
Model-Optimizer
A unified library of SOTA model optimization techniques like quantization, pruning, distillation, speculative decoding, etc. It compresses deep learning models for downstream deployment frameworks like TensorRT-LLM, TensorRT, vLLM, etc. to optimize inference speed.
Stars: 1960
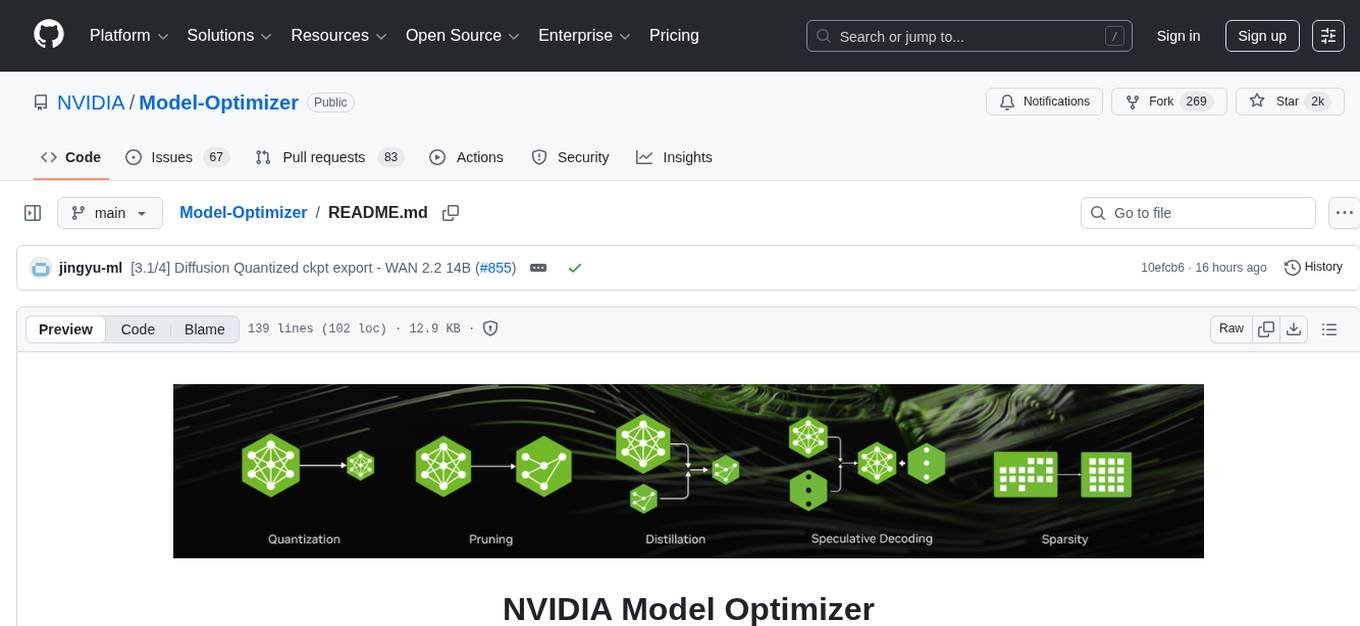
NVIDIA Model Optimizer is a library that offers state-of-the-art model optimization techniques like quantization, distillation, pruning, speculative decoding, and sparsity to accelerate models. It supports inputs of Hugging Face, PyTorch, or ONNX models, provides Python APIs for easy composition of optimization techniques, and exports optimized quantized checkpoints. Integrated with NVIDIA Megatron-Bridge, Megatron-LM, and Hugging Face Accelerate for training required inference optimization techniques. The generated quantized checkpoint is ready for deployment in downstream inference frameworks like SGLang, TensorRT-LLM, TensorRT, or vLLM.
README:
NVIDIA Model Optimizer (referred to as Model Optimizer, or ModelOpt) is a library comprising state-of-the-art model optimization techniques including quantization, distillation, pruning, speculative decoding and sparsity to accelerate models.
