
neuron-ai
The PHP Agentic Framework to build production-ready AI driven applications. Connect components (LLMs, vector DBs, memory) to agents that can interact with your data. With its modular architecture it's best suited for building RAG, multi-agent workflows, or business process automations.
Stars: 1668
Neuron is a PHP framework for creating and orchestrating AI Agents, providing tools for the entire agentic application development lifecycle. It allows integration of AI entities in existing PHP applications with a powerful and flexible architecture. Neuron offers tutorials and educational content to help users get started using AI Agents in their projects. The framework supports various LLM providers, tools, and toolkits, enabling users to create fully functional agents for tasks like data analysis, chatbots, and structured output. Neuron also facilitates monitoring and debugging of AI applications, ensuring control over agent behavior and decision-making processes.
README:
[!IMPORTANT] Get early access to new features, exclusive tutorials, and expert tips for building AI agents in PHP. Join a community of PHP developers pioneering the future of AI development. Subscribe to the newsletter
Before moving on, support the community giving a GitHub star ⭐️. Thank you!
Neuron is a PHP framework for creating and orchestrating AI Agents. It allows you to integrate AI entities in your existing PHP applications with a powerful and flexible architecture. We provide tools for the entire agentic application development lifecycle, from LLM interfaces, to data loading, to multi-agent orchestration, to monitoring and debugging. In addition, we provide tutorials and other educational content to help you get started using AI Agents in your projects.
- PHP: ^8.1
Go to the official documentation
Check out the technical guides and tutorials archive to learn how to start creating your AI Agents with Neuron https://docs.neuron-ai.dev/overview/fast-learning-by-video.
Neuron is the perfect AI architecture for your project.
Neuron offers a well-defined encapsulation pattern, allowing you to work on your AI components in a dedicated namespace. You can enjoy the exact same experience of the other ecosystem packages you already love, like Filament, Nova, Horizon, Pennant, etc.
All Neuron components belong to its own interface, so you can easily define dependencies and automate objects creation using the Symfony service container. Watch how it works in a real project.
- Install
- Create an Agent
- Talk to the Agent
- Monitoring
- Supported LLM Providers
- Tools & Toolkits
- MCP Connector
- Structured Output
- RAG
- Workflow
- AI Assisted Development
- Security Vulnerabilities
- Official Documentation
Install the latest version of the package:
composer require neuron-core/neuron-ai
Neuron provides you with the Agent class you can extend to inherit the main features of the framework and create fully functional agents. This class automatically manages some advanced mechanisms for you, such as memory, tools and function calls, up to the RAG systems. You can go deeper into these aspects in the documentation.
Let's create an Agent with the command below:
php vendor/bin/neuron make:agent DataAnalystAgent
<?php
namespace App\Neuron;
use NeuronAI\Agent;
use NeuronAI\SystemPrompt;
use NeuronAI\Providers\AIProviderInterface;
use NeuronAI\Providers\Anthropic\Anthropic;
class DataAnalystAgent extends Agent
{
protected function provider(): AIProviderInterface
{
return new Anthropic(
key: 'ANTHROPIC_API_KEY',
model: 'ANTHROPIC_MODEL',
);
}
protected function instructions(): string
{
return (string) new SystemPrompt(
background: [
"You are a data analyst expert in creating reports from SQL databases."
]
);
}
}The SystemPrompt class is designed to take your base instructions and build a consistent prompt for the underlying model
reducing the effort for prompt engineering.
Send a prompt to the agent to get a response from the underlying LLM:
$agent = DataAnalystAgent::make();
$response = $agent->chat(
new UserMessage("Hi, I'm Valerio. Who are you?")
);
echo $response->getContent();
// I'm a data analyst. How can I help you today?
$response = $agent->chat(
new UserMessage("Do you remember my name?")
);
echo $response->getContent();
// Your name is Valerio, as you said in your introduction.As you can see in the example above, the Agent has memory of the ongoing conversation. Learn more about memory in the documentation.
Integrating AI Agents into your application you’re not working only with functions and deterministic code, you program your agent also influencing probability distributions. Same input ≠ output. That means reproducibility, versioning, and debugging become real problems.
Many of the Agents you build with Neuron will contain multiple steps with multiple invocations of LLM calls, tool usage, access to external memories, etc. As these applications get more and more complex, it becomes crucial to be able to inspect what exactly your agent is doing and why.
