
honey
Bee is an AI, easy and high efficiency ORM framework,support JDBC,Cassandra,Mongodb,Sharding,Android,HarmonyOS. Honey is the implementation of the Bee.
Stars: 124
Bee is an ORM framework that provides easy and high-efficiency database operations, allowing developers to focus on business logic development. It supports various databases and features like automatic filtering, partial field queries, pagination, and JSON format results. Bee also offers advanced functionalities like sharding, transactions, complex queries, and MongoDB ORM. The tool is designed for rapid application development in Java, offering faster development for Java Web and Spring Cloud microservices. The Enterprise Edition provides additional features like financial computing support, automatic value insertion, desensitization, dictionary value conversion, multi-tenancy, and more.
README:
Easy for Stronger.
Bee is an ORM framework.
Bee is an easy and high efficiency ORM framework.
Coding Complexity is O(1),it means that Bee will do the Dao for you.
You don't need to write the Dao by yourself anymore.Help you to focus more on the development of business logic.
Good Feature: AI, Timesaving/Tasteful, Easy, Automatic (AiTeaSoft Style)
Newest version is:Bee V2.5.2 LTS(just 935k)
1.17.x LTS version:1.17.25
Sharding target: It is mainly transparent to business development and coding, with only a little sharding config.
Bee see:
https://github.com/automvc/bee
bee-ext:
https://github.com/automvc/bee-ext
Python ORM Bee:
https://github.com/automvc/BeePy
Easy to use:
- 1.Simple interface, convenient to use. The Suid interface provides four object-oriented methods corresponding to the SQL language's select, update, insert, and delete operations.
- 2.By using Bee, you no longer need to write separate DAO code. You can directly call Bee's API to perform operations on the database.
- 3.Convention-over-configuration: Javabean can no annotation, no xml.
- 4.Intelligent automatic filtering of null and empty string properties in entities eliminates the need for writing code to check for non-null values.
- 5.Easily implement partial field queries and native statement pagination.
- 6.Supports returning query results in JSON format; supports chaining.
- 7.Supports Sharding, both database and table Sharding; database-only Sharding; table-only Sharding; and read-write separation. This functionality is transparent to existing code and does not require additional coding.
- 8.Easily extendable with multiple database support (MySQL, MariaDB, Oracle, H2, SQLite, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, Access, Kingbase, Dameng, etc.), and theoretically supports any database supported by JDBC. Additionally, supports Android and Harmony.
- 9.Additional database pagination support for: MsAccess, Cubrid, HSQL, Derby, Firebird, etc.
- 10.Multiple databases can be used simultaneously (e.g., MySQL, Oracle, SQL Server).
Automatic, powerful:
- 11.Dynamic/arbitrary combination of query conditions without the need to prepare DAO interfaces in advance. New query requirements can be handled without modifying or adding interfaces.
- 12.Supports transactions, using the same connection for multiple ORM operations, FOR UPDATE, batch processing, executing native SQL statements, and stored procedures.
- 13.Supports object-oriented complex queries, multi-table queries (no N+1 problem), and supports one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-one, and many-to-many relationships. The result structure can differ based on whether the sub-table uses List;multi-table association update, insert, and delete(2.1.8).
- 14.MongoDB ORM and support for MongoDB Sharding.
- 15.Supports register, interceptor, multi-tenancy, and custom TypeHandlers for handling ResultSet results in queries. SetParaTypeConvert converts PreparedStatement parameter types.
- 16.Custom dynamic SQL tags, such as @in, @toIsNULL1, @toIsNULL2, , . Allows dynamic SQL, converting lists into statements like in (1,2,3) without requiring foreach loops. Batch insertion also does not require foreach.
- 17.Complex query can be automatically parsed by the frontend and backend.
- 18.L1 cache, simple in concept and powerful in function; L1 cache can also be fine tuned like the JVM; Support updatable long-term cache list and update configuration table without restart. Inherently resistant to cache penetration. L2 cache extension support; Redis L2 cache support.
- 19.No third-party plugin dependencies; can be used with zero configuration.
- 20.High performance: close to the speed of JDBC; small file size: Bee V1.17.25 is only 520k, V2.5.2 is only 935k.
Assist function: -
- Provides a naturally simple solution for generating distributed primary keys: generates globally unique, monotonically increasing (within a worker ID) numeric IDs in a distributed environment.
- 22.Supports automatic generation of Javabean corresponding to tables(support Swagger), creating tables based on Javabean, and automatically generating backend Javaweb code based on templates. Can print executable SQL statements without placeholders for easy debugging. Supports generating SQL scripts in JSON format.
- 23.Supports reading Excel files and importing data into the database; simple operations. Supports generating database tables from Excel configurations.
- 24.Stream tool class StreamUtil;DateUtil date conversion, judge date format, calculate age.
- 25.Rich annotation support: PrimaryKey, Column, Datetime, Createtime, Updatetime; JustFetch, ReplaceInto (MySQL), Dict, DictI18n,GridFs, etc.
- 26.Use entity name _F (automatically generated) to reference entity field names, e.g., Users_F.name or in SuidRichExt interface using the format Users::getName.
