
LLM-Scratch
None
Stars: 51
LLM-Scratch is a minimal implementation of a GPT-style Large Language Model built from scratch using PyTorch. It utilizes BPE tokenization, multi head self-attention, feed-forward layers, and layer normalization. The model is designed for learning and experimentation purposes, focusing on autoregressive text generation. The codebase is clean, modular, and extensible, with a character-level tokenizer for easy understanding and no external dependencies like BPE or SentencePiece. The model architecture includes token embedding, positional embedding, transformer blocks with masked self-attention, feed-forward network, residual connections, layer normalization, and a language modeling head. Training objective involves next-token prediction using Cross-Entropy Loss and AdamW optimizer, with training data sampled in fixed-length blocks and gradients backpropagated through time. Configuration parameters are centralized for easy experimentation and reproducibility.
README:
This project is a minimal implementation of a GPT-style Large Language Model built from scratch using PyTorch.
It is designed for learning and experimentation, not production use.
- Uses BPE tokenization
- Implements Multi head self-attention, feed-forward layers, and layer normalization
- Trains a GPT-like transformer on raw text
- Generates text autoregressively
Each module is intentionally separated to keep the codebase clean, modular, and extensible.
The model uses a character-level tokenizer, which:
- Converts each unique character into an integer ID
- Creates a small, fixed vocabulary
- Makes the learning process easier to understand
- Avoids external dependencies like BPE or SentencePiece
While inefficient for large-scale models, character tokenization is ideal for learning and experimentation.
The model follows a GPT-style Transformer architecture:
-
Token Embedding
Converts token IDs into dense vectors. -
Positional Embedding
Adds information about token positions in the sequence. -
Transformer Blocks (stacked)
- Masked self-attention
- Feed-forward network
- Residual connections
- Layer normalization
-
Language Modeling Head
Projects hidden states to vocabulary logits.
The model is trained using causal (autoregressive) language modeling, where it predicts the next token given previous tokens.
The training task is next-token prediction:
Given a sequence of tokens
Predict the next token at every position
- Loss function: Cross-Entropy Loss
- Optimizer: AdamW
- Training data is sampled in fixed-length blocks
- Gradients are backpropagated through time
All important parameters are defined in one place:
Examples:
- Batch size
- Context length (block size)
- Embedding dimension
- Number of attention heads
- Number of transformer layers
- Learning rate
- Training iterations
This makes experimentation simple and reproducible.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LLM-Scratch
Similar Open Source Tools

LLM-Scratch
LLM-Scratch is a minimal implementation of a GPT-style Large Language Model built from scratch using PyTorch. It utilizes BPE tokenization, multi head self-attention, feed-forward layers, and layer normalization. The model is designed for learning and experimentation purposes, focusing on autoregressive text generation. The codebase is clean, modular, and extensible, with a character-level tokenizer for easy understanding and no external dependencies like BPE or SentencePiece. The model architecture includes token embedding, positional embedding, transformer blocks with masked self-attention, feed-forward network, residual connections, layer normalization, and a language modeling head. Training objective involves next-token prediction using Cross-Entropy Loss and AdamW optimizer, with training data sampled in fixed-length blocks and gradients backpropagated through time. Configuration parameters are centralized for easy experimentation and reproducibility.
veScale
veScale is a PyTorch Native LLM Training Framework. It provides a set of tools and components to facilitate the training of large language models (LLMs) using PyTorch. veScale includes features such as 4D parallelism, fast checkpointing, and a CUDA event monitor. It is designed to be scalable and efficient, and it can be used to train LLMs on a variety of hardware platforms.
llms-learning
A repository sharing literatures and resources about Large Language Models (LLMs) and beyond. It includes tutorials, notebooks, course assignments, development stages, modeling, inference, training, applications, study, and basics related to LLMs. The repository covers various topics such as language models, transformers, state space models, multi-modal language models, training recipes, applications in autonomous driving, code, math, embodied intelligence, and more. The content is organized by different categories and provides comprehensive information on LLMs and related topics.
AI-Blueprints
This repository hosts a collection of AI blueprint projects for HP AI Studio, providing end-to-end solutions across key AI domains like data science, machine learning, deep learning, and generative AI. The projects are designed to be plug-and-play, utilizing open-source and hosted models to offer ready-to-use solutions. The repository structure includes projects related to classical machine learning, deep learning applications, generative AI, NGC integration, and troubleshooting guidelines for common issues. Each project is accompanied by detailed descriptions and use cases, showcasing the versatility and applicability of AI technologies in various domains.
eole
EOLE is an open language modeling toolkit based on PyTorch. It aims to provide a research-friendly approach with a comprehensive yet compact and modular codebase for experimenting with various types of language models. The toolkit includes features such as versatile training and inference, dynamic data transforms, comprehensive large language model support, advanced quantization, efficient finetuning, flexible inference, and tensor parallelism. EOLE is a work in progress with ongoing enhancements in configuration management, command line entry points, reproducible recipes, core API simplification, and plans for further simplification, refactoring, inference server development, additional recipes, documentation enhancement, test coverage improvement, logging enhancements, and broader model support.

