
ai-dial-chat
A default UI for AI DIAL
Stars: 463
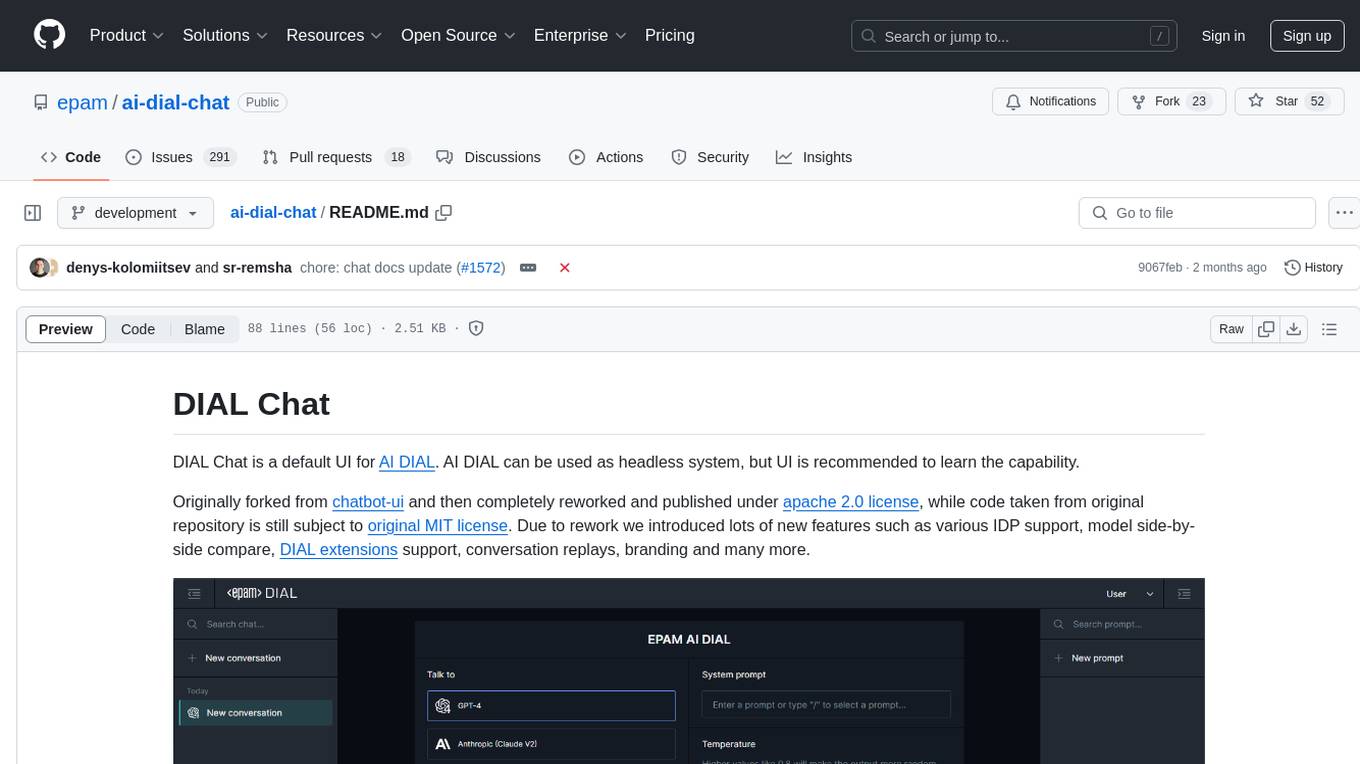
DIAL Chat is a default UI for AI DIAL, recommended for learning the capability of the headless system. It offers various features like IDP support, model comparison, DIAL extensions, conversation replays, and branding. Managed as a monorepo by NX tools, it provides documentation for DIAL Chat, Theming, Overlay, and Visualizer Connector. Users can find a user guide for the AI DIAL Chat application in the AI DIAL repository.
README:
DIAL Chat is a default UI for DIAL. DIAL can be used as headless system, but UI is recommended to learn the capability.
Originally forked from chatbot-ui and then completely reworked and published under apache 2.0 license, while code taken from original repository is still subject to original MIT license. Due to rework we introduced lots of new features such as various IDP support, model side-by-side compare, DIAL extensions support, conversation replays, branding and many more.
[!IMPORTANT] This repository is managed as monorepo by NX tools.
-
DIAL Chatdocumentation placed here. -
DIAL Chat Themingdocumentation is placed here. -
DIAL Overlaydocumentation is placed here. -
DIAL Chat Visualizer Connectordocumentation is placed here. -
DIAL Visualizer Connectordocumentation is placed here. -
DIAL Custom Viewersdocumentation is placed here. -
Isolated view modeis described in documentation.
[!TIP] In DIAL repository, you can find a user guide for the DIAL Chat application.
To work with this repo we are using NX.
Note: All commands could be found in scripts section in package.json.
npm iRun this command to build all projects which support this target (chat, overlay-sandbox):
npm run buildTo run the project, it is recommended to use npm run nx serve with the specified project name:
npm run nx serve project-nameRun this command to run tests for the full repository:
npm run testRun this command to initiate npm publish for all publishable libraries:
npm run publish -- --ver=*.*.* --tag=* --dry --developmentParameters (all optional):
ver - version to publish
dry - dry run
tag - tag to publish with (default: 'next')
development - if set without a version provided, will increment a version automatically according to the current version of the global package.json version (e.g. 0.5.0-rc.1, 0.5.0-rc.2, etc.)
