BioAgents
BioAgents: An AI scientist framework for autonomous deep research in biological sciences. Multi-agent system combining literature analysis agents with data scientist agents to enable deep research automation through user feedback integration and iterative scientific discovery. Inspired by advances in Edison Kosmos, Sakana AI, K-Dense and others.
Stars: 80
BioAgents AgentKit is an advanced AI agent framework tailored for biological and scientific research. It offers powerful conversational AI capabilities with specialized knowledge in biology, life sciences, and scientific research methodologies. The framework includes state-of-the-art analysis agents, configurable research agents, and a variety of specialized agents for tasks such as file parsing, research planning, literature search, data analysis, hypothesis generation, research reflection, and user-facing responses. BioAgents also provides support for LLM libraries, multiple search backends for literature agents, and two backends for data analysis. The project structure includes backend source code, services for chat, job queue system, real-time notifications, and JWT authentication, as well as a frontend UI built with Preact.
README:
An advanced AI agent framework for biological and scientific research. BioAgents provides powerful conversational AI capabilities with specialized knowledge in biology, life sciences, and scientific research methodologies.
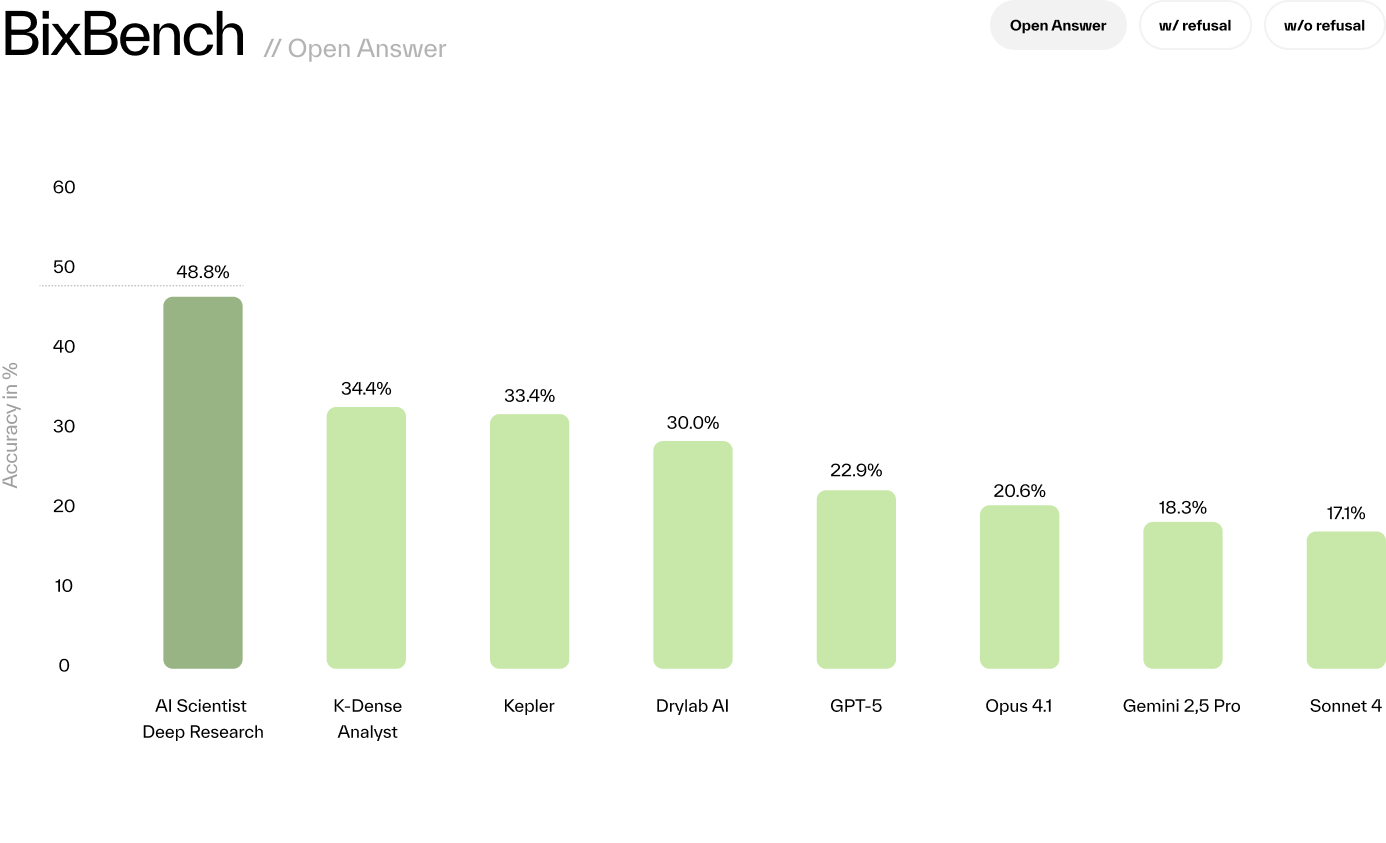
The BioAgents analysis agent achieves state-of-the-art performance on the BixBench benchmark, outperforming all existing solutions:
| Evaluation Mode | Score |
|---|---|
| Open-Answer | 48.78% |
| Multiple-Choice (with refusal) | 55.12% |
| Multiple-Choice (without refusal) | 64.39% |
These results outperform Kepler, GPT-5, and others across all evaluation modes.
Learn more:
- Introducing BioAgents - Detailed blog post about our literature and analysis agents
- Scientific Paper (arXiv) - Full technical details and methodology
BioAgents allows you to choose your primary literature and analysis agents. While multiple backends are supported, BIO is the recommended default:
| Agent Type | Primary (BIO) | Alternative |
|---|---|---|
| Literature | BioAgents Literature API - semantic search with LLM reranking | OpenScholar, Edison |
| Analysis | BioAgents Data Analysis - state-of-the-art benchmark performance | Edison |
Configure your preferred agents in .env:
PRIMARY_LITERATURE_AGENT=bio # or openscholar, edison
PRIMARY_ANALYSIS_AGENT=bio # or edisonCheck out SETUP.md
The system operates through two main routes:
- /api/chat - Agent-based chat for general research questions with automatic literature search
- /api/deep-research - Deep research mode with iterative hypothesis-driven investigation
Both routes use the same agent architecture but differ in their orchestration and iteration patterns.
