
shell-pilot
A simple, lightweight shell script to interact with OpenAI or Ollama or Mistral AI or LocalAI or ZhipuAI from the terminal, and enhancing intelligent system management without any dependencies(pure shell).
Stars: 73
Shell-pilot is a simple, lightweight shell script designed to interact with various AI models such as OpenAI, Ollama, Mistral AI, LocalAI, ZhipuAI, Anthropic, Moonshot, and Novita AI from the terminal. It enhances intelligent system management without any dependencies, offering features like setting up a local LLM repository, using official models and APIs, viewing history and session persistence, passing input prompts with pipe/redirector, listing available models, setting request parameters, generating and running commands in the terminal, easy configuration setup, system package version checking, and managing system aliases.
README:
A simple, lightweight shell script to interact with OpenAI or Ollama or Mistral AI or LocalAI or ZhipuAI or Athropic or Moonshot or Novita AI from the terminal, and enhancing intelligent system management without any dependencies(pure shell).
- Based on Ollama to setup a local LLM repository(
support llama3, gemma2), work with Ollama API - Use the official chatgpt model with the official ChatGPT API from the terminal
- Use the official Mistral AI model with the Mistral AI API
- Use the LocalAI model with the LocalAI API
- Use the ZhipuAI model with the ZhipuAI API
- Use the Anthropic model with the Anthropic API
- Use the Moonshot model with the Moonshot API
- Use the Novita AI model with the Novita AI API
- View your history and session persistence
- Chat context, GPT remembers previous chat questions and answers
- Pass the input prompt with pipe/redirector(
|,<), as a script parameter or normal chat mode(bash version: 4.0+) - List all available models
- Set OpenAI request parameters
- Generate a command and run it in terminal, and can use
code chat modeeasy to interact - Easy to set the config in command parameter or edit config with vi mode(option e)
- Enhanced system interaction and efficiency with features aimed at basic system management
-
Modular plugin designallows for easy expansion with each plugin introducing a new functionality, making the tool more powerful and adaptable to user needs.- Easy to check system package verison
- Easy to add/list/remove alias from command line
- This is still a test project for using online models and local LLM in shell environment.
It is not production ready, so do not use in critical/production system, and do not use to analyze customer data.
This script relies on curl for the requests to the api and jq to parse the json response.
-
MacOS: brew install curl Linux: should be installed by default dnf/yum/apt install curl
-
MacOS: brew install jq Linux: should be installed by default dnf/yum/apt install jq
-
An OpenAI API key. Create an account and get a free API Key at OpenAI
-
Optionally, you can install glow to render responses in markdown
- For setup
Ollamaenvironment, Manual install instructions, ollama usage, and Ollama model library
curl -fsSL https://ollama.com/install.sh | sh
ollama pull llama2 # used llama2 by default- For setup
LocalAIenvironment, Manual, and LocalAI github
docker run -p 8080:8080 --name local-ai -ti localai/localai:latest-aio-cpu
# Do you have a Nvidia GPUs? Use this instead
# CUDA 11
# docker run -p 8080:8080 --gpus all --name local-ai -ti localai/localai:latest-aio-gpu-nvidia-cuda-11
# CUDA 12
# docker run -p 8080:8080 --gpus all --name local-ai -ti localai/localai:latest-aio-gpu-nvidia-cuda-12- To install, run this in your terminal and provide your OpenAI API key when asked.
curl -sS -o spilot_install.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/reid41/shell-pilot/main/spilot_install.sh
bash spilot_install.sh- Set your local
Ollamaserver ip in configuration filespilot_common.shif not set during the installation
OLLAMA_SERVER_IP=<ollama server ip address>- You can also set the other parameters in
spilot_common.shbefore using.
e.g.
