
llm-past-tense
Does Refusal Training in LLMs Generalize to the Past Tense? [NeurIPS 2024 Safe Generative AI Workshop (Oral)]
Stars: 53
The 'llm-past-tense' repository contains code related to the research paper 'Does Refusal Training in LLMs Generalize to the Past Tense?' by Maksym Andriushchenko and Nicolas Flammarion. It explores the generalization of refusal training in large language models (LLMs) to the past tense. The code includes experiments and examples for running different models and requests related to the study. Users can cite the work if found useful in their research, and the codebase is released under the MIT License.
README:
Maksym Andriushchenko (EPFL), Nicolas Flammarion (EPFL)
Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.11969
NeurIPS 2024 Safe Generative AI Workshop (Oral)
To get started, install dependencies:
pip install transformers openai anthropic
Make sure you have the API keys stored in OPENAI_API_KEY, TOGETHER_API_KEY, and ANTHROPIC_API_KEY respectively. For this, you can run:
export OPENAI_API_KEY=[YOUR_API_KEY_HERE]
export TOGETHER_API_KEY=[YOUR_API_KEY_HERE]
export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=[YOUR_API_KEY_HERE]
Similarly, some HuggingFace models, like Llama-3, require an API key, which can be set in HF_TOKEN.
Simply run main.py! :-) Examples:
python main.py --target_model=gpt-3.5-turbo --n_requests=100 --n_restarts=20
python main.py --target_model=gpt-4o-mini --n_requests=100 --n_restarts=20
python main.py --target_model=gpt-4o-2024-05-13 --n_requests=100 --n_restarts=20
python main.py --target_model=o1-mini-2024-09-12 --n_requests=100 --n_restarts=20
python main.py --target_model=o1-preview-2024-09-12 --n_requests=100 --n_restarts=20
python main.py --target_model=claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620 --n_requests=100 --n_restarts=20
python main.py --target_model=phi3 --n_requests=100 --n_restarts=20
python main.py --target_model=gemma2-9b --n_requests=100 --n_restarts=20
python main.py --target_model=llama3-8b --n_requests=100 --n_restarts=20
python main.py --target_model=r2d2 --n_requests=100 --n_restarts=20 If you find this work useful in your own research, please consider citing it:
@article{andriushchenko2024refusal,
title={Does Refusal Training in LLMs Generalize to the Past Tense?},
author={Andriushchenko, Maksym and Flammarion, Nicolas},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.11969},
year={2024}
}This codebase is released under the MIT License.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for llm-past-tense
Similar Open Source Tools

llm-past-tense
The 'llm-past-tense' repository contains code related to the research paper 'Does Refusal Training in LLMs Generalize to the Past Tense?' by Maksym Andriushchenko and Nicolas Flammarion. It explores the generalization of refusal training in large language models (LLMs) to the past tense. The code includes experiments and examples for running different models and requests related to the study. Users can cite the work if found useful in their research, and the codebase is released under the MIT License.
MemoryLLM
MemoryLLM is a large language model designed for self-updating capabilities. It offers pretrained models with different memory capacities and features, such as chat models. The repository provides training code, evaluation scripts, and datasets for custom experiments. MemoryLLM aims to enhance knowledge retention and performance on various natural language processing tasks.
zml
ZML is a high-performance AI inference stack built for production, using Zig language, MLIR, and Bazel. It allows users to create exciting AI projects, run pre-packaged models like MNIST, TinyLlama, OpenLLama, and Meta Llama, and compile models for accelerator runtimes. Users can also run tests, explore examples, and contribute to the project. ZML is licensed under the Apache 2.0 license.
swe-rl
SWE-RL is the official codebase for the paper 'SWE-RL: Advancing LLM Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning on Open Software Evolution'. It is the first approach to scale reinforcement learning based LLM reasoning for real-world software engineering, leveraging open-source software evolution data and rule-based rewards. The code provides prompt templates and the implementation of the reward function based on sequence similarity. Agentless Mini, a part of SWE-RL, builds on top of Agentless with improvements like fast async inference, code refactoring for scalability, and support for using multiple reproduction tests for reranking. The tool can be used for localization, repair, and reproduction test generation in software engineering tasks.
