
code_puppy
Agentic AI for writing code
Stars: 154
Code Puppy is an AI-powered code generation agent designed to understand programming tasks, generate high-quality code, and explain its reasoning. It supports multi-language code generation, interactive CLI, and detailed code explanations. The tool requires Python 3.9+ and API keys for various models like GPT, Google's Gemini, Cerebras, and Claude. It also integrates with MCP servers for advanced features like code search and documentation lookups. Users can create custom JSON agents for specialized tasks and access a variety of tools for file management, code execution, and reasoning sharing.
README:
"Who needs an IDE?" - someone, probably.
This project was coded angrily in reaction to Windsurf and Cursor removing access to models and raising prices.
You could also run 50 code puppies at once if you were insane enough.
Would you rather plow a field with one ox or 1024 puppies? - If you pick the ox, better slam that back button in your browser.
Code Puppy is an AI-powered code generation agent, designed to understand programming tasks, generate high-quality code, and explain its reasoning similar to tools like Windsurf and Cursor.
uvx code-puppy -i
- Multi-language support: Capable of generating code in various programming languages.
- Interactive CLI: A command-line interface for interactive use.
- Detailed explanations: Provides insights into generated code to understand its logic and structure.
pip install code-puppy
export MODEL_NAME=gpt-5 # or gemini-2.5-flash-preview-05-20 as an example for Google Gemini models
export OPENAI_API_KEY=<your_openai_api_key> # or GEMINI_API_KEY for Google Gemini models
export CEREBRAS_API_KEY=<your_cerebras_api_key> # for Cerebras models
export YOLO_MODE=true # to bypass the safety confirmation prompt when running shell commands
# or ...
export AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY=...
export AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT=...
code-puppy --interactiveRun specific tasks or engage in interactive mode:
# Execute a task directly
code-puppy "write me a C++ hello world program in /tmp/main.cpp then compile it and run it"- Python 3.11+
- OpenAI API key (for GPT models)
- Gemini API key (for Google's Gemini models)
- Cerebras API key (for Cerebras models)
- Anthropic key (for Claude models)
- Ollama endpoint available
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
We support AGENT.md files for defining coding standards and styles that your code should comply with. These rules can cover various aspects such as formatting, naming conventions, and even design guidelines.
For examples and more information about agent rules, visit https://agent.md
Use the /mcp command to manage MCP (list, start, stop, status, etc.)
In the TUI you can click on MCP settings on the footer and interact with a mini-marketplace.
Watch this video for examples! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1t1zEetOqlo
Code Puppy supports Round Robin model distribution to help you overcome rate limits and distribute load across multiple AI models. This feature automatically cycles through configured models with each request, maximizing your API usage while staying within rate limits.
Add a round-robin model configuration to your ~/.code_puppy/extra_models.json file:
export CEREBRAS_API_KEY1=csk-...
export CEREBRAS_API_KEY2=csk-...
export CEREBRAS_API_KEY3=csk-...
{
"qwen1": {
"type": "cerebras",
"name": "qwen-3-coder-480b",
"custom_endpoint": {
"url": "https://api.cerebras.ai/v1",
"api_key": "$CEREBRAS_API_KEY1"
},
"context_length": 131072
},
"qwen2": {
"type": "cerebras",
"name": "qwen-3-coder-480b",
"custom_endpoint": {
"url": "https://api.cerebras.ai/v1",
"api_key": "$CEREBRAS_API_KEY2"
},
"context_length": 131072
},
"qwen3": {
"type": "cerebras",
"name": "qwen-3-coder-480b",
"custom_endpoint": {
"url": "https://api.cerebras.ai/v1",
"api_key": "$CEREBRAS_API_KEY3"
},
"context_length": 131072
},
"cerebras_round_robin": {
"type": "round_robin",
"models": ["qwen1", "qwen2", "qwen3"],
"rotate_every": 5
}
}Then just use /model and tab to select your round-robin model!
The rotate_every parameter controls how many requests are made to each model before rotating to the next one. In this example, the round-robin model will use each Qwen model for 5 consecutive requests before moving to the next model in the sequence.
Code Puppy features a flexible agent system that allows you to work with specialized AI assistants tailored for different coding tasks. The system supports both built-in Python agents and custom JSON agents that you can create yourself.
