
llm.nvim
A large language model (LLM) support for Neovim, provides commands to interact with LLM (like ChatGPT, ChatGLM, kimi, deepseek, openrouter and local llms). Support Github models.
Stars: 384
llm.nvim is a universal plugin for a large language model (LLM) designed to enable users to interact with LLM within neovim. Users can customize various LLMs such as gpt, glm, kimi, and local LLM. The plugin provides tools for optimizing code, comparing code, translating text, and more. It also supports integration with free models from Cloudflare, Github models, siliconflow, and others. Users can customize tools, chat with LLM, quickly translate text, and explain code snippets. The plugin offers a flexible window interface for easy interaction and customization.
README:
[!IMPORTANT] A large language model(LLM) plugin that allows you to interact with LLM in Neovim.
- Supports any LLM, such as GPT, GLM, Kimi, DeepSeek, Gemini, Qwen or local LLMs (such as ollama).
- Allows you to define your own AI tools, with different tools able to use different models.
- Most importantly, you can use free models provided by any platform (such as
Cloudflare,GitHub models,SiliconFlow,openrouteror other platforms).
[!NOTE] The configurations of different LLMs (such as ollama, deepseek), UI configurations, and AI tools (including code completion) should be checked in the examples first. Here you will find most of the information you want to know. Additionally, before using the plugin, you should ensure that your
LLM_KEYis valid and that the environment variable is in effect.
- Float-UI
- Split-UI
Streaming output | Non-streaming output
One-time, no history retained.
You can configure inline_assistant to decide whether to display diffs (default: show by pressing 'd').
You can configure inline_assistant to decide whether to display diffs (default: show by pressing 'd').
- virtual text
- blink.cmp or nvim-cmp
curl-
fzf >= 0.37.0: Optional. Split style preview of session history and image recognition tool image selection depends on fzf(The author's development environment is 0.39.0)
-
Register on the official website and obtain your API Key (Cloudflare needs to obtain an additional account).
-
Set the
LLM_KEY(Cloudflare needs to set an additionalACCOUNT) environment variable in yourzshrcorbashrc.
export LLM_KEY=<Your API_KEY>
export ACCOUNT=<Your ACCOUNT> # just for cloudflareExpand the table.
| Platform | Link to obtain api key | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Cloudflare | https://dash.cloudflare.com/ | You can see all of Cloudflare's models here, with the ones marked as beta being free models. |
| ChatGLM(智谱清言) | https://open.bigmodel.cn/ | |
| Kimi(月之暗面) | Moonshot AI 开放平台 | |
| Github Models | Github Token | |
| siliconflow (硅基流动) | siliconflow | You can see all models on Siliconflow here, and select 'Only Free' to see all free models. |
| Deepseek | https://platform.deepseek.com/api_keys | |
| Openrouter | https://openrouter.ai/ | |
| Chatanywhere | https://api.chatanywhere.org/v1/oauth/free/render | 200 free calls to GPT-4o-mini are available every day. |
For local llms, Set LLM_KEY to NONE in your zshrc or bashrc.
- lazy.nvim
{
"Kurama622/llm.nvim",
dependencies = { "nvim-lua/plenary.nvim", "MunifTanjim/nui.nvim"},
cmd = { "LLMSessionToggle", "LLMSelectedTextHandler", "LLMAppHandler" },
config = function()
require("llm").setup({
url = "https://models.inference.ai.azure.com/chat/completions",
model = "gpt-4o-mini",
api_type = "openai"
})
end,
keys = {
{ "<leader>ac", mode = "n", "<cmd>LLMSessionToggle<cr>" },
},
}- Mini.deps
require("mini.deps").setup()
MiniDeps.add({
source = "Kurama622/llm.nvim",
depends = { "nvim-lua/plenary.nvim", "MunifTanjim/nui.nvim" },
cmd = { "LLMSessionToggle", "LLMSelectedTextHandler", "LLMAppHandler" },
})
require("llm").setup({
url = "https://models.inference.ai.azure.com/chat/completions",
model = "gpt-4o-mini",
api_type = "openai"
})| Cmd | Description |
|---|---|
LLMSessionToggle |
Open/hide the Chat UI |
LLMSelectedTextHandler |
Handle the selected text, the way it is processed depends on the prompt words you input |
LLMAppHandler |
Call AI tools |
Expand the table.
| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| url | Model entpoint | String |
| model | Model name | String |
| api_type | Result parsing format |
workers-ai | zhipu|openai| ollama
|
| timeout | The maximum timeout for a response (in seconds) | Number |
| fetch_key | API key string or Function that returns the API key | Function | String |
| max_tokens | Limits the number of tokens generated in a response. | Number |
| temperature | From 0 to 1. The lower the number is, the more deterministic the response will be. The higher the number is the more creative the response will be, but moe likely to go off topic if it's too high |
Number |
| top_p | A threshold(From 0 to 1). The higher the threshold is the more diverse and the less repetetive the response will be. (But it could also lead to less likely tokens which also means: off-topic responses.) |
Number |
| enable_thinking | Activate the model's deep thinking ability (The model itself needs to ensure this feature.) | Boolean |
| thinking_budget | The maximum length of the thinking process only takes effect when enable_thinking is true. | Number |
| schema | Function-calling required function parameter description | Table |
| functions_tbl | Function dict required for Function-calling | Table |
| keep_alive | Maintain connection (usually for ollama) | see keep_alive/OLLAMA_KEEP_ALIVE |
| streaming_handler | Customize the parsing format of the streaming output | Function |
| parse_handler | Customize the parsing format for non-streaming output | Function |
Expand the table.
| Style | Keyname | Description | Default: [mode] keymap
|
Window |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| float | Input:Submit | Submit your question | [i] ctrl+g |
Input |
| float | Input:Cancel | Cancel dialog response | [i] ctrl+c |
Input |
| float | Input:Resend | Rerespond to the dialog | [i] ctrl+r |
Input |
| float | Input:HistoryNext | Select the next session history | [i] ctrl+j |
Input |
| float | Input:HistoryPrev | Select the previous session history | [i] ctrl+k |
Input |
| float | Input:ModelsNext | Select the next model | [i] ctrl+shift+j |
Input |
| float | Input:ModelsPrev | Select the previous model | [i] ctrl+shift+k |
Input |
| split | Output:Ask | Open the input box In the normal mode of the input box, press Enter to submit your question) |
[n] i |
Output |
| split | Output:Cancel | Cancel dialog response | [n] ctrl+c |
Output |
| split | Output:Resend | Rerespond to the dialog | [n] ctrl+r |
Output |
| float/split | Session:Toggle | Toggle session | [n] <leader>ac |
Input+Output |
| float/split | Session:Close | Close session | [n] <esc> |
float: Input+Outputsplit: Output |
| float/split | Session:New | Create a new session | [n] <C-n> |
float: Input+Outputsplit: Output |
| float/split | Session:Models | Open the model-list window | [n] ctrl+m |
float: App input windowsplit: Output |
| split | Session:History | Open the history window move: same as fzf configuration <cr>: select<esc>: close |
[n] ctrl+h |
Output |
| float | Focus:Input | Jump from the output window to the input window | - | Output |
| float | Focus:Output | Jump from the input window to the output window | - | Input |
| float | PageUp | Output Window page up | [n/i] Ctrl+b |
Input |
| float | PageDown | Output window page down | [n/i] Ctrl+f |
Input |
| float | HalfPageUp | Output Window page up (half) | [n/i] Ctrl+u |
Input |
| float | HalfPageDown | Output window page down (half) | [n/i] Ctrl+d |
Input |
| float | JumpToTop | Jump to the top (output window) | [n] gg |
Input |
| float | JumpToBottom | Jump to the bottom (output window) | [n] G |
Input |
| Handler name | Description |
|---|---|
| side_by_side_handler | Display results in two windows side by side |
| action_handler | Display results in the source file in the form of a diff |
| qa_handler | AI for single-round dialogue |
| flexi_handler | Results will be displayed in a flexible window (window size is automatically calculated based on the amount of output text) |
| disposable_ask_handler | Flexible questioning, you can choose a piece of code to ask about, or you can ask directly (the current buffer is the context) |
| attach_to_chat_handler | Attach the selected content to the context and ask a question. |
| completion_handler | Code completion |
| curl_request_handler | The simplest interaction between curl and LLM is generally used to query account balance or available model lists, etc. |
Each handler's parameters can be referred to here.