TEMPERATURE=0.6
MAX_TOKENS=4096
MODEL_OPENAI=gpt-3.5-turbo
MODEL_OLLAMA=llama2
CONTEXT=false
MULTI_LINE_PROMPT=false
ENABLE_DANGER_FLAG=falseIf you want to install it manually, all you have to do is:
- Download the shell-pilot project files in
git clone https://github.com/reid41/shell-pilot.git
cd shell-pilot/- If you want to reset
the script path(/usr/local/bin/ by default)oroutput store path(~/spilot_files_dir by default), try below:
# define the config dir if need to reset
new_config_path="/new/path/to/config/"
# define the tmp or output files dir
new_files_dir="/new/path/to/files/"
# create it if new
[[ ! -d ${new_config_path} ]] && mkdir ${new_config_path} -p
[[ ! -d "${new_config_path}/plugins" ]] && mkdir ${new_config_path}/plugins -p
[[ ! -d ${new_files_dir} ]] && mkdir ${new_files_dir} -p
# reset it
sed -i "s|SHELL_PILOT_CONFIG_PATH=\"/usr/local/bin/\"|SHELL_PILOT_CONFIG_PATH=\"$new_config_path\"|" s-pilot
sed -i "s|SPILOT_FILES_DEFAULT_DIR=~/spilot_files_dir|SPILOT_FILES_DEFAULT_DIR=$new_files_dir|" spilot_common.sh
# add ollama server host
ollama_server_ip_address=<ip>
echo "OLLAMA_SERVER_IP=${ollama_server_ip_address}" >> spilot_common.sh
# add localai server host
localai_server_ip_address=<ip>
echo "LOCALAI_SERVER_IP=${localai_server_ip_address}" >> spilot_common.sh- set the permissions
chmod +x s-pilot spilot_common.sh spilot_llm_rq_apis.sh plugins/*.sh- Move the files to the dir
cp s-pilot spilot_common.sh spilot_llm_rq_apis.sh ${new_config_path}
cp plugins/*.sh ${new_config_path}/plugins- Add settings into the profile file
# profile, e.g. .bash_profile
the_profile_file=$HOME/.bash_profile
# add the script/config path
echo "export PATH\=\$PATH\:${new_config_path}" >> $the_profile_file
# add source alias for alias option
echo "alias ss-pilot='source s-pilot'" >> $the_profile_file
# openai/mistral key if need
# openai
openai_api_key_value=<key>
echo "export OPENAI_KEY=${openai_api_key_value}" >> $the_profile_file
# mistral ai
mistralai_api_key_value=<key>
echo "export MISTRAL_API_KEY=${mistralai_api_key_value}" >> $the_profile_file
# zhipuai ai
zhipuai_api_key_value=<key>
echo "export ZHIPUAI_API_KEY=${zhipuai_api_key_value}" >> $the_profile_file
# anthropic ai
anthropic_api_key_value=<key>
echo "export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=${anthropic_api_key_value}" >> $the_profile_file
# moonshot ai
moonshot_api_key_value=<key>
echo "export MOONSHOT_API_KEY=${moonshot_api_key_value}" >> $the_profile_file
# novita ai
novita_api_key_value=<key>
echo "export NOVITA_API_KEY=${novita_api_key_value}" >> $the_profile_file
source $the_profile_file- Run the script by using the
s-pilotcommand anywhere:
$ s-pilot
Welcome to Shell Pilot!!
You can quit with 'q' or 'e'.
<<You>>- You can also use it in pipe mode:
$ echo "How to view running processes on RHEL8?" | s-pilot
You can view running processes on RHEL8 using the `ps` command. To see a list of running processes,
open a terminal and type `ps aux` or `ps -ef`. This will display a list of all processes currently
running on your system.
$ cat error.log | s-pilot
The log entries indicate the following events on the system:
1. April 7, 23:35:40: Log rotation initiated by systemd, then completed successfully.
2. April 8, 05:20:51: Error encountered during metadata download for repository$ s-pilot < ss.sh
The output will be:
Hello World test
$ s-pilot p "summarize" < ss.sh
This is a bash script that defines and invokes a function named "Hello".
The function takes two arguments, $1 and $2, and prints "Hello World" followed by these arguments...
$ s-pilot <<< "what is the best way to learn shell? Provide an example"
The best way to learn shell scripting is through hands-on practice and tutorials. Start by
understanding basic commands, then move on to writing simple scripts to automate tasks...
$ s-pilot << EOF
> how to learn python?
> provide a detail example.
> EOF
To learn Python, follow these steps:
1. **Understand the Basics**: Start with Python syntax, data types, variables, and basic operations.
2. **Control Structures**: Learn about loops (for, while), if statements, and functions...-
Help with
h,-h,--help: -
Check version:
s-pilot v
[Shell Pilot Version]: 1.5.5- Chat mode with initial prompt:
s-pilot ip "You are Linux Master. You should provide a detail and professional suggeston about Linux every time."
Welcome to Shell Pilot!!
You can quit with 'q' or 'e'.
<<You>>
what is shell?
<<ShellPilot>> A shell is a command-line interface that allows users to interact with the
operating system by running commands. It is a program that takes input from the user in the form of
commands and then executes them. The shell acts as an intermediary between the user and the
operating system, interpreting commands and running programs. There are different types of shells
available in Linux, such as bash (Bourne Again Shell), sh (Bourne Shell), csh (C Shell), ksh (Korn
Shell), and more. Each shell has its own set of features and capabilities, but they all serve the
same fundamental purpose of allowing users to interact with the system via the command line.- with
p:
s-pilot -p "What is the regex to match an ip address?"