/agentShows current active agent and all available agents
/agent <agent-name>Switches to the specified agent
/agent agent-creatorSwitches to the Agent Creator for building custom agents
-
Name:
code-puppy - Specialty: General-purpose coding assistant
- Personality: Playful, sarcastic, pedantic about code quality
- Tools: Full access to all tools
- Best for: All coding tasks, file management, execution
- Principles: Clean, concise code following YAGNI, SRP, DRY principles
- File limit: Max 600 lines per file (enforced!)
-
Name:
agent-creator - Specialty: Creating custom JSON agent configurations
- Tools: File operations, reasoning
- Best for: Building new specialized agents
- Features: Schema validation, guided creation process
Built-in agents implemented in Python with full system integration:
- Discovered automatically from
code_puppy/agents/directory - Inherit from
BaseAgentclass - Full access to system internals
- Examples:
code-puppy,agent-creator
User-created agents defined in JSON files:
- Stored in user's agents directory
- Easy to create, share, and modify
- Schema-validated configuration
- Custom system prompts and tool access
-
Switch to Agent Creator:
/agent agent-creator
-
Request agent creation:
I want to create a Python tutor agent -
Follow guided process to define:
- Name and description
- Available tools
- System prompt and behavior
- Custom settings
-
Test your new agent:
/agent your-new-agent-name
Create JSON files in your agents directory following this schema:
{
"name": "agent-name", // REQUIRED: Unique identifier (kebab-case)
"display_name": "Agent Name 🤖", // OPTIONAL: Pretty name with emoji
"description": "What this agent does", // REQUIRED: Clear description
"system_prompt": "Instructions...", // REQUIRED: Agent instructions
"tools": ["tool1", "tool2"], // REQUIRED: Array of tool names
"user_prompt": "How can I help?", // OPTIONAL: Custom greeting
"tools_config": { // OPTIONAL: Tool configuration
"timeout": 60
}
}-
name: Unique identifier (kebab-case, no spaces) -
description: What the agent does -
system_prompt: Agent instructions (string or array) -
tools: Array of available tool names
-
display_name: Pretty display name (defaults to title-cased name + 🤖) -
user_prompt: Custom user greeting -
tools_config: Tool configuration object
Agents can access these tools based on their configuration:
-
list_files: Directory and file listing -
read_file: File content reading -
grep: Text search across files -
edit_file: File editing and creation -
delete_file: File deletion -
agent_run_shell_command: Shell command execution -
agent_share_your_reasoning: Share reasoning with user
-
Read-only agent:
["list_files", "read_file", "grep"] -
File editor agent:
["list_files", "read_file", "edit_file"] - Full access agent: All tools (like Code-Puppy)
{
"system_prompt": "You are a helpful coding assistant that specializes in Python development."
}{
"system_prompt": [
"You are a helpful coding assistant.",
"You specialize in Python development.",
"Always provide clear explanations.",
"Include practical examples in your responses."
]
}{
"name": "python-tutor",
"display_name": "Python Tutor 🐍",
"description": "Teaches Python programming concepts with examples",
"system_prompt": [
"You are a patient Python programming tutor.",
"You explain concepts clearly with practical examples.",
"You help beginners learn Python step by step.",
"Always encourage learning and provide constructive feedback."
],
"tools": ["read_file", "edit_file", "agent_share_your_reasoning"],
"user_prompt": "What Python concept would you like to learn today?"
}{
"name": "code-reviewer",
"display_name": "Code Reviewer 🔍",
"description": "Reviews code for best practices, bugs, and improvements",
"system_prompt": [
"You are a senior software engineer doing code reviews.",
"You focus on code quality, security, and maintainability.",
"You provide constructive feedback with specific suggestions.",
"You follow language-specific best practices and conventions."
],
"tools": ["list_files", "read_file", "grep", "agent_share_your_reasoning"],
"user_prompt": "Which code would you like me to review?"
}{
"name": "devops-helper",
"display_name": "DevOps Helper ⚙️",
"description": "Helps with Docker, CI/CD, and deployment tasks",
"system_prompt": [
"You are a DevOps engineer specialized in containerization and CI/CD.",
"You help with Docker, Kubernetes, GitHub Actions, and deployment.",
"You provide practical, production-ready solutions.",
"You always consider security and best practices."
