
OpenManus
OpenManus is an open-source initiative to replicate the capabilities of the Manus AI agent, a state-of-the-art general-purpose AI developed by Monica, which excels in autonomously executing complex tasks.
Stars: 228
OpenManus is an open-source project aiming to replicate the capabilities of the Manus AI agent, known for autonomously executing complex tasks like travel planning and stock analysis. The project provides a modular, containerized framework using Docker, Python, and JavaScript, allowing developers to build, deploy, and experiment with a multi-agent AI system. Features include collaborative AI agents, Dockerized environment, task execution support, tool integration, modular design, and community-driven development. Users can interact with OpenManus via CLI, API, or web UI, and the project welcomes contributions to enhance its capabilities.
README:
OpenManus is an open-source project aimed at replicating the capabilities of the Manus AI agent, a groundbreaking general-purpose AI developed by Monica. Manus is known for its ability to autonomously execute complex tasks—ranging from personalized travel planning to stock analysis—surpassing models like GPT-4 on the GAIA benchmark. OpenManus seeks to bring these capabilities to the open-source community using a modular, containerized framework built with Docker, Python, and JavaScript.
This repository provides a starting point for developers and researchers to build, deploy, and experiment with a multi-agent AI system. Our goal is to create a flexible and extensible platform that mirrors Manus's autonomous task execution while fostering community contributions.
- Multi-Agent System: Collaborative AI agents working together to solve complex tasks.
- Dockerized Environment: Easy setup and deployment with containerization.
- Task Execution: Supports tasks like travel planning, data analysis, and content generation.
- Tool Integration: Web browsing, code execution, and data retrieval capabilities.
- Modular Design: Easily extendable with new agents, tools, or features.
- Community-Driven: Open to contributions and enhancements.
Before you begin, ensure you have the following installed:
- Docker (version 20.10 or higher)
- Docker Compose (version 1.29 or higher)
- Node.js (version 20.18 or higher, for local development)
- Python (version 3.9 or higher, for local development)
- Git (for cloning and contributing)
git clone https://github.com/henryalps/OpenManus.git
cd OpenManus# Build and start all containers
docker-compose up --buildThis will launch:
- Backend container with the multi-agent system and integrated tools
- Frontend container serving the Next.js web interface
- FastAPI server for task delegation and execution
Once running, you can interact with OpenManus via:
- CLI: Use the provided Python client (
python client.py) - API: Send requests to http://localhost:8000 (see API docs below)
- Web UI: Access http://localhost:3000
Example CLI command:
python client.py --task "Plan a 3-day trip to Tokyo"OpenManus/
├── docker/ # Docker configurations
│ ├── frontend/ # Next.js frontend container
│ │ └── Dockerfile # Frontend container configuration
│ └── unified/ # Backend container configuration
│ ├── Dockerfile # Backend container configuration
│ └── start.sh # Container startup script
├── src/ # Source code
│ ├── agents/ # Multi-agent logic (Python)
│ │ ├── nodes/ # Agent node implementations
│ │ ├── browser_agent.py
│ │ ├── coder_agent.py
│ │ ├── coordinator.py
│ │ ├── reporter_agent.py
│ │ └── research_agent.py
│ ├── components/ # React components
│ ├── config/ # Configuration files
│ ├── graph/ # Graph-based workflow
│ ├── llms/ # LLM integrations
│ ├── pages/ # Next.js pages
│ ├── prompts/ # Agent prompts
│ ├── service/ # Backend services
│ ├── tools/ # Tool implementations
│ ├── utils/ # Utility functions
│ ├── workflow/ # Workflow management
│ ├── client.py # CLI client for testing
│ └── server.py # FastAPI server
├── docs/ # Documentation and API specs
├── package.json # Next.js frontend dependencies
├── next.config.js # Next.js configuration
├── docker-compose.yml # Docker Compose configuration
└── README.md # This file
Edit the docker-compose.yml file to customize:
services:
backend:
build:
context: .
dockerfile: docker/unified/Dockerfile
ports:
- "8000:8000" # FastAPI port
environment:
- WEB_BROWSER_API_KEY=your_key_here
volumes:
- ./src:/app/src
- ./data:/app/data
frontend:
build:
context: .
dockerfile: docker/frontend/Dockerfile
ports:
- "3000:3000" # Web UI port
depends_on:
- backendThe agent server exposes a REST API at http://localhost:8000. Key endpoints:
POST /task: Submit a task for execution.