Why is the model taking certain decisions? What data is the model reacting to? Prompting is not programming in the common sense. No static types, small changes break output, long prompts cost latency, and no two models behave exactly the same with the same prompt.
The best way to take your AI application under control is with Inspector. After you sign up,
make sure to set the INSPECTOR_INGESTION_KEY variable in the application environment file to start monitoring:
INSPECTOR_INGESTION_KEY=fwe45gtxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxAfter configuring the environment variable, you will see the agent execution timeline in your Inspector dashboard.
Learn more about Monitoring in the documentation.
With Neuron, you can switch between LLM providers with just one line of code, without any impact on your agent implementation. Supported providers:
- Anthropic
- OpenAI (also as an embeddings provider)
- OpenAI on Azure
- Ollama (also as an embeddings provider)
- OpenAILike
- Gemini (also as an embeddings provider)
- Gemini Vertex
- Mistral
- HuggingFace
- Deepseek
- Grok
- AWS Bedrock Runtime
Make your agent able to perform concrete tasks, like reading from a database, by adding tools or toolkits (collections of tools).
<?php
namespace App\Neuron;
use NeuronAI\Agent;
use NeuronAI\Providers\AIProviderInterface;
use NeuronAI\Providers\Anthropic\Anthropic;
use NeuronAI\SystemPrompt;
use NeuronAI\Tools\ToolProperty;
use NeuronAI\Tools\Tool;
use NeuronAI\Tools\Toolkits\MySQL\MySQLToolkit;
class DataAnalystAgent extends Agent
{
protected function provider(): AIProviderInterface
{
return new Anthropic(
key: 'ANTHROPIC_API_KEY',
model: 'ANTHROPIC_MODEL',
);
}
protected function instructions(): string
{
return (string) new SystemPrompt(
background: [
"You are a data analyst expert in creating reports from SQL databases."
]
);
}
protected function tools(): array
{
return [
MySQLToolkit::make(
\DB::connection()->getPdo()
),
];
}
}Ask the agent something about your database:
$response = DataAnalystAgent::make()->chat(
new UserMessage("How many orders we received today?")
);
echo $response->getContent();Learn more about Tools in the documentation.
Instead of implementing tools manually, you can connect tools exposed by an MCP server with the McpConnector component:
<?php
namespace App\Neuron;
use NeuronAI\Agent;
use NeuronAI\MCP\McpConnector;
use NeuronAI\Providers\AIProviderInterface;
use NeuronAI\Providers\Anthropic\Anthropic;
use NeuronAI\Tools\ToolProperty;
use NeuronAI\Tools\Tool;
class DataAnalystAgent extends Agent
{
protected function provider(): AIProviderInterface
{
...
}
protected function instructions(): string
{
...
}
protected function tools(): array
{
return [
// Connect to an MCP server
...McpConnector::make([
'command' => 'npx',
'args' => ['-y', '@modelcontextprotocol/server-everything'],
])->tools(),
];
}
}Learn more about MCP connector in the documentation.
There are scenarios where you need Agents to understand natural language, but output in a structured format, like business processes automation, data extraction, etc. to use the output with some other downstream system.
use App\Neuron\MyAgent;
use NeuronAI\Chat\Messages\UserMessage;
use NeuronAI\StructuredOutput\SchemaProperty;
/*
* Define the output structure as a PHP class.
*/
class Person
{
#[SchemaProperty(description: 'The user name')]
public string $name;
#[SchemaProperty(description: 'What the user love to eat')]
public string $preference;
}
// Talk to the agent requiring the structured output
$person = MyAgent::make()->structured(
new UserMessage("I'm John and I like pizza!"),
Person::class
);
echo $person->name ' like '.$person->preference;
// John like pizzaLearn more about Structured Output on the documentation.
To create a RAG you need to attach some additional components other than the AI provider, such as a vector store,
and an embeddings provider.