],
"tools": [
"list_files",
"read_file",
"edit_file",
"agent_run_shell_command",
"agent_share_your_reasoning"
],
"user_prompt": "What DevOps task can I help you with today?"
}-
All platforms:
~/.code_puppy/agents/
-
Built-in:
code_puppy/agents/(in package)
- Use kebab-case (hyphens, not spaces)
- Be descriptive: "python-tutor" not "tutor"
- Avoid special characters
- Be specific about the agent's role
- Include personality traits
- Specify output format preferences
- Use array format for multi-line prompts
- Only include tools the agent actually needs
- Most agents need
agent_share_your_reasoning - File manipulation agents need
read_file,edit_file - Research agents need
grep,list_files
- Include relevant emoji for personality
- Make it friendly and recognizable
- Keep it concise
The system automatically discovers agents by:
-
Python Agents: Scanning
code_puppy/agents/for classes inheriting fromBaseAgent -
JSON Agents: Scanning user's agents directory for
*-agent.jsonfiles - Instantiating and registering discovered agents
JSON agents are powered by the JSONAgent class (code_puppy/agents/json_agent.py):
- Inherits from
BaseAgentfor full system integration - Loads configuration from JSON files with robust validation
- Supports all BaseAgent features (tools, prompts, settings)
- Cross-platform user directory support
- Built-in error handling and schema validation
Both Python and JSON agents implement this interface:
-
name: Unique identifier -
display_name: Human-readable name with emoji -
description: Brief description of purpose -
get_system_prompt(): Returns agent-specific system prompt -
get_available_tools(): Returns list of tool names
The agent_manager.py provides:
- Unified registry for both Python and JSON agents
- Seamless switching between agent types
- Configuration persistence across sessions
- Automatic caching for performance
-
Command Interface:
/agentcommand works with all agent types - Tool Filtering: Dynamic tool access control per agent
- Main Agent System: Loads and manages both agent types
- Cross-Platform: Consistent behavior across all platforms
To create a new Python agent:
- Create file in
code_puppy/agents/(e.g.,my_agent.py) - Implement class inheriting from
BaseAgent - Define required properties and methods
- Agent will be automatically discovered
Example implementation:
from .base_agent import BaseAgent
class MyCustomAgent(BaseAgent):
@property
def name(self) -> str:
return "my-agent"
@property
def display_name(self) -> str:
return "My Custom Agent ✨"
@property
def description(self) -> str:
return "A custom agent for specialized tasks"
def get_system_prompt(self) -> str:
return "Your custom system prompt here..."
def get_available_tools(self) -> list[str]:
return [
"list_files",
"read_file",
"grep",
"edit_file",
"delete_file",
"agent_run_shell_command",
"agent_share_your_reasoning"
]- Ensure JSON file is in correct directory
- Check JSON syntax is valid
- Restart Code Puppy or clear agent cache
- Verify filename ends with
-agent.json
- Use Agent Creator for guided validation
- Check all required fields are present
- Verify tool names are correct
- Ensure name uses kebab-case
- Make sure agents directory is writable
- Check file permissions on JSON files
- Verify directory path exists
{
"tools_config": {
"timeout": 120,
"max_retries": 3
}
}{
"system_prompt": [
"Line 1 of instructions",
"Line 2 of instructions",
"Line 3 of instructions"
]
}The agent system supports future expansion:
- Specialized Agents: Code reviewers, debuggers, architects
- Domain-Specific Agents: Web dev, data science, DevOps, mobile
- Personality Variations: Different communication styles
- Context-Aware Agents: Adapt based on project type
- Team Agents: Shared configurations for coding standards
- Plugin System: Community-contributed agents
- Easy Customization: Create agents without Python knowledge
- Team Sharing: JSON agents can be shared across teams
- Rapid Prototyping: Quick agent creation for specific workflows
- Version Control: JSON agents are git-friendly
- Built-in Validation: Schema validation with helpful error messages
- Cross-Platform: Works consistently across all platforms
- Backward Compatible: Doesn't affect existing Python agents
-
Core Implementation:
code_puppy/agents/json_agent.py -
Agent Discovery: Integrated in
code_puppy/agents/agent_manager.py -
Command Interface: Works through existing
/agentcommand -
Testing: Comprehensive test suite in
tests/test_json_agents.py
- System scans
~/.code_puppy/agents/for*-agent.jsonfiles -
JSONAgentclass loads and validates each JSON configuration - Agents are registered in unified agent registry
- Users can switch to JSON agents via
/agent <name>command - Tool access and system prompts work identically to Python agents
