
Tools4AI
Agentic Framework for Java, written in 100% Java using Gemini, OpenAI, LocalAI, Anthropic. Build Autonomous Agents in Java with Multi AI voting mechanism. Convert Prompt to HTTP REST Calls, Java Method calls, Shell script calls or swagger rest api calls. Selenium AI Integration, Image processing with AI, Actions on Images with AI
Stars: 106
Tools4AI is a Java-based Agentic Framework for building AI agents to integrate with enterprise Java applications. It enables the conversion of natural language prompts into actionable behaviors, streamlining user interactions with complex systems. By leveraging AI capabilities, it enhances productivity and innovation across diverse applications. The framework allows for seamless integration of AI with various systems, such as customer service applications, to interpret user requests, trigger actions, and streamline workflows. Prompt prediction anticipates user actions based on input prompts, enhancing user experience by proactively suggesting relevant actions or services based on context.
README:
- Rapid Start
- Tools4AI
- SetUp
- Reference Examples
- Prediction Loaders
- Response Validation
- Autonomous Agent
🧱 Do you want to start building ASAP , Look at Rapid start here https://github.com/vishalmysore/simplelam
🌱 Integration of Spring Controller and AI Actions - https://github.com/vishalmysore/SpringActions
👉 Live Demo - https://huggingface.co/spaces/VishalMysore/EnterpriseAIHub
Tools4AI is 100% Java based Agentic Framework which can be used to build Java based AI agents for integration with enterprise
Java applications.
This project illustrates the integration of AI Agents with enterprise tools or external tools, converting natural language prompts
into agent actions. These prompts can be called "actionble prompts"
or "agent prompts" By leveraging AI capabilities, it streamlines user interactions
with complex systems, enhancing productivity and innovation across diverse applications.
For example , we can integrate AI Agent with a customer service application. Users can interact with the AI agent by asking questions or making requests in natural language. For example, a user might ask,"Schedule a maintenance appointment for my car." The AI agent interprets the request, extracts relevant information such as the service required and preferred date, and then triggers the appropriate agent action in the customer service application to schedule the appointment. This seamless integration streamlines the process for users and enhances the efficiency of the customer service workflow through agentic ai automation.
| Prompt | Action |
|---|---|
| Create a new task for the marketing campaign. | The AI agent interprets the request and generates a new task entry within the project management tool dedicated to the marketing campaign, assigning it relevant details such as priority level, due date, and task description. |
| Generate a sales report for the previous quarter. | The AI agent accesses data from the company's sales database, analyzes the information for the previous quarter, and generates a comprehensive sales report, which is then delivered to the user or stored in the appropriate location for access. |
| Check the inventory status of product X. | The AI agent retrieves real-time inventory data for product X from the inventory management system and provides the user with information regarding current stock levels, including quantities available, locations, and any pending orders. |
| Schedule a video conference with the engineering team for next Monday at 10 AM. | The AI agent interfaces with the calendar and scheduling tool, creates a new event titled "Engineering Team Video Conference" for the specified date and time, and sends out meeting invitations to all members of the engineering team. |
| Submit a reimbursement request for the business trip expenses. | The AI agent guides the user through the reimbursement request process, collecting necessary details such as expense receipts, dates, amounts, and purpose of expenditure. Once compiled, the system submits the reimbursement request to the appropriate department for processing. |
Prompt prediction is a technique used to anticipate user actions based on their input prompts. For instance, if a user's prompt is "my car broke down," in addition to the action "bookTaxi," the AI agent can predict a set of subsequent actions such as "bookCarService" and "orderFood" (if it's dinner time). This predictive capability enhances the user experience by proactively suggesting relevant actions or services based on the context provided in the prompt.
Download source and build from scratch
mvn clean install
if you are using Intellij or eclipse make sure you set -parameters option for compiler
Or use as maven dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.vishalmysore</groupId>
<artifactId>tools4ai</artifactId>
<version>0.9.6</version>
</dependency>
check for latest version here https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/io/github/vishalmysore/tools4ai/
Make sure you have gcloud project set up and have enabled vertex API
String projectId = "cookgptserver" // this can be any server name you create in your GCloud
String location = "us-central1";
String modelName = "gemini-1.0-pro";
You have to mention your project id from Gcloud
If you plan to use OpenAI instead of Gemini you will need OpenAI api key Instructions here https://help.openai.com/en/articles/4936850-where-do-i-find-my-openai-api-key
If you plan to use Anthropic you will need anthropic api key https://docs.anthropic.com/claude/reference/getting-started-with-the-api
OpenAI
Gemini
Anthropic
Gemini1.5Pro
Fastest way to create agent action is by writing a java class with @Agent annotation and annotate its method with @Action
annotation.
@Agent Annotation: This is a class level annotation. It means this class is an AI agent. Methods in this class annotated with @Action will be added to the prediction list of actions. Methods which are not annoated with @Action will not be added to the prediction list.
(@Agent is the new name for @Predict since version 1.0.5)
@Action Annotation: This is a method level annotation. The action method within the Java class is annotated with @Action to specify the action's behaviour this is the actual method which will be triggered if the prompt matches by AI. You can have as many methods as you want with @Action annotation in the class.
Method Execution: When a prompt like "My friend's name is Vishal, I don’t know what to cook for him today."
is processed, the whatFoodDoesThisPersonLike method is automatically called with "Vishal" as the argument,
and it returns "Paneer Butter Masala" as Vishal's preference.
