
llm-d-kv-cache
Distributed KV cache scheduling & offloading libraries
Stars: 104
Efficiently caching Key & Value (KV) tensors is crucial for optimizing LLM inference. Reusing the KV-Cache significantly improves Time To First Token (TTFT) and overall throughput, maximizing system resource utilization. `llm-d-kv-cache` is a pluggable service for KV-Cache Aware Routing in vLLM-based serving platforms, providing comprehensive KV-Cache management capabilities. The repository includes the KV-Cache Indexer, a high-performance library for global KV-Cache block locality view across vLLM pods, powered by KVEvents for intelligent routing and optimal cache-aware placement decisions.
README:
Efficiently caching Key & Value (KV) tensors is crucial for optimizing LLM inference.
Reusing the KV-Cache, rather than recomputing it, significantly improves both Time To First Token (TTFT) and overall throughput, while also maximizing system resource-utilization.
As a distributed LLM inference platform, llm-d provides a comprehensive suite of KV-Cache management capabilities to achieve these goals.
This repository contains the llm-d-kv-cache, a pluggable service designed to enable KV-Cache Aware Routing and lay the foundation for advanced, cross-node cache coordination in vLLM-based serving platforms.
See the Project Northstar document for a detailed overview of the project's goals and vision.
The major component of this project is the KV-Cache Indexer is a high-performance library that keeps a global, near-real-time view of KV-Cache block locality across a fleet of vLLM pods.
It is powered by KVEvents streamed from vLLM, which provide structured metadata as KV-blocks are created or evicted from a vLLM instance's KV-cache.
This allows the indexer to track which blocks reside on which nodes and on which tier (e.g., GPU or CPU).
This metadata is the foundation for intelligent routing, enabling schedulers to make optimal, KV-cache-aware placement decisions.
The diagram below shows the primary data flows: the Read Path (scoring) and the Write Path (event ingestion).
graph TD
subgraph "Inference Scheduler"
A[Scheduler]
subgraph "KV-Cache"
B[`kvcache.Indexer`]
C[`kvblock.Index`]
D[`kvevents.Pool`]
end
end
subgraph "vLLM Fleet"
E[vLLM Pod 1]
F[vLLM Pod 2]
G[...]
end
A--"1: Score(prompt, pods)"-->B
B--"2: Query Index"-->C
B--"3: Return Scores"-->A
E--"A: Emit KVEvents"-->D
F--"A: Emit KVEvents"-->D
D--"B: Update Index"-->CRead Path:
- 1: Scoring Request: A scheduler asks the KVCache Indexer to score a set of pods for a given prompt
- 2: Index Query: The indexer calculates the necessary KV-block keys from the prompt and queries the KV-Block Index to see which pods have those blocks
- 3: Return Scores: The indexer returns a map of pods and their corresponding KV-cache-hit scores to the scheduler
Write Path:
- A: Event Ingestion: As vLLM pods create or evict KV-blocks, they emit
KVEventscontaining metadata about these changes - B: Index Update: The Event Subscriber consumes these events and updates the KV-Block Index in near-real-time
For a more detailed breakdown, please see the high-level Architecture and the Configuration docs.
-
KVCache Indexer:
A reference implementation showing how to run and use the
kvcache.Indexermodule -
KVCache Aware Scorer:
A reference implementation of how to integrate the
kvcache.Indexerinto a scheduler like thellm-d-inference-scheduler - KV-Events: Demonstrates how the KV-Cache libraries handles KV-Events through both an offline example with a dummy ZMQ publisher and an online example using a vLLM Helm chart.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for llm-d-kv-cache
Similar Open Source Tools

llm-d-kv-cache
Efficiently caching Key & Value (KV) tensors is crucial for optimizing LLM inference. Reusing the KV-Cache significantly improves Time To First Token (TTFT) and overall throughput, maximizing system resource utilization. `llm-d-kv-cache` is a pluggable service for KV-Cache Aware Routing in vLLM-based serving platforms, providing comprehensive KV-Cache management capabilities. The repository includes the KV-Cache Indexer, a high-performance library for global KV-Cache block locality view across vLLM pods, powered by KVEvents for intelligent routing and optimal cache-aware placement decisions.