- Invalid JSON syntax: Clear error messages with line numbers
- Missing required fields: Specific field validation errors
- Invalid tool names: Warning with list of available tools
- File permission issues: Helpful troubleshooting guidance
- Agent Templates: Pre-built JSON agents for common tasks
- Visual Editor: GUI for creating JSON agents
- Hot Reloading: Update agents without restart
- Agent Marketplace: Share and discover community agents
- Enhanced Validation: More sophisticated schema validation
- Team Agents: Shared configurations for coding standards
- Create and test your agent thoroughly
- Ensure it follows best practices
- Submit a pull request with agent JSON
- Include documentation and examples
- Test across different platforms
- Follow existing code style
- Include comprehensive tests
- Document the agent's purpose and usage
- Submit pull request for review
- Ensure backward compatibility
Consider contributing agent templates for:
- Code reviewers and auditors
- Language-specific tutors
- DevOps and deployment helpers
- Documentation writers
- Testing specialists
Happy Agent Building! 🚀 Code Puppy now supports both Python and JSON agents, making it easy for anyone to create custom AI coding assistants! 🐶✨
By using Code Puppy, you can maintain code quality and adhere to design guidelines with ease.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for code_puppy
Similar Open Source Tools

code_puppy
Code Puppy is an AI-powered code generation agent designed to understand programming tasks, generate high-quality code, and explain its reasoning. It supports multi-language code generation, interactive CLI, and detailed code explanations. The tool requires Python 3.9+ and API keys for various models like GPT, Google's Gemini, Cerebras, and Claude. It also integrates with MCP servers for advanced features like code search and documentation lookups. Users can create custom JSON agents for specialized tasks and access a variety of tools for file management, code execution, and reasoning sharing.
nanocoder
Nanocoder is a local-first CLI coding agent that supports multiple AI providers with tool support for file operations and command execution. It focuses on privacy and control, allowing users to code locally with AI tools. The tool is designed to bring the power of agentic coding tools to local models or controlled APIs like OpenRouter, promoting community-led development and inclusive collaboration in the AI coding space.
agentpress
AgentPress is a collection of simple but powerful utilities that serve as building blocks for creating AI agents. It includes core components for managing threads, registering tools, processing responses, state management, and utilizing LLMs. The tool provides a modular architecture for handling messages, LLM API calls, response processing, tool execution, and results management. Users can easily set up the environment, create custom tools with OpenAPI or XML schema, and manage conversation threads with real-time interaction. AgentPress aims to be agnostic, simple, and flexible, allowing users to customize and extend functionalities as needed.
aider-desk
AiderDesk is a desktop application that enhances coding workflow by leveraging AI capabilities. It offers an intuitive GUI, project management, IDE integration, MCP support, settings management, cost tracking, structured messages, visual file management, model switching, code diff viewer, one-click reverts, and easy sharing. Users can install it by downloading the latest release and running the executable. AiderDesk also supports Python version detection and auto update disabling. It includes features like multiple project management, context file management, model switching, chat mode selection, question answering, cost tracking, MCP server integration, and MCP support for external tools and context. Development setup involves cloning the repository, installing dependencies, running in development mode, and building executables for different platforms. Contributions from the community are welcome following specific guidelines.
mcp-omnisearch
mcp-omnisearch is a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that acts as a unified gateway to multiple search providers and AI tools. It integrates Tavily, Perplexity, Kagi, Jina AI, Brave, Exa AI, and Firecrawl to offer a wide range of search, AI response, content processing, and enhancement features through a single interface. The server provides powerful search capabilities, AI response generation, content extraction, summarization, web scraping, structured data extraction, and more. It is designed to work flexibly with the API keys available, enabling users to activate only the providers they have keys for and easily add more as needed.