Body: { "task": "Analyze Tesla stock trends" }
Response: { "status": "success", "result": "..." }GET /status: Check system health.
Response: { "status": "running" }Full API docs are available in docs/api.md.
We welcome contributions! To get started:
- Fork the repository.
- Create a feature branch (
git checkout -b feature/your-feature). - Commit your changes (
git commit -m "Add your feature"). - Push to your branch (
git push origin feature/your-feature). - Open a Pull Request.
Please read CONTRIBUTING.md for guidelines.
- Implement core multi-agent coordination.
- Add support for GAIA benchmark tasks.
- Integrate advanced NLP models (e.g., LLaMA, Grok).
- Enhance toolset with real-time web scraping and visualization.
- Release v1.0 with stable task execution.
OpenManus is inspired by:
- The langmanus project (GitHub).
- The official Manus project (manus.im).
- The open-Manus community effort (GitHub).
- GAIA benchmark for general AI assistants (arXiv).
This project is licensed under the UNLICENSE. See LICENSE for details.
For questions or collaboration, reach out via GitHub Issues or email [email protected].
Happy coding! Let's build the future of AI agents together!
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for OpenManus
Similar Open Source Tools

OpenManus
OpenManus is an open-source project aiming to replicate the capabilities of the Manus AI agent, known for autonomously executing complex tasks like travel planning and stock analysis. The project provides a modular, containerized framework using Docker, Python, and JavaScript, allowing developers to build, deploy, and experiment with a multi-agent AI system. Features include collaborative AI agents, Dockerized environment, task execution support, tool integration, modular design, and community-driven development. Users can interact with OpenManus via CLI, API, or web UI, and the project welcomes contributions to enhance its capabilities.
RooFlow
RooFlow is a VS Code extension that enhances AI-assisted development by providing persistent project context and optimized mode interactions. It reduces token consumption and streamlines workflow by integrating Architect, Code, Test, Debug, and Ask modes. The tool simplifies setup, offers real-time updates, and provides clearer instructions through YAML-based rule files. It includes components like Memory Bank, System Prompts, VS Code Integration, and Real-time Updates. Users can install RooFlow by downloading specific files, placing them in the project structure, and running an insert-variables script. They can then start a chat, select a mode, interact with Roo, and use the 'Update Memory Bank' command for synchronization. The Memory Bank structure includes files for active context, decision log, product context, progress tracking, and system patterns. RooFlow features persistent context, real-time updates, mode collaboration, and reduced token consumption.
sdk-python
Strands Agents is a lightweight and flexible SDK that takes a model-driven approach to building and running AI agents. It supports various model providers, offers advanced capabilities like multi-agent systems and streaming support, and comes with built-in MCP server support. Users can easily create tools using Python decorators, integrate MCP servers seamlessly, and leverage multiple model providers for different AI tasks. The SDK is designed to scale from simple conversational assistants to complex autonomous workflows, making it suitable for a wide range of AI development needs.
fraim
Fraim is an AI-powered toolkit designed for security engineers to enhance their workflows by leveraging AI capabilities. It offers solutions to find, detect, fix, and flag vulnerabilities throughout the development lifecycle. The toolkit includes features like Risk Flagger for identifying risks in code changes, Code Security Analysis for context-aware vulnerability detection, and Infrastructure as Code Analysis for spotting misconfigurations in cloud environments. Fraim can be run as a CLI tool or integrated into Github Actions, making it a versatile solution for security teams and organizations looking to enhance their security practices with AI technology.