VeritasGraph
VeritasGraph is an enterprise-grade graph RAG framework designed for secure, on-premise AI applications. It leverages a knowledge graph to perform complex, multi-hop reasoning, providing transparent, auditable reasoning paths with full source attribution. The framework excels at answering complex questions that traditional vector search engines struggle with, ensuring trust and reliability in enterprise AI. VeritasGraph offers full control over data and AI models, verifiable attribution for every claim, advanced graph reasoning capabilities, and open-source deployment with sovereignty and customization.
Mooncake
Mooncake is a serving platform for Kimi, a leading LLM service provided by Moonshot AI. It features a KVCache-centric disaggregated architecture that separates prefill and decoding clusters, leveraging underutilized CPU, DRAM, and SSD resources of the GPU cluster. Mooncake's scheduler balances throughput and latency-related SLOs, with a prediction-based early rejection policy for highly overloaded scenarios. It excels in long-context scenarios, achieving up to a 525% increase in throughput while handling 75% more requests under real workloads.
premsql
PremSQL is an open-source library designed to help developers create secure, fully local Text-to-SQL solutions using small language models. It provides essential tools for building and deploying end-to-end Text-to-SQL pipelines with customizable components, ideal for secure, autonomous AI-powered data analysis. The library offers features like Local-First approach, Customizable Datasets, Robust Executors and Evaluators, Advanced Generators, Error Handling and Self-Correction, Fine-Tuning Support, and End-to-End Pipelines. Users can fine-tune models, generate SQL queries from natural language inputs, handle errors, and evaluate model performance against predefined metrics. PremSQL is extendible for customization and private data usage.
XLearning
XLearning is a scheduling platform for big data and artificial intelligence, supporting various machine learning and deep learning frameworks. It runs on Hadoop Yarn and integrates frameworks like TensorFlow, MXNet, Caffe, Theano, PyTorch, Keras, XGBoost. XLearning offers scalability, compatibility, multiple deep learning framework support, unified data management based on HDFS, visualization display, and compatibility with code at native frameworks. It provides functions for data input/output strategies, container management, TensorBoard service, and resource usage metrics display. XLearning requires JDK >= 1.7 and Maven >= 3.3 for compilation, and deployment on CentOS 7.2 with Java >= 1.7 and Hadoop 2.6, 2.7, 2.8.
tinyllm
tinyllm is a lightweight framework designed for developing, debugging, and monitoring LLM and Agent powered applications at scale. It aims to simplify code while enabling users to create complex agents or LLM workflows in production. The core classes, Function and FunctionStream, standardize and control LLM, ToolStore, and relevant calls for scalable production use. It offers structured handling of function execution, including input/output validation, error handling, evaluation, and more, all while maintaining code readability. Users can create chains with prompts, LLM models, and evaluators in a single file without the need for extensive class definitions or spaghetti code. Additionally, tinyllm integrates with various libraries like Langfuse and provides tools for prompt engineering, observability, logging, and finite state machine design.
RainbowGPT
RainbowGPT is a versatile tool that offers a range of functionalities, including Stock Analysis for financial decision-making, MySQL Management for database navigation, and integration of AI technologies like GPT-4 and ChatGlm3. It provides a user-friendly interface suitable for all skill levels, ensuring seamless information flow and continuous expansion of emerging technologies. The tool enhances adaptability, creativity, and insight, making it a valuable asset for various projects and tasks.
kheish
Kheish is an open-source, multi-role agent designed for complex tasks that require structured, step-by-step collaboration with Large Language Models (LLMs). It acts as an intelligent agent that can request modules on demand, integrate user feedback, switch between specialized roles, and deliver refined results. By harnessing multiple 'sub-agents' within one framework, Kheish tackles tasks like security audits, file searches, RAG-based exploration, and more.
