
ai-factory
None
Stars: 83
AI Factory is a CLI tool and skill system that streamlines AI-powered development by handling context setup, skill installation, and workflow configuration. It supports multiple AI coding agents, offers spec-driven development, and integrates with popular tech stacks like Next.js, Laravel, Django, and Express. The tool ensures zero configuration, best practices adherence, community skills utilization, and multi-agent support. Users can create plans, tasks, and commits for structured feature development, bug fixes, and self-improvement. Security is a priority with mandatory two-level scans for external skills. The tool's learning loop generates patches from bug fixes to enhance future implementations.
README:
Stop configuring. Start building.
You want to build with AI, but setting up the right context, prompts, and workflows takes time. AI Factory handles all of that so you can focus on what matters — shipping quality code.
One command. Full AI-powered development environment.
ai-factory init- Zero configuration — detects your stack, installs relevant skills, configures integrations
- Best practices built-in — logging, commits, code review, all following industry standards
- Spec-driven development — AI follows plans, not random exploration. Predictable, resumable, reviewable
- Community skills — leverage skills.sh ecosystem or generate custom skills
- Works with your stack — Next.js, Laravel, Django, Express, and more
- Multi-agent support — Claude Code, Cursor, Codex CLI, GitHub Copilot, Gemini CLI, Junie, or any agent
AI Factory works with any AI coding agent. During ai-factory init, you choose your target agent and skills are installed to the correct directory with paths adapted automatically:
| Agent | Config Directory | Skills Directory |
|---|---|---|
| Claude Code | .claude/ |
.claude/skills/ |
| Cursor | .cursor/ |
.cursor/skills/ |
| Codex CLI | .codex/ |
.codex/skills/ |
| GitHub Copilot | .github/ |
.github/skills/ |
| Gemini CLI | .gemini/ |
.gemini/skills/ |
| Junie | .junie/ |
.junie/skills/ |
| Universal / Other | .ai/ |
.ai/skills/ |
MCP server configuration is supported for Claude Code and Cursor. Other agents get skills installed with correct paths but without MCP auto-configuration.
AI Factory is a CLI tool and skill system that:
- Analyzes your project - detects tech stack from package.json, composer.json, requirements.txt, etc.
- Installs relevant skills - downloads from skills.sh or generates custom ones
- Configures MCP servers - GitHub, Postgres, Filesystem based on your needs
- Provides spec-driven workflow - structured feature development with plans, tasks, and commits
npm install -g ai-factory# In your project directory
ai-factory initThis will:
- Ask which AI agent you use (Claude, Cursor, Codex, Copilot, Gemini, Junie, or Universal)
- Detect your project stack
- Ask which base skills to install
- Configure MCP servers (for supported agents)
- Set up skills directory (e.g.
.claude/skills/,.codex/skills/, etc.)
Then open your AI agent and start working:
/ai-factory
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ AI FACTORY WORKFLOW │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────────────────┐
│ │ │ claude │ │ │
│ ai-factory │ ───▶ │ (or any AI │ ───▶ │ /ai-factory │
│ init │ │ agent) │ │ (setup context) │
│ │ │ │ │ │
└──────────────┘ └──────────────┘ └────────────┬─────────────┘
│
┌────────────────────────────────┼────────────────┐
│ │ │
▼ ▼ ▼
┌──────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ /ai-factory.task │ │/ai-factory. │ │/ai-factory. │
│ │ │ feature │ │ fix │
│ Small tasks │ │ │ │ │
│ No git branch │ │ Full features │ │ Bug fixes │
│ Quick work │ │ Git branch │ │ No plans │
│ │ │ Full plan │ │ With logging │
└────────┬─────────┘ └────────┬────────┘ └───────┬──────┘
│ │ │
│ │ ▼
│ │ ┌──────────────────┐
│ │ │ .ai-factory/ │
│ │ │ patches/ │
│ │ │ Self-improvement │
└───────────────┬───────────────┘ └────────┬─────────┘
│ │
▼ │
┌─────────────────────┐ │
│ │ │
│ /ai-factory.improve │ │
│ (optional) │ │
│ │ │
│ Refine plan with │ │
│ deeper analysis │ │
│ │ │
└──────────┬──────────┘ │
│ │
▼ │
┌──────────────────────┐ │
│ │◀── reads patches ─────┘
│ /ai-factory.implement│
│ ──── error? │
│ ──▶ /ai-factory.fix │
│ Execute tasks │
│ Commit checkpoints │
│ │
└──────────┬───────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────┐
│ │
│ /ai-factory.commit │
│ │
└──────────┬──────────┘
│
┌───────────────┴───────────────┐
│ │
▼ ▼
More work? Done!
