
llm-d-inference-sim
A light weight vLLM simulator, for mocking out replicas.
Stars: 85
The `llm-d-inference-sim` is a lightweight, configurable, and real-time simulator designed to mimic the behavior of vLLM without the need for GPUs or running heavy models. It operates as an OpenAI-compliant server, allowing developers to test clients, schedulers, and infrastructure using realistic request-response cycles, token streaming, and latency patterns. The simulator offers modes of operation, response generation from predefined text or real datasets, latency simulation, tokenization options, LoRA management, KV cache simulation, failure injection, and deployment options for standalone or Kubernetes testing. It supports a subset of standard vLLM Prometheus metrics for observability.
README:
llm-d-inference-sim is a lightweight, configurable, and real-time simulator designed to mimic the behavior of vLLM without the need for GPUs or running actual heavy models. It operates as a fully OpenAI-compliant server, allowing developers to test clients, schedulers, and infrastructure using realistic request-response cycles, token streaming, and latency patterns.
Running full LLM inference requires significant GPU resources and introduces non-deterministic latency, making it difficult to isolate infrastructure bugs or iterate quickly on control-plane logic. This simulator decouples development from heavy inference, offering a controlled environment to:
- Accelerate Infrastructure Development: Test routing, scheduling, and KV cache locality logic without waiting for slow, expensive GPU operations.
- Ensure Deterministic Testing: simulate precise token timing and latency to isolate performance regressions and bugs in a way that is impossible with non-deterministic real models.
- Validate Observability: Mirror vLLM’s Prometheus metrics to ensure monitoring and alerting systems are functioning correctly before deploying to production.
- Test Advanced Features: Safely develop complex logic such as LoRA adapter lifecycles (loading, unloading, and switching) and Disaggregated Prefill integrations.
The simulator is designed to act as a drop-in replacement for vLLM, sitting between your client/infrastructure and the void where the GPU usually resides. It processes requests through a configurable simulation engine that governs what is returned and when it is returned.
For detailed configuraiton definitions see the Configuration Guide
The simulator decides the content of the response based on two primary modes:
-
Echo Mode (--mode echo):
Acts as a loopback. The response content mirrors the input (e.g., the last user message in a chat request). Useful for network throughput testing where content validity is irrelevant. -
Random Mode (--mode random):
The default mode. Generates synthetic responses based on requested parameters (like max_tokens). Utilizes probabilistic histograms to determine response length. Content is sourced from either a set of pre-defined sentences or a custom dataset (see below).
Natively supports both HTTP (OpenAI-compatible) and gRPC (vLLM-compatible) interfaces on the same port, allowing for versatile integration testing across different client architectures.
For detailed API definitions see the APIs Guide.
In Random Mode, the simulator can generate content in two ways:
-
Predefined Text: By default, it constructs responses by concatenating random sentences from a built-in list until the target token length is met.
-
Real Datasets: If a dataset is provided (via --dataset-path or --dataset-url), the simulator attempts to match the hash of the incoming prompt to a conversation history in the database. If a match is found, it returns the stored response. If no match is found, it falls back to a random response from the dataset or predefined text.
Supports downloading SQLite datasets directly from HuggingFace.
For response generation algorithms details see Response Generation Guide.
Unlike simple mock servers that just "sleep" for a fixed time, this simulator models the physics of LLM inference:
-
Time to first token: Simulates the prefill phase latency, including configurable standard deviation (jitter) for realism.
-
Inter-token latency: Simulates the decode phase, adding delays between every subsequent token generation.
-
Load Simulation: The simulator automatically increases latency as the number of concurrent requests becomes higher.
-
Disaggregated Prefill (PD): Can simulate KV-cache transfer latency instead of standard TTFT when mimicking Prefill/Decode disaggregation architectures.
The simulator offers flexible tokenization to balance accuracy vs. performance. The simulator automatically selects between two tokenization modes based on the provided --model name:
-
HuggingFace Mode: Used for real models (e.g.,
meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct). Downloads actual tokenizers for exact accuracy. - Simulated Mode: Used for dummy/non-existent model names. Uses a fast regex tokenizer for maximum performance with zero startup overhead.
For details on caching, environment variables (HF_TOKEN), and performance tuning, see the Tokenization Guide.
Simulates the lifecycle (loading/unloading) of LoRA adapters without occupying actual memory. Reports LoRA related Prometheus metrics.
Tracks simulated memory usage and publishes ZMQ events for cache block allocation and eviction.
Can randomly inject specific errors (e.g., rate_limit, model_not_found) to test client resilience.
The simulator is designed to run either as a standalone binary or within a Kubernetes Pod (e.g., for testing with Kind).
