
PINNeAPPle
Pinneaple is an open-source Physics AI toolkit for Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs), scientific ML, geometry processing, solvers, and reproducible training pipelines.
Stars: 160
Pinneaple is an open-source Python platform that unifies physical data, geometry, numerical solvers, and machine learning models for Physics-Informed AI. It emphasizes physical consistency, scalability, auditability, and interoperability with CFD/CAD/scientific data formats. It provides tools for unified physical dataset representation, data pipelines, geometry and mesh operations, a model zoo, physics loss factory, solvers, synthetic data generation, training and evaluation. The platform is designed for physics AI researchers, CFD/FEA/climate ML teams, industrial R&D groups, scientific ML practitioners, and anyone building surrogates, inverse models, or hybrid solvers.
README:
Unified Physical Data, Geometry, Models and Training for Physics AI
Pinneaple is an open-source Python platform designed to bridge real physical data, geometry, numerical solvers, and machine learning models into a single coherent ecosystem for Physics-Informed AI.
It is built to serve both research and industrial workflows, with strong emphasis on:
- Physical consistency
- Scalability
- Auditability
- Interoperability with CFD / CAD / scientific data formats
A standardized abstraction to represent physical samples, including:
- Physical state (grids, meshes, graphs)
- Geometry (CAD / mesh)
- Governing equations, ICs, BCs, forcings
- Units, regimes, metadata and provenance
Used consistently across data loading, training, validation, and inference.
- NASA / scientific-ready data pipelines
- Zarr-backed datasets with:
- Lazy loading
- Sharding
- Adaptive prefetch
- Byte-based LRU caching
- Deterministic shard-aware iterators
- Physical validation and schema enforcement
- CAD generation (CadQuery)
- STL / mesh IO (trimesh, meshio, OpenFOAM MVP)
- Mesh repair, remeshing and simplification
- Sampling (points, grids, barycentric)
- Geometry-aware feature extraction
A curated catalog of architectures commonly used in Physics AI:
- PINNs (Vanilla, XPINN, VPINN, XTFC, Inverse PINN, PIELM)
- Neural Operators (FNO, DeepONet, PINO, GNO, UNO)
- Graph Neural Networks (GraphCast-style, GNN-ODE, equivariant GNNs)
- Transformers (Informer, FEDformer, Autoformer, TFT)
- Reduced Order Models (POD, DMD, HAVOK, Operator Inference)
- Classical & hybrid models (Kalman, ARIMA, Koopman, ESN)
- Physics-aware & structure-preserving networks
All models are discoverable via a central registry.
- Symbolic PDE definitions (SymPy-based)
- Automatic differentiation graph construction
- PINN-ready residuals and constraints
- Works directly with UPD samples
Numerical solvers and mathematical tools used for:
- Data generation
- Feature extraction
- Validation
Includes:
- FEM / FVM (MVP)
- FFT
- Hilbert–Huang Transform
- Adapters to/from UPD
Generate datasets from:
- Symbolic PDEs
- Parametric distributions
- Curve fitting from real data
- Images and signals
- Geometry perturbations and CAD parameter sweeps
- Deterministic, auditable training
- Dataset splitting (train/val/test)
- Preprocessing pipelines & normalizers
- Metrics & visualization
- Physics-aware loss integration
- Reproducible runs (seeds, env fingerprinting)
- Checkpointing & inference utilities
Pinneaple is currently distributed as an open-source research & industry framework directly from GitHub.
- Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/barrosyan/pinneaple.git
cd pinneaple- Create a virtual environment (strongly recommended)
Python ≥ 3.10 is recommended (3.11 works well; 3.13 may require extra care on Windows).
