github.com/jefs42/libretranslate
- C++: https://github.com/argosopentech/LibreTranslate-cpp
- Swift: https://github.com/wacumov/libretranslate
- Unix: https://github.com/argosopentech/LibreTranslate-sh
- Shell: https://github.com/Hayao0819/Hayao-Tools/tree/master/libretranslate-sh
- Java: https://github.com/suuft/libretranslate-java
- Ruby: https://github.com/noesya/libretranslate
- R: https://github.com/myanesp/libretranslateR
- [ ] Remove mutex block that currently limits the software to process one single translation request at a time due to a possible bug in llama.cpp.
- [ ] Cancel inference (stop generating tokens) when HTTP connections are aborted by clients. I'm unsure how this could done with actix-web.
- [ ] Add support for
/translate_file(ability to translate files). - [ ] Add support for sentence splitting. Currently text is sent to the LLM as-is, but longer texts (like documents) should be split into chunks, translated and merged back.
- [ ] Better language detection for short texts (port LexiLang to Rust)
- [ ] Test/add more LLM models aside from Gemma3
- [ ] Create comparative benchmarks between LTEngine and proprietary software.
- [ ] Add support for command line inference (run
./ltengine translateas a command line app separate from./ltengine server) - [ ] Make ltengine available as a library, possibly creating bindings for other languages like Python.
- [ ] Automated builds / CI
- [ ] Your ideas? We welcome contributions.
We welcome contributions! Just open a pull request.
This work is largely possible thanks llama-cpp-rs which provide the Rust bindings to llama.cpp.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LTEngine
Similar Open Source Tools

LTEngine
LTEngine is a free and open-source local AI machine translation API written in Rust. It is self-hosted and compatible with LibreTranslate. LTEngine utilizes large language models (LLMs) via llama.cpp, offering high-quality translations that rival or surpass DeepL for certain languages. It supports various accelerators like CUDA, Metal, and Vulkan, with the largest model 'gemma3-27b' fitting on a single consumer RTX 3090. LTEngine is actively developed, with a roadmap outlining future enhancements and features.
SynapseML
SynapseML (previously known as MMLSpark) is an open-source library that simplifies the creation of massively scalable machine learning (ML) pipelines. It provides simple, composable, and distributed APIs for various machine learning tasks such as text analytics, vision, anomaly detection, and more. Built on Apache Spark, SynapseML allows seamless integration of models into existing workflows. It supports training and evaluation on single-node, multi-node, and resizable clusters, enabling scalability without resource wastage. Compatible with Python, R, Scala, Java, and .NET, SynapseML abstracts over different data sources for easy experimentation. Requires Scala 2.12, Spark 3.4+, and Python 3.8+.
CrackSQL
CrackSQL is a powerful SQL dialect translation tool that integrates rule-based strategies with large language models (LLMs) for high accuracy. It enables seamless conversion between dialects (e.g., PostgreSQL → MySQL) with flexible access through Python API, command line, and web interface. The tool supports extensive dialect compatibility, precision & advanced processing, and versatile access & integration. It offers three modes for dialect translation and demonstrates high translation accuracy over collected benchmarks. Users can deploy CrackSQL using PyPI package installation or source code installation methods. The tool can be extended to support additional syntax, new dialects, and improve translation efficiency. The project is actively maintained and welcomes contributions from the community.
llm
llm.rb is a zero-dependency Ruby toolkit for Large Language Models that includes OpenAI, Gemini, Anthropic, xAI (Grok), DeepSeek, Ollama, and LlamaCpp. The toolkit provides full support for chat, streaming, tool calling, audio, images, files, and structured outputs (JSON Schema). It offers a single unified interface for multiple providers, zero dependencies outside Ruby's standard library, smart API design, and optional per-provider process-wide connection pool. Features include chat, agents, media support (text-to-speech, transcription, translation, image generation, editing), embeddings, model management, and more.

EasySteer
EasySteer is a unified framework built on vLLM for high-performance LLM steering. It offers fast, flexible, and easy-to-use steering capabilities with features like high performance, modular design, fine-grained control, pre-computed steering vectors, and an interactive demo. Users can interactively configure models, adjust steering parameters, and test interventions without writing code. The tool supports OpenAI-compatible APIs and provides modules for hidden states extraction, analysis-based steering, learning-based steering, and a frontend web interface for interactive steering and ReFT interventions.
curator
Bespoke Curator is an open-source tool for data curation and structured data extraction. It provides a Python library for generating synthetic data at scale, with features like programmability, performance optimization, caching, and integration with HuggingFace Datasets. The tool includes a Curator Viewer for dataset visualization and offers a rich set of functionalities for creating and refining data generation strategies.