ZerePy
ZerePy is an open-source Python framework for deploying agents on X using OpenAI or Anthropic LLMs. It offers CLI interface, Twitter integration, and modular connection system. Users can fine-tune models for creative outputs and create agents with specific tasks. The tool requires Python 3.10+, Poetry 1.5+, and API keys for LLM, OpenAI, Anthropic, and X API.
core
CORE is an open-source unified, persistent memory layer for all AI tools, allowing developers to maintain context across different tools like Cursor, ChatGPT, and Claude. It aims to solve the issue of context switching and information loss between sessions by creating a knowledge graph that remembers conversations, decisions, and insights. With features like unified memory, temporal knowledge graph, browser extension, chat with memory, auto-sync from apps, and MCP integration hub, CORE provides a seamless experience for managing and recalling context. The tool's ingestion pipeline captures evolving context through normalization, extraction, resolution, and graph integration, resulting in a dynamic memory that grows and changes with the user. When recalling from memory, CORE utilizes search, re-ranking, filtering, and output to provide relevant and contextual answers. Security measures include data encryption, authentication, access control, and vulnerability reporting.

agent-sdk-go
Agent Go SDK is a powerful Go framework for building production-ready AI agents that seamlessly integrates memory management, tool execution, multi-LLM support, and enterprise features into a flexible, extensible architecture. It offers core capabilities like multi-model intelligence, modular tool ecosystem, advanced memory management, and MCP integration. The SDK is enterprise-ready with built-in guardrails, complete observability, and support for enterprise multi-tenancy. It provides a structured task framework, declarative configuration, and zero-effort bootstrapping for development experience. The SDK supports environment variables for configuration and includes features like creating agents with YAML configuration, auto-generating agent configurations, using MCP servers with an agent, and CLI tool for headless usage.
hayhooks
Hayhooks is a tool that simplifies the deployment and serving of Haystack pipelines as REST APIs. It allows users to wrap their pipelines with custom logic and expose them via HTTP endpoints, including OpenAI-compatible chat completion endpoints. With Hayhooks, users can easily convert their Haystack pipelines into API services with minimal boilerplate code.
orra
Orra is a tool for building production-ready multi-agent applications that handle complex real-world interactions. It coordinates tasks across existing stack, agents, and tools run as services using intelligent reasoning. With features like smart pre-evaluated execution plans, domain grounding, durable execution, and automatic service health monitoring, Orra enables users to go fast with tools as services and revert state to handle failures. It provides real-time status tracking and webhook result delivery, making it ideal for developers looking to move beyond simple crews and agents.
LightRAG
LightRAG is a repository hosting the code for LightRAG, a system that supports seamless integration of custom knowledge graphs, Oracle Database 23ai, Neo4J for storage, and multiple file types. It includes features like entity deletion, batch insert, incremental insert, and graph visualization. LightRAG provides an API server implementation for RESTful API access to RAG operations, allowing users to interact with it through HTTP requests. The repository also includes evaluation scripts, code for reproducing results, and a comprehensive code structure.

golf
Golf is a simple command-line tool for calculating the distance between two geographic coordinates. It uses the Haversine formula to accurately determine the distance between two points on the Earth's surface. This tool is useful for developers working on location-based applications or projects that require distance calculations. With Golf, users can easily input latitude and longitude coordinates and get the precise distance in kilometers or miles. The tool is lightweight, easy to use, and can be integrated into various programming workflows.
Agentarium
Agentarium is a powerful Python framework for managing and orchestrating AI agents with ease. It provides a flexible and intuitive way to create, manage, and coordinate interactions between multiple AI agents in various environments. The framework offers advanced agent management, robust interaction management, a checkpoint system for saving and restoring agent states, data generation through agent interactions, performance optimization, flexible environment configuration, and an extensible architecture for customization.
Groqqle
Groqqle 2.1 is a revolutionary, free AI web search and API that instantly returns ORIGINAL content derived from source articles, websites, videos, and even foreign language sources, for ANY target market of ANY reading comprehension level! It combines the power of large language models with advanced web and news search capabilities, offering a user-friendly web interface, a robust API, and now a powerful Groqqle_web_tool for seamless integration into your projects. Developers can instantly incorporate Groqqle into their applications, providing a powerful tool for content generation, research, and analysis across various domains and languages.
