ColossalAI
Making large AI models cheaper, faster and more accessible
Stars: 40323

Colossal-AI is a deep learning system for large-scale parallel training. It provides a unified interface to scale sequential code of model training to distributed environments. Colossal-AI supports parallel training methods such as data, pipeline, tensor, and sequence parallelism and is integrated with heterogeneous training and zero redundancy optimizer.
README:
Colossal-AI: Making large AI models cheaper, faster, and more accessible
Paper | Documentation | Examples | Forum | GPU Cloud Playground | Blog
Access high-end, on-demand compute for your research instantly—no setup needed.
Sign up now and get $10 in credits!
Limited Academic Bonuses:
- Top up $1,000 and receive 300 credits
- Top up $500 and receive 100 credits
- [2025/02] DeepSeek 671B Fine-Tuning Guide Revealed—Unlock the Upgraded DeepSeek Suite with One Click, AI Players Ecstatic!
- [2024/12] The development cost of video generation models has saved by 50%! Open-source solutions are now available with H200 GPU vouchers [code] [vouchers]
- [2024/10] How to build a low-cost Sora-like app? Solutions for you
- [2024/09] Singapore Startup HPC-AI Tech Secures 50 Million USD in Series A Funding to Build the Video Generation AI Model and GPU Platform
- [2024/09] Reducing AI Large Model Training Costs by 30% Requires Just a Single Line of Code From FP8 Mixed Precision Training Upgrades
- [2024/06] Open-Sora Continues Open Source: Generate Any 16-Second 720p HD Video with One Click, Model Weights Ready to Use
- [2024/05] Large AI Models Inference Speed Doubled, Colossal-Inference Open Source Release
- [2024/04] Open-Sora Unveils Major Upgrade: Embracing Open Source with Single-Shot 16-Second Video Generation and 720p Resolution
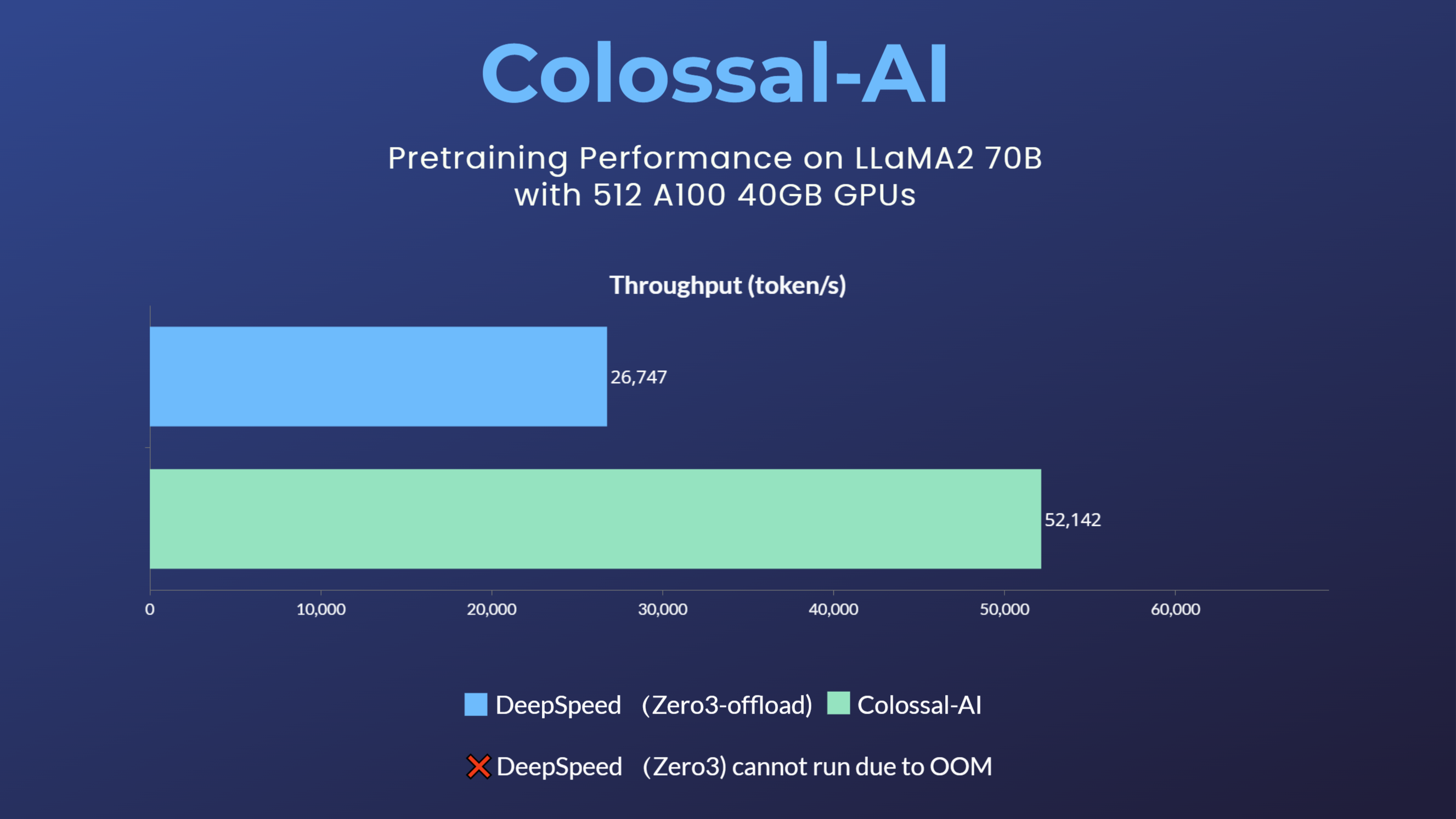
- [2024/04] Most cost-effective solutions for inference, fine-tuning and pretraining, tailored to LLaMA3 series
- Why Colossal-AI
- Features
-
Colossal-AI for Real World Applications
- Open-Sora: Revealing Complete Model Parameters, Training Details, and Everything for Sora-like Video Generation Models
- Colossal-LLaMA-2: One Half-Day of Training Using a Few Hundred Dollars Yields Similar Results to Mainstream Large Models, Open-Source and Commercial-Free Domain-Specific Llm Solution
- ColossalChat: An Open-Source Solution for Cloning ChatGPT With a Complete RLHF Pipeline
- AIGC: Acceleration of Stable Diffusion
- Biomedicine: Acceleration of AlphaFold Protein Structure
- Parallel Training Demo
- Single GPU Training Demo
- Inference
- Installation
- Use Docker
- Community
- Contributing
- Cite Us

Prof. James Demmel (UC Berkeley): Colossal-AI makes training AI models efficient, easy, and scalable.
Colossal-AI provides a collection of parallel components for you. We aim to support you to write your distributed deep learning models just like how you write your model on your laptop. We provide user-friendly tools to kickstart distributed training and inference in a few lines.
-
Parallelism strategies
- Data Parallelism
- Pipeline Parallelism
- 1D, 2D, 2.5D, 3D Tensor Parallelism
- Sequence Parallelism
- Zero Redundancy Optimizer (ZeRO)
- Auto-Parallelism
-