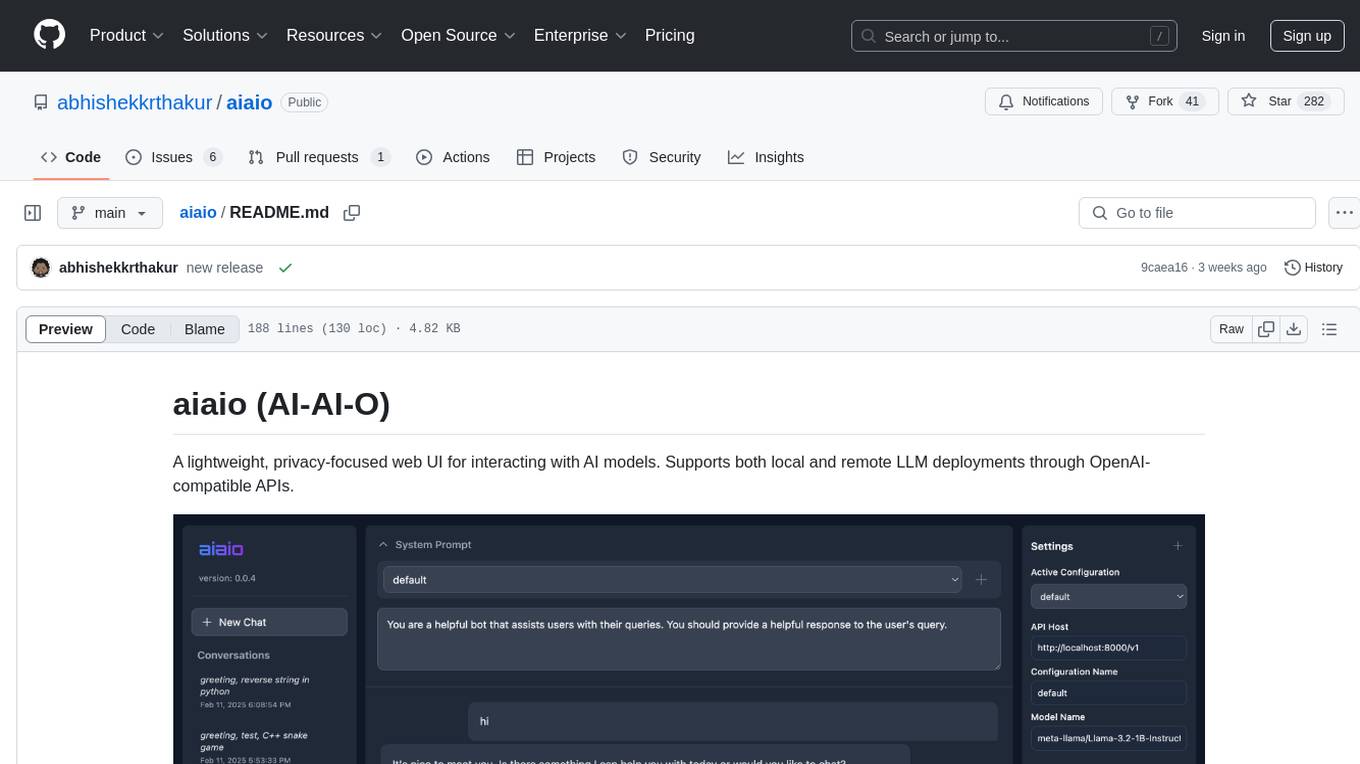
aiaio
aiaio (AI-AI-O) is a lightweight, privacy-focused web UI for interacting with AI models. It supports both local and remote LLM deployments through OpenAI-compatible APIs. The tool provides features such as dark/light mode support, local SQLite database for conversation storage, file upload and processing, configurable model parameters through UI, privacy-focused design, responsive design for mobile/desktop, syntax highlighting for code blocks, real-time conversation updates, automatic conversation summarization, customizable system prompts, WebSocket support for real-time updates, Docker support for deployment, multiple API endpoint support, and multiple system prompt support. Users can configure model parameters and API settings through the UI, handle file uploads, manage conversations, and use keyboard shortcuts for efficient interaction. The tool uses SQLite for storage with tables for conversations, messages, attachments, and settings. Contributions to the project are welcome under the Apache License 2.0.
