
bittensor
Internet-scale Neural Networks
Stars: 987
Bittensor is an internet-scale neural network that incentivizes computers to provide access to machine learning models in a decentralized and censorship-resistant manner. It operates through a token-based mechanism where miners host, train, and procure machine learning systems to fulfill verification problems defined by validators. The network rewards miners and validators for their contributions, ensuring continuous improvement in knowledge output. Bittensor allows anyone to participate, extract value, and govern the network without centralized control. It supports tasks such as generating text, audio, images, and extracting numerical representations.
README:
- Overview of Bittensor
- The Bittensor SDK
- Is Bittensor a blockchain or an AI platform?
- Subnets
- Subnet validators and subnet miners
- Yuma Consensus
- Release Notes
- Install Bittensor SDK
- Upgrade
- Install on macOS and Linux
- Release Guidelines
- Contributions
- License
- Acknowledgments
Welcome! Bittensor is an open source platform on which you can produce competitive digital commodities. These digital commodities can be machine intelligence, storage space, compute power, protein folding, financial markets prediction, and many more. You are rewarded in TAO when you produce best digital commodities.
The Opentensor Foundation (OTF) provides all the open source tools, including this Bittensor SDK, the codebase and the documentation, with step-by-step tutorials and guides, to enable you to participate in the Bittensor ecosystem.
- Developer documentation: https://docs.bittensor.com.
- A Beginner's Q and A on Bittensor: https://docs.bittensor.com/questions-and-answers.
- Bittensor whitepaper: https://bittensor.com/whitepaper.
This Bittensor SDK contains ready-to-use Python packages for interacting with the Bittensor ecosystem, writing subnet incentive mechanisms, subnet miners, subnet validators and querying the subtensor (the blockchain part of the Bittensor network).
In Bittensor there is one blockchain, and many platforms that are connected to this one blockchain. We call these platforms as subnets, and this one blockchain subtensor. So, a subnet can be AI-related or it can be something else. The Bittensor network has a number of distinct subnets. All these subnets interact with subtensor blockchain. If you are thinking, "So, subnets are not part of the blockchain but only interact with it?" then the answer is "yes, exactly."
Each category of the digital commodity is produced in a distinct subnet. Applications are built on these specific subnets. End-users of these applications would be served by these applications.
Subnets, which exist outside the blockchain and are connected to it, are off-chain competitions where only the best producers are rewarded. A subnet consists of off-chain subnet validators who initiate the competition for a specific digital commodity, and off-chain subnet miners who compete and respond by producing the best quality digital commodity.
Scores are assigned to the top-performing subnet miners and subnet validators. The on-chain Yuma Consensus determines the TAO rewards for these top performers. The Bittensor blockchain, the subtensor, runs on decentralized validation nodes, just like any blockchain.
This SDK repo is for Bittensor platform only This Bittensor SDK codebase is for the Bittensor platform only, designed to help developers create subnets and build tools on Bittensor. For subnets and applications, refer to subnet-specific websites, which are maintained by subnet owners.
See Bittensor SDK Release Notes.
Before you can start developing, you must install Bittensor SDK and then create Bittensor wallet.
If you already installed Bittensor SDK, make sure you upgrade to the latest version. Run the below command:
python3 -m pip install --upgrade bittensorYou can install Bittensor SDK on your local machine in either of the following ways. Make sure you verify your installation after you install:
This is the most straightforward method. It is recommended for a beginner as it will pre-install requirements like Python, if they are not already present on your machine. Copy and paste the following bash command into your terminal:
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/opentensor/bittensor/master/scripts/install.sh)"For Ubuntu-Linux users
If you are using Ubuntu-Linux, the script will prompt for sudo access to install all required apt-get packages.
python3 -m venv bt_venv
source bt_venv/bin/activate
pip install bittensor-
Create and activate a virtual environment
-
Create Python virtual environment. Follow this guide on python.org.
-
Activate the new environment. Follow this guide on python.org
-
-
Clone the Bittensor SDK repo
git clone https://github.com/opentensor/bittensor.git- Install
You can install using any of the below options:
-
Install SDK: Run the below command to install Bittensor SDK in the above virtual environment. This will also install
btcli.pip install bittensor
-
Install SDK with
torch: Install Bittensor SDK withtorch.pip install bittensor[torch]
In some environments the above command may fail, in which case run the command with added quotes as shown below:
pip install "bittensor[torch]"
-
Install SDK with
cubit: Install Bittensor SDK withcubit.- Install
cubitfirst. See the Install section. Only Python 3.9 and 3.10 versions are supported. - Then install SDK with
pip install bittensor.