exllamav3
ExLlamaV3 is an inference library for running local LLMs on modern consumer GPUs. It features a new EXL3 quantization format based on QTIP, flexible tensor-parallel and expert-parallel inference, OpenAI-compatible server via TabbyAPI, continuous dynamic batching, HF Transformers plugin, speculative decoding, multimodal support, and more. The library supports various architectures and aims to simplify and optimize the quantization process for large models, offering efficient conversion with reduced GPU-hours and cost. It provides a streamlined variant of QTIP, enabling fast and memory-bound latency for inference on GPUs.
llms-interview-questions
This repository contains a comprehensive collection of 63 must-know Large Language Models (LLMs) interview questions. It covers topics such as the architecture of LLMs, transformer models, attention mechanisms, training processes, encoder-decoder frameworks, differences between LLMs and traditional statistical language models, handling context and long-term dependencies, transformers for parallelization, applications of LLMs, sentiment analysis, language translation, conversation AI, chatbots, and more. The readme provides detailed explanations, code examples, and insights into utilizing LLMs for various tasks.

MM-RLHF
MM-RLHF is a comprehensive project for aligning Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) with human preferences. It includes a high-quality MLLM alignment dataset, a Critique-Based MLLM reward model, a novel alignment algorithm MM-DPO, and benchmarks for reward models and multimodal safety. The dataset covers image understanding, video understanding, and safety-related tasks with model-generated responses and human-annotated scores. The reward model generates critiques of candidate texts before assigning scores for enhanced interpretability. MM-DPO is an alignment algorithm that achieves performance gains with simple adjustments to the DPO framework. The project enables consistent performance improvements across 10 dimensions and 27 benchmarks for open-source MLLMs.
erag
ERAG is an advanced system that combines lexical, semantic, text, and knowledge graph searches with conversation context to provide accurate and contextually relevant responses. This tool processes various document types, creates embeddings, builds knowledge graphs, and uses this information to answer user queries intelligently. It includes modules for interacting with web content, GitHub repositories, and performing exploratory data analysis using various language models.
erag
ERAG is an advanced system that combines lexical, semantic, text, and knowledge graph searches with conversation context to provide accurate and contextually relevant responses. It processes various document types, creates embeddings, builds knowledge graphs, and uses this information to answer user queries intelligently. The tool includes modules for interacting with web content, GitHub repositories, and performing exploratory data analysis using various language models. It offers a GUI for managing local LLaMA.cpp servers, customizable settings, and advanced search utilities. ERAG supports multi-model collaboration, iterative knowledge refinement, automated quality assessment, and structured knowledge format enforcement. Users can generate specific knowledge entries, full-size textbooks, or datasets using AI-generated questions and answers.
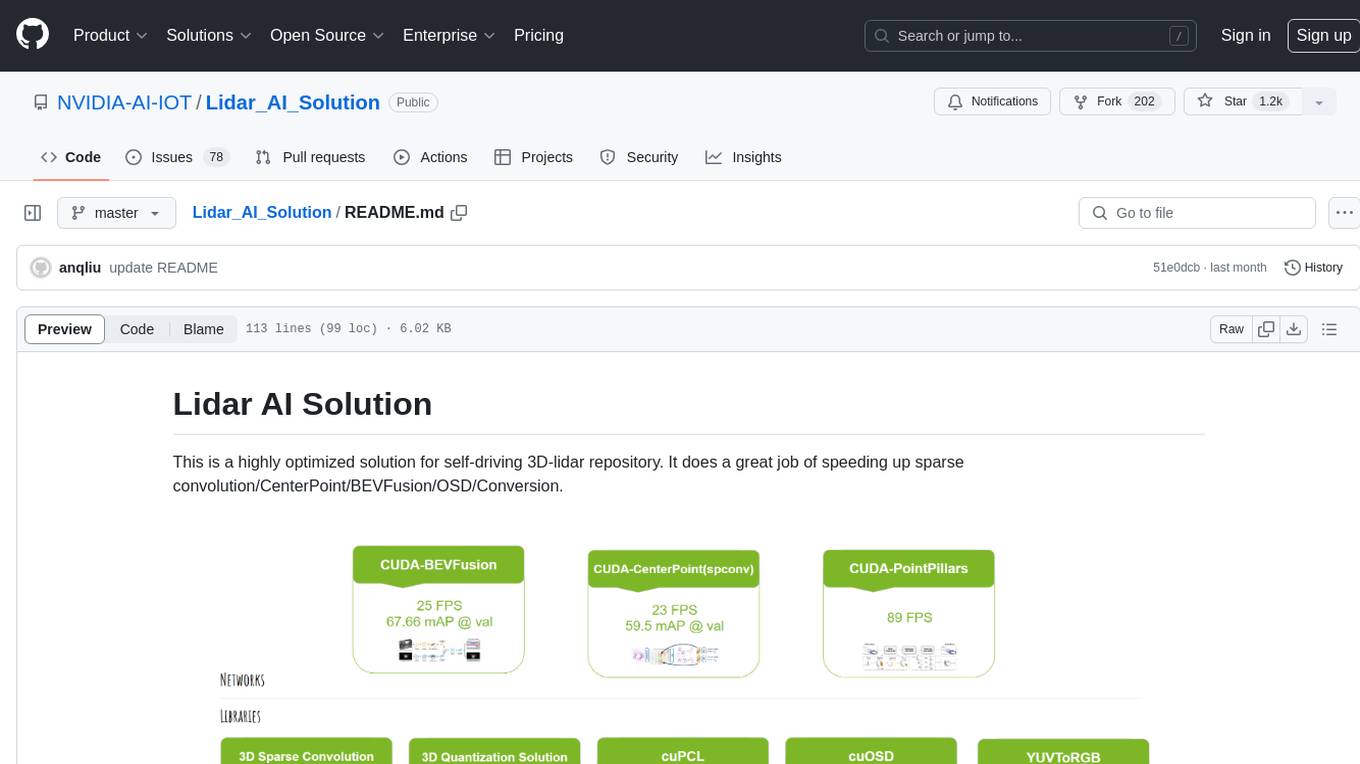
Lidar_AI_Solution
