
A-mem
A-MEM: Agentic Memory for LLM Agents
Stars: 144
A-MEM is a novel agentic memory system designed for Large Language Model (LLM) agents to dynamically organize memories in an agentic way. It introduces advanced memory organization capabilities, intelligent indexing, and linking of memories, comprehensive note generation, interconnected knowledge networks, continuous memory evolution, and agent-driven decision making for adaptive memory management. The system facilitates agent construction and enables dynamic memory operations and flexible agent-memory interactions.
README:
A novel agentic memory system for LLM agents that can dynamically organize memories in an agentic way.
Large Language Model (LLM) agents have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in handling complex real-world tasks through external tool usage. However, to effectively leverage historical experiences, they require sophisticated memory systems. Traditional memory systems, while providing basic storage and retrieval functionality, often lack advanced memory organization capabilities.
Our project introduces an innovative Agentic Memory system that revolutionizes how LLM agents manage and utilize their memories:


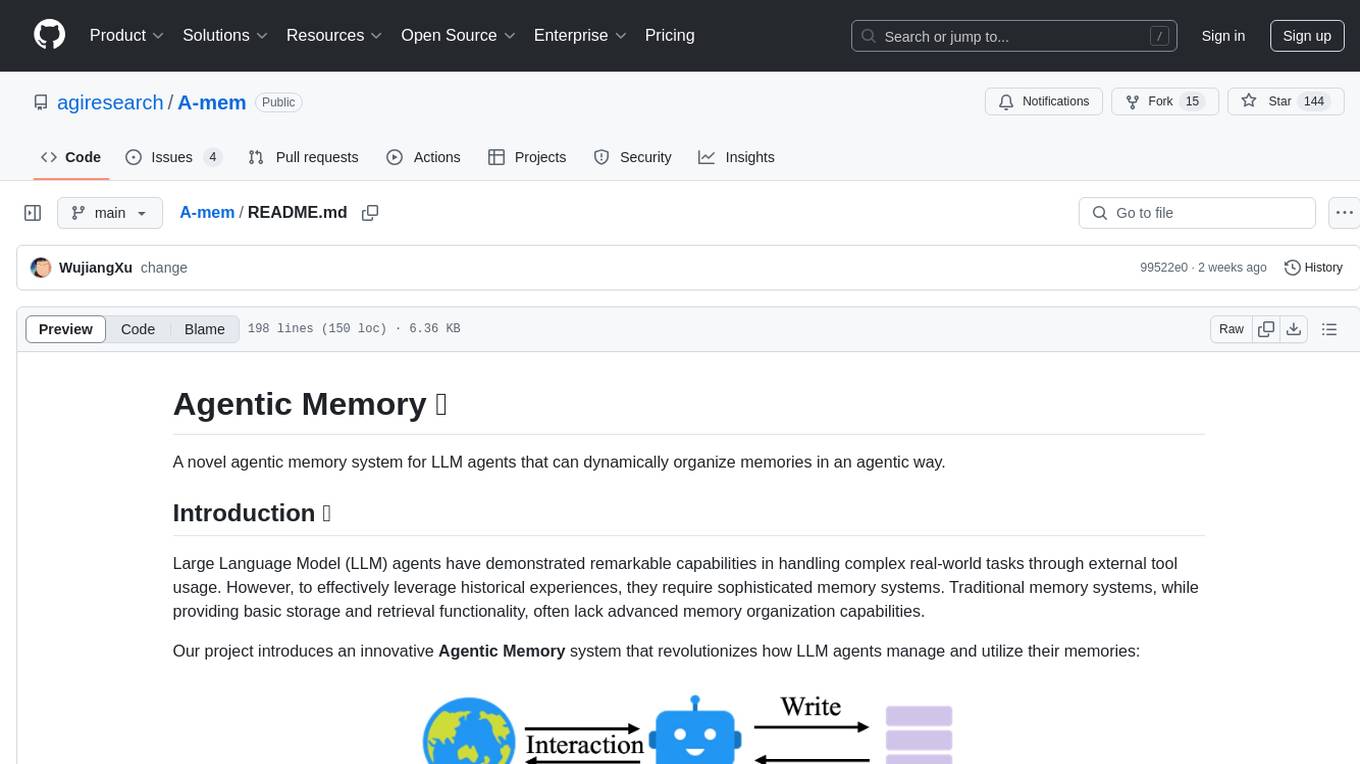
Comparison between traditional memory system (top) and our proposed agentic memory (bottom). Our system enables dynamic memory operations and flexible agent-memory interactions.