Let's create a RAG with the command below:
php vendor/bin/neuron make:rag MyChatBot
Here is an example of a RAG implementation:
<?php
namespace App\Neuron;
use NeuronAI\Providers\AIProviderInterface;
use NeuronAI\Providers\Anthropic\Anthropic;
use NeuronAI\RAG\Embeddings\EmbeddingsProviderInterface;
use NeuronAI\RAG\Embeddings\VoyageEmbeddingProvider;
use NeuronAI\RAG\RAG;
use NeuronAI\RAG\VectorStore\PineconeVectorStore;
use NeuronAI\RAG\VectorStore\VectorStoreInterface;
class MyChatBot extends RAG
{
protected function provider(): AIProviderInterface
{
return new Anthropic(
key: 'ANTHROPIC_API_KEY',
model: 'ANTHROPIC_MODEL',
);
}
protected function embeddings(): EmbeddingsProviderInterface
{
return new VoyageEmbeddingProvider(
key: 'VOYAGE_API_KEY',
model: 'VOYAGE_MODEL'
);
}
protected function vectorStore(): VectorStoreInterface
{
return new PineconeVectorStore(
key: 'PINECONE_API_KEY',
indexUrl: 'PINECONE_INDEX_URL'
);
}
}Learn more about RAG in the documentation.
Think of a Workflow as a smart flowchart for your AI applications. The idea behind Workflow is to allow developers to use all the Neuron components like AI providers, embeddings, data loaders, chat history, vector store, etc, as standalone components to create totally customized agentic entities.
Agent and RAG classes represent a ready to use implementation of the most common patterns when it comes to retrieval use cases, or tool calls, structured output, etc. Workflow allows you to program your agentic system completely from scratch. Agent and RAG can be used inside a Workflow to complete tasks as any other component if you need their built-in capabilities.
Neuron Workflow supports a robust human-in-the-loop pattern, enabling human intervention at any point in an automated process. This is especially useful in large language model (LLM)-driven applications where model output may require validation, correction, or additional context to complete the task.
Learn more about Workflow on the documentation.
The official of Neuron AI documentation is also available and searchable as a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server.
This allows AI assistants to access Neuron AI documentation content directly, making it easy for tools like Claude Code, Cursor, and VS Code extensions reliably understand what Neuron AI can do, its components, how to configure them, and how to compose workflows agents and RAG.
Configure the MCP server: https://docs.neuron-ai.dev/~gitbook/mcp
If you discover a security vulnerability within Neuron, please send an e-mail to the Inspector team via [email protected]. All security vulnerabilities will be promptly addressed.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for neuron-ai
Similar Open Source Tools

neuron-ai
Neuron is a PHP framework for creating and orchestrating AI Agents, providing tools for the entire agentic application development lifecycle. It allows integration of AI entities in existing PHP applications with a powerful and flexible architecture. Neuron offers tutorials and educational content to help users get started using AI Agents in their projects. The framework supports various LLM providers, tools, and toolkits, enabling users to create fully functional agents for tasks like data analysis, chatbots, and structured output. Neuron also facilitates monitoring and debugging of AI applications, ensuring control over agent behavior and decision-making processes.
neuron-ai
Neuron AI is a PHP framework that provides an Agent class for creating fully functional agents to perform tasks like analyzing text for SEO optimization. The framework manages advanced mechanisms such as memory, tools, and function calls. Users can extend the Agent class to create custom agents and interact with them to get responses based on the underlying LLM. Neuron AI aims to simplify the development of AI-powered applications by offering a structured framework with documentation and guidelines for contributions under the MIT license.

project_alice
Alice is an agentic workflow framework that integrates task execution and intelligent chat capabilities. It provides a flexible environment for creating, managing, and deploying AI agents for various purposes, leveraging a microservices architecture with MongoDB for data persistence. The framework consists of components like APIs, agents, tasks, and chats that interact to produce outputs through files, messages, task results, and URL references. Users can create, test, and deploy agentic solutions in a human-language framework, making it easy to engage with by both users and agents. The tool offers an open-source option, user management, flexible model deployment, and programmatic access to tasks and chats.
langchain
LangChain is a framework for developing Elixir applications powered by language models. It enables applications to connect language models to other data sources and interact with the environment. The library provides components for working with language models and off-the-shelf chains for specific tasks. It aims to assist in building applications that combine large language models with other sources of computation or knowledge. LangChain is written in Elixir and is not aimed for parity with the JavaScript and Python versions due to differences in programming paradigms and design choices. The library is designed to make it easy to integrate language models into applications and expose features, data, and functionality to the models.