dom-to-semantic-markdown
DOM to Semantic Markdown is a tool that converts HTML DOM to Semantic Markdown for use in Large Language Models (LLMs). It maximizes semantic information, token efficiency, and preserves metadata to enhance LLMs' processing capabilities. The tool captures rich web content structure, including semantic tags, image metadata, table structures, and link destinations. It offers customizable conversion options and supports both browser and Node.js environments.
mlx-llm
mlx-llm is a library that allows you to run Large Language Models (LLMs) on Apple Silicon devices in real-time using Apple's MLX framework. It provides a simple and easy-to-use API for creating, loading, and using LLM models, as well as a variety of applications such as chatbots, fine-tuning, and retrieval-augmented generation.

rl
TorchRL is an open-source Reinforcement Learning (RL) library for PyTorch. It provides pytorch and **python-first** , low and high level abstractions for RL that are intended to be **efficient** , **modular** , **documented** and properly **tested**. The code is aimed at supporting research in RL. Most of it is written in python in a highly modular way, such that researchers can easily swap components, transform them or write new ones with little effort.
freeGPT
freeGPT provides free access to text and image generation models. It supports various models, including gpt3, gpt4, alpaca_7b, falcon_40b, prodia, and pollinations. The tool offers both asynchronous and non-asynchronous interfaces for text completion and image generation. It also features an interactive Discord bot that provides access to all the models in the repository. The tool is easy to use and can be integrated into various applications.
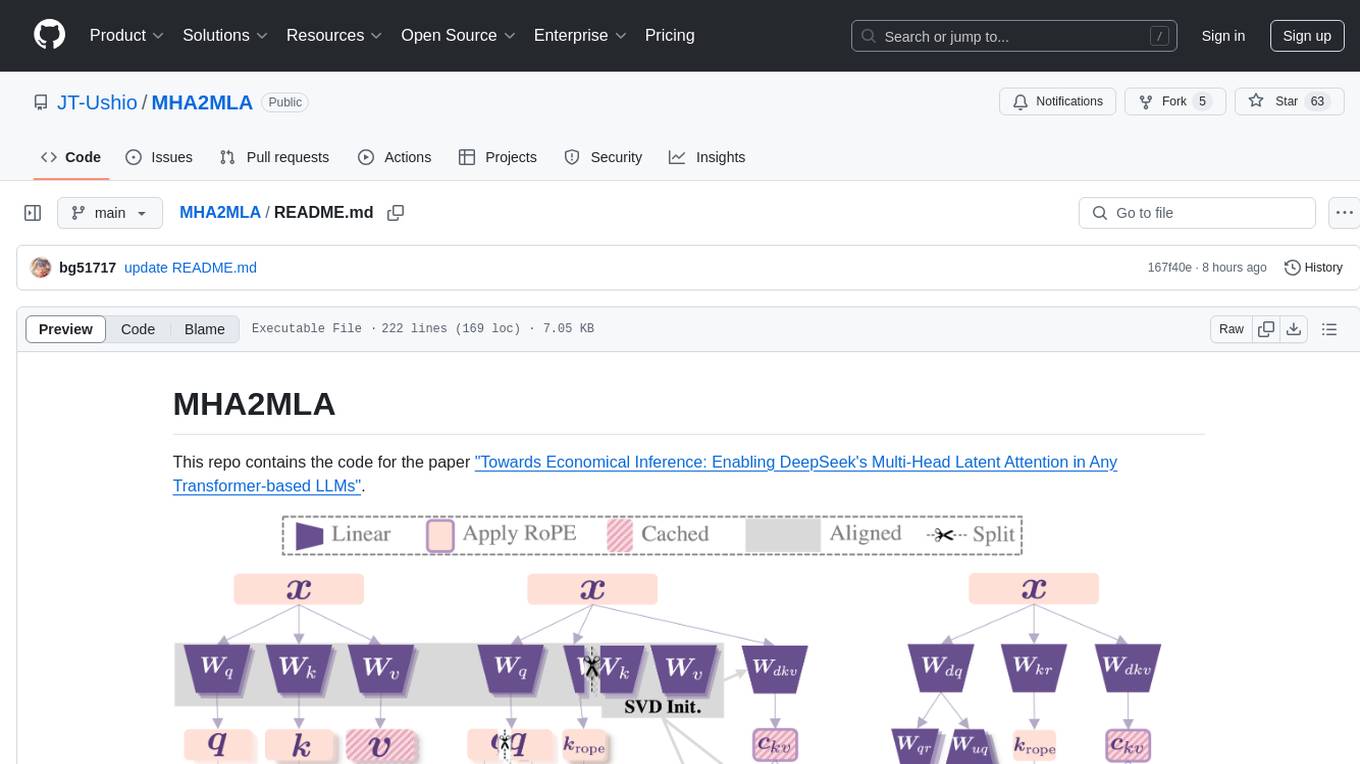
MHA2MLA
This repository contains the code for the paper 'Towards Economical Inference: Enabling DeepSeek's Multi-Head Latent Attention in Any Transformer-based LLMs'. It provides tools for fine-tuning and evaluating Llama models, converting models between different frameworks, processing datasets, and performing specific model training tasks like Partial-RoPE Fine-Tuning and Multiple-Head Latent Attention Fine-Tuning. The repository also includes commands for model evaluation using Lighteval and LongBench, along with necessary environment setup instructions.
