
trpc-agent-go
trpc-agent-go is a powerful Go framework for building intelligent agent systems using large language models (LLMs) and tools.
Stars: 880
A powerful Go framework for building intelligent agent systems with large language models (LLMs), hierarchical planners, memory, telemetry, and a rich tool ecosystem. tRPC-Agent-Go enables the creation of autonomous or semi-autonomous agents that reason, call tools, collaborate with sub-agents, and maintain long-term state. The framework provides detailed documentation, examples, and tools for accelerating the development of AI applications.
README:
English | 中文
A powerful Go framework for building intelligent agent systems that transforms how you create AI applications. Build autonomous agents that think, remember, collaborate, and act with unprecedented ease.
Why tRPC-Agent-Go?
- Intelligent Reasoning: Advanced hierarchical planners and multi-agent orchestration
- Rich Tool Ecosystem: Seamless integration with external APIs, databases, and services
- Persistent Memory: Long-term state management and contextual awareness
- Multi-Agent Collaboration: Chain, parallel, and graph-based agent workflows
- GraphAgent: Type-safe graph workflows with multi-conditional routing, functionally equivalent to LangGraph for Go
-
Agent Skills: Reusable
SKILL.mdworkflows with safe execution - Artifacts: Versioned storage for files produced by agents and tools
- Prompt Caching: Automatic cost optimization with 90% savings on cached content
- Evaluation & Benchmarks: Eval sets + metrics to measure quality over time
- UI & Server Integration: AG-UI (Agent-User Interaction), and Agent-to-Agent (A2A) interoperability
- Production Ready: Built-in telemetry, tracing, and enterprise-grade reliability
- High Performance: Optimized for scalability and low latency
Perfect for building:
- Customer Support Bots - Intelligent agents that understand context and solve complex queries
- Data Analysis Assistants - Agents that query databases, generate reports, and provide insights
- DevOps Automation - Smart deployment, monitoring, and incident response systems
- Business Process Automation - Multi-step workflows with human-in-the-loop capabilities
- Research & Knowledge Management - RAG-powered agents for document analysis and Q&A
// Chain agents for complex workflows
pipeline := chainagent.New("pipeline",
chainagent.WithSubAgents([]agent.Agent{
analyzer, processor, reporter,
}))
// Or run them in parallel
parallel := parallelagent.New("concurrent",
parallelagent.WithSubAgents(tasks)) |
// Persistent memory with search
memory := memorysvc.NewInMemoryService()
agent := llmagent.New("assistant",
llmagent.WithTools(memory.Tools()),
llmagent.WithModel(model))
// Memory service managed at runner level
runner := runner.NewRunner("app", agent,
runner.WithMemoryService(memory))
// Agents remember context across sessions |
// Any function becomes a tool
calculator := function.NewFunctionTool(
calculate,
function.WithName("calculator"),
function.WithDescription("Math operations"))
// MCP protocol support
mcpTool := mcptool.New(serverConn) |
// Start Langfuse integration
clean, _ := langfuse.Start(ctx)
defer clean(ctx)
runner := runner.NewRunner("app", agent)
// Run with Langfuse attributes
events, _ := runner.Run(ctx, "user-1", "session-1",
model.NewUserMessage("Hello"),
agent.WithSpanAttributes(
attribute.String("langfuse.user.id", "user-1"),
attribute.String("langfuse.session.id", "session-1"),
)) |
// Skills are folders with a SKILL.md spec.
repo, _ := skill.NewFSRepository("./skills")
// Let the agent load and run skills on demand.
tools := []tool.Tool{
skilltool.NewLoadTool(repo),
skilltool.NewRunTool(repo, localexec.New()),
}
|
evaluator, _ := evaluation.New("app", runner, evaluation.WithNumRuns(3))
defer evaluator.Close()
result, _ := evaluator.Evaluate(ctx, "math-basic")
_ = result.OverallStatus |
- tRPC-Agent-Go
Ready to dive into tRPC-Agent-Go? Our documentation covers everything from basic concepts to advanced techniques, helping you build powerful AI applications with confidence. Whether you're new to AI agents or an experienced developer, you'll find detailed guides, practical examples, and best practices to accelerate your development journey.