Note: This repository provides a memory system to facilitate agent construction. If you want to reproduce the results presented in our paper, please refer to: https://github.com/WujiangXu/AgenticMemory
For more details, please refer to our paper: A-MEM: Agentic Memory for LLM Agents
- 🔄 Dynamic memory organization based on Zettelkasten principles
- 🔍 Intelligent indexing and linking of memories
- 📝 Comprehensive note generation with structured attributes
- 🌐 Interconnected knowledge networks
- 🧬 Continuous memory evolution and refinement
- 🤖 Agent-driven decision making for adaptive memory management

The framework of our Agentic Memory system showing the dynamic interaction between LLM agents and memory components.
When a new memory is added to the system:
- Generates comprehensive notes with structured attributes
- Creates contextual descriptions and tags
- Analyzes historical memories for relevant connections
- Establishes meaningful links based on similarities
- Enables dynamic memory evolution and updates
Empirical experiments conducted on six foundation models demonstrate superior performance compared to existing SOTA baselines.
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/WujiangXu/AgenticMemory.git
cd AgenticMemory- Install dependencies: Option 1: Using venv (Python virtual environment)
# Create and activate virtual environment
python -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate # Linux/Mac
.venv\Scripts\activate # Windows
# Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txtOption 2: Using Conda
# Create and activate conda environment
conda create -n myenv python=3.9
conda activate myenv
# Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt- Usage Examples 💡
Here's how to use the Agentic Memory system for basic operations:
from memory_system import AgenticMemorySystem
# Initialize the memory system 🚀
memory_system = AgenticMemorySystem(
model_name='all-MiniLM-L6-v2', # Embedding model for semantic search
llm_backend="openai", # LLM backend (openai/mock/ollama)
llm_model="gpt-4" # LLM model name
)
# Create (Add) Memories ➕
# Simple creation
memory_id = memory_system.create("Deep learning neural networks")
# Creation with metadata
memory_id = memory_system.create(
content="Machine learning project notes",
tags=["ml", "project"],
category="Research",
timestamp="202503021500" # YYYYMMDDHHmm format
)
# Read (Retrieve) Memories 📖
# Get memory by ID
memory = memory_system.read(memory_id)
print(f"Content: {memory.content}")
print(f"Tags: {memory.tags}")
print(f"Context: {memory.context}")
print(f"Keywords: {memory.keywords}")
# Search memories
results = memory_system.search("neural networks", k=5)
for result in results:
print(f"ID: {result['id']}")
print(f"Content: {result['content']}")
print(f"Score: {result['score']}")
print("---")
# Update Memories 🔄
memory_system.update(memory_id, "Updated content about deep learning")
# Delete Memories ❌
memory_system.delete(memory_id)
# Memory Evolution 🧬
# The system automatically evolves memories by:
# 1. Finding semantic relationships
# 2. Updating metadata and context
# 3. Creating connections between related memories
# This happens automatically when creating or updating memories!-
Hybrid Search 🔍
- Combines ChromaDB vector search and embedding-based retrieval
- Automatically deduplicates and ranks results
- Returns most relevant memories first
-
Memory Evolution 🧬
- Automatically analyzes content relationships
- Updates tags and context based on related memories
- Creates semantic connections between memories
-
Flexible Metadata 📋
- Custom tags and categories
- Automatic keyword extraction
- Context generation
- Timestamp tracking
-
Multiple LLM Backends 🤖
- OpenAI (GPT-4, GPT-3.5)
- Ollama (for local deployment)
-
Memory Creation ✨:
- Provide clear, specific content
- Add relevant tags for better organization
- Let the system handle context and keyword generation
-
Memory Retrieval 🔍:
- Use specific search queries
- Adjust 'k' parameter based on needed results
- Consider both exact and semantic matches
-
Memory Evolution 🧬:
- Allow automatic evolution to organize memories
- Review generated connections periodically