Examples can be seen AI Tools Configuration
See UI Configuration and nui/popup
For streaming output, we use our custom streaming_handler; for AI tools that return output results in one go, we use our custom parse_handler.
Below is an example of ollama running llama3.2:1b.
Expand the code.
local function local_llm_streaming_handler(chunk, ctx, F)
if not chunk then
return ctx.assistant_output
end
local tail = chunk:sub(-1, -1)
if tail:sub(1, 1) ~= "}" then
ctx.line = ctx.line .. chunk
else
ctx.line = ctx.line .. chunk
local status, data = pcall(vim.fn.json_decode, ctx.line)
if not status or not data.message.content then
return ctx.assistant_output
end
ctx.assistant_output = ctx.assistant_output .. data.message.content
F.WriteContent(ctx.bufnr, ctx.winid, data.message.content)
ctx.line = ""
end
return ctx.assistant_output
end
local function local_llm_parse_handler(chunk)
local assistant_output = chunk.message.content
return assistant_output
end
return {
{
"Kurama622/llm.nvim",
dependencies = { "nvim-lua/plenary.nvim", "MunifTanjim/nui.nvim" },
cmd = { "LLMSessionToggle", "LLMSelectedTextHandler" },
config = function()
require("llm").setup({
url = "http://localhost:11434/api/chat", -- your url
model = "llama3.2:1b",
streaming_handler = local_llm_streaming_handler,
app_handler = {
WordTranslate = {
handler = tools.flexi_handler,
prompt = "Translate the following text to Chinese, please only return the translation",
opts = {
parse_handler = local_llm_parse_handler,
exit_on_move = true,
enter_flexible_window = false,
},
},
}
})
end,
keys = {
{ "<leader>ac", mode = "n", "<cmd>LLMSessionToggle<cr>" },
},
}
}We would like to express our heartfelt gratitude to the contributors of the following open-source projects, whose code has provided invaluable inspiration and reference for the development of llm.nvim:
- olimorris/codecompanion.nvim: Diff style and prompt.
- SmiteshP/nvim-navbuddy: UI.
- milanglacier/minuet-ai.nvim: Code completions.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for llm.nvim
Similar Open Source Tools

llm.nvim
llm.nvim is a universal plugin for a large language model (LLM) designed to enable users to interact with LLM within neovim. Users can customize various LLMs such as gpt, glm, kimi, and local LLM. The plugin provides tools for optimizing code, comparing code, translating text, and more. It also supports integration with free models from Cloudflare, Github models, siliconflow, and others. Users can customize tools, chat with LLM, quickly translate text, and explain code snippets. The plugin offers a flexible window interface for easy interaction and customization.
EVE
EVE is an official PyTorch implementation of Unveiling Encoder-Free Vision-Language Models. The project aims to explore the removal of vision encoders from Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and transfer LLMs to encoder-free VLMs efficiently. It also focuses on bridging the performance gap between encoder-free and encoder-based VLMs. EVE offers a superior capability with arbitrary image aspect ratio, data efficiency by utilizing publicly available data for pre-training, and training efficiency with a transparent and practical strategy for developing a pure decoder-only architecture across modalities.
DeepRetrieval
DeepRetrieval is a tool designed to enhance search engines and retrievers using Large Language Models (LLMs) and Reinforcement Learning (RL). It allows LLMs to learn how to search effectively by integrating with search engine APIs and customizing reward functions. The tool provides functionalities for data preparation, training, evaluation, and monitoring search performance. DeepRetrieval aims to improve information retrieval tasks by leveraging advanced AI techniques.
hcaptcha-challenger
hCaptcha Challenger is a tool designed to gracefully face hCaptcha challenges using a multimodal large language model. It does not rely on Tampermonkey scripts or third-party anti-captcha services, instead implementing interfaces for 'AI vs AI' scenarios. The tool supports various challenge types such as image labeling, drag and drop, and advanced tasks like self-supervised challenges and Agentic Workflow. Users can access documentation in multiple languages and leverage resources for tasks like model training, dataset annotation, and model upgrading. The tool aims to enhance user experience in handling hCaptcha challenges with innovative AI capabilities.