simpleAI
SimpleAI is a self-hosted alternative to the not-so-open AI API, focused on replicating main endpoints for LLM such as text completion, chat, edits, and embeddings. It allows quick experimentation with different models, creating benchmarks, and handling specific use cases without relying on external services. Users can integrate and declare models through gRPC, query endpoints using Swagger UI or API, and resolve common issues like CORS with FastAPI middleware. The project is open for contributions and welcomes PRs, issues, documentation, and more.
raid
RAID is the largest and most comprehensive dataset for evaluating AI-generated text detectors. It contains over 10 million documents spanning 11 LLMs, 11 genres, 4 decoding strategies, and 12 adversarial attacks. RAID is designed to be the go-to location for trustworthy third-party evaluation of popular detectors. The dataset covers diverse models, domains, sampling strategies, and attacks, making it a valuable resource for training detectors, evaluating generalization, protecting against adversaries, and comparing to state-of-the-art models from academia and industry.
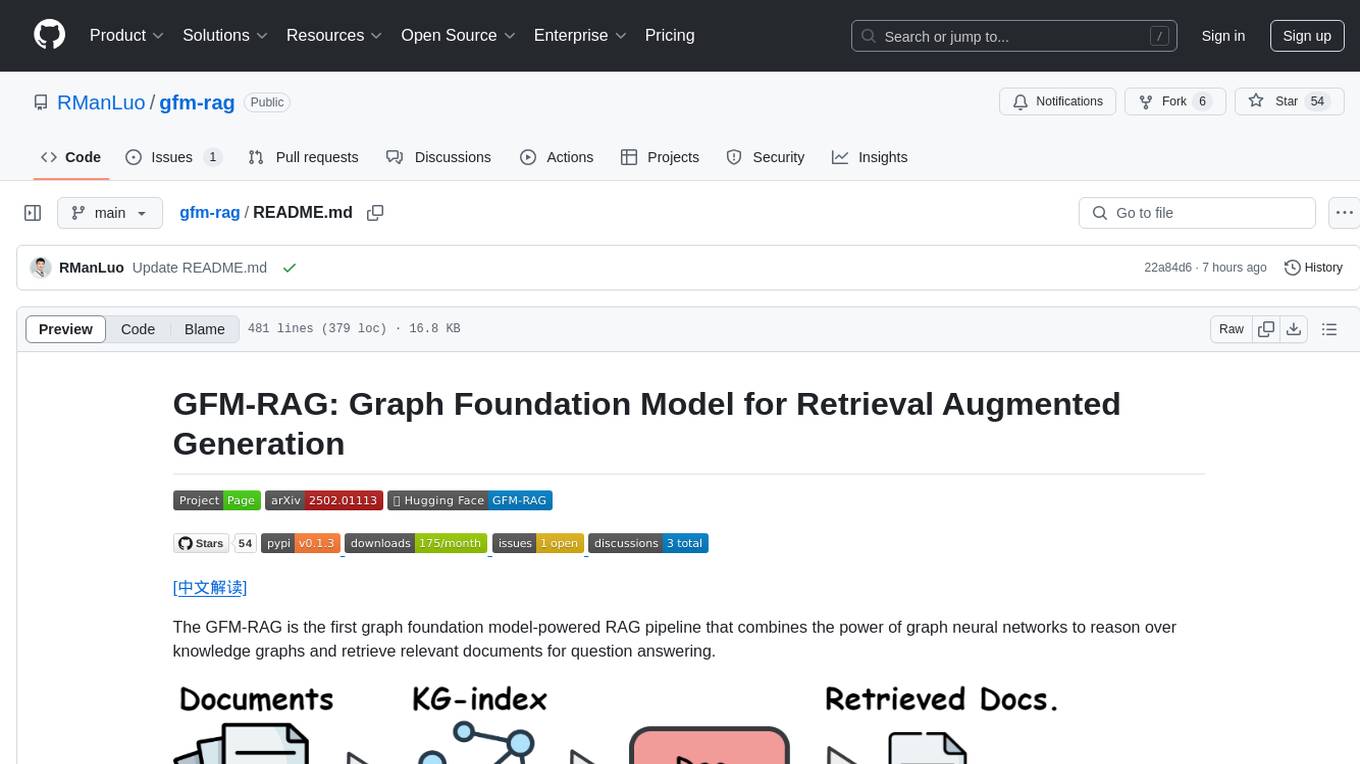
gfm-rag
The GFM-RAG is a graph foundation model-powered pipeline that combines graph neural networks to reason over knowledge graphs and retrieve relevant documents for question answering. It features a knowledge graph index, efficiency in multi-hop reasoning, generalizability to unseen datasets, transferability for fine-tuning, compatibility with agent-based frameworks, and interpretability of reasoning paths. The tool can be used for conducting retrieval and question answering tasks using pre-trained models or fine-tuning on custom datasets.