- Use consistent tagging conventions
-
Error Handling
⚠️ :- Always check return values
- Handle potential KeyError for non-existent memories
- Use try-except blocks for LLM operations
If you use this code in your research, please cite our work:
@article{xu2025mem,
title={A-mem: Agentic memory for llm agents},
author={Xu, Wujiang and Liang, Zujie and Mei, Kai and Gao, Hang and Tan, Juntao and Zhang, Yongfeng},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.12110},
year={2025}
}This project is licensed under the MIT License. See LICENSE for details.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for A-mem
Similar Open Source Tools

A-mem
A-MEM is a novel agentic memory system designed for Large Language Model (LLM) agents to dynamically organize memories in an agentic way. It introduces advanced memory organization capabilities, intelligent indexing, and linking of memories, comprehensive note generation, interconnected knowledge networks, continuous memory evolution, and agent-driven decision making for adaptive memory management. The system facilitates agent construction and enables dynamic memory operations and flexible agent-memory interactions.
tinyllm
tinyllm is a lightweight framework designed for developing, debugging, and monitoring LLM and Agent powered applications at scale. It aims to simplify code while enabling users to create complex agents or LLM workflows in production. The core classes, Function and FunctionStream, standardize and control LLM, ToolStore, and relevant calls for scalable production use. It offers structured handling of function execution, including input/output validation, error handling, evaluation, and more, all while maintaining code readability. Users can create chains with prompts, LLM models, and evaluators in a single file without the need for extensive class definitions or spaghetti code. Additionally, tinyllm integrates with various libraries like Langfuse and provides tools for prompt engineering, observability, logging, and finite state machine design.
Controllable-RAG-Agent
This repository contains a sophisticated deterministic graph-based solution for answering complex questions using a controllable autonomous agent. The solution is designed to ensure that answers are solely based on the provided data, avoiding hallucinations. It involves various steps such as PDF loading, text preprocessing, summarization, database creation, encoding, and utilizing large language models. The algorithm follows a detailed workflow involving planning, retrieval, answering, replanning, content distillation, and performance evaluation. Heuristics and techniques implemented focus on content encoding, anonymizing questions, task breakdown, content distillation, chain of thought answering, verification, and model performance evaluation.

UltraRAG
The UltraRAG framework is a researcher and developer-friendly RAG system solution that simplifies the process from data construction to model fine-tuning in domain adaptation. It introduces an automated knowledge adaptation technology system, supporting no-code programming, one-click synthesis and fine-tuning, multidimensional evaluation, and research-friendly exploration work integration. The architecture consists of Frontend, Service, and Backend components, offering flexibility in customization and optimization. Performance evaluation in the legal field shows improved results compared to VanillaRAG, with specific metrics provided. The repository is licensed under Apache-2.0 and encourages citation for support.
VeritasGraph
VeritasGraph is an enterprise-grade graph RAG framework designed for secure, on-premise AI applications. It leverages a knowledge graph to perform complex, multi-hop reasoning, providing transparent, auditable reasoning paths with full source attribution. The framework excels at answering complex questions that traditional vector search engines struggle with, ensuring trust and reliability in enterprise AI. VeritasGraph offers full control over data and AI models, verifiable attribution for every claim, advanced graph reasoning capabilities, and open-source deployment with sovereignty and customization.