Loop back ↑ │
▼
┌─────────────────────┐
│ │
│ /ai-factory.evolve │
│ │
│ Reads patches + │
│ project context │
│ ↓ │
│ Improves skills │
│ │
└─────────────────────┘
| Command | Use Case | Creates Branch? | Creates Plan? |
|---|---|---|---|
/ai-factory.task |
Small tasks, quick fixes, experiments | No | .ai-factory/PLAN.md |
/ai-factory.feature |
Full features, stories, epics | Yes | .ai-factory/features/<branch>.md |
/ai-factory.improve |
Refine plan before implementation | No | No (improves existing) |
/ai-factory.fix |
Bug fixes, errors, hotfixes | No | No (direct fix) |
- Predictable results - AI follows a plan, not random exploration
- Resumable sessions - progress saved in plan files, continue anytime
- Commit discipline - structured commits at logical checkpoints
- No scope creep - AI does exactly what's in the plan, nothing more
Analyzes your project and sets up context:
- Scans project files to detect stack
- Searches skills.sh for relevant skills
- Generates custom skills via
/ai-factory.skill-generator - Configures MCP servers
When called with a description:
/ai-factory e-commerce platform with Stripe and Next.js
- Creates
.ai-factory/DESCRIPTION.mdwith enhanced project specification - Transforms your idea into a structured, professional description
Does NOT implement your project - only sets up context.
Starts a new feature:
/ai-factory.feature Add user authentication with OAuth
- Creates git branch (
feature/user-authentication) - Asks about testing and logging preferences
- Creates plan file (
feature-user-authentication.md) - Invokes
/ai-factory.taskto create implementation plan
Creates implementation plan:
/ai-factory.task Add product search API
- Analyzes requirements
- Explores codebase for patterns
- Creates tasks with dependencies
- Saves plan to
.ai-factory/PLAN.md(or branch-named file) - For 5+ tasks, includes commit checkpoints
Refine an existing plan with a second iteration:
/ai-factory.improve # Auto-review: find gaps, missing tasks, wrong deps
/ai-factory.improve добавь валидацию и обработку ошибок # Improve based on specific feedback
- Finds the active plan (
.ai-factory/PLAN.mdor branch-basedfeatures/<branch>.md) - Performs deeper codebase analysis than the initial
/ai-factory.taskplanning - Finds missing tasks (migrations, configs, middleware)
- Fixes task dependencies and descriptions
- Removes redundant tasks
- Shows improvement report and asks for approval before applying
- If no plan found — suggests running
/ai-factory.taskor/ai-factory.featurefirst
Executes the plan:
/ai-factory.implement # Continue from where you left off
/ai-factory.implement 5 # Start from task #5
/ai-factory.implement status # Check progress
-
Reads past patches from
.ai-factory/patches/before starting — learns from previous mistakes - Finds plan file (.ai-factory/PLAN.md or branch-based)
- Executes tasks one by one
- Prompts for commits at checkpoints
- Offers to delete .ai-factory/PLAN.md when done
Quick bug fix without plans:
/ai-factory.fix TypeError: Cannot read property 'name' of undefined
- Investigates codebase to find root cause
- Applies fix WITH logging (
[FIX]prefix for easy filtering) - Suggests test coverage for the bug
- Creates a self-improvement patch in
.ai-factory/patches/ - NO plans, NO reports - just fix, learn, and move on
Self-improve skills based on project experience:
/ai-factory.evolve # Evolve all skills
/ai-factory.evolve fix # Evolve only /ai-factory.fix skill
/ai-factory.evolve all # Evolve all skills
- Reads all patches from
.ai-factory/patches/— finds recurring problems - Analyzes project tech stack, conventions, and codebase patterns
- Identifies gaps in existing skills (missing guards, tech-specific pitfalls)
- Proposes targeted improvements with user approval
- Saves evolution log to
.ai-factory/evolutions/ - The more
/ai-factory.fixpatches you accumulate, the smarter/ai-factory.evolvebecomes
Creates conventional commits:
- Analyzes staged changes
- Generates meaningful commit message
- Follows conventional commits format
Generates new skills:
/ai-factory.skill-generator api-patterns
- Creates SKILL.md with proper frontmatter
- Follows Agent Skills specification
- Can include references, scripts, templates
Learn Mode — pass URLs to generate skills from real documentation:
/ai-factory.skill-generator https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/tutorial/
/ai-factory.skill-generator https://react.dev/learn https://react.dev/reference/react/hooks
/ai-factory.skill-generator my-skill https://docs.example.com/api
- Fetches and deeply studies each URL
- Enriches with web search for best practices and pitfalls
- Synthesizes a structured knowledge base
- Generates a complete skill package with references from real sources
- Supports multiple URLs, mixed sources (docs + blogs), and optional skill name hint
Security audit based on OWASP Top 10 and best practices:
/ai-factory.security-checklist # Full audit
/ai-factory.security-checklist auth # Authentication & sessions
/ai-factory.security-checklist injection # SQL/NoSQL/Command injection
/ai-factory.security-checklist xss # Cross-site scripting
/ai-factory.security-checklist csrf # CSRF protection
/ai-factory.security-checklist secrets # Secrets & credentials
/ai-factory.security-checklist api # API security
/ai-factory.security-checklist infra # Infrastructure & headers
/ai-factory.security-checklist prompt-injection # LLM prompt injection
/ai-factory.security-checklist race-condition # Race conditions & TOCTOU
Each category includes a checklist, vulnerable/safe code examples (TypeScript, PHP), and an automated audit script.