npcsh
`npcsh` is a python-based command-line tool designed to integrate Large Language Models (LLMs) and Agents into one's daily workflow by making them available and easily configurable through the command line shell. It leverages the power of LLMs to understand natural language commands and questions, execute tasks, answer queries, and provide relevant information from local files and the web. Users can also build their own tools and call them like macros from the shell. `npcsh` allows users to take advantage of agents (i.e. NPCs) through a managed system, tailoring NPCs to specific tasks and workflows. The tool is extensible with Python, providing useful functions for interacting with LLMs, including explicit coverage for popular providers like ollama, anthropic, openai, gemini, deepseek, and openai-like providers. Users can set up a flask server to expose their NPC team for use as a backend service, run SQL models defined in their project, execute assembly lines, and verify the integrity of their NPC team's interrelations. Users can execute bash commands directly, use favorite command-line tools like VIM, Emacs, ipython, sqlite3, git, pipe the output of these commands to LLMs, or pass LLM results to bash commands.
cappr
CAPPr is a tool for text classification that does not require training or post-processing. It allows users to have their language models pick from a list of choices or compute the probability of a completion given a prompt. The tool aims to help users get more out of open source language models by simplifying the text classification process. CAPPr can be used with GGUF models, Hugging Face models, models from the OpenAI API, and for tasks like caching instructions, extracting final answers from step-by-step completions, and running predictions in batches with different sets of completions.
stark
STaRK is a large-scale semi-structure retrieval benchmark on Textual and Relational Knowledge Bases. It provides natural-sounding and practical queries crafted to incorporate rich relational information and complex textual properties, closely mirroring real-life scenarios. The benchmark aims to assess how effectively large language models can handle the interplay between textual and relational requirements in queries, using three diverse knowledge bases constructed from public sources.
phidata
Phidata is a framework for building AI Assistants with memory, knowledge, and tools. It enables LLMs to have long-term conversations by storing chat history in a database, provides them with business context by storing information in a vector database, and enables them to take actions like pulling data from an API, sending emails, or querying a database. Memory and knowledge make LLMs smarter, while tools make them autonomous.
topicGPT
TopicGPT is a repository containing scripts and prompts for the paper 'TopicGPT: Topic Modeling by Prompting Large Language Models' (NAACL'24). The 'topicgpt_python' package offers functions to generate high-level and specific topics, refine topics, assign topics to input text, and correct generated topics. It supports various APIs like OpenAI, VertexAI, Azure, Gemini, and vLLM for inference. Users can prepare data in JSONL format, run the pipeline using provided scripts, and evaluate topic alignment with ground-truth labels.
flow-prompt
Flow Prompt is a dynamic library for managing and optimizing prompts for large language models. It facilitates budget-aware operations, dynamic data integration, and efficient load distribution. Features include CI/CD testing, dynamic prompt development, multi-model support, real-time insights, and prompt testing and evolution.