graphiti
Graphiti is a framework for building and querying temporally-aware knowledge graphs, tailored for AI agents in dynamic environments. It continuously integrates user interactions, structured and unstructured data, and external information into a coherent, queryable graph. The framework supports incremental data updates, efficient retrieval, and precise historical queries without complete graph recomputation, making it suitable for developing interactive, context-aware AI applications.
llm-d-inference-sim
The `llm-d-inference-sim` is a lightweight, configurable, and real-time simulator designed to mimic the behavior of vLLM without the need for GPUs or running heavy models. It operates as an OpenAI-compliant server, allowing developers to test clients, schedulers, and infrastructure using realistic request-response cycles, token streaming, and latency patterns. The simulator offers modes of operation, response generation from predefined text or real datasets, latency simulation, tokenization options, LoRA management, KV cache simulation, failure injection, and deployment options for standalone or Kubernetes testing. It supports a subset of standard vLLM Prometheus metrics for observability.

exllamav3
ExLlamaV3 is an inference library for running local LLMs on modern consumer GPUs. It features a new EXL3 quantization format based on QTIP, flexible tensor-parallel and expert-parallel inference, OpenAI-compatible server via TabbyAPI, continuous dynamic batching, HF Transformers plugin, speculative decoding, multimodal support, and more. The library supports various architectures and aims to simplify and optimize the quantization process for large models, offering efficient conversion with reduced GPU-hours and cost. It provides a streamlined variant of QTIP, enabling fast and memory-bound latency for inference on GPUs.
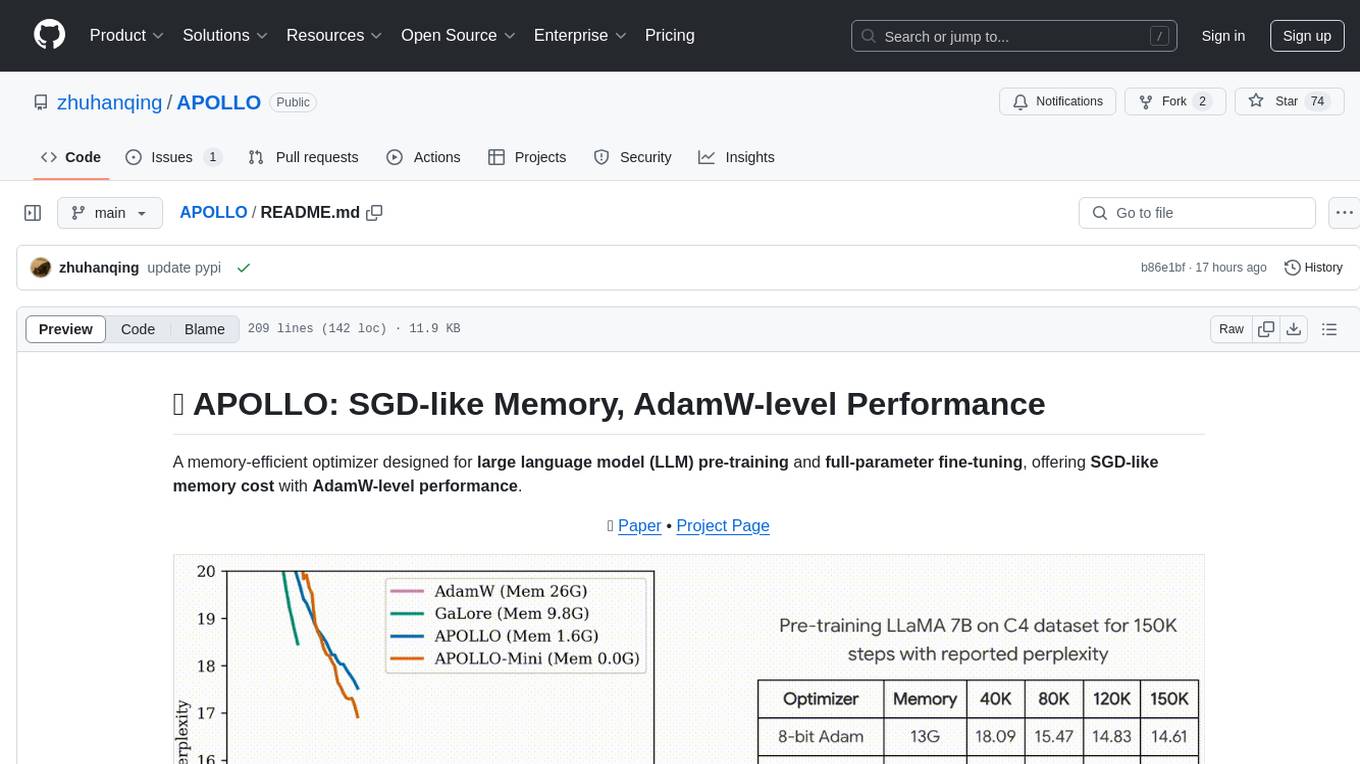
APOLLO
APOLLO is a memory-efficient optimizer designed for large language model (LLM) pre-training and full-parameter fine-tuning. It offers SGD-like memory cost with AdamW-level performance. The optimizer integrates low-rank approximation and optimizer state redundancy reduction to achieve significant memory savings while maintaining or surpassing the performance of Adam(W). Key contributions include structured learning rate updates for LLM training, approximated channel-wise gradient scaling in a low-rank auxiliary space, and minimal-rank tensor-wise gradient scaling. APOLLO aims to optimize memory efficiency during training large language models.

MInference