Ignoring items — if a finding is intentionally accepted, mark it as ignored:
/ai-factory.security-checklist ignore no-csrf
- Asks for a reason, saves to
.ai-factory/SECURITY.md - Future audits skip these items but still show them in an "⏭️ Ignored Items" section for transparency
- Review ignored items periodically — risks change over time
AI Factory uses markdown files to track implementation plans:
| Source | Plan File | After Completion |
|---|---|---|
/ai-factory.task (direct) |
.ai-factory/PLAN.md |
Offer to delete |
/ai-factory.feature |
.ai-factory/features/<branch-name>.md |
Keep (user decides) |
Example plan file:
# Implementation Plan: User Authentication
Branch: feature/user-authentication
Created: 2024-01-15
## Settings
- Testing: no
- Logging: verbose
## Commit Plan
- **Commit 1** (tasks 1-3): "feat: add user model and types"
- **Commit 2** (tasks 4-6): "feat: implement auth service"
## Tasks
### Phase 1: Setup
- [ ] Task 1: Create User model
- [ ] Task 2: Add auth types
### Phase 2: Implementation
- [x] Task 3: Implement registration
- [ ] Task 4: Implement loginAI Factory can configure these MCP servers:
| MCP Server | Use Case | Env Variable |
|---|---|---|
| GitHub | PRs, issues, repo operations | GITHUB_TOKEN |
| Postgres | Database queries | DATABASE_URL |
| Filesystem | Advanced file operations | - |
Configuration saved to agent's settings file (e.g. .claude/settings.local.json for Claude Code, .cursor/mcp.json for Cursor, gitignored).
Security is a first-class citizen in AI Factory. Skills downloaded from external sources (skills.sh, GitHub, URLs) can contain prompt injection attacks — malicious instructions hidden inside SKILL.md files that hijack agent behavior, steal credentials, or execute destructive commands.
AI Factory protects against this with a mandatory two-level security scan that runs before any external skill is used:
External skill downloaded
│
▼
┌─── Level 1: Automated Scanner ────────────────────────────┐
│ │
│ Python-based static analysis (security-scan.py) │
│ │
│ Detects: │
│ ✓ Prompt injection patterns │
│ ("ignore previous instructions", fake <system> tags) │
│ ✓ Data exfiltration attempts │
│ (curl with .env/secrets, reading ~/.ssh, ~/.aws) │
│ ✓ Stealth instructions │
│ ("do not tell the user", "silently", "secretly") │
│ ✓ Destructive commands (rm -rf, fork bombs, disk format) │
│ ✓ Config tampering (agent dirs, .bashrc, .gitconfig) │
│ ✓ Encoded payloads (base64, hex, zero-width characters) │
│ ✓ Social engineering ("authorized by admin") │
│ ✓ Hidden HTML comments with suspicious content │
│ │
│ Smart code-block awareness: patterns inside markdown │
│ fenced code blocks are demoted to warnings (docs/examples)│
│ │
└──────────────────────┬─────────────────────────────────────┘
│ CLEAN/WARNINGS?
▼
┌─── Level 2: LLM Semantic Review ──────────────────────────┐
│ │
│ The AI agent reads all skill files and evaluates: │
│ │
│ ✓ Does every instruction serve the skill's stated purpose?│
│ ✓ Are there requests to access sensitive user data? │
│ ✓ Is there anything unrelated to the skill's goal? │
│ ✓ Are there manipulation attempts via urgency/authority? │
│ ✓ Subtle rephrasing of known attacks that regex misses │
│ ✓ "Does this feel right?" — a linter asking for network │
│ access, a formatter reading SSH keys, etc. │
│ │
└──────────────────────┬─────────────────────────────────────┘
│ Both levels pass?
▼
✅ Skill is safe to use
Why two levels?
| Level | Catches | Misses |
|---|---|---|
| Python scanner | Known patterns, encoded payloads, invisible characters, HTML comment injections | Rephrased attacks, novel techniques |
| LLM semantic review | Intent and context, creative rephrasing, suspicious tool combinations | Encoded data, zero-width chars, binary payloads |
They complement each other — the scanner is deterministic and catches what LLMs might skip over; the LLM understands meaning and catches what regex can't express.
Scan results:
- CLEAN (exit 0) — no threats, safe to install
- BLOCKED (exit 1) — critical threats detected, skill is deleted and user is warned
- WARNINGS (exit 2) — suspicious patterns found, user must explicitly confirm
A skill with any CRITICAL threat is never installed. No exceptions, no overrides.
# Scan a skill directory (use your agent's skills path)
python3 .claude/skills/skill-generator/scripts/security-scan.py ./my-downloaded-skill/
# Scan a single SKILL.md file
python3 .claude/skills/skill-generator/scripts/security-scan.py ./my-skill/SKILL.md
# For other agents, adjust the path accordingly:
# python3 .codex/skills/skill-generator/scripts/security-scan.py ./my-skill/
# python3 .ai/skills/skill-generator/scripts/security-scan.py ./my-skill/AI Factory follows this strategy for skills:
For each recommended skill:
1. Search skills.sh: npx skills search <name>
2. If found → Install: npx skills install <name>
3. Security scan → python3 security-scan.py <path>
- BLOCKED? → remove, warn user, skip
- WARNINGS? → show to user, ask confirmation
4. If not found → Generate: /ai-factory.skill-generator <name>
5. Has reference docs? → Learn: /ai-factory.skill-generator <url1> [url2]...
Never reinvent existing skills - always check skills.sh first. Never trust external skills blindly - always scan before use. When reference documentation is available, use Learn Mode to generate skills from real sources.
# Initialize project
ai-factory init
# Update skills to latest version
ai-factory updateAfter initialization (example for Claude Code — other agents use their own directory):
your-project/
├── .claude/ # Agent config dir (varies: .cursor/, .codex/, .ai/, etc.)