The simulator supports a subset of standard vLLM Prometheus metrics.
For detailes see the Metrics Guide
To build a Docker image of the vLLM Simulator, run:
make image-buildPlease note that the default image tag is ghcr.io/llm-d/llm-d-inference-sim:dev.
The following environment variables can be used to change the image tag
| Variable | Descriprtion | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| IMAGE_REGISTRY | Name of the repo | ghcr.io/llm-d |
| IMAGE_TAG_BASE | Image base name | $(IMAGE_REGISTRY)/llm-d-inference-sim |
| SIM_TAG | Image tag | dev |
| IMG | The full image specification | $(IMAGE_TAG_BASE):$(SIM_TAG) |
To run the vLLM Simulator image under Docker, run:
docker run --rm --publish 8000:8000 ghcr.io/llm-d/llm-d-inference-sim:dev --port 8000 --model "Qwen/Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct" --lora-modules '{"name":"tweet-summary-0"}' '{"name":"tweet-summary-1"}'Note: To run the vLLM Simulator with the latest release version, in the above docker command replace dev with the current release which can be found on GitHub.
Note: The above command exposes the simulator on port 8000, and serves the Qwen/Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct model.
To build the vLLM simulator to run locally as an executable, run:
make buildTo run the vLLM simulator in a standalone test environment:
- Set the PYTHONPATH environment variable (needed for the tokenization code) by running:
. env-setup.sh- Start the simulator:
./bin/llm-d-inference-sim --model my_model --port 8000To run the vLLM simulator in a Kubernetes cluster, run:
kubectl apply -f manifests/deployment.yamlWhen testing locally with kind, build the docker image with make build-image then load into the cluster:
kind load --name kind docker-image ghcr.io/llm-d/llm-d-inference-sim:devUpdate the deployment.yaml file to use the dev tag.
To verify the deployment is available, run:
kubectl get deployment vllm-llama3-8b-instruct
kubectl get service vllm-llama3-8b-instruct-svcUse kubectl port-forward to expose the service on your local machine:
kubectl port-forward svc/vllm-llama3-8b-instruct-svc 8000:8000Test the API with curl
curl -X POST http://localhost:8000/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct",
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"}
]
}'An example configuration for P/D (Prefill/Decode) disaggregation deployment can be found in manifests/disaggregation.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for llm-d-inference-sim
Similar Open Source Tools

llm-d-inference-sim
The `llm-d-inference-sim` is a lightweight, configurable, and real-time simulator designed to mimic the behavior of vLLM without the need for GPUs or running heavy models. It operates as an OpenAI-compliant server, allowing developers to test clients, schedulers, and infrastructure using realistic request-response cycles, token streaming, and latency patterns. The simulator offers modes of operation, response generation from predefined text or real datasets, latency simulation, tokenization options, LoRA management, KV cache simulation, failure injection, and deployment options for standalone or Kubernetes testing. It supports a subset of standard vLLM Prometheus metrics for observability.
arbigent
Arbigent (Arbiter-Agent) is an AI agent testing framework designed to make AI agent testing practical for modern applications. It addresses challenges faced by traditional UI testing frameworks and AI agents by breaking down complex tasks into smaller, dependent scenarios. The framework is customizable for various AI providers, operating systems, and form factors, empowering users with extensive customization capabilities. Arbigent offers an intuitive UI for scenario creation and a powerful code interface for seamless test execution. It supports multiple form factors, optimizes UI for AI interaction, and is cost-effective by utilizing models like GPT-4o mini. With a flexible code interface and open-source nature, Arbigent aims to revolutionize AI agent testing in modern applications.
premsql
PremSQL is an open-source library designed to help developers create secure, fully local Text-to-SQL solutions using small language models. It provides essential tools for building and deploying end-to-end Text-to-SQL pipelines with customizable components, ideal for secure, autonomous AI-powered data analysis. The library offers features like Local-First approach, Customizable Datasets, Robust Executors and Evaluators, Advanced Generators, Error Handling and Self-Correction, Fine-Tuning Support, and End-to-End Pipelines. Users can fine-tune models, generate SQL queries from natural language inputs, handle errors, and evaluate model performance against predefined metrics. PremSQL is extendible for customization and private data usage.
VoiceStreamAI
VoiceStreamAI is a Python 3-based server and JavaScript client solution for near-realtime audio streaming and transcription using WebSocket. It employs Huggingface's Voice Activity Detection (VAD) and OpenAI's Whisper model for accurate speech recognition. The system features real-time audio streaming, modular design for easy integration of VAD and ASR technologies, customizable audio chunk processing strategies, support for multilingual transcription, and secure sockets support. It uses a factory and strategy pattern implementation for flexible component management and provides a unit testing framework for robust development.