In dry mode, nothing is published, just displayed on the screen:
npm run publish -- --dryor
npm run publish:dryFor Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for ai-dial-chat
Similar Open Source Tools

ai-dial-chat
DIAL Chat is a default UI for AI DIAL, recommended for learning the capability of the headless system. It offers various features like IDP support, model comparison, DIAL extensions, conversation replays, and branding. Managed as a monorepo by NX tools, it provides documentation for DIAL Chat, Theming, Overlay, and Visualizer Connector. Users can find a user guide for the AI DIAL Chat application in the AI DIAL repository.
gitingest
GitIngest is a tool that allows users to turn any Git repository into a prompt-friendly text ingest for LLMs. It provides easy code context by generating a text digest from a git repository URL or directory. The tool offers smart formatting for optimized output format for LLM prompts and provides statistics about file and directory structure, size of the extract, and token count. GitIngest can be used as a CLI tool on Linux and as a Python package for code integration. The tool is built using Tailwind CSS for frontend, FastAPI for backend framework, tiktoken for token estimation, and apianalytics.dev for simple analytics. Users can self-host GitIngest by building the Docker image and running the container. Contributions to the project are welcome, and the tool aims to be beginner-friendly for first-time contributors with a simple Python and HTML codebase.
tiledesk-dashboard
Tiledesk is an open-source live chat platform with integrated chatbots written in Node.js and Express. It is designed to be a multi-channel platform for web, Android, and iOS, and it can be used to increase sales or provide post-sales customer service. Tiledesk's chatbot technology allows for automation of conversations, and it also provides APIs and webhooks for connecting external applications. Additionally, it offers a marketplace for apps and features such as CRM, ticketing, and data export.
pear-landing-page
PearAI Landing Page is an open-source AI-powered code editor managed by Nang and Pan. It is built with Next.js, Vercel, Tailwind CSS, and TypeScript. The project requires setting up environment variables for proper configuration. Users can run the project locally by starting the development server and visiting the specified URL in the browser. Recommended extensions include Prettier, ESLint, and JavaScript and TypeScript Nightly. Contributions to the project are welcomed and appreciated.
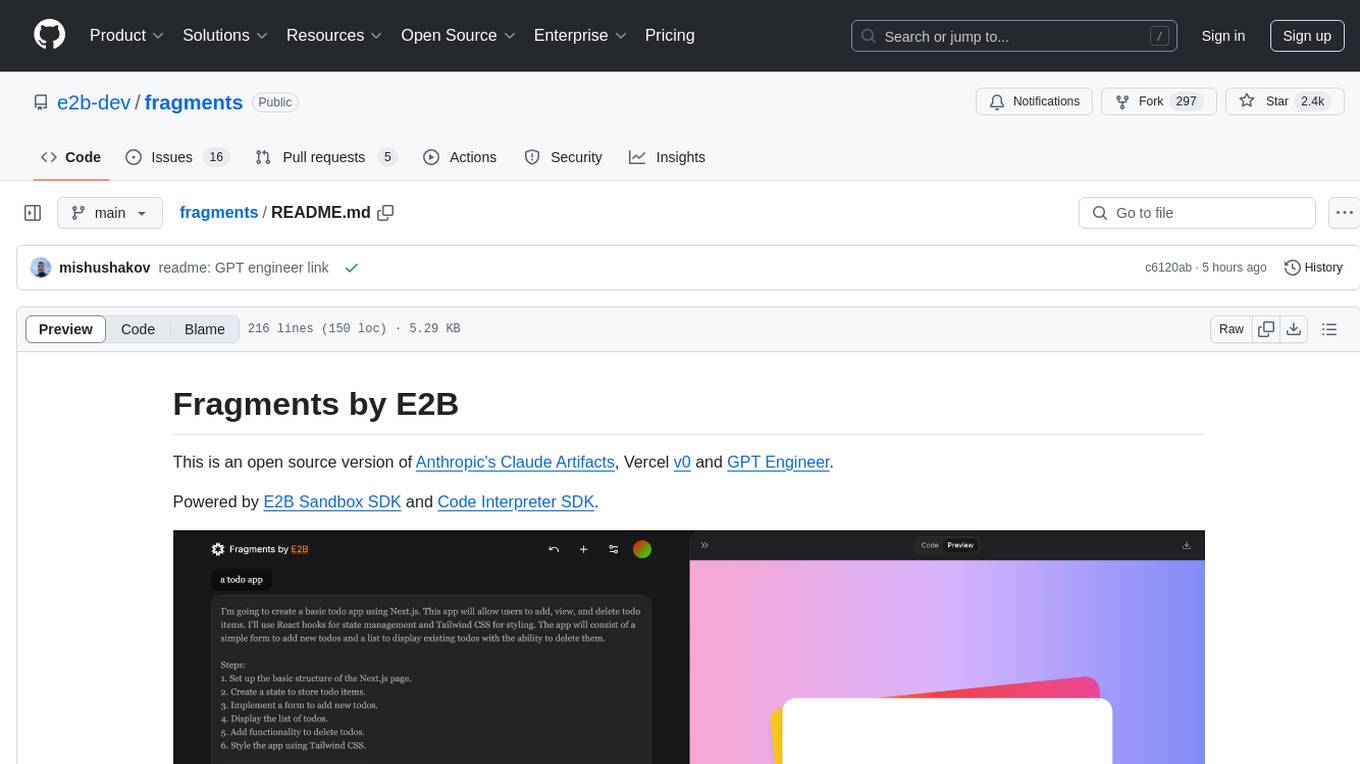
fragments
Fragments is an open-source tool that leverages Anthropic's Claude Artifacts, Vercel v0, and GPT Engineer. It is powered by E2B Sandbox SDK and Code Interpreter SDK, allowing secure execution of AI-generated code. The tool is based on Next.js 14, shadcn/ui, TailwindCSS, and Vercel AI SDK. Users can stream in the UI, install packages from npm and pip, and add custom stacks and LLM providers. Fragments enables users to build web apps with Python interpreter, Next.js, Vue.js, Streamlit, and Gradio, utilizing providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, Google AI, and more.