Macaw-LLM
Macaw-LLM is a pioneering multi-modal language modeling tool that seamlessly integrates image, audio, video, and text data. It builds upon CLIP, Whisper, and LLaMA models to process and analyze multi-modal information effectively. The tool boasts features like simple and fast alignment, one-stage instruction fine-tuning, and a new multi-modal instruction dataset. It enables users to align multi-modal features efficiently, encode instructions, and generate responses across different data types.
RainbowGPT
RainbowGPT is a versatile tool that offers a range of functionalities, including Stock Analysis for financial decision-making, MySQL Management for database navigation, and integration of AI technologies like GPT-4 and ChatGlm3. It provides a user-friendly interface suitable for all skill levels, ensuring seamless information flow and continuous expansion of emerging technologies. The tool enhances adaptability, creativity, and insight, making it a valuable asset for various projects and tasks.
arbigent
Arbigent (Arbiter-Agent) is an AI agent testing framework designed to make AI agent testing practical for modern applications. It addresses challenges faced by traditional UI testing frameworks and AI agents by breaking down complex tasks into smaller, dependent scenarios. The framework is customizable for various AI providers, operating systems, and form factors, empowering users with extensive customization capabilities. Arbigent offers an intuitive UI for scenario creation and a powerful code interface for seamless test execution. It supports multiple form factors, optimizes UI for AI interaction, and is cost-effective by utilizing models like GPT-4o mini. With a flexible code interface and open-source nature, Arbigent aims to revolutionize AI agent testing in modern applications.

sdialog
SDialog is an MIT-licensed open-source toolkit for building, simulating, and evaluating LLM-based conversational agents end-to-end. It aims to bridge agent construction, user simulation, dialog generation, and evaluation in a single reproducible workflow, enabling the generation of reliable, controllable dialog systems or data at scale. The toolkit standardizes a Dialog schema, offers persona-driven multi-agent simulation with LLMs, provides composable orchestration for precise control over behavior and flow, includes built-in evaluation metrics, and offers mechanistic interpretability. It allows for easy creation of user-defined components and interoperability across various AI platforms.
LightAgent