See it in Action: [Demo GIF placeholder - showing agent reasoning and tool usage]
- Go 1.21 or later
- LLM provider API key (OpenAI, DeepSeek, etc.)
- 5 minutes to build your first intelligent agent
Get started in 3 simple steps:
# 1. Clone and setup
git clone https://github.com/trpc-group/trpc-agent-go.git
cd trpc-agent-go
# 2. Configure your LLM
export OPENAI_API_KEY="your-api-key-here"
export OPENAI_BASE_URL="your-base-url-here" # Optional
# 3. Run your first agent!
cd examples/runner
go run . -model="gpt-4o-mini" -streaming=trueWhat you'll see:
- Interactive chat with your AI agent
- Real-time streaming responses
- Tool usage (calculator + time tools)
- Multi-turn conversations with memory
Try asking: "What's the current time? Then calculate 15 * 23 + 100"
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"trpc.group/trpc-go/trpc-agent-go/agent/llmagent"
"trpc.group/trpc-go/trpc-agent-go/model"
"trpc.group/trpc-go/trpc-agent-go/model/openai"
"trpc.group/trpc-go/trpc-agent-go/runner"
"trpc.group/trpc-go/trpc-agent-go/tool"
"trpc.group/trpc-go/trpc-agent-go/tool/function"
)
func main() {
// Create model.
modelInstance := openai.New("deepseek-chat")
// Create tool.
calculatorTool := function.NewFunctionTool(
calculator,
function.WithName("calculator"),
function.WithDescription("Execute addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. "+
"Parameters: a, b are numeric values, op takes values add/sub/mul/div; "+
"returns result as the calculation result."),
)
// Enable streaming output.
genConfig := model.GenerationConfig{
Stream: true,
}
// Create Agent.
agent := llmagent.New("assistant",
llmagent.WithModel(modelInstance),
llmagent.WithTools([]tool.Tool{calculatorTool}),
llmagent.WithGenerationConfig(genConfig),
)
// Create Runner.
runner := runner.NewRunner("calculator-app", agent)
// Execute conversation.
ctx := context.Background()
events, err := runner.Run(ctx,
"user-001",
"session-001",
model.NewUserMessage("Calculate what 2+3 equals"),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Process event stream.
for event := range events {
if event.Object == "chat.completion.chunk" {
fmt.Print(event.Response.Choices[0].Delta.Content)
}
}
fmt.Println()
}
func calculator(ctx context.Context, req calculatorReq) (calculatorRsp, error) {
var result float64
switch req.Op {
case "add", "+":
result = req.A + req.B
case "sub", "-":
result = req.A - req.B
case "mul", "*":
result = req.A * req.B
case "div", "/":
result = req.A / req.B
default:
return calculatorRsp{}, fmt.Errorf("invalid operation: %s", req.Op)
}
return calculatorRsp{Result: result}, nil
}
type calculatorReq struct {
A float64 `json:"A" jsonschema:"description=First integer operand,required"`
B float64 `json:"B" jsonschema:"description=Second integer operand,required"`
Op string `json:"Op" jsonschema:"description=Operation type,enum=add,enum=sub,enum=mul,enum=div,required"`
}
type calculatorRsp struct {
Result float64 `json:"result"`
}Sometimes your Agent must be created per request (for example: different
prompt, model, tools, sandbox instance). In that case, you can let Runner build
a fresh Agent for every Run(...):
r := runner.NewRunnerWithAgentFactory(
"my-app",
"assistant",
func(ctx context.Context, ro agent.RunOptions) (agent.Agent, error) {
// Use ro to build an Agent for this request.
a := llmagent.New("assistant",
llmagent.WithInstruction(ro.Instruction),
)
return a, nil
},
)
events, err := r.Run(ctx,
"user-001",
"session-001",
model.NewUserMessage("Hello"),
agent.WithInstruction("You are a helpful assistant."),
)
_ = events
_ = errIf you want to interrupt a running agent, cancel the context you passed to
Runner.Run (recommended). This stops model calls and tool calls safely and
lets the runner clean up.
