
ksail
Tool for creating, maintaining and operating Kubernetes clusters with ease.
Stars: 129
KSail is a tool that bundles common Kubernetes tooling into a single binary, providing a unified workflow for creating clusters, deploying workloads, and operating cloud-native stacks across different distributions and providers. It eliminates the need for multiple CLI tools and bespoke scripts, offering features like one binary for provisioning and deployment, support for various cluster configurations, mirror registries, GitOps integration, customizable stack selection, built-in SOPS for secrets management, AI assistant for interactive chat, and a VSCode extension for cluster management.
README:
KSail is a tool that bundles common Kubernetes tooling into a single binary. It provides a VSCode Extension, CLI, AI-Enabled Chat TUI or MCP interface to create clusters, deploy workloads, and operate cloud-native stacks across different distributions and providers.
Setting up and operating Kubernetes clusters often requires juggling multiple CLI tools, writing bespoke scripts, and dealing with inconsistent workflows. KSail removes the tooling overhead so you can focus on your workloads.
No Vendor Lock-In: KSail works with native distribution configurations (Kind's kind.yaml, K3d's config, Talos patches) — you can run the same cluster outside KSail using the underlying tools directly. KSail is a superset that provides a unified workflow while preserving full compatibility with Kind, K3d, and Talos.
- 📦 One Binary — Embeds cluster provisioning, GitOps engines, and deployment tooling. No tool sprawl.
- ☸️ Simple Clusters — Spin up Vanilla, K3s, or Talos clusters with one command. Same workflow across distributions.
- 🔓 No Lock-In — Uses native configs (
kind.yaml,k3d.yaml, Talos patches). Run clusters with or without KSail. - 📥 Mirror Registries — Avoid rate limits, and store images once. Same mirrors used by different clusters.
- 📄 Everything as Code — Cluster settings, distribution configs, and workloads in version-controlled files.
- 🔄 GitOps Native — Built-in Flux or ArgoCD support with bootstrap, push, and reconcile commands.
- ⚙️ Customizable Stack — Select your CNI, CSI, policy engine, cert-manager, and mirror registries.
- 🔐 SOPS Built In — Encrypt, decrypt, and edit secrets with integrated cipher commands.
- 🤖 AI Assistant — Interactive chat powered by GitHub Copilot for configuration and troubleshooting.
- 💻 VSCode Extension — Manage clusters from VSCode with wizards, sidebar views, and command palette.
KSail works on all major operating systems and CPU architectures:
| OS | Architecture |
|---|---|
| 🐧 Linux | amd64, arm64 |
| macOS | arm64 |
| ⊞ Windows (native untested; WSL2 recommended) | amd64, arm64 |
Docker is required for local clusters. Install Docker Desktop/Engine and ensure docker ps works.
Supported distributions run on different infrastructure providers:
| Provider | Vanilla | K3s | Talos |
|---|---|---|---|
| Docker | ✅ (Kind) | ✅ (K3d) | ✅ |
| Hetzner | — | — | ✅ |
See the Installation Guide for detailed installation instructions.
For VSCode users, install the KSail extension to manage clusters directly from your editor. See the extension documentation for features and usage.
# 1. Initialize a new project with your preferred stack
ksail cluster init \
--name <cluster-name> \
--distribution <Vanilla|K3s|Talos> \
--cni <Default|Cilium|Calico> \
--csi <Default|Enabled|Disabled> \
--metrics-server <Default|Enabled|Disabled> \
--cert-manager <Enabled|Disabled> \
--policy-engine <None|Kyverno|Gatekeeper> \
--gitops-engine <None|Flux|ArgoCD> \
--mirror-registry <host>=<upstream>
# 2. Create and start the cluster
ksail cluster create
# 3. Add your manifests to the k8s/ directory
# 4. Deploy your workloads
ksail workload apply -k ./k8s # kubectl workflow
ksail workload reconcile # gitops workflow
# 5. Update cluster configuration (modify ksail.yaml, then run)
ksail cluster update # Apply configuration changes
# 6. Connect to the cluster with K9s
ksail cluster connectKSail generates standard distribution configuration files that you can use directly with the underlying tools:
# After ksail cluster init, you'll find native configs:
# - kind.yaml (for Vanilla/Kind clusters)
# - k3d.yaml (for K3s clusters)
# - talos/ (for Talos clusters)
# You can use these configs directly without KSail:
kind create cluster --config kind.yaml
k3d cluster create --config k3d.yaml
talosctl cluster create --config-patch @talos/cluster/patches.yaml
# Or let KSail manage the lifecycle:
ksail cluster createThis means you're never locked into KSail — you can migrate away at any time or use both KSail and native tools interchangeably.