flute
FLUTE (Flexible Lookup Table Engine for LUT-quantized LLMs) is a tool designed for uniform quantization and lookup table quantization of weights in lower-precision intervals. It offers flexibility in mapping intervals to arbitrary values through a lookup table. FLUTE supports various quantization formats such as int4, int3, int2, fp4, fp3, fp2, nf4, nf3, nf2, and even custom tables. The tool also introduces new quantization algorithms like Learned Normal Float (NFL) for improved performance and calibration data learning. FLUTE provides benchmarks, model zoo, and integration with frameworks like vLLM and HuggingFace for easy deployment and usage.
gollama
Gollama is a tool designed for managing Ollama models through a Text User Interface (TUI). Users can list, inspect, delete, copy, and push Ollama models, as well as link them to LM Studio. The application offers interactive model selection, sorting by various criteria, and actions using hotkeys. It provides features like sorting and filtering capabilities, displaying model metadata, model linking, copying, pushing, and more. Gollama aims to be user-friendly and useful for managing models, especially for cleaning up old models.
chat-your-doc
Chat Your Doc is an experimental project exploring various applications based on LLM technology. It goes beyond being just a chatbot project, focusing on researching LLM applications using tools like LangChain and LlamaIndex. The project delves into UX, computer vision, and offers a range of examples in the 'Lab Apps' section. It includes links to different apps, descriptions, launch commands, and demos, aiming to showcase the versatility and potential of LLM applications.

OpenGateLLM
OpenGateLLM is an open-source API gateway developed by the French Government, designed to serve AI models in production. It follows OpenAI standards and offers robust features like RAG integration, audio transcription, OCR, and more. With support for multiple AI backends and built-in security, OpenGateLLM provides a production-ready solution for various AI tasks.

EasyEdit
EasyEdit is a Python package for edit Large Language Models (LLM) like `GPT-J`, `Llama`, `GPT-NEO`, `GPT2`, `T5`(support models from **1B** to **65B**), the objective of which is to alter the behavior of LLMs efficiently within a specific domain without negatively impacting performance across other inputs. It is designed to be easy to use and easy to extend.
DownEdit
DownEdit is a fast and powerful program for downloading and editing videos from platforms like TikTok, Douyin, and Kuaishou. It allows users to effortlessly grab videos, make bulk edits, and utilize advanced AI features for generating videos, images, and sounds in bulk. The tool offers features like video, photo, and sound editing, downloading videos without watermarks, bulk AI generation, and AI editing for content enhancement.
DownEdit
DownEdit is a fast and powerful program for downloading and editing videos from top platforms like TikTok, Douyin, and Kuaishou. Effortlessly grab videos from user profiles, make bulk edits throughout the entire directory with just one click. Advanced Chat & AI features let you download, edit, and generate videos, images, and sounds in bulk. Exciting new features are coming soon—stay tuned!
DownEdit
DownEdit is a powerful program that allows you to download videos from various social media platforms such as TikTok, Douyin, Kuaishou, and more. With DownEdit, you can easily download videos from user profiles and edit them in bulk. You have the option to flip the videos horizontally or vertically throughout the entire directory with just a single click. Stay tuned for more exciting features coming soon!
YuLan-Mini
YuLan-Mini is a lightweight language model with 2.4 billion parameters that achieves performance comparable to industry-leading models despite being pre-trained on only 1.08T tokens. It excels in mathematics and code domains. The repository provides pre-training resources, including data pipeline, optimization methods, and annealing approaches. Users can pre-train their own language models, perform learning rate annealing, fine-tune the model, research training dynamics, and synthesize data. The team behind YuLan-Mini is AI Box at Renmin University of China. The code is released under the MIT License with future updates on model weights usage policies. Users are advised on potential safety concerns and ethical use of the model.
portkey-python-sdk
The Portkey Python SDK is a control panel for AI apps that allows seamless integration of Portkey's advanced features with OpenAI methods. It provides features such as AI gateway for unified API signature, interoperability, automated fallbacks & retries, load balancing, semantic caching, virtual keys, request timeouts, observability with logging, requests tracing, custom metadata, feedback collection, and analytics. Users can make requests to OpenAI using Portkey SDK and also use async functionality. The SDK is compatible with OpenAI SDK methods and offers Portkey-specific methods like feedback and prompts. It supports various providers and encourages contributions through Github issues or direct contact via email or Discord.