Heterogeneous Memory Management
-
Friendly Usage
- Parallelism based on the configuration file
Open-Sora:Revealing Complete Model Parameters, Training Details, and Everything for Sora-like Video Generation Models [code] [blog] [Model weights] [Demo] [GPU Cloud Playground] [OpenSora Image]
[GPU Cloud Playground] [LLaMA3 Image]
-
7B: One half-day of training using a few hundred dollars yields similar results to mainstream large models, open-source and commercial-free domain-specific LLM solution. [code] [blog] [HuggingFace model weights] [Modelscope model weights]
-
13B: Construct refined 13B private model with just $5000 USD. [code] [blog] [HuggingFace model weights] [Modelscope model weights]
| Model | Backbone | Tokens Consumed | MMLU (5-shot) | CMMLU (5-shot) | AGIEval (5-shot) | GAOKAO (0-shot) | CEval (5-shot) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baichuan-7B | - | 1.2T | 42.32 (42.30) | 44.53 (44.02) | 38.72 | 36.74 | 42.80 |
| Baichuan-13B-Base | - | 1.4T | 50.51 (51.60) | 55.73 (55.30) | 47.20 | 51.41 | 53.60 |
| Baichuan2-7B-Base | - | 2.6T | 46.97 (54.16) | 57.67 (57.07) | 45.76 | 52.60 | 54.00 |
| Baichuan2-13B-Base | - | 2.6T | 54.84 (59.17) | 62.62 (61.97) | 52.08 | 58.25 | 58.10 |
| ChatGLM-6B | - | 1.0T | 39.67 (40.63) | 41.17 (-) | 40.10 | 36.53 | 38.90 |
| ChatGLM2-6B | - | 1.4T | 44.74 (45.46) | 49.40 (-) | 46.36 | 45.49 | 51.70 |
| InternLM-7B | - | 1.6T | 46.70 (51.00) | 52.00 (-) | 44.77 | 61.64 | 52.80 |
| Qwen-7B | - | 2.2T | 54.29 (56.70) | 56.03 (58.80) | 52.47 | 56.42 | 59.60 |
| Llama-2-7B | - | 2.0T | 44.47 (45.30) | 32.97 (-) | 32.60 | 25.46 | - |
| Linly-AI/Chinese-LLaMA-2-7B-hf | Llama-2-7B | 1.0T | 37.43 | 29.92 | 32.00 | 27.57 | - |
| wenge-research/yayi-7b-llama2 | Llama-2-7B | - | 38.56 | 31.52 | 30.99 | 25.95 | - |
| ziqingyang/chinese-llama-2-7b | Llama-2-7B | - | 33.86 | 34.69 | 34.52 | 25.18 | 34.2 |
| TigerResearch/tigerbot-7b-base | Llama-2-7B | 0.3T | 43.73 | 42.04 | 37.64 | 30.61 | - |
| LinkSoul/Chinese-Llama-2-7b | Llama-2-7B | - | 48.41 | 38.31 | 38.45 | 27.72 | - |
| FlagAlpha/Atom-7B | Llama-2-7B | 0.1T | 49.96 | 41.10 | 39.83 | 33.00 | - |
| IDEA-CCNL/Ziya-LLaMA-13B-v1.1 | Llama-13B | 0.11T | 50.25 | 40.99 | 40.04 | 30.54 | - |
| Colossal-LLaMA-2-7b-base | Llama-2-7B | 0.0085T | 53.06 | 49.89 | 51.48 | 58.82 | 50.2 |
| Colossal-LLaMA-2-13b-base | Llama-2-13B | 0.025T | 56.42 | 61.80 | 54.69 | 69.53 | 60.3 |
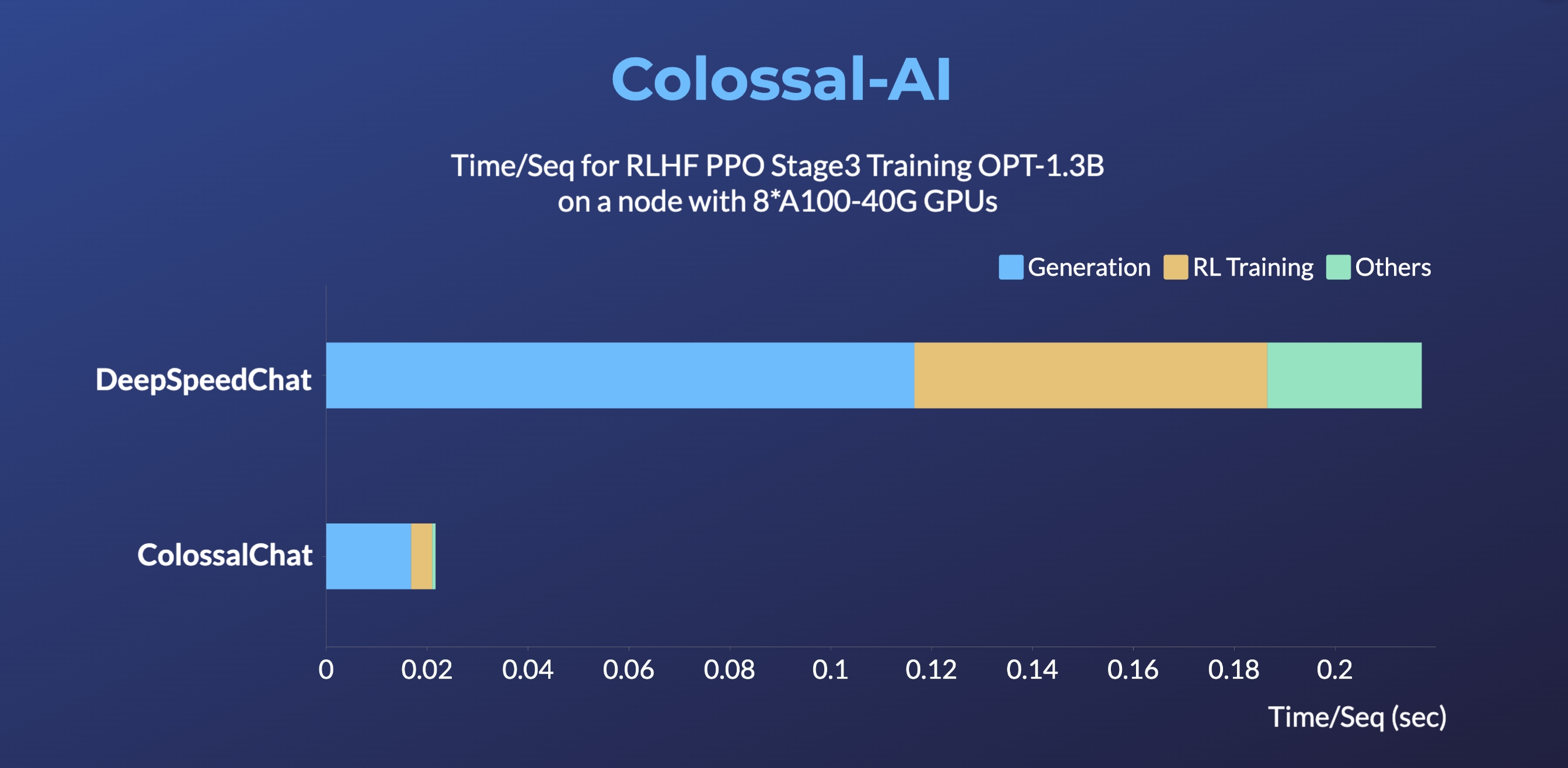
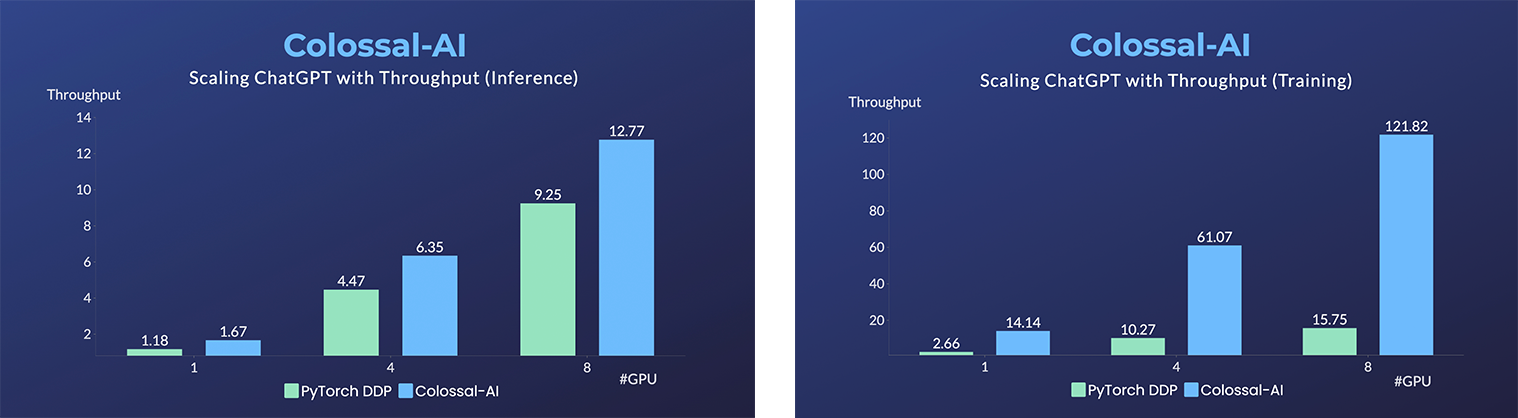
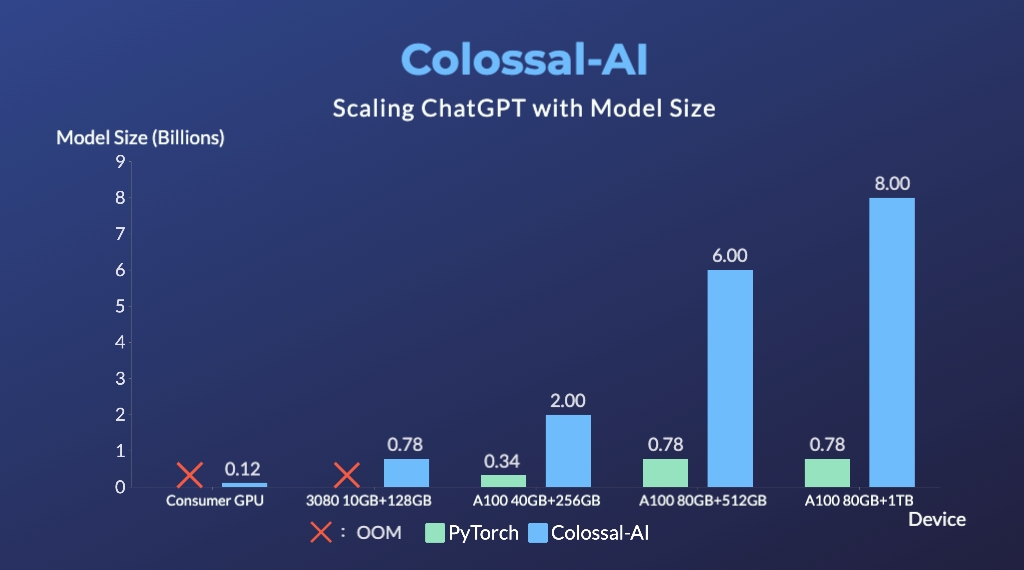
ColossalChat: An open-source solution for cloning ChatGPT with a complete RLHF pipeline. [code] [blog] [demo] [tutorial]
- Up to 10 times faster for RLHF PPO Stage3 Training
- Up to 7.73 times faster for single server training and 1.42 times faster for single-GPU inference
- Up to 10.3x growth in model capacity on one GPU
- A mini demo training process requires only 1.62GB of GPU memory (any consumer-grade GPU)
- Increase the capacity of the fine-tuning model by up to 3.7 times on a single GPU
- Keep at a sufficiently high running speed
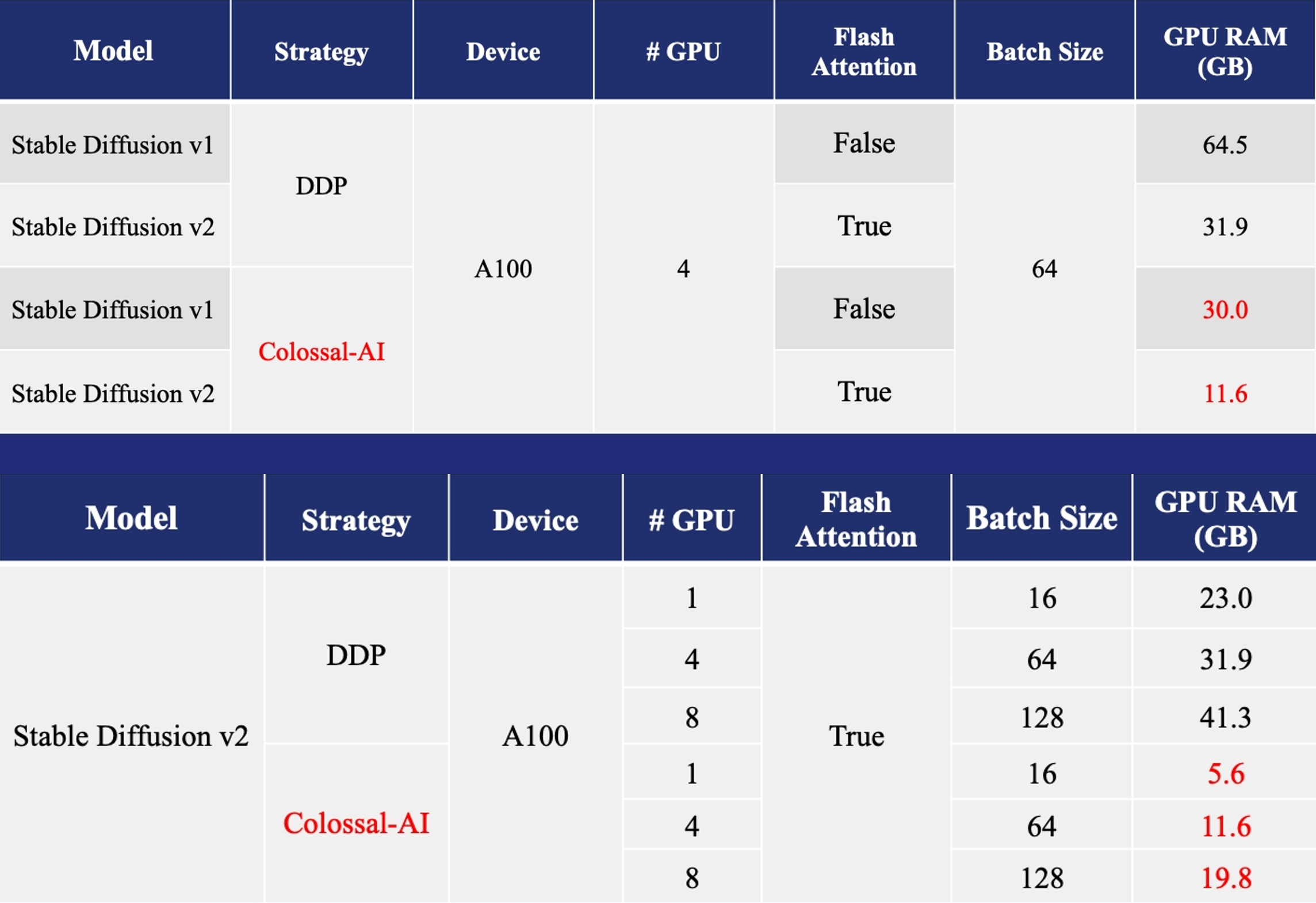
Acceleration of AIGC (AI-Generated Content) models such as Stable Diffusion v1 and Stable Diffusion v2.