The regex to match an IP address is:
(?:\d{1,3}\.){3}\d{1,3}
$ cat error.log | s-pilot p "find the errors and provide solution"
Errors:
1. Inconsistent date formats: "Apr 7" and "Apr 8".
2. Inconsistency in log times: "23:35:40" and "10:03:28" for the same date.
Solutions:
1. Standardize date format: Use a consistent date format throughout the log entries.
2. Ensure log times are in chronological order within the same date.- change model provider:
s-pilot cmp ollama
Attempting to update USE_API to ollama.
Backup file removed after successful update.
The setting will save in the configuration file.
Here is the checklist to change the model provider:
USE_API=ollama- list models:
s-pilot lm
{
"name": "llama2:13b",
"size": "6.86 GB",
"format": "gguf",
"parameter_size": "13B",
"quantization_level": "Q4_0"
}- list config
s-pilot lc
# Configuration settings
USE_API=ollama
# Define prompts using the adjusted settings
CHAT_INIT_PROMPT="You are $MODEL_NAME, a Large Language Model trained by $ORGANIZATION. You will be answering questions from users. Answer as concisely as possible for each response.
...- Update the chat setting in
spilot_common.sh
s-pilot t 0.9
Attempting to update TEMPERATURE to 0.9.
Backup file removed after successful update.
The setting will save in the configuration file.
Here is the checklist to change the temperature:
TEMPERATURE=0.9-
historyTo view your chat history, typehistory
$ s-pilot
Welcome to Shell Pilot!!
You can quit with 'q' or 'e'.
<<You>>
history
2024-04-08 18:51 hi
Hello! How can I assist you today?-
modelsTo get a list of the models available at OpenAI API/Ollama, typemodels
$ s-pilot
Welcome to Shell Pilot!!
You can quit with 'q' or 'e'.
<<You>>
models
{
"name": "llama2:13b",
"size": "6.86 GB",
"format": "gguf",
"parameter_size": "13B",
"quantization_level": "Q4_0"
}-
model:To view all the information on a specific model, start a prompt withmodel:and the modelid, pleasedo not use space between model: and id,e.g.
$ s-pilot
Welcome to Shell Pilot!!
You can quit with 'q' or 'e'.
<<You>>
model:llama2
License: LLAMA 2 COMMUNITY LICENSE AGREEMENT
Llama 2 Version Release Date: July 18, 2023
...
Format: gguf
Family: llama
Parameter Size: 7B
Quantization Level: Q4_0-
cmd:To get a command with the specified functionality and run it, just typecmd:and explain what you want to achieve. The script will always ask you if you want to execute the command. i.e. If a command modifies your file system or dowloads external files the script will show a warning before executing, but if the execution flag is disabled by default if found danger.
# >>>>>> MacOS
s-pilot
Welcome to Shell Pilot!!
You can quit with 'q' or 'e'.
<<You>>
cmd: list the files in /tmp/
<<ShellPilot>> ls /tmp
Would you like to execute it? (Yes/No)
y
Executing command: ls /tmp
com.xx.launchd.xx com.x.xx com.xx.out
com.xx.launchd.xx com.x.err powerlog
# >>>>>> Linux
<<You>>
cmd: update my os
<<ShellPilot>> sudo dnf update
Would you like to execute it? (Yes/No)
n
# >>>>>> The danger cmd example:
<<You>>
cmd: remove the files in /tmp/
<<ShellPilot>> rm -r /tmp/*
Warning: This command can change your file system or download external scripts & data.
Please do not execute code that you don't understand completely.
Info: Execution of potentially dangerous commands has been disabled.- One-shot Command Mode
# s-pilot cr test p "please remember my lucky number is 5"
I've noted that your lucky number is 5!
# s-pilot lr
==> Here are the chat record files[<name>-chat_record.spilot]:
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 149 Apr 28 10:07 test-chat_record.spilot
# s-pilot lr test
==> Here is the chat record file content:
[
{
"role": "user",
"content": "please remember my lucky number is 5\n"
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "I've noted that your lucky number is 5!\n"
}
]
# s-pilot cr test p "use my lucky number plus 20"
Using your lucky number (5) + 20 gives us... 25!
# s-pilot dr test
rm: remove regular file '/root/spilot_files_dir/test-chat_record.spilot'? y
File /root/spilot_files_dir/test-chat_record.spilot has been deleted successfully.- Interactive Session Mode
# s-pilot cr test1
Welcome to Shell Pilot!!
