
llmos
The flagship example—the OS simulation
Stars: 68
LLMos is an operating system designed for physical AI agents, providing a hybrid runtime environment where AI agents can perceive, reason, act on hardware, and evolve over time locally without cloud dependency. It allows natural language programming, dual-brain architecture for fast instinct and deep planner brains, markdown-as-code for defining agents and skills, and supports swarm intelligence and cognitive world models. The tool is built on a tech stack including Next.js, Electron, Python, and WebAssembly, and is structured around a dual-brain cognitive architecture, volume system, HAL for hardware abstraction, applet system for dynamic UI, and dreaming & evolution for robot improvement. The project is in Phase 1 (Foundation) and aims to move into Phase 2 (Dual-Brain & Local Intelligence), with contributions welcomed under the Apache 2.0 license by Evolving Agents Labs.
README:
A hybrid runtime environment where AI agents are first-class citizens that can perceive, reason, act on hardware, and evolve over time — all running locally, no cloud required.
LLMos is an "Operating System" designed for the era of physical AI. Unlike traditional robotics frameworks (ROS) or simple LLM chatbots, LLMos treats Agentic Behaviors as installable software.
It allows you to program robots using natural language, compiles those intentions into executable "Skills," and provides a Dual-Brain cognitive architecture that thinks deeply and reacts instantly.
- Natural Language Programming: Type "Create a robot that avoids walls" and the system generates the code, HAL bindings, and logic.
- Dual-Brain Architecture: Fast instinct brain (Qwen3-VL-8B multimodal single-pass, ~200-500ms) handles reactive perception and avoidance. Deep planner brain (Qwen3-VL-8B + RSA, 3-8s) handles goal planning and exploration.
- Zero Cloud Dependency: Runs fully offline on a host computer with GPU. No API costs. No latency.
- Markdown-as-Code: Agents, Skills, and Tools are defined in human-readable Markdown files that serve as both documentation and executable logic.
- Hybrid Runtime: Runs entirely in the browser (via WebAssembly/Pyodide), on Desktop (Electron), or deploys to physical hardware (ESP32).
- Swarm Intelligence: Multiple robots merge world models via RSA consensus — the "MapReduce for physical intelligence."
- Cognitive World Model: A persistent spatial-temporal grid that allows robots to track object permanence and detect changes over time.
graph TB
subgraph "Sensing"
CAM[Camera]
DIST[Distance Sensors]
end
subgraph "Perception + Cognition (Unified VLM)"
CAM --> VLM[Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct<br/>Direct image + text<br/>~200-500ms]
DIST --> VLM
VLM --> VF[VisionFrame JSON<br/>objects + depth + scene + reasoning]
VF --> INSTINCT[INSTINCT Brain<br/>Reactive rules + VLM single-pass<br/>~200-500ms]
VF --> PLANNER[PLANNER Brain<br/>Qwen3-VL-8B + RSA<br/>3-8 seconds]
INSTINCT --> |Escalate when stuck<br/>or complex goal| PLANNER
end
subgraph "Action"
INSTINCT --> HAL[HAL]
PLANNER --> HAL
HAL --> SIM[Simulator]
HAL --> ESP[ESP32 Robot]
end
The Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct model serves as a unified vision-language backbone — it processes raw camera frames directly (no separate object detector needed), producing structured VisionFrame data with scene understanding, depth estimates, and OCR. This replaces the previous MobileNet SSD + Qwen3-4B two-model pipeline with a single multimodal model.
The Instinct brain handles immediate decisions: obstacle avoidance, wall following, simple tracking. The Planner brain handles deep reasoning: exploration strategy, skill generation, multi-robot coordination.
RSA (Recursive Self-Aggregation) enables the local model (Qwen3-VL-8B, 8B parameters) to match the reasoning quality of much larger cloud models like o3-mini and DeepSeek-R1 by recursively aggregating multiple candidate reasoning chains.
- Frontend/Desktop: Next.js 14, Electron, Tailwind CSS, React Flow.
- Simulation: Three.js, React-Three-Fiber.
- Runtime Logic: TypeScript, Python (via Pyodide), WebAssembly (@wasmer/sdk).
- Intelligence: Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct (unified vision-language model) + RSA (local).
- Storage: Browser-native Virtual File System (VFS) with LightningFS.
- Hardware: ESP32-S3 (C++ Firmware, WASM runtime).