@Agent
public class SimpleAction {
@Action( description = "what is the food preference of this person")
public String whatFoodDoesThisPersonLike(String name) {
if("vishal".equalsIgnoreCase(name))
return "Paneer Butter Masala";
else if ("vinod".equalsIgnoreCase(name)) {
return "aloo kofta";
}else
return "something yummy";
}
}
This class can contain any number of methods both public or private. All the methods with @Action annotation
in this class are going be added to the prediction list. In this case it is just whatFoodDoesThisPersonLike.
This method can contain any number of parameters (Objects, Pojos, Arrays etc) and can be of have any return value, everythign will
be mapped at runtime using prompt. @Action annotation also takes additional values for ActionRisk and Description.
When you send a prompt to action processor (OpenAIActionProcessor, GeminiActionProcessor or AnthoripicActionProcessor)
String cookPromptSingleText = "My friends name is Vishal ," +
"I dont know what to cook for him today.";
OpenAiActionProcessor tra = new OpenAiActionProcessor();
String functionResponse = (String)tra.processSingleAction(cookPromptSingleText);
//functionResponse will be Paneer Butter Masala
String aiResponse = tra.query(cookPromptSingleText,functionResponse);
//aiResponse will be well forumulated response something like "Hey looks like your friend likes Panner Butter Masala
The above action will be called with name = Vishal automatically based on the action name and prompt type.
AI will figure out that this is the correct action to call. You can also add grouping information in Predict annotation to
make it even more targeted. You don't have to specify the Action explicitly if its not a High Risk action
Convert prompt to Pojo
You can convert any Prompt into a Java Pojo object. Your pojo can be simple or complex , it can have arrays, list maps and other pojos and they all will be mapped based on the prompt
OpenAIPromptTransformer tra = new OpenAIPromptTransformer();
String promptText = "Mhahrukh Khan works for MovieHits inc and his salary is $ 100 he joined Toronto on
Labor day, his tasks are acting and dancing. He also works out of Montreal and Bombay. Krithik roshan is
another employee of same company based in Chennai his taks are jumping and Gym he joined on Indian Independce
Day";
Organization org = (Organization) tra.transformIntoPojo(promptText, Organization.class.getName(),"","");
Assertions.assertTrue(org.getEm().get(0).getName().contains("Mhahrukh"));
Assertions.assertTrue(org.getEm().get(1).getName().contains("Krithik"));
The above code will map the prompt and convert into Organization Pojo object
Trigger Action
Trigger action based on prompt, in case its MyDiary action MyDiaryAction
OpenAiActionProcessor tra = new OpenAiActionProcessor();
String promptText = "I have dentist appointment on 3rd July, then i have Gym appointment on 7th August
and I am meeting famous Bollywood actor Shahrukh Khan on 19 Sep. My friends Rahul, Dhawal, Aravind are
coming with me. My employee Jhonny Napper is comign with me he joined on Indian Independce day.
My customer name is Sumitabh Bacchan he wants to learn acting form me he joined on labor day";
MyDiaryAction action = new MyDiaryAction();
MyDiary dict = (MyDiary) tra.processSingleAction(promptText,action);
log.info(dict.toString());
If you do not specify any action then it will be predicted based on prompt and groups for example
MyDiary dict = (MyDiary) tra.processSingleAction(promptText)
As you can notice we are not passing any action with the prompt the AI will figure out the action correctly
A simple Java action can be written like this
@Agent(groupName = "buildMyDiary" , groupDescription = "This is my diary details")
public class MyDiaryAction implements JavaMethodAction {
@Action
public MyDiary buildMyDiary(MyDiary diary) {
//take whatever action you want to take
return diary;
}
}
Here the actionName is buildMyDiary, MyDiary pojo will be created automatically based on prompt
Action groups
@Agent(groupName = "personal", groupDescription = "all personal actions are here")
Actions have to be annontated with @Agent to be added to prediction list , they can be grouped together with the groupName.
Custom Pojo
There are different annontations which be used for special Pojo mapping
Mapping list
@ListType(Employee.class)
List<Employee> em;
@ListType(String.class)
List<String> locations;
Mapping Maps in objects
@Agent(actionName = "addSports",description = "add new Sports into the map")
public class MapAction implements JavaMethodAction {
public Map<Integer,String> addSports(@MapKeyType(Integer.class) @MapValueType(String.class) Map<Integer,String> mapOfSportsName) {
return mapOfSportsName;
}
}
Special Instructions
@Prompt(describe = "convert this to Hindi")
private String reasonForCalling;
The above instruction will fetch the reason for calling from the user prompt and convert it into Hindi and put
it inside the reasonForCalling String
Ignore Field
@Prompt(ignore = true)
private String location;
If you do not want to populate a field you can annotate it as ignore
Format Date
@Prompt(dateFormat = "yyyy-MM-dd" ,describe = "if you dont find date provide todays date in fieldValue")
private Date dateJoined;
The above will fetch the dateJoined from the prompt and convert it into the format. So if your prompt is "Book my dinner reservation on Indian Independence day" , the dateJoined will be 2024-08-15
Muliple Special Prompts
public class MyTranslatePojo {
@Prompt(describe = "translate to Hindi")
String answerInHindi;
@Prompt(describe = "translate to Punjabi")
String answerInPunJabi;
@Prompt(describe = "translate to Tamil")
String answerInTamil;
}
The above Pojo can be used to translate the prompt in multiple language and populate the result in variables
OpenAIPromptTransformer tra = new OpenAIPromptTransformer();
String promptTxt = "paneer is so good";
MyTranslatePojo myp = (MyTranslatePojo)tra.transformIntoPojo(promptTxt,MyTranslatePojo.class.getName());
System.out.println(myp);
Result will look something like this
MyTranslatePojo(answerInHindi=पनीर इतना अच्छा है, answerInPunJabi=ਪਨੀਰ ਬਹੁਤ ਵਧੀਆ ਹੈ, answerInTamil=பனீர் எப்படி நல்லது)
High Risk Actions
There might be some actions which you do not want to be triggered automatically but passed explicitly in the processor
such actions can be annotated with HighRisk
@Agent(actionName = "restartTheECOMServer",description = "will be used to restart the server" ,
riskLevel = ActionRisk.HIGH, groupName = "customer support",
groupDescription = "actions related to customer support")
public class ServerRestartAction implements JavaMethodAction {
public String restartTheECOMServer(String reasonForRestart, String requestedBy) {
return " Server has been restarted by "+requestedBy+" due to following reason "+reasonForRestart;
}
}
The above action is marked as High Risk action so if you try to call it with simple prompt
OpenAiActionProcessor processor = new OpenAiActionProcessor()
String restartPrompt = "Hey I am Vishal , restart the server as its very slow ";
String functionResponse = (String)processor.processSingleAction("restartPrompt");
It will not be triggered even though the AI will correct identify which action to trigger still it will get blocked.