You can quit with 'q' or 'e'.
<<You>>
please remember my favorite color is blue
<<ShellPilot>> I've made a note that your favorite color is blue!
<<You>>
q # quit
# s-pilot cr test1
Welcome to Shell Pilot!!
You can quit with 'q' or 'e'.
<<You>>
what is my favorite color?
<<ShellPilot>> Your favorite color is blue!- For models other than
gpt-3.5-turboandgpt-4where the chat context is not supported by the OpenAI api, you can use the chat context build in this script. You can enable chat context mode for the model to remember your previous chat questions and answers. This way you can ask follow-up questions. In chat context the model gets a prompt to act as ChatGPT and is aware of today's date and that it's trained with data up until 2021. To enable this mode start the script withc,-cor--chat-context. i.e.s-pilot c trueto enable it.
- You can set your own initial chat prompt to use in chat context mode. The initial prompt will be sent on every request along with your regular prompt so that the OpenAI model will "stay in character". To set your own custom initial chat prompt use
ip-ipor--init-promptfollowed by your initial prompt i.e. see theScript Parametersusage example. - You can also set an initial chat prompt from a file with
--init-prompt-from-filei.e.s-pilot --init-prompt-from-file myprompt.txt
*When you set an initial prompt you don't need to enable the chat context.
-
The default model used when starting the script is
gpt-3.5-turbofor OpenAI. -
The default model used when starting the script is
llama2for Ollama. -
The default model used when starting the script is
mistral-smallfor MistralAI.
-
If you have access to the GPT4 model you can use it by setting the model to
gpt-4, i.e.s-pilot --model gpt-4. -
For
Ollama, you can pull first from the ollama server, i.e.ollama pull mistral,s-pilot eto set. -
For
MistralAI, you can check withs-pilot lm, and set withs-pilot e.
-
To set request parameters you can start the script like this:
s-pilot t 0.9. -
The setting will save in
spilot_common.sh, no need to change or mention every time.The available parameters are:
- temperature,
tor-tor--temperature - model,
mor-mor--model - max number of tokens,
mt,-mt,--max-tokens - prompt,
p,-por--prompt - prompt from a file in your file system,
pfor-pfor--prompt-from-file
For OpenAI: OpenAI API documentation For Ollama: Ollama API documentation
- temperature,
- pv: check the system package version(so far support MacOS/RHEL/CentOS/Fedora)
$ s-pilot pv
Check the system package version
Usage: /usr/local/bin/s-pilot pv [-f] <pkg1> [pkg2] ...
$ s-pilot pv bc go xx
Check the system package version
✔ bc version 6.5.0
✔ go version 1.19.6
✗ Package xx not found on macOS.
$ s-pilot pv -f usb
Check the system package version
✔ libusb version 1.0.27
✔ usb.ids version 2024.03.18
✔ usbredir version 0.14.0- sa: manage the system alias
# use `ss-pilot` to execute(not `s-pilot`), it will set it after installation
# ss-pilot sa a lx "ls -l /tmp/" lxx "ls -ld /etc" cdetc "cd /etc"
==> Alias 'lx' added to /root/spilot_files_dir/shell_pilot_system_aliases and is active.
==> Alias 'lxx' added to /root/spilot_files_dir/shell_pilot_system_aliases and is active.
==> Alias 'cdetc' added to /root/spilot_files_dir/shell_pilot_system_aliases and is active.
# ss-pilot sa l
==> Aliase List:
alias lx='ls -l /tmp/'
alias lxx='ls -ld /etc'
alias cdetc='cd /etc'
# lx
total 0
# cdetc
# pwd
/etc
# ss-pilot sa r lx lxx cdetc
==> Alias 'lx' removed from /root/spilot_files_dir/shell_pilot_system_aliases
==> Alias 'lxx' removed from /root/spilot_files_dir/shell_pilot_system_aliases
==> Alias 'cdetc' removed from /root/spilot_files_dir/shell_pilot_system_aliases
# lx
-bash: lx: command not foundThe following projects are worth remarking. They were studied during development of this script and used as referencial code sources.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for shell-pilot
Similar Open Source Tools

shell-pilot
Shell-pilot is a simple, lightweight shell script designed to interact with various AI models such as OpenAI, Ollama, Mistral AI, LocalAI, ZhipuAI, Anthropic, Moonshot, and Novita AI from the terminal. It enhances intelligent system management without any dependencies, offering features like setting up a local LLM repository, using official models and APIs, viewing history and session persistence, passing input prompts with pipe/redirector, listing available models, setting request parameters, generating and running commands in the terminal, easy configuration setup, system package version checking, and managing system aliases.