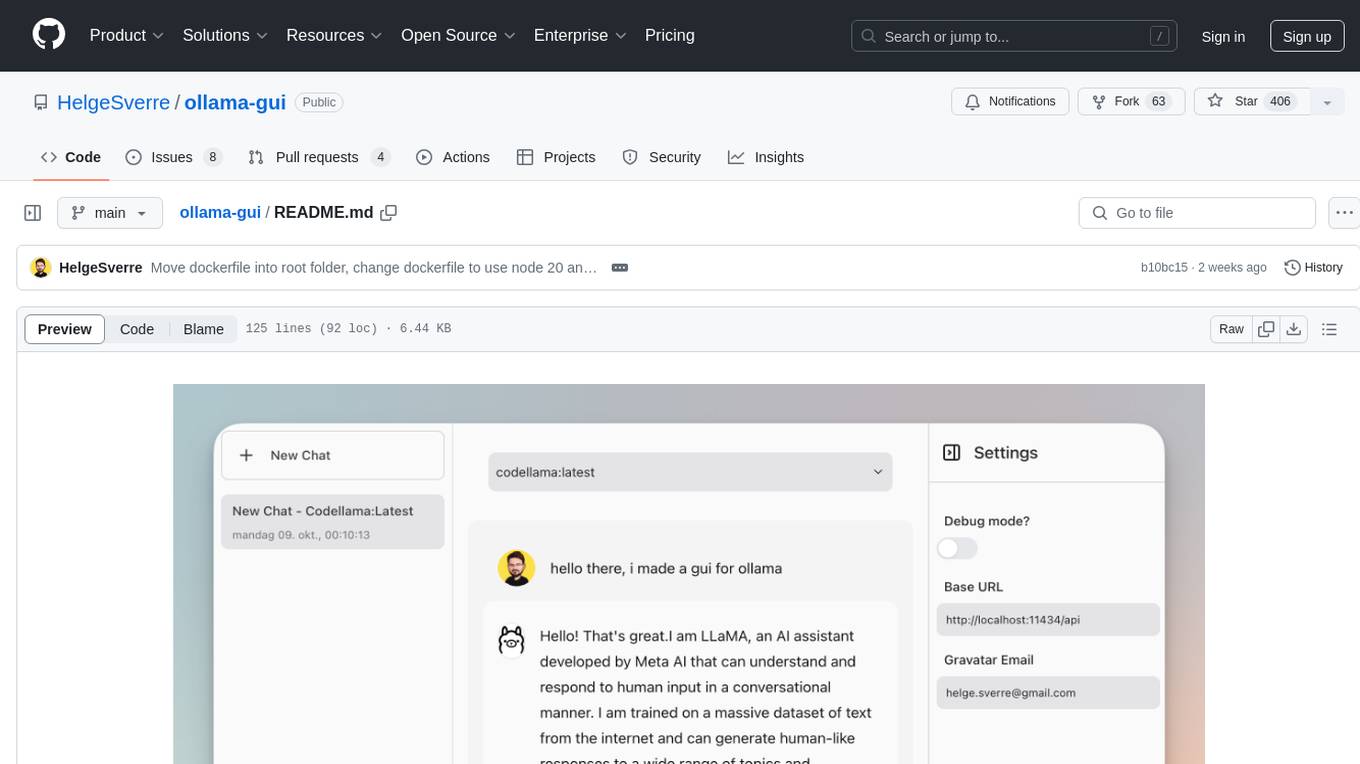
ollama-gui
Ollama GUI is a web interface for ollama.ai, a tool that enables running Large Language Models (LLMs) on your local machine. It provides a user-friendly platform for chatting with LLMs and accessing various models for text generation. Users can easily interact with different models, manage chat history, and explore available models through the web interface. The tool is built with Vue.js, Vite, and Tailwind CSS, offering a modern and responsive design for seamless user experience.