You will have to call it explicitly this way
OpenAiActionProcessor processor = new OpenAiActionProcessor()
String restartPrompt = "Hey I am Vishal , restart the server as its very slow ";
ServerRestartAction restartAction = new ServerRestartAction();
String functionResponse = (String)processor.processSingleAction("restartPrompt", restartAction);
Any application exposing HTTP REST API can be converted into actions for example here is my sample swagger_actions.json. All the REST calls such as get, post, put, delete will be mapped to actions and based on the prompts they can be triggered automatically
{
"endpoints" : [
{
"swaggerurl": "https://fakerestapi.azurewebsites.net/swagger/v1/swagger.json",
"group": "Books Author Activity",
"description": "This is for all the actions related books , Authors, photos and users trying to read books and view photos",
"baseurl": "https://fakerestapi.azurewebsites.net/",
"id": "fakerestapi"
},
{
"swaggerurl": "https://petstore3.swagger.io/api/v3/openapi.json",
"baseurl": "https://petstore3.swagger.io/",
"group": "Petstore API",
"description": "This is for all the actions related to pets",
"id": "petstore"
} ,
{
"swaggerurl": "https://vishalmysore-instaservice.hf.space/v3/api-docs",
"baseurl": "https://vishalmysore-instaservice.hf.space/",
"group": "Enterprise Support and Tickeing System",
"description": "This action is to create tickets track bugs across the enterprise",
"id": "InstaService"
}
]
}
Books related api are put in a group called Books Author Activity group, similarly Petstore API is group for all the rest calls exposed by Petstore app if you provide a prompt "create a ticket for me with number 1 and issue is compture not working" it will automatically create a ticket on InstaService you can view the logs here https://huggingface.co/spaces/VishalMysore/InstaService?logs=container
@Test
public void testHttpActionOpenAI() throws AIProcessingException, IOException {
OpenAiActionProcessor processor = new OpenAiActionProcessor();
String postABook = "post a book harry poster with id 189 the publish date is 2024-03-22 and the description
is about harry who likes poster its around 500 pages ";
String result = (String)processor.processSingleAction(postABook);
Assertions.assertNotNull(result);
String success = TestHelperOpenAI.getInstance().sendMessage("Look at this message - "+result+" -
was it a success? - Reply in true or false only");
log.debug(success);
Assertions.assertTrue("True".equalsIgnoreCase(success));
}
This will automatically trigger HTTP post call with correct parameters
Read the complete link on how this has been deployed here
Any kind of script can be coverted into Action for function calling by configuring the script in shell_actions.yml
groups:
- name: Employee Actions
description : This is actions for all the new employees
scripts:
- scriptName: "test_script.cmd"
actionName: saveEmployeeInformation
parameters: employeeName,employeeLocation
description: This is a command which will save employee information
Here we are creating a group called Employee Actions and adding an action called saveEmployeeInformation into the group. The parameters it takes are employeeName and employeeLocation
Calling and actionprocessor with these kinds of prompt will trigger this Action
OpenAiActionProcessor tra = new OpenAiActionProcessor();
String promptText = "A new employee joined today in Toronto. Her name is Madhuri Khanna";
tra.processSingleAction(promptText);
As You can notice we are not passing the action explicitly , it will be predicted by the AI at runtime and triggered.
If you do not have swagger URL and would like to configure HTTP rest end points it can be done via Custom HTTP Actions by configuring them in http_actions.json
{
"endpoints": [
{
"actionName": "getUserDetails",
"description" : " this will fetch User details from the user inventory corporate application",
"url": "https://api.example.com/users/",
"type": "GET",
"input_object": [
{
"name": "userId",
"type": "path_parameter",
"description": "User ID"
}
],
"output_object": {
"type": "json",
"description": "User object"
},
"auth_interface": {
"type": "Bearer Token",
"description": "Authentication token required"
}
},
{
"actionName": "somethingNotVeryUseful",
"url": "https://api.example.com/temperature",
"description" : " this will get real time temperature from the weather api",
"type": "GET",
"input_object":[
{
"name": "locationId",
"type": "query_parameter",
"description": "Location ID"
}
],
"output_object": {
"type": "json",
"description": "Real-time temperature data"
},
"auth_interface": {
"type": "API Key",
"description": "API key required"
}
}
]
}
Tools4AI uses Gemini (gemini-1.0-pro-vision) to enhance AI capabilities by enabling the system to analyze images and automatically execute relevant actions based on the visual data it processes. This development is particularly crucial in emergency management, where speed and accuracy of response can save lives and property.