python-tgpt
Python-tgpt is a Python package that enables seamless interaction with over 45 free LLM providers without requiring an API key. It also provides image generation capabilities. The name _python-tgpt_ draws inspiration from its parent project tgpt, which operates on Golang. Through this Python adaptation, users can effortlessly engage with a number of free LLMs available, fostering a smoother AI interaction experience.
fish-ai
fish-ai is a tool that adds AI functionality to Fish shell. It can be integrated with various AI providers like OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Google, Hugging Face, Mistral, or a self-hosted LLM. Users can transform comments into commands, autocomplete commands, and suggest fixes. The tool allows customization through configuration files and supports switching between contexts. Data privacy is maintained by redacting sensitive information before submission to the AI models. Development features include debug logging, testing, and creating releases.
ChatDBG
ChatDBG is an AI-based debugging assistant for C/C++/Python/Rust code that integrates large language models into a standard debugger (`pdb`, `lldb`, `gdb`, and `windbg`) to help debug your code. With ChatDBG, you can engage in a dialog with your debugger, asking open-ended questions about your program, like `why is x null?`. ChatDBG will _take the wheel_ and steer the debugger to answer your queries. ChatDBG can provide error diagnoses and suggest fixes. As far as we are aware, ChatDBG is the _first_ debugger to automatically perform root cause analysis and to provide suggested fixes.
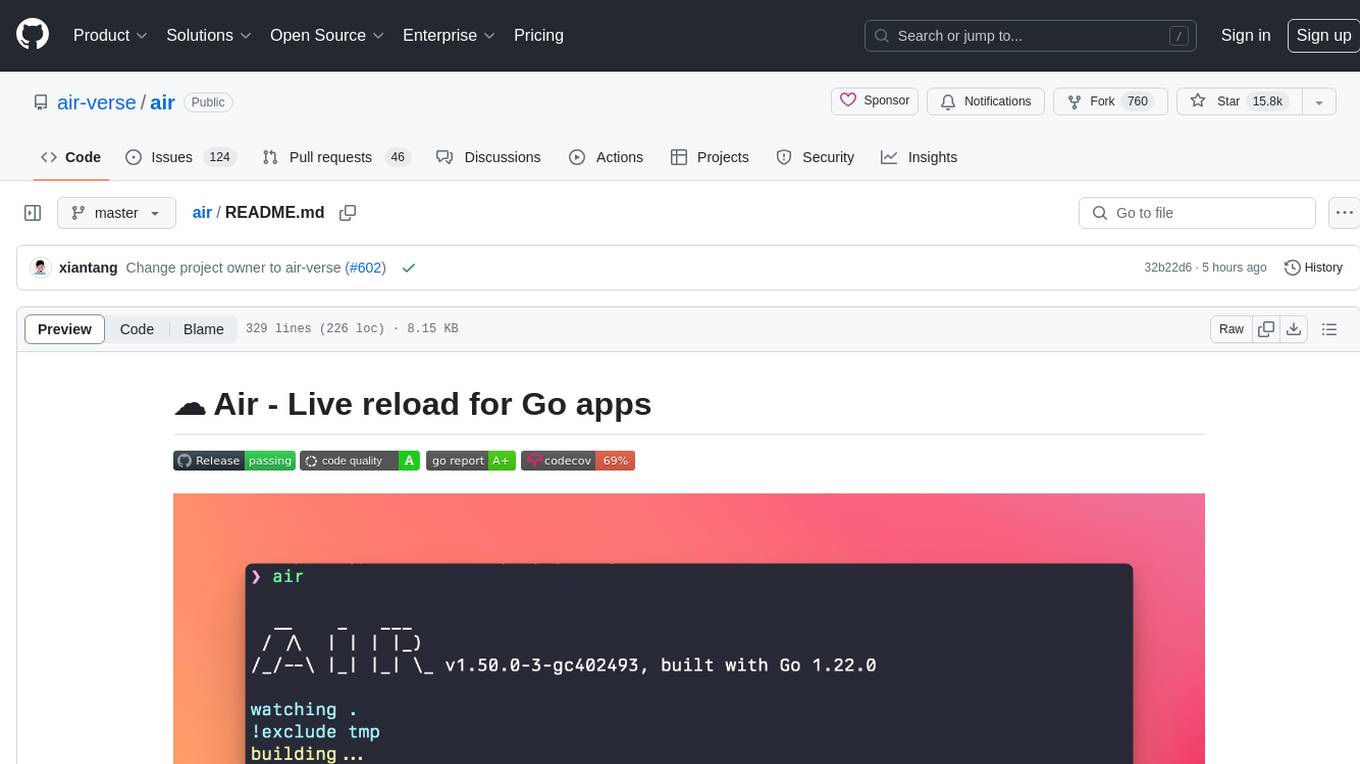
air
Air is a live-reloading command line utility for developing Go applications. It provides colorful log output, customizable build or any command, support for excluding subdirectories, and allows watching new directories after Air started. Users can overwrite specific configuration from arguments and pass runtime arguments for running the built binary. Air can be installed via `go install`, `install.sh`, or `goblin.run`, and can also be used with Docker/Podman. It supports debugging, Docker Compose, and provides a Q&A section for common issues. The tool requires Go 1.16+ for development and welcomes pull requests. Air is released under the GNU General Public License v3.0.