2.5.2.1 New Year
- MongoDB update,delete,deleteById support for sharding
- MongoDB modify sharding cache enhance
- MongoDB index support for sharding
- add ShardingFullOpTemplate
- ObjSQLRich(SuidRich) add selectByTemplate for select
2.5.2.2 - fixed bug for MongodbShardingDdlEngine
- record and print sql execute time
bee.osql.showSqlExecuteTime=true
bee.osql.minSqlExecuteTime=0
8.use CQRS(Command Query Responsibility Segregation) operate database 2.5.2.6 - open some config in Honeyconfig as default
openEntityCanExtend = true
showSQL = true
showShardingSQL = true
showSqlExecuteTime = true
minSqlExecuteTime = 5; //ms - column allow use keyword
#there is a switch for it, default is true
bee.osql.naming.allowKeyWordInColumn=true
#define for append if bee do not contain them
bee.osql.naming.sqlKeyWordInColumn - separate logger; initialize config independently first
- BeeSimpleDataSourceBuilder is compatible with different style configurations
- GenFiles support genFileViaStream
- Genbean:update genFieldFile,toString, add method setUpperFieldNameInFieldFile
- update DoNotSetTabShadngValue tip message(Sharding insert need set the sharding value)
- SuidRich selectById,deleteById support sharding
- Condition support clone
- fixed bug:
sharding select all(no paging)
sharding modify cache
1.MySQL
2.Oracle
3.SQL Server
4.MariaDB
5.H2
6.SQLite
7.PostgreSQL
8.MS Access
9.Kingbase
10.DM
11.OceanBase
12.Cubrid,HSQL,Derby,Firebird
13.Other DB that support JDBC
NOSQL:
14.Mongodb
15.ElasticSearch
16.Cassandra
Mobile environment (database):
17.Android
18.Harmony
Test Evn : Local windows.
DB: MySQL (Version 5.6.24).
Test point: Batch Insert;Paging Select; Transaction(update and select).
Batch Insert(unit: ms) |
|||||
| 5k | 1w | 2w | 5w | 10w | |
| Bee | 529.00 | 458.33 | 550.00 | 1315.67 | 4056.67 |
| MyBatis | 1193 | 713 | 1292.67 | 1824.33 | Exception |
Paging Select(unit: ms) |
|||||
| 20 | 50 | 100 | 200 | 500 | |
| Bee | 17.33 | 58.67 | 52.33 | 38.33 | 57.33 |
| MyBatis | 314.33 | 446.00 | 1546.00 | 2294.33 | 6216.67 |
Transaction(update and select) (unit: ms) |
|||||
| 20 | 50 | 100 | 200 | 500 | |
| Bee | 1089.00 | 70.00 | 84.00 | 161.33 | 31509.33 |
| MyBatis | 1144 | 35 | 79.67 | 146.00 | 32155.33 |
Bee need files
orm\compare\bee\service\BeeOrdersService.java
MyBatis need files
orm\compare\mybatis\service\MybatisOrdersService.java
orm\compare\mybatis\dao\OrdersDao.java
orm\compare\mybatis\dao\OrdersMapper.java
orm\compare\mybatis\dao\impl\OrdersDaoImpl.java
common,Javabean and Service interface:
Orders.java
OrdersService.java
Performance comparison data of Bee application in app development
Operate 10000 records, and the use time comparison is as follows.
Operate 10000 records(unit: ms) |
|||
| insert | query | delete | |
| greenDao(Android) | 104666 | 600 | 47 |
| Bee(Android 8.1) | 747 | 184 | 25 |
| Bee(HarmonyOS P40 Pro simulator) | 339 | 143 | 2 |
<dependency>
<groupId>org.teasoft</groupId>
<artifactId>bee-all</artifactId>
<version>2.5.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Mysql config.You need change it to the real database config. -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>Gradle
implementation group: 'org.teasoft', name: 'bee-all', version: '2.5.2'
//Gradle(Short)
implementation 'org.teasoft:bee-all:2.5.2'eg:
Create one database,default name is bee.
Create the tables and init the data by run the init-data(user-orders)-mysql.sql file(it is mysql sql script).
If no the bee.properties file, you can create it by yourself.