Reference code is here
Detailed article on the same is avaiable here
package org.example.image;
import com.t4a.processor.AIProcessingException;
import com.t4a.processor.GeminiImageActionProcessor;
import com.t4a.processor.GeminiV2ActionProcessor;
public class ImageActionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws AIProcessingException {
GeminiImageActionProcessor processor = new GeminiImageActionProcessor();
String imageDisription = processor.imageToText(args[0]);
GeminiV2ActionProcessor actionProcessor = new GeminiV2ActionProcessor();
Object obj = actionProcessor.processSingleAction(imageDisription);
String str = actionProcessor.summarize(imageDisription+obj.toString());
System.out.println(str);
}
}
If you execute the ImageActionExample with above image as source it correctly identifies that we need to call Ambulance
The image depicts a car accident involving a blue car and a red car on a city street. The blue car has front-end damage while the red car has rear-end damage. Debris from the accident is scattered on the street and a
police officer is present at the scene. An ambulance has been called and is seen in the background.
Direct Action from Visual Cues: Whether it's a surveillance image of a car accident or a live feed of a residential fire, Tools4AI can immediately recognize critical situations and initiate appropriate emergency protocols without human input. A sample action is written and the code is available here
@Agent(actionName = "callEmergencyServices", description = "This action will be called in case of emergency", groupName = "emergency")
public class EmergencyAction implements JavaMethodAction {
public String callEmergencyServices(@Prompt(describe = "Ambulance, Fire or Police") String typeOfEmergency) {
return typeOfEmergency+" has been called";
}
}
Images can also be converted into Json and Pojos for UI based validations. You can use selenium with Tools4AI to validated your UI instead of using elements from the web page , more details here
The above image can be converted into a Pojo object with help of Tools4AI
WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup();
ChromeOptions options = new ChromeOptions();
options.addArguments("--headless"); // Setting headless mode
ptions.addArguments("--disable-gpu"); // GPU hardware acceleration isn't useful in headless mode
options.addArguments("--window-size=1920,1080"); // Set the window size
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver(options);
driver.get("https://google.com");
// Your code to interact with the page and take screenshots
// Take screenshot and save it as file or use as bytes
TakesScreenshot ts = (TakesScreenshot) driver;
byte[] screenshotBytes = ts.getScreenshotAs(OutputType.BYTES);
GeminiImageActionProcessor imageActionProcessor = new GeminiImageActionProcessor();
imageActionProcessor.imageToText(screenshotBytes)
//File srcFile = ts.getScreenshotAs(OutputType.FILE);
//File destFile = new File("screenshot.png");
//FileHandler.copy(srcFile, destFile);
driver.quit();
The pojo it will convert to is
import lombok.*;
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class AutoRepairScreen {
double fullInspectionValue;
double tireRotationValue;
double oilChangeValue;
Integer phoneNumber;
String email;
String[] customerReviews;
}
Integrating Tools4AI with Selenium offers a revolutionary approach to UI validation, streamlining the testing process by validating UI elements in their entirety. Rather than the traditional method of scrutinizing each element individually, this integration enables comprehensive, automated verification of tags and elements. It simplifies the UI Validation workflow, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in confirming the UI's adherence to design specifications
Tools4AI's integration with Selenium introduces a flexible way to automate UI testing. Instead of traditional Java code for Selenium scripts, Tools4AI allows you to define test scenarios in plain English, offering a more accessible approach to testing web applications. These English-based commands can be converted into Selenium code to automate web-based interactions and streamline testing.
Example of Selenium Test with Tools4AI
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver(options);
SeleniumProcessor processor = new SeleniumProcessor(driver);
processor.processWebAction("go to website https://the-internet.herokuapp.com");
boolean buttonPresent = processor.trueFalseQuery("do you see Add/Remove Elements?");
if(buttonPresent) {
processor.processWebAction("click on Add/Remove Elements");
// perform other function in simple english
} //else {
// processor.processSingleAction("Create Jira by taking screenshot");
// }
processor.processWebAction("go to website https://the-internet.herokuapp.com");
boolean isCheckboxPresent = processor.trueFalseQuery("do you see Checkboxes?");
if(isCheckboxPresent) {
processor.processWebAction("click on Checkboxes");
processor.processWebAction("select checkbox 1");
}
In this example, the SeleniumProcessor processes commands in plain English and converts them into Selenium
actions. This approach allows for complex interactions without manually writing Java code for each test.
Tools4AI serves as a bridge between natural language and Selenium, making it easier to automate UI testing in
a way that is both efficient and intuitive.
This integration offers substantial benefits for teams looking to streamline their UI validation process. By enabling a more straightforward way to define and execute Selenium scripts, Tools4AI provides a flexible framework for automating Selenium-based tests.
All the action processors have Spring integration as well
SpringAnthropicProcessor springAnthropic = new SpringAnthropicProcessor(applicationContext)
SpringGeminiProcessor springGemini = new SpringGeminiProcessor();
SpringOpenAIProcessor springOpenAI = new SpringOpenAIProcessor();
You can use this for spring injection and it works exactly as all other action processors , only difference is that instead of creating new action beans it will reuse the beans already created by spring
look at the example here https://github.com/vishalmysore/SpringActions
Look at the java docs here - https://javadoc.io/doc/io.github.vishalmysore/tools4ai/latest/index.html
All the classes implementing JavaMethodAction interfaces and having annotation @Agent are added to prediction list
JavaMethodAction is integral to creating all AI-related actions, with each action implemented as a function adhering to the principles of functional programming. The function's name should be descriptive, aligning closely with the action it performs
@Agent Annotation: This annotation ensures that the AIAction object is included in our prediction list. While not mandatory, it's advisable to mark all actions with @Agent for automatic execution. However, for highly customized actions like deleting records or canceling reservations, omitting this annotation might be preferable to prevent automatic execution.
actionName the descriptive name of the primary function within the class. It's crucial to name this function accurately, as AI utilizes semantic mapping at runtime to correlate the function.