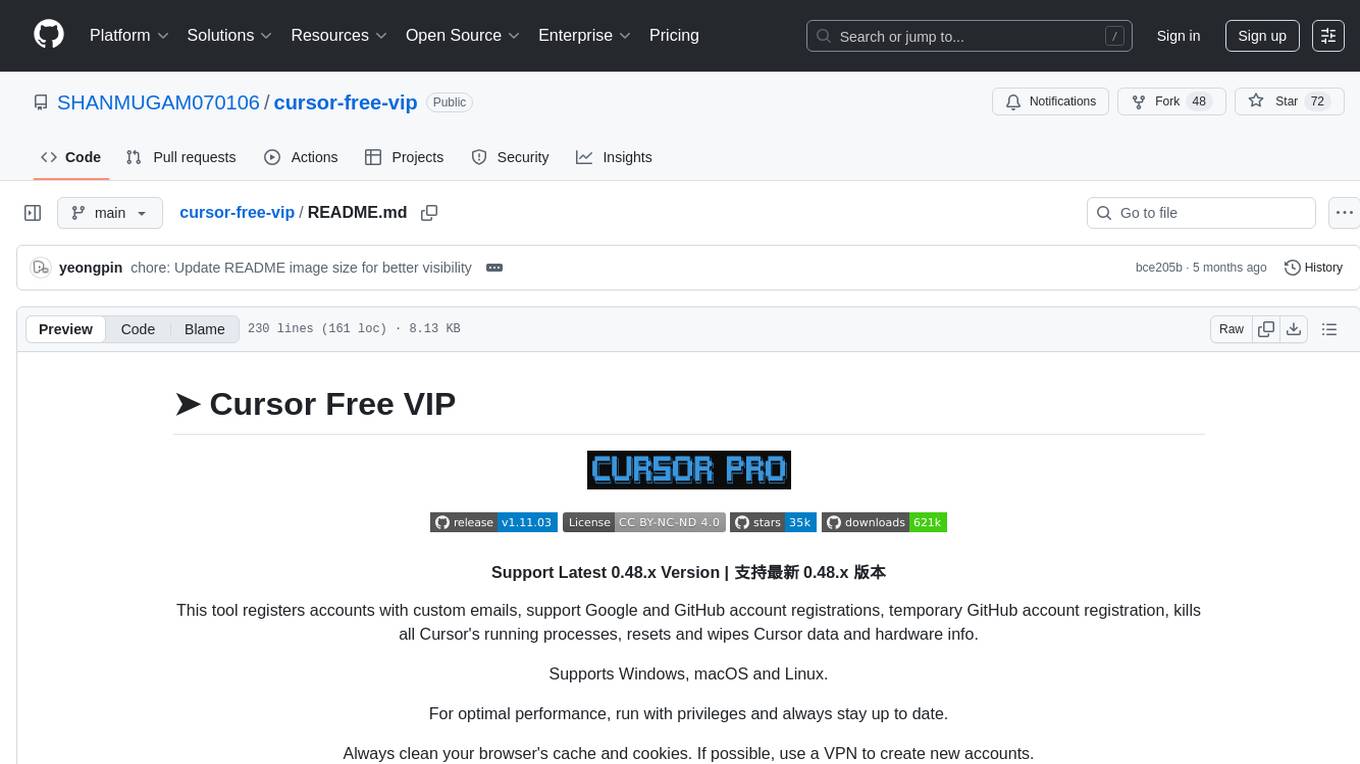
cursor-free-vip
Cursor Free VIP is an automation tool that registers accounts with custom emails, supports Google and GitHub account registrations, temporary GitHub account registration, kills all Cursor's running processes, resets and wipes Cursor data and hardware info. It supports Windows, macOS, and Linux systems. For optimal performance, run with privileges and always stay up to date. Always clean your browser's cache and cookies. The tool is designed for learning and research purposes, and users should comply with relevant software usage terms. It offers multi-language support and various features like Google OAuth Authentication, GitHub OAuth Authentication, automatic Cursor membership registration, system support for Windows, macOS, and Linux, and more.