CyberStrikeAI
CyberStrikeAI is an AI-native security testing platform built in Go that integrates 100+ security tools, an intelligent orchestration engine, role-based testing with predefined security roles, a skills system with specialized testing skills, and comprehensive lifecycle management capabilities. It enables end-to-end automation from conversational commands to vulnerability discovery, attack-chain analysis, knowledge retrieval, and result visualization, delivering an auditable, traceable, and collaborative testing environment for security teams. The platform features an AI decision engine with OpenAI-compatible models, native MCP implementation with various transports, prebuilt tool recipes, large-result pagination, attack-chain graph, password-protected web UI, knowledge base with vector search, vulnerability management, batch task management, role-based testing, and skills system.
receipt-ocr
An efficient OCR engine for receipt image processing, providing a comprehensive solution for Optical Character Recognition (OCR) on receipt images. The repository includes a dedicated Tesseract OCR module and a general receipt processing package using LLMs. Users can extract structured data from receipts, configure environment variables for multiple LLM providers, process receipts using CLI or programmatically in Python, and run the OCR engine as a Docker web service. The project also offers direct OCR capabilities using Tesseract and provides troubleshooting tips, contribution guidelines, and license information under the MIT license.
For similar tasks
agentscope
AgentScope is a multi-agent platform designed to empower developers to build multi-agent applications with large-scale models. It features three high-level capabilities: Easy-to-Use, High Robustness, and Actor-Based Distribution. AgentScope provides a list of `ModelWrapper` to support both local model services and third-party model APIs, including OpenAI API, DashScope API, Gemini API, and ollama. It also enables developers to rapidly deploy local model services using libraries such as ollama (CPU inference), Flask + Transformers, Flask + ModelScope, FastChat, and vllm. AgentScope supports various services, including Web Search, Data Query, Retrieval, Code Execution, File Operation, and Text Processing. Example applications include Conversation, Game, and Distribution. AgentScope is released under Apache License 2.0 and welcomes contributions.
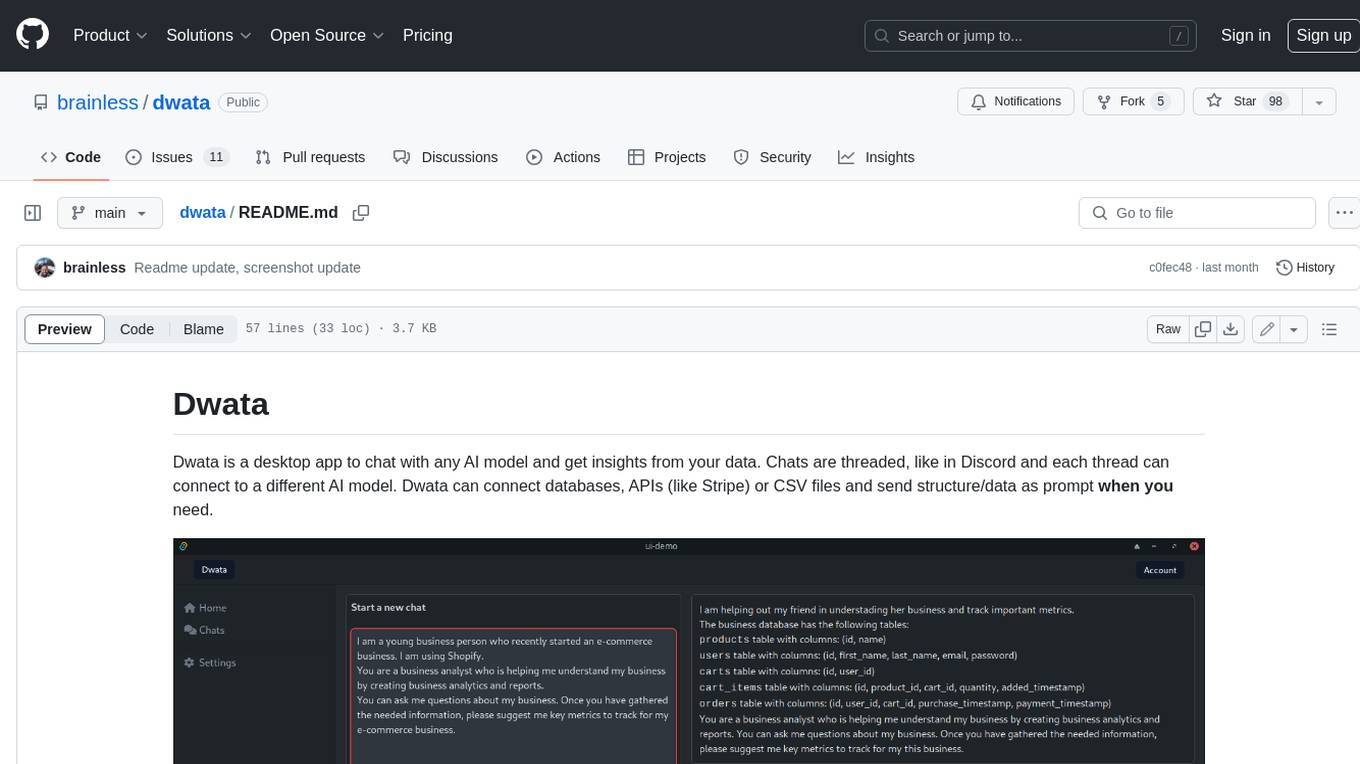
dwata