@Agent(actionName = "whatFoodDoesThisPersonLike", description = "what is the food preference of this person ")
public class SimpleAction implements JavaMethodAction {
public String whatFoodDoesThisPersonLike(String name) {
if("vishal".equalsIgnoreCase(name))
return "Paneer Butter Masala";
else if ("vinod".equalsIgnoreCase(name)) {
return "aloo kofta";
}else
return "something yummy";
}
}
So prompt like Hey Vishal is coming to my house for dinner will automatically trigger method whatFoodDoesThisPersonLike with name Vishal
The prediction loader is responsible for loading command scripts, shell scripts, Python scripts, or any other type of script from configuration files. It utilizes the actionName field from the configuration to map to prompts in real-time. Here's an example configuration entry:
- scriptName: "test_script.cmd"
actionName: saveEmployeeInformation
parameters: employeeName,employeeLocation
description: This is a command which will save employee information
During runtime, the prediction loader dynamically extracts parameters from the prompt. Subsequently, it invokes the corresponding script based on the action name. Upon execution, the script processes the parameters and generates a result, which is then sent back to the AI system. Finally, the AI system formulates a response based on the received result and provides feedback accordingly. User: "Hey, Bahubali joined the IFC and we are so happy."
In this prompt:
"Hey" serves as a casual greeting. "Bahubali" represents the name of the new joiner, which needs to be extracted as a parameter. "joined the IFC" implies an action, where the specifics of the action need to be determined. "IFC" is the name of the organization. "we are so happy" provides additional context but doesn't directly affect the action to be taken. The AI system first matches the user's intent with a list of all available actions. In this case, it selects the "saveEmployeeInformation" action as the best match. Then, it maps the parameters accordingly: "Bahubali" as the employee's name and "IFC" as the organization's name. This allows the AI system to accurately understand and execute the user's request.
The Swagger Prediction Loader is capable of directly loading HTTP endpoints as predictions, enabling automatic
execution of commands that semantically match the endpoints with extracted parameters. The screenshot provided
is from https://fakerestapi.azurewebsites.net/index.html, included as an example. Each endpoint within this
API is converted to an HttpPredictedAction and dynamically added to the prediction list in real-time by the
SwaggerPredictionLoader.
This seamless integration allows for streamlined execution of commands based on the available HTTP endpoints. Parsing Swagger/OpenAPI Specification: The Swagger Prediction Loader reads the Swagger/OpenAPI specification file, which describes the available endpoints, their methods (e.g., GET, POST), parameters, and other details.
Endpoint Extraction: The loader extracts each endpoint from the specification, along with its associated metadata such as method, path, parameters, etc.
Action Mapping: For each endpoint, the loader creates an HttpPredictedAction object. This action represents the corresponding HTTP operation (e.g., GET, POST) that clients can perform on the endpoint.
Parameter Extraction: The loader extracts parameters defined for each endpoint, such as query parameters, path parameters, headers, etc.
Action Configuration: The extracted parameters are configured within the HttpPredictedAction object, allowing for dynamic parameterization during execution. Parameters may be mapped to placeholders within the endpoint URL or included in the request body, headers, etc., as specified by the endpoint definition.
Addition to Prediction List: Finally, the HttpPredictedAction objects are added to the prediction list, making them available for automatic execution based on user prompts. Users can invoke actions by providing prompts that match the semantic intent of the mapped endpoints, and the system will execute the corresponding HTTP operation with the extracted parameters.
In essence, the Swagger Prediction Loader leverages the structure and metadata defined in the Swagger/OpenAPI specification to dynamically create HttpPredictedAction objects, allowing for seamless integration of HTTP endpoints into the prediction system
HttpPredictionLoader is responsible for loading the manual http endpoint configuration which look something like this
"endpoints": [
{
"actionName": "getUserDetails",
"description" : " this will fetch User details from the user inventory corporate application",
"url": "https://api.example.com/users/",
"type": "GET",
"input_object": [
{
"name": "userId",
"type": "path_parameter",
"description": "User ID"
}
],
"output_object": {
"type": "json",
"description": "User object"
},
"auth_interface": {
"type": "Bearer Token",
"description": "Authentication token required"
}
},
For the manual definition of HTTP endpoints using a configuration file like the one provided, the process involves specifying each endpoint along with its associated details such as action name, description, URL, HTTP method (type), input parameters, output object, and authentication interface. Here's how the mapping process occurs:
Configuration File Parsing: The application parses the configuration file to extract each endpoint definition along with its metadata.
Endpoint Mapping: For each endpoint defined in the configuration file, an HttpPredictedAction object is created to represent the corresponding HTTP operation.
Action Configuration: The metadata provided in the configuration file is used to configure the HttpPredictedAction object:
Action Name: Specifies the name of the action, which serves as a unique identifier.
Description: Provides a brief description of what the action does or its purpose.
URL: Defines the endpoint URL to which the HTTP request will be sent.
HTTP Method (Type): Specifies the HTTP method (e.g., GET, POST) to be used for the request.
Input Parameters: Describes the input parameters required for the HTTP request, such as path parameters, query parameters, etc.
Output Object: Defines the format and structure of the response expected from the endpoint.
Authentication Interface: Specifies the authentication mechanism required to access the endpoint, along with any necessary credentials.