- Node.js 18+
- Python 3.10+ (for backend services/compilation)
- Git
- GPU with 8GB+ VRAM (for local Qwen3-VL-8B inference — optional, cloud API via OpenRouter available at $0.08/M input)
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/EvolvingAgentsLabs/llmos cd llmos -
Install dependencies:
npm install -
Run in Development Mode:
-
Web Mode (Simulator Only):
npm run dev -
Desktop Mode (Electron + Hardware Access):
npm run electron:dev
-
Web Mode (Simulator Only):
-
Setup Keys: Upon launch, the setup wizard will ask for your LLM API Key (OpenRouter, Gemini, or OpenAI). This key is stored locally in your browser/desktop storage and is never sent to our servers. For fully offline operation, set up a local Qwen3-VL-8B server (see ROADMAP.md Phase 2).
LLMos is built on five pillars that distinguish it from standard agent frameworks.
Two cognitive layers run in parallel:
- Instinct Brain — Reactive rules + single-pass Qwen3-VL-8B (~200-500ms). Handles obstacle avoidance, wall following, simple tracking.
- Planner Brain — RSA-enhanced Qwen3-VL-8B (3-8s). Handles exploration planning, skill generation, swarm coordination.
- Unified VLM Vision — Qwen3-VL-8B processes raw camera frames directly (no separate object detector). Produces structured VisionFrame JSON with scene understanding, depth estimation, and OCR.
The file system is the database. Data is organized into hierarchical volumes:
- System Volume: Read-only core agents, Standard Library tools, and certified Skills.
- Team Volume: Shared skills and knowledge patterns discovered by the "Dreaming Engine."
- User Volume: Your local projects, custom agents, and interaction traces.
The HAL allows the exact same Agent code to run in the 3D Simulator and on physical robots.
-
Tools: Defined in Markdown (e.g.,
hal_drive.md,hal_vision_scan.md). -
Validation: A
CommandValidatorintercepts LLM instructions to ensure physical safety before they reach the motors.
LLMos includes a dynamic UI system called "Applets." These are micro-applications that Agents can generate on the fly to help users complete tasks.
Robots improve while idle. The "Dreaming Engine" analyzes BlackBox recordings of failed interactions:
- Replay: Simulates the failure scenario in Three.js.
- Mutate: The LLM generates variations of the code to fix the issue.
- Evaluate: Successful mutations are patched into the Skill Markdown file.
llmos/
├── app/ # Next.js App Router (UI Pages & API Routes)
├── components/ # React Components
│ ├── applets/ # Dynamic Applet UI System
│ ├── canvas/ # Three.js Visualization & Sim
│ ├── chat/ # Agent Chat Interface
│ ├── robot/ # Robot Control Panels
│ └── visualization/ # Decision Trees & Flow Graphs
├── electron/ # Electron Main Process & Native Bridges
├── firmware/ # ESP32 C++ Code & WASM Runtimes
├── lib/ # Core Logic
│ ├── agents/ # Agent Orchestrators & Compilers
│ ├── evolution/ # Dreaming Engine & Self-Correction
│ ├── hal/ # Hardware Abstraction Layer
│ ├── kernel/ # OS Boot Logic & Process Mgmt
│ ├── runtime/ # Cognitive Runtimes
│ │ ├── rsa-engine.ts # RSA + multimodal RSA algorithm
│ │ ├── dual-brain-controller.ts # Instinct + Planner orchestration
│ │ ├── jepa-mental-model.ts # JEPA-inspired abstract state
│ │ ├── world-model.ts # Grid-based spatial model
│ │ └── vision/
│ │ ├── vlm-vision-detector.ts # Qwen3-VL-8B unified vision detector
│ │ └── mobilenet-detector.ts # Vision types + utility functions
│ └── virtual-fs.ts # In-browser File System
├── volumes/ # The "Brain" (Markdown Knowledge Base)
│ ├── system/ # Built-in Agents & Skills
│ └── user/ # User Data (Local)
└── __tests__/ # Integration Tests
To use LLMos with real hardware, you need an ESP32-S3.
Basic Wiring:
- Motors: GPIO 12/13/14/15 -> Motor Driver
- Sensors: GPIO 16/17 -> HC-SR04 (Ultrasonic)
- Connection: Connect via USB. The Electron app will auto-detect the serial port.
See docs/hardware/STANDARD_ROBOT_V1.md for full schematics.
This project builds on:
| Paper / Model | Role in LLMos |
|---|---|
| Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct | Unified vision-language backbone — perceives images + reasons in one pass |
| RSA: Recursive Self-Aggregation Unlocks Deep Thinking in LLMs | Planner brain — enables local model to match cloud-scale reasoning |
| JEPA: A Path Towards Autonomous Machine Intelligence | Mental model architecture — predict-before-act paradigm |
| MobileNet V2 | Vision type definitions and depth estimation utilities |
We are in Phase 1 (Foundation) heading into Phase 2 (Dual-Brain & Local Intelligence).