quantalogic
QuantaLogic is a ReAct framework for building advanced AI agents that seamlessly integrates large language models with a robust tool system. It aims to bridge the gap between advanced AI models and practical implementation in business processes by enabling agents to understand, reason about, and execute complex tasks through natural language interaction. The framework includes features such as ReAct Framework, Universal LLM Support, Secure Tool System, Real-time Monitoring, Memory Management, and Enterprise Ready components.
dspy.rb
DSPy.rb is a Ruby framework for building reliable LLM applications using composable, type-safe modules. It enables developers to define typed signatures and compose them into pipelines, offering a more structured approach compared to traditional prompting. The framework embraces Ruby conventions and adds innovations like CodeAct agents and enhanced production instrumentation, resulting in scalable LLM applications that are robust and efficient. DSPy.rb is actively developed, with a focus on stability and real-world feedback through the 0.x series before reaching a stable v1.0 API.

req_llm
ReqLLM is a Req-based library for LLM interactions, offering a unified interface to AI providers through a plugin-based architecture. It brings composability and middleware advantages to LLM interactions, with features like auto-synced providers/models, typed data structures, ergonomic helpers, streaming capabilities, usage & cost extraction, and a plugin-based provider system. Users can easily generate text, structured data, embeddings, and track usage costs. The tool supports various AI providers like Anthropic, OpenAI, Groq, Google, and xAI, and allows for easy addition of new providers. ReqLLM also provides API key management, detailed documentation, and a roadmap for future enhancements.
DeepResearch
Tongyi DeepResearch is an agentic large language model with 30.5 billion total parameters, designed for long-horizon, deep information-seeking tasks. It demonstrates state-of-the-art performance across various search benchmarks. The model features a fully automated synthetic data generation pipeline, large-scale continual pre-training on agentic data, end-to-end reinforcement learning, and compatibility with two inference paradigms. Users can download the model directly from HuggingFace or ModelScope. The repository also provides benchmark evaluation scripts and information on the Deep Research Agent Family.
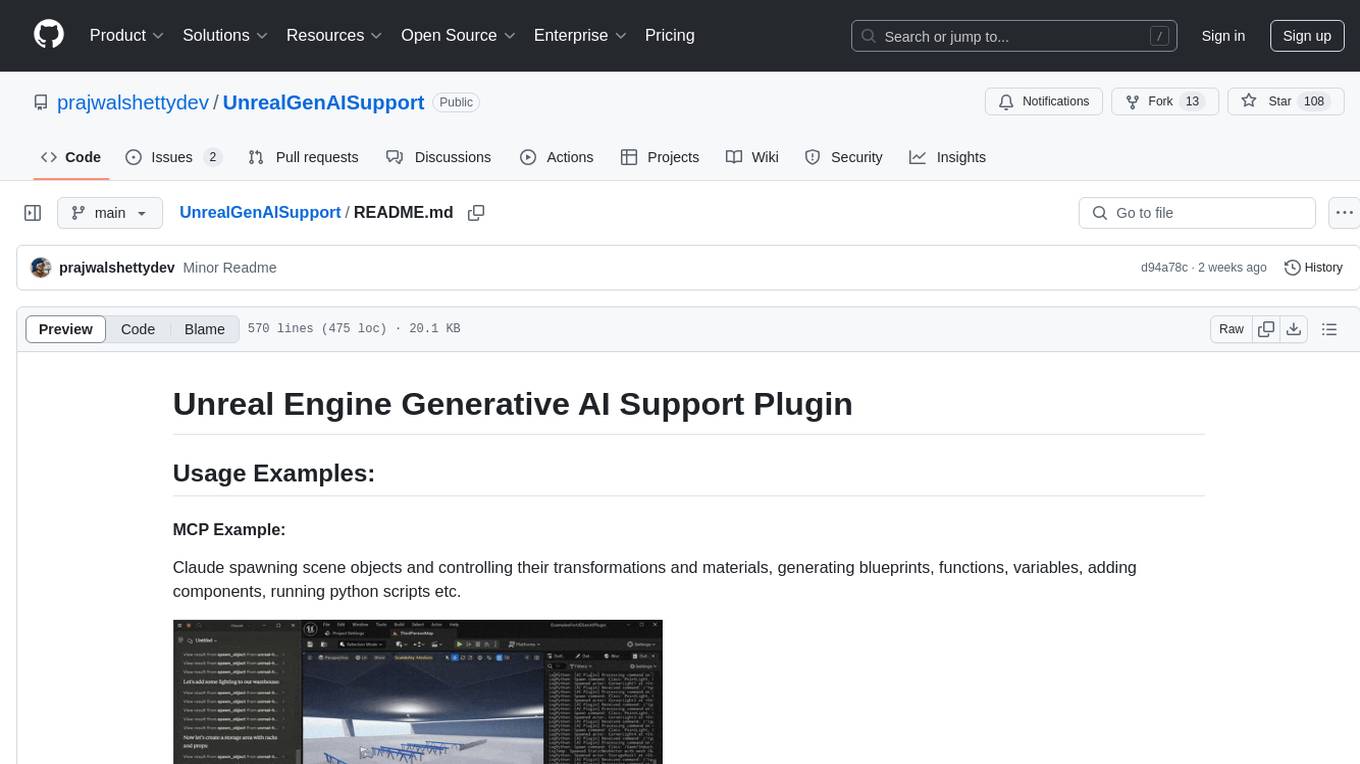
UnrealGenAISupport
The Unreal Engine Generative AI Support Plugin is a tool designed to integrate various cutting-edge LLM/GenAI models into Unreal Engine for game development. It aims to simplify the process of using AI models for game development tasks, such as controlling scene objects, generating blueprints, running Python scripts, and more. The plugin currently supports models from organizations like OpenAI, Anthropic, XAI, Google Gemini, Meta AI, Deepseek, and Baidu. It provides features like API support, model control, generative AI capabilities, UI generation, project file management, and more. The plugin is still under development but offers a promising solution for integrating AI models into game development workflows.