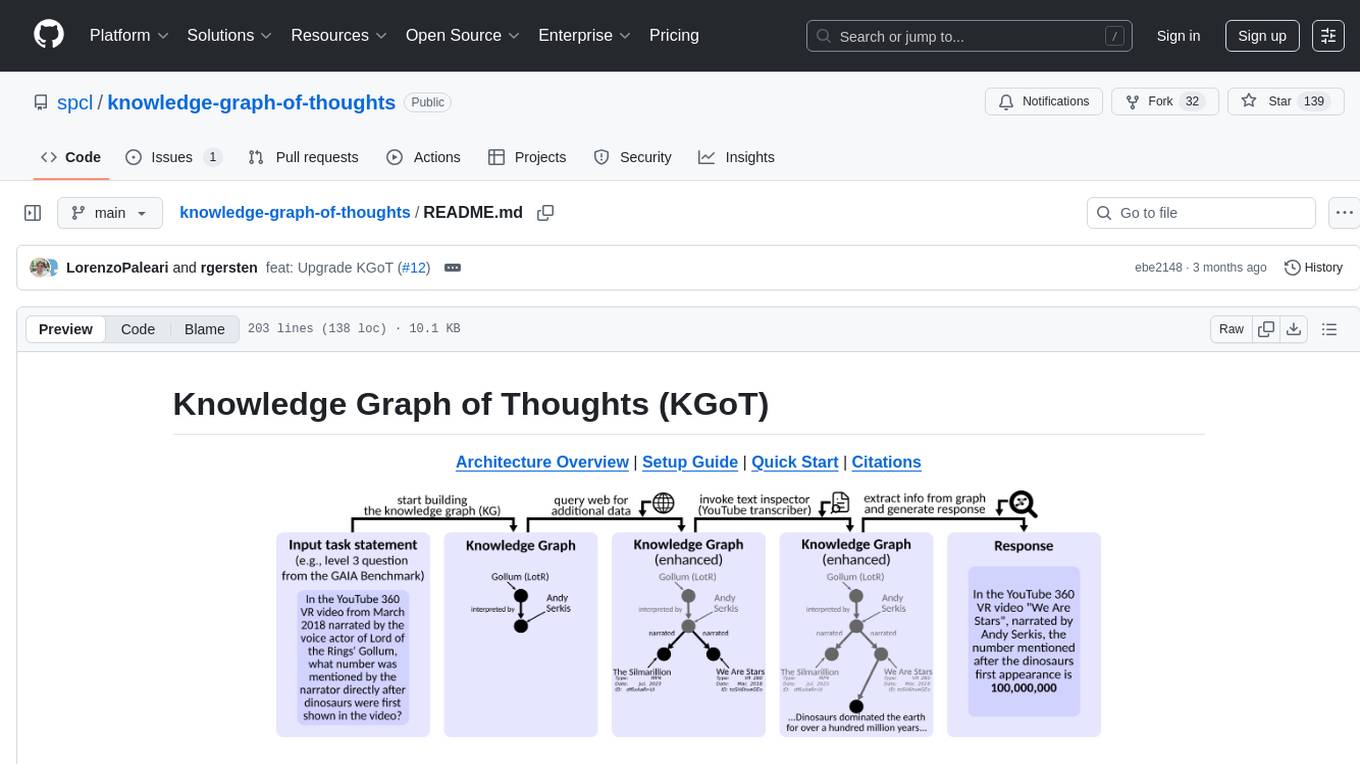
knowledge-graph-of-thoughts
Knowledge Graph of Thoughts (KGoT) is an innovative AI assistant architecture that integrates LLM reasoning with dynamically constructed knowledge graphs (KGs). KGoT extracts and structures task-relevant knowledge into a dynamic KG representation, iteratively enhanced through external tools such as math solvers, web crawlers, and Python scripts. Such structured representation of task-relevant knowledge enables low-cost models to solve complex tasks effectively. The KGoT system consists of three main components: the Controller, the Graph Store, and the Integrated Tools, each playing a critical role in the task-solving process.
agentscript
AgentScript is an open-source framework for building AI agents that think in code. It prompts a language model to generate JavaScript code, which is then executed in a dedicated runtime with resumability, state persistence, and interactivity. The framework allows for abstract task execution without needing to know all the data beforehand, making it flexible and efficient. AgentScript supports tools, deterministic functions, and LLM-enabled functions, enabling dynamic data processing and decision-making. It also provides state management and human-in-the-loop capabilities, allowing for pausing, serialization, and resumption of execution.