Agents are the core concept in this repository. Each agent is a self-contained, independent function that performs a specific task in the research workflow. Agents are designed to be modular and reusable across different routes and contexts.
-
File Upload Agent - Handles file parsing, storage, and automatic description generation
- Supports PDF, Excel, CSV, MD, JSON, TXT files
- Generates AI-powered descriptions for each dataset
- Stores files in cloud storage with metadata
-
Planning Agent - Creates research plans based on user questions
- Analyzes available datasets and research context
- Generates task sequences (LITERATURE or ANALYSIS)
- Updates current research objectives
-
Literature Agent - Searches and synthesizes scientific literature
- OPENSCHOLAR: General scientific literature search with citations
- EDISON: Edison AI literature search (deep research mode only)
- KNOWLEDGE: Searches your custom knowledge base with semantic search and reranking
- Returns synthesized findings with inline citations in format:
(claim)[DOI or URL]
-
Analysis Agent - Performs data analysis on uploaded datasets
- EDISON: Deep analysis via Edison AI agent with file upload to Edison storage
- BIO: Basic analysis via BioAgents Data Analysis Agent
- Uploads datasets to analysis service and retrieves results
-
Hypothesis Agent - Generates research hypotheses
- Synthesizes findings from literature and analysis
- Creates testable hypotheses with inline citations
- Considers current research context and objectives
-
Reflection Agent - Reflects on research progress
- Extracts key insights and discoveries
- Updates research methodology
- Maintains conversation-level understanding
-
Reply Agent - Generates user-facing responses
- Deep Research Mode: Includes current objective, next steps, and asks for feedback
- Chat Mode: Concise answers without next steps
- Preserves inline citations throughout
To add a new agent:
- Create a folder in
src/agents/ - Implement the main agent function in
index.ts - Add supporting logic in separate files within the folder
- Export the agent function for use in routes
- Shared utilities go in src/utils
State is separated into two types:
Message State (State):
- Ephemeral, tied to a single message
- Contains processing details for that message only
- Automatically cleared after processing
- Used for temporary data like raw file buffers
Conversation State (ConversationState):
- Persistent across the entire conversation
- Contains cumulative research data:
- Uploaded datasets with descriptions
- Current plan and completed tasks
- Key insights and discoveries
- Current hypothesis and methodology
- Research objectives
- Stored in database and maintained across requests
- This is the primary state that drives the research workflow
The LLM library provides a unified interface for multiple LLM providers. It allows you to use any Anthropic/OpenAI/Google or OpenRouter LLM via the same interface. Examples of calling the LLM library can be found in all agents.