python -m venv .venvActivate it:
Linux / macOS
source .venv/bin/activateWindows (PowerShell)
.venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1- Install core dependencies
Install Pinneaple in editable (development) mode:
pip install -e .This installs:
pinneaple_data
pinneaple_geom
pinneaple_models
pinneaple_pinn
pinneaple_pdb
pinneaple_solvers
pinneaple_train
- Optional dependencies (recommended)
Pinneaple is modular. Install only what you need:
🔹 Geometry / CAD / Mesh
pip install trimesh meshio
pip install cadquery # requires OCC stackconda create -n pinneaple-cq python=3.10 cadquery -c conda-forge
conda activate pinneaple-cq
pip install -e .🔹 Scientific & ML stack
pip install torch numpy scipy sympyOptional (recommended for performance & operators):
pip install zarr numcodecs
pip install open3d fast-simplification
5️. Development & testing tools
For contributors:
pip install -e ".[dev]"- Verify installation
Quick smoke test:
from pinneaple_models.register_all import register_all
from pinneaple_models.registry import ModelRegistry
register_all()
print("Registered models:", len(ModelRegistry.list()))🧠 Notes
Pinneaple is not yet released on PyPI — cloning the repo is required.
Some features (CFD, CAD, large-scale Zarr) rely on optional native backends.
All examples in examples/ are runnable after installation.
from pinneaple_data.physical_sample import PhysicalSample
import xarray as xr
import numpy as np
ds = xr.Dataset(
data_vars=dict(T2M=(("t","x"), np.random.randn(24,16))),
coords=dict(t=np.arange(24), x=np.arange(16))
)
sample = PhysicalSample(
state=ds,
domain={"type": "grid"},
schema={"governing": "toy"},
)
print(sample.summary())- Physics AI researchers
- CFD / FEA / climate ML teams
- Industrial R&D groups
- Scientific ML practitioners
- Anyone building surrogates, inverse models, or hybrid solvers
We welcome contributions in:
- New datasets & adapters
- Models and solvers
- Benchmarks
- Documentation
See CONTRIBUTING.md.
Apache 2.0 — see LICENSE.
If you use Pinneaple in research, please cite via CITATION.cff.
Pinneaple is not a single model or method.
It is a platform — designed to let physical data, geometry, equations and learning systems interact cleanly, reproducibly, and at scale.
From raw physics to deployable intelligence.
Status: Early but ambitious.
Feedback & collaboration welcome.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for PINNeAPPle
Similar Open Source Tools

PINNeAPPle
Pinneaple is an open-source Python platform that unifies physical data, geometry, numerical solvers, and machine learning models for Physics-Informed AI. It emphasizes physical consistency, scalability, auditability, and interoperability with CFD/CAD/scientific data formats. It provides tools for unified physical dataset representation, data pipelines, geometry and mesh operations, a model zoo, physics loss factory, solvers, synthetic data generation, training and evaluation. The platform is designed for physics AI researchers, CFD/FEA/climate ML teams, industrial R&D groups, scientific ML practitioners, and anyone building surrogates, inverse models, or hybrid solvers.
executorch
ExecuTorch is an end-to-end solution for enabling on-device inference capabilities across mobile and edge devices including wearables, embedded devices and microcontrollers. It is part of the PyTorch Edge ecosystem and enables efficient deployment of PyTorch models to edge devices. Key value propositions of ExecuTorch are: * **Portability:** Compatibility with a wide variety of computing platforms, from high-end mobile phones to highly constrained embedded systems and microcontrollers. * **Productivity:** Enabling developers to use the same toolchains and SDK from PyTorch model authoring and conversion, to debugging and deployment to a wide variety of platforms. * **Performance:** Providing end users with a seamless and high-performance experience due to a lightweight runtime and utilizing full hardware capabilities such as CPUs, NPUs, and DSPs.
llms-interview-questions
This repository contains a comprehensive collection of 63 must-know Large Language Models (LLMs) interview questions. It covers topics such as the architecture of LLMs, transformer models, attention mechanisms, training processes, encoder-decoder frameworks, differences between LLMs and traditional statistical language models, handling context and long-term dependencies, transformers for parallelization, applications of LLMs, sentiment analysis, language translation, conversation AI, chatbots, and more. The readme provides detailed explanations, code examples, and insights into utilizing LLMs for various tasks.