pydantic-ai
PydanticAI is a Python agent framework designed to make it less painful to build production grade applications with Generative AI. It is built by the Pydantic Team and supports various AI models like OpenAI, Anthropic, Gemini, Ollama, Groq, and Mistral. PydanticAI seamlessly integrates with Pydantic Logfire for real-time debugging, performance monitoring, and behavior tracking of LLM-powered applications. It is type-safe, Python-centric, and offers structured responses, dependency injection system, and streamed responses. PydanticAI is in early beta, offering a Python-centric design to apply standard Python best practices in AI-driven projects.
fabrice-ai
A lightweight, functional, and composable framework for building AI agents that work together to solve complex tasks. Built with TypeScript and designed to be serverless-ready. Fabrice embraces functional programming principles, remains stateless, and stays focused on composability. It provides core concepts like easy teamwork creation, infrastructure-agnosticism, statelessness, and includes all tools and features needed to build AI teams. Agents are specialized workers with specific roles and capabilities, able to call tools and complete tasks. Workflows define how agents collaborate to achieve a goal, with workflow states representing the current state of the workflow. Providers handle requests to the LLM and responses. Tools extend agent capabilities by providing concrete actions they can perform. Execution involves running the workflow to completion, with options for custom execution and BDD testing.

crewAI
CrewAI is a cutting-edge framework designed to orchestrate role-playing autonomous AI agents. By fostering collaborative intelligence, CrewAI empowers agents to work together seamlessly, tackling complex tasks. It enables AI agents to assume roles, share goals, and operate in a cohesive unit, much like a well-oiled crew. Whether you're building a smart assistant platform, an automated customer service ensemble, or a multi-agent research team, CrewAI provides the backbone for sophisticated multi-agent interactions. With features like role-based agent design, autonomous inter-agent delegation, flexible task management, and support for various LLMs, CrewAI offers a dynamic and adaptable solution for both development and production workflows.
multilspy
Multilspy is a Python library developed for research purposes to facilitate the creation of language server clients for querying and obtaining results of static analyses from various language servers. It simplifies the process by handling server setup, communication, and configuration parameters, providing a common interface for different languages. The library supports features like finding function/class definitions, callers, completions, hover information, and document symbols. It is designed to work with AI systems like Large Language Models (LLMs) for tasks such as Monitor-Guided Decoding to ensure code generation correctness and boost compilability.
mosec
Mosec is a high-performance and flexible model serving framework for building ML model-enabled backend and microservices. It bridges the gap between any machine learning models you just trained and the efficient online service API. * **Highly performant** : web layer and task coordination built with Rust 🦀, which offers blazing speed in addition to efficient CPU utilization powered by async I/O * **Ease of use** : user interface purely in Python 🐍, by which users can serve their models in an ML framework-agnostic manner using the same code as they do for offline testing * **Dynamic batching** : aggregate requests from different users for batched inference and distribute results back * **Pipelined stages** : spawn multiple processes for pipelined stages to handle CPU/GPU/IO mixed workloads * **Cloud friendly** : designed to run in the cloud, with the model warmup, graceful shutdown, and Prometheus monitoring metrics, easily managed by Kubernetes or any container orchestration systems * **Do one thing well** : focus on the online serving part, users can pay attention to the model optimization and business logic
llamabot
LlamaBot is a Pythonic bot interface to Large Language Models (LLMs), providing an easy way to experiment with LLMs in Jupyter notebooks and build Python apps utilizing LLMs. It supports all models available in LiteLLM. Users can access LLMs either through local models with Ollama or by using API providers like OpenAI and Mistral. LlamaBot offers different bot interfaces like SimpleBot, ChatBot, QueryBot, and ImageBot for various tasks such as rephrasing text, maintaining chat history, querying documents, and generating images. The tool also includes CLI demos showcasing its capabilities and supports contributions for new features and bug reports from the community.
rosa
ROSA is an AI Agent designed to interact with ROS-based robotics systems using natural language queries. It can generate system reports, read and parse ROS log files, adapt to new robots, and run various ROS commands using natural language. The tool is versatile for robotics research and development, providing an easy way to interact with robots and the ROS environment.