Key Features:
- Unified API across providers (Anthropic, OpenAI, Google, OpenRouter)
- Extended thinking support for Anthropic models
- System instruction support
- Streaming and non-streaming responses
- Examples in every agent implementation
The Literature Agent includes multiple search backends:
OPENSCHOLAR (Optional):
- General scientific literature search with high-quality citations
- Requires custom deployment and configuration
- Set
OPENSCHOLAR_API_URLandOPENSCHOLAR_API_KEYto enable - Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.14199
- Deployment: https://github.com/bio-xyz/bio-openscholar
EDISON (Optional):
- Edison AI literature search (deep research mode only)
- Requires custom deployment and configuration
- Set
EDISON_API_URLandEDISON_API_KEYto enable - Deployment: https://github.com/bio-xyz/bio-edison-api
KNOWLEDGE (Customizable):
- Vector database with semantic search (embeddings)
- Cohere reranker for improved results (requires
COHERE_API_KEY) - Document processing from docs directory
- Documents are processed once per filename and stored in vector DB
To add custom knowledge:
- Place documents in the
docs/directory- Supported formats: PDF, Markdown (.md), DOCX, TXT
- Documents are automatically processed on startup
- Vector embeddings are generated and stored
- Available to Literature Agent via KNOWLEDGE tasks
Docker Deployment Note: When deploying with Docker, agent-specific documentation in docs/ and branding images in client/public/images/ are persisted using Docker volumes. These directories are excluded from git (see .gitignore) but automatically mounted in your Docker containers via volume mounts defined in docker-compose.yml. This allows you to customize your agent with private documentation without committing it to the repository.
The Analysis Agent supports two backends for data analysis:
EDISON (Default):
- Deep analysis via Edison AI agent
- Automatic file upload to Edison storage service
- Requires
EDISON_API_URLandEDISON_API_KEY - https://github.com/bio-xyz/bio-edison-api
BIO (Alternative):
- Basic analysis via BioAgents Data Analysis Agent
- Set
PRIMARY_ANALYSIS_AGENT=bioin.env - Requires
DATA_ANALYSIS_API_URLandDATA_ANALYSIS_API_KEY - https://github.com/bio-xyz/bio-data-analysis
Both backends receive datasets and analysis objectives, execute analysis code, and return results.
The character file defines your agent's identity and system instructions. It's now simplified to focus on core behavior:
- name: Your agent's name
- system: System prompt that guides agent behavior across all interactions
The character's system instruction is automatically included in LLM calls for planning, hypothesis generation, and replies, ensuring consistent behavior throughout the research workflow. You can enable the system prompt in any LLM call by setting the 'systemInstruction' parameter.