#bee.databaseName=MySQL
bee.db.dbName=MySQL
bee.db.driverName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
#bee.db.url =jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bee?characterEncoding=UTF-8
bee.db.url =jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/bee?characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
bee.db.username = root
bee.db.password =
#print log
bee.osql.showSQL=true
bee.osql.showSql.showType=true
bee.osql.showSql.showExecutableSql=true
# since 2.1.7 sqlFormat=true,will format the executable sql
bee.osql.showSql.sqlFormat=false
#log4j>slf4j>log4j2>androidLog>harmonyLog>systemLogger>fileLogger>noLogging>jdkLog>commonsLog
bee.osql.loggerType=systemLogger
Orders(Javabean)
Auto Genernate Javabean
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.List;
import org.teasoft.bee.osql.BeeException;
import org.teasoft.bee.osql.Suid;
import org.teasoft.honey.osql.core.BeeFactoryHelper;
import org.teasoft.honey.osql.core.Logger;
/**
* @author Kingstar
* @since 1.0
*/
public class SuidExamEN {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Suid suid = BeeFactoryHelper.getSuid();
Orders orders1 = new Orders();//need gen the Javabean
orders1.setId(100001L);
orders1.setName("Bee(ORM Framework)");
List<Orders> list1 = suid.select(orders1); // 1. select
for (int i = 0; i < list1.size(); i++) {
Logger.info(list1.get(i).toString());
}
//Condition condition=BF.getCondition(); // The SuidRich interface has many methods with the Condition parameter
//condition.op(Orders_F.userid, Op.ge, 0); // userid>=0
//Op supports: =,>,<,>=,<=,!=, Like, in, not in, etc
orders1.setName("Bee(ORM Framework)");
int updateNum = suid.update(orders1); //2. update
Logger.info("update record:" + updateNum);
Orders orders2 = new Orders();
orders2.setUserid("bee");
orders2.setName("Bee(ORM Framework)");
orders2.setTotal(new BigDecimal("91.99"));
orders2.setRemark(""); // empty String test
int insertNum = suid.insert(orders2); // 3. insert
Logger.info("insert record:" + insertNum);
int deleteNum = suid.delete(orders2); // 4. delete
Logger.info("delete record:" + deleteNum);
} catch (BeeException e) {
Logger.error("In SuidExamEN (BeeException):" + e.getMessage());
//e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
Logger.error("In SuidExamEN (Exception):" + e.getMessage());
//e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// notice: this is just a simple sample. Bee suport transaction,paging,complicate select,slect json,and so on. bee.db.isAndroid=true
bee.db.androidDbName=account.db
bee.db.androidDbVersion=1
bee.osql.loggerType=androidLog
#turn on query result field type conversion, and more types will be supported
bee.osql.openFieldTypeHandler=true
#If you are allowed to delete and update the whole table, you need to remove the comments
#bee.osql.notDeleteWholeRecords=false
#bee.osql.notUpdateWholeRecords=falsepublic class YourAppCreateAndUpgrade implements CreateAndUpgrade{
@Override
public void onCreate() {
// You can create tables in an object-oriented way
Ddl.createTable(new Orders(), false);
Ddl.createTable(new TestUser(), false);
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
if(newVersion==2) {
Ddl.createTable(new LeafAlloc(), true);
Log.i("onUpgrade", "你在没有卸载的情况下,在线更新到版本:"+newVersion);
}
}
}
Configure android:name to BeeApplication in AndroidManifest.xml file.
package com.aiteasoft.util;
import org.teasoft.bee.android.CreateAndUpgradeRegistry;
import org.teasoft.beex.android.ApplicationRegistry;
public class BeeApplication extends Application {
private static Context context;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
ApplicationRegistry.register(this);//注册上下文
CreateAndUpgradeRegistry.register(YourAppCreateAndUpgrade.class);
}
}
// 并在AndroidManifest.xml,配置android:name为BeeApplication
<application
android:icon="@drawable/appicon"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:name="com.aiteasoft.util.BeeApplication"
>Suid suid=BF.getSuid();
List<Orders> list = suid.select(new Orders()); Performance comparison data of Bee application in app development
Operate 10000 records, and the use time comparison is as follows.
Operate 10000 records(unit: ms) |
|||
| insert | query | delete | |
| greenDao(Android) | 104666 | 600 | 47 |
| Bee(Android 8.1) | 747 | 184 | 25 |
| Bee(HarmonyOS P40 Pro simulator) | 339 | 143 | 2 |
Let Java more quicker programming than php and Rails.
Faster development of new combinations for Java Web:
Bee+Spring+SpringMVC
Faster development of new combinations for Spring Cloud microservices:
Bee + Spring Boot
Rapid Application Code Generation Platform--AiTea Soft made in China!
...
API-V1.17.x(Newest) SourceCode contain bee-1.17 CN & EN API,bee-1.17 CN SourceCode
API-V2.x(Newest) bee-2.5.2 EN API
Author's email: [email protected]
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for honey
Similar Open Source Tools

honey
Bee is an ORM framework that provides easy and high-efficiency database operations, allowing developers to focus on business logic development. It supports various databases and features like automatic filtering, partial field queries, pagination, and JSON format results. Bee also offers advanced functionalities like sharding, transactions, complex queries, and MongoDB ORM. The tool is designed for rapid application development in Java, offering faster development for Java Web and Spring Cloud microservices. The Enterprise Edition provides additional features like financial computing support, automatic value insertion, desensitization, dictionary value conversion, multi-tenancy, and more.
bee
Bee is an easy and high efficiency ORM framework that simplifies database operations by providing a simple interface and eliminating the need to write separate DAO code. It supports various features such as automatic filtering of properties, partial field queries, native statement pagination, JSON format results, sharding, multiple database support, and more. Bee also offers powerful functionalities like dynamic query conditions, transactions, complex queries, MongoDB ORM, cache management, and additional tools for generating distributed primary keys, reading Excel files, and more. The newest versions introduce enhancements like placeholder precompilation, default date sharding, ElasticSearch ORM support, and improved query capabilities.
sophia
Sophia is an open-source TypeScript platform designed for autonomous AI agents and LLM based workflows. It aims to automate processes, review code, assist with refactorings, and support various integrations. The platform offers features like advanced autonomous agents, reasoning/planning inspired by Google's Self-Discover paper, memory and function call history, adaptive iterative planning, and more. Sophia supports multiple LLMs/services, CLI and web interface, human-in-the-loop interactions, flexible deployment options, observability with OpenTelemetry tracing, and specific agents for code editing, software engineering, and code review. It provides a flexible platform for the TypeScript community to expand and support various use cases and integrations.