MInference is a tool designed to accelerate pre-filling for long-context Language Models (LLMs) by leveraging dynamic sparse attention. It achieves up to a 10x speedup for pre-filling on an A100 while maintaining accuracy. The tool supports various decoding LLMs, including LLaMA-style models and Phi models, and provides custom kernels for attention computation. MInference is useful for researchers and developers working with large-scale language models who aim to improve efficiency without compromising accuracy.

cosdata
Cosdata is a cutting-edge AI data platform designed to power the next generation search pipelines. It features immutability, version control, and excels in semantic search, structured knowledge graphs, hybrid search capabilities, real-time search at scale, and ML pipeline integration. The platform is customizable, scalable, efficient, enterprise-grade, easy to use, and can manage multi-modal data. It offers high performance, indexing, low latency, and high requests per second. Cosdata is designed to meet the demands of modern search applications, empowering businesses to harness the full potential of their data.
sec-parser
The `sec-parser` project simplifies extracting meaningful information from SEC EDGAR HTML documents by organizing them into semantic elements and a tree structure. It helps in parsing SEC filings for financial and regulatory analysis, analytics and data science, AI and machine learning, causal AI, and large language models. The tool is especially beneficial for AI, ML, and LLM applications by streamlining data pre-processing and feature extraction.
kollektiv
Kollektiv is a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system designed to enable users to chat with their favorite documentation easily. It aims to provide LLMs with access to the most up-to-date knowledge, reducing inaccuracies and improving productivity. The system utilizes intelligent web crawling, advanced document processing, vector search, multi-query expansion, smart re-ranking, AI-powered responses, and dynamic system prompts. The technical stack includes Python/FastAPI for backend, Supabase, ChromaDB, and Redis for storage, OpenAI and Anthropic Claude 3.5 Sonnet for AI/ML, and Chainlit for UI. Kollektiv is licensed under a modified version of the Apache License 2.0, allowing free use for non-commercial purposes.
For similar tasks

llm-d-kv-cache
Efficiently caching Key & Value (KV) tensors is crucial for optimizing LLM inference. Reusing the KV-Cache significantly improves Time To First Token (TTFT) and overall throughput, maximizing system resource utilization. `llm-d-kv-cache` is a pluggable service for KV-Cache Aware Routing in vLLM-based serving platforms, providing comprehensive KV-Cache management capabilities. The repository includes the KV-Cache Indexer, a high-performance library for global KV-Cache block locality view across vLLM pods, powered by KVEvents for intelligent routing and optimal cache-aware placement decisions.