Important: do not just “break” your event loop and walk away — the agent goroutine may keep running and can block on channel writes. Always cancel, then keep draining the event channel until it is closed.
Convert Ctrl+C into context cancellation:
ctx, stop := signal.NotifyContext(context.Background(), os.Interrupt)
defer stop()
events, err := r.Run(ctx, userID, sessionID, message)
if err != nil {
return err
}
for range events {
// Drain until the runner stops (ctx canceled or run completed).
}ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())
defer cancel()
events, err := r.Run(ctx, userID, sessionID, message)
if err != nil {
return err
}
go func() {
time.Sleep(2 * time.Second)
cancel()
}()
for range events {
// Keep draining until the channel is closed.
}requestID := "req-123"
events, err := r.Run(ctx, userID, sessionID, message,
agent.WithRequestID(requestID),
)
mr := r.(runner.ManagedRunner)
_ = mr.Cancel(requestID)For more details (including detached cancellation, resume, and server cancel
routes), see docs/mkdocs/en/runner.md and docs/mkdocs/en/agui.md.
The examples directory contains runnable demos covering every major feature.
- examples/agenttool – Wrap agents as callable tools.
- examples/multitools – Multiple tools orchestration.
- examples/duckduckgo – Web search tool integration.
- examples/filetoolset – File operations as tools.
- examples/fileinput – Provide files as inputs.
- examples/agenttool shows streaming and non-streaming patterns.
Example: examples/llmagent
- Wrap any chat-completion model as an
LLMAgent. - Configure system instructions, temperature, max tokens, etc.
- Receive incremental
event.Eventupdates while the model streams.
Example: examples/multiagent
- ChainAgent – linear pipeline of sub-agents.
- ParallelAgent – run sub-agents concurrently and merge results.
- CycleAgent – iterate until a termination condition is met.
Example: examples/graph
-
GraphAgent – demonstrates building and executing complex, conditional workflows using the
graphandagent/graphpackages. It shows how to construct a graph-based agent, manage state safely, implement conditional routing, and orchestrate execution with the Runner. -
Multi-conditional fan-out routing:
// Return multiple branch keys and run targets in parallel.
sg := graph.NewStateGraph(schema)
sg.AddNode("router", func(ctx context.Context, s graph.State) (any, error) {
return nil, nil
})
sg.AddNode("A", func(ctx context.Context, s graph.State) (any, error) {
return graph.State{"a": 1}, nil
})
sg.AddNode("B", func(ctx context.Context, s graph.State) (any, error) {
return graph.State{"b": 1}, nil
})
sg.SetEntryPoint("router")
sg.AddMultiConditionalEdges(
"router",
func(ctx context.Context, s graph.State) ([]string, error) {
return []string{"goA", "goB"}, nil
},
map[string]string{"goA": "A", "goB": "B"}, // Path map or ends map
)
sg.SetFinishPoint("A").SetFinishPoint("B")Example: examples/memory
- In‑memory and Redis memory services with CRUD, search and tool integration.
- How to configure, call tools and customize prompts.
Example: examples/knowledge
- Basic RAG example: load sources, embed to a vector store, and search.
- How to use conversation context and tune loading/concurrency options.
Example: examples/telemetry
- OpenTelemetry hooks across model, tool and runner layers.
- Export traces to OTLP endpoint for real-time analysis.
Example: examples/mcptool
- Wrapper utilities around trpc-mcp-go, an implementation of the Model Context Protocol (MCP).