- Training: Reduce Stable Diffusion memory consumption by up to 5.6x and hardware cost by up to 46x (from A100 to RTX3060).
- DreamBooth Fine-tuning: Personalize your model using just 3-5 images of the desired subject.
- Inference: Reduce inference GPU memory consumption by 2.5x.
Acceleration of AlphaFold Protein Structure
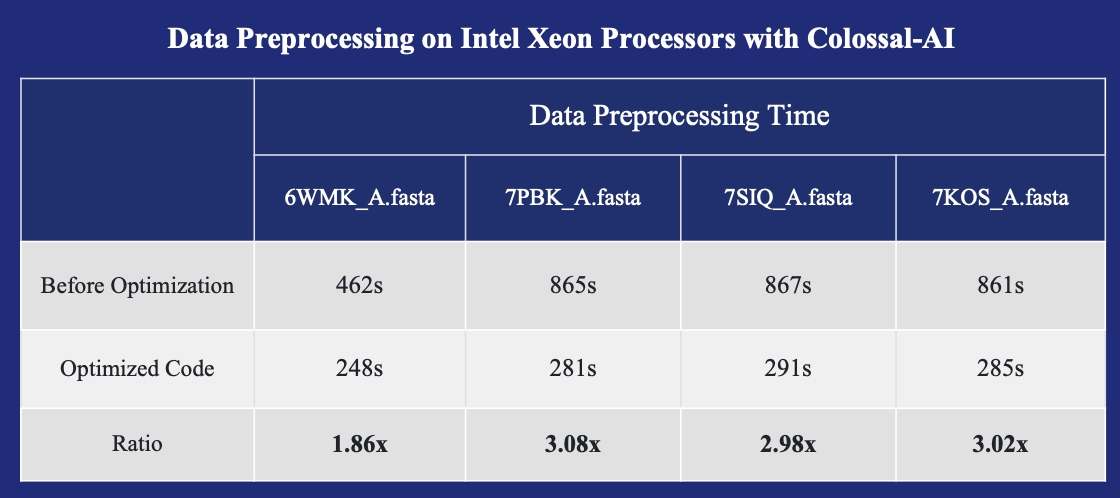
- FastFold: Accelerating training and inference on GPU Clusters, faster data processing, inference sequence containing more than 10000 residues.
- FastFold with Intel: 3x inference acceleration and 39% cost reduce.
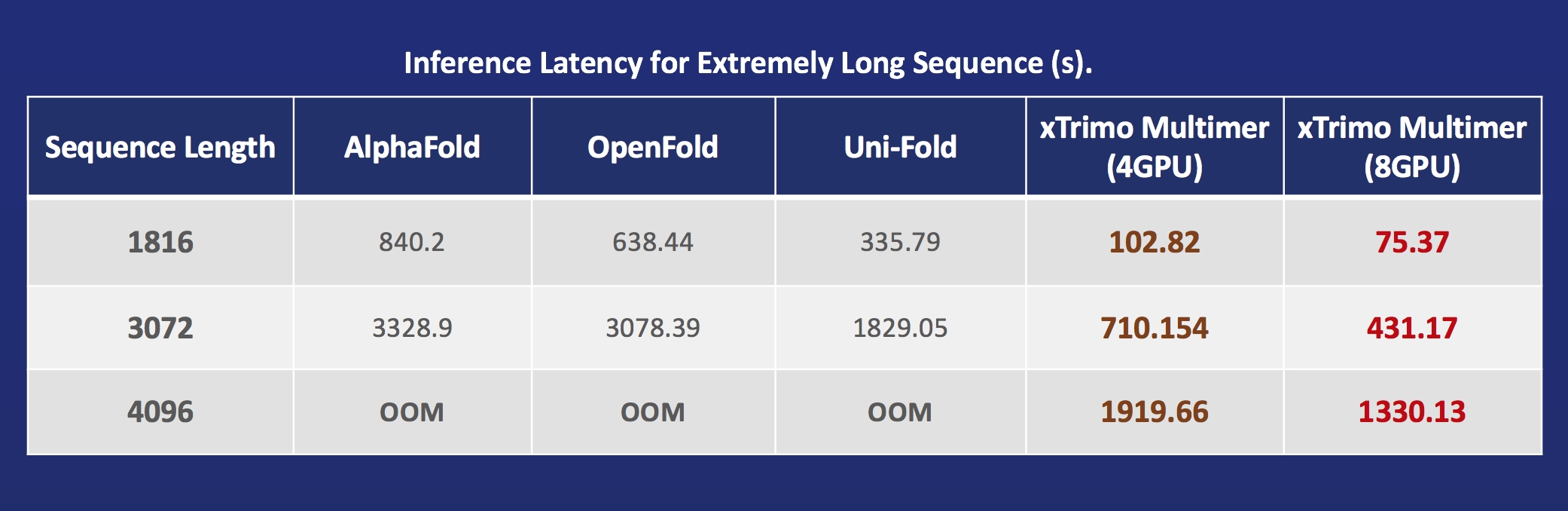
- xTrimoMultimer: accelerating structure prediction of protein monomers and multimer by 11x.