Parameter Extraction: The input parameters defined for each endpoint are extracted and configured within the HttpPredictedAction object.
Addition to Prediction List: Finally, the HttpPredictedAction objects representing the manually defined endpoints are added to the prediction list, making them available for automatic execution based on user prompts.
This approach allows for flexibility in defining HTTP endpoints outside of a Swagger/OpenAPI specification, enabling the manual configuration of endpoints to suit specific application requirements.
The ExtendedPredictionLoader offers a mechanism for creating custom prediction loaders. While Shell, HTTP, and Java Methods are supported by default, there may arise situations or use cases necessitating a custom set of actions. It's important to note the distinction between custom actions and ExtendedPredictedAction. Custom actions can be created by implementing the AIAction class, while ExtendedPredictedAction have their own loading mechanism. These actions are already present in the prediction list by default and cannot be predicted again.
To create custom implementations of ExtendedPredictionLoader, you need to annotate the loader class with @ActivateLoader. Prediction loader will then identify all classes with this annotation and call the getExtendedActions() method. This method should return the action names along with their corresponding ExtendedPredictOptions, allowing for the seamless integration of custom actions into the prediction system.
If you have a complete script written in English , ScriptProcessor will process the script and provide consolidated results
ScriptProcessor script = new ScriptProcessor();
ScriptResult result = script.process("complexTest.action");
String resultsString = script.summarize(result)
log.info(resultsString)
Sample script is here
can you reserve the flight for Vishal from Toronto to Bangalore for 3 Days on 7th december
If flight booking is successful, can you reserve the car for Vishal from Bangalore to Toronto for 10 Days on 17th december
if car booking is successful and flight cost are less than $1000 then book the sight seeing attraction called 5 star palace
if car booking is successful and flight cost are more than $1000 then book the sight seeing attraction called peanut palace
ZeroShotHallucinationDetector is designed to assess the consistency of responses generated by a Large Language Model (LLM) and detect potential hallucinations. It operates by breaking down an original question into multiple granular questions, each probing different aspects or variations of the inquiry. These granular questions are then presented to the LLM separately, generating responses that are subsequently compared to the original question within its original context.
During comparison, factors such as semantic coherence, relevance, and contextual alignment are evaluated to quantify the consistency between each response and the original question. This evaluation results in a percentage score for each response, representing its level of conformity with the original query.
Finally, these individual percentage scores are aggregated to calculate a cumulative percentage. If the cumulative percentage surpasses a predefined threshold, it indicates a discrepancy or potential hallucination.
By systematically analyzing responses in this manner, the class provides a robust mechanism for assessing the reliability and coherence of LLM-generated content.
This method employs a Zero Shot approach to detect hallucination, utilizing a straightforward methodology devoid of external sources. It operates as follows:
Input: The method takes in responses generated by the Large Language Model (LLM) without relying on any additional data sources.
Granular Analysis: It breaks down the original question into multiple granular inquiries, covering diverse aspects or variations of the initial query.
Zero Shot Evaluation: Without external references, the method evaluates each response against the original question, assessing factors such as semantic coherence and contextual relevance.
Consistency Assessment: Based on the comparison, the method quantifies the consistency of each response, assigning a score indicative of its conformity with the original query.
Cumulative Evaluation: These individual scores are then aggregated to derive a cumulative assessment, providing insight into the overall coherence of the LLM-generated responses.
By employing a simple yet effective Zero Shot technique, this method offers a streamlined approach to detect potential hallucinations in LLM-generated content, contributing to the reliability and trustworthiness of AI-generated outputs.
This will do a google search and return the result can be combined with multiaction
ActionProcessor processor = new ActionProcessor();
String news = (String)processor.processSingleAction("can you search the web for Indian news");
Guard Rails with Spring security
Security - Guard Rails using Spring Security TBD
Application Checkout and monitoring using with Gemini - Prompt - Check if my restaurant system is up and running and able to book the reservation TBD
Validation with Prompt - Prompt - What happened the the flight booking i made whats the status?TBD
Can you check if my movie booking system can handle 50 reservations in 1 min
what happens if my cookgpt is giving only vegetarian recipes
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Tools4AI
Similar Open Source Tools

Tools4AI
Tools4AI is a Java-based Agentic Framework for building AI agents to integrate with enterprise Java applications. It enables the conversion of natural language prompts into actionable behaviors, streamlining user interactions with complex systems. By leveraging AI capabilities, it enhances productivity and innovation across diverse applications. The framework allows for seamless integration of AI with various systems, such as customer service applications, to interpret user requests, trigger actions, and streamline workflows. Prompt prediction anticipates user actions based on input prompts, enhancing user experience by proactively suggesting relevant actions or services based on context.
airflow-ai-sdk
This repository contains an SDK for working with LLMs from Apache Airflow, based on Pydantic AI. It allows users to call LLMs and orchestrate agent calls directly within their Airflow pipelines using decorator-based tasks. The SDK leverages the familiar Airflow `@task` syntax with extensions like `@task.llm`, `@task.llm_branch`, and `@task.agent`. Users can define tasks that call language models, orchestrate multi-step AI reasoning, change the control flow of a DAG based on LLM output, and support various models in the Pydantic AI library. The SDK is designed to integrate LLM workflows into Airflow pipelines, from simple LLM calls to complex agentic workflows.