- Provides structured prompts, tool calls, resource and session messages that follow the MCP specification.
- Enables dynamic tool execution and context-rich interactions between agents and LLMs.
Example: examples/agui
- Exposes a Runner through the AG-UI (Agent-User Interaction) protocol.
- Built-in Server-Sent Events (SSE) server, plus client samples (for example, CopilotKit and TDesign Chat).
Example: examples/evaluation
- Evaluate an agent with repeatable eval sets and pluggable metrics.
- Includes local file-backed runs and in-memory runs.
Example: examples/skillrun
- Skills are folders with a
SKILL.mdspec + optional docs/scripts. - Built-in tools:
skill_load,skill_list_docs,skill_select_docs,skill_run(runs commands in an isolated workspace). - Prefer using
skill_runonly for commands required by the selected skill docs, not for generic shell exploration.
Example: examples/artifact
- Save and retrieve versioned files (images, text, reports) produced by tools.
- Supports multiple backends (in-memory, S3, COS).
Example: examples/a2aadk
- Agent-to-Agent (A2A) interop with an ADK Python A2A server.
- Demonstrates streaming, tool calls, and code execution across runtimes.
Other notable examples:
- examples/humaninloop – Human in the loop.
- examples/codeexecution – Secure code execution.
See individual README.md files in each example folder for usage details.
Architecture
- Runner orchestrates the entire execution pipeline with session management
- Agent processes requests using multiple specialized components
- Planner determines the optimal strategy and tool selection
- Tools execute specific tasks (API calls, calculations, web searches)
- Memory maintains context and learns from interactions
- Knowledge provides RAG capabilities for document understanding
Key packages:
| Package | Responsibility |
|---|---|
agent |
Core execution unit, responsible for processing user input and generating responses. |
runner |
Agent executor, responsible for managing execution flow and connecting Session/Memory Service capabilities. |
model |
Supports multiple LLM models (OpenAI, DeepSeek, etc.). |
tool |
Provides various tool capabilities (Function, MCP, DuckDuckGo, etc.). |
session |
Manages user session state and events. |
memory |
Records user long-term memory and personalized information. |
knowledge |
Implements RAG knowledge retrieval capabilities. |
planner |
Provides Agent planning and reasoning capabilities. |
artifact |
Stores and retrieves versioned files produced by agents and tools (images, reports, etc.). |
skill |
Loads and executes reusable Agent Skills defined by SKILL.md. |
event |
Defines event types and streaming payloads used across Runner and servers. |
evaluation |
Evaluates agents on eval sets using pluggable metrics and stores results. |
server |
Exposes HTTP servers (AG-UI, A2A) for integration and UIs. |
telemetry |
OpenTelemetry tracing and metrics instrumentation. |
For most applications you do not need to implement the agent.Agent
interface yourself. The framework already ships with several ready-to-use
agents that you can compose like Lego bricks:
| Agent | Purpose |
|---|---|
LLMAgent |
Wraps an LLM chat-completion model as an agent. |
ChainAgent |
Executes sub-agents sequentially. |
ParallelAgent |
Executes sub-agents concurrently and merges output. |
CycleAgent |
Loops over a planner + executor until stop signal. |
// 1. Create a base LLM agent.
base := llmagent.New(
"assistant",
llmagent.WithModel(openai.New("gpt-4o-mini")),
)
// 2. Create a second LLM agent with a different instruction.
translator := llmagent.New(
"translator",
llmagent.WithInstruction("Translate everything to French"),
llmagent.WithModel(openai.New("gpt-3.5-turbo")),
)
// 3. Combine them in a chain.
pipeline := chainagent.New(
"pipeline",
chainagent.WithSubAgents([]agent.Agent{base, translator}),
)
// 4. Run through the runner for sessions & telemetry.
run := runner.NewRunner("demo-app", pipeline)
events, _ := run.Run(ctx, "user-1", "sess-1",
model.NewUserMessage("Hello!"))
for ev := range events { /* ... */ }The composition API lets you nest chains, cycles, or parallels to build complex workflows without low-level plumbing.