typedai
TypedAI is a TypeScript-first AI platform designed for developers to create and run autonomous AI agents, LLM based workflows, and chatbots. It offers advanced autonomous agents, software developer agents, pull request code review agent, AI chat interface, Slack chatbot, and supports various LLM services. The platform features configurable Human-in-the-loop settings, functional callable tools/integrations, CLI and Web UI interface, and can be run locally or deployed on the cloud with multi-user/SSO support. It leverages the Python AI ecosystem through executing Python scripts/packages and provides flexible run/deploy options like single user mode, Firestore & Cloud Run deployment, and multi-user SSO enterprise deployment. TypedAI also includes UI examples, code examples, and automated LLM function schemas for seamless development and execution of AI workflows.
MarkLLM
MarkLLM is an open-source toolkit designed for watermarking technologies within large language models (LLMs). It simplifies access, understanding, and assessment of watermarking technologies, supporting various algorithms, visualization tools, and evaluation modules. The toolkit aids researchers and the community in ensuring the authenticity and origin of machine-generated text.
inferable
Inferable is an open source platform that helps users build reliable LLM-powered agentic automations at scale. It offers a managed agent runtime, durable tool calling, zero network configuration, multiple language support, and is fully open source under the MIT license. Users can define functions, register them with Inferable, and create runs that utilize these functions to automate tasks. The platform supports Node.js/TypeScript, Go, .NET, and React, and provides SDKs, core services, and bootstrap templates for various languages.
DB-GPT
DB-GPT is a personal database administrator that can solve database problems by reading documents, using various tools, and writing analysis reports. It is currently undergoing an upgrade. **Features:** * **Online Demo:** * Import documents into the knowledge base * Utilize the knowledge base for well-founded Q&A and diagnosis analysis of abnormal alarms * Send feedbacks to refine the intermediate diagnosis results * Edit the diagnosis result * Browse all historical diagnosis results, used metrics, and detailed diagnosis processes * **Language Support:** * English (default) * Chinese (add "language: zh" in config.yaml) * **New Frontend:** * Knowledgebase + Chat Q&A + Diagnosis + Report Replay * **Extreme Speed Version for localized llms:** * 4-bit quantized LLM (reducing inference time by 1/3) * vllm for fast inference (qwen) * Tiny LLM * **Multi-path extraction of document knowledge:** * Vector database (ChromaDB) * RESTful Search Engine (Elasticsearch) * **Expert prompt generation using document knowledge** * **Upgrade the LLM-based diagnosis mechanism:** * Task Dispatching -> Concurrent Diagnosis -> Cross Review -> Report Generation * Synchronous Concurrency Mechanism during LLM inference * **Support monitoring and optimization tools in multiple levels:** * Monitoring metrics (Prometheus) * Flame graph in code level * Diagnosis knowledge retrieval (dbmind) * Logical query transformations (Calcite) * Index optimization algorithms (for PostgreSQL) * Physical operator hints (for PostgreSQL) * Backup and Point-in-time Recovery (Pigsty) * **Continuously updated papers and experimental reports** This project is constantly evolving with new features. Don't forget to star ⭐ and watch 👀 to stay up to date.

rl
TorchRL is an open-source Reinforcement Learning (RL) library for PyTorch. It provides pytorch and **python-first** , low and high level abstractions for RL that are intended to be **efficient** , **modular** , **documented** and properly **tested**. The code is aimed at supporting research in RL. Most of it is written in python in a highly modular way, such that researchers can easily swap components, transform them or write new ones with little effort.
LLM4Decompile
LLM4Decompile is an open-source large language model dedicated to decompilation of Linux x86_64 binaries, supporting GCC's O0 to O3 optimization levels. It focuses on assessing re-executability of decompiled code through HumanEval-Decompile benchmark. The tool includes models with sizes ranging from 1.3 billion to 33 billion parameters, available on Hugging Face. Users can preprocess C code into binary and assembly instructions, then decompile assembly instructions into C using LLM4Decompile. Ongoing efforts aim to expand capabilities to support more architectures and configurations, integrate with decompilation tools like Ghidra and Rizin, and enhance performance with larger training datasets.