Dwata is a desktop application that allows users to chat with any AI model and gain insights from their data. Chats are organized into threads, similar to Discord, with each thread connecting to a different AI model. Dwata can connect to databases, APIs (such as Stripe), or CSV files and send structured data as prompts when needed. The AI's response will often include SQL or Python code, which can be used to extract the desired insights. Dwata can validate AI-generated SQL to ensure that the tables and columns referenced are correct and can execute queries against the database from within the application. Python code (typically using Pandas) can also be executed from within Dwata, although this feature is still in development. Dwata supports a range of AI models, including OpenAI's GPT-4, GPT-4 Turbo, and GPT-3.5 Turbo; Groq's LLaMA2-70b and Mixtral-8x7b; Phind's Phind-34B and Phind-70B; Anthropic's Claude; and Ollama's Llama 2, Mistral, and Phi-2 Gemma. Dwata can compare chats from different models, allowing users to see the responses of multiple models to the same prompts. Dwata can connect to various data sources, including databases (PostgreSQL, MySQL, MongoDB), SaaS products (Stripe, Shopify), CSV files/folders, and email (IMAP). The desktop application does not collect any private or business data without the user's explicit consent.
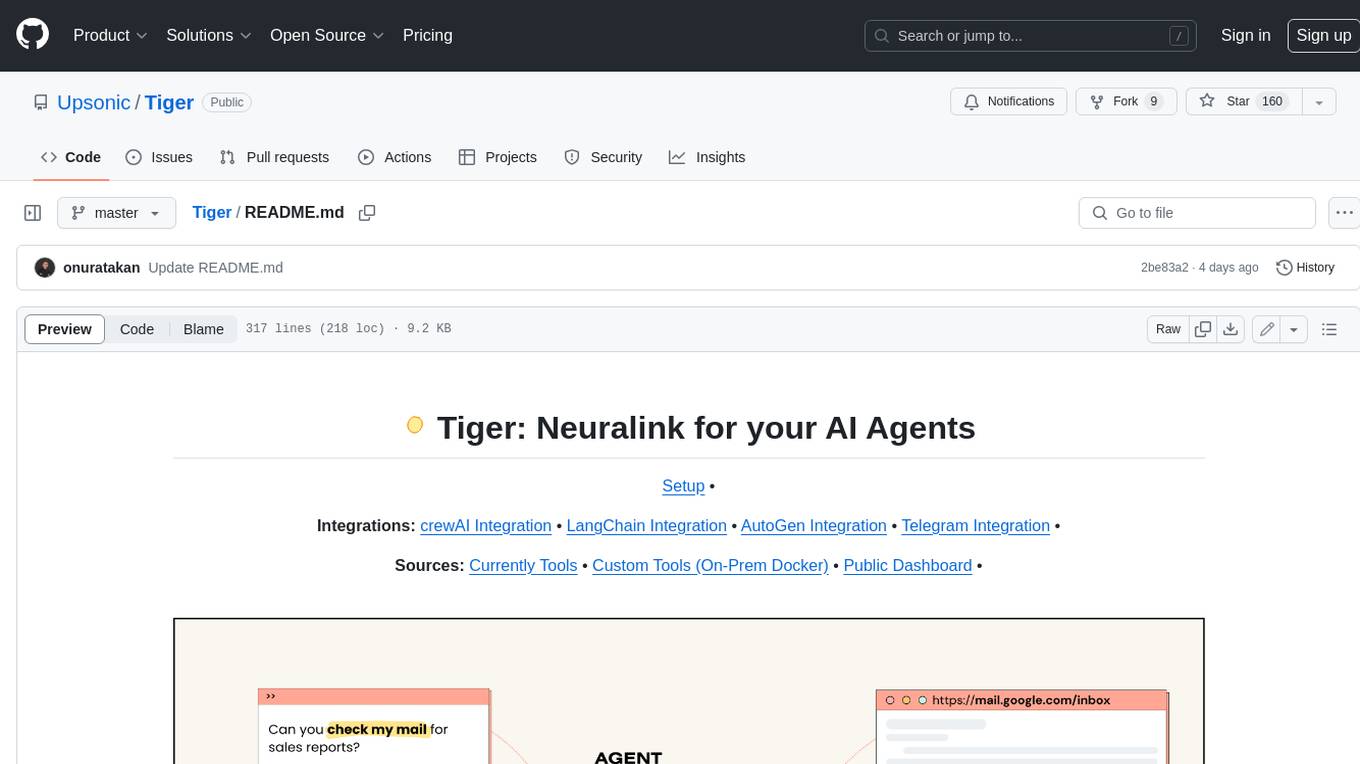
Tiger
Tiger is a community-driven project developing a reusable and integrated tool ecosystem for LLM Agent Revolution. It utilizes Upsonic for isolated tool storage, profiling, and automatic document generation. With Tiger, you can create a customized environment for your agents or leverage the robust and publicly maintained Tiger curated by the community itself.
SWE-agent
SWE-agent is a tool that turns language models (e.g. GPT-4) into software engineering agents capable of fixing bugs and issues in real GitHub repositories. It achieves state-of-the-art performance on the full test set by resolving 12.29% of issues. The tool is built and maintained by researchers from Princeton University. SWE-agent provides a command line tool and a graphical web interface for developers to interact with. It introduces an Agent-Computer Interface (ACI) to facilitate browsing, viewing, editing, and executing code files within repositories. The tool includes features such as a linter for syntax checking, a specialized file viewer, and a full-directory string searching command to enhance the agent's capabilities. SWE-agent aims to improve prompt engineering and ACI design to enhance the performance of language models in software engineering tasks.