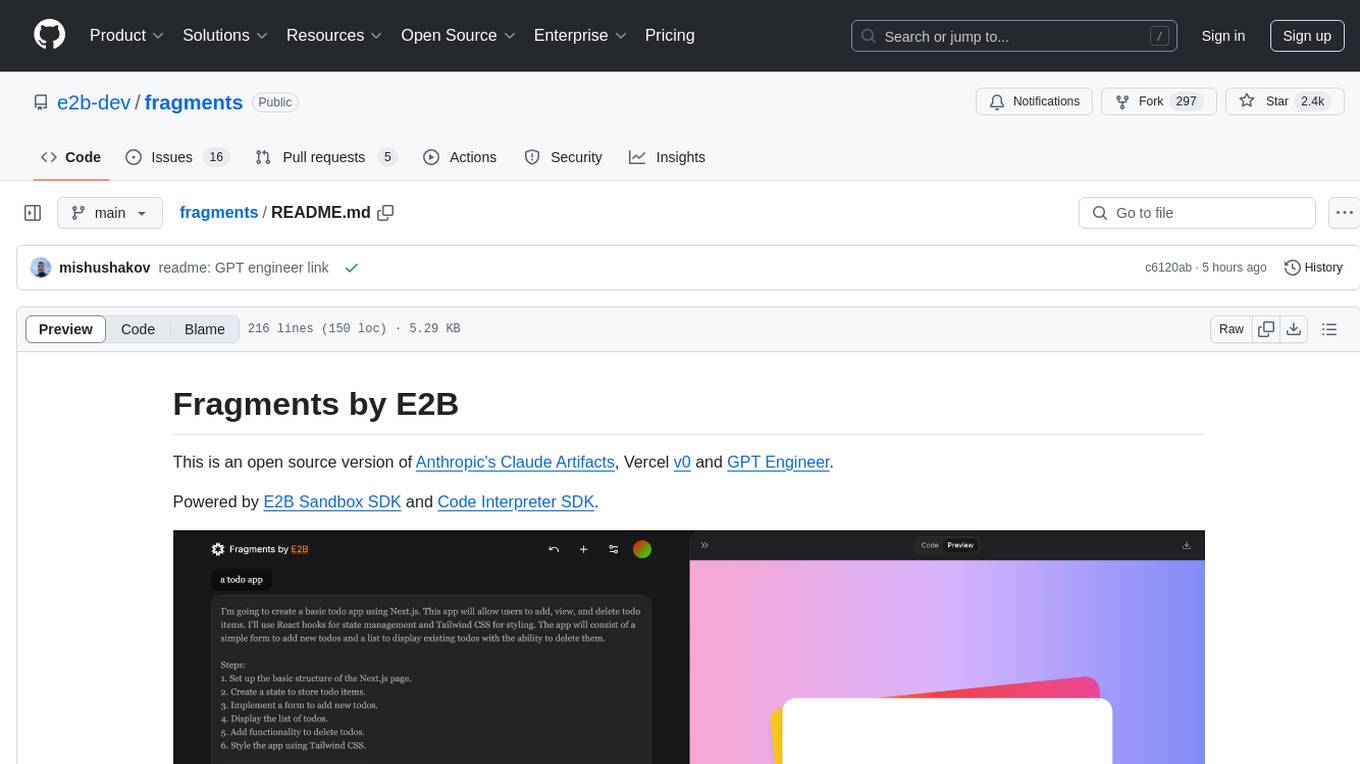
fragments
Fragments is an open-source tool that leverages Anthropic's Claude Artifacts, Vercel v0, and GPT Engineer. It is powered by E2B Sandbox SDK and Code Interpreter SDK, allowing secure execution of AI-generated code. The tool is based on Next.js 14, shadcn/ui, TailwindCSS, and Vercel AI SDK. Users can stream in the UI, install packages from npm and pip, and add custom stacks and LLM providers. Fragments enables users to build web apps with Python interpreter, Next.js, Vue.js, Streamlit, and Gradio, utilizing providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, Google AI, and more.