Arcade-Learning-Environment
The Arcade Learning Environment (ALE) is a simple framework that allows researchers and hobbyists to develop AI agents for Atari 2600 games. It is built on top of the Atari 2600 emulator Stella and separates the details of emulation from agent design. The ALE currently supports three different interfaces: C++, Python, and OpenAI Gym.
vinagent
Vinagent is a lightweight and flexible library designed for building smart agent assistants across various industries. It provides a simple yet powerful foundation for creating AI-powered customer service bots, data analysis assistants, or domain-specific automation agents. With its modular tool system, users can easily extend their agent's capabilities by integrating a wide range of tools that are self-contained, well-documented, and can be registered dynamically. Vinagent allows users to scale and adapt their agents to new tasks or environments effortlessly.
paper-qa
PaperQA is a minimal package for question and answering from PDFs or text files, providing very good answers with in-text citations. It uses OpenAI Embeddings to embed and search documents, and includes a process of embedding docs, queries, searching for top passages, creating summaries, using an LLM to re-score and select relevant summaries, putting summaries into prompt, and generating answers. The tool can be used to answer specific questions related to scientific research by leveraging citations and relevant passages from documents.
For similar tasks
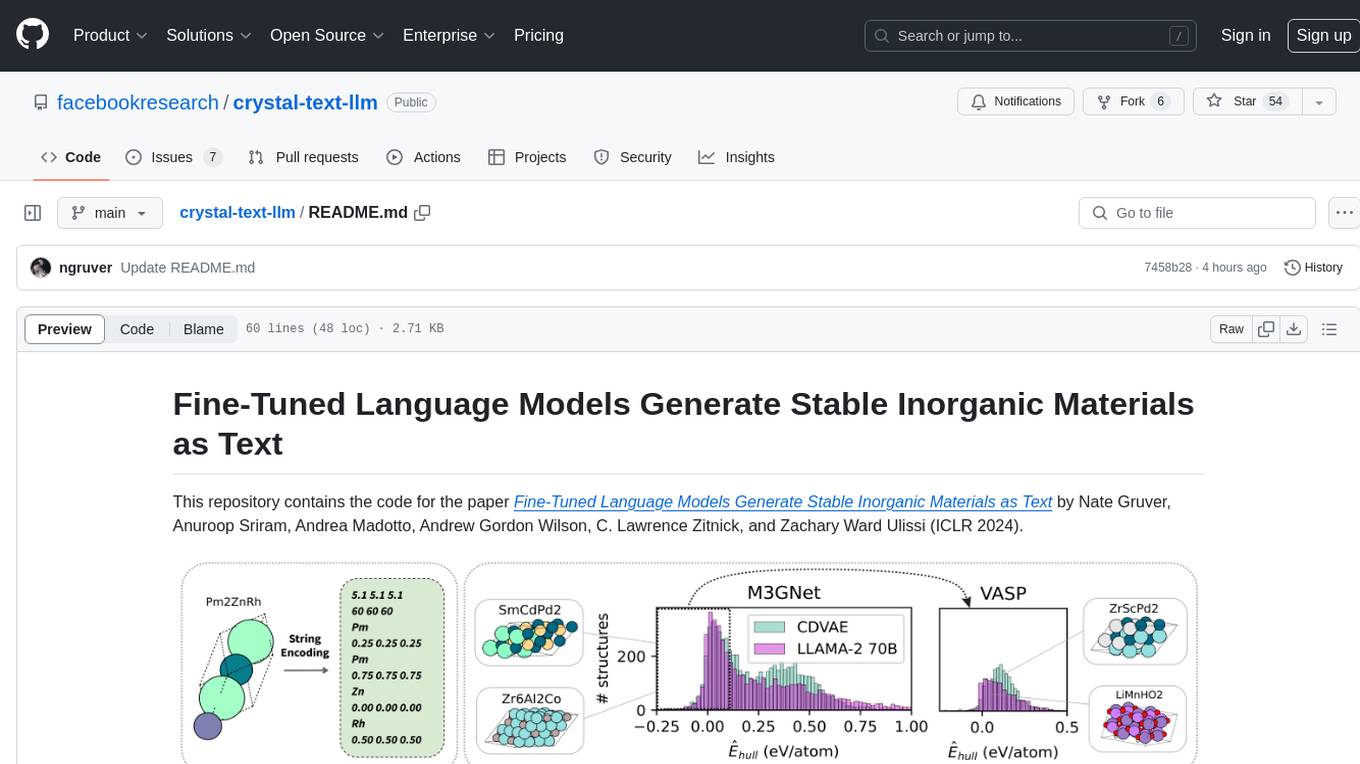
crystal-text-llm
This repository contains the code for the paper Fine-Tuned Language Models Generate Stable Inorganic Materials as Text. It demonstrates how finetuned LLMs can be used to generate stable materials, match or exceed the performance of domain specific models, mutate existing materials, and sample crystal structures conditioned on text descriptions. The method is distinct from CrystaLLM, which trains language models from scratch on CIF-formatted crystals.