- Install
To install and run Bittensor SDK on Windows you must install WSL 2 (Windows Subsystem for Linux) on Windows and select Ubuntu Linux distribution.
After you installed the above, follow the same installation steps described above in Install on macOS and Linux.
ALERT: Limited support on Windows While wallet transactions like delegating, transfer, registering, staking can be performed on a Windows machine using WSL 2, the mining and validating operations are not recommended and are not supported on Windows machines.
You can verify your installation in either of the below ways:
python3 -m bittensorThe above command will show you the version of the btsdk you just installed.
-
Launch the Python interpreter on your terminal.
python3
-
Enter the following two lines in the Python interpreter.
import bittensor as bt print( bt.__version__ )
The Python interpreter output will look like below:
Python 3.11.6 (main, Oct 2 2023, 13:45:54) [Clang 15.0.0 (clang-1500.0.40.1)] on darwin Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>> import bittensor as bt >>> print( bt.__version__ ) <version number>
You will see the version number you installed in place of <version number>.
You can also verify the Bittensor SDK installation by listing the axon information for the neurons. Enter the following lines in the Python interpreter.
import bittensor
metagraph = bittensor.Metagraph(1)
metagraph.axons[:10]The Python interpreter output will look like below.
[AxonInfo( /ipv4/3.139.80.241:11055, 5GqDsK6SAPyQtG243hbaKTsoeumjQQLhUu8GyrXikPTmxjn7, 5D7u5BTqF3j1XHnizp9oR67GFRr8fBEFhbdnuVQEx91vpfB5, 600 ), AxonInfo( /ipv4/8.222.132.190:5108, 5CwqDkDt1uk2Bngvf8avrapUshGmiUvYZjYa7bfA9Gv9kn1i, 5HQ9eTDorvovKTxBc9RUD22FZHZzpy1KRfaxCnRsT9QhuvR6, 600 ), AxonInfo( /ipv4/34.90.71.181:8091, 5HEo565WAy4Dbq3Sv271SAi7syBSofyfhhwRNjFNSM2gP9M2, 5ChuGqW2cxc5AZJ29z6vyTkTncg75L9ovfp8QN8eB8niSD75, 601 ), AxonInfo( /ipv4/64.247.206.79:8091, 5HK5tp6t2S59DywmHRWPBVJeJ86T61KjurYqeooqj8sREpeN, 5E7W9QXNoW7se7B11vWRMKRCSWkkAu9EYotG5Ci2f9cqV8jn, 601 ), AxonInfo( /ipv4/51.91.30.166:40203, 5EXYcaCdnvnMZbozeknFWbj6aKXojfBi9jUpJYHea68j4q1a, 5CsxoeDvWsQFZJnDCyzxaNKgA8pBJGUJyE1DThH8xU25qUMg, 601 ), AxonInfo( /ipv4/149.137.225.62:8091, 5F4tQyWrhfGVcNhoqeiNsR6KjD4wMZ2kfhLj4oHYuyHbZAc3, 5Ccmf1dJKzGtXX7h17eN72MVMRsFwvYjPVmkXPUaapczECf6, 600 ), AxonInfo( /ipv4/38.147.83.11:8091, 5Hddm3iBFD2GLT5ik7LZnT3XJUnRnN8PoeCFgGQgawUVKNm8, 5DCQw11aUW7bozAKkB8tB5bHqAjiu4F6mVLZBdgJnk8dzUoV, 610 ), AxonInfo( /ipv4/38.147.83.30:41422, 5HNQURvmjjYhTSksi8Wfsw676b4owGwfLR2BFAQzG7H3HhYf, 5EZUTdAbXyLmrs3oiPvfCM19nG6oRs4X7zpgxG5oL1iK4MAh, 610 ), AxonInfo( /ipv4/54.227.25.215:10022, 5DxrZuW8kmkZPKGKp1RBVovaP5zHtPLDHYc5Yu82Z1fWqK5u, 5FhXUSmSZ2ec7ozRSA8Bg3ywmGwrjoLLzsXjNcwmZme2GcSC, 601 ), AxonInfo( /ipv4/52.8.243.76:40033, 5EnZN591jjsKKbt3yBtfGKWHxhxRH9cJonqTKRT5yTRUyNon, 5ChzhHyGmWwEdHjuvAxoUifHEZ6xpUjR67fDd4a42UrPysyB, 601 )]
>>>Instructions for the release manager: RELEASE_GUIDELINES.md document.