transformerlab-app
Transformer Lab is an app that allows users to experiment with Large Language Models by providing features such as one-click download of popular models, finetuning across different hardware, RLHF and Preference Optimization, working with LLMs across different operating systems, chatting with models, using different inference engines, evaluating models, building datasets for training, calculating embeddings, providing a full REST API, running in the cloud, converting models across platforms, supporting plugins, embedded Monaco code editor, prompt editing, inference logs, all through a simple cross-platform GUI.
abi
ABI (Agentic Brain Infrastructure) is a Python-based AI Operating System designed to serve as the core infrastructure for building an Agentic AI Ontology Engine. It empowers organizations to integrate, manage, and scale AI-driven operations with multiple AI models, focusing on ontology, agent-driven workflows, and analytics. ABI emphasizes modularity and customization, providing a customizable framework aligned with international standards and regulatory frameworks. It offers features such as configurable AI agents, ontology management, integrations with external data sources, data processing pipelines, workflow automation, analytics, and data handling capabilities.
llamafarm
LlamaFarm is a comprehensive AI framework that empowers users to build powerful AI applications locally, with full control over costs and deployment options. It provides modular components for RAG systems, vector databases, model management, prompt engineering, and fine-tuning. Users can create differentiated AI products without needing extensive ML expertise, using simple CLI commands and YAML configs. The framework supports local-first development, production-ready components, strategy-based configuration, and deployment anywhere from laptops to the cloud.
llmos
LLMos is an operating system designed for physical AI agents, providing a hybrid runtime environment where AI agents can perceive, reason, act on hardware, and evolve over time locally without cloud dependency. It allows natural language programming, dual-brain architecture for fast instinct and deep planner brains, markdown-as-code for defining agents and skills, and supports swarm intelligence and cognitive world models. The tool is built on a tech stack including Next.js, Electron, Python, and WebAssembly, and is structured around a dual-brain cognitive architecture, volume system, HAL for hardware abstraction, applet system for dynamic UI, and dreaming & evolution for robot improvement. The project is in Phase 1 (Foundation) and aims to move into Phase 2 (Dual-Brain & Local Intelligence), with contributions welcomed under the Apache 2.0 license by Evolving Agents Labs.
ai
Jetify's AI SDK for Go is a unified interface for interacting with multiple AI providers including OpenAI, Anthropic, and more. It addresses the challenges of fragmented ecosystems, vendor lock-in, poor Go developer experience, and complex multi-modal handling by providing a unified interface, Go-first design, production-ready features, multi-modal support, and extensible architecture. The SDK supports language models, embeddings, image generation, multi-provider support, multi-modal inputs, tool calling, and structured outputs.
Caissa
Caissa is a strong, UCI command-line chess engine optimized for regular chess, FRC, and DFRC. It features its own neural network trained with self-play games, supports various UCI options, and provides different EXE versions for different CPU architectures. The engine uses advanced search algorithms, neural network evaluation, and endgame tablebases. It offers outstanding performance in ultra-short games and is written in C++ with modules for backend, frontend, and utilities like neural network trainer and self-play data generator.

chunkhound
ChunkHound is a modern tool for transforming your codebase into a searchable knowledge base for AI assistants. It utilizes semantic search via the cAST algorithm and regex search, integrating with AI assistants through the Model Context Protocol (MCP). With features like cAST Algorithm, Multi-Hop Semantic Search, Regex search, and support for 22 languages, ChunkHound offers a local-first approach to code analysis and discovery. It provides intelligent code discovery, universal language support, and real-time indexing capabilities, making it a powerful tool for developers looking to enhance their coding experience.

chunkhound
ChunkHound is a tool that transforms your codebase into a searchable knowledge base for AI assistants using semantic and regex search. It integrates with AI assistants via the Model Context Protocol (MCP) and offers features such as cAST algorithm for semantic code chunking, multi-hop semantic search, natural language queries, regex search without API keys, support for 22 languages, and local-first architecture. It provides intelligent code discovery by following semantic relationships and discovering related implementations. ChunkHound is built on the cAST algorithm from Carnegie Mellon University, ensuring structure-aware chunking that preserves code meaning. It supports universal language parsing and offers efficient updates for large codebases.