[Input] Model Optimizer currently supports inputs of a Hugging Face, PyTorch or ONNX model.
[Optimize] Model Optimizer provides Python APIs for users to easily compose the above model optimization techniques and export an optimized quantized checkpoint. Model Optimizer is also integrated with NVIDIA Megatron-Bridge, Megatron-LM and Hugging Face Accelerate for training required inference optimization techniques.
[Export for deployment] Seamlessly integrated within the NVIDIA AI software ecosystem, the quantized checkpoint generated from Model Optimizer is ready for deployment in downstream inference frameworks like SGLang, TensorRT-LLM, TensorRT, or vLLM.
- [2025/12/11] BLOG: Top 5 AI Model Optimization Techniques for Faster, Smarter Inference
- [2025/12/08] NVIDIA TensorRT Model Optimizer is now officially rebranded as NVIDIA Model Optimizer.
- [2025/10/07] BLOG: Pruning and Distilling LLMs Using NVIDIA Model Optimizer
- [2025/09/17] BLOG: An Introduction to Speculative Decoding for Reducing Latency in AI Inference
- [2025/09/11] BLOG: How Quantization Aware Training Enables Low-Precision Accuracy Recovery
- [2025/08/29] BLOG: Fine-Tuning gpt-oss for Accuracy and Performance with Quantization Aware Training
- [2025/08/01] BLOG: Optimizing LLMs for Performance and Accuracy with Post-Training Quantization
- [2025/06/24] BLOG: Introducing NVFP4 for Efficient and Accurate Low-Precision Inference
- [2025/05/14] NVIDIA TensorRT Unlocks FP4 Image Generation for NVIDIA Blackwell GeForce RTX 50 Series GPUs
- [2025/04/21] Adobe optimized deployment using Model-Optimizer + TensorRT leading to a 60% reduction in diffusion latency, a 40% reduction in total cost of ownership
- [2025/04/05] NVIDIA Accelerates Inference on Meta Llama 4 Scout and Maverick. Check out how to quantize Llama4 for deployment acceleration here
- [2025/03/18] World's Fastest DeepSeek-R1 Inference with Blackwell FP4 & Increasing Image Generation Efficiency on Blackwell
- [2025/02/25] Model Optimizer quantized NVFP4 models available on Hugging Face for download: DeepSeek-R1-FP4, Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct-FP4, Llama-3.1-405B-Instruct-FP4
- [2025/01/28] Model Optimizer has added support for NVFP4. Check out an example of NVFP4 PTQ here.
- [2025/01/28] Model Optimizer is now open source!
Previous News
- [2024/10/23] Model Optimizer quantized FP8 Llama-3.1 Instruct models available on Hugging Face for download: 8B, 70B, 405B.
- [2024/09/10] Post-Training Quantization of LLMs with NVIDIA NeMo and Model Optimizer.
- [2024/08/28] Boosting Llama 3.1 405B Performance up to 44% with Model Optimizer on NVIDIA H200 GPUs
- [2024/08/28] Up to 1.9X Higher Llama 3.1 Performance with Medusa
- [2024/08/15] New features in recent releases: Cache Diffusion, QLoRA workflow with NVIDIA NeMo, and more. Check out our blog for details.
- [2024/06/03] Model Optimizer now has an experimental feature to deploy to vLLM as part of our effort to support popular deployment frameworks. Check out the workflow here
- [2024/05/08] Announcement: Model Optimizer Now Formally Available to Further Accelerate GenAI Inference Performance
- [2024/03/27] Model Optimizer supercharges TensorRT-LLM to set MLPerf LLM inference records
- [2024/03/18] GTC Session: Optimize Generative AI Inference with Quantization in TensorRT-LLM and TensorRT
- [2024/03/07] Model Optimizer's 8-bit Post-Training Quantization enables TensorRT to accelerate Stable Diffusion to nearly 2x faster
- [2024/02/01] Speed up inference with Model Optimizer quantization techniques in TRT-LLM
To install stable release packages for Model Optimizer with pip from PyPI:
pip install -U nvidia-modelopt[all]To install from source in editable mode with all development dependencies or to use the latest features, run:
# Clone the Model Optimizer repository
git clone [email protected]:NVIDIA/Model-Optimizer.git
cd Model-Optimizer
pip install -e .[dev]You can also directly use the TensorRT-LLM docker images
(e.g., nvcr.io/nvidia/tensorrt-llm/release:<version>), which have Model Optimizer pre-installed.