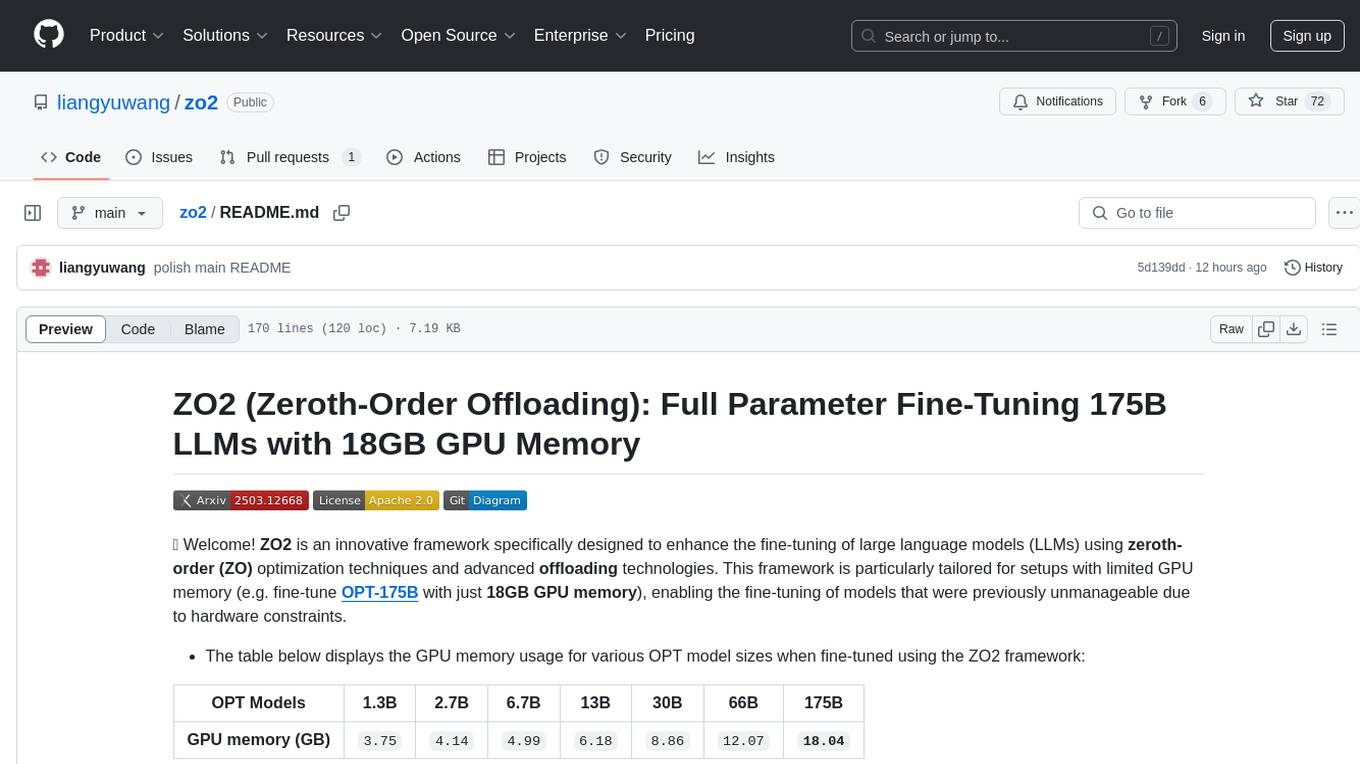
zo2
ZO2 (Zeroth-Order Offloading) is an innovative framework designed to enhance the fine-tuning of large language models (LLMs) using zeroth-order (ZO) optimization techniques and advanced offloading technologies. It is tailored for setups with limited GPU memory, enabling the fine-tuning of models with over 175 billion parameters on single GPUs with as little as 18GB of memory. ZO2 optimizes CPU offloading, incorporates dynamic scheduling, and has the capability to handle very large models efficiently without extra time costs or accuracy losses.
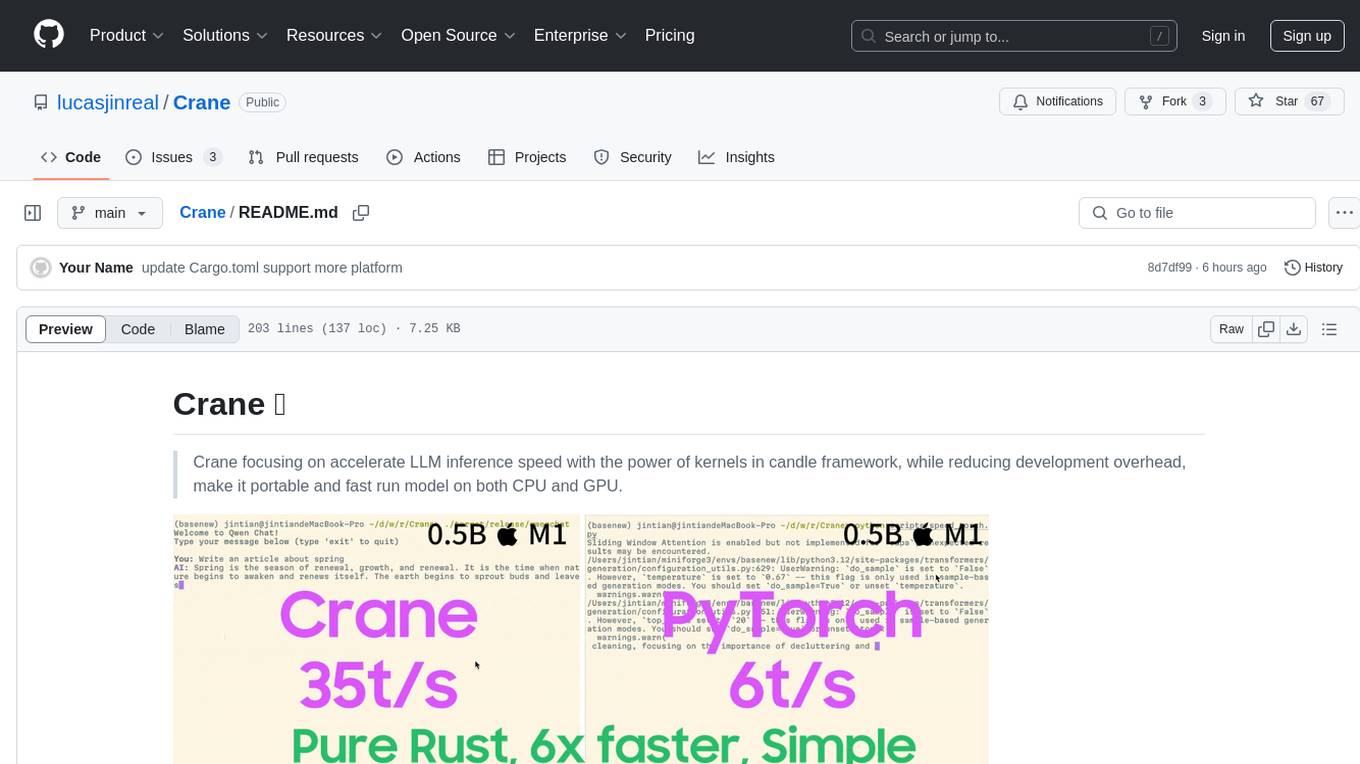
Crane
Crane is a high-performance inference framework leveraging Rust's Candle for maximum speed on CPU/GPU. It focuses on accelerating LLM inference speed with optimized kernels, reducing development overhead, and ensuring portability for running models on both CPU and GPU. Supported models include TTS systems like Spark-TTS and Orpheus-TTS, foundation models like Qwen2.5 series and basic LLMs, and multimodal models like Namo-R1 and Qwen2.5-VL. Key advantages of Crane include blazing-fast inference outperforming native PyTorch, Rust-powered to eliminate C++ complexity, Apple Silicon optimized for GPU acceleration via Metal, and hardware agnostic with a unified codebase for CPU/CUDA/Metal execution. Crane simplifies deployment with the ability to add new models with less than 100 lines of code in most cases.
CrackSQL
CrackSQL is a powerful SQL dialect translation tool that integrates rule-based strategies with large language models (LLMs) for high accuracy. It enables seamless conversion between dialects (e.g., PostgreSQL → MySQL) with flexible access through Python API, command line, and web interface. The tool supports extensive dialect compatibility, precision & advanced processing, and versatile access & integration. It offers three modes for dialect translation and demonstrates high translation accuracy over collected benchmarks. Users can deploy CrackSQL using PyPI package installation or source code installation methods. The tool can be extended to support additional syntax, new dialects, and improve translation efficiency. The project is actively maintained and welcomes contributions from the community.

starwhale
Starwhale is an MLOps/LLMOps platform that brings efficiency and standardization to machine learning operations. It streamlines the model development lifecycle, enabling teams to optimize workflows around key areas like model building, evaluation, release, and fine-tuning. Starwhale abstracts Model, Runtime, and Dataset as first-class citizens, providing tailored capabilities for common workflow scenarios including Models Evaluation, Live Demo, and LLM Fine-tuning. It is an open-source platform designed for clarity and ease of use, empowering developers to build customized MLOps features tailored to their needs.