Ready to contribute? Read the contributing guide before making a pull request.
The MIT License (MIT) Copyright © 2024 The Opentensor Foundation
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the “Software”), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS IS”, WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
learning-at-home/hivemind
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for bittensor
Similar Open Source Tools

bittensor
Bittensor is an internet-scale neural network that incentivizes computers to provide access to machine learning models in a decentralized and censorship-resistant manner. It operates through a token-based mechanism where miners host, train, and procure machine learning systems to fulfill verification problems defined by validators. The network rewards miners and validators for their contributions, ensuring continuous improvement in knowledge output. Bittensor allows anyone to participate, extract value, and govern the network without centralized control. It supports tasks such as generating text, audio, images, and extracting numerical representations.
restai
RestAI is an AIaaS (AI as a Service) platform that allows users to create and consume AI agents (projects) using a simple REST API. It supports various types of agents, including RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation), RAGSQL (RAG for SQL), inference, vision, and router. RestAI features automatic VRAM management, support for any public LLM supported by LlamaIndex or any local LLM supported by Ollama, a user-friendly API with Swagger documentation, and a frontend for easy access. It also provides evaluation capabilities for RAG agents using deepeval.
BehaviorTree.CPP
BehaviorTree.CPP is a C++ 17 library that provides a framework to create BehaviorTrees. It was designed to be flexible, easy to use, reactive and fast. Even if our main use-case is robotics, you can use this library to build AI for games, or to replace Finite State Machines. There are few features which make BehaviorTree.CPP unique, when compared to other implementations: It makes asynchronous Actions, i.e. non-blocking, a first-class citizen. You can build reactive behaviors that execute multiple Actions concurrently (orthogonality). Trees are defined using a Domain Specific scripting language (based on XML), and can be loaded at run-time; in other words, even if written in C++, the morphology of the Trees is not hard-coded. You can statically link your custom TreeNodes or convert them into plugins and load them at run-time. It provides a type-safe and flexible mechanism to do Dataflow between Nodes of the Tree. It includes a logging/profiling infrastructure that allows the user to visualize, record, replay and analyze state transitions.
testzeus-hercules
Hercules is the world’s first open-source testing agent designed to handle the toughest testing tasks for modern web applications. It turns simple Gherkin steps into fully automated end-to-end tests, making testing simple, reliable, and efficient. Hercules adapts to various platforms like Salesforce and is suitable for CI/CD pipelines. It aims to democratize and disrupt test automation, making top-tier testing accessible to everyone. The tool is transparent, reliable, and community-driven, empowering teams to deliver better software. Hercules offers multiple ways to get started, including using PyPI package, Docker, or building and running from source code. It supports various AI models, provides detailed installation and usage instructions, and integrates with Nuclei for security testing and WCAG for accessibility testing. The tool is production-ready, open core, and open source, with plans for enhanced LLM support, advanced tooling, improved DOM distillation, community contributions, extensive documentation, and a bounty program.
Sanmill
Sanmill is a free, powerful UCI-like N men's morris program with CUI, Flutter GUI and Qt GUI. Nine men's morris is a strategy board game for two players dating at least to the Roman Empire. The game is also known as nine-man morris , mill , mills , the mill game , merels , merrills , merelles , marelles , morelles , and ninepenny marl in English.

crawlee-python
Crawlee-python is a web scraping and browser automation library that covers crawling and scraping end-to-end, helping users build reliable scrapers fast. It allows users to crawl the web for links, scrape data, and store it in machine-readable formats without worrying about technical details. With rich configuration options, users can customize almost any aspect of Crawlee to suit their project's needs.
burpference
Burpference is an open-source extension designed to capture in-scope HTTP requests and responses from Burp's proxy history and send them to a remote LLM API in JSON format. It automates response capture, integrates with APIs, optimizes resource usage, provides color-coded findings visualization, offers comprehensive logging, supports native Burp reporting, and allows flexible configuration. Users can customize system prompts, API keys, and remote hosts, and host models locally to prevent high inference costs. The tool is ideal for offensive web application engagements to surface findings and vulnerabilities.