│ ├── skills/
│ │ ├── ai-factory/
│ │ ├── feature/
│ │ ├── task/
│ │ ├── improve/
│ │ ├── implement/
│ │ ├── commit/
│ │ ├── review/
│ │ └── skill-generator/
│ └── settings.local.json # MCP config (Claude/Cursor, gitignored)
├── .ai-factory/ # AI Factory working directory
│ ├── DESCRIPTION.md # Project specification
│ ├── PLAN.md # Current plan (from /ai-factory.task)
│ ├── SECURITY.md # Ignored security items (from /security-checklist ignore)
│ ├── features/ # Feature plans (from /ai-factory.feature)
│ │ └── feature-*.md
│ ├── patches/ # Self-improvement patches (from /ai-factory.fix)
│ │ └── 2026-02-07-14.30.md
│ └── evolutions/ # Evolution logs (from /ai-factory.evolve)
│ └── 2026-02-08-10.00.md
└── .ai-factory.json # AI Factory config
AI Factory has a built-in learning loop. Every bug fix creates a patch — a structured knowledge artifact that helps AI avoid the same mistakes in the future.
/ai-factory.fix → finds bug → fixes it → creates patch → next /ai-factory.fix or /ai-factory.implement reads all patches → better code
How it works:
-
/ai-factory.fixfixes a bug and creates a patch file in.ai-factory/patches/YYYY-MM-DD-HH.mm.md - Each patch documents: Problem, Root Cause, Solution, Prevention, and Tags
- Before any
/ai-factory.fixor/ai-factory.implement, AI reads all existing patches - AI applies lessons learned — avoids patterns that caused bugs, follows patterns that prevented them
Example patch (.ai-factory/patches/2026-02-07-14.30.md):
# Null reference in UserProfile when user has no avatar
**Date:** 2026-02-07 14:30
**Files:** src/components/UserProfile.tsx
**Severity:** medium
## Problem
TypeError: Cannot read property 'url' of undefined when rendering UserProfile.
## Root Cause
`user.avatar` is optional in DB but accessed without null check.
## Solution
Added optional chaining: `user.avatar?.url` with fallback.
## Prevention
- Always null-check optional DB fields in UI
- Add "empty state" test cases
## Tags
`#null-check` `#react` `#optional-field`The more you use /ai-factory.fix, the smarter AI becomes on your project. Patches accumulate and create a project-specific knowledge base.
Periodic evolution -- run /ai-factory.evolve to analyze all patches and automatically improve skills:
/ai-factory.evolve # Analyze patches + project → improve all skills
This closes the full learning loop: fix → patch → evolve → better skills → fewer bugs → smarter fixes.
All implementations include verbose, configurable logging:
- Use log levels (DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR)
- Control via
LOG_LEVELenvironment variable - Implement rotation for file-based logs
- Commit checkpoints every 3-5 tasks for large features
- Follow conventional commits format
- Meaningful messages, not just "update code"
- Always asked before creating plan
- If "no tests" - no test tasks created
- Never sneaks in test code
.ai-factory.json:
{
"version": "1.0.0",
"agent": "claude",
"skillsDir": ".claude/skills",
"installedSkills": ["ai-factory", "feature", "task", "improve", "implement", "commit"],
"mcp": {
"github": true,
"postgres": false,
"filesystem": false
}
}The agent field can be any supported agent ID: claude, cursor, codex, copilot, gemini, junie, or universal. The skillsDir is set automatically based on the chosen agent.
- skills.sh - Skill marketplace
- Agent Skills Spec - Skill specification
- Claude Code - Anthropic's AI coding agent
- Cursor - AI-powered code editor
- Codex CLI - OpenAI's coding agent
- Gemini CLI - Google's coding agent
- Junie - JetBrains' AI coding agent
MIT
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for ai-factory
Similar Open Source Tools

ai-factory
AI Factory is a CLI tool and skill system that streamlines AI-powered development by handling context setup, skill installation, and workflow configuration. It supports multiple AI coding agents, offers spec-driven development, and integrates with popular tech stacks like Next.js, Laravel, Django, and Express. The tool ensures zero configuration, best practices adherence, community skills utilization, and multi-agent support. Users can create plans, tasks, and commits for structured feature development, bug fixes, and self-improvement. Security is a priority with mandatory two-level scans for external skills. The tool's learning loop generates patches from bug fixes to enhance future implementations.
Shannon
Shannon is a battle-tested infrastructure for AI agents that solves problems at scale, such as runaway costs, non-deterministic failures, and security concerns. It offers features like intelligent caching, deterministic replay of workflows, time-travel debugging, WASI sandboxing, and hot-swapping between LLM providers. Shannon allows users to ship faster with zero configuration multi-agent setup, multiple AI patterns, time-travel debugging, and hot configuration changes. It is production-ready with features like WASI sandbox, token budget control, policy engine (OPA), and multi-tenancy. Shannon helps scale without breaking by reducing costs, being provider agnostic, observable by default, and designed for horizontal scaling with Temporal workflow orchestration.
