
DistillKit
An Open Source Toolkit For LLM Distillation
Stars: 104
DistillKit is an open-source research effort by Arcee.AI focusing on model distillation methods for Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides tools for improving model performance and efficiency through logit-based and hidden states-based distillation methods. The tool supports supervised fine-tuning and aims to enhance the adoption of open-source LLM distillation techniques.
README:
DistillKit is an open-source research effort in model distillation by Arcee.AI. Our goal is to provide the community with easy-to-use tools for researching, exploring, and enhancing the adoption of open-source Large Language Model (LLM) distillation methods. This release focuses on practical, effective techniques for improving model performance and efficiency.
- Logit-based Distillation (models must be the same architecture)
- Hidden States-based Distillation (models can be different architectures)
- Support for Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) - DPO and CPT to come at a later date.
For a quick and easy installation, you can use our setup script:
./setup.shIf you prefer to install dependencies manually, follow these steps:
-
Install basic requirements:
pip install torch wheel ninja packaging
-
Install Flash Attention:
pip install flash-attn
-
Install DeepSpeed:
pip install deepspeed
-
Install remaining requirements:
pip install -r requirements.txt
For simplicity, we've set the config settings directly within the training script. You can customize the configuration as follows:
config = {
"project_name": "distil-logits",
"dataset": {
"name": "mlabonne/FineTome-100k", # Only sharegpt format is currently supported.
"split": "train",
# "num_samples": , # You can pass a number here to limit the number of samples to use.
"seed": 42
},
"models": {
"teacher": "arcee-ai/Arcee-Spark",
"student": "Qwen/Qwen2-1.5B"
},
"tokenizer": {
"max_length": 4096,
"chat_template": "{% for message in messages %}{% if loop.first and messages[0]['role'] != 'system' %}{{ '<|im_start|>system\nYou are a helpful assistant.<|im_end|>\n' }}{% endif %}{{'<|im_start|>' + message['role'] + '\n' + message['content'] + '<|im_end|>' + '\n'}}{% endfor %}{% if add_generation_prompt %}{{ '<|im_start|>assistant\n' }}{% endif %}"
},
"training": {
"output_dir": "./results",
"num_train_epochs": 3,
"per_device_train_batch_size": 1,
"gradient_accumulation_steps": 8,
"save_steps": 1000,
"logging_steps": 1,
"learning_rate": 2e-5,
"weight_decay": 0.05,
"warmup_ratio": 0.1,
"lr_scheduler_type": "cosine",
"resume_from_checkpoint": None, # Set to a path or True to resume from the latest checkpoint
"fp16": False,
"bf16": True
},
"distillation": {
"temperature": 2.0,
"alpha": 0.5
},
"model_config": {
"use_flash_attention": True
}
# "spectrum": {
# "layers_to_unfreeze": "/workspace/spectrum/snr_results_Qwen-Qwen2-1.5B_unfrozenparameters_50percent.yaml" # You can pass a spectrum yaml file here to freeze layers identified by spectrum.
# }
}If you want to use a chat template other than chatml, copy it from the model's tokenizer_config.json, and replace the current chat_template entry in the configuration.
You can use Spectrum to increase speed (but not memory overhead). To enable Spectrum, uncomment the "spectrum" section in the configuration and provide the path to your Spectrum YAML file. Please note that further evaluations with Spectrum are TBD.
To launch DistillKit, use the following command:
accelerate launch distil_logits.pyYou can replace distil_logits.py with whichever script you want to use.
If you wish to use DeepSpeed, Fully Sharded Data Parallel (FSDP), or Megatron sharding, you can set up your configuration using:
accelerate configFollow the prompts to configure your desired setup.
We provide sample DeepSpeed configuration files in the ./deepspeed_configs directory. These configurations are shamelessly stolen from the Axolotl (thanks to Wing Lian and the Axolotl team for their excellent work!).
To use a specific DeepSpeed configuration, you can specify it in your accelerate config.
DistillKit supports two primary distillation methods:
-
Logit-based Distillation: This method transfers knowledge from a larger teacher model to a smaller student model by using both hard targets (actual labels) and soft targets (teacher logits). The soft target loss, computed using Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence, encourages the student to mimic the teacher's output distribution. This method enhances the student model's generalization and efficiency while maintaining performance closer to the teacher model.