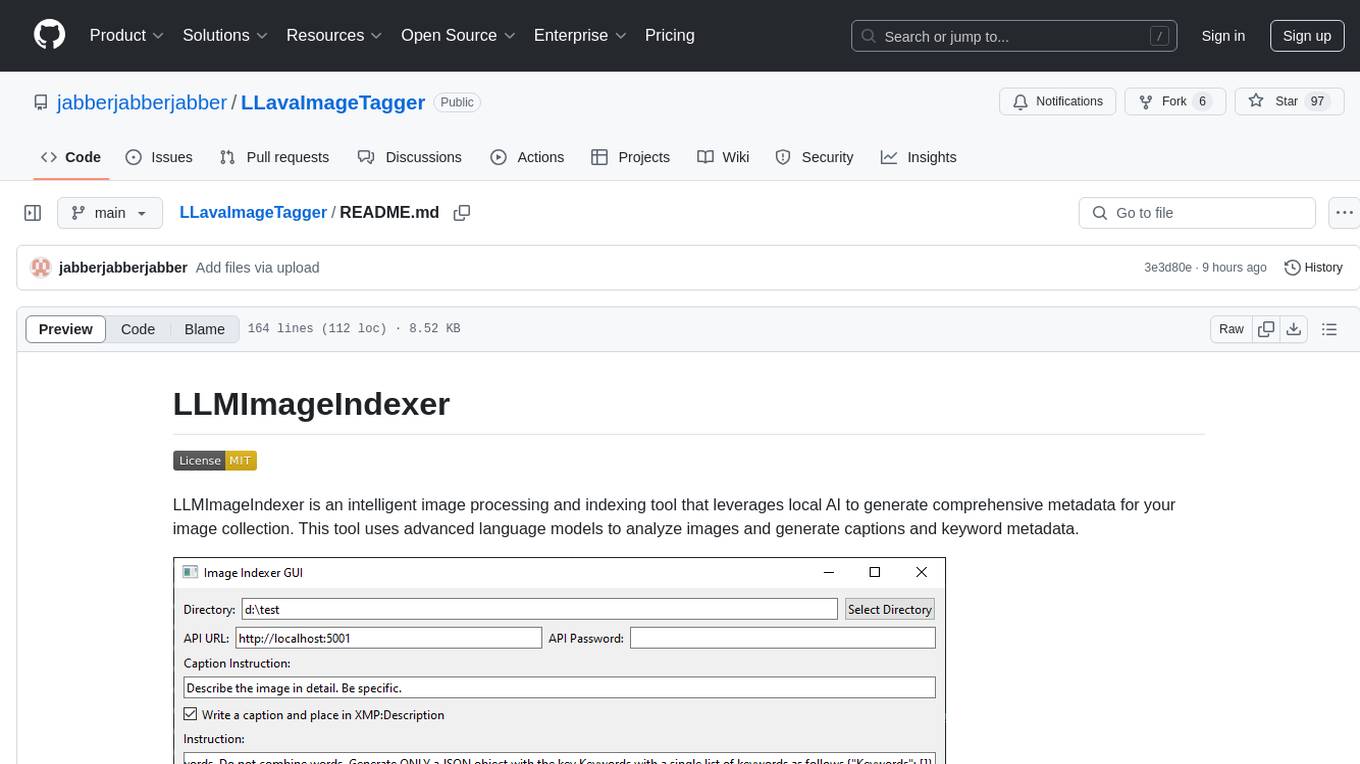
LLavaImageTagger
LLMImageIndexer is an intelligent image processing and indexing tool that leverages local AI to generate comprehensive metadata for your image collection. It uses advanced language models to analyze images and generate captions and keyword metadata. The tool offers features like intelligent image analysis, metadata enhancement, local processing, multi-format support, user-friendly GUI, GPU acceleration, cross-platform support, stop and start capability, and keyword post-processing. It operates directly on image file metadata, allowing users to manage files, add new files, and run the tool multiple times without reprocessing previously keyworded files. Installation instructions are provided for Windows, macOS, and Linux platforms, along with usage guidelines and configuration options.