codellm-devkit
Codellm-devkit (CLDK) is a Python library that serves as a multilingual program analysis framework bridging traditional static analysis tools and Large Language Models (LLMs) specialized for code (CodeLLMs). It simplifies the process of analyzing codebases across multiple programming languages, enabling the extraction of meaningful insights and facilitating LLM-based code analysis. The library provides a unified interface for integrating outputs from various analysis tools and preparing them for effective use by CodeLLMs. Codellm-devkit aims to enable the development and experimentation of robust analysis pipelines that combine traditional program analysis tools and CodeLLMs, reducing friction in multi-language code analysis and ensuring compatibility across different tools and LLM platforms. It is designed to seamlessly integrate with popular analysis tools like WALA, Tree-sitter, LLVM, and CodeQL, acting as a crucial intermediary layer for efficient communication between these tools and CodeLLMs. The project is continuously evolving to include new tools and frameworks, maintaining its versatility for code analysis and LLM integration.
artkit
ARTKIT is a Python framework developed by BCG X for automating prompt-based testing and evaluation of Gen AI applications. It allows users to develop automated end-to-end testing and evaluation pipelines for Gen AI systems, supporting multi-turn conversations and various testing scenarios like Q&A accuracy, brand values, equitability, safety, and security. The framework provides a simple API, asynchronous processing, caching, model agnostic support, end-to-end pipelines, multi-turn conversations, robust data flows, and visualizations. ARTKIT is designed for customization by data scientists and engineers to enhance human-in-the-loop testing and evaluation, emphasizing the importance of tailored testing for each Gen AI use case.
aisuite
Aisuite is a simple, unified interface to multiple Generative AI providers. It allows developers to easily interact with various Language Model (LLM) providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure, Google, AWS, and more through a standardized interface. The library focuses on chat completions and provides a thin wrapper around python client libraries, enabling creators to test responses from different LLM providers without changing their code. Aisuite maximizes stability by using HTTP endpoints or SDKs for making calls to the providers. Users can install the base package or specific provider packages, set up API keys, and utilize the library to generate chat completion responses from different models.
For similar tasks
nagato-ai
Nagato-AI is an intuitive AI Agent library that supports multiple LLMs including OpenAI's GPT, Anthropic's Claude, Google's Gemini, and Groq LLMs. Users can create agents from these models and combine them to build an effective AI Agent system. The library is named after the powerful ninja Nagato from the anime Naruto, who can control multiple bodies with different abilities. Nagato-AI acts as a linchpin to summon and coordinate AI Agents for specific missions. It provides flexibility in programming and supports tools like Coordinator, Researcher, Critic agents, and HumanConfirmInputTool.
surfkit
Surfkit is a versatile toolkit designed for building and sharing AI agents that can operate on various devices. Users can create multimodal agents, share them with the community, run them locally or in the cloud, manage agent tasks at scale, and track and observe agent actions. The toolkit provides functionalities for creating agents, devices, solving tasks, managing devices, tracking tasks, and publishing agents. It also offers integrations with libraries like MLLM, Taskara, Skillpacks, and Threadmem. Surfkit aims to simplify the development and deployment of AI agents across different environments.
labo
LABO is a time series forecasting and analysis framework that integrates pre-trained and fine-tuned LLMs with multi-domain agent-based systems. It allows users to create and tune agents easily for various scenarios, such as stock market trend prediction and web public opinion analysis. LABO requires a specific runtime environment setup, including system requirements, Python environment, dependency installations, and configurations. Users can fine-tune their own models using LABO's Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) for computational efficiency and continuous model updates. Additionally, LABO provides a Python library for building model training pipelines and customizing agents for specific tasks.
intentkit
IntentKit is an autonomous agent framework that enables the creation and management of AI agents with capabilities including blockchain interactions, social media management, and custom skill integration. It supports multiple agents, autonomous agent management, blockchain integration, social media integration, extensible skill system, and plugin system. The project is in alpha stage and not recommended for production use. It provides quick start guides for Docker and local development, integrations with Twitter and Coinbase, configuration options using environment variables or AWS Secrets Manager, project structure with core application code, entry points, configuration management, database models, skills, skill sets, and utility functions. Developers can add new skills by creating, implementing, and registering them in the skill directory.