- Check
ROADMAP.mdfor current priorities. - Look for "Good First Issues" related to UI polish or new HAL tool definitions.
- Ensure all new logic includes tests in
__tests__/.
Apache 2.0 - Open Source. Built by Evolving Agents Labs.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for llmos
Similar Open Source Tools

llmos
LLMos is an operating system designed for physical AI agents, providing a hybrid runtime environment where AI agents can perceive, reason, act on hardware, and evolve over time locally without cloud dependency. It allows natural language programming, dual-brain architecture for fast instinct and deep planner brains, markdown-as-code for defining agents and skills, and supports swarm intelligence and cognitive world models. The tool is built on a tech stack including Next.js, Electron, Python, and WebAssembly, and is structured around a dual-brain cognitive architecture, volume system, HAL for hardware abstraction, applet system for dynamic UI, and dreaming & evolution for robot improvement. The project is in Phase 1 (Foundation) and aims to move into Phase 2 (Dual-Brain & Local Intelligence), with contributions welcomed under the Apache 2.0 license by Evolving Agents Labs.
OpenViking
OpenViking is an open-source Context Database designed specifically for AI Agents. It aims to solve challenges in agent development by unifying memories, resources, and skills in a filesystem management paradigm. The tool offers tiered context loading, directory recursive retrieval, visualized retrieval trajectory, and automatic session management. Developers can interact with OpenViking like managing local files, enabling precise context manipulation and intuitive traceable operations. The tool supports various model services like OpenAI and Volcengine, enhancing semantic retrieval and context understanding for AI Agents.
GPT4Point
GPT4Point is a unified framework for point-language understanding and generation. It aligns 3D point clouds with language, providing a comprehensive solution for tasks such as 3D captioning and controlled 3D generation. The project includes an automated point-language dataset annotation engine, a novel object-level point cloud benchmark, and a 3D multi-modality model. Users can train and evaluate models using the provided code and datasets, with a focus on improving models' understanding capabilities and facilitating the generation of 3D objects.
executorch
ExecuTorch is an end-to-end solution for enabling on-device inference capabilities across mobile and edge devices including wearables, embedded devices and microcontrollers. It is part of the PyTorch Edge ecosystem and enables efficient deployment of PyTorch models to edge devices. Key value propositions of ExecuTorch are: * **Portability:** Compatibility with a wide variety of computing platforms, from high-end mobile phones to highly constrained embedded systems and microcontrollers. * **Productivity:** Enabling developers to use the same toolchains and SDK from PyTorch model authoring and conversion, to debugging and deployment to a wide variety of platforms. * **Performance:** Providing end users with a seamless and high-performance experience due to a lightweight runtime and utilizing full hardware capabilities such as CPUs, NPUs, and DSPs.
transformerlab-app
Transformer Lab is an app that allows users to experiment with Large Language Models by providing features such as one-click download of popular models, finetuning across different hardware, RLHF and Preference Optimization, working with LLMs across different operating systems, chatting with models, using different inference engines, evaluating models, building datasets for training, calculating embeddings, providing a full REST API, running in the cloud, converting models across platforms, supporting plugins, embedded Monaco code editor, prompt editing, inference logs, all through a simple cross-platform GUI.

layra
LAYRA is the world's first visual-native AI automation engine that sees documents like a human, preserves layout and graphical elements, and executes arbitrarily complex workflows with full Python control. It empowers users to build next-generation intelligent systems with no limits or compromises. Built for Enterprise-Grade deployment, LAYRA features a modern frontend, high-performance backend, decoupled service architecture, visual-native multimodal document understanding, and a powerful workflow engine.
shards
Shards is a high-performance, multi-platform, type-safe programming language designed for visual development. It is a dataflow visual programming language that enables building full-fledged apps and games without traditional coding. Shards features automatic type checking, optimized shard implementations for high performance, and an intuitive visual workflow for beginners. The language allows seamless round-trip engineering between code and visual models, empowering users to create multi-platform apps easily. Shards also powers an upcoming AI-powered game creation system, enabling real-time collaboration and game development in a low to no-code environment.
trpc-agent-go
A powerful Go framework for building intelligent agent systems with large language models (LLMs), hierarchical planners, memory, telemetry, and a rich tool ecosystem. tRPC-Agent-Go enables the creation of autonomous or semi-autonomous agents that reason, call tools, collaborate with sub-agents, and maintain long-term state. The framework provides detailed documentation, examples, and tools for accelerating the development of AI applications.