Browse the documentation at https://ksail.devantler.tech (GitHub Pages)
Contributions are welcome! Please read CONTRIBUTING.md for details on our development process, coding standards, and how to submit pull requests.
KSail is a powerful tool that can be used in many different ways. Here are some projects that use KSail in their setup:
| Project | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| devantler-tech/platform | My personal homelab | Platform |
If you use KSail in your project, feel free to open a PR to add it to the list, so others can see how you use KSail.
- KSail - a Kubernetes SDK for local GitOps development and CI - A presentation on KSail at KCD2024 (Early version of KSail that was built in .NET).
- Local Kubernetes Development with KSail and Kind
- Local Kubernetes Development with KSail and K3d
- Local Kubernetes Development with KSail and Talos
- Creating Kubernetes Clusters on Hetzner with KSail and Talos
- AI-first TUI for KSail with Copilot SDK and Bubbletea
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for ksail
Similar Open Source Tools

ksail
KSail is a tool that bundles common Kubernetes tooling into a single binary, providing a unified workflow for creating clusters, deploying workloads, and operating cloud-native stacks across different distributions and providers. It eliminates the need for multiple CLI tools and bespoke scripts, offering features like one binary for provisioning and deployment, support for various cluster configurations, mirror registries, GitOps integration, customizable stack selection, built-in SOPS for secrets management, AI assistant for interactive chat, and a VSCode extension for cluster management.
kubesphere
KubeSphere is a distributed operating system for cloud-native application management, using Kubernetes as its kernel. It provides a plug-and-play architecture, allowing third-party applications to be seamlessly integrated into its ecosystem. KubeSphere is also a multi-tenant container platform with full-stack automated IT operation and streamlined DevOps workflows. It provides developer-friendly wizard web UI, helping enterprises to build out a more robust and feature-rich platform, which includes most common functionalities needed for enterprise Kubernetes strategy.
ToolJet
ToolJet is an open-source platform for building and deploying internal tools, workflows, and AI agents. It offers a visual builder with drag-and-drop UI, integrations with databases, APIs, SaaS apps, and object storage. The community edition includes features like a visual app builder, ToolJet database, multi-page apps, collaboration tools, extensibility with plugins, code execution, and security measures. ToolJet AI, the enterprise version, adds AI capabilities for app generation, query building, debugging, agent creation, security compliance, user management, environment management, GitSync, branding, access control, embedded apps, and enterprise support.

toolhive-studio
ToolHive Studio is an experimental project under active development and testing, providing an easy way to discover, deploy, and manage Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers securely. Users can launch any MCP server in a locked-down container with just a few clicks, eliminating manual setup, security concerns, and runtime issues. The tool ensures instant deployment, default security measures, cross-platform compatibility, and seamless integration with popular clients like GitHub Copilot, Cursor, and Claude Code.

clearml
ClearML is a suite of tools designed to streamline the machine learning workflow. It includes an experiment manager, MLOps/LLMOps, data management, and model serving capabilities. ClearML is open-source and offers a free tier hosting option. It supports various ML/DL frameworks and integrates with Jupyter Notebook and PyCharm. ClearML provides extensive logging capabilities, including source control info, execution environment, hyper-parameters, and experiment outputs. It also offers automation features, such as remote job execution and pipeline creation. ClearML is designed to be easy to integrate, requiring only two lines of code to add to existing scripts. It aims to improve collaboration, visibility, and data transparency within ML teams.