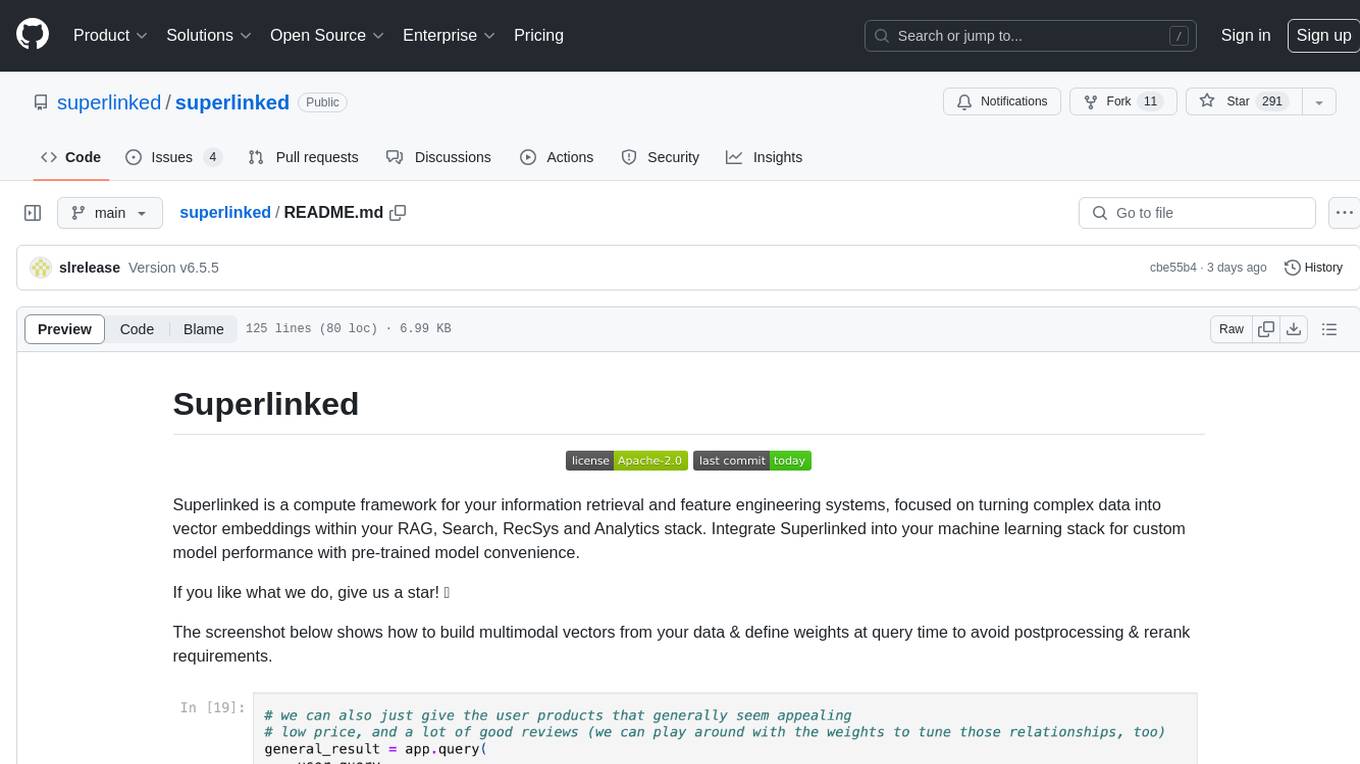
superlinked
Superlinked is a compute framework for information retrieval and feature engineering systems, focusing on converting complex data into vector embeddings for RAG, Search, RecSys, and Analytics stack integration. It enables custom model performance in machine learning with pre-trained model convenience. The tool allows users to build multimodal vectors, define weights at query time, and avoid postprocessing & rerank requirements. Users can explore the computational model through simple scripts and python notebooks, with a future release planned for production usage with built-in data infra and vector database integrations.
kernel-memory
Kernel Memory (KM) is a multi-modal AI Service specialized in the efficient indexing of datasets through custom continuous data hybrid pipelines, with support for Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), synthetic memory, prompt engineering, and custom semantic memory processing. KM is available as a Web Service, as a Docker container, a Plugin for ChatGPT/Copilot/Semantic Kernel, and as a .NET library for embedded applications. Utilizing advanced embeddings and LLMs, the system enables Natural Language querying for obtaining answers from the indexed data, complete with citations and links to the original sources. Designed for seamless integration as a Plugin with Semantic Kernel, Microsoft Copilot and ChatGPT, Kernel Memory enhances data-driven features in applications built for most popular AI platforms.
easy-dataset
Easy Dataset is a specialized application designed to streamline the creation of fine-tuning datasets for Large Language Models (LLMs). It offers an intuitive interface for uploading domain-specific files, intelligently splitting content, generating questions, and producing high-quality training data for model fine-tuning. With Easy Dataset, users can transform domain knowledge into structured datasets compatible with all OpenAI-format compatible LLM APIs, making the fine-tuning process accessible and efficient.
For similar tasks
venice
Venice is a derived data storage platform, providing the following characteristics: 1. High throughput asynchronous ingestion from batch and streaming sources (e.g. Hadoop and Samza). 2. Low latency online reads via remote queries or in-process caching. 3. Active-active replication between regions with CRDT-based conflict resolution. 4. Multi-cluster support within each region with operator-driven cluster assignment. 5. Multi-tenancy, horizontal scalability and elasticity within each cluster. The above makes Venice particularly suitable as the stateful component backing a Feature Store, such as Feathr. AI applications feed the output of their ML training jobs into Venice and then query the data for use during online inference workloads.