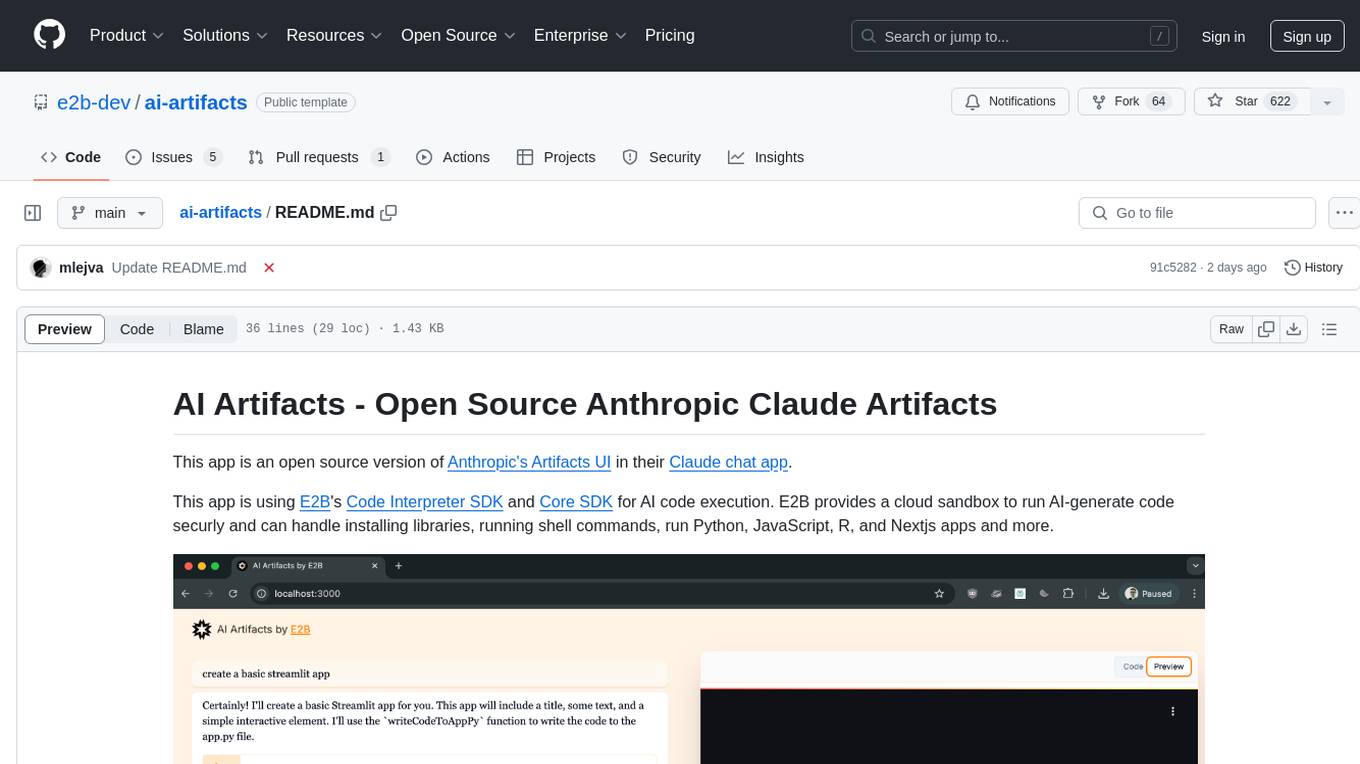
ai-artifacts
AI Artifacts is an open source tool that replicates Anthropic's Artifacts UI in the Claude chat app. It utilizes E2B's Code Interpreter SDK and Core SDK for secure AI code execution in a cloud sandbox environment. Users can run AI-generated code in various languages such as Python, JavaScript, R, and Nextjs apps. The tool also supports running AI-generated Python in Jupyter notebook, Next.js apps, and Streamlit apps. Additionally, it offers integration with Vercel AI SDK for tool calling and streaming responses from the model.