AgC
AgC is an open-core platform designed for deploying, running, and orchestrating AI agents at scale. It treats agents as first-class compute units, providing a modular, observable, cloud-neutral, and production-ready environment. Open Agentic Compute empowers developers and organizations to run agents like cloud-native workloads without lock-in.
llmxcpg
LLMxCPG is a framework for vulnerability detection using Code Property Graphs (CPG) and Large Language Models (LLM). It involves a two-phase process: Slice Construction where an LLM generates queries for a CPG to extract a code slice, and Vulnerability Detection where another LLM classifies the code slice as vulnerable or safe. The repository includes implementations of baseline models, information on datasets, scripts for running models, prompt templates, query generation examples, and configurations for fine-tuning models.
llamafarm
LlamaFarm is a comprehensive AI framework that empowers users to build powerful AI applications locally, with full control over costs and deployment options. It provides modular components for RAG systems, vector databases, model management, prompt engineering, and fine-tuning. Users can create differentiated AI products without needing extensive ML expertise, using simple CLI commands and YAML configs. The framework supports local-first development, production-ready components, strategy-based configuration, and deployment anywhere from laptops to the cloud.
bifrost
Bifrost is a high-performance AI gateway that unifies access to multiple providers through a single OpenAI-compatible API. It offers features like automatic failover, load balancing, semantic caching, and enterprise-grade functionalities. Users can deploy Bifrost in seconds with zero configuration, benefiting from its core infrastructure, advanced features, enterprise and security capabilities, and developer experience. The repository structure is modular, allowing for maximum flexibility. Bifrost is designed for quick setup, easy configuration, and seamless integration with various AI models and tools.
BioAgents
BioAgents AgentKit is an advanced AI agent framework tailored for biological and scientific research. It offers powerful conversational AI capabilities with specialized knowledge in biology, life sciences, and scientific research methodologies. The framework includes state-of-the-art analysis agents, configurable research agents, and a variety of specialized agents for tasks such as file parsing, research planning, literature search, data analysis, hypothesis generation, research reflection, and user-facing responses. BioAgents also provides support for LLM libraries, multiple search backends for literature agents, and two backends for data analysis. The project structure includes backend source code, services for chat, job queue system, real-time notifications, and JWT authentication, as well as a frontend UI built with Preact.
sandboxed.sh
sandboxed.sh is a self-hosted cloud orchestrator for AI coding agents that provides isolated Linux workspaces with Claude Code, OpenCode & Amp runtimes. It allows users to hand off entire development cycles, run multi-day operations unattended, and keep sensitive data local by analyzing data against scientific literature. The tool features dual runtime support, mission control for remote agent management, isolated workspaces, a git-backed library, MCP registry, and multi-platform support with a web dashboard and iOS app.
shannon
Shannon is an AI pentester that delivers actual exploits, not just alerts. It autonomously hunts for attack vectors in your code, then uses its built-in browser to execute real exploits, such as injection attacks, and auth bypass, to prove the vulnerability is actually exploitable. Shannon closes the security gap by acting as your on-demand whitebox pentester, providing concrete proof of vulnerabilities to let you ship with confidence. It is a core component of the Keygraph Security and Compliance Platform, automating penetration testing and compliance journey. Shannon Lite achieves a 96.15% success rate on a hint-free, source-aware XBOW benchmark.
tensorzero
TensorZero is an open-source platform that helps LLM applications graduate from API wrappers into defensible AI products. It enables a data & learning flywheel for LLMs by unifying inference, observability, optimization, and experimentation. The platform includes a high-performance model gateway, structured schema-based inference, observability, experimentation, and data warehouse for analytics. TensorZero Recipes optimize prompts and models, and the platform supports experimentation features and GitOps orchestration for deployment.
For similar tasks

llmos
LLMos is an operating system designed for physical AI agents, providing a hybrid runtime environment where AI agents can perceive, reason, act on hardware, and evolve over time locally without cloud dependency. It allows natural language programming, dual-brain architecture for fast instinct and deep planner brains, markdown-as-code for defining agents and skills, and supports swarm intelligence and cognitive world models. The tool is built on a tech stack including Next.js, Electron, Python, and WebAssembly, and is structured around a dual-brain cognitive architecture, volume system, HAL for hardware abstraction, applet system for dynamic UI, and dreaming & evolution for robot improvement. The project is in Phase 1 (Foundation) and aims to move into Phase 2 (Dual-Brain & Local Intelligence), with contributions welcomed under the Apache 2.0 license by Evolving Agents Labs.