llm-vscode
llm-vscode is an extension designed for all things LLM, utilizing llm-ls as its backend. It offers features such as code completion with 'ghost-text' suggestions, the ability to choose models for code generation via HTTP requests, ensuring prompt size fits within the context window, and code attribution checks. Users can configure the backend, suggestion behavior, keybindings, llm-ls settings, and tokenization options. Additionally, the extension supports testing models like Code Llama 13B, Phind/Phind-CodeLlama-34B-v2, and WizardLM/WizardCoder-Python-34B-V1.0. Development involves cloning llm-ls, building it, and setting up the llm-vscode extension for use.
bilingual_book_maker
The bilingual_book_maker is an AI translation tool that uses ChatGPT to assist users in creating multi-language versions of epub/txt/srt files and books. It supports various models like gpt-4, gpt-3.5-turbo, claude-2, palm, llama-2, azure-openai, command-nightly, and gemini. Users need ChatGPT or OpenAI token, epub/txt books, internet access, and Python 3.8+. The tool provides options to specify OpenAI API key, model selection, target language, proxy server, context addition, translation style, and more. It generates bilingual books in epub format after translation. Users can test translations, set batch size, tweak prompts, and use different models like DeepL, Google Gemini, Tencent TranSmart, and more. The tool also supports retranslation, translating specific tags, and e-reader type specification. Docker usage is available for easy setup.

air
Air is a live-reloading command line utility for developing Go applications. It provides colorful log output, allows customization of build or any command, supports excluding subdirectories, and allows watching new directories after Air has started. Air can be installed via `go install`, `install.sh`, `goblin.run`, or Docker/Podman. To use Air, simply run `air` in your project root directory and leave it alone to focus on your code. Air has nothing to do with hot-deploy for production.
chat-ui
A chat interface using open source models, eg OpenAssistant or Llama. It is a SvelteKit app and it powers the HuggingChat app on hf.co/chat.
tenere
Tenere is a TUI interface for Language Model Libraries (LLMs) written in Rust. It provides syntax highlighting, chat history, saving chats to files, Vim keybindings, copying text from/to clipboard, and supports multiple backends. Users can configure Tenere using a TOML configuration file, set key bindings, and use different LLMs such as ChatGPT, llama.cpp, and ollama. Tenere offers default key bindings for global and prompt modes, with features like starting a new chat, saving chats, scrolling, showing chat history, and quitting the app. Users can interact with the prompt in different modes like Normal, Visual, and Insert, with various key bindings for navigation, editing, and text manipulation.
chatgpt-cli
ChatGPT CLI provides a powerful command-line interface for seamless interaction with ChatGPT models via OpenAI and Azure. It features streaming capabilities, extensive configuration options, and supports various modes like streaming, query, and interactive mode. Users can manage thread-based context, sliding window history, and provide custom context from any source. The CLI also offers model and thread listing, advanced configuration options, and supports GPT-4, GPT-3.5-turbo, and Perplexity's models. Installation is available via Homebrew or direct download, and users can configure settings through default values, a config.yaml file, or environment variables.
mods
AI for the command line, built for pipelines. LLM based AI is really good at interpreting the output of commands and returning the results in CLI friendly text formats like Markdown. Mods is a simple tool that makes it super easy to use AI on the command line and in your pipelines. Mods works with OpenAI, Groq, Azure OpenAI, and LocalAI To get started, install Mods and check out some of the examples below. Since Mods has built-in Markdown formatting, you may also want to grab Glow to give the output some _pizzazz_.