We love contributions! Join our growing community of developers building the future of AI agents.
- Report bugs or suggest features via Issues
- Improve documentation - help others learn faster
- Submit PRs - bug fixes, new features, or examples
- Share your use cases - inspire others with your agent applications
# Fork & clone the repo
git clone https://github.com/YOUR_USERNAME/trpc-agent-go.git
cd trpc-agent-go
# Run tests to ensure everything works
go test ./...
go vet ./...
# Make your changes and submit a PR!Please read CONTRIBUTING.md for detailed guidelines and coding standards.
Special thanks to Tencent's business units including Tencent Yuanbao, Tencent Video, Tencent News, IMA, and QQ Music for their invaluable support and real-world validation. Production usage drives framework excellence!
Inspired by amazing frameworks like ADK, Agno, CrewAI, AutoGen, and many others. Standing on the shoulders of giants!
Licensed under the Apache 2.0 License - see LICENSE file for details.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for trpc-agent-go
Similar Open Source Tools

trpc-agent-go
A powerful Go framework for building intelligent agent systems with large language models (LLMs), hierarchical planners, memory, telemetry, and a rich tool ecosystem. tRPC-Agent-Go enables the creation of autonomous or semi-autonomous agents that reason, call tools, collaborate with sub-agents, and maintain long-term state. The framework provides detailed documentation, examples, and tools for accelerating the development of AI applications.
agentfield
AgentField is an open-source control plane designed for autonomous AI agents, providing infrastructure for agents to make decisions beyond chatbots. It offers features like scaling infrastructure, routing & discovery, async execution, durable state, observability, trust infrastructure with cryptographic identity, verifiable credentials, and policy enforcement. Users can write agents in Python, Go, TypeScript, or interact via REST APIs. The tool enables the creation of AI backends that reason autonomously within defined boundaries, offering predictability and flexibility. AgentField aims to bridge the gap between AI frameworks and production-ready infrastructure for AI agents.
alphora
Alphora is a full-stack framework for building production AI agents, providing agent orchestration, prompt engineering, tool execution, memory management, streaming, and deployment with an async-first, OpenAI-compatible design. It offers features like agent derivation, reasoning-action loop, async streaming, visual debugger, OpenAI compatibility, multimodal support, tool system with zero-config tools and type safety, prompt engine with dynamic prompts, memory and storage management, sandbox for secure execution, deployment as API, and more. Alphora allows users to build sophisticated AI agents easily and efficiently.
GPTSwarm
GPTSwarm is a graph-based framework for LLM-based agents that enables the creation of LLM-based agents from graphs and facilitates the customized and automatic self-organization of agent swarms with self-improvement capabilities. The library includes components for domain-specific operations, graph-related functions, LLM backend selection, memory management, and optimization algorithms to enhance agent performance and swarm efficiency. Users can quickly run predefined swarms or utilize tools like the file analyzer. GPTSwarm supports local LM inference via LM Studio, allowing users to run with a local LLM model. The framework has been accepted by ICML2024 and offers advanced features for experimentation and customization.
quantalogic
QuantaLogic is a ReAct framework for building advanced AI agents that seamlessly integrates large language models with a robust tool system. It aims to bridge the gap between advanced AI models and practical implementation in business processes by enabling agents to understand, reason about, and execute complex tasks through natural language interaction. The framework includes features such as ReAct Framework, Universal LLM Support, Secure Tool System, Real-time Monitoring, Memory Management, and Enterprise Ready components.
code_puppy
Code Puppy is an AI-powered code generation agent designed to understand programming tasks, generate high-quality code, and explain its reasoning. It supports multi-language code generation, interactive CLI, and detailed code explanations. The tool requires Python 3.9+ and API keys for various models like GPT, Google's Gemini, Cerebras, and Claude. It also integrates with MCP servers for advanced features like code search and documentation lookups. Users can create custom JSON agents for specialized tasks and access a variety of tools for file management, code execution, and reasoning sharing.