ChatGPT
The ChatGPT API Free Reverse Proxy provides free self-hosted API access to ChatGPT (`gpt-3.5-turbo`) with OpenAI's familiar structure, eliminating the need for code changes. It offers streaming response, API endpoint compatibility, and complimentary access without an API key. Installation options include Docker, PC/Server, and Termux on Android devices. The API can be accessed through a self-hosted local server or a pre-hosted API with an API key obtained from the Discord server. Usage examples are provided for Python and Node.js, and the project is licensed under AGPL-3.0.
steel-browser
Steel is an open-source browser API designed for AI agents and applications, simplifying the process of building live web agents and browser automation tools. It serves as a core building block for a production-ready, containerized browser sandbox with features like stealth capabilities, text-to-markdown session management, UI for session viewing/debugging, and full browser control through popular automation frameworks. Steel allows users to control, run, and manage a production-ready browser environment via a REST API, offering features such as full browser control, session management, proxy support, extension support, debugging tools, anti-detection mechanisms, resource management, and various browser tools. It aims to streamline complex browsing tasks programmatically, enabling users to focus on their AI applications while Steel handles the underlying complexity.
lexido
Lexido is an innovative assistant for the Linux command line, designed to boost your productivity and efficiency. Powered by Gemini Pro 1.0 and utilizing the free API, Lexido offers smart suggestions for commands based on your prompts and importantly your current environment. Whether you're installing software, managing files, or configuring system settings, Lexido streamlines the process, making it faster and more intuitive.
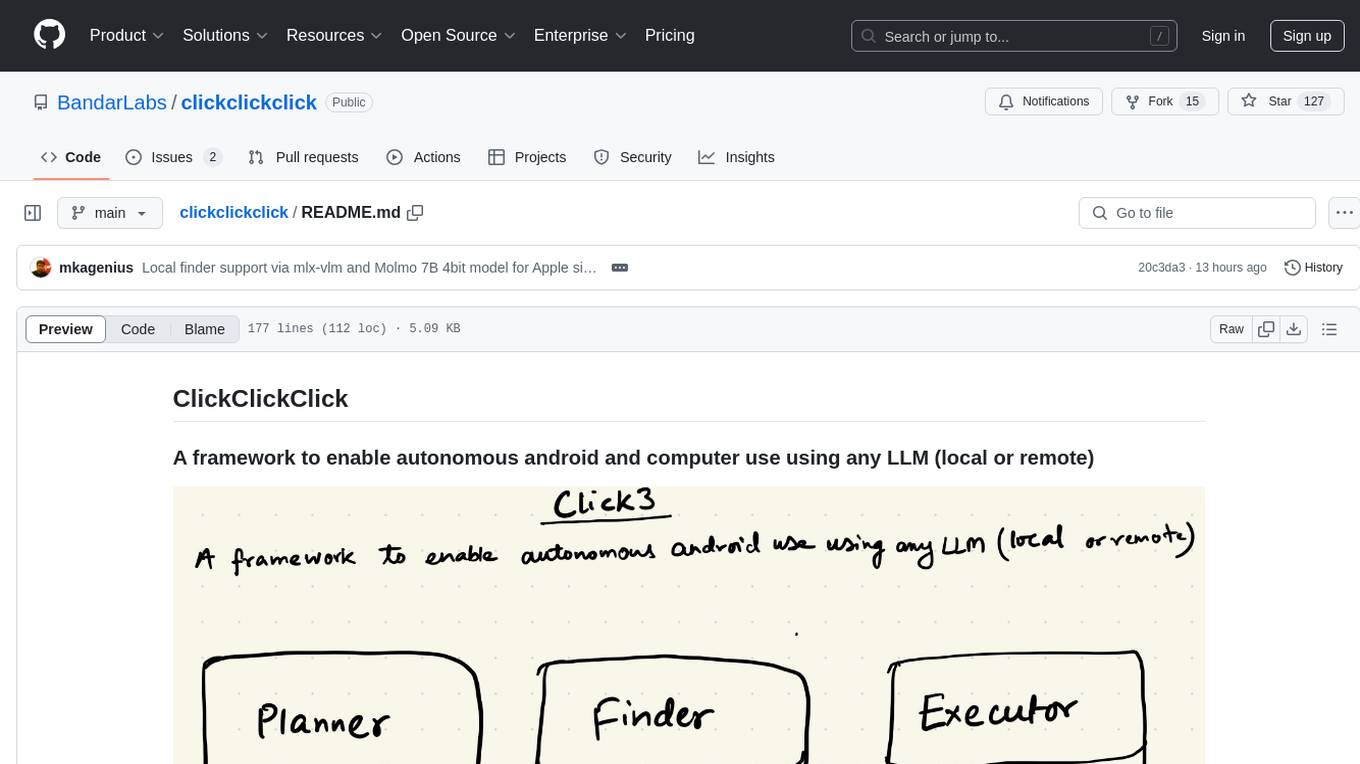
clickclickclick
ClickClickClick is a framework designed to enable autonomous Android and computer use using various LLM models, both locally and remotely. It supports tasks such as drafting emails, opening browsers, and starting games, with current support for local models via Ollama, Gemini, and GPT 4o. The tool is highly experimental and evolving, with the best results achieved using specific model combinations. Users need prerequisites like `adb` installation and USB debugging enabled on Android phones. The tool can be installed via cloning the repository, setting up a virtual environment, and installing dependencies. It can be used as a CLI tool or script, allowing users to configure planner and finder models for different tasks. Additionally, it can be used as an API to execute tasks based on provided prompts, platform, and models.