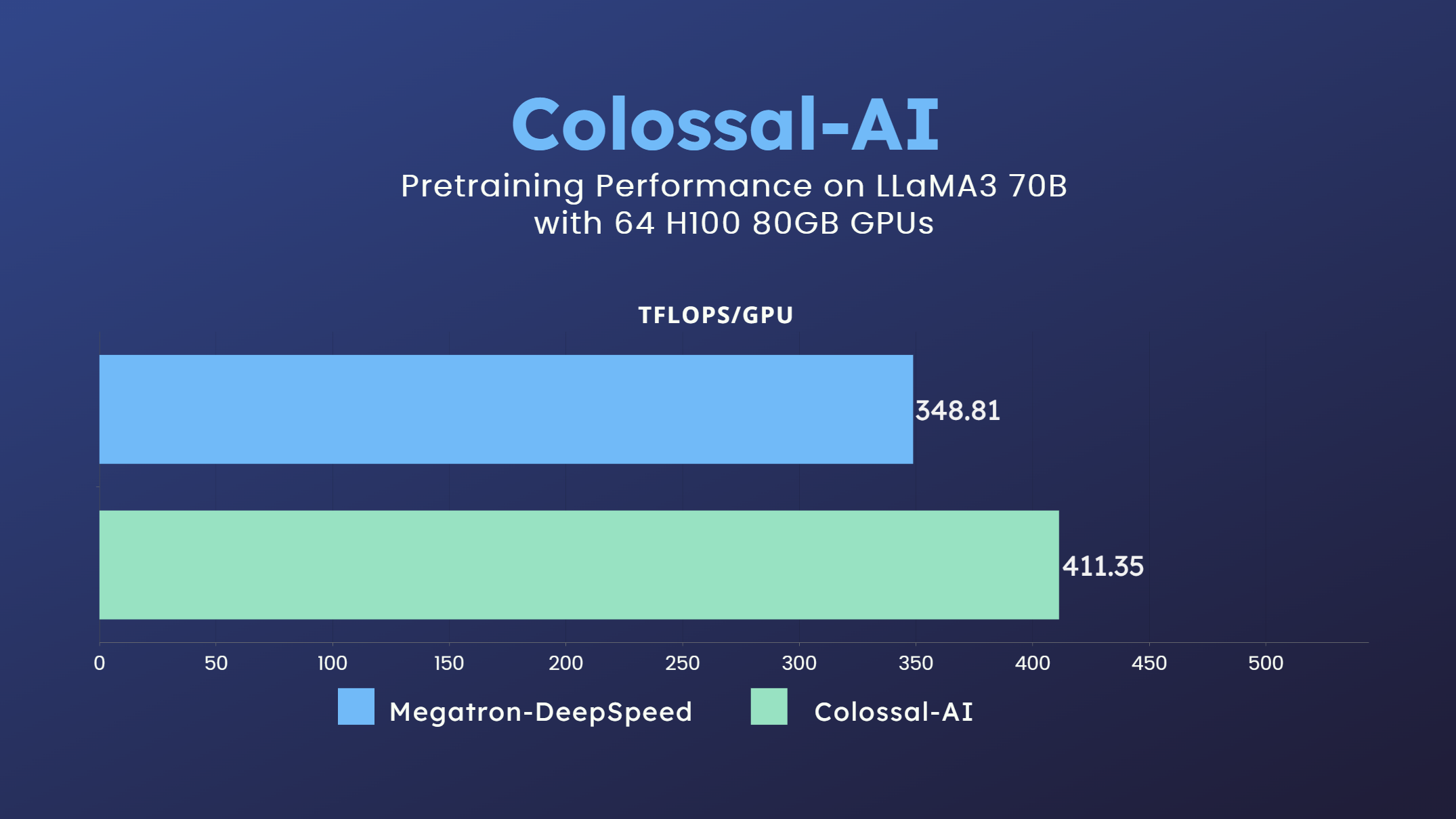
- 70 billion parameter LLaMA3 model training accelerated by 18% [code] [GPU Cloud Playground] [LLaMA3 Image]
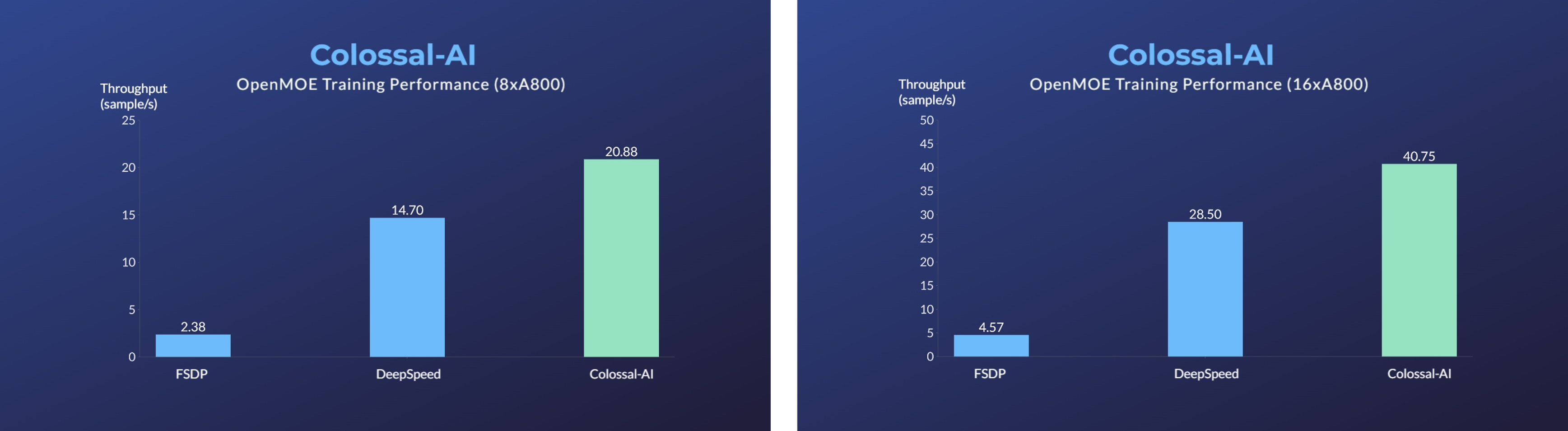
- Enhanced MoE parallelism, Open-source MoE model training can be 9 times more efficient [code] [blog]
- Save 50% GPU resources and 10.7% acceleration
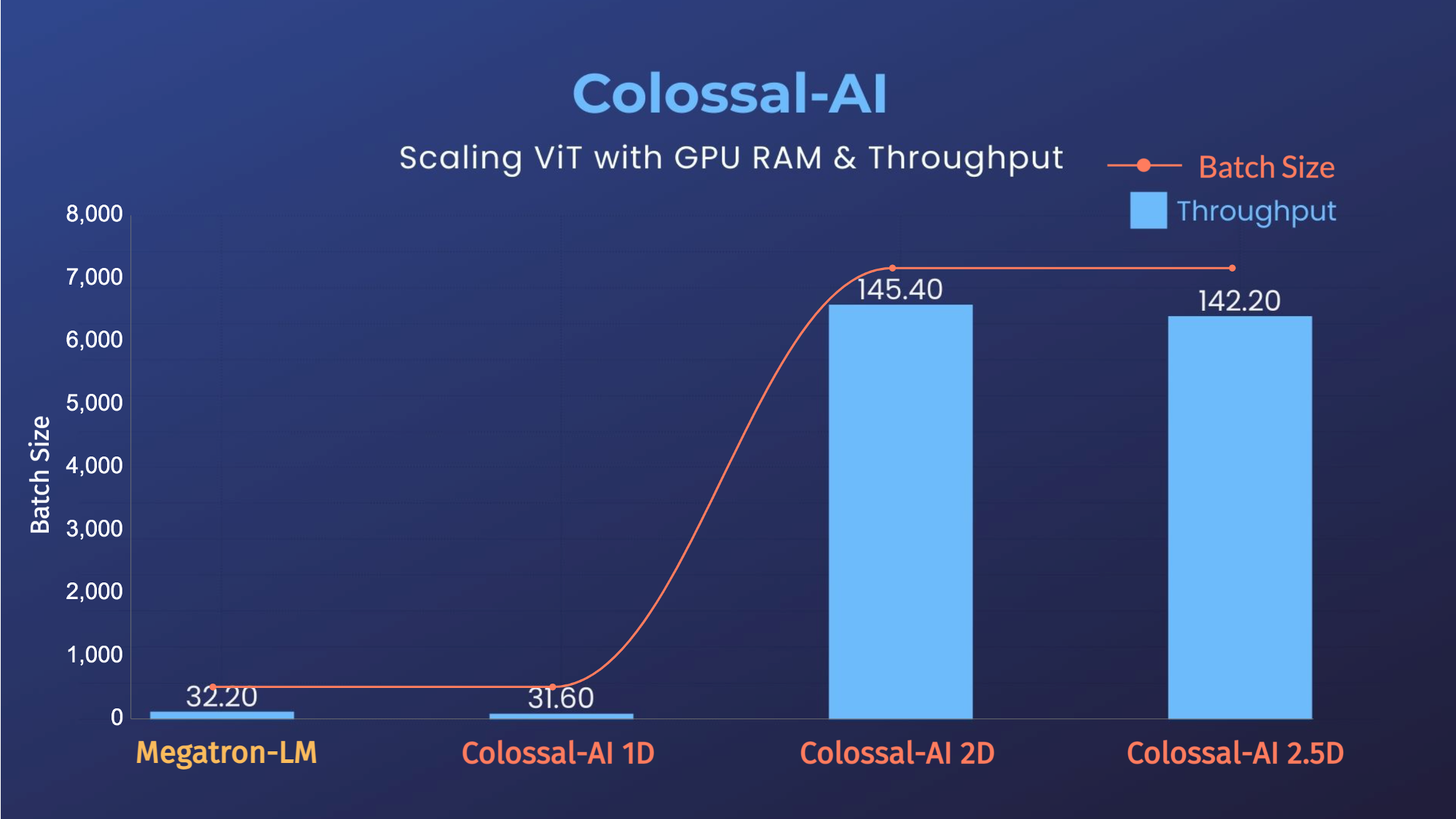
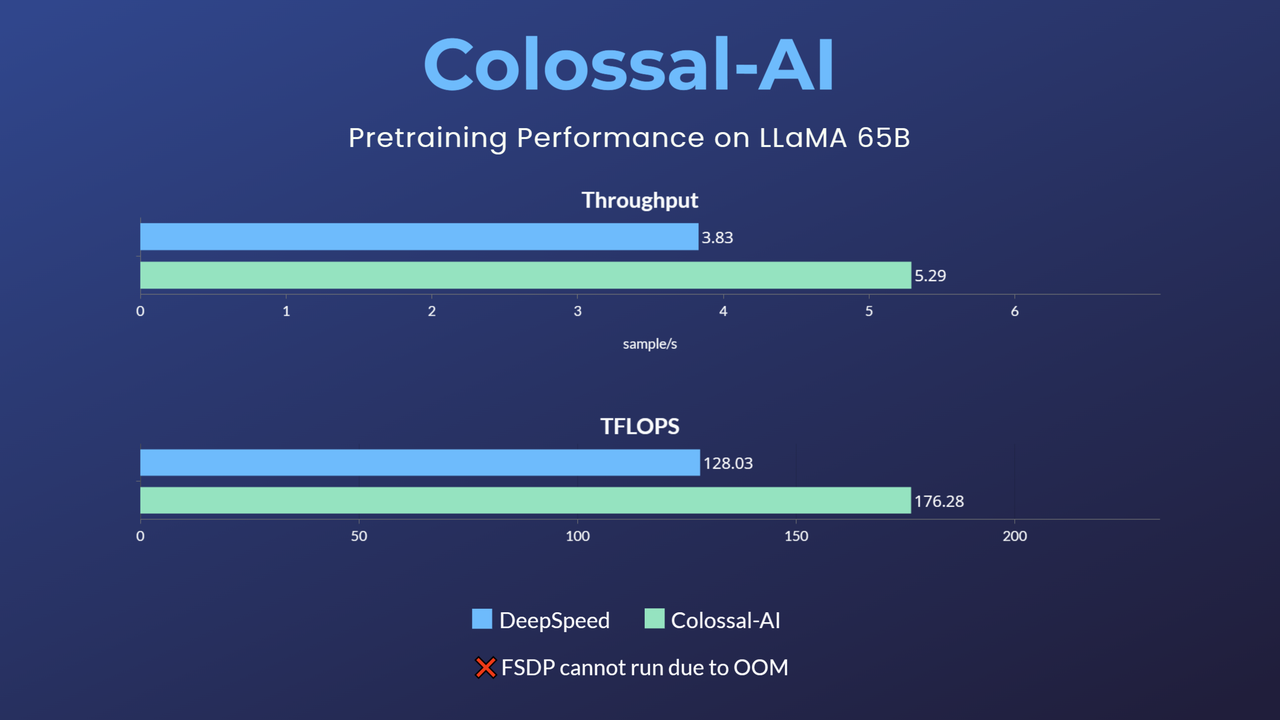
- 11x lower GPU memory consumption, and superlinear scaling efficiency with Tensor Parallelism
- 24x larger model size on the same hardware
- over 3x acceleration
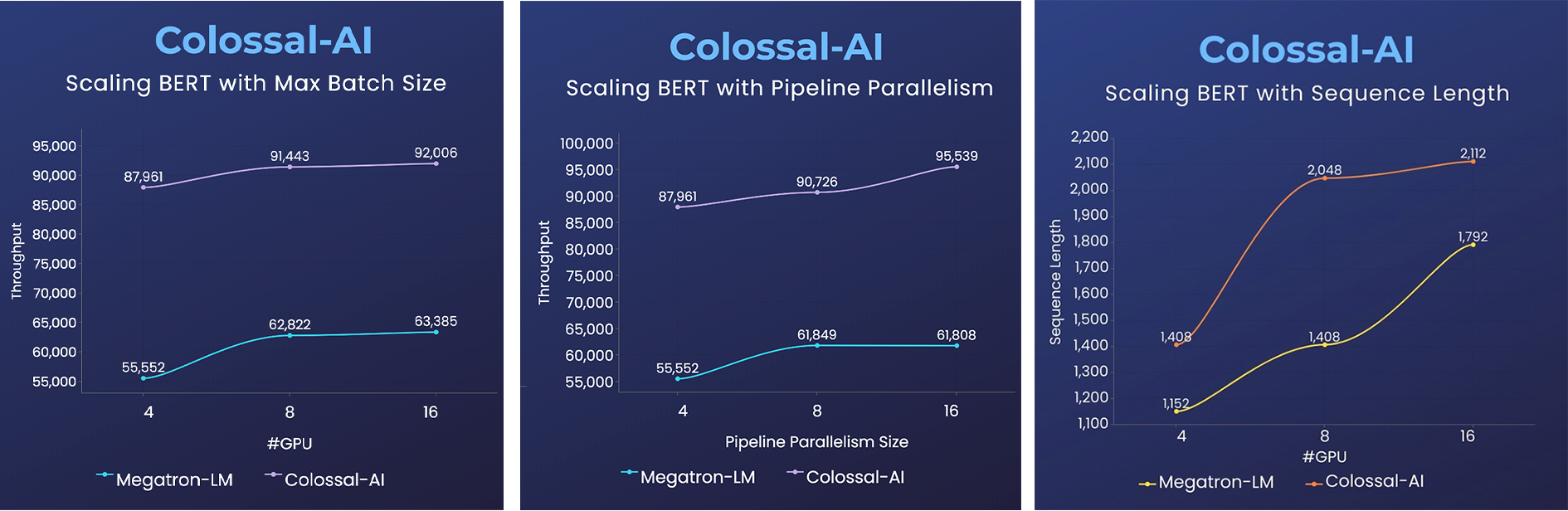