guidellm
GuideLLM is a platform for evaluating and optimizing the deployment of large language models (LLMs). By simulating real-world inference workloads, GuideLLM enables users to assess the performance, resource requirements, and cost implications of deploying LLMs on various hardware configurations. This approach ensures efficient, scalable, and cost-effective LLM inference serving while maintaining high service quality. The tool provides features for performance evaluation, resource optimization, cost estimation, and scalability testing.
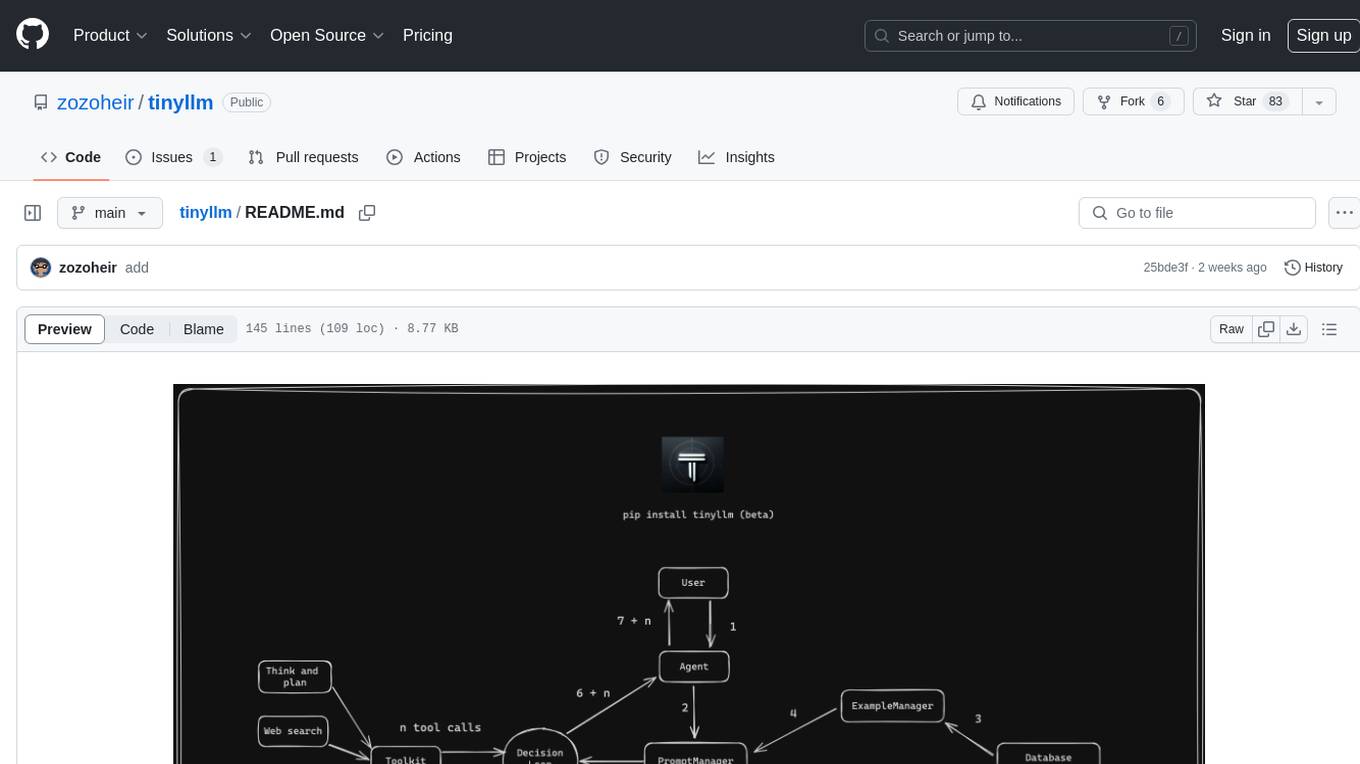
tinyllm
tinyllm is a lightweight framework designed for developing, debugging, and monitoring LLM and Agent powered applications at scale. It aims to simplify code while enabling users to create complex agents or LLM workflows in production. The core classes, Function and FunctionStream, standardize and control LLM, ToolStore, and relevant calls for scalable production use. It offers structured handling of function execution, including input/output validation, error handling, evaluation, and more, all while maintaining code readability. Users can create chains with prompts, LLM models, and evaluators in a single file without the need for extensive class definitions or spaghetti code. Additionally, tinyllm integrates with various libraries like Langfuse and provides tools for prompt engineering, observability, logging, and finite state machine design.
atropos
Atropos is a robust and scalable framework for Reinforcement Learning Environments with Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides a flexible platform to accelerate LLM-based RL research across diverse interactive settings. Atropos supports multi-turn and asynchronous RL interactions, integrates with various inference APIs, offers a standardized training interface for experimenting with different RL algorithms, and allows for easy scalability by launching more environment instances. The framework manages diverse environment types concurrently for heterogeneous, multi-modal training.