For similar tasks

llm.nvim
llm.nvim is a universal plugin for a large language model (LLM) designed to enable users to interact with LLM within neovim. Users can customize various LLMs such as gpt, glm, kimi, and local LLM. The plugin provides tools for optimizing code, comparing code, translating text, and more. It also supports integration with free models from Cloudflare, Github models, siliconflow, and others. Users can customize tools, chat with LLM, quickly translate text, and explain code snippets. The plugin offers a flexible window interface for easy interaction and customization.
gpt_academic
GPT Academic is a powerful tool that leverages the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) to enhance academic research and writing. It provides a user-friendly interface that allows researchers, students, and professionals to interact with LLMs and utilize their abilities for various academic tasks. With GPT Academic, users can access a wide range of features and functionalities, including: * **Summarization and Paraphrasing:** GPT Academic can summarize complex texts, articles, and research papers into concise and informative summaries. It can also paraphrase text to improve clarity and readability. * **Question Answering:** Users can ask GPT Academic questions related to their research or studies, and the tool will provide comprehensive and well-informed answers based on its knowledge and understanding of the relevant literature. * **Code Generation and Explanation:** GPT Academic can generate code snippets and provide explanations for complex coding concepts. It can also help debug code and suggest improvements. * **Translation:** GPT Academic supports translation of text between multiple languages, making it a valuable tool for researchers working with international collaborations or accessing resources in different languages. * **Citation and Reference Management:** GPT Academic can help users manage their citations and references by automatically generating citations in various formats and providing suggestions for relevant references based on the user's research topic. * **Collaboration and Note-Taking:** GPT Academic allows users to collaborate on projects and take notes within the tool. They can share their work with others and access a shared workspace for real-time collaboration. * **Customizable Interface:** GPT Academic offers a customizable interface that allows users to tailor the tool to their specific needs and preferences. They can choose from a variety of themes, adjust the layout, and add or remove features to create a personalized workspace. Overall, GPT Academic is a versatile and powerful tool that can significantly enhance the productivity and efficiency of academic research and writing. It empowers users to leverage the capabilities of LLMs and unlock new possibilities for academic exploration and knowledge creation.
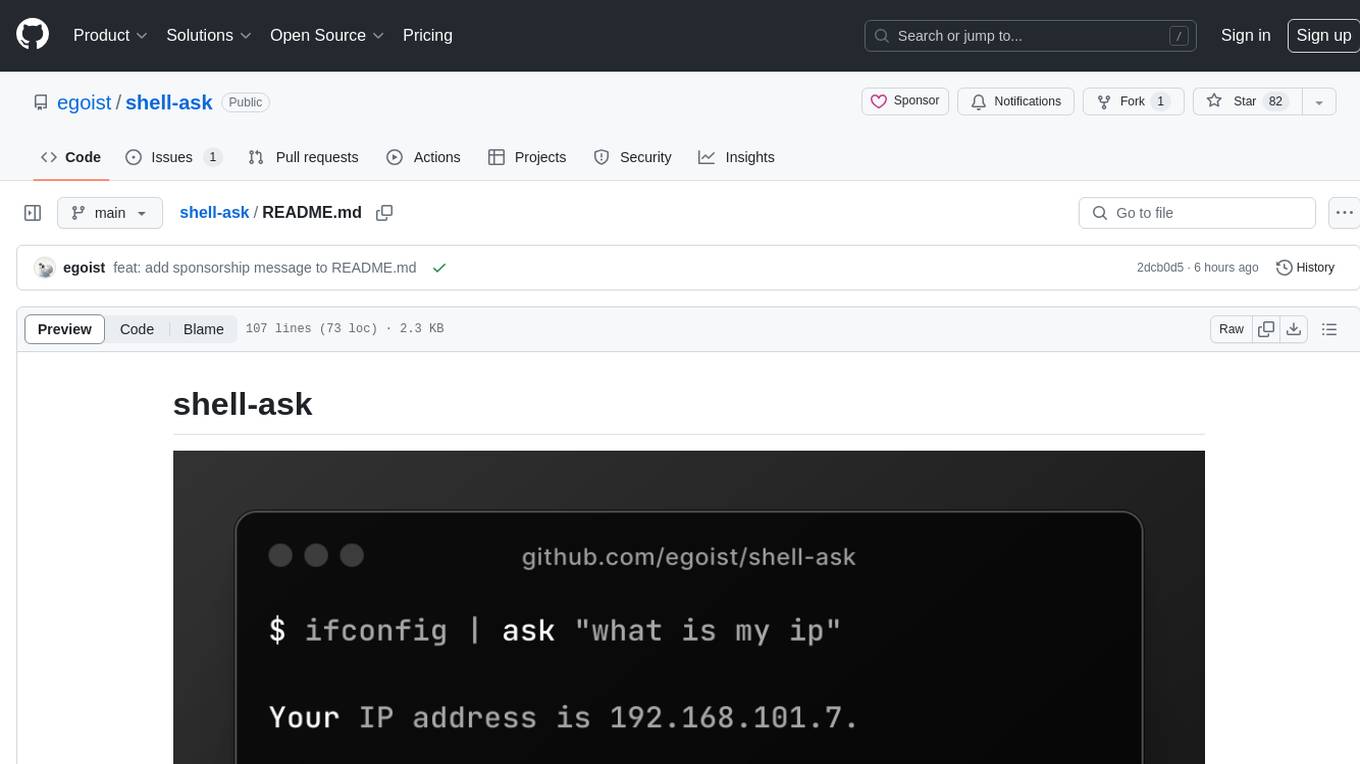
shell-ask
Shell Ask is a command-line tool that enables users to interact with various language models through a simple interface. It supports multiple LLMs such as OpenAI, Anthropic, Ollama, and Google Gemini. Users can ask questions, provide context through command output, select models interactively, and define reusable AI commands. The tool allows piping the output of other programs for enhanced functionality. With AI command presets and configuration options, Shell Ask provides a versatile and efficient way to leverage language models for various tasks.