Make sure to upgrade Model Optimizer to the latest version using pip as described above.
Visit our installation guide for
more fine-grained control on installed dependencies or for alternative docker images and environment variables to setup.
| Technique | Description | Examples | Docs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post Training Quantization | Compress model size by 2x-4x, speeding up inference while preserving model quality! | [LLMs] [diffusers] [VLMs] [onnx] [windows] | [docs] |
| Quantization Aware Training | Refine accuracy even further with a few training steps! | [NeMo] [Hugging Face] | [docs] |
| Pruning | Reduce your model size and accelerate inference by removing unnecessary weights! | [PyTorch] | [docs] |
| Distillation | Reduce deployment model size by teaching small models to behave like larger models! | [NeMo] [Hugging Face] | [docs] |
| Speculative Decoding | Train draft modules to predict extra tokens during inference! | [Megatron] [Hugging Face] | [docs] |
| Sparsity | Efficiently compress your model by storing only its non-zero parameter values and their locations | [PyTorch] | [docs] |
- Ready-to-deploy checkpoints [🤗 Hugging Face - Nvidia Model Optimizer Collection]
- Deployable on TensorRT-LLM, vLLM and SGLang
- More models coming soon!
| Model Type | Support Matrix |
|---|---|
| LLM Quantization | View Support Matrix |
| Diffusers Quantization | View Support Matrix |
| VLM Quantization | View Support Matrix |
| ONNX Quantization | View Support Matrix |
| Windows Quantization | View Support Matrix |
| Quantization Aware Training | View Support Matrix |
| Pruning | View Support Matrix |
| Distillation | View Support Matrix |
| Speculative Decoding | View Support Matrix |
Model Optimizer is now open source! We welcome any feedback, feature requests and PRs. Please read our Contributing guidelines for details on how to contribute to this project.
Happy optimizing!
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Model-Optimizer
Similar Open Source Tools

Model-Optimizer
NVIDIA Model Optimizer is a library that offers state-of-the-art model optimization techniques like quantization, distillation, pruning, speculative decoding, and sparsity to accelerate models. It supports inputs of Hugging Face, PyTorch, or ONNX models, provides Python APIs for easy composition of optimization techniques, and exports optimized quantized checkpoints. Integrated with NVIDIA Megatron-Bridge, Megatron-LM, and Hugging Face Accelerate for training required inference optimization techniques. The generated quantized checkpoint is ready for deployment in downstream inference frameworks like SGLang, TensorRT-LLM, TensorRT, or vLLM.
TensorRT-Model-Optimizer
The NVIDIA TensorRT Model Optimizer is a library designed to quantize and compress deep learning models for optimized inference on GPUs. It offers state-of-the-art model optimization techniques including quantization and sparsity to reduce inference costs for generative AI models. Users can easily stack different optimization techniques to produce quantized checkpoints from torch or ONNX models. The quantized checkpoints are ready for deployment in inference frameworks like TensorRT-LLM or TensorRT, with planned integrations for NVIDIA NeMo and Megatron-LM. The tool also supports 8-bit quantization with Stable Diffusion for enterprise users on NVIDIA NIM. Model Optimizer is available for free on NVIDIA PyPI, and this repository serves as a platform for sharing examples, GPU-optimized recipes, and collecting community feedback.