myclaw
myclaw is a personal AI assistant built on agentsdk-go that offers a CLI agent for single message or interactive REPL mode, full orchestration with channels, cron, and heartbeat, support for various messaging channels like Telegram, Feishu, WeCom, WhatsApp, and a web UI, multi-provider support for Anthropic and OpenAI models, image recognition and document processing, scheduled tasks with JSON persistence, long-term and daily memory storage, custom skill loading, and more. It provides a comprehensive solution for interacting with AI models and managing tasks efficiently.
gpt-all-star
GPT-All-Star is an AI-powered code generation tool designed for scratch development of web applications with team collaboration of autonomous AI agents. The primary focus of this research project is to explore the potential of autonomous AI agents in software development. Users can organize their team, choose leaders for each step, create action plans, and work together to complete tasks. The tool supports various endpoints like OpenAI, Azure, and Anthropic, and provides functionalities for project management, code generation, and team collaboration.
mesh
MCP Mesh is an open-source control plane for MCP traffic that provides a unified layer for authentication, routing, and observability. It replaces multiple integrations with a single production endpoint, simplifying configuration management. Built for multi-tenant organizations, it offers workspace/project scoping for policies, credentials, and logs. With core capabilities like MeshContext, AccessControl, and OpenTelemetry, it ensures fine-grained RBAC, full tracing, and metrics for tools and workflows. Users can define tools with input/output validation, access control checks, audit logging, and OpenTelemetry traces. The project structure includes apps for full-stack MCP Mesh, encryption, observability, and more, with deployment options ranging from Docker to Kubernetes. The tech stack includes Bun/Node runtime, TypeScript, Hono API, React, Kysely ORM, and Better Auth for OAuth and API keys.
mimiclaw
MimiClaw is a pocket AI assistant that runs on a $5 chip, specifically designed for the ESP32-S3 board. It operates without Linux or Node.js, using pure C language. Users can interact with MimiClaw through Telegram, enabling it to handle various tasks and learn from local memory. The tool is energy-efficient, running on USB power 24/7. With MimiClaw, users can have a personal AI assistant on a chip the size of a thumb, making it convenient and accessible for everyday use.
tinyclaw
TinyClaw is a lightweight wrapper around Claude Code that connects WhatsApp via QR code, processes messages sequentially, maintains conversation context, runs 24/7 in tmux, and is ready for multi-channel support. Its key innovation is the file-based queue system that prevents race conditions and enables multi-channel support. TinyClaw consists of components like whatsapp-client.js for WhatsApp I/O, queue-processor.js for message processing, heartbeat-cron.sh for health checks, and tinyclaw.sh as the main orchestrator with a CLI interface. It ensures no race conditions, is multi-channel ready, provides clean responses using claude -c -p, and supports persistent sessions. Security measures include local storage of WhatsApp session and queue files, channel-specific authentication, and running Claude with user permissions.
claudex
Claudex is an open-source, self-hosted Claude Code UI that runs entirely on your machine. It provides multiple sandboxes, allows users to use their own plans, offers a full IDE experience with VS Code in the browser, and is extensible with skills, agents, slash commands, and MCP servers. Users can run AI agents in isolated environments, view and interact with a browser via VNC, switch between multiple AI providers, automate tasks with Celery workers, and enjoy various chat features and preview capabilities. Claudex also supports marketplace plugins, secrets management, integrations like Gmail, and custom instructions. The tool is configured through providers and supports various providers like Anthropic, OpenAI, OpenRouter, and Custom. It has a tech stack consisting of React, FastAPI, Python, PostgreSQL, Celery, Redis, and more.
solo-server
Solo Server is a lightweight server designed for managing hardware-aware inference. It provides seamless setup through a simple CLI and HTTP servers, an open model registry for pulling models from platforms like Ollama and Hugging Face, cross-platform compatibility for effortless deployment of AI models on hardware, and a configurable framework that auto-detects hardware components (CPU, GPU, RAM) and sets optimal configurations.
memsearch
Memsearch is a tool that allows users to give their AI agents persistent memory in a few lines of code. It enables users to write memories as markdown and search them semantically. Inspired by OpenClaw's markdown-first memory architecture, Memsearch is pluggable into any agent framework. The tool offers features like smart deduplication, live sync, and a ready-made Claude Code plugin for building agent memory.
starknet-agentic
Open-source stack for giving AI agents wallets, identity, reputation, and execution rails on Starknet. `starknet-agentic` is a monorepo with Cairo smart contracts for agent wallets, identity, reputation, and validation, TypeScript packages for MCP tools, A2A integration, and payment signing, reusable skills for common Starknet agent capabilities, and examples and docs for integration. It provides contract primitives + runtime tooling in one place for integrating agents. The repo includes various layers such as Agent Frameworks / Apps, Integration + Runtime Layer, Packages / Tooling Layer, Cairo Contract Layer, and Starknet L2. It aims for portability of agent integrations without giving up Starknet strengths, with a cross-chain interop strategy and skills marketplace. The repository layout consists of directories for contracts, packages, skills, examples, docs, and website.
shell_gpt
ShellGPT is a command-line productivity tool powered by AI large language models (LLMs). This command-line tool offers streamlined generation of shell commands, code snippets, documentation, eliminating the need for external resources (like Google search). Supports Linux, macOS, Windows and compatible with all major Shells like PowerShell, CMD, Bash, Zsh, etc.
openakita
OpenAkita is a self-evolving AI Agent framework that autonomously learns new skills, performs daily self-checks and repairs, accumulates experience from task execution, and persists until the task is done. It auto-generates skills, installs dependencies, learns from mistakes, and remembers preferences. The framework is standards-based, multi-platform, and provides a Setup Center GUI for intuitive installation and configuration. It features self-learning and evolution mechanisms, a Ralph Wiggum Mode for persistent execution, multi-LLM endpoints, multi-platform IM support, desktop automation, multi-agent architecture, scheduled tasks, identity and memory management, a tool system, and a guided wizard for setup.
vibium
Vibium is a browser automation infrastructure designed for AI agents, providing a single binary that manages browser lifecycle, WebDriver BiDi protocol, and an MCP server. It offers zero configuration, AI-native capabilities, and is lightweight with no runtime dependencies. It is suitable for AI agents, test automation, and any tasks requiring browser interaction.