Component system:
- Custom hooks in
client/src/hooks/ - UI components in
client/src/components/ui/ - Lucide icons via
client/src/components/icons/
Styling:
- Main styles:
client/src/styles/global.css - Button styles:
client/src/styles/buttons.css - Mobile-first responsive design
Payment Integration:
The UI includes integrated support for x402 micropayments using Coinbase embedded wallets:
- Embedded wallet authentication via
client/src/components/EmbeddedWalletAuth.tsx - x402 payment hooks in
client/src/hooks/useX402Payment.ts - Seamless USDC payment flow for paid API requests
- Toast notifications for payment status
BioAgents supports two independent auth systems:
| Setting | Options | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
AUTH_MODE |
none / jwt
|
JWT authentication for external frontends |
X402_ENABLED |
true / false
|
x402 USDC micropayments |
For external frontends connecting to the API:
# .env
AUTH_MODE=jwt
BIOAGENTS_SECRET=your-secure-secret # Generate with: openssl rand -hex 32Your backend signs JWTs with the shared secret:
// Your backend generates JWT for authenticated users
const jwt = await new jose.SignJWT({ sub: userId }) // sub must be valid UUID
.setProtectedHeader({ alg: 'HS256' })
.setExpirationTime('1h')
.sign(new TextEncoder().encode(process.env.BIOAGENTS_SECRET));
// Call BioAgents API
fetch('https://your-bioagents-api/api/chat', {
headers: { 'Authorization': `Bearer ${jwt}` },
body: JSON.stringify({ message: 'What is rapamycin?' })
});📖 See AUTH.md for complete JWT integration guide
For pay-per-request access using USDC micropayments:
# .env
X402_ENABLED=true
X402_ENVIRONMENT=testnet # or mainnet
X402_PAYMENT_ADDRESS=0xYourWalletAddress📖 See AUTH.md for x402 configuration details
BioAgents supports BullMQ for reliable background job processing with:
- Horizontal scaling: Run multiple worker instances
- Job persistence: Jobs survive server restarts
- Automatic retries: Failed jobs retry with exponential backoff
- Real-time updates: WebSocket notifications for job progress
-
Admin dashboard: Bull Board UI at
/admin/queues
# Enable job queue
USE_JOB_QUEUE=true
REDIS_URL=redis://localhost:6379
# Start API server and worker separately
bun run dev # API server
bun run worker # Worker process📖 See JOB_QUEUE.md for complete setup and configuration guide
├── src/ # Backend source
│ ├── index.ts # API server entry point
│ ├── worker.ts # BullMQ worker entry point
│ ├── routes/ # HTTP route handlers
│ │ ├── chat.ts # Agent-based chat endpoint
│ │ ├── deep-research/ # Deep research endpoints
│ │ ├── x402/ # x402 payment-gated routes
│ │ ├── b402/ # b402 payment-gated routes
│ │ └── admin/ # Bull Board dashboard
│ ├── agents/ # Independent agent modules
│ │ ├── fileUpload/ # File parsing & storage
│ │ ├── planning/ # Research planning
│ │ ├── literature/ # Literature search (OPENSCHOLAR, EDISON, KNOWLEDGE)
│ │ ├── analysis/ # Data analysis (EDISON, BIO)
│ │ ├── hypothesis/ # Hypothesis generation
│ │ ├── reflection/ # Research reflection
│ │ └── reply/ # User-facing responses
│ ├── services/ # Business logic layer
│ │ ├── chat/ # Chat-related services
│ │ ├── queue/ # BullMQ job queue system
│ │ │ ├── connection.ts # Redis connection management
│ │ │ ├── queues.ts # Queue definitions & config
│ │ │ ├── workers/ # Job processors
│ │ │ └── notify.ts # Pub/Sub notifications
│ │ ├── websocket/ # Real-time notifications
│ │ │ ├── handler.ts # WebSocket endpoint
│ │ │ └── subscribe.ts # Redis Pub/Sub subscriber
│ │ └── jwt.ts # JWT verification service
│ ├── middleware/ # Request/response middleware
│ │ ├── authResolver.ts # Multi-method authentication
│ │ ├── rateLimiter.ts # Rate limiting
│ │ ├── x402/ # x402 payment protocol (Base/USDC)
│ │ └── b402/ # b402 payment protocol (BNB/USDT)
│ ├── llm/ # LLM providers & interfaces
│ ├── embeddings/ # Vector database & document processing
│ ├── db/ # Database operations
│ ├── storage/ # File storage (S3-compatible)
│ ├── utils/ # Shared utilities
│ ├── types/ # TypeScript types
│ └── character.ts # Agent identity & system prompt
├── client/ # Frontend UI (Preact)
│ ├── src/
│ │ ├── components/ # UI components
│ │ ├── hooks/ # Custom hooks (chat, payments, etc.)