neuron-ai
Neuron is a PHP framework for creating and orchestrating AI Agents, providing tools for the entire agentic application development lifecycle. It allows integration of AI entities in existing PHP applications with a powerful and flexible architecture. Neuron offers tutorials and educational content to help users get started using AI Agents in their projects. The framework supports various LLM providers, tools, and toolkits, enabling users to create fully functional agents for tasks like data analysis, chatbots, and structured output. Neuron also facilitates monitoring and debugging of AI applications, ensuring control over agent behavior and decision-making processes.
For similar jobs

promptflow
**Prompt flow** is a suite of development tools designed to streamline the end-to-end development cycle of LLM-based AI applications, from ideation, prototyping, testing, evaluation to production deployment and monitoring. It makes prompt engineering much easier and enables you to build LLM apps with production quality.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.

MegaDetector
MegaDetector is an AI model that identifies animals, people, and vehicles in camera trap images (which also makes it useful for eliminating blank images). This model is trained on several million images from a variety of ecosystems. MegaDetector is just one of many tools that aims to make conservation biologists more efficient with AI. If you want to learn about other ways to use AI to accelerate camera trap workflows, check out our of the field, affectionately titled "Everything I know about machine learning and camera traps".

leapfrogai
LeapfrogAI is a self-hosted AI platform designed to be deployed in air-gapped resource-constrained environments. It brings sophisticated AI solutions to these environments by hosting all the necessary components of an AI stack, including vector databases, model backends, API, and UI. LeapfrogAI's API closely matches that of OpenAI, allowing tools built for OpenAI/ChatGPT to function seamlessly with a LeapfrogAI backend. It provides several backends for various use cases, including llama-cpp-python, whisper, text-embeddings, and vllm. LeapfrogAI leverages Chainguard's apko to harden base python images, ensuring the latest supported Python versions are used by the other components of the stack. The LeapfrogAI SDK provides a standard set of protobuffs and python utilities for implementing backends and gRPC. LeapfrogAI offers UI options for common use-cases like chat, summarization, and transcription. It can be deployed and run locally via UDS and Kubernetes, built out using Zarf packages. LeapfrogAI is supported by a community of users and contributors, including Defense Unicorns, Beast Code, Chainguard, Exovera, Hypergiant, Pulze, SOSi, United States Navy, United States Air Force, and United States Space Force.

llava-docker
This Docker image for LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant) provides a convenient way to run LLaVA locally or on RunPod. LLaVA is a powerful AI tool that combines natural language processing and computer vision capabilities. With this Docker image, you can easily access LLaVA's functionalities for various tasks, including image captioning, visual question answering, text summarization, and more. The image comes pre-installed with LLaVA v1.2.0, Torch 2.1.2, xformers 0.0.23.post1, and other necessary dependencies. You can customize the model used by setting the MODEL environment variable. The image also includes a Jupyter Lab environment for interactive development and exploration. Overall, this Docker image offers a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for leveraging LLaVA's capabilities.

carrot
The 'carrot' repository on GitHub provides a list of free and user-friendly ChatGPT mirror sites for easy access. The repository includes sponsored sites offering various GPT models and services. Users can find and share sites, report errors, and access stable and recommended sites for ChatGPT usage. The repository also includes a detailed list of ChatGPT sites, their features, and accessibility options, making it a valuable resource for ChatGPT users seeking free and unlimited GPT services.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.

AI-YinMei
AI-YinMei is an AI virtual anchor Vtuber development tool (N card version). It supports fastgpt knowledge base chat dialogue, a complete set of solutions for LLM large language models: [fastgpt] + [one-api] + [Xinference], supports docking bilibili live broadcast barrage reply and entering live broadcast welcome speech, supports Microsoft edge-tts speech synthesis, supports Bert-VITS2 speech synthesis, supports GPT-SoVITS speech synthesis, supports expression control Vtuber Studio, supports painting stable-diffusion-webui output OBS live broadcast room, supports painting picture pornography public-NSFW-y-distinguish, supports search and image search service duckduckgo (requires magic Internet access), supports image search service Baidu image search (no magic Internet access), supports AI reply chat box [html plug-in], supports AI singing Auto-Convert-Music, supports playlist [html plug-in], supports dancing function, supports expression video playback, supports head touching action, supports gift smashing action, supports singing automatic start dancing function, chat and singing automatic cycle swing action, supports multi scene switching, background music switching, day and night automatic switching scene, supports open singing and painting, let AI automatically judge the content.