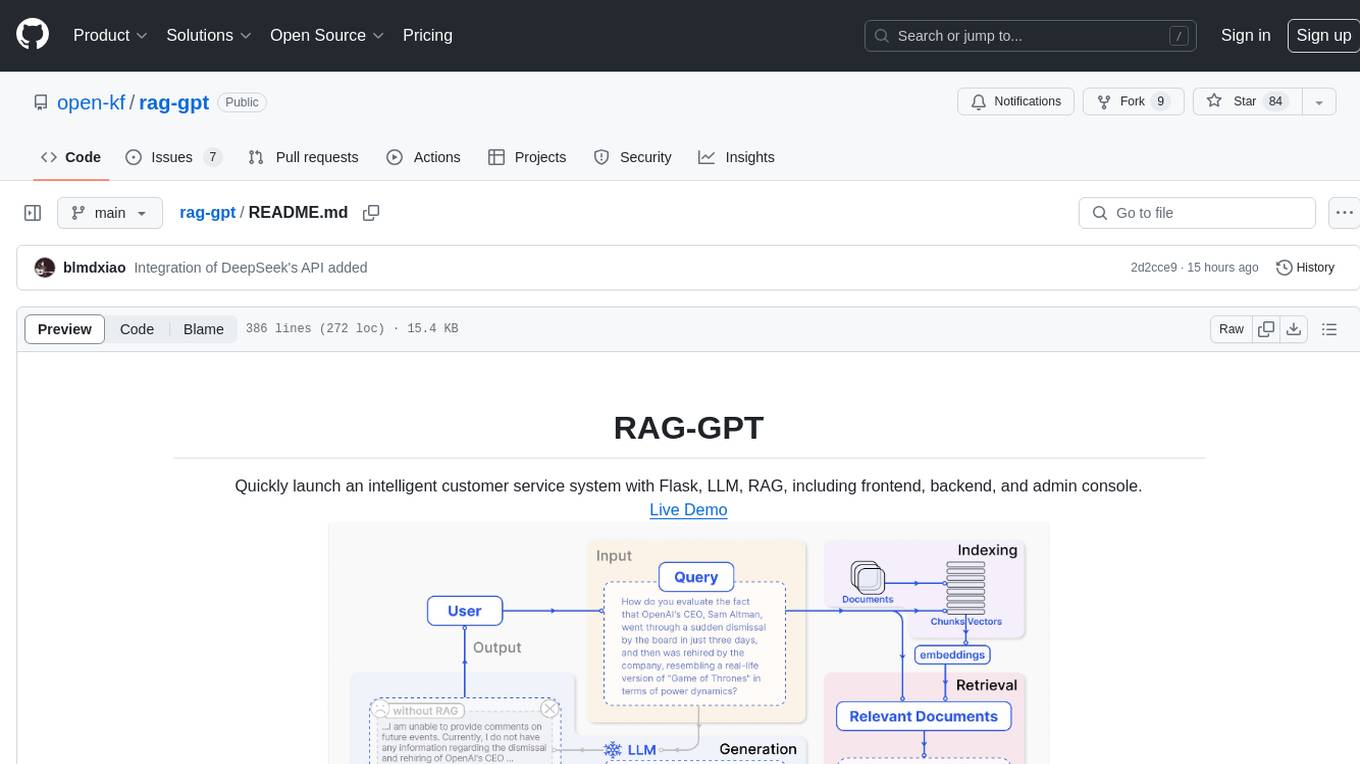
rag-gpt
RAG-GPT is a tool that allows users to quickly launch an intelligent customer service system with Flask, LLM, and RAG. It includes frontend, backend, and admin console components. The tool supports cloud-based and local LLMs, enables deployment of conversational service robots in minutes, integrates diverse knowledge bases, offers flexible configuration options, and features an attractive user interface.
backend.ai-webui
Backend.AI Web UI is a user-friendly web and app interface designed to make AI accessible for end-users, DevOps, and SysAdmins. It provides features for session management, inference service management, pipeline management, storage management, node management, statistics, configurations, license checking, plugins, help & manuals, kernel management, user management, keypair management, manager settings, proxy mode support, service information, and integration with the Backend.AI Web Server. The tool supports various devices, offers a built-in websocket proxy feature, and allows for versatile usage across different platforms. Users can easily manage resources, run environment-supported apps, access a web-based terminal, use Visual Studio Code editor, manage experiments, set up autoscaling, manage pipelines, handle storage, monitor nodes, view statistics, configure settings, and more.
chat-ui
A chat interface using open source models, eg OpenAssistant or Llama. It is a SvelteKit app and it powers the HuggingChat app on hf.co/chat.
trieve
Trieve is an advanced relevance API for hybrid search, recommendations, and RAG. It offers a range of features including self-hosting, semantic dense vector search, typo tolerant full-text/neural search, sub-sentence highlighting, recommendations, convenient RAG API routes, the ability to bring your own models, hybrid search with cross-encoder re-ranking, recency biasing, tunable popularity-based ranking, filtering, duplicate detection, and grouping. Trieve is designed to be flexible and customizable, allowing users to tailor it to their specific needs. It is also easy to use, with a simple API and well-documented features.

web-ui
WebUI is a user-friendly tool built on Gradio that enhances website accessibility for AI agents. It supports various Large Language Models (LLMs) and allows custom browser integration for seamless interaction. The tool eliminates the need for re-login and authentication challenges, offering high-definition screen recording capabilities.