LightAgent is a lightweight, open-source Agentic AI development framework with memory, tools, and a tree of thought. It supports multi-agent collaboration, autonomous learning, tool integration, complex task handling, and multi-model support. It also features a streaming API, tool generator, agent self-learning, adaptive tool mechanism, and more. LightAgent is designed for intelligent customer service, data analysis, automated tools, and educational assistance.
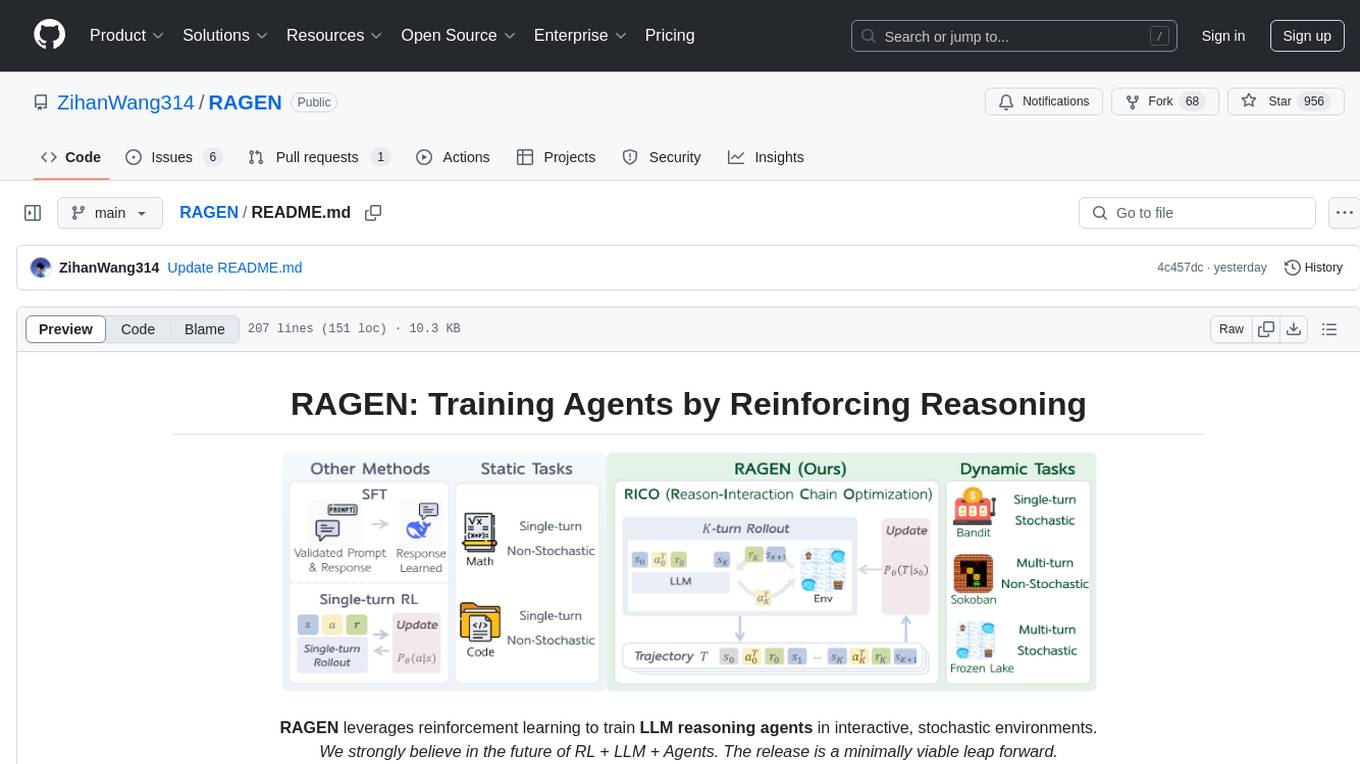
RAGEN
RAGEN is a reinforcement learning framework designed to train reasoning-capable large language model (LLM) agents in interactive, stochastic environments. It addresses challenges such as multi-turn interactions and stochastic environments through a Markov Decision Process (MDP) formulation, Reason-Interaction Chain Optimization (RICO) algorithm, and progressive reward normalization strategies. The framework enables LLMs to reason and interact with the environment, optimizing entire trajectories for long-horizon reasoning while maintaining computational efficiency.
core
CORE is an open-source unified, persistent memory layer for all AI tools, allowing developers to maintain context across different tools like Cursor, ChatGPT, and Claude. It aims to solve the issue of context switching and information loss between sessions by creating a knowledge graph that remembers conversations, decisions, and insights. With features like unified memory, temporal knowledge graph, browser extension, chat with memory, auto-sync from apps, and MCP integration hub, CORE provides a seamless experience for managing and recalling context. The tool's ingestion pipeline captures evolving context through normalization, extraction, resolution, and graph integration, resulting in a dynamic memory that grows and changes with the user. When recalling from memory, CORE utilizes search, re-ranking, filtering, and output to provide relevant and contextual answers. Security measures include data encryption, authentication, access control, and vulnerability reporting.
agents
The LiveKit Agent Framework is designed for building real-time, programmable participants that run on servers. Easily tap into LiveKit WebRTC sessions and process or generate audio, video, and data streams. The framework includes plugins for common workflows, such as voice activity detection and speech-to-text. Agents integrates seamlessly with LiveKit server, offloading job queuing and scheduling responsibilities to it. This eliminates the need for additional queuing infrastructure. Agent code developed on your local machine can scale to support thousands of concurrent sessions when deployed to a server in production.