rag-experiment-accelerator
The RAG Experiment Accelerator is a versatile tool that helps you conduct experiments and evaluations using Azure AI Search and RAG pattern. It offers a rich set of features, including experiment setup, integration with Azure AI Search, Azure Machine Learning, MLFlow, and Azure OpenAI, multiple document chunking strategies, query generation, multiple search types, sub-querying, re-ranking, metrics and evaluation, report generation, and multi-lingual support. The tool is designed to make it easier and faster to run experiments and evaluations of search queries and quality of response from OpenAI, and is useful for researchers, data scientists, and developers who want to test the performance of different search and OpenAI related hyperparameters, compare the effectiveness of various search strategies, fine-tune and optimize parameters, find the best combination of hyperparameters, and generate detailed reports and visualizations from experiment results.
langchain
LangChain is a framework for developing Elixir applications powered by language models. It enables applications to connect language models to other data sources and interact with the environment. The library provides components for working with language models and off-the-shelf chains for specific tasks. It aims to assist in building applications that combine large language models with other sources of computation or knowledge. LangChain is written in Elixir and is not aimed for parity with the JavaScript and Python versions due to differences in programming paradigms and design choices. The library is designed to make it easy to integrate language models into applications and expose features, data, and functionality to the models.
chatmemory
ChatMemory is a simple yet powerful long-term memory manager that facilitates communication between AI and users. It organizes conversation data into history, summary, and knowledge entities, enabling quick retrieval of context and generation of clear, concise answers. The tool leverages vector search on summaries/knowledge and detailed history to provide accurate responses. It balances speed and accuracy by using lightweight retrieval and fallback detailed search mechanisms, ensuring efficient memory management and response generation beyond mere data retrieval.
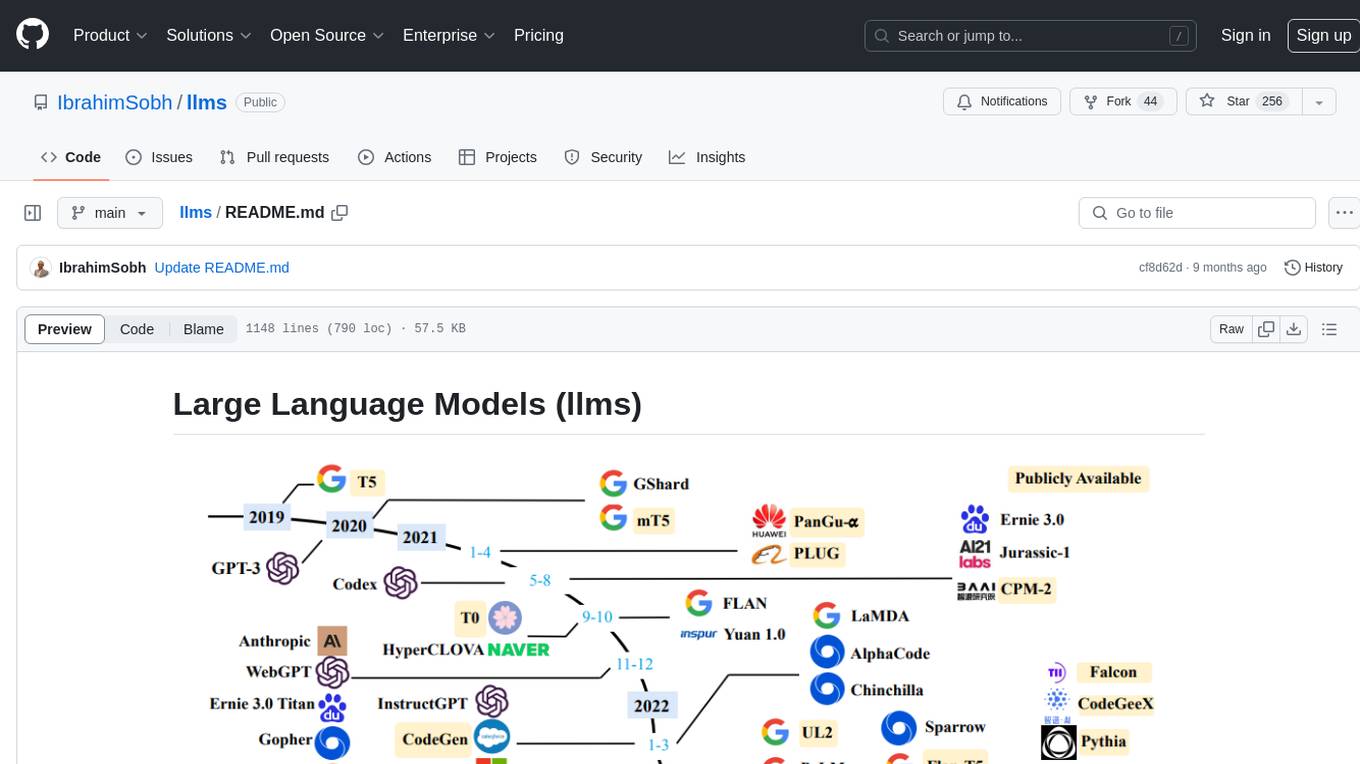
llms
The 'llms' repository is a comprehensive guide on Large Language Models (LLMs), covering topics such as language modeling, applications of LLMs, statistical language modeling, neural language models, conditional language models, evaluation methods, transformer-based language models, practical LLMs like GPT and BERT, prompt engineering, fine-tuning LLMs, retrieval augmented generation, AI agents, and LLMs for computer vision. The repository provides detailed explanations, examples, and tools for working with LLMs.
cameratrapai
SpeciesNet is an ensemble of AI models designed for classifying wildlife in camera trap images. It consists of an object detector that finds objects of interest in wildlife camera images and an image classifier that classifies those objects to the species level. The ensemble combines these two models using heuristics and geographic information to assign each image to a single category. The models have been trained on a large dataset of camera trap images and are used for species recognition in the Wildlife Insights platform.