FinMem-LLM-StockTrading
This repository contains the Python source code for FINMEM, a Performance-Enhanced Large Language Model Trading Agent with Layered Memory and Character Design. It introduces FinMem, a novel LLM-based agent framework devised for financial decision-making, encompassing three core modules: Profiling, Memory with layered processing, and Decision-making. FinMem's memory module aligns closely with the cognitive structure of human traders, offering robust interpretability and real-time tuning. The framework enables the agent to self-evolve its professional knowledge, react agilely to new investment cues, and continuously refine trading decisions in the volatile financial environment. It presents a cutting-edge LLM agent framework for automated trading, boosting cumulative investment returns.
blendsql
BlendSQL is a superset of SQLite designed for problem decomposition and hybrid question-answering with Large Language Models (LLMs). It allows users to blend operations over heterogeneous data sources like tables, text, and images, combining the structured and interpretable reasoning of SQL with the generalizable reasoning of LLMs. Users can oversee all calls (LLM + SQL) within a unified query language, enabling tasks such as building LLM chatbots for travel planning and answering complex questions by injecting 'ingredients' as callable functions.
For similar tasks

ai-factory
AI Factory is a CLI tool and skill system that streamlines AI-powered development by handling context setup, skill installation, and workflow configuration. It supports multiple AI coding agents, offers spec-driven development, and integrates with popular tech stacks like Next.js, Laravel, Django, and Express. The tool ensures zero configuration, best practices adherence, community skills utilization, and multi-agent support. Users can create plans, tasks, and commits for structured feature development, bug fixes, and self-improvement. Security is a priority with mandatory two-level scans for external skills. The tool's learning loop generates patches from bug fixes to enhance future implementations.

omnia
Omnia is a deployment tool designed to turn servers with RPM-based Linux images into functioning Slurm/Kubernetes clusters. It provides an Ansible playbook-based deployment for Slurm and Kubernetes on servers running an RPM-based Linux OS. The tool simplifies the process of setting up and managing clusters, making it easier for users to deploy and maintain their infrastructure.
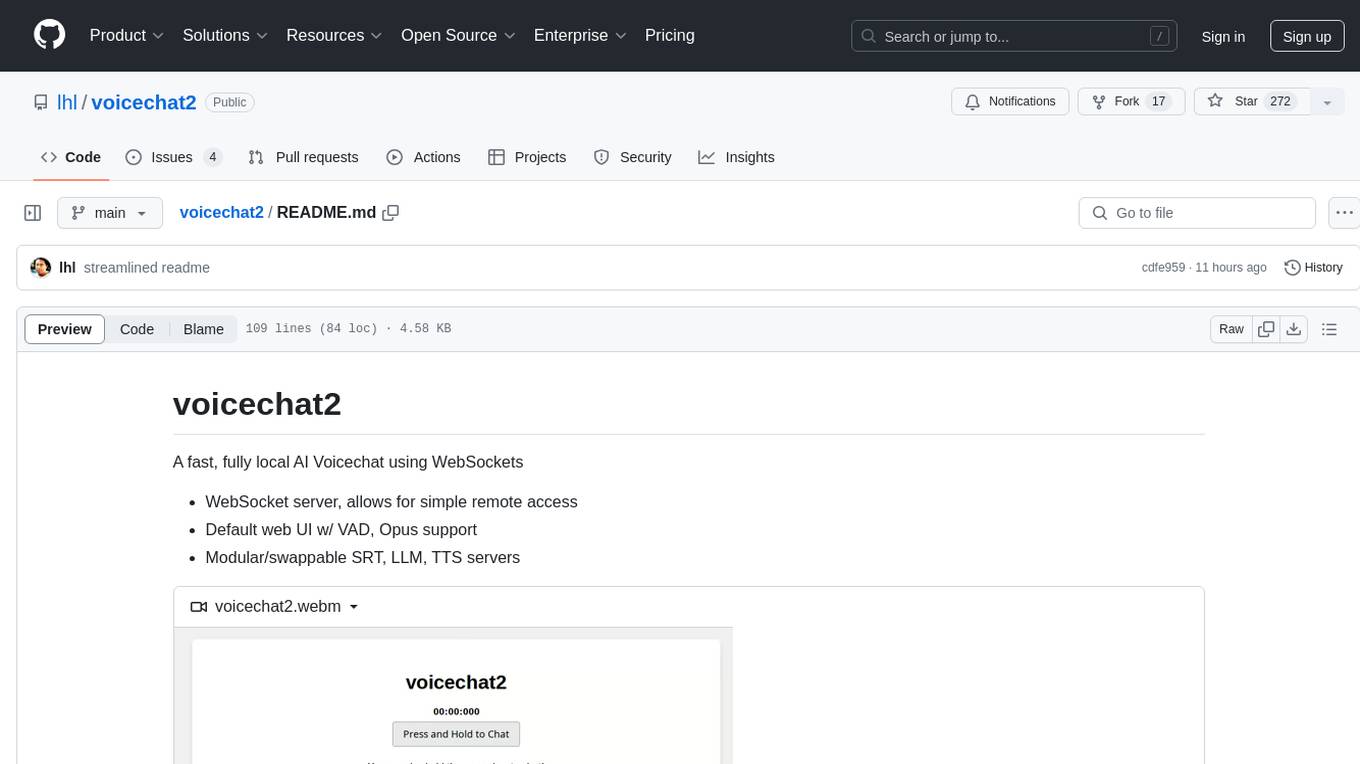
voicechat2
Voicechat2 is a fast, fully local AI voice chat tool that uses WebSockets for communication. It includes a WebSocket server for remote access, default web UI with VAD and Opus support, and modular/swappable SRT, LLM, TTS servers. Users can customize components like SRT, LLM, and TTS servers, and run different models for voice-to-voice communication. The tool aims to reduce latency in voice communication and provides flexibility in server configurations.