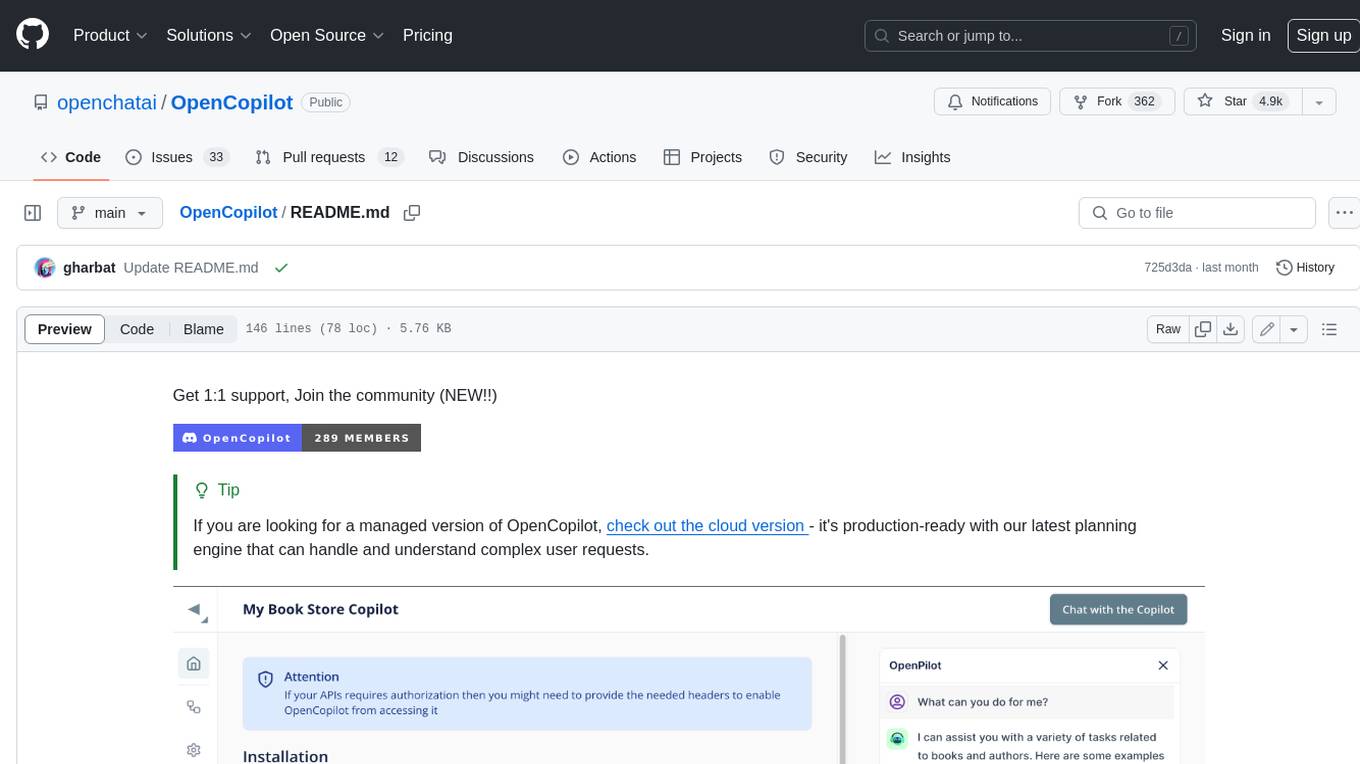
OpenCopilot
OpenCopilot allows you to have your own product's AI copilot. It integrates with your underlying APIs and can execute API calls whenever needed. It uses LLMs to determine if the user's request requires calling an API endpoint. Then, it decides which endpoint to call and passes the appropriate payload based on the given API definition.