- 2x faster training, or 50% longer sequence length
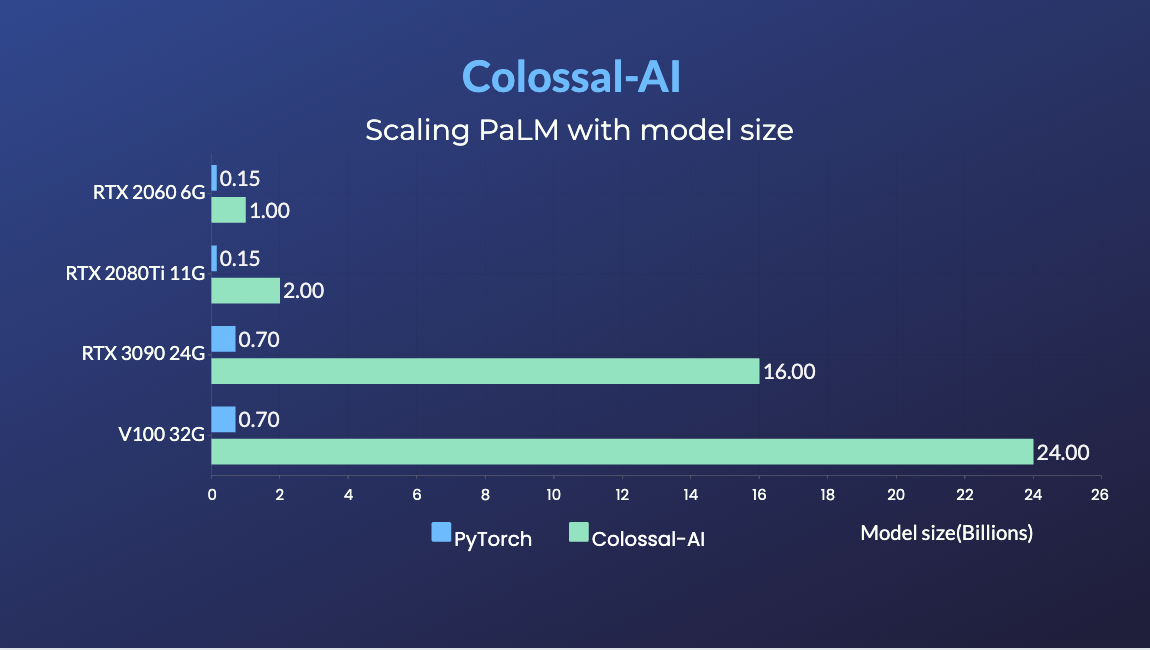
- PaLM-colossalai: Scalable implementation of Google's Pathways Language Model (PaLM).
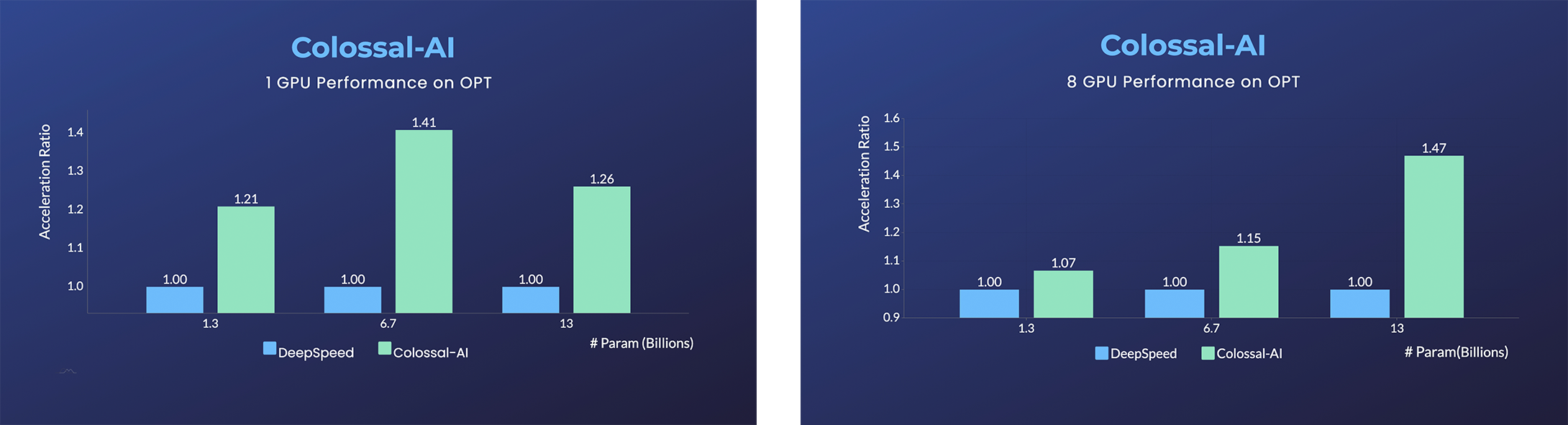
- Open Pretrained Transformer (OPT), a 175-Billion parameter AI language model released by Meta, which stimulates AI programmers to perform various downstream tasks and application deployments because of public pre-trained model weights.
- 45% speedup fine-tuning OPT at low cost in lines. [Example] [Online Serving]
Please visit our documentation and examples for more details.