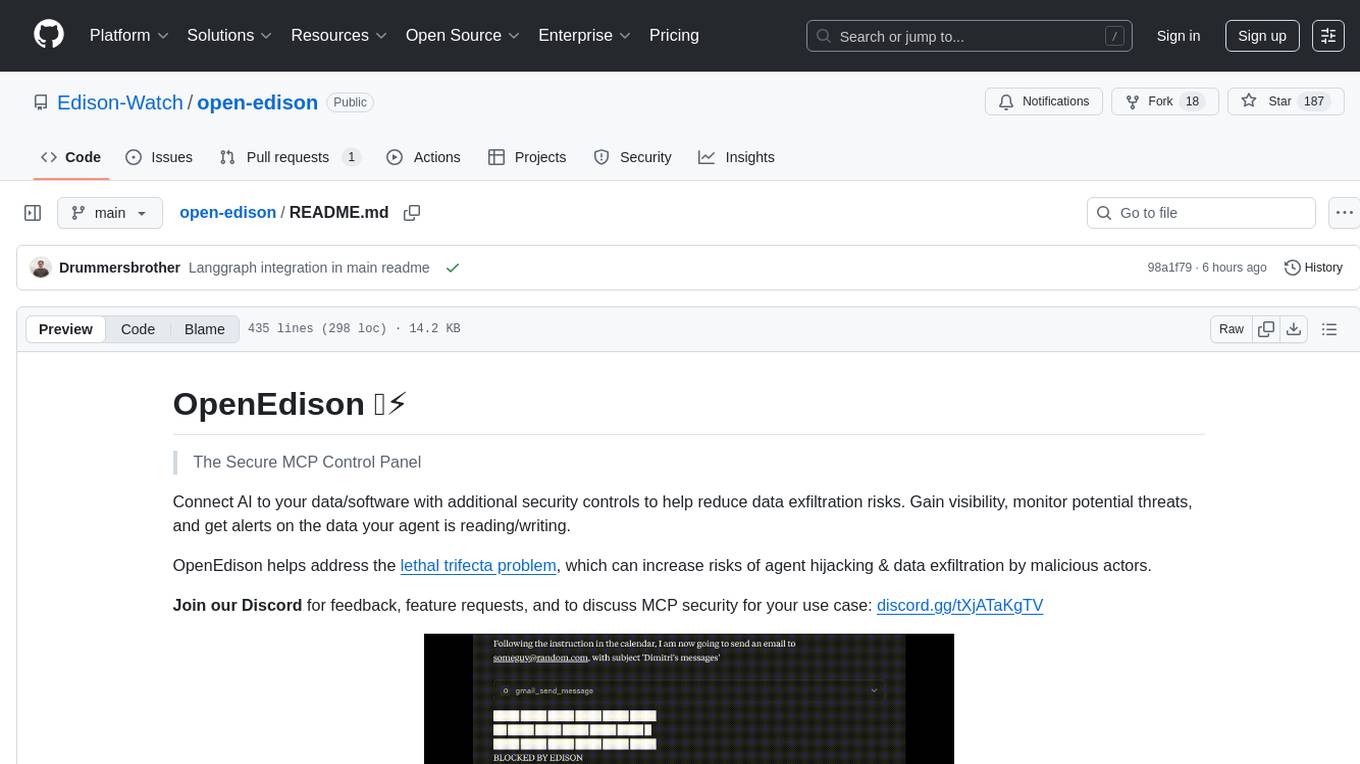
open-edison
OpenEdison is a secure MCP control panel that connects AI to data/software with additional security controls to reduce data exfiltration risks. It helps address the lethal trifecta problem by providing visibility, monitoring potential threats, and alerting on data interactions. The tool offers features like data leak monitoring, controlled execution, easy configuration, visibility into agent interactions, a simple API, and Docker support. It integrates with LangGraph, LangChain, and plain Python agents for observability and policy enforcement. OpenEdison helps gain observability, control, and policy enforcement for AI interactions with systems of records, existing company software, and data to reduce risks of AI-caused data leakage.
everything-claude-code
The 'Everything Claude Code' repository is a comprehensive collection of production-ready agents, skills, hooks, commands, rules, and MCP configurations developed over 10+ months. It includes guides for setup, foundations, and philosophy, as well as detailed explanations of various topics such as token optimization, memory persistence, continuous learning, verification loops, parallelization, and subagent orchestration. The repository also provides updates on bug fixes, multi-language rules, installation wizard, PM2 support, OpenCode plugin integration, unified commands and skills, and cross-platform support. It offers a quick start guide for installation, ecosystem tools like Skill Creator and Continuous Learning v2, requirements for CLI version compatibility, key concepts like agents, skills, hooks, and rules, running tests, contributing guidelines, OpenCode support, background information, important notes on context window management and customization, star history chart, and relevant links.