For similar tasks
arena-hard-auto
Arena-Hard-Auto-v0.1 is an automatic evaluation tool for instruction-tuned LLMs. It contains 500 challenging user queries. The tool prompts GPT-4-Turbo as a judge to compare models' responses against a baseline model (default: GPT-4-0314). Arena-Hard-Auto employs an automatic judge as a cheaper and faster approximator to human preference. It has the highest correlation and separability to Chatbot Arena among popular open-ended LLM benchmarks. Users can evaluate their models' performance on Chatbot Arena by using Arena-Hard-Auto.

max
The Modular Accelerated Xecution (MAX) platform is an integrated suite of AI libraries, tools, and technologies that unifies commonly fragmented AI deployment workflows. MAX accelerates time to market for the latest innovations by giving AI developers a single toolchain that unlocks full programmability, unparalleled performance, and seamless hardware portability.
ai-hub
AI Hub Project aims to continuously test and evaluate mainstream large language models, while accumulating and managing various effective model invocation prompts. It has integrated all mainstream large language models in China, including OpenAI GPT-4 Turbo, Baidu ERNIE-Bot-4, Tencent ChatPro, MiniMax abab5.5-chat, and more. The project plans to continuously track, integrate, and evaluate new models. Users can access the models through REST services or Java code integration. The project also provides a testing suite for translation, coding, and benchmark testing.
long-context-attention
Long-Context-Attention (YunChang) is a unified sequence parallel approach that combines the strengths of DeepSpeed-Ulysses-Attention and Ring-Attention to provide a versatile and high-performance solution for long context LLM model training and inference. It addresses the limitations of both methods by offering no limitation on the number of heads, compatibility with advanced parallel strategies, and enhanced performance benchmarks. The tool is verified in Megatron-LM and offers best practices for 4D parallelism, making it suitable for various attention mechanisms and parallel computing advancements.

marlin
Marlin is a highly optimized FP16xINT4 matmul kernel designed for large language model (LLM) inference, offering close to ideal speedups up to batchsizes of 16-32 tokens. It is suitable for larger-scale serving, speculative decoding, and advanced multi-inference schemes like CoT-Majority. Marlin achieves optimal performance by utilizing various techniques and optimizations to fully leverage GPU resources, ensuring efficient computation and memory management.