-
Hidden States-based Distillation: This method involves transferring knowledge by aligning the intermediate layer representations of the student model with those of the teacher model. This process enhances the student's learning by providing richer, layer-wise guidance, improving its performance and generalization. This method allows for cross-architecture distillation, providing flexibility in model architecture choices.
While the implementation of DistillKit is relatively straightforward, the memory requirements for distillation are higher compared to standard SFT. We are actively working on scaling DistillKit to support models larger than 70B parameters, which will involve advanced techniques and efficiency improvements.
Our experiments have shown promising results in both general-purpose and domain-specific tasks. Key findings include:
- Both logit-based and hidden states-based distillation methods show improvements over standard SFT across most benchmarks.
- Significant performance gains were observed when distilling models for domain-specific tasks.
- Using the same training dataset for distillation as was used for the teacher model can lead to higher performance gains.
For detailed results and analysis, please refer to our case studies and experimental here.
This release marks the debut of Arcee-Labs, a division of Arcee.ai dedicated to accelerating open-source research. Our mission is to rapidly deploy resources, models, and research findings to empower both Arcee and the wider community. In an era of increasingly frequent breakthroughs in LLM research, models, and techniques, we recognize the need for agility and adaptability. Through our efforts, we strive to significantly contribute to the advancement of open-source AI technology and support the community in keeping pace with these rapid developments.
We are excited to see how the community will use and improve DistillKit. Future releases will include Continued Pre-Training (CPT) and Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) distillation methods. We welcome community contributions in the form of new distillation methods, training routine improvements, and memory optimizations.
We welcome contributions from the community! If you have ideas for improvements, new features, or bug fixes, please feel free to open an issue or submit a pull request.
For more information about Arcee.AI and our training platform, visit our website at https://arcee.ai.
For technical questions or support, please open an issue in this repository.
While our work is ultimately quite different - this project was inspired by Towards Cross-Tokenizer Distillation: the Universal Logit Distillation Loss for LLMs. We thank the authors for their efforts and contributions. We would like to thank the open-source community and all at arcee.ai who have helped make DistillKit possible. We're just getting started.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for DistillKit
Similar Open Source Tools

DistillKit
DistillKit is an open-source research effort by Arcee.AI focusing on model distillation methods for Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides tools for improving model performance and efficiency through logit-based and hidden states-based distillation methods. The tool supports supervised fine-tuning and aims to enhance the adoption of open-source LLM distillation techniques.

DeepFabric
Deepfabric is an SDK and CLI tool that leverages large language models to generate high-quality synthetic datasets. It's designed for researchers and developers building teacher-student distillation pipelines, creating evaluation benchmarks for models and agents, or conducting research requiring diverse training data. The key innovation lies in Deepfabric's graph and tree-based architecture, which uses structured topic nodes as generation seeds. This approach ensures the creation of datasets that are both highly diverse and domain-specific, while minimizing redundancy and duplication across generated samples.
LongBench
LongBench v2 is a benchmark designed to assess the ability of large language models (LLMs) to handle long-context problems requiring deep understanding and reasoning across various real-world multitasks. It consists of 503 challenging multiple-choice questions with contexts ranging from 8k to 2M words, covering six major task categories. The dataset is collected from nearly 100 highly educated individuals with diverse professional backgrounds and is designed to be challenging even for human experts. The evaluation results highlight the importance of enhanced reasoning ability and scaling inference-time compute to tackle the long-context challenges in LongBench v2.
kafka-ml
Kafka-ML is a framework designed to manage the pipeline of Tensorflow/Keras and PyTorch machine learning models on Kubernetes. It enables the design, training, and inference of ML models with datasets fed through Apache Kafka, connecting them directly to data streams like those from IoT devices. The Web UI allows easy definition of ML models without external libraries, catering to both experts and non-experts in ML/AI.
llms
The 'llms' repository is a comprehensive guide on Large Language Models (LLMs), covering topics such as language modeling, applications of LLMs, statistical language modeling, neural language models, conditional language models, evaluation methods, transformer-based language models, practical LLMs like GPT and BERT, prompt engineering, fine-tuning LLMs, retrieval augmented generation, AI agents, and LLMs for computer vision. The repository provides detailed explanations, examples, and tools for working with LLMs.