mem0
Mem0 is a tool that provides a smart, self-improving memory layer for Large Language Models, enabling personalized AI experiences across applications. It offers persistent memory for users, sessions, and agents, self-improving personalization, a simple API for easy integration, and cross-platform consistency. Users can store memories, retrieve memories, search for related memories, update memories, get the history of a memory, and delete memories using Mem0. It is designed to enhance AI experiences by enabling long-term memory storage and retrieval.

agent-sdk-go
Agent Go SDK is a powerful Go framework for building production-ready AI agents that seamlessly integrates memory management, tool execution, multi-LLM support, and enterprise features into a flexible, extensible architecture. It offers core capabilities like multi-model intelligence, modular tool ecosystem, advanced memory management, and MCP integration. The SDK is enterprise-ready with built-in guardrails, complete observability, and support for enterprise multi-tenancy. It provides a structured task framework, declarative configuration, and zero-effort bootstrapping for development experience. The SDK supports environment variables for configuration and includes features like creating agents with YAML configuration, auto-generating agent configurations, using MCP servers with an agent, and CLI tool for headless usage.
LLMTSCS
LLMLight is a novel framework that employs Large Language Models (LLMs) as decision-making agents for Traffic Signal Control (TSC). The framework leverages the advanced generalization capabilities of LLMs to engage in a reasoning and decision-making process akin to human intuition for effective traffic control. LLMLight has been demonstrated to be remarkably effective, generalizable, and interpretable against various transportation-based and RL-based baselines on nine real-world and synthetic datasets.
logicstamp-context
LogicStamp Context is a static analyzer that extracts deterministic component contracts from TypeScript codebases, providing structured architectural context for AI coding assistants. It helps AI assistants understand architecture by extracting props, hooks, and dependencies without implementation noise. The tool works with React, Next.js, Vue, Express, and NestJS, and is compatible with various AI assistants like Claude, Cursor, and MCP agents. It offers features like watch mode for real-time updates, breaking change detection, and dependency graph creation. LogicStamp Context is a security-first tool that protects sensitive data, runs locally, and is non-opinionated about architectural decisions.
CyberStrikeAI
CyberStrikeAI is an AI-native security testing platform built in Go that integrates 100+ security tools, an intelligent orchestration engine, role-based testing with predefined security roles, a skills system with specialized testing skills, and comprehensive lifecycle management capabilities. It enables end-to-end automation from conversational commands to vulnerability discovery, attack-chain analysis, knowledge retrieval, and result visualization, delivering an auditable, traceable, and collaborative testing environment for security teams. The platform features an AI decision engine with OpenAI-compatible models, native MCP implementation with various transports, prebuilt tool recipes, large-result pagination, attack-chain graph, password-protected web UI, knowledge base with vector search, vulnerability management, batch task management, role-based testing, and skills system.
OpenMemory
OpenMemory is a cognitive memory engine for AI agents, providing real long-term memory capabilities beyond simple embeddings. It is self-hosted and supports Python + Node SDKs, with integrations for various tools like LangChain, CrewAI, AutoGen, and more. Users can ingest data from sources like GitHub, Notion, Google Drive, and others directly into memory. OpenMemory offers explainable traces for recalled information and supports multi-sector memory, temporal reasoning, decay engine, waypoint graph, and more. It aims to provide a true memory system rather than just a vector database with marketing copy, enabling users to build agents, copilots, journaling systems, and coding assistants that can remember and reason effectively.