AgentGym
AgentGym is a framework designed to help the AI community evaluate and develop generally-capable Large Language Model-based agents. It features diverse interactive environments and tasks with real-time feedback and concurrency. The platform supports 14 environments across various domains like web navigating, text games, house-holding tasks, digital games, and more. AgentGym includes a trajectory set (AgentTraj) and a benchmark suite (AgentEval) to facilitate agent exploration and evaluation. The framework allows for agent self-evolution beyond existing data, showcasing comparable results to state-of-the-art models.
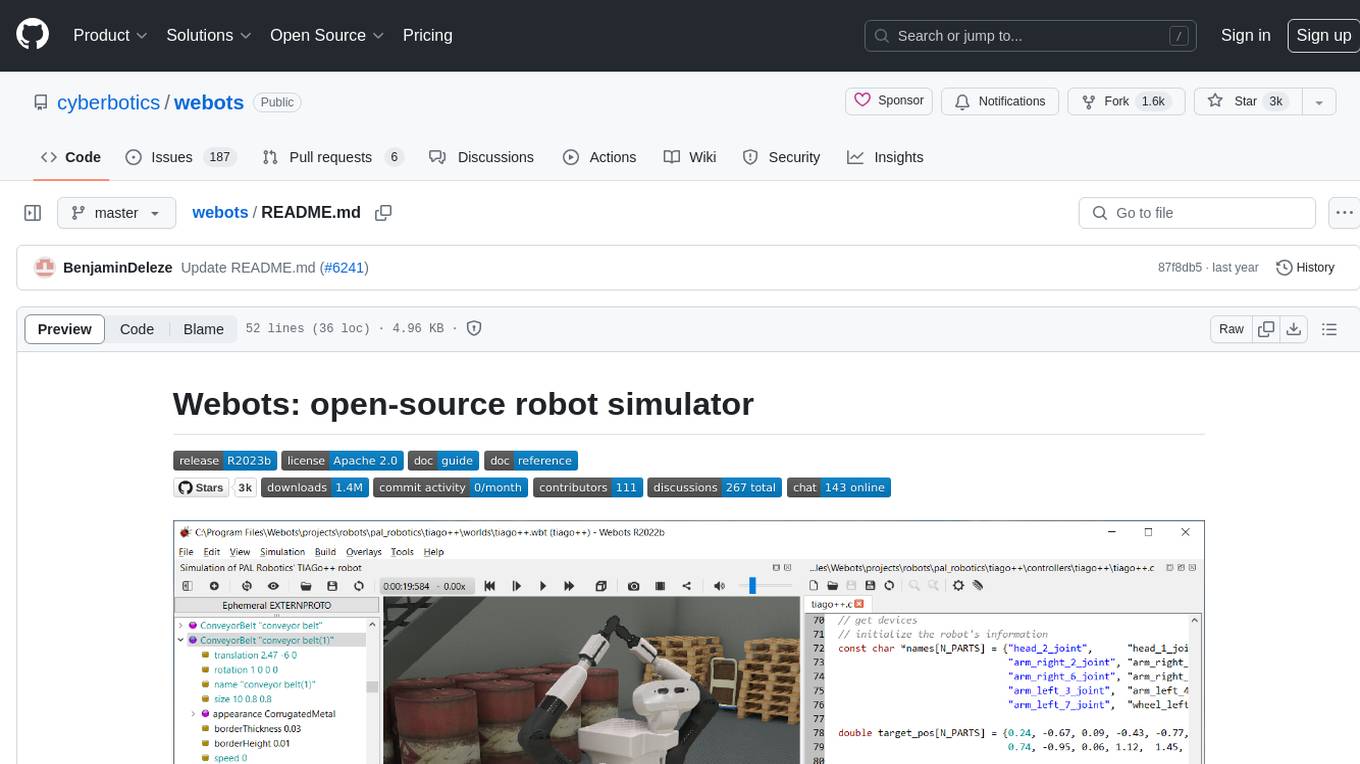
webots
Webots is an open-source robot simulator that provides a complete development environment to model, program, and simulate robots, vehicles, and mechanical systems. It was originally designed at EPFL in 1996 and further developed and commercialized by Cyberbotics since 1998. Webots was open-sourced in December 2018 and continues to be developed by Cyberbotics with paid customer support, training, and consulting services for industry and academic research projects.