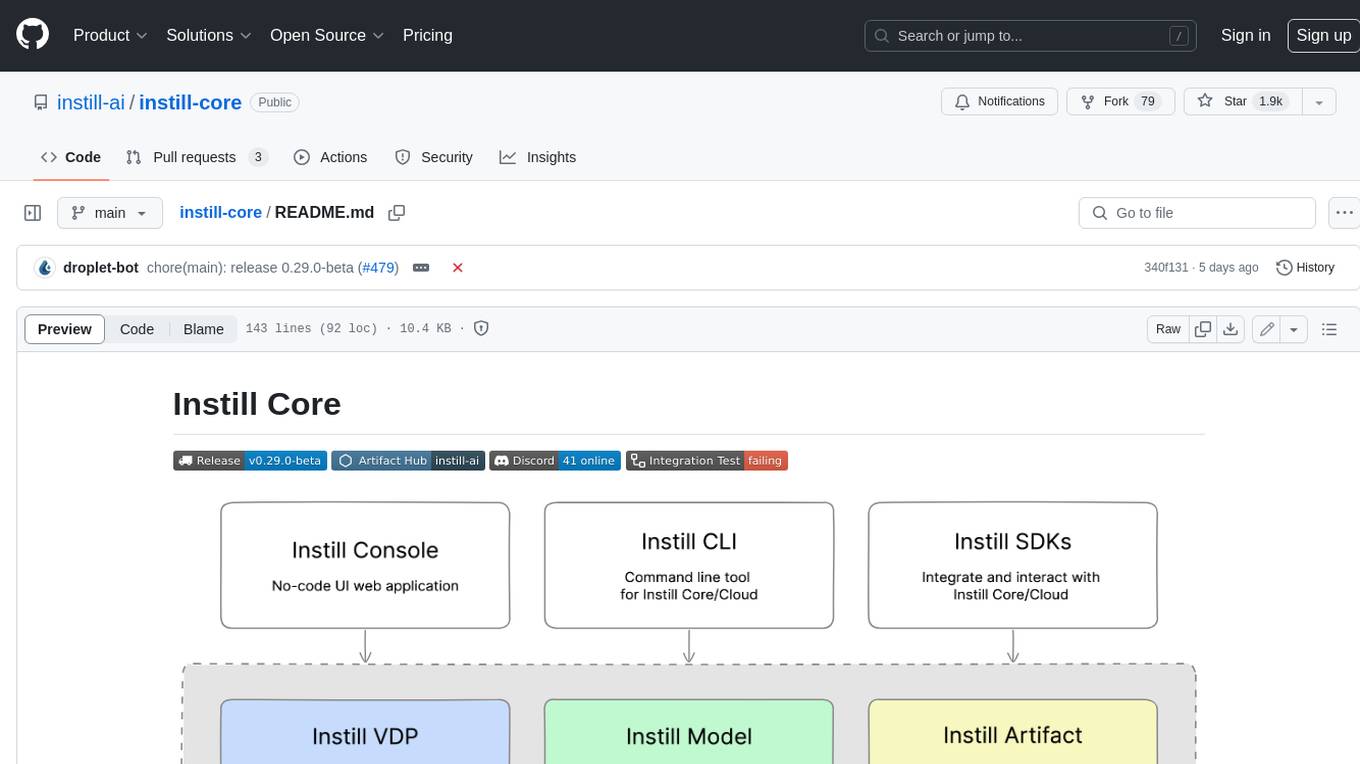
instill-core
Instill Core is an open-source orchestrator comprising a collection of source-available projects designed to streamline every aspect of building versatile AI features with unstructured data. It includes Instill VDP (Versatile Data Pipeline) for unstructured data, AI, and pipeline orchestration, Instill Model for scalable MLOps and LLMOps for open-source or custom AI models, and Instill Artifact for unified unstructured data management. Instill Core can be used for tasks such as building, testing, and sharing pipelines, importing, serving, fine-tuning, and monitoring ML models, and transforming documents, images, audio, and video into a unified AI-ready format.

clearml
ClearML is an auto-magical suite of tools designed to streamline AI workflows. It includes modules for experiment management, MLOps/LLMOps, data management, model serving, and more. ClearML offers features like experiment tracking, model serving, orchestration, and automation. It supports various ML/DL frameworks and integrates with Jupyter Notebook and PyCharm for remote debugging. ClearML aims to simplify collaboration, automate processes, and enhance visibility in AI projects.

kalavai-client
Kalavai is an open-source platform that transforms everyday devices into an AI supercomputer by aggregating resources from multiple machines. It facilitates matchmaking of resources for large AI projects, making AI hardware accessible and affordable. Users can create local and public pools, connect with the community's resources, and share computing power. The platform aims to be a management layer for research groups and organizations, enabling users to unlock the power of existing hardware without needing a devops team. Kalavai CLI tool helps manage both versions of the platform.