indexify
Indexify is an open-source engine for building fast data pipelines for unstructured data (video, audio, images, and documents) using reusable extractors for embedding, transformation, and feature extraction. LLM Applications can query transformed content friendly to LLMs by semantic search and SQL queries. Indexify keeps vector databases and structured databases (PostgreSQL) updated by automatically invoking the pipelines as new data is ingested into the system from external data sources. **Why use Indexify** * Makes Unstructured Data **Queryable** with **SQL** and **Semantic Search** * **Real-Time** Extraction Engine to keep indexes **automatically** updated as new data is ingested. * Create **Extraction Graph** to describe **data transformation** and extraction of **embedding** and **structured extraction**. * **Incremental Extraction** and **Selective Deletion** when content is deleted or updated. * **Extractor SDK** allows adding new extraction capabilities, and many readily available extractors for **PDF**, **Image**, and **Video** indexing and extraction. * Works with **any LLM Framework** including **Langchain**, **DSPy**, etc. * Runs on your laptop during **prototyping** and also scales to **1000s of machines** on the cloud. * Works with many **Blob Stores**, **Vector Stores**, and **Structured Databases** * We have even **Open Sourced Automation** to deploy to Kubernetes in production.
joliGEN
JoliGEN is an integrated framework for training custom generative AI image-to-image models. It implements GAN, Diffusion, and Consistency models for various image translation tasks, including domain and style adaptation with conservation of semantics. The tool is designed for real-world applications such as Controlled Image Generation, Augmented Reality, Dataset Smart Augmentation, and Synthetic to Real transforms. JoliGEN allows for fast and stable training with a REST API server for simplified deployment. It offers a wide range of options and parameters with detailed documentation available for models, dataset formats, and data augmentation.
vearch
Vearch is a cloud-native distributed vector database designed for efficient similarity search of embedding vectors in AI applications. It supports hybrid search with vector search and scalar filtering, offers fast vector retrieval from millions of objects in milliseconds, and ensures scalability and reliability through replication and elastic scaling out. Users can deploy Vearch cluster on Kubernetes, add charts from the repository or locally, start with Docker-compose, or compile from source code. The tool includes components like Master for schema management, Router for RESTful API, and PartitionServer for hosting document partitions with raft-based replication. Vearch can be used for building visual search systems for indexing images and offers a Python SDK for easy installation and usage. The tool is suitable for AI developers and researchers looking for efficient vector search capabilities in their applications.

layra
LAYRA is the world's first visual-native AI automation engine that sees documents like a human, preserves layout and graphical elements, and executes arbitrarily complex workflows with full Python control. It empowers users to build next-generation intelligent systems with no limits or compromises. Built for Enterprise-Grade deployment, LAYRA features a modern frontend, high-performance backend, decoupled service architecture, visual-native multimodal document understanding, and a powerful workflow engine.
shards
Shards is a high-performance, multi-platform, type-safe programming language designed for visual development. It is a dataflow visual programming language that enables building full-fledged apps and games without traditional coding. Shards features automatic type checking, optimized shard implementations for high performance, and an intuitive visual workflow for beginners. The language allows seamless round-trip engineering between code and visual models, empowering users to create multi-platform apps easily. Shards also powers an upcoming AI-powered game creation system, enabling real-time collaboration and game development in a low to no-code environment.
For similar tasks

lhotse
Lhotse is a Python library designed to make speech and audio data preparation flexible and accessible. It aims to attract a wider community to speech processing tasks by providing a Python-centric design and an expressive command-line interface. Lhotse offers standard data preparation recipes, PyTorch Dataset classes for speech tasks, and efficient data preparation for model training with audio cuts. It supports data augmentation, feature extraction, and feature-space cut mixing. The tool extends Kaldi's data preparation recipes with seamless PyTorch integration, human-readable text manifests, and convenient Python classes.
bittensor
Bittensor is an internet-scale neural network that incentivizes computers to provide access to machine learning models in a decentralized and censorship-resistant manner. It operates through a token-based mechanism where miners host, train, and procure machine learning systems to fulfill verification problems defined by validators. The network rewards miners and validators for their contributions, ensuring continuous improvement in knowledge output. Bittensor allows anyone to participate, extract value, and govern the network without centralized control. It supports tasks such as generating text, audio, images, and extracting numerical representations.