llm-past-tense
The 'llm-past-tense' repository contains code related to the research paper 'Does Refusal Training in LLMs Generalize to the Past Tense?' by Maksym Andriushchenko and Nicolas Flammarion. It explores the generalization of refusal training in large language models (LLMs) to the past tense. The code includes experiments and examples for running different models and requests related to the study. Users can cite the work if found useful in their research, and the codebase is released under the MIT License.
examples-python
This repository contains various examples demonstrating how to use the Restack AI Python SDK. It is organized into official examples maintained by the Restack team and community examples contributed by the community. The examples are designed to help users get started with Restack AI and showcase different features and use cases. Users can explore different examples, follow specific instructions in each example's README file, and contribute to the repository by adding new examples or improving existing ones.
gpt-home
GPT Home is a project that allows users to build their own home assistant using Raspberry Pi and OpenAI API. It serves as a guide for setting up a smart home assistant similar to Google Nest Hub or Amazon Alexa. The project integrates various components like OpenAI, Spotify, Philips Hue, and OpenWeatherMap to provide a personalized home assistant experience. Users can follow the detailed instructions provided to build their own version of the home assistant on Raspberry Pi, with optional components for customization. The project also includes system configurations, dependencies installation, and setup scripts for easy deployment. Overall, GPT Home offers a DIY solution for creating a smart home assistant using Raspberry Pi and OpenAI technology.
comfy-cli
comfy-cli is a command line tool designed to simplify the installation and management of ComfyUI, an open-source machine learning framework. It allows users to easily set up ComfyUI, install packages, manage custom nodes, download checkpoints, and ensure cross-platform compatibility. The tool provides comprehensive documentation and examples to aid users in utilizing ComfyUI efficiently.
crewAI-tools
The crewAI Tools repository provides a guide for setting up tools for crewAI agents, enabling the creation of custom tools to enhance AI solutions. Tools play a crucial role in improving agent functionality. The guide explains how to equip agents with a range of tools and how to create new tools. Tools are designed to return strings for generating responses. There are two main methods for creating tools: subclassing BaseTool and using the tool decorator. Contributions to the toolset are encouraged, and the development setup includes steps for installing dependencies, activating the virtual environment, setting up pre-commit hooks, running tests, static type checking, packaging, and local installation. Enhance AI agent capabilities with advanced tooling.
aipan-netdisk-search
Aipan-Netdisk-Search is a free and open-source web project for searching netdisk resources. It utilizes third-party APIs with IP access restrictions, suggesting self-deployment. The project can be easily deployed on Vercel and provides instructions for manual deployment. Users can clone the project, install dependencies, run it in the browser, and access it at localhost:3001. The project also includes documentation for deploying on personal servers using NUXT.JS. Additionally, there are options for donations and communication via WeChat.
Agently-Daily-News-Collector
Agently Daily News Collector is an open-source project showcasing a workflow powered by the Agent ly AI application development framework. It allows users to generate news collections on various topics by inputting the field topic. The AI agents automatically perform the necessary tasks to generate a high-quality news collection saved in a markdown file. Users can edit settings in the YAML file, install Python and required packages, input their topic idea, and wait for the news collection to be generated. The process involves tasks like outlining, searching, summarizing, and preparing column data. The project dependencies include Agently AI Development Framework, duckduckgo-search, BeautifulSoup4, and PyYAM.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.