SwiftSage
SwiftSage is a tool designed for conducting experiments in the field of machine learning and artificial intelligence. It provides a platform for researchers and developers to implement and test various algorithms and models. The tool is particularly useful for exploring new ideas and conducting experiments in a controlled environment. SwiftSage aims to streamline the process of developing and testing machine learning models, making it easier for users to iterate on their ideas and achieve better results. With its user-friendly interface and powerful features, SwiftSage is a valuable tool for anyone working in the field of AI and ML.
PromptAgent
PromptAgent is a repository for a novel automatic prompt optimization method that crafts expert-level prompts using language models. It provides a principled framework for prompt optimization by unifying prompt sampling and rewarding using MCTS algorithm. The tool supports different models like openai, palm, and huggingface models. Users can run PromptAgent to optimize prompts for specific tasks by strategically sampling model errors, generating error feedbacks, simulating future rewards, and searching for high-reward paths leading to expert prompts.
RLHF-Reward-Modeling
This repository contains code for training reward models for Deep Reinforcement Learning-based Reward-modulated Hierarchical Fine-tuning (DRL-based RLHF), Iterative Selection Fine-tuning (Rejection sampling fine-tuning), and iterative Decision Policy Optimization (DPO). The reward models are trained using a Bradley-Terry model based on the Gemma and Mistral language models. The resulting reward models achieve state-of-the-art performance on the RewardBench leaderboard for reward models with base models of up to 13B parameters.
Open-Prompt-Injection
OpenPromptInjection is an open-source toolkit for attacks and defenses in LLM-integrated applications, enabling easy implementation, evaluation, and extension of attacks, defenses, and LLMs. It supports various attack and defense strategies, including prompt injection, paraphrasing, retokenization, data prompt isolation, instructional prevention, sandwich prevention, perplexity-based detection, LLM-based detection, response-based detection, and know-answer detection. Users can create models, tasks, and apps to evaluate different scenarios. The toolkit currently supports PaLM2 and provides a demo for querying models with prompts. Users can also evaluate ASV for different scenarios by injecting tasks and querying models with attacked data prompts.
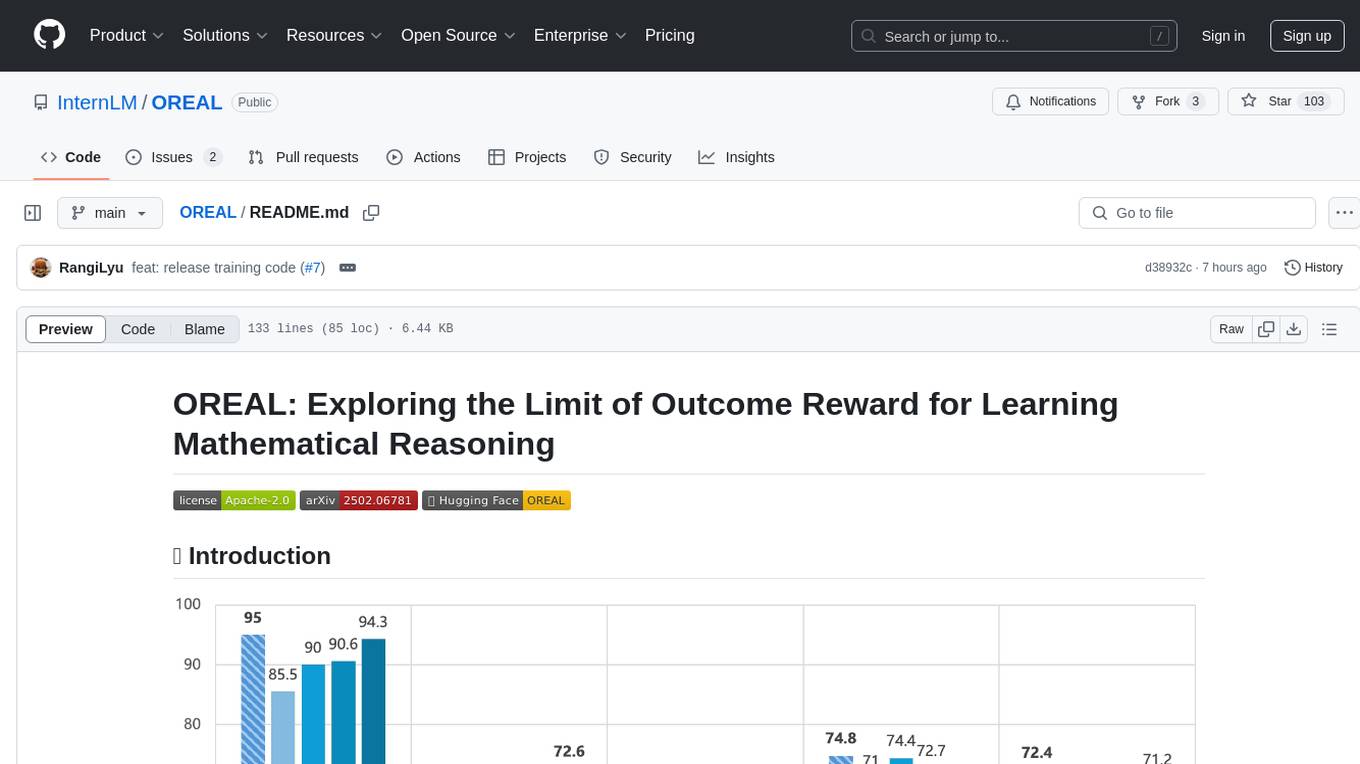
OREAL
OREAL is a reinforcement learning framework designed for mathematical reasoning tasks, aiming to achieve optimal performance through outcome reward-based learning. The framework utilizes behavior cloning, reshaping rewards, and token-level reward models to address challenges in sparse rewards and partial correctness. OREAL has achieved significant results, with a 7B model reaching 94.0 pass@1 accuracy on MATH-500 and surpassing previous 32B models. The tool provides training tutorials and Hugging Face model repositories for easy access and implementation.