ray
Ray is a unified framework for scaling AI and Python applications. It consists of a core distributed runtime and a set of AI libraries for simplifying ML compute, including Data, Train, Tune, RLlib, and Serve. Ray runs on any machine, cluster, cloud provider, and Kubernetes, and features a growing ecosystem of community integrations. With Ray, you can seamlessly scale the same code from a laptop to a cluster, making it easy to meet the compute-intensive demands of modern ML workloads.
vasttools
This repository contains a collection of tools that can be used with vastai. The tools are free to use, modify and distribute. If you find this useful and wish to donate your welcome to send your donations to the following wallets. BTC 15qkQSYXP2BvpqJkbj2qsNFb6nd7FyVcou XMR 897VkA8sG6gh7yvrKrtvWningikPteojfSgGff3JAUs3cu7jxPDjhiAZRdcQSYPE2VGFVHAdirHqRZEpZsWyPiNK6XPQKAg RVN RSgWs9Co8nQeyPqQAAqHkHhc5ykXyoMDUp USDT(ETH ERC20) 0xa5955cf9fe7af53bcaa1d2404e2b17a1f28aac4f Paypal PayPal.Me/cryptolabsZA
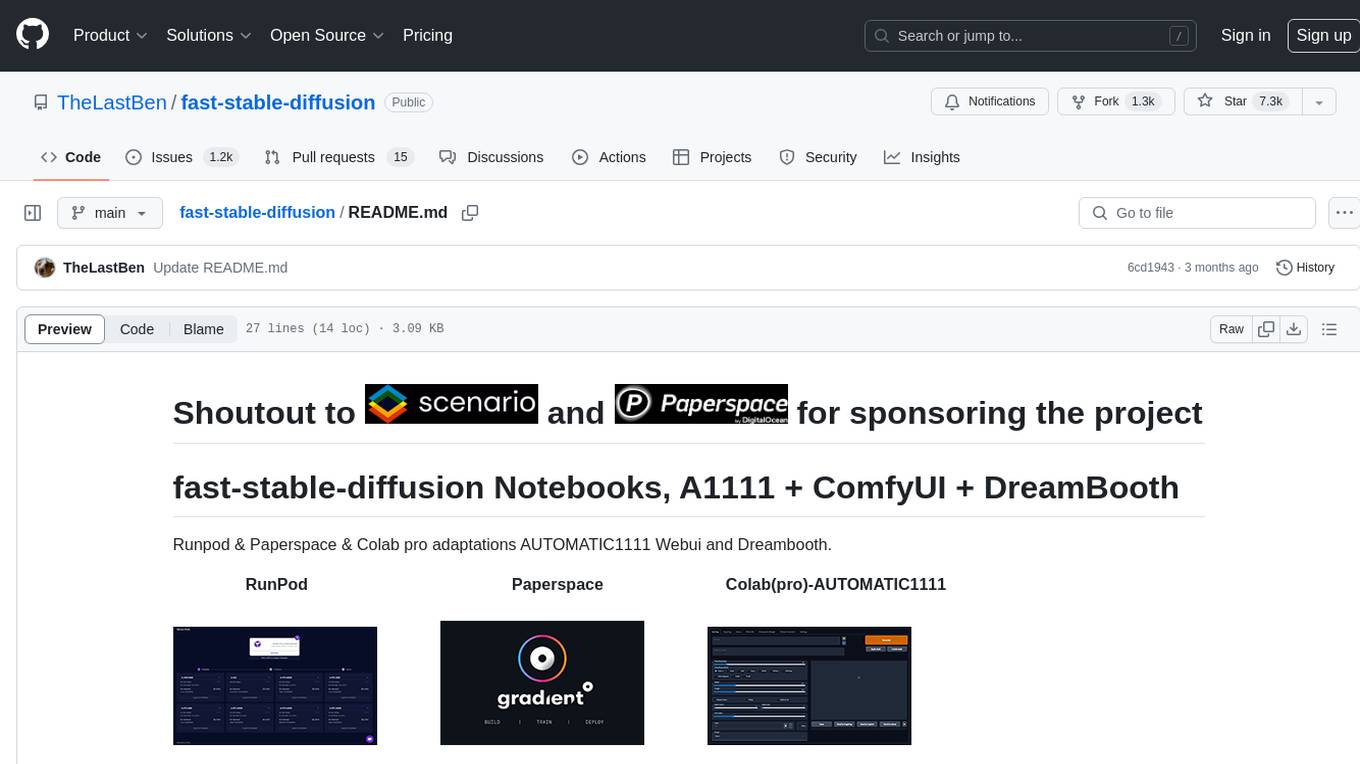
fast-stable-diffusion
Fast-stable-diffusion is a project that offers notebooks for RunPod, Paperspace, and Colab Pro adaptations with AUTOMATIC1111 Webui and Dreambooth. It provides tools for running and implementing Dreambooth, a stable diffusion project. The project includes implementations by XavierXiao and is sponsored by Runpod, Paperspace, and Colab Pro.