ai-counsel
AI Counsel is a true deliberative consensus MCP server where AI models engage in actual debate, refine positions across multiple rounds, and converge with voting and confidence levels. It features two modes (quick and conference), mixed adapters (CLI tools and HTTP services), auto-convergence, structured voting, semantic grouping, model-controlled stopping, evidence-based deliberation, local model support, data privacy, context injection, semantic search, fault tolerance, and full transcripts. Users can run local and cloud models to deliberate on various questions, ground decisions in reality by querying code and files, and query past decisions for analysis. The tool is designed for critical technical decisions requiring multi-model deliberation and consensus building.
sdk-typescript
Strands Agents - TypeScript SDK is a lightweight and flexible SDK that takes a model-driven approach to building and running AI agents in TypeScript/JavaScript. It brings key features from the Python Strands framework to Node.js environments, enabling type-safe agent development for various applications. The SDK supports model agnostic development with first-class support for Amazon Bedrock and OpenAI, along with extensible architecture for custom providers. It also offers built-in MCP support, real-time response streaming, extensible hooks, and conversation management features. With tools for interaction with external systems and seamless integration with MCP servers, the SDK provides a comprehensive solution for developing AI agents.
BrowserAI
BrowserAI is a tool that allows users to run large language models (LLMs) directly in the browser, providing a simple, fast, and open-source solution. It prioritizes privacy by processing data locally, is cost-effective with no server costs, works offline after initial download, and offers WebGPU acceleration for high performance. It is developer-friendly with a simple API, supports multiple engines, and comes with pre-configured models for easy use. Ideal for web developers, companies needing privacy-conscious AI solutions, researchers experimenting with browser-based AI, and hobbyists exploring AI without infrastructure overhead.
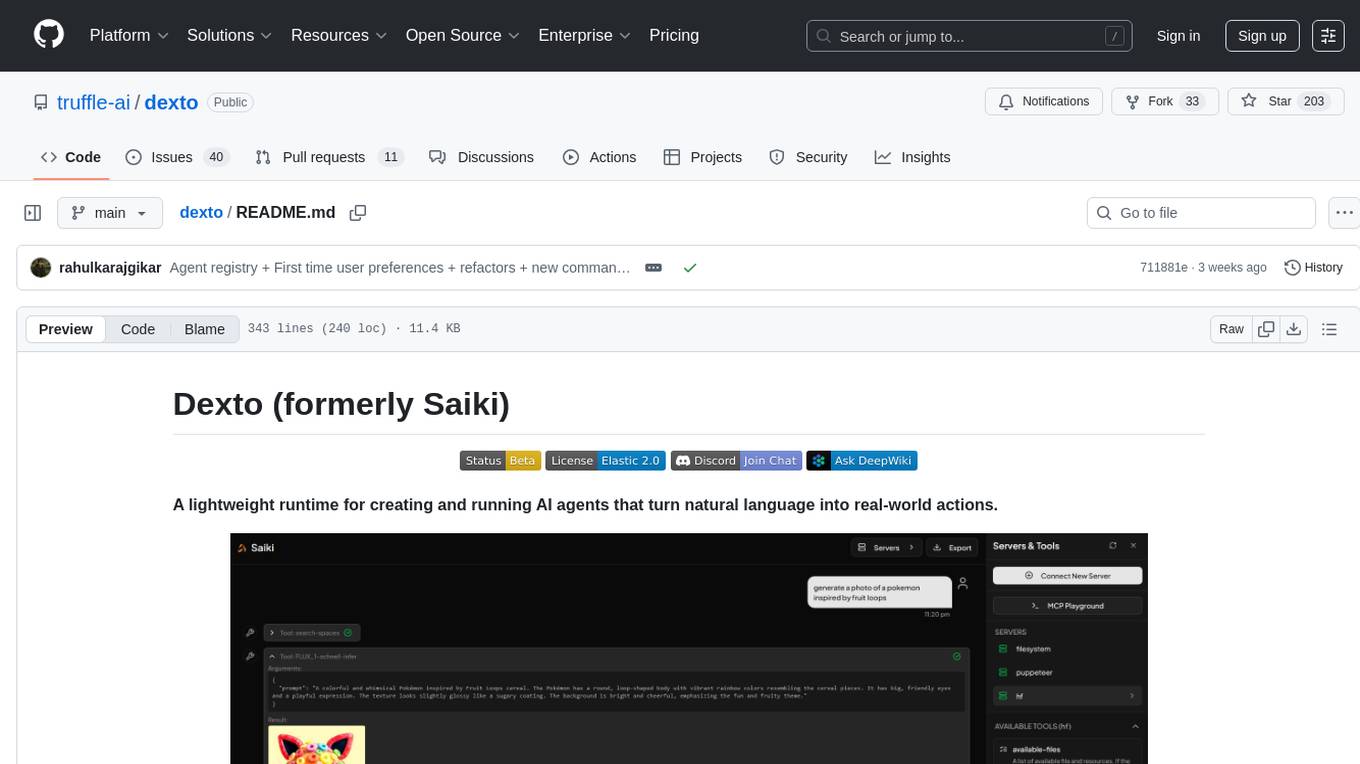
dexto
Dexto is a lightweight runtime for creating and running AI agents that turn natural language into real-world actions. It serves as the missing intelligence layer for building AI applications, standalone chatbots, or as the reasoning engine inside larger products. Dexto features a powerful CLI and Web UI for running AI agents, supports multiple interfaces, allows hot-swapping of LLMs from various providers, connects to remote tool servers via the Model Context Protocol, is config-driven with version-controlled YAML, offers production-ready core features, extensibility for custom services, and enables multi-agent collaboration via MCP and A2A.
For similar tasks

trpc-agent-go