│ │ └── styles/ # CSS files
│ └── public/ # Static assets
├── documentation/ # Project documentation
│ └── docs/ # Detailed guides (AUTH.md, SETUP.md, JOB_QUEUE.md)
├── docs/ # Custom knowledge base documents (scientific papers)
└── package.json
Built with Bun - A fast all-in-one JavaScript runtime.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for BioAgents
Similar Open Source Tools

BioAgents
BioAgents AgentKit is an advanced AI agent framework tailored for biological and scientific research. It offers powerful conversational AI capabilities with specialized knowledge in biology, life sciences, and scientific research methodologies. The framework includes state-of-the-art analysis agents, configurable research agents, and a variety of specialized agents for tasks such as file parsing, research planning, literature search, data analysis, hypothesis generation, research reflection, and user-facing responses. BioAgents also provides support for LLM libraries, multiple search backends for literature agents, and two backends for data analysis. The project structure includes backend source code, services for chat, job queue system, real-time notifications, and JWT authentication, as well as a frontend UI built with Preact.
OpenViking
OpenViking is an open-source Context Database designed specifically for AI Agents. It aims to solve challenges in agent development by unifying memories, resources, and skills in a filesystem management paradigm. The tool offers tiered context loading, directory recursive retrieval, visualized retrieval trajectory, and automatic session management. Developers can interact with OpenViking like managing local files, enabling precise context manipulation and intuitive traceable operations. The tool supports various model services like OpenAI and Volcengine, enhancing semantic retrieval and context understanding for AI Agents.
paelladoc
PAELLADOC is an intelligent documentation system that uses AI to analyze code repositories and generate comprehensive technical documentation. It offers a modular architecture with MECE principles, interactive documentation process, key features like Orchestrator and Commands, and a focus on context for successful AI programming. The tool aims to streamline documentation creation, code generation, and product management tasks for software development teams, providing a definitive standard for AI-assisted development documentation.
shannon
Shannon is an AI pentester that delivers actual exploits, not just alerts. It autonomously hunts for attack vectors in your code, then uses its built-in browser to execute real exploits, such as injection attacks, and auth bypass, to prove the vulnerability is actually exploitable. Shannon closes the security gap by acting as your on-demand whitebox pentester, providing concrete proof of vulnerabilities to let you ship with confidence. It is a core component of the Keygraph Security and Compliance Platform, automating penetration testing and compliance journey. Shannon Lite achieves a 96.15% success rate on a hint-free, source-aware XBOW benchmark.
WebAI-to-API
This project implements a web API that offers a unified interface to Google Gemini and Claude 3. It provides a self-hosted, lightweight, and scalable solution for accessing these AI models through a streaming API. The API supports both Claude and Gemini models, allowing users to interact with them in real-time. The project includes a user-friendly web UI for configuration and documentation, making it easy to get started and explore the capabilities of the API.
mcp-gateway-registry
The MCP Gateway & Registry is a unified, enterprise-ready platform that centralizes access to both MCP Servers and AI Agents using the Model Context Protocol (MCP). It serves as a Unified MCP Server Gateway, MCP Servers Registry, and Agent Registry & A2A Communication Hub. The platform integrates with external registries, providing a single control plane for tool access, agent orchestration, and communication patterns. It transforms the chaos of managing individual MCP server configurations into an organized approach with secure, governed access to curated servers and registered agents. The platform supports dynamic tool discovery, autonomous agent communication, and unified policies for server and agent access.
Archon
Archon is an AI meta-agent designed to autonomously build, refine, and optimize other AI agents. It serves as a practical tool for developers and an educational framework showcasing the evolution of agentic systems. Through iterative development, Archon demonstrates the power of planning, feedback loops, and domain-specific knowledge in creating robust AI agents.
llmos
LLMos is an operating system designed for physical AI agents, providing a hybrid runtime environment where AI agents can perceive, reason, act on hardware, and evolve over time locally without cloud dependency. It allows natural language programming, dual-brain architecture for fast instinct and deep planner brains, markdown-as-code for defining agents and skills, and supports swarm intelligence and cognitive world models. The tool is built on a tech stack including Next.js, Electron, Python, and WebAssembly, and is structured around a dual-brain cognitive architecture, volume system, HAL for hardware abstraction, applet system for dynamic UI, and dreaming & evolution for robot improvement. The project is in Phase 1 (Foundation) and aims to move into Phase 2 (Dual-Brain & Local Intelligence), with contributions welcomed under the Apache 2.0 license by Evolving Agents Labs.