MMC
This repository, MMC, focuses on advancing multimodal chart understanding through large-scale instruction tuning. It introduces a dataset supporting various tasks and chart types, a benchmark for evaluating reasoning capabilities over charts, and an assistant achieving state-of-the-art performance on chart QA benchmarks. The repository provides data for chart-text alignment, benchmarking, and instruction tuning, along with existing datasets used in experiments. Additionally, it offers a Gradio demo for the MMCA model.
Tiktoken
Tiktoken is a high-performance implementation focused on token count operations. It provides various encodings like o200k_base, cl100k_base, r50k_base, p50k_base, and p50k_edit. Users can easily encode and decode text using the provided API. The repository also includes a benchmark console app for performance tracking. Contributions in the form of PRs are welcome.
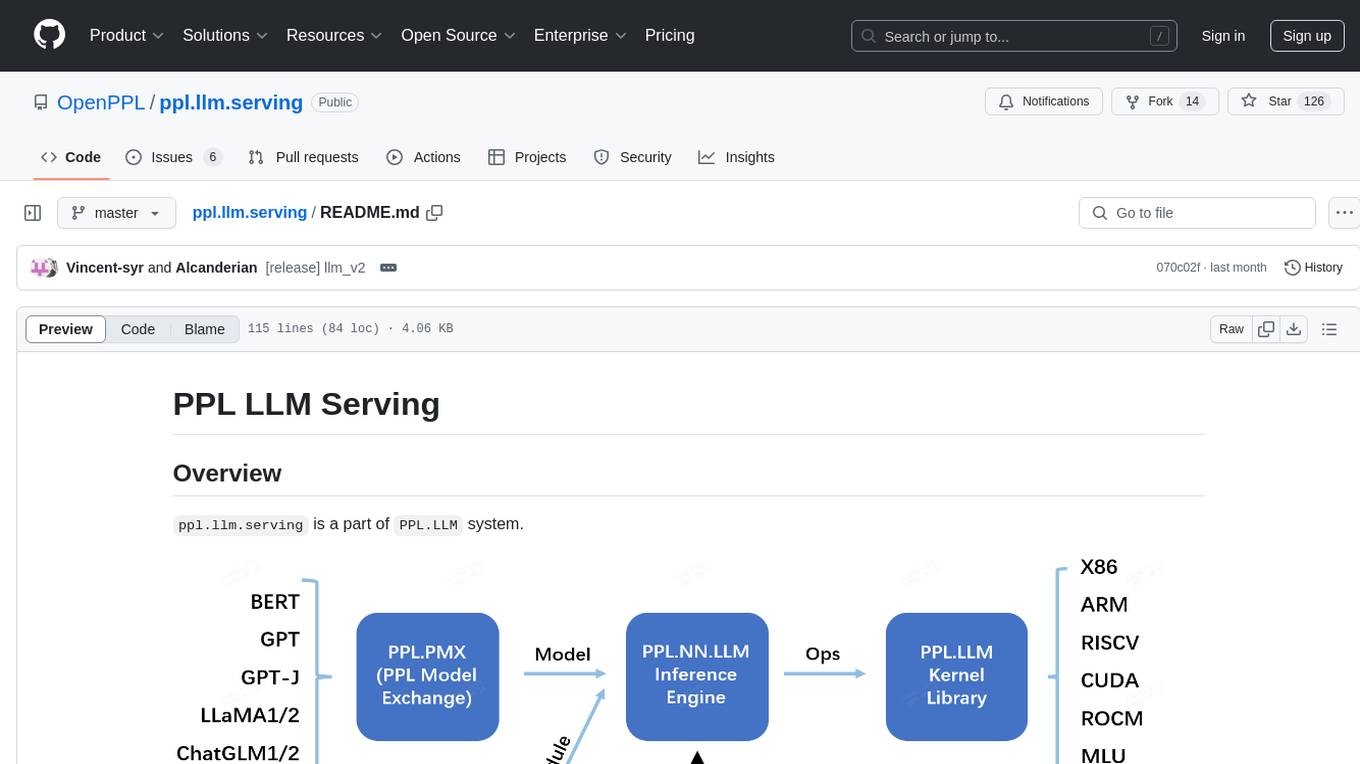
ppl.llm.serving
ppl.llm.serving is a serving component for Large Language Models (LLMs) within the PPL.LLM system. It provides a server based on gRPC and supports inference for LLaMA. The repository includes instructions for prerequisites, quick start guide, model exporting, server setup, client usage, benchmarking, and offline inference. Users can refer to the LLaMA Guide for more details on using this serving component.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.