AIOS
AIOS, a Large Language Model (LLM) Agent operating system, embeds large language model into Operating Systems (OS) as the brain of the OS, enabling an operating system "with soul" -- an important step towards AGI. AIOS is designed to optimize resource allocation, facilitate context switch across agents, enable concurrent execution of agents, provide tool service for agents, maintain access control for agents, and provide a rich set of toolkits for LLM Agent developers.
aegis-stack
Aegis Stack is a system for creating and evolving modular Python applications quickly, without the need for extensive testing or clean architecture. It allows users to go from idea to working prototype rapidly, using familiar tools. The stack includes a CLI, a built-in system dashboard called Overseer, and an optional conversational interface named Illiana. Users can start with basic components and add or remove features as needed, without being locked into initial choices. Aegis Stack aims to provide a flexible and efficient development environment for Python applications.
plandex
Plandex is an open source, terminal-based AI coding engine designed for complex tasks. It uses long-running agents to break up large tasks into smaller subtasks, helping users work through backlogs, navigate unfamiliar technologies, and save time on repetitive tasks. Plandex supports various AI models, including OpenAI, Anthropic Claude, Google Gemini, and more. It allows users to manage context efficiently in the terminal, experiment with different approaches using branches, and review changes before applying them. The tool is platform-independent and runs from a single binary with no dependencies.

gptme
Personal AI assistant/agent in your terminal, with tools for using the terminal, running code, editing files, browsing the web, using vision, and more. A great coding agent that is general-purpose to assist in all kinds of knowledge work, from a simple but powerful CLI. An unconstrained local alternative to ChatGPT with 'Code Interpreter', Cursor Agent, etc. Not limited by lack of software, internet access, timeouts, or privacy concerns if using local models.
higress
Higress is an open-source cloud-native API gateway built on the core of Istio and Envoy, based on Alibaba's internal practice of Envoy Gateway. It is designed for AI-native API gateway, serving AI businesses such as Tongyi Qianwen APP, Bailian Big Model API, and Machine Learning PAI platform. Higress provides capabilities to interface with LLM model vendors, AI observability, multi-model load balancing/fallback, AI token flow control, and AI caching. It offers features for AI gateway, Kubernetes Ingress gateway, microservices gateway, and security protection gateway, with advantages in production-level scalability, stream processing, extensibility, and ease of use.

xpander.ai
xpander.ai is a Backend-as-a-Service for autonomous agents that abstracts the ops layer, allowing AI engineers to focus on behavior and outcomes. It provides managed agent hosting with version control and CI/CD, a fully managed PostgreSQL memory layer, and a library of 2,000+ functions. The platform features an AI native triggering system that processes inputs from various sources and delivers unified messages to agents. With support for any agent framework or SDK, including Agno and OpenAI, xpander.ai enables users to build intelligent, production-ready AI agents without dealing with infrastructure complexity.
OmAgent
OmAgent is an open-source agent framework designed to streamline the development of on-device multimodal agents. It enables agents to empower various hardware devices, integrates speed-optimized SOTA multimodal models, provides SOTA multimodal agent algorithms, and focuses on optimizing the end-to-end computing pipeline for real-time user interaction experience. Key features include easy connection to diverse devices, scalability, flexibility, and workflow orchestration. The architecture emphasizes graph-based workflow orchestration, native multimodality, and device-centricity, allowing developers to create bespoke intelligent agent programs.

helix-db
HelixDB is a database designed specifically for AI applications, providing a single platform to manage all components needed for AI applications. It supports graph + vector data model and also KV, documents, and relational data. Key features include built-in tools for MCP, embeddings, knowledge graphs, RAG, security, logical isolation, and ultra-low latency. Users can interact with HelixDB using the Helix CLI tool and SDKs in TypeScript and Python. The roadmap includes features like organizational auth, server code improvements, 3rd party integrations, educational content, and binary quantisation for better performance. Long term projects involve developing in-house tools for knowledge graph ingestion, graph-vector storage engine, and network protocol & serdes libraries.
For similar tasks

ksail
KSail is a tool that bundles common Kubernetes tooling into a single binary, providing a unified workflow for creating clusters, deploying workloads, and operating cloud-native stacks across different distributions and providers. It eliminates the need for multiple CLI tools and bespoke scripts, offering features like one binary for provisioning and deployment, support for various cluster configurations, mirror registries, GitOps integration, customizable stack selection, built-in SOPS for secrets management, AI assistant for interactive chat, and a VSCode extension for cluster management.