AutoAgent
AutoAgent is a fully-automated and zero-code framework that enables users to create and deploy LLM agents through natural language alone. It is a top performer on the GAIA Benchmark, equipped with a native self-managing vector database, and allows for easy creation of tools, agents, and workflows without any coding. AutoAgent seamlessly integrates with a wide range of LLMs and supports both function-calling and ReAct interaction modes. It is designed to be dynamic, extensible, customized, and lightweight, serving as a personal AI assistant.
For similar tasks

ai-dial-chat
DIAL Chat is a default UI for AI DIAL, recommended for learning the capability of the headless system. It offers various features like IDP support, model comparison, DIAL extensions, conversation replays, and branding. Managed as a monorepo by NX tools, it provides documentation for DIAL Chat, Theming, Overlay, and Visualizer Connector. Users can find a user guide for the AI DIAL Chat application in the AI DIAL repository.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

fasttrackml
FastTrackML is an experiment tracking server focused on speed and scalability, fully compatible with MLFlow. It provides a user-friendly interface to track and visualize your machine learning experiments, making it easy to compare different models and identify the best performing ones. FastTrackML is open source and can be easily installed and run with pip or Docker. It is also compatible with the MLFlow Python package, making it easy to integrate with your existing MLFlow workflows.
ScandEval
ScandEval is a framework for evaluating pretrained language models on mono- or multilingual language tasks. It provides a unified interface for benchmarking models on a variety of tasks, including sentiment analysis, question answering, and machine translation. ScandEval is designed to be easy to use and extensible, making it a valuable tool for researchers and practitioners alike.
opencompass
OpenCompass is a one-stop platform for large model evaluation, aiming to provide a fair, open, and reproducible benchmark for large model evaluation. Its main features include: * Comprehensive support for models and datasets: Pre-support for 20+ HuggingFace and API models, a model evaluation scheme of 70+ datasets with about 400,000 questions, comprehensively evaluating the capabilities of the models in five dimensions. * Efficient distributed evaluation: One line command to implement task division and distributed evaluation, completing the full evaluation of billion-scale models in just a few hours. * Diversified evaluation paradigms: Support for zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought evaluations, combined with standard or dialogue-type prompt templates, to easily stimulate the maximum performance of various models. * Modular design with high extensibility: Want to add new models or datasets, customize an advanced task division strategy, or even support a new cluster management system? Everything about OpenCompass can be easily expanded! * Experiment management and reporting mechanism: Use config files to fully record each experiment, and support real-time reporting of results.
lighteval