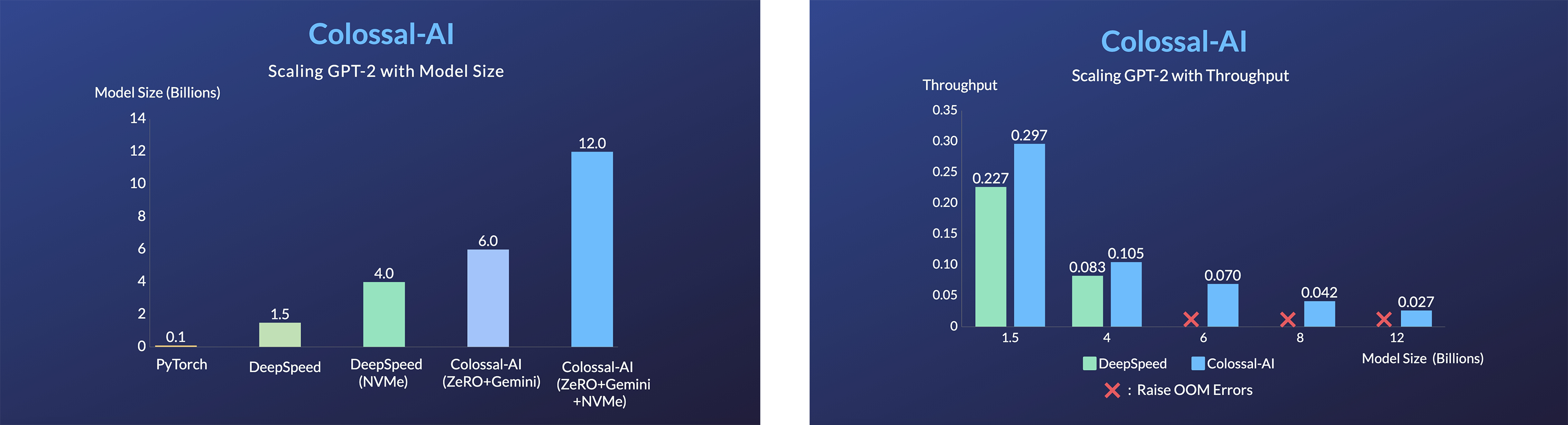
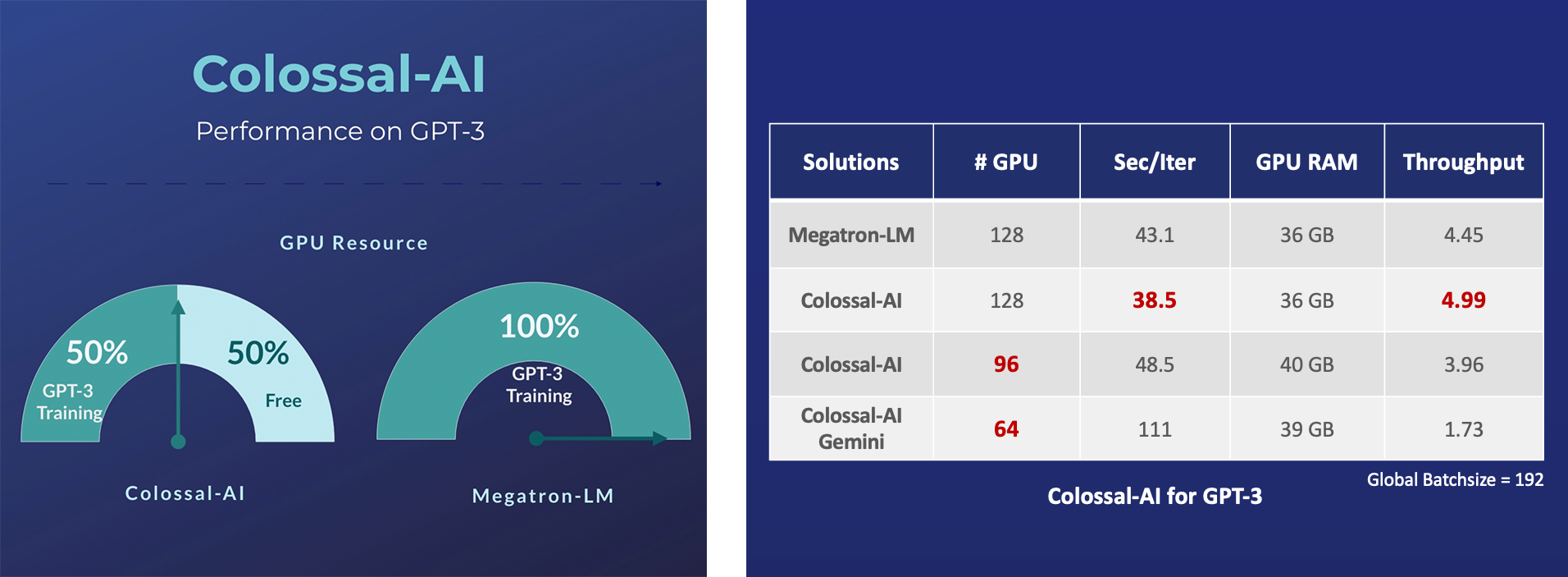
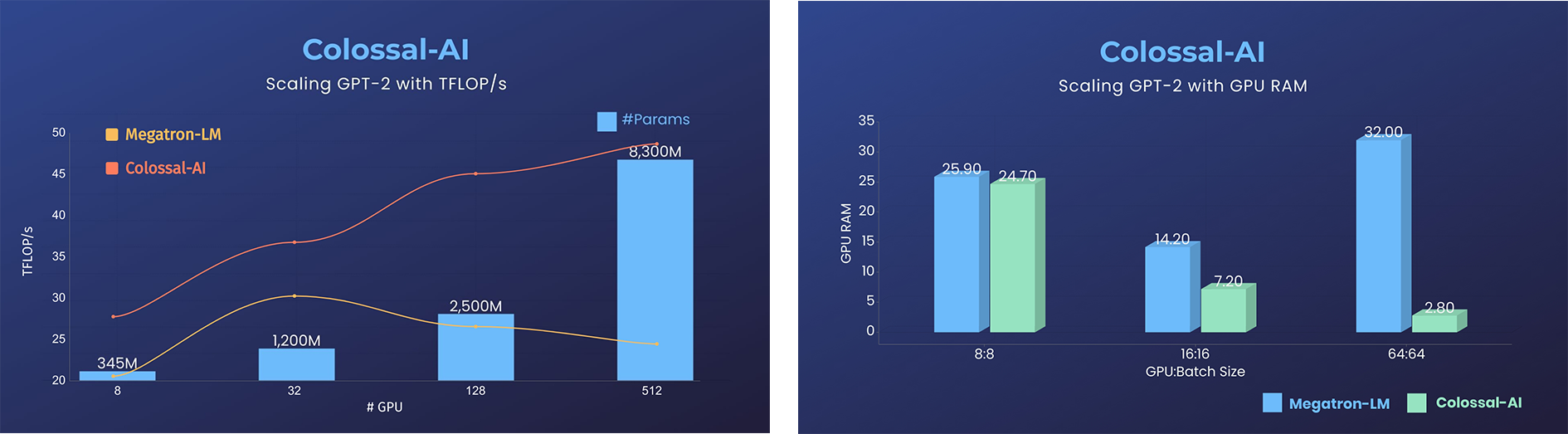
- 14x larger batch size, and 5x faster training for Tensor Parallelism = 64
- Cached Embedding, utilize software cache to train larger embedding tables with a smaller GPU memory budget.
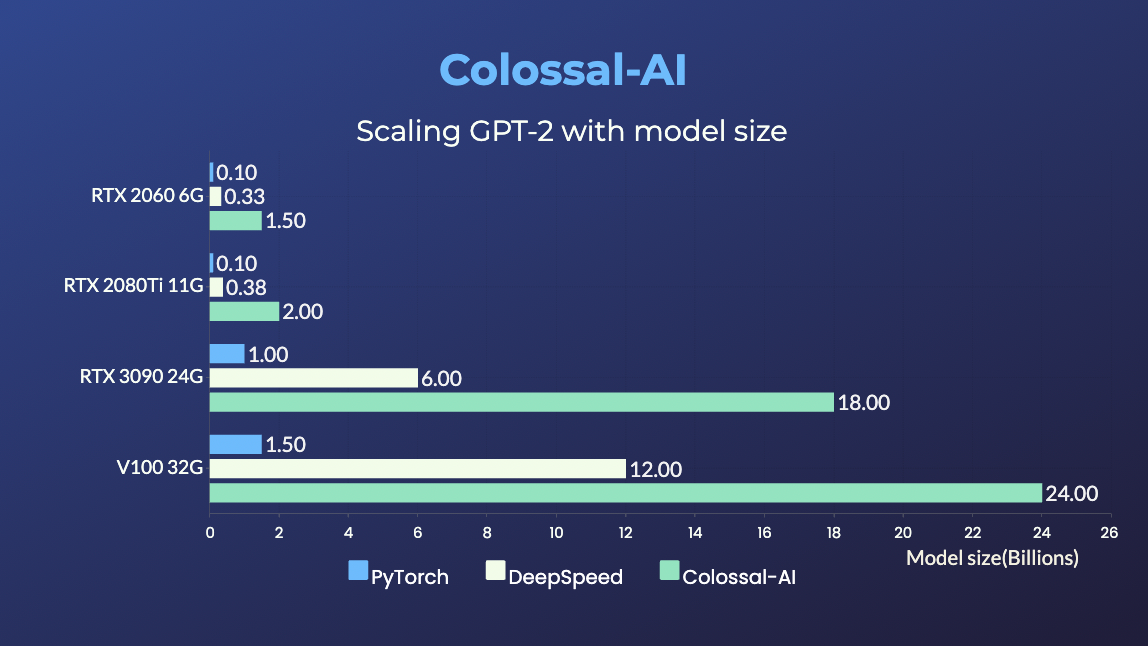
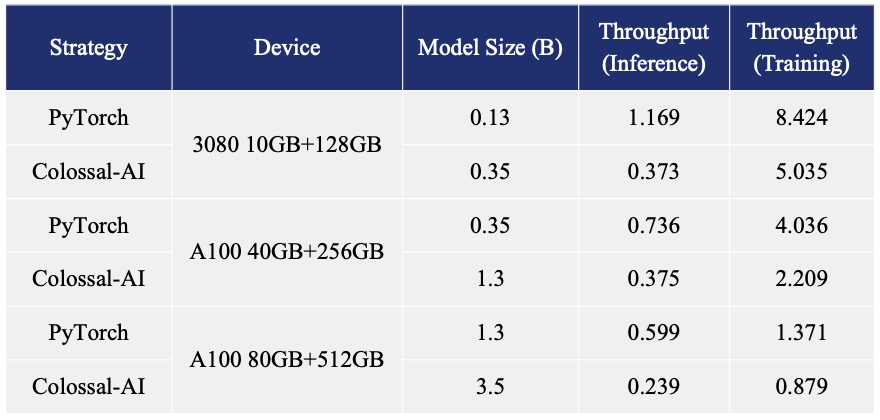
- 20x larger model size on the same hardware
- 120x larger model size on the same hardware (RTX 3080)
- 34x larger model size on the same hardware
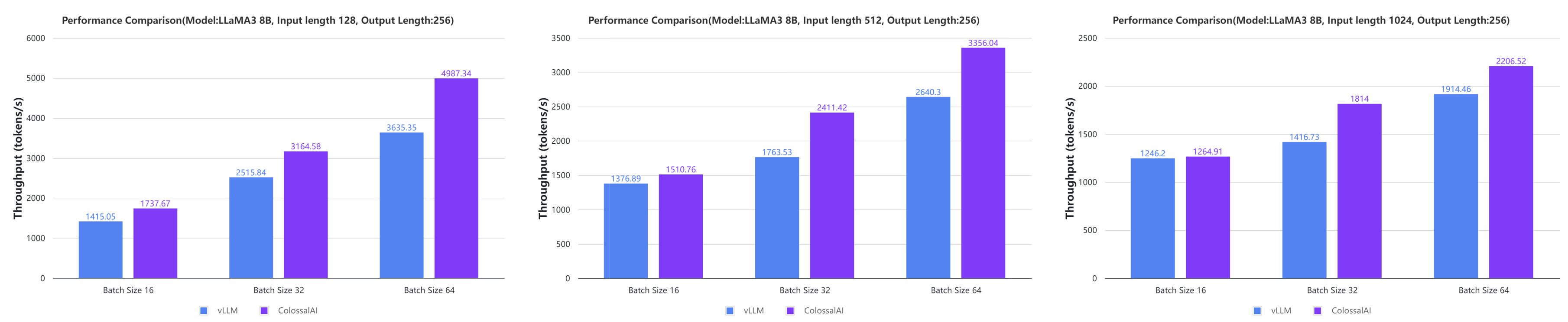
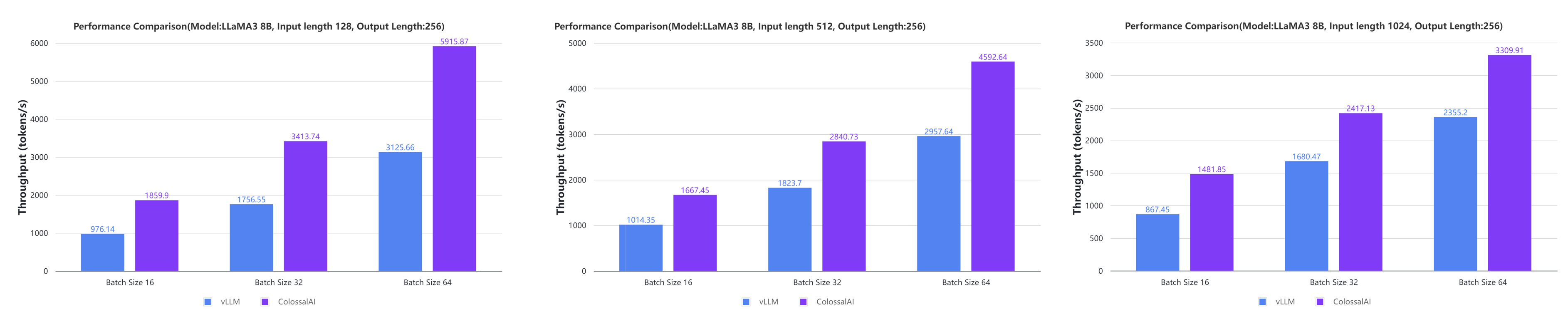
- Large AI models inference speed doubled, compared to the offline inference performance of vLLM in some cases. [code] [blog] [GPU Cloud Playground] [LLaMA3 Image]
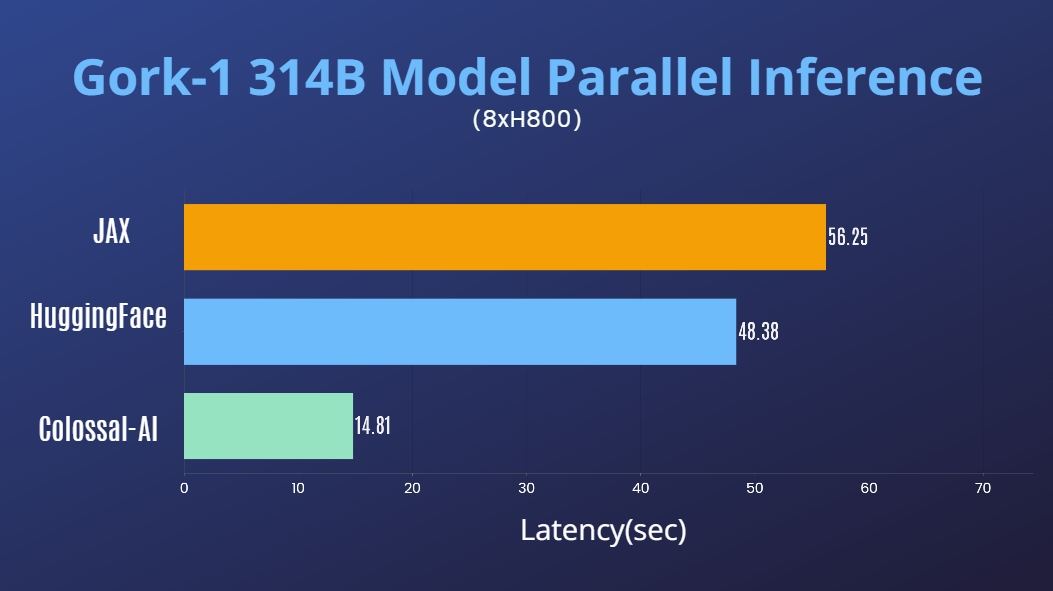
- 314 Billion Parameter Grok-1 Inference Accelerated by 3.8x, an easy-to-use Python + PyTorch + HuggingFace version for Inference.
[code] [blog] [HuggingFace Grok-1 PyTorch model weights] [ModelScope Grok-1 PyTorch model weights]
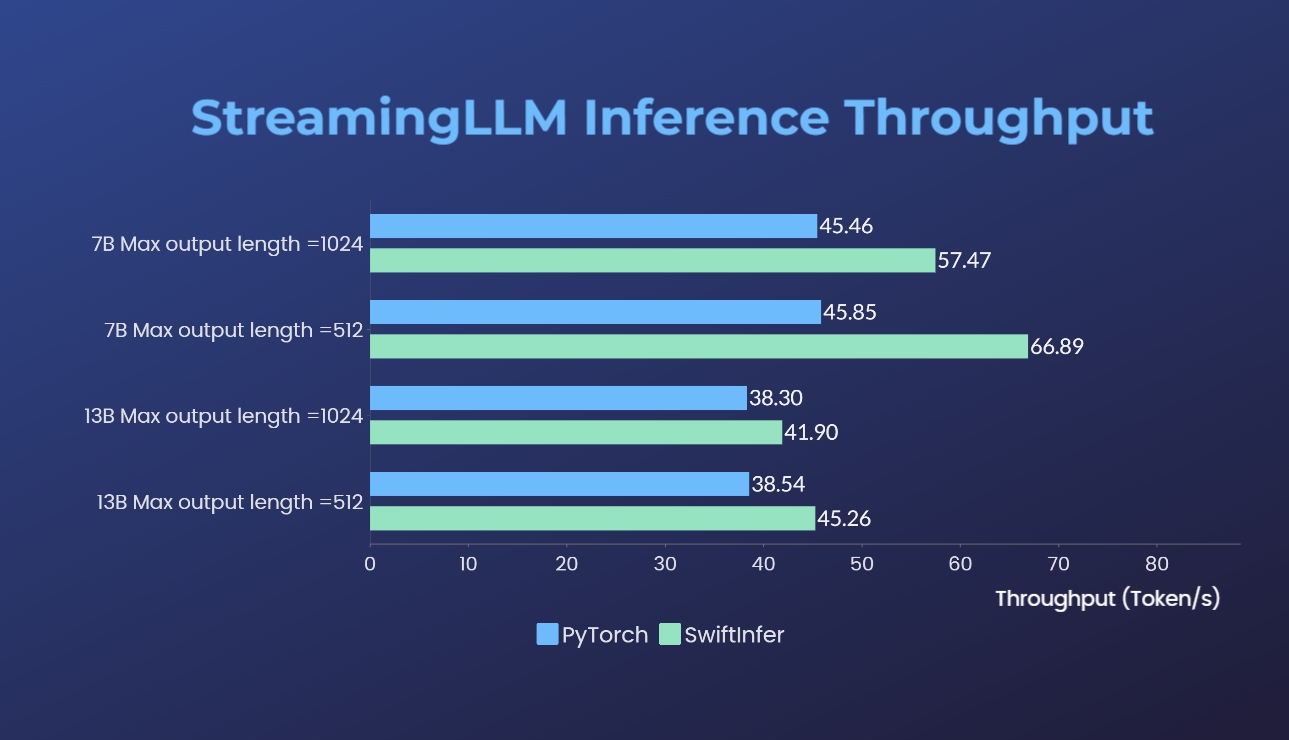
- SwiftInfer: Inference performance improved by 46%, open source solution breaks the length limit of LLM for multi-round conversations
Requirements:
- PyTorch >= 2.2
- Python >= 3.7
- CUDA >= 11.0
- NVIDIA GPU Compute Capability >= 7.0 (V100/RTX20 and higher)
- Linux OS
If you encounter any problem with installation, you may want to raise an issue in this repository.
You can easily install Colossal-AI with the following command. By default, we do not build PyTorch extensions during installation.
pip install colossalaiNote: only Linux is supported for now.
However, if you want to build the PyTorch extensions during installation, you can set BUILD_EXT=1.
BUILD_EXT=1 pip install colossalaiOtherwise, CUDA kernels will be built during runtime when you actually need them.
We also keep releasing the nightly version to PyPI every week. This allows you to access the unreleased features and bug fixes in the main branch. Installation can be made via