smile
Smile (Statistical Machine Intelligence and Learning Engine) is a comprehensive machine learning, NLP, linear algebra, graph, interpolation, and visualization system in Java and Scala. It covers every aspect of machine learning, including classification, regression, clustering, association rule mining, feature selection, manifold learning, multidimensional scaling, genetic algorithms, missing value imputation, efficient nearest neighbor search, etc. Smile implements major machine learning algorithms and provides interactive shells for Java, Scala, and Kotlin. It supports model serialization, data visualization using SmilePlot and declarative approach, and offers a gallery showcasing various algorithms and visualizations.
RVC_CLI
RVC_CLI is a command line interface tool for retrieval-based voice conversion. It provides functionalities for installation, getting started, inference, training, UVR, additional features, and API integration. Users can perform tasks like single inference, batch inference, TTS inference, preprocess dataset, extract features, start training, generate index file, model extract, model information, model blender, launch TensorBoard, download models, audio analyzer, and prerequisites download. The tool is built on various projects like ContentVec, HIFIGAN, audio-slicer, python-audio-separator, RMVPE, FCPE, VITS, So-Vits-SVC, Harmonify, and others.
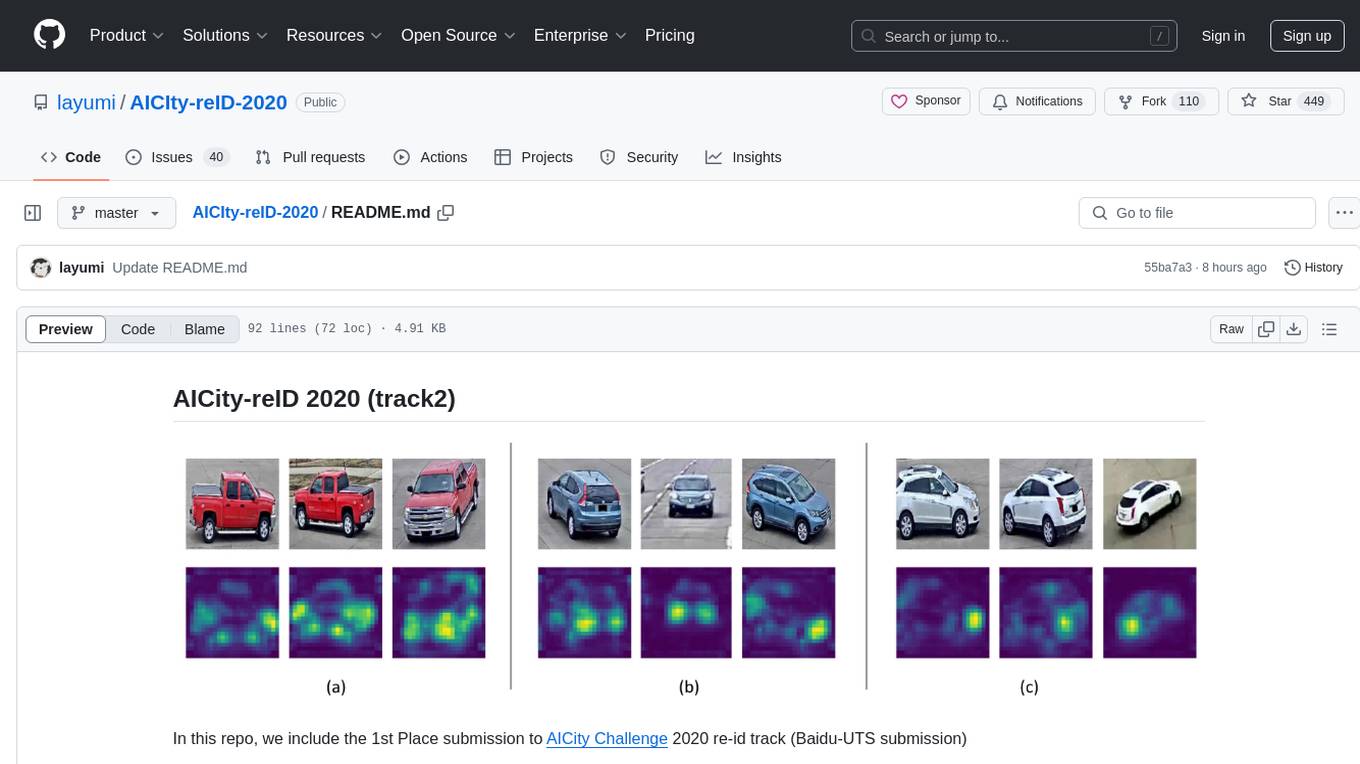
AICIty-reID-2020
AICIty-reID 2020 is a repository containing the 1st Place submission to AICity Challenge 2020 re-id track by Baidu-UTS. It includes models trained on Paddlepaddle and Pytorch, with performance metrics and trained models provided. Users can extract features, perform camera and direction prediction, and access related repositories for drone-based building re-id, vehicle re-ID, person re-ID baseline, and person/vehicle generation. Citations are also provided for research purposes.