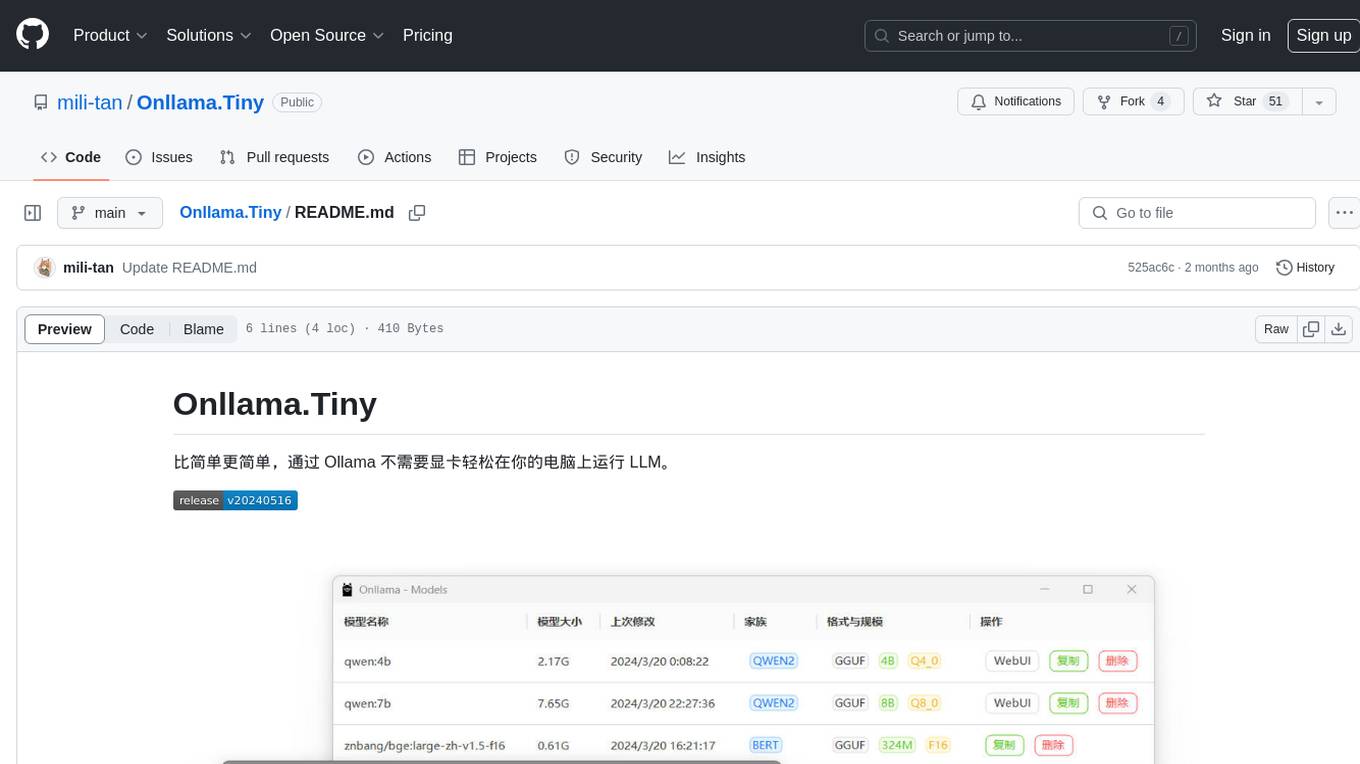
Onllama.Tiny
Onllama.Tiny is a lightweight tool that allows you to easily run LLM on your computer without the need for a dedicated graphics card. It simplifies the process of running LLM, making it more accessible for users. The tool provides a user-friendly interface and streamlines the setup and configuration required to run LLM on your machine. With Onllama.Tiny, users can quickly set up and start using LLM for various applications and projects.