cosdata
Cosdata is a cutting-edge AI data platform designed to power the next generation search pipelines. It features immutability, version control, and excels in semantic search, structured knowledge graphs, hybrid search capabilities, real-time search at scale, and ML pipeline integration. The platform is customizable, scalable, efficient, enterprise-grade, easy to use, and can manage multi-modal data. It offers high performance, indexing, low latency, and high requests per second. Cosdata is designed to meet the demands of modern search applications, empowering businesses to harness the full potential of their data.
graphiti
Graphiti is a framework for building and querying temporally-aware knowledge graphs, tailored for AI agents in dynamic environments. It continuously integrates user interactions, structured and unstructured data, and external information into a coherent, queryable graph. The framework supports incremental data updates, efficient retrieval, and precise historical queries without complete graph recomputation, making it suitable for developing interactive, context-aware AI applications.
llm-on-ray
LLM-on-Ray is a comprehensive solution for building, customizing, and deploying Large Language Models (LLMs). It simplifies complex processes into manageable steps by leveraging the power of Ray for distributed computing. The tool supports pretraining, finetuning, and serving LLMs across various hardware setups, incorporating industry and Intel optimizations for performance. It offers modular workflows with intuitive configurations, robust fault tolerance, and scalability. Additionally, it provides an Interactive Web UI for enhanced usability, including a chatbot application for testing and refining models.

guidellm
GuideLLM is a powerful tool for evaluating and optimizing the deployment of large language models (LLMs). By simulating real-world inference workloads, GuideLLM helps users gauge the performance, resource needs, and cost implications of deploying LLMs on various hardware configurations. This approach ensures efficient, scalable, and cost-effective LLM inference serving while maintaining high service quality. Key features include performance evaluation, resource optimization, cost estimation, and scalability testing.
InfLLM
InfLLM is a training-free memory-based method that unveils the intrinsic ability of LLMs to process streaming long sequences. It stores distant contexts into additional memory units and employs an efficient mechanism to lookup token-relevant units for attention computation. Thereby, InfLLM allows LLMs to efficiently process long sequences while maintaining the ability to capture long-distance dependencies. Without any training, InfLLM enables LLMs pre-trained on sequences of a few thousand tokens to achieve superior performance than competitive baselines continually training these LLMs on long sequences. Even when the sequence length is scaled to 1, 024K, InfLLM still effectively captures long-distance dependencies.
kaito
KAITO is an operator that automates the AI/ML model inference or tuning workload in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, provides preset configurations to avoid adjusting workload parameters based on GPU hardware, supports popular open-sourced inference runtimes, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry. Using KAITO simplifies the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes.
llm-ls
llm-ls is a Language Server Protocol (LSP) server that utilizes Large Language Models (LLMs) to enhance the development experience. It aims to serve as a foundation for IDE extensions by simplifying interactions with LLMs, enabling lightweight extension code. The server offers features such as context-based prompt generation, telemetry for retraining, code completion based on AST analysis, and compatibility with various backends like Hugging Face's APIs and llama.cpp server bindings.

fuse-med-ml
FuseMedML is a Python framework designed to accelerate machine learning-based discovery in the medical field by promoting code reuse. It provides a flexible design concept where data is stored in a nested dictionary, allowing easy handling of multi-modality information. The framework includes components for creating custom models, loss functions, metrics, and data processing operators. Additionally, FuseMedML offers 'batteries included' key components such as fuse.data for data processing, fuse.eval for model evaluation, and fuse.dl for reusable deep learning components. It supports PyTorch and PyTorch Lightning libraries and encourages the creation of domain extensions for specific medical domains.
BentoML
BentoML is an open-source model serving library for building performant and scalable AI applications with Python. It comes with everything you need for serving optimization, model packaging, and production deployment.
For similar tasks

llm-d-inference-sim
The `llm-d-inference-sim` is a lightweight, configurable, and real-time simulator designed to mimic the behavior of vLLM without the need for GPUs or running heavy models. It operates as an OpenAI-compliant server, allowing developers to test clients, schedulers, and infrastructure using realistic request-response cycles, token streaming, and latency patterns. The simulator offers modes of operation, response generation from predefined text or real datasets, latency simulation, tokenization options, LoRA management, KV cache simulation, failure injection, and deployment options for standalone or Kubernetes testing. It supports a subset of standard vLLM Prometheus metrics for observability.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.