Awesome-LLM
Awesome-LLM is a curated list of resources related to large language models, focusing on papers, projects, frameworks, tools, tutorials, courses, opinions, and other useful resources in the field. It covers trending LLM projects, milestone papers, other papers, open LLM projects, LLM training frameworks, LLM evaluation frameworks, tools for deploying LLM, prompting libraries & tools, tutorials, courses, books, and opinions. The repository provides a comprehensive overview of the latest advancements and resources in the field of large language models.

ColossalAI
Colossal-AI is a deep learning system for large-scale parallel training. It provides a unified interface to scale sequential code of model training to distributed environments. Colossal-AI supports parallel training methods such as data, pipeline, tensor, and sequence parallelism and is integrated with heterogeneous training and zero redundancy optimizer.

xtuner
XTuner is an efficient, flexible, and full-featured toolkit for fine-tuning large models. It supports various LLMs (InternLM, Mixtral-8x7B, Llama 2, ChatGLM, Qwen, Baichuan, ...), VLMs (LLaVA), and various training algorithms (QLoRA, LoRA, full-parameter fine-tune). XTuner also provides tools for chatting with pretrained / fine-tuned LLMs and deploying fine-tuned LLMs with any other framework, such as LMDeploy.
FlagEmbedding
FlagEmbedding focuses on retrieval-augmented LLMs, consisting of the following projects currently: * **Long-Context LLM** : Activation Beacon * **Fine-tuning of LM** : LM-Cocktail * **Embedding Model** : Visualized-BGE, BGE-M3, LLM Embedder, BGE Embedding * **Reranker Model** : llm rerankers, BGE Reranker * **Benchmark** : C-MTEB
stm32ai-modelzoo
The STM32 AI model zoo is a collection of reference machine learning models optimized to run on STM32 microcontrollers. It provides a large collection of application-oriented models ready for re-training, scripts for easy retraining from user datasets, pre-trained models on reference datasets, and application code examples generated from user AI models. The project offers training scripts for transfer learning or training custom models from scratch. It includes performances on reference STM32 MCU and MPU for float and quantized models. The project is organized by application, providing step-by-step guides for training and deploying models.
RAG-Retrieval
RAG-Retrieval provides full-chain RAG retrieval fine-tuning and inference code. It supports fine-tuning any open-source RAG retrieval models, including vector (embedding, graph a), delayed interactive models (ColBERT, graph d), interactive models (cross encoder, graph c). For inference, RAG-Retrieval focuses on ranking (reranker) and has developed a lightweight Python library rag-retrieval, providing a unified way to call any different RAG ranking models.
nncf
Neural Network Compression Framework (NNCF) provides a suite of post-training and training-time algorithms for optimizing inference of neural networks in OpenVINO™ with a minimal accuracy drop. It is designed to work with models from PyTorch, TorchFX, TensorFlow, ONNX, and OpenVINO™. NNCF offers samples demonstrating compression algorithms for various use cases and models, with the ability to add different compression algorithms easily. It supports GPU-accelerated layers, distributed training, and seamless combination of pruning, sparsity, and quantization algorithms. NNCF allows exporting compressed models to ONNX or TensorFlow formats for use with OpenVINO™ toolkit, and supports Accuracy-Aware model training pipelines via Adaptive Compression Level Training and Early Exit Training.
RAG-Retrieval
RAG-Retrieval is an end-to-end code repository that provides training, inference, and distillation capabilities for the RAG retrieval model. It supports fine-tuning of various open-source RAG retrieval models, including embedding models, late interactive models, and reranker models. The repository offers a lightweight Python library for calling different RAG ranking models and allows distillation of LLM-based reranker models into bert-based reranker models. It includes features such as support for end-to-end fine-tuning, distillation of large models, advanced algorithms like MRL, multi-GPU training strategy, and a simple code structure for easy modifications.