pip install colossalai-nightlyThe version of Colossal-AI will be in line with the main branch of the repository. Feel free to raise an issue if you encounter any problems. :)
git clone https://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI.git
cd ColossalAI
# install colossalai
pip install .By default, we do not compile CUDA/C++ kernels. ColossalAI will build them during runtime. If you want to install and enable CUDA kernel fusion (compulsory installation when using fused optimizer):
BUILD_EXT=1 pip install .For Users with CUDA 10.2, you can still build ColossalAI from source. However, you need to manually download the cub library and copy it to the corresponding directory.
# clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI.git
cd ColossalAI
# download the cub library
wget https://github.com/NVIDIA/cub/archive/refs/tags/1.8.0.zip
unzip 1.8.0.zip
cp -r cub-1.8.0/cub/ colossalai/kernel/cuda_native/csrc/kernels/include/
# install
BUILD_EXT=1 pip install .You can directly pull the docker image from our DockerHub page. The image is automatically uploaded upon release.
Run the following command to build a docker image from Dockerfile provided.
Building Colossal-AI from scratch requires GPU support, you need to use Nvidia Docker Runtime as the default when doing
docker build. More details can be found here. We recommend you install Colossal-AI from our project page directly.
cd ColossalAI
docker build -t colossalai ./dockerRun the following command to start the docker container in interactive mode.
docker run -ti --gpus all --rm --ipc=host colossalai bashJoin the Colossal-AI community on Forum, Slack, and WeChat(微信) to share your suggestions, feedback, and questions with our engineering team.
Referring to the successful attempts of BLOOM and Stable Diffusion, any and all developers and partners with computing powers, datasets, models are welcome to join and build the Colossal-AI community, making efforts towards the era of big AI models!
You may contact us or participate in the following ways:
- Leaving a Star ⭐ to show your like and support. Thanks!