OnAIR
The On-board Artificial Intelligence Research (OnAIR) Platform is a framework that enables AI algorithms written in Python to interact with NASA's cFS. It is intended to explore research concepts in autonomous operations in a simulated environment. The platform provides tools for generating environments, handling telemetry data through Redis, running unit tests, and contributing to the repository. Users can set up a conda environment, configure telemetry and Redis examples, run simulations, and conduct unit tests to ensure the functionality of their AI algorithms. The platform also includes guidelines for licensing, copyright, and contributions to the repository.
For similar jobs
Qwen-TensorRT-LLM
Qwen-TensorRT-LLM is a project developed for the NVIDIA TensorRT Hackathon 2023, focusing on accelerating inference for the Qwen-7B-Chat model using TRT-LLM. The project offers various functionalities such as FP16/BF16 support, INT8 and INT4 quantization options, Tensor Parallel for multi-GPU parallelism, web demo setup with gradio, Triton API deployment for maximum throughput/concurrency, fastapi integration for openai requests, CLI interaction, and langchain support. It supports models like qwen2, qwen, and qwen-vl for both base and chat models. The project also provides tutorials on Bilibili and blogs for adapting Qwen models in NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM, along with hardware requirements and quick start guides for different model types and quantization methods.
dl_model_infer
This project is a c++ version of the AI reasoning library that supports the reasoning of tensorrt models. It provides accelerated deployment cases of deep learning CV popular models and supports dynamic-batch image processing, inference, decode, and NMS. The project has been updated with various models and provides tutorials for model exports. It also includes a producer-consumer inference model for specific tasks. The project directory includes implementations for model inference applications, backend reasoning classes, post-processing, pre-processing, and target detection and tracking. Speed tests have been conducted on various models, and onnx downloads are available for different models.
joliGEN
JoliGEN is an integrated framework for training custom generative AI image-to-image models. It implements GAN, Diffusion, and Consistency models for various image translation tasks, including domain and style adaptation with conservation of semantics. The tool is designed for real-world applications such as Controlled Image Generation, Augmented Reality, Dataset Smart Augmentation, and Synthetic to Real transforms. JoliGEN allows for fast and stable training with a REST API server for simplified deployment. It offers a wide range of options and parameters with detailed documentation available for models, dataset formats, and data augmentation.
ai-edge-torch
AI Edge Torch is a Python library that supports converting PyTorch models into a .tflite format for on-device applications on Android, iOS, and IoT devices. It offers broad CPU coverage with initial GPU and NPU support, closely integrating with PyTorch and providing good coverage of Core ATen operators. The library includes a PyTorch converter for model conversion and a Generative API for authoring mobile-optimized PyTorch Transformer models, enabling easy deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) on mobile devices.
awesome-RK3588
RK3588 is a flagship 8K SoC chip by Rockchip, integrating Cortex-A76 and Cortex-A55 cores with NEON coprocessor for 8K video codec. This repository curates resources for developing with RK3588, including official resources, RKNN models, projects, development boards, documentation, tools, and sample code.

cl-waffe2
cl-waffe2 is an experimental deep learning framework in Common Lisp, providing fast, systematic, and customizable matrix operations, reverse mode tape-based Automatic Differentiation, and neural network model building and training features accelerated by a JIT Compiler. It offers abstraction layers, extensibility, inlining, graph-level optimization, visualization, debugging, systematic nodes, and symbolic differentiation. Users can easily write extensions and optimize their networks without overheads. The framework is designed to eliminate barriers between users and developers, allowing for easy customization and extension.
TensorRT-Model-Optimizer
The NVIDIA TensorRT Model Optimizer is a library designed to quantize and compress deep learning models for optimized inference on GPUs. It offers state-of-the-art model optimization techniques including quantization and sparsity to reduce inference costs for generative AI models. Users can easily stack different optimization techniques to produce quantized checkpoints from torch or ONNX models. The quantized checkpoints are ready for deployment in inference frameworks like TensorRT-LLM or TensorRT, with planned integrations for NVIDIA NeMo and Megatron-LM. The tool also supports 8-bit quantization with Stable Diffusion for enterprise users on NVIDIA NIM. Model Optimizer is available for free on NVIDIA PyPI, and this repository serves as a platform for sharing examples, GPU-optimized recipes, and collecting community feedback.
depthai
This repository contains a demo application for DepthAI, a tool that can load different networks, create pipelines, record video, and more. It provides documentation for installation and usage, including running programs through Docker. Users can explore DepthAI features via command line arguments or a clickable QT interface. Supported models include various AI models for tasks like face detection, human pose estimation, and object detection. The tool collects anonymous usage statistics by default, which can be disabled. Users can report issues to the development team for support and troubleshooting.