LightEval is a lightweight LLM evaluation suite that Hugging Face has been using internally with the recently released LLM data processing library datatrove and LLM training library nanotron. We're releasing it with the community in the spirit of building in the open. Note that it is still very much early so don't expect 100% stability ^^' In case of problems or question, feel free to open an issue!
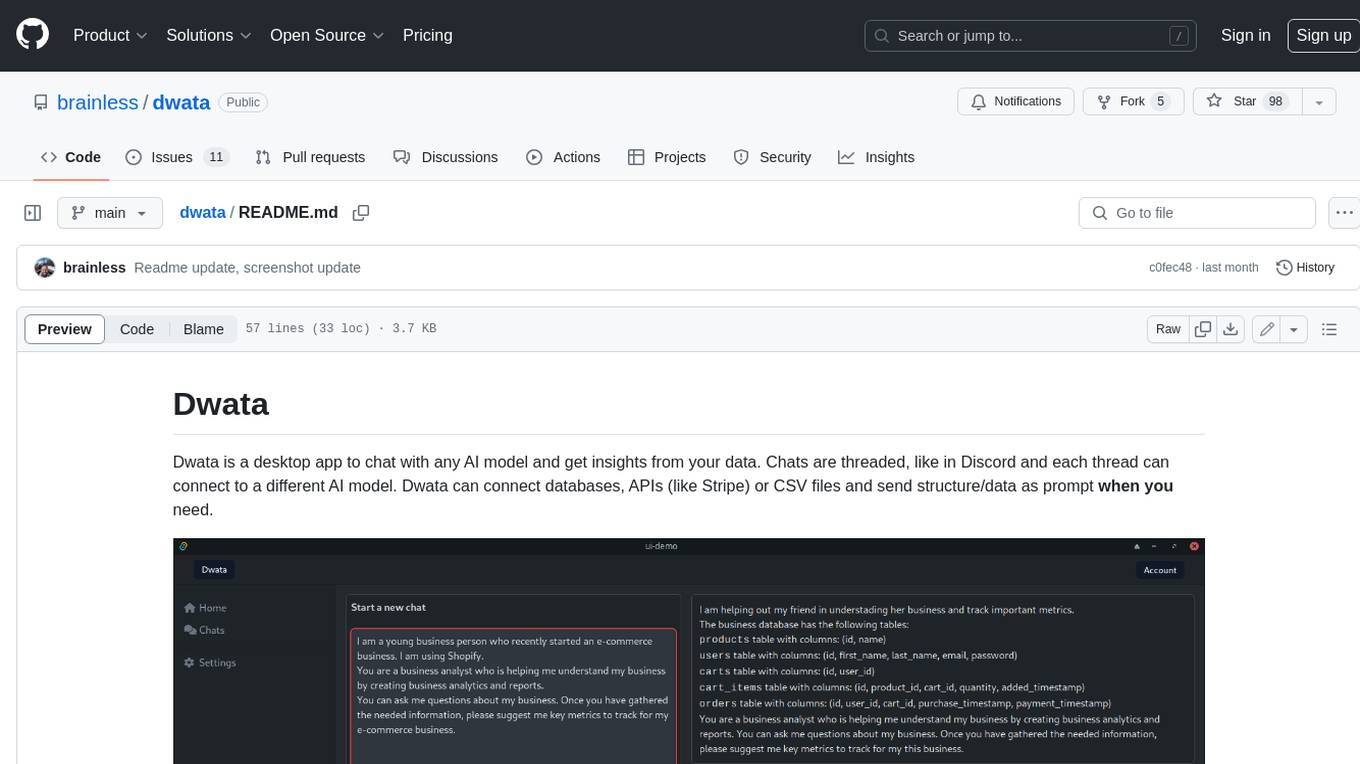
dwata
Dwata is a desktop application that allows users to chat with any AI model and gain insights from their data. Chats are organized into threads, similar to Discord, with each thread connecting to a different AI model. Dwata can connect to databases, APIs (such as Stripe), or CSV files and send structured data as prompts when needed. The AI's response will often include SQL or Python code, which can be used to extract the desired insights. Dwata can validate AI-generated SQL to ensure that the tables and columns referenced are correct and can execute queries against the database from within the application. Python code (typically using Pandas) can also be executed from within Dwata, although this feature is still in development. Dwata supports a range of AI models, including OpenAI's GPT-4, GPT-4 Turbo, and GPT-3.5 Turbo; Groq's LLaMA2-70b and Mixtral-8x7b; Phind's Phind-34B and Phind-70B; Anthropic's Claude; and Ollama's Llama 2, Mistral, and Phi-2 Gemma. Dwata can compare chats from different models, allowing users to see the responses of multiple models to the same prompts. Dwata can connect to various data sources, including databases (PostgreSQL, MySQL, MongoDB), SaaS products (Stripe, Shopify), CSV files/folders, and email (IMAP). The desktop application does not collect any private or business data without the user's explicit consent.
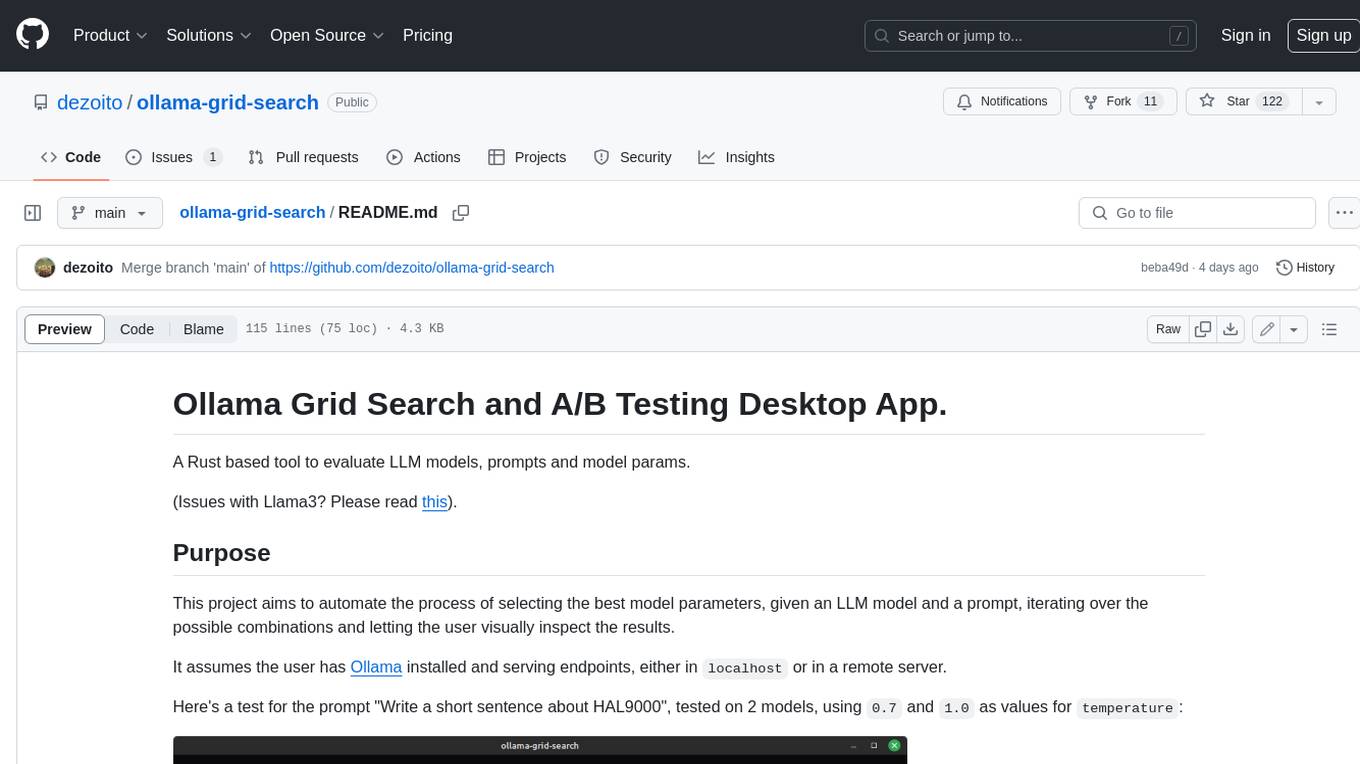
ollama-grid-search
A Rust based tool to evaluate LLM models, prompts and model params. It automates the process of selecting the best model parameters, given an LLM model and a prompt, iterating over the possible combinations and letting the user visually inspect the results. The tool assumes the user has Ollama installed and serving endpoints, either in `localhost` or in a remote server. Key features include: * Automatically fetches models from local or remote Ollama servers * Iterates over different models and params to generate inferences * A/B test prompts on different models simultaneously * Allows multiple iterations for each combination of parameters * Makes synchronous inference calls to avoid spamming servers * Optionally outputs inference parameters and response metadata (inference time, tokens and tokens/s) * Refetching of individual inference calls * Model selection can be filtered by name * List experiments which can be downloaded in JSON format * Configurable inference timeout * Custom default parameters and system prompts can be defined in settings
For similar jobs
responsible-ai-toolbox
Responsible AI Toolbox is a suite of tools providing model and data exploration and assessment interfaces and libraries for understanding AI systems. It empowers developers and stakeholders to develop and monitor AI responsibly, enabling better data-driven actions. The toolbox includes visualization widgets for model assessment, error analysis, interpretability, fairness assessment, and mitigations library. It also offers a JupyterLab extension for managing machine learning experiments and a library for measuring gender bias in NLP datasets.