AIFoundation
AIFoundation focuses on AI Foundation, large model systems. Large models optimize the performance of full-stack hardware and software based on AI clusters. The training process requires distributed parallelism, cluster communication algorithms, and continuous evolution in the field of large models such as intelligent agents. The course covers modules like AI chip principles, communication & storage, AI clusters, computing architecture, communication architecture, large model algorithms, training, inference, and analysis of hot technologies in the large model field.
compute-blade
Compute Blade is a feature-rich carrier board designed for the Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4 and compatible alternatives, aimed at simplifying and automating the development and management of on-premise cluster environments. The solution streamlines complex processes, making cluster setup and management efficient and manageable for users, from homelabs to advanced AI clusters at scale.
bigtop-manager
Apache Bigtop Manager is a modern, AI-driven web application designed to simplify the complexity of bigdata cluster management. It provides an easy deployment solution not only for Apache Bigtop components, but also other community version bigdata components. The platform aims to streamline the management of bigdata clusters by leveraging AI technology and user-friendly interfaces.
kubewall
kubewall is an open-source, single-binary Kubernetes dashboard with multi-cluster management and AI integration. It provides a simple and rich real-time interface to manage and investigate your clusters. With features like multi-cluster management, AI-powered troubleshooting, real-time monitoring, single-binary deployment, in-depth resource views, browser-based access, search and filter capabilities, privacy by default, port forwarding, live refresh, aggregated pod logs, and clean resource management, kubewall offers a comprehensive solution for Kubernetes cluster management.
For similar jobs
flux-aio
Flux All-In-One is a lightweight distribution optimized for running the GitOps Toolkit controllers as a single deployable unit on Kubernetes clusters. It is designed for bare clusters, edge clusters, clusters with restricted communication, clusters with egress via proxies, and serverless clusters. The distribution follows semver versioning and provides documentation for specifications, installation, upgrade, OCI sync configuration, Git sync configuration, and multi-tenancy configuration. Users can deploy Flux using Timoni CLI and a Timoni Bundle file, fine-tune installation options, sync from public Git repositories, bootstrap repositories, and uninstall Flux without affecting reconciled workloads.
paddler
Paddler is an open-source load balancer and reverse proxy designed specifically for optimizing servers running llama.cpp. It overcomes typical load balancing challenges by maintaining a stateful load balancer that is aware of each server's available slots, ensuring efficient request distribution. Paddler also supports dynamic addition or removal of servers, enabling integration with autoscaling tools.
DaoCloud-docs
DaoCloud Enterprise 5.0 Documentation provides detailed information on using DaoCloud, a Certified Kubernetes Service Provider. The documentation covers current and legacy versions, workflow control using GitOps, and instructions for opening a PR and previewing changes locally. It also includes naming conventions, writing tips, references, and acknowledgments to contributors. Users can find guidelines on writing, contributing, and translating pages, along with using tools like MkDocs, Docker, and Poetry for managing the documentation.
ztncui-aio
This repository contains a Docker image with ZeroTier One and ztncui to set up a standalone ZeroTier network controller with a web user interface. It provides features like Golang auto-mkworld for generating a planet file, supports local persistent storage configuration, and includes a public file server. Users can build the Docker image, set up the container with specific environment variables, and manage the ZeroTier network controller through the web interface.
devops-gpt
DevOpsGPT is a revolutionary tool designed to streamline your workflow and empower you to build systems and automate tasks with ease. Tired of spending hours on repetitive DevOps tasks? DevOpsGPT is here to help! Whether you're setting up infrastructure, speeding up deployments, or tackling any other DevOps challenge, our app can make your life easier and more productive. With DevOpsGPT, you can expect faster task completion, simplified workflows, and increased efficiency. Ready to experience the DevOpsGPT difference? Visit our website, sign in or create an account, start exploring the features, and share your feedback to help us improve. DevOpsGPT will become an essential tool in your DevOps toolkit.