MiniCPM-V
MiniCPM-V is a series of end-side multimodal LLMs designed for vision-language understanding. The models take image and text inputs to provide high-quality text outputs. The series includes models like MiniCPM-Llama3-V 2.5 with 8B parameters surpassing proprietary models, and MiniCPM-V 2.0, a lighter model with 2B parameters. The models support over 30 languages, efficient deployment on end-side devices, and have strong OCR capabilities. They achieve state-of-the-art performance on various benchmarks and prevent hallucinations in text generation. The models can process high-resolution images efficiently and support multilingual capabilities.
dl_model_infer
This project is a c++ version of the AI reasoning library that supports the reasoning of tensorrt models. It provides accelerated deployment cases of deep learning CV popular models and supports dynamic-batch image processing, inference, decode, and NMS. The project has been updated with various models and provides tutorials for model exports. It also includes a producer-consumer inference model for specific tasks. The project directory includes implementations for model inference applications, backend reasoning classes, post-processing, pre-processing, and target detection and tracking. Speed tests have been conducted on various models, and onnx downloads are available for different models.
TokenPacker
TokenPacker is a novel visual projector that compresses visual tokens by 75%∼89% with high efficiency. It adopts a 'coarse-to-fine' scheme to generate condensed visual tokens, achieving comparable or better performance across diverse benchmarks. The tool includes TokenPacker for general use and TokenPacker-HD for high-resolution image understanding. It provides training scripts, checkpoints, and supports various compression ratios and patch numbers.

MNN
MNN is a highly efficient and lightweight deep learning framework that supports inference and training of deep learning models. It has industry-leading performance for on-device inference and training. MNN has been integrated into various Alibaba Inc. apps and is used in scenarios like live broadcast, short video capture, search recommendation, and product searching by image. It is also utilized on embedded devices such as IoT. MNN-LLM and MNN-Diffusion are specific runtime solutions developed based on the MNN engine for deploying language models and diffusion models locally on different platforms. The framework is optimized for devices, supports various neural networks, and offers high performance with optimized assembly code and GPU support. MNN is versatile, easy to use, and supports hybrid computing on multiple devices.
lemonade
Lemonade is a tool that helps users run local Large Language Models (LLMs) with high performance by configuring state-of-the-art inference engines for their Neural Processing Units (NPUs) and Graphics Processing Units (GPUs). It is used by startups, research teams, and large companies to run LLMs efficiently. Lemonade provides a high-level Python API for direct integration of LLMs into Python applications and a CLI for mixing and matching LLMs with various features like prompting templates, accuracy testing, performance benchmarking, and memory profiling. The tool supports both GGUF and ONNX models and allows importing custom models from Hugging Face using the Model Manager. Lemonade is designed to be easy to use and switch between different configurations at runtime, making it a versatile tool for running LLMs locally.
ReST-MCTS
ReST-MCTS is a reinforced self-training approach that integrates process reward guidance with tree search MCTS to collect higher-quality reasoning traces and per-step value for training policy and reward models. It eliminates the need for manual per-step annotation by estimating the probability of steps leading to correct answers. The inferred rewards refine the process reward model and aid in selecting high-quality traces for policy model self-training.
For similar tasks
edgeai
Embedded inference of Deep Learning models is quite challenging due to high compute requirements. TI’s Edge AI software product helps optimize and accelerate inference on TI’s embedded devices. It supports heterogeneous execution of DNNs across cortex-A based MPUs, TI’s latest generation C7x DSP, and DNN accelerator (MMA). The solution simplifies the product life cycle of DNN development and deployment by providing a rich set of tools and optimized libraries.