eole
EOLE is an open language modeling toolkit based on PyTorch. It aims to provide a research-friendly approach with a comprehensive yet compact and modular codebase for experimenting with various types of language models. The toolkit includes features such as versatile training and inference, dynamic data transforms, comprehensive large language model support, advanced quantization, efficient finetuning, flexible inference, and tensor parallelism. EOLE is a work in progress with ongoing enhancements in configuration management, command line entry points, reproducible recipes, core API simplification, and plans for further simplification, refactoring, inference server development, additional recipes, documentation enhancement, test coverage improvement, logging enhancements, and broader model support.
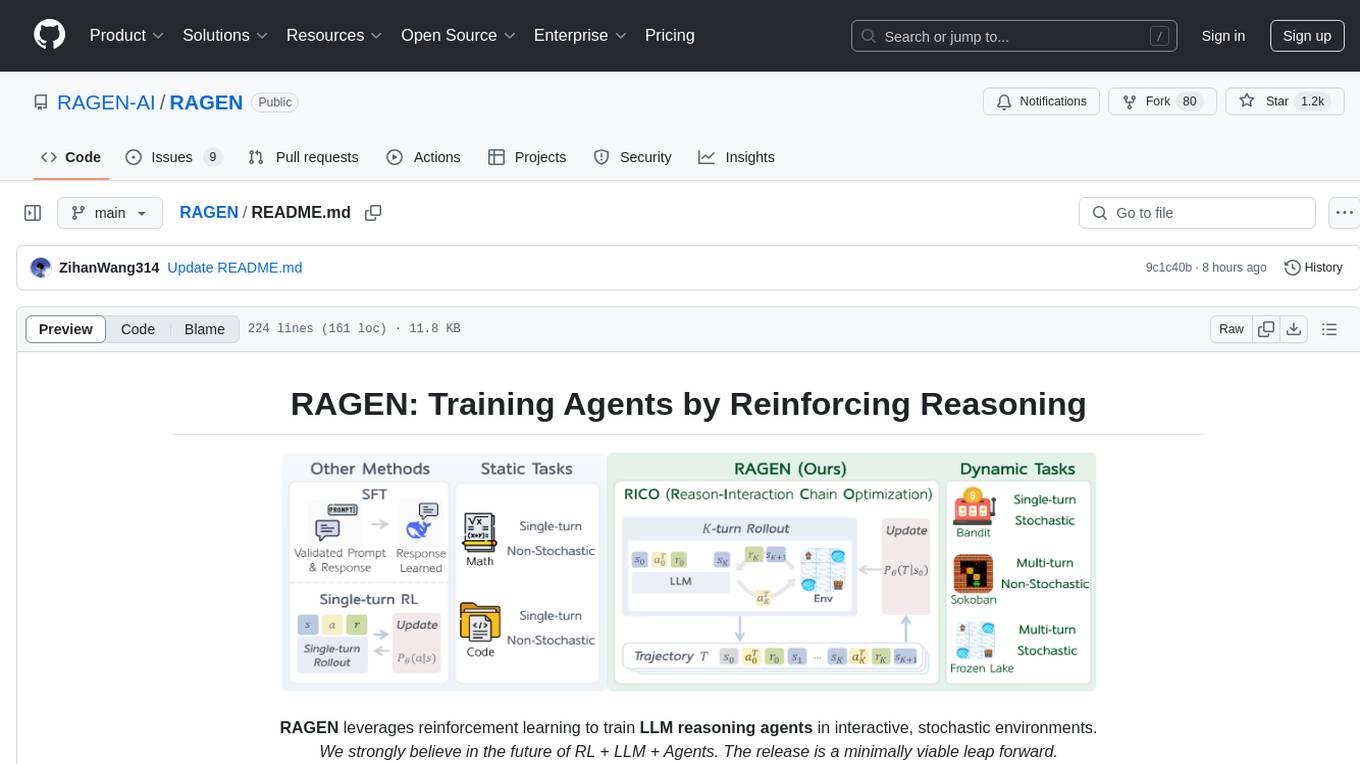
RAGEN
RAGEN is a reinforcement learning framework designed to train reasoning-capable large language model (LLM) agents in interactive, stochastic environments. It addresses challenges such as multi-turn interactions and stochastic environments through a Markov Decision Process (MDP) formulation, Reason-Interaction Chain Optimization (RICO) algorithm, and progressive reward normalization strategies. The framework consists of MDP formulation, RICO algorithm with rollout and update stages, and reward normalization strategies to stabilize training. RAGEN aims to optimize reasoning and action strategies for LLM agents operating in complex environments.