For similar jobs
llm-resource
llm-resource is a comprehensive collection of high-quality resources for Large Language Models (LLM). It covers various aspects of LLM including algorithms, training, fine-tuning, alignment, inference, data engineering, compression, evaluation, prompt engineering, AI frameworks, AI basics, AI infrastructure, AI compilers, LLM application development, LLM operations, AI systems, and practical implementations. The repository aims to gather and share valuable resources related to LLM for the community to benefit from.
LitServe
LitServe is a high-throughput serving engine designed for deploying AI models at scale. It generates an API endpoint for models, handles batching, streaming, and autoscaling across CPU/GPUs. LitServe is built for enterprise scale with a focus on minimal, hackable code-base without bloat. It supports various model types like LLMs, vision, time-series, and works with frameworks like PyTorch, JAX, Tensorflow, and more. The tool allows users to focus on model performance rather than serving boilerplate, providing full control and flexibility.
how-to-optim-algorithm-in-cuda
This repository documents how to optimize common algorithms based on CUDA. It includes subdirectories with code implementations for specific optimizations. The optimizations cover topics such as compiling PyTorch from source, NVIDIA's reduce optimization, OneFlow's elementwise template, fast atomic add for half data types, upsample nearest2d optimization in OneFlow, optimized indexing in PyTorch, OneFlow's softmax kernel, linear attention optimization, and more. The repository also includes learning resources related to deep learning frameworks, compilers, and optimization techniques.
aiac
AIAC is a library and command line tool to generate Infrastructure as Code (IaC) templates, configurations, utilities, queries, and more via LLM providers such as OpenAI, Amazon Bedrock, and Ollama. Users can define multiple 'backends' targeting different LLM providers and environments using a simple configuration file. The tool allows users to ask a model to generate templates for different scenarios and composes an appropriate request to the selected provider, storing the resulting code to a file and/or printing it to standard output.
ENOVA
ENOVA is an open-source service for Large Language Model (LLM) deployment, monitoring, injection, and auto-scaling. It addresses challenges in deploying stable serverless LLM services on GPU clusters with auto-scaling by deconstructing the LLM service execution process and providing configuration recommendations and performance detection. Users can build and deploy LLM with few command lines, recommend optimal computing resources, experience LLM performance, observe operating status, achieve load balancing, and more. ENOVA ensures stable operation, cost-effectiveness, efficiency, and strong scalability of LLM services.
jina
Jina is a tool that allows users to build multimodal AI services and pipelines using cloud-native technologies. It provides a Pythonic experience for serving ML models and transitioning from local deployment to advanced orchestration frameworks like Docker-Compose, Kubernetes, or Jina AI Cloud. Users can build and serve models for any data type and deep learning framework, design high-performance services with easy scaling, serve LLM models while streaming their output, integrate with Docker containers via Executor Hub, and host on CPU/GPU using Jina AI Cloud. Jina also offers advanced orchestration and scaling capabilities, a smooth transition to the cloud, and easy scalability and concurrency features for applications. Users can deploy to their own cloud or system with Kubernetes and Docker Compose integration, and even deploy to JCloud for autoscaling and monitoring.
vidur
Vidur is a high-fidelity and extensible LLM inference simulator designed for capacity planning, deployment configuration optimization, testing new research ideas, and studying system performance of models under different workloads and configurations. It supports various models and devices, offers chrome trace exports, and can be set up using mamba, venv, or conda. Users can run the simulator with various parameters and monitor metrics using wandb. Contributions are welcome, subject to a Contributor License Agreement and adherence to the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct.
AI-System-School
AI System School is a curated list of research in machine learning systems, focusing on ML/DL infra, LLM infra, domain-specific infra, ML/LLM conferences, and general resources. It provides resources such as data processing, training systems, video systems, autoML systems, and more. The repository aims to help users navigate the landscape of AI systems and machine learning infrastructure, offering insights into conferences, surveys, books, videos, courses, and blogs related to the field.