astrsk
astrsk is a tool that pushes the boundaries of AI storytelling by offering advanced AI agents, customizable response formatting, and flexible prompt editing for immersive roleplaying experiences. It provides complete AI agent control, a visual flow editor for conversation flows, and ensures 100% local-first data storage. The tool is true cross-platform with support for various AI providers and modern technologies like React, TypeScript, and Tailwind CSS. Coming soon features include cross-device sync, enhanced session customization, and community features.

probe
Probe is an AI-friendly, fully local, semantic code search tool designed to power the next generation of AI coding assistants. It combines the speed of ripgrep with the code-aware parsing of tree-sitter to deliver precise results with complete code blocks, making it perfect for large codebases and AI-driven development workflows. Probe is fully local, keeping code on the user's machine without relying on external APIs. It supports multiple languages, offers various search options, and can be used in CLI mode, MCP server mode, AI chat mode, and web interface. The tool is designed to be flexible, fast, and accurate, providing developers and AI models with full context and relevant code blocks for efficient code exploration and understanding.
OpenManus
OpenManus is an open-source project aiming to replicate the capabilities of the Manus AI agent, known for autonomously executing complex tasks like travel planning and stock analysis. The project provides a modular, containerized framework using Docker, Python, and JavaScript, allowing developers to build, deploy, and experiment with a multi-agent AI system. Features include collaborative AI agents, Dockerized environment, task execution support, tool integration, modular design, and community-driven development. Users can interact with OpenManus via CLI, API, or web UI, and the project welcomes contributions to enhance its capabilities.
lyraios
LYRAIOS (LLM-based Your Reliable AI Operating System) is an advanced AI assistant platform built with FastAPI and Streamlit, designed to serve as an operating system for AI applications. It offers core features such as AI process management, memory system, and I/O system. The platform includes built-in tools like Calculator, Web Search, Financial Analysis, File Management, and Research Tools. It also provides specialized assistant teams for Python and research tasks. LYRAIOS is built on a technical architecture comprising FastAPI backend, Streamlit frontend, Vector Database, PostgreSQL storage, and Docker support. It offers features like knowledge management, process control, and security & access control. The roadmap includes enhancements in core platform, AI process management, memory system, tools & integrations, security & access control, open protocol architecture, multi-agent collaboration, and cross-platform support.
ccprompts
ccprompts is a collection of ~70 Claude Code commands for software development workflows with agent generation capabilities. It includes safety validation and can be used directly with Claude Code or adapted for specific needs. The agent template system provides a wizard for creating specialized sub-agents (e.g., security auditors, systems architects) with standardized formatting and proper tool access. The repository is under active development, so caution is advised when using it in production environments.

MassGen
MassGen is a cutting-edge multi-agent system that leverages the power of collaborative AI to solve complex tasks. It assigns a task to multiple AI agents who work in parallel, observe each other's progress, and refine their approaches to converge on the best solution to deliver a comprehensive and high-quality result. The system operates through an architecture designed for seamless multi-agent collaboration, with key features including cross-model/agent synergy, parallel processing, intelligence sharing, consensus building, and live visualization. Users can install the system, configure API settings, and run MassGen for various tasks such as question answering, creative writing, research, development & coding tasks, and web automation & browser tasks. The roadmap includes plans for advanced agent collaboration, expanded model, tool & agent integration, improved performance & scalability, enhanced developer experience, and a web interface.
tambourine-voice
Tambourine is a personal voice interface tool that allows users to speak naturally and have their words appear wherever the cursor is. It is powered by customizable AI voice dictation, providing a universal voice-to-text interface for emails, messages, documents, code editors, and terminals. Users can capture ideas quickly, type at the speed of thought, and benefit from AI formatting that cleans up speech, adds punctuation, and applies personal dictionaries. Tambourine offers full control and transparency, with the ability to customize AI providers, formatting, and extensions. The tool supports dual-mode recording, real-time speech-to-text, LLM text formatting, context-aware formatting, customizable prompts, and more, making it a versatile solution for dictation and transcription tasks.
claude-code-settings
A repository collecting best practices for Claude Code settings and customization. It provides configuration files for customizing Claude Code's behavior and building an efficient development environment. The repository includes custom agents and skills for specific domains, interactive development workflow features, efficient development rules, and team workflow with Codex MCP. Users can leverage the provided configuration files and tools to enhance their development process and improve code quality.