shandu
Shandu is an advanced AI research system that automates comprehensive research processes using language models, web scraping, and iterative exploration to generate well-structured reports with citations. It features intelligent state-based workflow, deep exploration, multi-source information synthesis, enhanced web scraping, smart source evaluation, content analysis pipeline, comprehensive report generation, parallel processing, adaptive search strategy, and full citation management.
For similar tasks

A-mem
A-MEM is a novel agentic memory system designed for Large Language Model (LLM) agents to dynamically organize memories in an agentic way. It introduces advanced memory organization capabilities, intelligent indexing, and linking of memories, comprehensive note generation, interconnected knowledge networks, continuous memory evolution, and agent-driven decision making for adaptive memory management. The system facilitates agent construction and enables dynamic memory operations and flexible agent-memory interactions.
obsidian-systemsculpt-ai
SystemSculpt AI is a comprehensive AI-powered plugin for Obsidian, integrating advanced AI capabilities into note-taking, task management, knowledge organization, and content creation. It offers modules for brain integration, chat conversations, audio recording and transcription, note templates, and task generation and management. Users can customize settings, utilize AI services like OpenAI and Groq, and access documentation for detailed guidance. The plugin prioritizes data privacy by storing sensitive information locally and offering the option to use local AI models for enhanced privacy.
note-gen
Note-gen is a simple tool for generating notes automatically based on user input. It uses natural language processing techniques to analyze text and extract key information to create structured notes. The tool is designed to save time and effort for users who need to summarize large amounts of text or generate notes quickly. With note-gen, users can easily create organized and concise notes for study, research, or any other purpose.
memU
MemU is an open-source memory framework designed for AI companions, offering high accuracy, fast retrieval, and cost-effectiveness. It serves as an intelligent 'memory folder' that adapts to various AI companion scenarios. With MemU, users can create AI companions that remember them, learn their preferences, and evolve through interactions. The framework provides advanced retrieval strategies, 24/7 support, and is specialized for AI companions. MemU offers cloud, enterprise, and self-hosting options, with features like memory organization, interconnected knowledge graph, continuous self-improvement, and adaptive forgetting mechanism. It boasts high memory accuracy, fast retrieval, and low cost, making it suitable for building intelligent agents with persistent memory capabilities.
DataEngineeringPilipinas
DataEngineeringPilipinas is a repository dedicated to data engineering resources in the Philippines. It serves as a platform for data engineering professionals to contribute and access high-quality content related to data engineering. The repository provides guidelines for contributing, including forking the repository, making changes, and submitting contributions. It emphasizes the importance of quality, relevance, and respect in the contributions made to the project. By following the guidelines and contributing to the repository, users can help build a valuable resource for the data engineering community in the Philippines and beyond.
slidev-mcp
slidev-mcp is an intelligent slide generation tool based on Slidev that integrates large language model technology, allowing users to automatically generate professional online PPT presentations with simple descriptions. It dramatically lowers the barrier to using Slidev, provides natural language interactive slide creation, and offers automated generation of professional presentations. The tool also includes various features for environment and project management, slide content management, and utility tools to enhance the slide creation process.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.