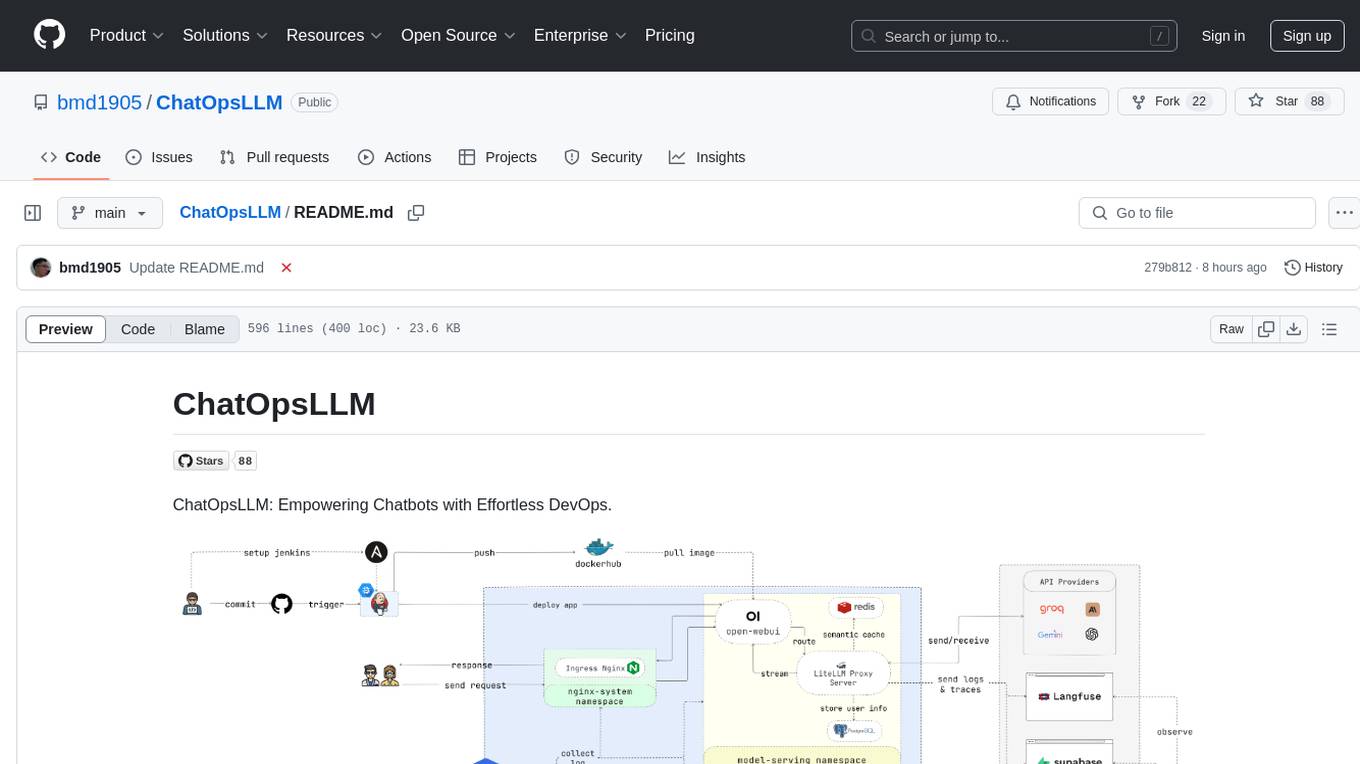
ChatOpsLLM
ChatOpsLLM is a project designed to empower chatbots with effortless DevOps capabilities. It provides an intuitive interface and streamlined workflows for managing and scaling language models. The project incorporates robust MLOps practices, including CI/CD pipelines with Jenkins and Ansible, monitoring with Prometheus and Grafana, and centralized logging with the ELK stack. Developers can find detailed documentation and instructions on the project's website.
aiops-modules
AIOps Modules is a collection of reusable Infrastructure as Code (IAC) modules that work with SeedFarmer CLI. The modules are decoupled and can be aggregated using GitOps principles to achieve desired use cases, removing heavy lifting for end users. They must be generic for reuse in Machine Learning and Foundation Model Operations domain, adhering to SeedFarmer Guide structure. The repository includes deployment steps, project manifests, and various modules for SageMaker, Mlflow, FMOps/LLMOps, MWAA, Step Functions, EKS, and example use cases. It also supports Industry Data Framework (IDF) and Autonomous Driving Data Framework (ADDF) Modules.
3FS
The Fire-Flyer File System (3FS) is a high-performance distributed file system designed for AI training and inference workloads. It leverages modern SSDs and RDMA networks to provide a shared storage layer that simplifies development of distributed applications. Key features include performance, disaggregated architecture, strong consistency, file interfaces, data preparation, dataloaders, checkpointing, and KVCache for inference. The system is well-documented with design notes, setup guide, USRBIO API reference, and P specifications. Performance metrics include peak throughput, GraySort benchmark results, and KVCache optimization. The source code is available on GitHub for cloning and installation of dependencies. Users can build 3FS and run test clusters following the provided instructions. Issues can be reported on the GitHub repository.