Instrukt
Instrukt is a terminal-based AI integrated environment that allows users to create and instruct modular AI agents, generate document indexes for question-answering, and attach tools to any agent. It provides a platform for users to interact with AI agents in natural language and run them inside secure containers for performing tasks. The tool supports custom AI agents, chat with code and documents, tools customization, prompt console for quick interaction, LangChain ecosystem integration, secure containers for agent execution, and developer console for debugging and introspection. Instrukt aims to make AI accessible to everyone by providing tools that empower users without relying on external APIs and services.
craftium
Craftium is an open-source platform based on the Minetest voxel game engine and the Gymnasium and PettingZoo APIs, designed for creating fast, rich, and diverse single and multi-agent environments. It allows for connecting to Craftium's Python process, executing actions as keyboard and mouse controls, extending the Lua API for creating RL environments and tasks, and supporting client/server synchronization for slow agents. Craftium is fully extensible, extensively documented, modern RL API compatible, fully open source, and eliminates the need for Java. It offers a variety of environments for research and development in reinforcement learning.
uwazi
Uwazi is a flexible database application designed for capturing and organizing collections of information, with a focus on document management. It is developed and supported by HURIDOCS, benefiting human rights organizations globally. The tool requires NodeJs, ElasticSearch, ICU Analysis Plugin, MongoDB, Yarn, and pdftotext for installation. It offers production and development installation guides, including Docker setup. Uwazi supports hot reloading, unit and integration testing with JEST, and end-to-end testing with Nightmare or Puppeteer. The system requirements include RAM, CPU, and disk space recommendations for on-premises and development usage.

dataline
DataLine is an AI-driven data analysis and visualization tool designed for technical and non-technical users to explore data quickly. It offers privacy-focused data storage on the user's device, supports various data sources, generates charts, executes queries, and facilitates report building. The tool aims to speed up data analysis tasks for businesses and individuals by providing a user-friendly interface and natural language querying capabilities.

air-script
Air Script is a versatile tool designed for Wi-Fi penetration testing, offering automated and user-friendly features to streamline the hacking process. It allows users to easily capture handshakes from nearby networks, automate attacks, and even send email notifications upon completion. The tool is ideal for individuals looking to efficiently pwn Wi-Fi networks without extensive manual input. With additional tools and options available, Air Script caters to a wide range of users, including script kiddies, hackers, pentesters, and security researchers. Whether on the go or using a Raspberry Pi, Air Script provides a convenient solution for network penetration testing and password cracking.

cognita
Cognita is an open-source framework to organize your RAG codebase along with a frontend to play around with different RAG customizations. It provides a simple way to organize your codebase so that it becomes easy to test it locally while also being able to deploy it in a production ready environment. The key issues that arise while productionizing RAG system from a Jupyter Notebook are: 1. **Chunking and Embedding Job** : The chunking and embedding code usually needs to be abstracted out and deployed as a job. Sometimes the job will need to run on a schedule or be trigerred via an event to keep the data updated. 2. **Query Service** : The code that generates the answer from the query needs to be wrapped up in a api server like FastAPI and should be deployed as a service. This service should be able to handle multiple queries at the same time and also autoscale with higher traffic. 3. **LLM / Embedding Model Deployment** : Often times, if we are using open-source models, we load the model in the Jupyter notebook. This will need to be hosted as a separate service in production and model will need to be called as an API. 4. **Vector DB deployment** : Most testing happens on vector DBs in memory or on disk. However, in production, the DBs need to be deployed in a more scalable and reliable way. Cognita makes it really easy to customize and experiment everything about a RAG system and still be able to deploy it in a good way. It also ships with a UI that makes it easier to try out different RAG configurations and see the results in real time. You can use it locally or with/without using any Truefoundry components. However, using Truefoundry components makes it easier to test different models and deploy the system in a scalable way. Cognita allows you to host multiple RAG systems using one app. ### Advantages of using Cognita are: 1. A central reusable repository of parsers, loaders, embedders and retrievers. 2. Ability for non-technical users to play with UI - Upload documents and perform QnA using modules built by the development team. 3. Fully API driven - which allows integration with other systems. > If you use Cognita with Truefoundry AI Gateway, you can get logging, metrics and feedback mechanism for your user queries. ### Features: 1. Support for multiple document retrievers that use `Similarity Search`, `Query Decompostion`, `Document Reranking`, etc 2. Support for SOTA OpenSource embeddings and reranking from `mixedbread-ai` 3. Support for using LLMs using `Ollama` 4. Support for incremental indexing that ingests entire documents in batches (reduces compute burden), keeps track of already indexed documents and prevents re-indexing of those docs.
llm-answer-engine
This repository contains the code and instructions needed to build a sophisticated answer engine that leverages the capabilities of Groq, Mistral AI's Mixtral, Langchain.JS, Brave Search, Serper API, and OpenAI. Designed to efficiently return sources, answers, images, videos, and follow-up questions based on user queries, this project is an ideal starting point for developers interested in natural language processing and search technologies.