- Posting an issue, or submitting a PR on GitHub follow the guideline in Contributing
- Send your official proposal to email [email protected]
Thanks so much to all of our amazing contributors!
We leverage the power of GitHub Actions to automate our development, release and deployment workflows. Please check out this documentation on how the automated workflows are operated.
This project is inspired by some related projects (some by our team and some by other organizations). We would like to credit these amazing projects as listed in the Reference List.
To cite this project, you can use the following BibTeX citation.
@inproceedings{10.1145/3605573.3605613,
author = {Li, Shenggui and Liu, Hongxin and Bian, Zhengda and Fang, Jiarui and Huang, Haichen and Liu, Yuliang and Wang, Boxiang and You, Yang},
title = {Colossal-AI: A Unified Deep Learning System For Large-Scale Parallel Training},
year = {2023},
isbn = {9798400708435},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3605573.3605613},
doi = {10.1145/3605573.3605613},
abstract = {The success of Transformer models has pushed the deep learning model scale to billions of parameters, but the memory limitation of a single GPU has led to an urgent need for training on multi-GPU clusters. However, the best practice for choosing the optimal parallel strategy is still lacking, as it requires domain expertise in both deep learning and parallel computing. The Colossal-AI system addressed the above challenge by introducing a unified interface to scale your sequential code of model training to distributed environments. It supports parallel training methods such as data, pipeline, tensor, and sequence parallelism and is integrated with heterogeneous training and zero redundancy optimizer. Compared to the baseline system, Colossal-AI can achieve up to 2.76 times training speedup on large-scale models.},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 52nd International Conference on Parallel Processing},
pages = {766–775},
numpages = {10},
keywords = {datasets, gaze detection, text tagging, neural networks},
location = {Salt Lake City, UT, USA},
series = {ICPP '23}
}
Colossal-AI has been accepted as official tutorial by top conferences NeurIPS, SC, AAAI, PPoPP, CVPR, ISC, NVIDIA GTC ,etc.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for ColossalAI
Similar Open Source Tools

ColossalAI
Colossal-AI is a deep learning system for large-scale parallel training. It provides a unified interface to scale sequential code of model training to distributed environments. Colossal-AI supports parallel training methods such as data, pipeline, tensor, and sequence parallelism and is integrated with heterogeneous training and zero redundancy optimizer.
TokenPacker
TokenPacker is a novel visual projector that compresses visual tokens by 75%∼89% with high efficiency. It adopts a 'coarse-to-fine' scheme to generate condensed visual tokens, achieving comparable or better performance across diverse benchmarks. The tool includes TokenPacker for general use and TokenPacker-HD for high-resolution image understanding. It provides training scripts, checkpoints, and supports various compression ratios and patch numbers.
ExplainableAI.jl
ExplainableAI.jl is a Julia package that implements interpretability methods for black-box classifiers, focusing on local explanations and attribution maps in input space. The package requires models to be differentiable with Zygote.jl. It is similar to Captum and Zennit for PyTorch and iNNvestigate for Keras models. Users can analyze and visualize explanations for model predictions, with support for different XAI methods and customization. The package aims to provide transparency and insights into model decision-making processes, making it a valuable tool for understanding and validating machine learning models.
MiniCPM-V
MiniCPM-V is a series of end-side multimodal LLMs designed for vision-language understanding. The models take image and text inputs to provide high-quality text outputs. The series includes models like MiniCPM-Llama3-V 2.5 with 8B parameters surpassing proprietary models, and MiniCPM-V 2.0, a lighter model with 2B parameters. The models support over 30 languages, efficient deployment on end-side devices, and have strong OCR capabilities. They achieve state-of-the-art performance on various benchmarks and prevent hallucinations in text generation. The models can process high-resolution images efficiently and support multilingual capabilities.
BitBLAS
BitBLAS is a library for mixed-precision BLAS operations on GPUs, for example, the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ mixed-precision matrix multiplication where $C_{cdtype}[M, N] = A_{adtype}[M, K] \times W_{wdtype}[N, K]$. BitBLAS aims to support efficient mixed-precision DNN model deployment, especially the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ quantization in large language models (LLMs), for example, the $W_{UINT4}A_{FP16}$ in GPTQ, the $W_{INT2}A_{FP16}$ in BitDistiller, the $W_{INT2}A_{INT8}$ in BitNet-b1.58. BitBLAS is based on techniques from our accepted submission at OSDI'24.

llm4ad
LLM4AD is an open-source Python-based platform leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for Automatic Algorithm Design (AD). It provides unified interfaces for methods, tasks, and LLMs, along with features like evaluation acceleration, secure evaluation, logs, GUI support, and more. The platform was originally developed for optimization tasks but is versatile enough to be used in other areas such as machine learning, science discovery, game theory, and engineering design. It offers various search methods and algorithm design tasks across different domains. LLM4AD supports remote LLM API, local HuggingFace LLM deployment, and custom LLM interfaces. The project is licensed under the MIT License and welcomes contributions, collaborations, and issue reports.
KwaiAgents
KwaiAgents is a series of Agent-related works open-sourced by the [KwaiKEG](https://github.com/KwaiKEG) from [Kuaishou Technology](https://www.kuaishou.com/en). The open-sourced content includes: 1. **KAgentSys-Lite**: a lite version of the KAgentSys in the paper. While retaining some of the original system's functionality, KAgentSys-Lite has certain differences and limitations when compared to its full-featured counterpart, such as: (1) a more limited set of tools; (2) a lack of memory mechanisms; (3) slightly reduced performance capabilities; and (4) a different codebase, as it evolves from open-source projects like BabyAGI and Auto-GPT. Despite these modifications, KAgentSys-Lite still delivers comparable performance among numerous open-source Agent systems available. 2. **KAgentLMs**: a series of large language models with agent capabilities such as planning, reflection, and tool-use, acquired through the Meta-agent tuning proposed in the paper. 3. **KAgentInstruct**: over 200k Agent-related instructions finetuning data (partially human-edited) proposed in the paper. 4. **KAgentBench**: over 3,000 human-edited, automated evaluation data for testing Agent capabilities, with evaluation dimensions including planning, tool-use, reflection, concluding, and profiling.
IDvs.MoRec
This repository contains the source code for the SIGIR 2023 paper 'Where to Go Next for Recommender Systems? ID- vs. Modality-based Recommender Models Revisited'. It provides resources for evaluating foundation, transferable, multi-modal, and LLM recommendation models, along with datasets, pre-trained models, and training strategies for IDRec and MoRec using in-batch debiased cross-entropy loss. The repository also offers large-scale datasets, code for SASRec with in-batch debias cross-entropy loss, and information on joining the lab for research opportunities.
MooER
MooER (摩耳) is an LLM-based speech recognition and translation model developed by Moore Threads. It allows users to transcribe speech into text (ASR) and translate speech into other languages (AST) in an end-to-end manner. The model was trained using 5K hours of data and is now also available with an 80K hours version. MooER is the first LLM-based speech model trained and inferred using domestic GPUs. The repository includes pretrained models, inference code, and a Gradio demo for a better user experience.
ReST-MCTS
ReST-MCTS is a reinforced self-training approach that integrates process reward guidance with tree search MCTS to collect higher-quality reasoning traces and per-step value for training policy and reward models. It eliminates the need for manual per-step annotation by estimating the probability of steps leading to correct answers. The inferred rewards refine the process reward model and aid in selecting high-quality traces for policy model self-training.
VILA
VILA is a family of open Vision Language Models optimized for efficient video understanding and multi-image understanding. It includes models like NVILA, LongVILA, VILA-M3, VILA-U, and VILA-1.5, each offering specific features and capabilities. The project focuses on efficiency, accuracy, and performance in various tasks related to video, image, and language understanding and generation. VILA models are designed to be deployable on diverse NVIDIA GPUs and support long-context video understanding, medical applications, and multi-modal design.
Q-Bench
Q-Bench is a benchmark for general-purpose foundation models on low-level vision, focusing on multi-modality LLMs performance. It includes three realms for low-level vision: perception, description, and assessment. The benchmark datasets LLVisionQA and LLDescribe are collected for perception and description tasks, with open submission-based evaluation. An abstract evaluation code is provided for assessment using public datasets. The tool can be used with the datasets API for single images and image pairs, allowing for automatic download and usage. Various tasks and evaluations are available for testing MLLMs on low-level vision tasks.
generative-ai-with-javascript
The 'Generative AI with JavaScript' repository is a comprehensive resource hub for JavaScript developers interested in delving into the world of Generative AI. It provides code samples, tutorials, and resources from a video series, offering best practices and tips to enhance AI skills. The repository covers the basics of generative AI, guides on building AI applications using JavaScript, from local development to deployment on Azure, and scaling AI models. It is a living repository with continuous updates, making it a valuable resource for both beginners and experienced developers looking to explore AI with JavaScript.
ShapeLLM
ShapeLLM is the first 3D Multimodal Large Language Model designed for embodied interaction, exploring a universal 3D object understanding with 3D point clouds and languages. It supports single-view colored point cloud input and introduces a robust 3D QA benchmark, 3D MM-Vet, encompassing various variants. The model extends the powerful point encoder architecture, ReCon++, achieving state-of-the-art performance across a range of representation learning tasks. ShapeLLM can be used for tasks such as training, zero-shot understanding, visual grounding, few-shot learning, and zero-shot learning on 3D MM-Vet.
LongLoRA
LongLoRA is a tool for efficient fine-tuning of long-context large language models. It includes LongAlpaca data with long QA data collected and short QA sampled, models from 7B to 70B with context length from 8k to 100k, and support for GPTNeoX models. The tool supports supervised fine-tuning, context extension, and improved LoRA fine-tuning. It provides pre-trained weights, fine-tuning instructions, evaluation methods, local and online demos, streaming inference, and data generation via Pdf2text. LongLoRA is licensed under Apache License 2.0, while data and weights are under CC-BY-NC 4.0 License for research use only.
For similar tasks

ColossalAI
Colossal-AI is a deep learning system for large-scale parallel training. It provides a unified interface to scale sequential code of model training to distributed environments. Colossal-AI supports parallel training methods such as data, pipeline, tensor, and sequence parallelism and is integrated with heterogeneous training and zero redundancy optimizer.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.










GPT-2.png)