LLMLingua
LLMLingua is a tool that utilizes a compact, well-trained language model to identify and remove non-essential tokens in prompts. This approach enables efficient inference with large language models, achieving up to 20x compression with minimal performance loss. The tool includes LLMLingua, LongLLMLingua, and LLMLingua-2, each offering different levels of prompt compression and performance improvements for tasks involving large language models.
llm-examples
Starter examples for building LLM apps with Streamlit. This repository showcases a growing collection of LLM minimum working examples, including a Chatbot, File Q&A, Chat with Internet search, LangChain Quickstart, LangChain PromptTemplate, and Chat with user feedback. Users can easily get their own OpenAI API key and set it as an environment variable in Streamlit apps to run the examples locally.

LMOps
LMOps is a research initiative focusing on fundamental research and technology for building AI products with foundation models, particularly enabling AI capabilities with Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generative AI models. The project explores various aspects such as prompt optimization, longer context handling, LLM alignment, acceleration of LLMs, LLM customization, and understanding in-context learning. It also includes tools like Promptist for automatic prompt optimization, Structured Prompting for efficient long-sequence prompts consumption, and X-Prompt for extensible prompts beyond natural language. Additionally, LLMA accelerators are developed to speed up LLM inference by referencing and copying text spans from documents. The project aims to advance technologies that facilitate prompting language models and enhance the performance of LLMs in various scenarios.
awesome-tool-llm
This repository focuses on exploring tools that enhance the performance of language models for various tasks. It provides a structured list of literature relevant to tool-augmented language models, covering topics such as tool basics, tool use paradigm, scenarios, advanced methods, and evaluation. The repository includes papers, preprints, and books that discuss the use of tools in conjunction with language models for tasks like reasoning, question answering, mathematical calculations, accessing knowledge, interacting with the world, and handling non-textual modalities.
gaianet-node
GaiaNet-node is a tool that allows users to run their own GaiaNet node, enabling them to interact with an AI agent. The tool provides functionalities to install the default node software stack, initialize the node with model files and vector database files, start the node, stop the node, and update configurations. Users can use pre-set configurations or pass a custom URL for initialization. The tool is designed to facilitate communication with the AI agent and access node information via a browser. GaiaNet-node requires sudo privilege for installation but can also be installed without sudo privileges with specific commands.
llmops-duke-aipi
LLMOps Duke AIPI is a course focused on operationalizing Large Language Models, teaching methodologies for developing applications using software development best practices with large language models. The course covers various topics such as generative AI concepts, setting up development environments, interacting with large language models, using local large language models, applied solutions with LLMs, extensibility using plugins and functions, retrieval augmented generation, introduction to Python web frameworks for APIs, DevOps principles, deploying machine learning APIs, LLM platforms, and final presentations. Students will learn to build, share, and present portfolios using Github, YouTube, and Linkedin, as well as develop non-linear life-long learning skills. Prerequisites include basic Linux and programming skills, with coursework available in Python or Rust. Additional resources and references are provided for further learning and exploration.
Awesome-AISourceHub
Awesome-AISourceHub is a repository that collects high-quality information sources in the field of AI technology. It serves as a synchronized source of information to avoid information gaps and information silos. The repository aims to provide valuable resources for individuals such as AI book authors, enterprise decision-makers, and tool developers who frequently use Twitter to share insights and updates related to AI advancements. The platform emphasizes the importance of accessing information closer to the source for better quality content. Users can contribute their own high-quality information sources to the repository by following specific steps outlined in the contribution guidelines. The repository covers various platforms such as Twitter, public accounts, knowledge planets, podcasts, blogs, websites, YouTube channels, and more, offering a comprehensive collection of AI-related resources for individuals interested in staying updated with the latest trends and developments in the AI field.