For similar tasks

lhotse
Lhotse is a Python library designed to make speech and audio data preparation flexible and accessible. It aims to attract a wider community to speech processing tasks by providing a Python-centric design and an expressive command-line interface. Lhotse offers standard data preparation recipes, PyTorch Dataset classes for speech tasks, and efficient data preparation for model training with audio cuts. It supports data augmentation, feature extraction, and feature-space cut mixing. The tool extends Kaldi's data preparation recipes with seamless PyTorch integration, human-readable text manifests, and convenient Python classes.

bittensor
Bittensor is an internet-scale neural network that incentivizes computers to provide access to machine learning models in a decentralized and censorship-resistant manner. It operates through a token-based mechanism where miners host, train, and procure machine learning systems to fulfill verification problems defined by validators. The network rewards miners and validators for their contributions, ensuring continuous improvement in knowledge output. Bittensor allows anyone to participate, extract value, and govern the network without centralized control. It supports tasks such as generating text, audio, images, and extracting numerical representations.
smile
Smile (Statistical Machine Intelligence and Learning Engine) is a comprehensive machine learning, NLP, linear algebra, graph, interpolation, and visualization system in Java and Scala. It covers every aspect of machine learning, including classification, regression, clustering, association rule mining, feature selection, manifold learning, multidimensional scaling, genetic algorithms, missing value imputation, efficient nearest neighbor search, etc. Smile implements major machine learning algorithms and provides interactive shells for Java, Scala, and Kotlin. It supports model serialization, data visualization using SmilePlot and declarative approach, and offers a gallery showcasing various algorithms and visualizations.
RVC_CLI
RVC_CLI is a command line interface tool for retrieval-based voice conversion. It provides functionalities for installation, getting started, inference, training, UVR, additional features, and API integration. Users can perform tasks like single inference, batch inference, TTS inference, preprocess dataset, extract features, start training, generate index file, model extract, model information, model blender, launch TensorBoard, download models, audio analyzer, and prerequisites download. The tool is built on various projects like ContentVec, HIFIGAN, audio-slicer, python-audio-separator, RMVPE, FCPE, VITS, So-Vits-SVC, Harmonify, and others.
AICIty-reID-2020
AICIty-reID 2020 is a repository containing the 1st Place submission to AICity Challenge 2020 re-id track by Baidu-UTS. It includes models trained on Paddlepaddle and Pytorch, with performance metrics and trained models provided. Users can extract features, perform camera and direction prediction, and access related repositories for drone-based building re-id, vehicle re-ID, person re-ID baseline, and person/vehicle generation. Citations are also provided for research purposes.
VideoTree
VideoTree is an official implementation for a query-adaptive and hierarchical framework for understanding long videos with LLMs. It dynamically extracts query-related information from input videos and builds a tree-based video representation for LLM reasoning. The tool requires Python 3.8 or above and leverages models like LaViLa and EVA-CLIP-8B for feature extraction. It also provides scripts for tasks like Adaptive Breath Expansion, Relevance-based Depth Expansion, and LLM Reasoning. The codebase is being updated to incorporate scripts/captions for NeXT-QA and IntentQA in the future.
MachineLearning
MachineLearning is a repository focused on practical applications in various algorithm scenarios such as ship, education, and enterprise development. It covers a wide range of topics from basic machine learning and deep learning to object detection and the latest large models. The project utilizes mature third-party libraries, open-source pre-trained models, and the latest technologies from related papers to document the learning process and facilitate direct usage by a wider audience.
AudioMuse-AI
AudioMuse-AI is a deep learning-based tool for audio analysis and music generation. It provides a user-friendly interface for processing audio data and generating music compositions. The tool utilizes state-of-the-art machine learning algorithms to analyze audio signals and extract meaningful features for music generation. With AudioMuse-AI, users can explore the possibilities of AI in music creation and experiment with different styles and genres. Whether you are a music enthusiast, a researcher, or a developer, AudioMuse-AI offers a versatile platform for audio analysis and music generation.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.