For similar tasks
awesome-mobile-robotics
The 'awesome-mobile-robotics' repository is a curated list of important content related to Mobile Robotics and AI. It includes resources such as courses, books, datasets, software and libraries, podcasts, conferences, journals, companies and jobs, laboratories and research groups, and miscellaneous resources. The repository covers a wide range of topics in the field of Mobile Robotics and AI, providing valuable information for enthusiasts, researchers, and professionals in the domain.
fiftyone-brain
FiftyOne Brain contains the open source AI/ML capabilities for the FiftyOne ecosystem, enabling users to automatically analyze and manipulate their datasets and models. Features include visual similarity search, query by text, finding unique and representative samples, finding media quality problems and annotation mistakes, and more.

mmf
MMF is a modular framework for vision and language multimodal research from Facebook AI Research. It contains reference implementations of state-of-the-art vision and language models, allowing distributed training. MMF serves as a starter codebase for challenges around vision and language datasets, such as The Hateful Memes, TextVQA, TextCaps, and VQA challenges. It is scalable, fast, and un-opinionated, providing a solid foundation for vision and language multimodal research projects.
doris
Doris is a lightweight and user-friendly data visualization tool designed for quick and easy exploration of datasets. It provides a simple interface for users to upload their data and generate interactive visualizations without the need for coding. With Doris, users can easily create charts, graphs, and dashboards to analyze and present their data in a visually appealing way. The tool supports various data formats and offers customization options to tailor visualizations to specific needs. Whether you are a data analyst, researcher, or student, Doris simplifies the process of data exploration and presentation.
EScAIP
EScAIP is an Efficiently Scaled Attention Interatomic Potential that leverages a novel multi-head self-attention formulation within graph neural networks to predict energy and forces between atoms in molecules and materials. It achieves substantial gains in efficiency, at least 10x speed up in inference time and 5x less memory usage compared to existing models. EScAIP represents a philosophy towards developing general-purpose Neural Network Interatomic Potentials that achieve better expressivity through scaling and continue to scale efficiently with increased computational resources and training data.

BioAgents
BioAgents AgentKit is an advanced AI agent framework tailored for biological and scientific research. It offers powerful conversational AI capabilities with specialized knowledge in biology, life sciences, and scientific research methodologies. The framework includes state-of-the-art analysis agents, configurable research agents, and a variety of specialized agents for tasks such as file parsing, research planning, literature search, data analysis, hypothesis generation, research reflection, and user-facing responses. BioAgents also provides support for LLM libraries, multiple search backends for literature agents, and two backends for data analysis. The project structure includes backend source code, services for chat, job queue system, real-time notifications, and JWT authentication, as well as a frontend UI built with Preact.

gptme
GPTMe is a tool that allows users to interact with an LLM assistant directly in their terminal in a chat-style interface. The tool provides features for the assistant to run shell commands, execute code, read/write files, and more, making it suitable for various development and terminal-based tasks. It serves as a local alternative to ChatGPT's 'Code Interpreter,' offering flexibility and privacy when using a local model. GPTMe supports code execution, file manipulation, context passing, self-correction, and works with various AI models like GPT-4. It also includes a GitHub Bot for requesting changes and operates entirely in GitHub Actions. In progress features include handling long contexts intelligently, a web UI and API for conversations, web and desktop vision, and a tree-based conversation structure.
LAMBDA
LAMBDA is a code-free multi-agent data analysis system that utilizes large models to address data analysis challenges in complex data-driven applications. It allows users to perform complex data analysis tasks through human language instruction, seamlessly generate and debug code using two key agent roles, integrate external models and algorithms, and automatically generate reports. The system has demonstrated strong performance on various machine learning datasets, enhancing data science practice by integrating human and artificial intelligence.