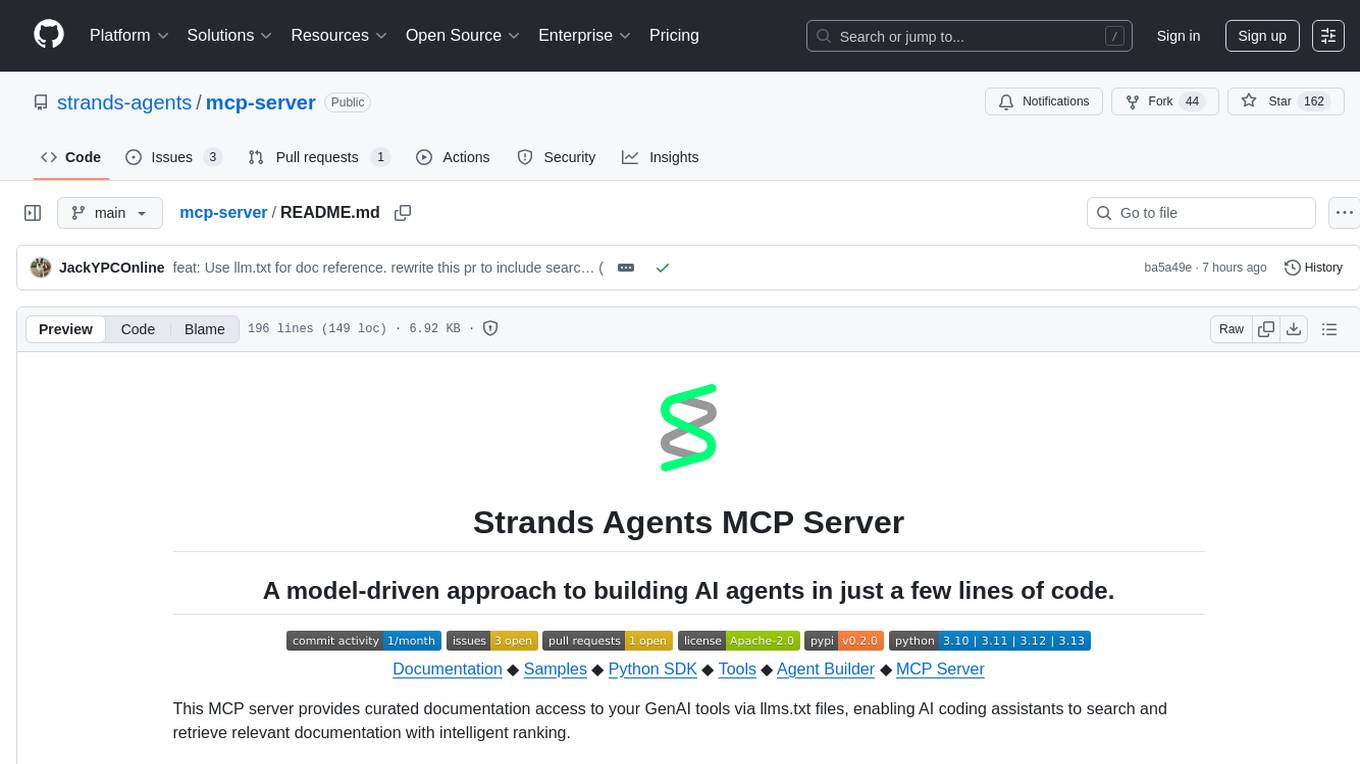
mcp-server
The Strands Agents MCP Server is a model-driven approach to building AI agents in just a few lines of code. It provides curated documentation access to GenAI tools via llms.txt files, enabling AI coding assistants to search and retrieve relevant documentation with intelligent ranking. Features include smart document search, curated content indexing, on-demand fetching, snippet generation, and real URL support. The server can be used with various applications that support MCP servers, such as Amazon Q Developer CLI, Anthropic Claude Code, Cline, and Cursor. Users can quickly test the MCP server using the MCP Inspector and follow the provided steps to configure their MCP client and start using the documentation tools. The project welcomes contributions and is licensed under the Apache License 2.0.