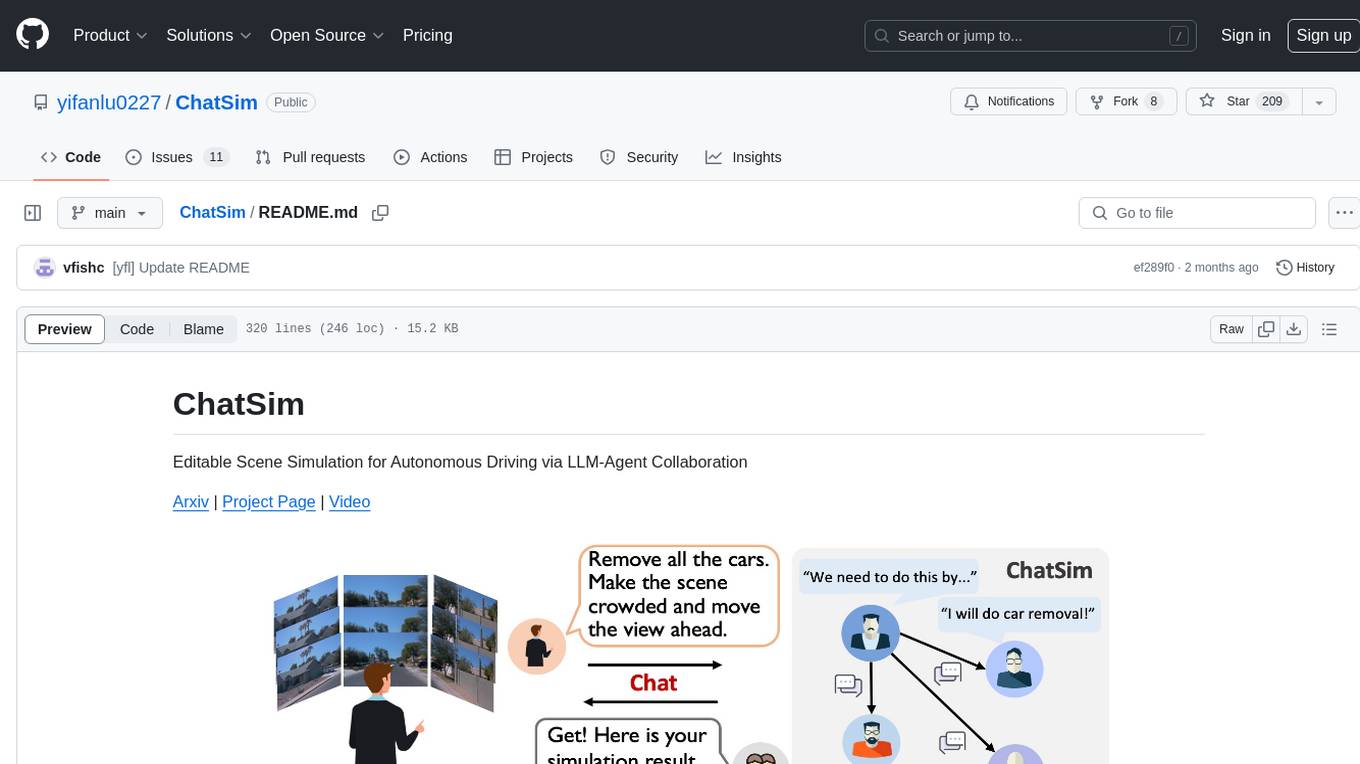
ChatSim
ChatSim is a tool designed for editable scene simulation for autonomous driving via LLM-Agent collaboration. It provides functionalities for setting up the environment, installing necessary dependencies like McNeRF and Inpainting tools, and preparing data for simulation. Users can train models, simulate scenes, and track trajectories for smoother and more realistic results. The tool integrates with Blender software and offers options for training McNeRF models and McLight's skydome estimation network. It also includes a trajectory tracking module for improved trajectory tracking. ChatSim aims to facilitate the simulation of autonomous driving scenarios with collaborative LLM-Agents.
agenticSeek
AgenticSeek is a voice-enabled AI assistant powered by DeepSeek R1 agents, offering a fully local alternative to cloud-based AI services. It allows users to interact with their filesystem, code in multiple languages, and perform various tasks autonomously. The tool is equipped with memory to remember user preferences and past conversations, and it can divide tasks among multiple agents for efficient execution. AgenticSeek prioritizes privacy by running entirely on the user's hardware without sending data to the cloud.
top_secret
Top Secret is a Ruby gem designed to filter sensitive information from free text before sending it to external services or APIs, such as chatbots and LLMs. It provides default filters for credit cards, emails, phone numbers, social security numbers, people's names, and locations, with the ability to add custom filters. Users can configure the tool to handle sensitive information redaction, scan for sensitive data, batch process messages, and restore filtered text from external services. Top Secret uses Regex and NER filters to detect and redact sensitive information, allowing users to override default filters, disable specific filters, and add custom filters globally. The tool is suitable for applications requiring data privacy and security measures.