pinecone-ts-client
The official Node.js client for Pinecone, written in TypeScript. This client library provides a high-level interface for interacting with the Pinecone vector database service. With this client, you can create and manage indexes, upsert and query vector data, and perform other operations related to vector search and retrieval. The client is designed to be easy to use and provides a consistent and idiomatic experience for Node.js developers. It supports all the features and functionality of the Pinecone API, making it a comprehensive solution for building vector-powered applications in Node.js.

honey
Bee is an ORM framework that provides easy and high-efficiency database operations, allowing developers to focus on business logic development. It supports various databases and features like automatic filtering, partial field queries, pagination, and JSON format results. Bee also offers advanced functionalities like sharding, transactions, complex queries, and MongoDB ORM. The tool is designed for rapid application development in Java, offering faster development for Java Web and Spring Cloud microservices. The Enterprise Edition provides additional features like financial computing support, automatic value insertion, desensitization, dictionary value conversion, multi-tenancy, and more.
llama_index
LlamaIndex is a data framework for building LLM applications. It provides tools for ingesting, structuring, and querying data, as well as integrating with LLMs and other tools. LlamaIndex is designed to be easy to use for both beginner and advanced users, and it provides a comprehensive set of features for building LLM applications.

kernel-memory
Kernel Memory (KM) is a multi-modal AI Service specialized in the efficient indexing of datasets through custom continuous data hybrid pipelines, with support for Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), synthetic memory, prompt engineering, and custom semantic memory processing. KM is available as a Web Service, as a Docker container, a Plugin for ChatGPT/Copilot/Semantic Kernel, and as a .NET library for embedded applications. Utilizing advanced embeddings and LLMs, the system enables Natural Language querying for obtaining answers from the indexed data, complete with citations and links to the original sources. Designed for seamless integration as a Plugin with Semantic Kernel, Microsoft Copilot and ChatGPT, Kernel Memory enhances data-driven features in applications built for most popular AI platforms.