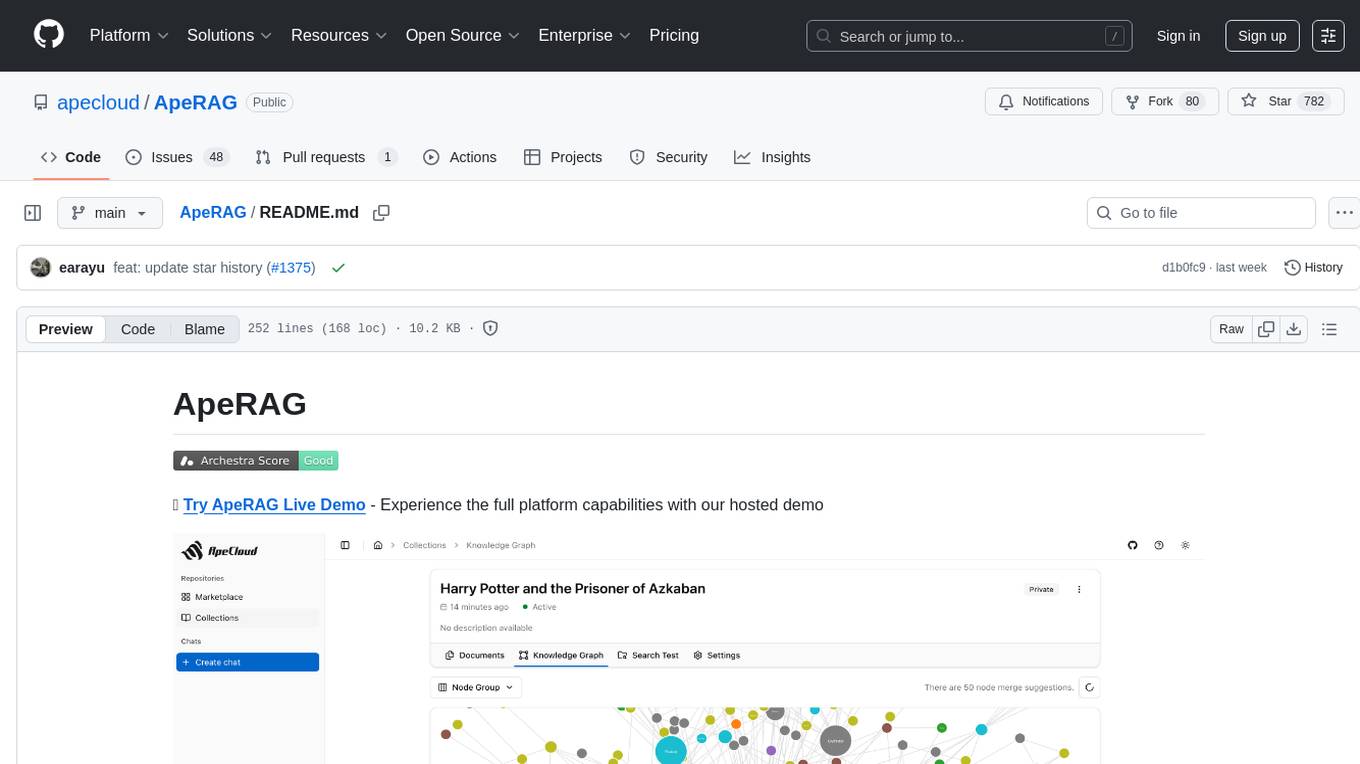
ApeRAG
ApeRAG is a production-ready platform for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) that combines Graph RAG, vector search, and full-text search with advanced AI agents. It is ideal for building Knowledge Graphs, Context Engineering, and deploying intelligent AI agents for autonomous search and reasoning across knowledge bases. The platform offers features like advanced index types, intelligent AI agents with MCP support, enhanced Graph RAG with entity normalization, multimodal processing, hybrid retrieval engine, MinerU integration for document parsing, production-grade deployment with Kubernetes, enterprise management features, MCP integration, and developer-friendly tools for customization and contribution.
gateway
CentralMind Gateway is an AI-first data gateway that securely connects any data source and automatically generates secure, LLM-optimized APIs. It filters out sensitive data, adds traceability, and optimizes for AI workloads. Suitable for companies deploying AI agents for customer support and analytics.
gemini-coder
Gemini Coder is a free 2M context AI coding assistant that allows users to conveniently copy folders and files for chatbots. It provides FIM completions, file refactoring, and AI-suggested changes. The extension is versatile, private, and lightweight, offering unmatched accuracy, speed, and cost in AI assistance. Users have full control over the context and coding conventions included, ensuring high performance and signal to noise ratio. Gemini Coder supports various chatbots and provides quick start guides for chat and FIM completions. It also offers commands for FIM completions, refactoring, applying changes, chat, and context copying. Users can set up custom model providers for API features and contribute to the project through pull requests or discussions. The tool is licensed under the MIT License.
openhands-aci
Agent-Computer Interface (ACI) for OpenHands is a deprecated repository that provided essential tools and interfaces for AI agents to interact with computer systems for software development tasks. It included a code editor interface, code linting capabilities, and utility functions for common operations. The package aimed to enhance software development agents' capabilities in editing code, managing configurations, analyzing code, and executing shell commands.
mysql_mcp_server
A Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that enables secure interaction with MySQL databases. This server allows AI assistants to list tables, read data, and execute SQL queries through a controlled interface, making database exploration and analysis safer and more structured. It provides features such as listing available MySQL tables as resources, reading table contents, executing SQL queries with proper error handling, secure database access through environment variables, and comprehensive logging. The tool ensures security best practices by never committing environment variables or credentials, using a database user with minimal required permissions, implementing query whitelisting for production use, and monitoring and logging all database operations.