Model-Optimizer
NVIDIA Model Optimizer is a library that offers state-of-the-art model optimization techniques like quantization, distillation, pruning, speculative decoding, and sparsity to accelerate models. It supports inputs of Hugging Face, PyTorch, or ONNX models, provides Python APIs for easy composition of optimization techniques, and exports optimized quantized checkpoints. Integrated with NVIDIA Megatron-Bridge, Megatron-LM, and Hugging Face Accelerate for training required inference optimization techniques. The generated quantized checkpoint is ready for deployment in downstream inference frameworks like SGLang, TensorRT-LLM, TensorRT, or vLLM.
ck
Collective Mind (CM) is a collection of portable, extensible, technology-agnostic and ready-to-use automation recipes with a human-friendly interface (aka CM scripts) to unify and automate all the manual steps required to compose, run, benchmark and optimize complex ML/AI applications on any platform with any software and hardware: see online catalog and source code. CM scripts require Python 3.7+ with minimal dependencies and are continuously extended by the community and MLCommons members to run natively on Ubuntu, MacOS, Windows, RHEL, Debian, Amazon Linux and any other operating system, in a cloud or inside automatically generated containers while keeping backward compatibility - please don't hesitate to report encountered issues here and contact us via public Discord Server to help this collaborative engineering effort! CM scripts were originally developed based on the following requirements from the MLCommons members to help them automatically compose and optimize complex MLPerf benchmarks, applications and systems across diverse and continuously changing models, data sets, software and hardware from Nvidia, Intel, AMD, Google, Qualcomm, Amazon and other vendors: * must work out of the box with the default options and without the need to edit some paths, environment variables and configuration files; * must be non-intrusive, easy to debug and must reuse existing user scripts and automation tools (such as cmake, make, ML workflows, python poetry and containers) rather than substituting them; * must have a very simple and human-friendly command line with a Python API and minimal dependencies; * must require minimal or zero learning curve by using plain Python, native scripts, environment variables and simple JSON/YAML descriptions instead of inventing new workflow languages; * must have the same interface to run all automations natively, in a cloud or inside containers. CM scripts were successfully validated by MLCommons to modularize MLPerf inference benchmarks and help the community automate more than 95% of all performance and power submissions in the v3.1 round across more than 120 system configurations (models, frameworks, hardware) while reducing development and maintenance costs.
aimet
AIMET is a library that provides advanced model quantization and compression techniques for trained neural network models. It provides features that have been proven to improve run-time performance of deep learning neural network models with lower compute and memory requirements and minimal impact to task accuracy. AIMET is designed to work with PyTorch, TensorFlow and ONNX models. We also host the AIMET Model Zoo - a collection of popular neural network models optimized for 8-bit inference. We also provide recipes for users to quantize floating point models using AIMET.
byteir
The ByteIR Project is a ByteDance model compilation solution. ByteIR includes compiler, runtime, and frontends, and provides an end-to-end model compilation solution. Although all ByteIR components (compiler/runtime/frontends) are together to provide an end-to-end solution, and all under the same umbrella of this repository, each component technically can perform independently. The name, ByteIR, comes from a legacy purpose internally. The ByteIR project is NOT an IR spec definition project. Instead, in most scenarios, ByteIR directly uses several upstream MLIR dialects and Google Mhlo. Most of ByteIR compiler passes are compatible with the selected upstream MLIR dialects and Google Mhlo.
hqq
HQQ is a fast and accurate model quantizer that skips the need for calibration data. It's super simple to implement (just a few lines of code for the optimizer). It can crunch through quantizing the Llama2-70B model in only 4 minutes! 🚀
effort
Effort is an example implementation of the bucketMul algorithm, which allows for real-time adjustment of the number of calculations performed during inference of an LLM model. At 50% effort, it performs as fast as regular matrix multiplications on Apple Silicon chips; at 25% effort, it is twice as fast while still retaining most of the quality. Additionally, users have the option to skip loading the least important weights.
neural-compressor
Intel® Neural Compressor is an open-source Python library that supports popular model compression techniques such as quantization, pruning (sparsity), distillation, and neural architecture search on mainstream frameworks such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, ONNX Runtime, and MXNet. It provides key features, typical examples, and open collaborations, including support for a wide range of Intel hardware, validation of popular LLMs, and collaboration with cloud marketplaces, software platforms, and open AI ecosystems.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.