Woodpecker
Woodpecker is a tool designed to correct hallucinations in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) by introducing a training-free method that picks out and corrects inconsistencies between generated text and image content. It consists of five stages: key concept extraction, question formulation, visual knowledge validation, visual claim generation, and hallucination correction. Woodpecker can be easily integrated with different MLLMs and provides interpretable results by accessing intermediate outputs of the stages. The tool has shown significant improvements in accuracy over baseline models like MiniGPT-4 and mPLUG-Owl.
aligner
Aligner is a model-agnostic alignment tool designed to efficiently correct responses from large language models. It redistributes initial answers to align with human intentions, improving performance across various LLMs. The tool can be applied with minimal training, enhancing upstream models and reducing hallucination. Aligner's 'copy and correct' method preserves the base structure while enhancing responses. It achieves significant performance improvements in helpfulness, harmlessness, and honesty dimensions, with notable success in boosting Win Rates on evaluation leaderboards.
storm
STORM is a LLM system that writes Wikipedia-like articles from scratch based on Internet search. While the system cannot produce publication-ready articles that often require a significant number of edits, experienced Wikipedia editors have found it helpful in their pre-writing stage. **Try out our [live research preview](https://storm.genie.stanford.edu/) to see how STORM can help your knowledge exploration journey and please provide feedback to help us improve the system 🙏!**
Aidan-Bench
Aidan Bench is a tool that rewards creativity, reliability, contextual attention, and instruction following. It is weakly correlated with Lmsys, has no score ceiling, and aligns with real-world open-ended use. The tool involves giving LLMs open-ended questions and evaluating their answers based on novelty scores. Users can set up the tool by installing required libraries and setting up API keys. The project allows users to run benchmarks for different models and provides flexibility in threading options.
artkit
ARTKIT is a Python framework developed by BCG X for automating prompt-based testing and evaluation of Gen AI applications. It allows users to develop automated end-to-end testing and evaluation pipelines for Gen AI systems, supporting multi-turn conversations and various testing scenarios like Q&A accuracy, brand values, equitability, safety, and security. The framework provides a simple API, asynchronous processing, caching, model agnostic support, end-to-end pipelines, multi-turn conversations, robust data flows, and visualizations. ARTKIT is designed for customization by data scientists and engineers to enhance human-in-the-loop testing and evaluation, emphasizing the importance of tailored testing for each Gen AI use case.