loz
Loz is a command-line tool that integrates AI capabilities with Unix tools, enabling users to execute system commands and utilize Unix pipes. It supports multiple LLM services like OpenAI API, Microsoft Copilot, and Ollama. Users can run Linux commands based on natural language prompts, enhance Git commit formatting, and interact with the tool in safe mode. Loz can process input from other command-line tools through Unix pipes and automatically generate Git commit messages. It provides features like chat history access, configurable LLM settings, and contribution opportunities.
For similar tasks
spring-ai
The Spring AI project provides a Spring-friendly API and abstractions for developing AI applications. It offers a portable client API for interacting with generative AI models, enabling developers to easily swap out implementations and access various models like OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, and HuggingFace. Spring AI also supports prompt engineering, providing classes and interfaces for creating and parsing prompts, as well as incorporating proprietary data into generative AI without retraining the model. This is achieved through Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), which involves extracting, transforming, and loading data into a vector database for use by AI models. Spring AI's VectorStore abstraction allows for seamless transitions between different vector database implementations.
ruby-nano-bots
Ruby Nano Bots is an implementation of the Nano Bots specification supporting various AI providers like Cohere Command, Google Gemini, Maritaca AI MariTalk, Mistral AI, Ollama, OpenAI ChatGPT, and others. It allows calling tools (functions) and provides a helpful assistant for interacting with AI language models. The tool can be used both from the command line and as a library in Ruby projects, offering features like REPL, debugging, and encryption for data privacy.
rag-chat
The `@upstash/rag-chat` package simplifies the development of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) chat applications by providing Next.js compatibility with streaming support, built-in vector store, optional Redis compatibility for fast chat history management, rate limiting, and disableRag option. Users can easily set up the environment variables and initialize RAGChat to interact with AI models, manage knowledge base, chat history, and enable debugging features. Advanced configuration options allow customization of RAGChat instance with built-in rate limiting, observability via Helicone, and integration with Next.js route handlers and Vercel AI SDK. The package supports OpenAI models, Upstash-hosted models, and custom providers like TogetherAi and Replicate.
ryoma
Ryoma is an AI Powered Data Agent framework that offers a comprehensive solution for data analysis, engineering, and visualization. It leverages cutting-edge technologies like Langchain, Reflex, Apache Arrow, Jupyter Ai Magics, Amundsen, Ibis, and Feast to provide seamless integration of language models, build interactive web applications, handle in-memory data efficiently, work with AI models, and manage machine learning features in production. Ryoma also supports various data sources like Snowflake, Sqlite, BigQuery, Postgres, MySQL, and different engines like Apache Spark and Apache Flink. The tool enables users to connect to databases, run SQL queries, and interact with data and AI models through a user-friendly UI called Ryoma Lab.

shell-pilot
Shell-pilot is a simple, lightweight shell script designed to interact with various AI models such as OpenAI, Ollama, Mistral AI, LocalAI, ZhipuAI, Anthropic, Moonshot, and Novita AI from the terminal. It enhances intelligent system management without any dependencies, offering features like setting up a local LLM repository, using official models and APIs, viewing history and session persistence, passing input prompts with pipe/redirector, listing available models, setting request parameters, generating and running commands in the terminal, easy configuration setup, system package version checking, and managing system aliases.

awesome-llm-web-ui
Curating the best Large Language Model (LLM) Web User Interfaces that facilitate interaction with powerful AI models. Explore and catalogue intuitive, feature-rich, and innovative web interfaces for interacting with LLMs, ranging from simple chatbots to comprehensive platforms equipped with functionalities like PDF generation and web search.
java-sdk
The MCP Java SDK is a set of projects that provide Java SDK integration for the Model Context Protocol. It enables Java applications to interact with AI models and tools through a standardized interface, supporting both synchronous and asynchronous communication patterns.
myclaw
myclaw is a personal AI assistant built on agentsdk-go that offers a CLI agent for single message or interactive REPL mode, full orchestration with channels, cron, and heartbeat, support for various messaging channels like Telegram, Feishu, WeCom, WhatsApp, and a web UI, multi-provider support for Anthropic and OpenAI models, image recognition and document processing, scheduled tasks with JSON persistence, long-term and daily memory storage, custom skill loading, and more. It provides a comprehensive solution for interacting with AI models and managing tasks efficiently.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.