NeoGPT
NeoGPT is an AI assistant that transforms your local workspace into a powerhouse of productivity from your CLI. With features like code interpretation, multi-RAG support, vision models, and LLM integration, NeoGPT redefines how you work and create. It supports executing code seamlessly, multiple RAG techniques, vision models, and interacting with various language models. Users can run the CLI to start using NeoGPT and access features like Code Interpreter, building vector database, running Streamlit UI, and changing LLM models. The tool also offers magic commands for chat sessions, such as resetting chat history, saving conversations, exporting settings, and more. Join the NeoGPT community to experience a new era of efficiency and contribute to its evolution.
Phi-3-Vision-MLX
Phi-3-MLX is a versatile AI framework that leverages both the Phi-3-Vision multimodal model and the Phi-3-Mini-128K language model optimized for Apple Silicon using the MLX framework. It provides an easy-to-use interface for a wide range of AI tasks, from advanced text generation to visual question answering and code execution. The project features support for batched generation, flexible agent system, custom toolchains, model quantization, LoRA fine-tuning capabilities, and API integration for extended functionality.
llm-sandbox
LLM Sandbox is a lightweight and portable sandbox environment designed to securely execute large language model (LLM) generated code in a safe and isolated manner using Docker containers. It provides an easy-to-use interface for setting up, managing, and executing code in a controlled Docker environment, simplifying the process of running code generated by LLMs. The tool supports multiple programming languages, offers flexibility with predefined Docker images or custom Dockerfiles, and allows scalability with support for Kubernetes and remote Docker hosts.
lovelaice
Lovelaice is an AI-powered assistant for your terminal and editor. It can run bash commands, search the Internet, answer general and technical questions, complete text files, chat casually, execute code in various languages, and more. Lovelaice is configurable with API keys and LLM models, and can be used for a wide range of tasks requiring bash commands or coding assistance. It is designed to be versatile, interactive, and helpful for daily tasks and projects.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.