deeplake
Deep Lake is a Database for AI powered by a storage format optimized for deep-learning applications. Deep Lake can be used for: 1. Storing data and vectors while building LLM applications 2. Managing datasets while training deep learning models Deep Lake simplifies the deployment of enterprise-grade LLM-based products by offering storage for all data types (embeddings, audio, text, videos, images, pdfs, annotations, etc.), querying and vector search, data streaming while training models at scale, data versioning and lineage, and integrations with popular tools such as LangChain, LlamaIndex, Weights & Biases, and many more. Deep Lake works with data of any size, it is serverless, and it enables you to store all of your data in your own cloud and in one place. Deep Lake is used by Intel, Bayer Radiology, Matterport, ZERO Systems, Red Cross, Yale, & Oxford.

databend
Databend is an open-source cloud data warehouse that serves as a cost-effective alternative to Snowflake. With its focus on fast query execution and data ingestion, it's designed for complex analysis of the world's largest datasets.
db-ally
db-ally is a library for creating natural language interfaces to data sources. It allows developers to outline specific use cases for a large language model (LLM) to handle, detailing the desired data format and the possible operations to fetch this data. db-ally effectively shields the complexity of the underlying data source from the model, presenting only the essential information needed for solving the specific use cases. Instead of generating arbitrary SQL, the model is asked to generate responses in a simplified query language.
For similar jobs
db2rest
DB2Rest is a modern low-code REST DATA API platform that simplifies the development of intelligent applications. It seamlessly integrates existing and new databases with language models (LMs/LLMs) and vector stores, enabling the rapid delivery of context-aware, reasoning applications without vendor lock-in.
kitops
KitOps is a packaging and versioning system for AI/ML projects that uses open standards so it works with the AI/ML, development, and DevOps tools you are already using. KitOps simplifies the handoffs between data scientists, application developers, and SREs working with LLMs and other AI/ML models. KitOps' ModelKits are a standards-based package for models, their dependencies, configurations, and codebases. ModelKits are portable, reproducible, and work with the tools you already use.
kweaver
KWeaver is an open-source cognitive intelligence development framework that provides data scientists, application developers, and domain experts with the ability for rapid development, comprehensive openness, and high-performance knowledge network generation and cognitive intelligence large model framework. It offers features such as automated and visual knowledge graph construction, visualization and analysis of knowledge graph data, knowledge graph integration, knowledge graph resource management, large model prompt engineering and debugging, and visual configuration for large model access.

honey
Bee is an ORM framework that provides easy and high-efficiency database operations, allowing developers to focus on business logic development. It supports various databases and features like automatic filtering, partial field queries, pagination, and JSON format results. Bee also offers advanced functionalities like sharding, transactions, complex queries, and MongoDB ORM. The tool is designed for rapid application development in Java, offering faster development for Java Web and Spring Cloud microservices. The Enterprise Edition provides additional features like financial computing support, automatic value insertion, desensitization, dictionary value conversion, multi-tenancy, and more.
moxin
Moxin is an AI LLM client written in Rust to demonstrate the functionality of the Robius framework for multi-platform application development. It is currently in early stages of development and not fully functional. The tool supports building and running on macOS and Linux systems, with packaging options available for distribution. Users can install the required WasmEdge WASM runtime and dependencies to build and run Moxin. Packaging for distribution includes generating `.deb` Debian packages, AppImage, and pacman installation packages for Linux, as well as `.app` bundles and `.dmg` disk images for macOS. The macOS app is not signed, leading to a warning on installation, which can be resolved by removing the quarantine attribute from the installed app.

choco-builder
ChocoBuilder (aka Chocolate Factory) is an open-source LLM application development framework designed to help you easily create powerful software development SDLC + LLM generation assistants. It provides modules for integration into JVM projects, usage with RAGScript, and local deployment examples. ChocoBuilder follows a Domain Driven Problem-Solving design philosophy with key concepts like ProblemClarifier, ProblemAnalyzer, SolutionDesigner, SolutionReviewer, and SolutionExecutor. It offers use cases for desktop/IDE, server, and Android applications, with examples for frontend design, semantic code search, testcase generation, and code interpretation.
aidldemo
This repository demonstrates how to achieve cross-process bidirectional communication and large file transfer using AIDL and anonymous shared memory. AIDL is a way to implement Inter-Process Communication in Android, based on Binder. To overcome the data size limit of Binder, anonymous shared memory is used for large file transfer. Shared memory allows processes to share memory by mapping a common memory area into their respective process spaces. While efficient for transferring large data between processes, shared memory lacks synchronization mechanisms, requiring additional mechanisms like semaphores. Android's anonymous shared memory (Ashmem) is based on Linux shared memory and facilitates shared memory transfer using Binder and FileDescriptor. The repository provides practical examples of bidirectional communication and large file transfer between client and server using AIDL interfaces and MemoryFile in Android.
cube
Cube is a semantic layer for building data applications, helping data engineers and application developers access data from modern data stores, organize it into consistent definitions, and deliver it to every application. It works with SQL-enabled data sources, providing sub-second latency and high concurrency for API requests. Cube addresses SQL code organization, performance, and access control issues in data applications, enabling efficient data modeling, access control, and performance optimizations for various tools like embedded analytics, dashboarding, reporting, and data notebooks.