DevoxxGenieIDEAPlugin
Devoxx Genie is a Java-based IntelliJ IDEA plugin that integrates with local and cloud-based LLM providers to aid in reviewing, testing, and explaining project code. It supports features like code highlighting, chat conversations, and adding files/code snippets to context. Users can modify REST endpoints and LLM parameters in settings, including support for cloud-based LLMs. The plugin requires IntelliJ version 2023.3.4 and JDK 17. Building and publishing the plugin is done using Gradle tasks. Users can select an LLM provider, choose code, and use commands like review, explain, or generate unit tests for code analysis.
neural
Neural is a Vim and Neovim plugin that integrates various machine learning tools to assist users in writing code, generating text, and explaining code or paragraphs. It supports multiple machine learning models, focuses on privacy, and is compatible with Vim 8.0+ and Neovim 0.8+. Users can easily configure Neural to interact with third-party machine learning tools, such as OpenAI, to enhance code generation and completion. The plugin also provides commands like `:NeuralExplain` to explain code or text and `:NeuralStop` to stop Neural from working. Neural is maintained by the Dense Analysis team and comes with a disclaimer about sending input data to third-party servers for machine learning queries.
fittencode.nvim
Fitten Code AI Programming Assistant for Neovim provides fast completion using AI, asynchronous I/O, and support for various actions like document code, edit code, explain code, find bugs, generate unit test, implement features, optimize code, refactor code, start chat, and more. It offers features like accepting suggestions with Tab, accepting line with Ctrl + Down, accepting word with Ctrl + Right, undoing accepted text, automatic scrolling, and multiple HTTP/REST backends. It can run as a coc.nvim source or nvim-cmp source.
chatgpt
The ChatGPT R package provides a set of features to assist in R coding. It includes addins like Ask ChatGPT, Comment selected code, Complete selected code, Create unit tests, Create variable name, Document code, Explain selected code, Find issues in the selected code, Optimize selected code, and Refactor selected code. Users can interact with ChatGPT to get code suggestions, explanations, and optimizations. The package helps in improving coding efficiency and quality by providing AI-powered assistance within the RStudio environment.
scalene
Scalene is a high-performance CPU, GPU, and memory profiler for Python that provides detailed information and runs faster than many other profilers. It incorporates AI-powered proposed optimizations, allowing users to generate optimization suggestions by clicking on specific lines or regions of code. Scalene separates time spent in Python from native code, highlights hotspots, and identifies memory usage per line. It supports GPU profiling on NVIDIA-based systems and detects memory leaks. Users can generate reduced profiles, profile specific functions using decorators, and suspend/resume profiling for background processes. Scalene is available as a pip or conda package and works on various platforms. It offers features like profiling at the line level, memory trends, copy volume reporting, and leak detection.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.