chunkr
Chunkr is an open-source document intelligence API that provides a production-ready service for document layout analysis, OCR, and semantic chunking. It allows users to convert PDFs, PPTs, Word docs, and images into RAG/LLM-ready chunks. The API offers features such as layout analysis, OCR with bounding boxes, structured HTML and markdown output, and VLM processing controls. Users can interact with Chunkr through a Python SDK, enabling them to upload documents, process them, and export results in various formats. The tool also supports self-hosted deployment options using Docker Compose or Kubernetes, with configurations for different AI models like OpenAI, Google AI Studio, and OpenRouter. Chunkr is dual-licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License v3.0 (AGPL-3.0) and a commercial license, providing flexibility for different usage scenarios.
inferable
Inferable is an open source platform that helps users build reliable LLM-powered agentic automations at scale. It offers a managed agent runtime, durable tool calling, zero network configuration, multiple language support, and is fully open source under the MIT license. Users can define functions, register them with Inferable, and create runs that utilize these functions to automate tasks. The platform supports Node.js/TypeScript, Go, .NET, and React, and provides SDKs, core services, and bootstrap templates for various languages.
rag-chat
The `@upstash/rag-chat` package simplifies the development of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) chat applications by providing Next.js compatibility with streaming support, built-in vector store, optional Redis compatibility for fast chat history management, rate limiting, and disableRag option. Users can easily set up the environment variables and initialize RAGChat to interact with AI models, manage knowledge base, chat history, and enable debugging features. Advanced configuration options allow customization of RAGChat instance with built-in rate limiting, observability via Helicone, and integration with Next.js route handlers and Vercel AI SDK. The package supports OpenAI models, Upstash-hosted models, and custom providers like TogetherAi and Replicate.

infinity
Infinity is an AI-native database designed for LLM applications, providing incredibly fast full-text and vector search capabilities. It supports a wide range of data types, including vectors, full-text, and structured data, and offers a fused search feature that combines multiple embeddings and full text. Infinity is easy to use, with an intuitive Python API and a single-binary architecture that simplifies deployment. It achieves high performance, with 0.1 milliseconds query latency on million-scale vector datasets and up to 15K QPS.
For similar tasks

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.

sorrentum
Sorrentum is an open-source project that aims to combine open-source development, startups, and brilliant students to build machine learning, AI, and Web3 / DeFi protocols geared towards finance and economics. The project provides opportunities for internships, research assistantships, and development grants, as well as the chance to work on cutting-edge problems, learn about startups, write academic papers, and get internships and full-time positions at companies working on Sorrentum applications.

tidb
TiDB is an open-source distributed SQL database that supports Hybrid Transactional and Analytical Processing (HTAP) workloads. It is MySQL compatible and features horizontal scalability, strong consistency, and high availability.

zep-python
Zep is an open-source platform for building and deploying large language model (LLM) applications. It provides a suite of tools and services that make it easy to integrate LLMs into your applications, including chat history memory, embedding, vector search, and data enrichment. Zep is designed to be scalable, reliable, and easy to use, making it a great choice for developers who want to build LLM-powered applications quickly and easily.

telemetry-airflow
This repository codifies the Airflow cluster that is deployed at workflow.telemetry.mozilla.org (behind SSO) and commonly referred to as "WTMO" or simply "Airflow". Some links relevant to users and developers of WTMO: * The `dags` directory in this repository contains some custom DAG definitions * Many of the DAGs registered with WTMO don't live in this repository, but are instead generated from ETL task definitions in bigquery-etl * The Data SRE team maintains a WTMO Developer Guide (behind SSO)

mojo
Mojo is a new programming language that bridges the gap between research and production by combining Python syntax and ecosystem with systems programming and metaprogramming features. Mojo is still young, but it is designed to become a superset of Python over time.

pandas-ai
PandasAI is a Python library that makes it easy to ask questions to your data in natural language. It helps you to explore, clean, and analyze your data using generative AI.

databend
Databend is an open-source cloud data warehouse that serves as a cost-effective alternative to Snowflake. With its focus on fast query execution and data ingestion, it's designed for complex analysis of the world's largest datasets.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.