pgai
pgai simplifies the process of building search and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) AI applications with PostgreSQL. It brings embedding and generation AI models closer to the database, allowing users to create embeddings, retrieve LLM chat completions, reason over data for classification, summarization, and data enrichment directly from within PostgreSQL in a SQL query. The tool requires an OpenAI API key and a PostgreSQL client to enable AI functionality in the database. Users can install pgai from source, run it in a pre-built Docker container, or enable it in a Timescale Cloud service. The tool provides functions to handle API keys using psql or Python, and offers various AI functionalities like tokenizing, detokenizing, embedding, chat completion, and content moderation.
agentscript
AgentScript is an open-source framework for building AI agents that think in code. It prompts a language model to generate JavaScript code, which is then executed in a dedicated runtime with resumability, state persistence, and interactivity. The framework allows for abstract task execution without needing to know all the data beforehand, making it flexible and efficient. AgentScript supports tools, deterministic functions, and LLM-enabled functions, enabling dynamic data processing and decision-making. It also provides state management and human-in-the-loop capabilities, allowing for pausing, serialization, and resumption of execution.
OlympicArena
OlympicArena is a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate advanced AI capabilities across various disciplines. It aims to push AI towards superintelligence by tackling complex challenges in science and beyond. The repository provides detailed data for different disciplines, allows users to run inference and evaluation locally, and offers a submission platform for testing models on the test set. Additionally, it includes an annotation interface and encourages users to cite their paper if they find the code or dataset helpful.
nagato-ai
Nagato-AI is an intuitive AI Agent library that supports multiple LLMs including OpenAI's GPT, Anthropic's Claude, Google's Gemini, and Groq LLMs. Users can create agents from these models and combine them to build an effective AI Agent system. The library is named after the powerful ninja Nagato from the anime Naruto, who can control multiple bodies with different abilities. Nagato-AI acts as a linchpin to summon and coordinate AI Agents for specific missions. It provides flexibility in programming and supports tools like Coordinator, Researcher, Critic agents, and HumanConfirmInputTool.
eval-dev-quality
DevQualityEval is an evaluation benchmark and framework designed to compare and improve the quality of code generation of Language Model Models (LLMs). It provides developers with a standardized benchmark to enhance real-world usage in software development and offers users metrics and comparisons to assess the usefulness of LLMs for their tasks. The tool evaluates LLMs' performance in solving software development tasks and measures the quality of their results through a point-based system. Users can run specific tasks, such as test generation, across different programming languages to evaluate LLMs' language understanding and code generation capabilities.
ReasonablePlanningAI
Reasonable Planning AI is a robust design and data-driven AI solution for game developers. It provides an AI Editor that allows creating AI without Blueprints or C++. The AI can think for itself, plan actions, adapt to the game environment, and act dynamically. It consists of Core components like RpaiGoalBase, RpaiActionBase, RpaiPlannerBase, RpaiReasonerBase, and RpaiBrainComponent, as well as Composer components for easier integration by Game Designers. The tool is extensible, cross-compatible with Behavior Trees, and offers debugging features like visual logging and heuristics testing. It follows a simple path of execution and supports versioning for stability and compatibility with Unreal Engine versions.
LongRAG
This repository contains the code for LongRAG, a framework that enhances retrieval-augmented generation with long-context LLMs. LongRAG introduces a 'long retriever' and a 'long reader' to improve performance by using a 4K-token retrieval unit, offering insights into combining RAG with long-context LLMs. The repo provides instructions for installation, quick start, corpus preparation, long retriever, and long reader.

pydantic-ai
PydanticAI is a Python agent framework designed to make it less painful to build production grade applications with Generative AI. It is built by the Pydantic Team and supports various AI models like OpenAI, Anthropic, Gemini, Ollama, Groq, and Mistral. PydanticAI seamlessly integrates with Pydantic Logfire for real-time debugging, performance monitoring, and behavior tracking of LLM-powered applications. It is type-safe, Python-centric, and offers structured responses, dependency injection system, and streamed responses. PydanticAI is in early beta, offering a Python-centric design to apply standard Python best practices in AI-driven projects.
py-vectara-agentic
The `vectara-agentic` Python library is designed for developing powerful AI assistants using Vectara and Agentic-RAG. It supports various agent types, includes pre-built tools for domains like finance and legal, and enables easy creation of custom AI assistants and agents. The library provides tools for summarizing text, rephrasing text, legal tasks like summarizing legal text and critiquing as a judge, financial tasks like analyzing balance sheets and income statements, and database tools for inspecting and querying databases. It also supports observability via LlamaIndex and Arize Phoenix integration.
For similar tasks

Tools4AI
Tools4AI is a Java-based Agentic Framework for building AI agents to integrate with enterprise Java applications. It enables the conversion of natural language prompts into actionable behaviors, streamlining user interactions with complex systems. By leveraging AI capabilities, it enhances productivity and innovation across diverse applications. The framework allows for seamless integration of AI with various systems, such as customer service applications, to interpret user requests, trigger actions, and streamline workflows. Prompt prediction anticipates user actions based on input prompts, enhancing user experience by proactively suggesting relevant actions or services based on context.

AirGym
AirGym is an open source Python quadrotor simulator based on IsaacGym, providing a high-fidelity dynamics and Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) framework for quadrotor robot learning research. It offers a lightweight and customizable platform with strict alignment with PX4 logic, multiple control modes, and Sim-to-Real toolkits. Users can perform tasks such as Hovering, Balloon, Tracking, Avoid, and Planning, with the ability to create customized environments and tasks. The tool also supports training from scratch, visual encoding approaches, playing and testing of trained models, and customization of new tasks and assets.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.