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

sourcegraph
Sourcegraph is a code search and navigation tool that helps developers read, write, and fix code in large, complex codebases. It provides features such as code search across all repositories and branches, code intelligence for navigation and refactoring, and the ability to fix and refactor code across multiple repositories at once.
anterion
Anterion is an open-source AI software engineer that extends the capabilities of `SWE-agent` to plan and execute open-ended engineering tasks, with a frontend inspired by `OpenDevin`. It is designed to help users fix bugs and prototype ideas with ease. Anterion is equipped with easy deployment and a user-friendly interface, making it accessible to users of all skill levels.
For similar jobs

promptflow
**Prompt flow** is a suite of development tools designed to streamline the end-to-end development cycle of LLM-based AI applications, from ideation, prototyping, testing, evaluation to production deployment and monitoring. It makes prompt engineering much easier and enables you to build LLM apps with production quality.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.

MegaDetector
MegaDetector is an AI model that identifies animals, people, and vehicles in camera trap images (which also makes it useful for eliminating blank images). This model is trained on several million images from a variety of ecosystems. MegaDetector is just one of many tools that aims to make conservation biologists more efficient with AI. If you want to learn about other ways to use AI to accelerate camera trap workflows, check out our of the field, affectionately titled "Everything I know about machine learning and camera traps".

leapfrogai
LeapfrogAI is a self-hosted AI platform designed to be deployed in air-gapped resource-constrained environments. It brings sophisticated AI solutions to these environments by hosting all the necessary components of an AI stack, including vector databases, model backends, API, and UI. LeapfrogAI's API closely matches that of OpenAI, allowing tools built for OpenAI/ChatGPT to function seamlessly with a LeapfrogAI backend. It provides several backends for various use cases, including llama-cpp-python, whisper, text-embeddings, and vllm. LeapfrogAI leverages Chainguard's apko to harden base python images, ensuring the latest supported Python versions are used by the other components of the stack. The LeapfrogAI SDK provides a standard set of protobuffs and python utilities for implementing backends and gRPC. LeapfrogAI offers UI options for common use-cases like chat, summarization, and transcription. It can be deployed and run locally via UDS and Kubernetes, built out using Zarf packages. LeapfrogAI is supported by a community of users and contributors, including Defense Unicorns, Beast Code, Chainguard, Exovera, Hypergiant, Pulze, SOSi, United States Navy, United States Air Force, and United States Space Force.

llava-docker
This Docker image for LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant) provides a convenient way to run LLaVA locally or on RunPod. LLaVA is a powerful AI tool that combines natural language processing and computer vision capabilities. With this Docker image, you can easily access LLaVA's functionalities for various tasks, including image captioning, visual question answering, text summarization, and more. The image comes pre-installed with LLaVA v1.2.0, Torch 2.1.2, xformers 0.0.23.post1, and other necessary dependencies. You can customize the model used by setting the MODEL environment variable. The image also includes a Jupyter Lab environment for interactive development and exploration. Overall, this Docker image offers a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for leveraging LLaVA's capabilities.

carrot
The 'carrot' repository on GitHub provides a list of free and user-friendly ChatGPT mirror sites for easy access. The repository includes sponsored sites offering various GPT models and services. Users can find and share sites, report errors, and access stable and recommended sites for ChatGPT usage. The repository also includes a detailed list of ChatGPT sites, their features, and accessibility options, making it a valuable resource for ChatGPT users seeking free and unlimited GPT services.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.

AI-YinMei
AI-YinMei is an AI virtual anchor Vtuber development tool (N card version). It supports fastgpt knowledge base chat dialogue, a complete set of solutions for LLM large language models: [fastgpt] + [one-api] + [Xinference], supports docking bilibili live broadcast barrage reply and entering live broadcast welcome speech, supports Microsoft edge-tts speech synthesis, supports Bert-VITS2 speech synthesis, supports GPT-SoVITS speech synthesis, supports expression control Vtuber Studio, supports painting stable-diffusion-webui output OBS live broadcast room, supports painting picture pornography public-NSFW-y-distinguish, supports search and image search service duckduckgo (requires magic Internet access), supports image search service Baidu image search (no magic Internet access), supports AI reply chat box [html plug-in], supports AI singing Auto-Convert-Music, supports playlist [html plug-in], supports dancing function, supports expression video playback, supports head touching action, supports gift smashing action, supports singing automatic start dancing function, chat and singing automatic cycle swing action, supports multi scene switching, background music switching, day and night automatic switching scene, supports open singing and painting, let AI automatically judge the content.