VideoTree
VideoTree is an official implementation for a query-adaptive and hierarchical framework for understanding long videos with LLMs. It dynamically extracts query-related information from input videos and builds a tree-based video representation for LLM reasoning. The tool requires Python 3.8 or above and leverages models like LaViLa and EVA-CLIP-8B for feature extraction. It also provides scripts for tasks like Adaptive Breath Expansion, Relevance-based Depth Expansion, and LLM Reasoning. The codebase is being updated to incorporate scripts/captions for NeXT-QA and IntentQA in the future.
MachineLearning
MachineLearning is a repository focused on practical applications in various algorithm scenarios such as ship, education, and enterprise development. It covers a wide range of topics from basic machine learning and deep learning to object detection and the latest large models. The project utilizes mature third-party libraries, open-source pre-trained models, and the latest technologies from related papers to document the learning process and facilitate direct usage by a wider audience.
AudioMuse-AI
AudioMuse-AI is a deep learning-based tool for audio analysis and music generation. It provides a user-friendly interface for processing audio data and generating music compositions. The tool utilizes state-of-the-art machine learning algorithms to analyze audio signals and extract meaningful features for music generation. With AudioMuse-AI, users can explore the possibilities of AI in music creation and experiment with different styles and genres. Whether you are a music enthusiast, a researcher, or a developer, AudioMuse-AI offers a versatile platform for audio analysis and music generation.
For similar jobs
PaddleScience
PaddleScience is a scientific computing suite developed based on the deep learning framework PaddlePaddle. It utilizes the learning ability of deep neural networks and the automatic (higher-order) differentiation mechanism of PaddlePaddle to solve problems in physics, chemistry, meteorology, and other fields. It supports three solving methods: physics mechanism-driven, data-driven, and mathematical fusion, and provides basic APIs and detailed documentation for users to use and further develop.
PDEBench
PDEBench provides a diverse and comprehensive set of benchmarks for scientific machine learning, including challenging and realistic physical problems. The repository consists of code for generating datasets, uploading and downloading datasets, training and evaluating machine learning models as baselines. It features a wide range of PDEs, realistic and difficult problems, ready-to-use datasets with various conditions and parameters. PDEBench aims for extensibility and invites participation from the SciML community to improve and extend the benchmark.

PINNeAPPle
Pinneaple is an open-source Python platform that unifies physical data, geometry, numerical solvers, and machine learning models for Physics-Informed AI. It emphasizes physical consistency, scalability, auditability, and interoperability with CFD/CAD/scientific data formats. It provides tools for unified physical dataset representation, data pipelines, geometry and mesh operations, a model zoo, physics loss factory, solvers, synthetic data generation, training and evaluation. The platform is designed for physics AI researchers, CFD/FEA/climate ML teams, industrial R&D groups, scientific ML practitioners, and anyone building surrogates, inverse models, or hybrid solvers.

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.