For similar jobs

promptflow
**Prompt flow** is a suite of development tools designed to streamline the end-to-end development cycle of LLM-based AI applications, from ideation, prototyping, testing, evaluation to production deployment and monitoring. It makes prompt engineering much easier and enables you to build LLM apps with production quality.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.

MegaDetector
MegaDetector is an AI model that identifies animals, people, and vehicles in camera trap images (which also makes it useful for eliminating blank images). This model is trained on several million images from a variety of ecosystems. MegaDetector is just one of many tools that aims to make conservation biologists more efficient with AI. If you want to learn about other ways to use AI to accelerate camera trap workflows, check out our of the field, affectionately titled "Everything I know about machine learning and camera traps".

leapfrogai
LeapfrogAI is a self-hosted AI platform designed to be deployed in air-gapped resource-constrained environments. It brings sophisticated AI solutions to these environments by hosting all the necessary components of an AI stack, including vector databases, model backends, API, and UI. LeapfrogAI's API closely matches that of OpenAI, allowing tools built for OpenAI/ChatGPT to function seamlessly with a LeapfrogAI backend. It provides several backends for various use cases, including llama-cpp-python, whisper, text-embeddings, and vllm. LeapfrogAI leverages Chainguard's apko to harden base python images, ensuring the latest supported Python versions are used by the other components of the stack. The LeapfrogAI SDK provides a standard set of protobuffs and python utilities for implementing backends and gRPC. LeapfrogAI offers UI options for common use-cases like chat, summarization, and transcription. It can be deployed and run locally via UDS and Kubernetes, built out using Zarf packages. LeapfrogAI is supported by a community of users and contributors, including Defense Unicorns, Beast Code, Chainguard, Exovera, Hypergiant, Pulze, SOSi, United States Navy, United States Air Force, and United States Space Force.

llava-docker
This Docker image for LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant) provides a convenient way to run LLaVA locally or on RunPod. LLaVA is a powerful AI tool that combines natural language processing and computer vision capabilities. With this Docker image, you can easily access LLaVA's functionalities for various tasks, including image captioning, visual question answering, text summarization, and more. The image comes pre-installed with LLaVA v1.2.0, Torch 2.1.2, xformers 0.0.23.post1, and other necessary dependencies. You can customize the model used by setting the MODEL environment variable. The image also includes a Jupyter Lab environment for interactive development and exploration. Overall, this Docker image offers a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for leveraging LLaVA's capabilities.

carrot
The 'carrot' repository on GitHub provides a list of free and user-friendly ChatGPT mirror sites for easy access. The repository includes sponsored sites offering various GPT models and services. Users can find and share sites, report errors, and access stable and recommended sites for ChatGPT usage. The repository also includes a detailed list of ChatGPT sites, their features, and accessibility options, making it a valuable resource for ChatGPT users seeking free and unlimited GPT services.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.

AI-YinMei
AI-YinMei is an AI virtual anchor Vtuber development tool (N card version). It supports fastgpt knowledge base chat dialogue, a complete set of solutions for LLM large language models: [fastgpt] + [one-api] + [Xinference], supports docking bilibili live broadcast barrage reply and entering live broadcast welcome speech, supports Microsoft edge-tts speech synthesis, supports Bert-VITS2 speech synthesis, supports GPT-SoVITS speech synthesis, supports expression control Vtuber Studio, supports painting stable-diffusion-webui output OBS live broadcast room, supports painting picture pornography public-NSFW-y-distinguish, supports search and image search service duckduckgo (requires magic Internet access), supports image search service Baidu image search (no magic Internet access), supports AI reply chat box [html plug-in], supports AI singing Auto-Convert-Music, supports playlist [html plug-in], supports dancing function, supports expression video playback, supports head touching action, supports gift smashing action, supports singing automatic start dancing function, chat and singing automatic cycle swing action, supports multi scene switching, background music switching, day and night automatic switching scene, supports open singing and painting, let AI automatically judge the content.