AIW
AIW is a code base for experiments and raw data related to Alice in Wonderland, showcasing complete reasoning breakdown in state-of-the-art large language models. Users can collect experiments data using LiteLLM and TogetherAI, and plot the data using provided scripts. The tool allows for executing experiments over LiteLLM and lmsys, with options for different prompt types and AIW variations. The project also includes acknowledgments and a citation for reference.
For similar tasks

DistillKit
DistillKit is an open-source research effort by Arcee.AI focusing on model distillation methods for Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides tools for improving model performance and efficiency through logit-based and hidden states-based distillation methods. The tool supports supervised fine-tuning and aims to enhance the adoption of open-source LLM distillation techniques.

mindsdb
MindsDB is a platform for customizing AI from enterprise data. You can create, serve, and fine-tune models in real-time from your database, vector store, and application data. MindsDB "enhances" SQL syntax with AI capabilities to make it accessible for developers worldwide. With MindsDB’s nearly 200 integrations, any developer can create AI customized for their purpose, faster and more securely. Their AI systems will constantly improve themselves — using companies’ own data, in real-time.
training-operator
Kubeflow Training Operator is a Kubernetes-native project for fine-tuning and scalable distributed training of machine learning (ML) models created with various ML frameworks such as PyTorch, Tensorflow, XGBoost, MPI, Paddle and others. Training Operator allows you to use Kubernetes workloads to effectively train your large models via Kubernetes Custom Resources APIs or using Training Operator Python SDK. > Note: Before v1.2 release, Kubeflow Training Operator only supports TFJob on Kubernetes. * For a complete reference of the custom resource definitions, please refer to the API Definition. * TensorFlow API Definition * PyTorch API Definition * Apache MXNet API Definition * XGBoost API Definition * MPI API Definition * PaddlePaddle API Definition * For details of all-in-one operator design, please refer to the All-in-one Kubeflow Training Operator * For details on its observability, please refer to the monitoring design doc.
helix
HelixML is a private GenAI platform that allows users to deploy the best of open AI in their own data center or VPC while retaining complete data security and control. It includes support for fine-tuning models with drag-and-drop functionality. HelixML brings the best of open source AI to businesses in an ergonomic and scalable way, optimizing the tradeoff between GPU memory and latency.
nntrainer
NNtrainer is a software framework for training neural network models on devices with limited resources. It enables on-device fine-tuning of neural networks using user data for personalization. NNtrainer supports various machine learning algorithms and provides examples for tasks such as few-shot learning, ResNet, VGG, and product rating. It is optimized for embedded devices and utilizes CBLAS and CUBLAS for accelerated calculations. NNtrainer is open source and released under the Apache License version 2.0.

petals
Petals is a tool that allows users to run large language models at home in a BitTorrent-style manner. It enables fine-tuning and inference up to 10x faster than offloading. Users can generate text with distributed models like Llama 2, Falcon, and BLOOM, and fine-tune them for specific tasks directly from their desktop computer or Google Colab. Petals is a community-run system that relies on people sharing their GPUs to increase its capacity and offer a distributed network for hosting model layers.
LLaVA-pp
This repository, LLaVA++, extends the visual capabilities of the LLaVA 1.5 model by incorporating the latest LLMs, Phi-3 Mini Instruct 3.8B, and LLaMA-3 Instruct 8B. It provides various models for instruction-following LMMS and academic-task-oriented datasets, along with training scripts for Phi-3-V and LLaMA-3-V. The repository also includes installation instructions and acknowledgments to related open-source contributions.

KULLM
KULLM (구름) is a Korean Large Language Model developed by Korea University NLP & AI Lab and HIAI Research Institute. It is based on the upstage/SOLAR-10.7B-v1.0 model and has been fine-tuned for instruction. The model has been trained on 8×A100 GPUs and is capable of generating responses in Korean language. KULLM exhibits hallucination and repetition phenomena due to its decoding strategy. Users should be cautious as the model may produce inaccurate or harmful results. Performance may vary in benchmarks without a fixed system prompt.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.