A powerful Go framework for building intelligent agent systems with large language models (LLMs), hierarchical planners, memory, telemetry, and a rich tool ecosystem. tRPC-Agent-Go enables the creation of autonomous or semi-autonomous agents that reason, call tools, collaborate with sub-agents, and maintain long-term state. The framework provides detailed documentation, examples, and tools for accelerating the development of AI applications.
MiniAgents
MiniAgents is an open-source Python framework designed to simplify the creation of multi-agent AI systems. It offers a parallelism and async-first design, allowing users to focus on building intelligent agents while handling concurrency challenges. The framework, built on asyncio, supports LLM-based applications with immutable messages and seamless asynchronous token and message streaming between agents.
AutoAgents
AutoAgents is a cutting-edge multi-agent framework built in Rust that enables the creation of intelligent, autonomous agents powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) and Ractor. Designed for performance, safety, and scalability. AutoAgents provides a robust foundation for building complex AI systems that can reason, act, and collaborate. With AutoAgents you can create Cloud Native Agents, Edge Native Agents and Hybrid Models as well. It is so extensible that other ML Models can be used to create complex pipelines using Actor Framework.
hello-agents
Hello-Agents is a comprehensive tutorial on building intelligent agent systems, covering both theoretical foundations and practical applications. The tutorial aims to guide users in understanding and building AI-native agents, diving deep into core principles, architectures, and paradigms of intelligent agents. Users will learn to develop their own multi-agent applications from scratch, gaining hands-on experience with popular low-code platforms and agent frameworks. The tutorial also covers advanced topics such as memory systems, context engineering, communication protocols, and model training. By the end of the tutorial, users will have the skills to develop real-world projects like intelligent travel assistants and cyber towns.
EverMemOS
EverMemOS is an AI memory system that enables AI to not only remember past events but also understand the meaning behind memories and use them to guide decisions. It achieves 93% reasoning accuracy on the LoCoMo benchmark by providing long-term memory capabilities for conversational AI agents through structured extraction, intelligent retrieval, and progressive profile building. The tool is production-ready with support for Milvus vector DB, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, and Redis, and offers easy integration via a simple REST API. Users can store and retrieve memories using Python code and benefit from features like multi-modal memory storage, smart retrieval mechanisms, and advanced techniques for memory management.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.