Lidar AI Solution is a highly optimized repository for self-driving 3D lidar, providing solutions for sparse convolution, BEVFusion, CenterPoint, OSD, and Conversion. It includes CUDA and TensorRT implementations for various tasks such as 3D sparse convolution, BEVFusion, CenterPoint, PointPillars, V2XFusion, cuOSD, cuPCL, and YUV to RGB conversion. The repository offers easy-to-use solutions, high accuracy, low memory usage, and quantization options for different tasks related to self-driving technology.
trustgraph
TrustGraph is a tool that deploys private GraphRAG pipelines to build a RDF style knowledge graph from data, enabling accurate and secure `RAG` requests compatible with cloud LLMs and open-source SLMs. It showcases the reliability and efficiencies of GraphRAG algorithms, capturing contextual language flags missed in conventional RAG approaches. The tool offers features like PDF decoding, text chunking, inference of various LMs, RDF-aligned Knowledge Graph extraction, and more. TrustGraph is designed to be modular, supporting multiple Language Models and environments, with a plug'n'play architecture for easy customization.
VeritasGraph
VeritasGraph is an enterprise-grade graph RAG framework designed for secure, on-premise AI applications. It leverages a knowledge graph to perform complex, multi-hop reasoning, providing transparent, auditable reasoning paths with full source attribution. The framework excels at answering complex questions that traditional vector search engines struggle with, ensuring trust and reliability in enterprise AI. VeritasGraph offers full control over data and AI models, verifiable attribution for every claim, advanced graph reasoning capabilities, and open-source deployment with sovereignty and customization.
JamAIBase
JamAI Base is an open-source platform integrating SQLite and LanceDB databases with managed memory and RAG capabilities. It offers built-in LLM, vector embeddings, and reranker orchestration accessible through a spreadsheet-like UI and REST API. Users can transform static tables into dynamic entities, facilitate real-time interactions, manage structured data, and simplify chatbot development. The tool focuses on ease of use, scalability, flexibility, declarative paradigm, and innovative RAG techniques, making complex data operations accessible to users with varying technical expertise.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.
awesome-hallucination-detection
This repository provides a curated list of papers, datasets, and resources related to the detection and mitigation of hallucinations in large language models (LLMs). Hallucinations refer to the generation of factually incorrect or nonsensical text by LLMs, which can be a significant challenge for their use in real-world applications. The resources in this repository aim to help researchers and practitioners better understand and address this issue.
For similar tasks

LLM-Scratch
LLM-Scratch is a minimal implementation of a GPT-style Large Language Model built from scratch using PyTorch. It utilizes BPE tokenization, multi head self-attention, feed-forward layers, and layer normalization. The model is designed for learning and experimentation purposes, focusing on autoregressive text generation. The codebase is clean, modular, and extensible, with a character-level tokenizer for easy understanding and no external dependencies like BPE or SentencePiece. The model architecture includes token embedding, positional embedding, transformer blocks with masked self-attention, feed-forward network, residual connections, layer normalization, and a language modeling head. Training objective involves next-token prediction using Cross-Entropy Loss and AdamW optimizer, with training data sampled in fixed-length blocks and gradients backpropagated through time. Configuration parameters are centralized for easy experimentation and reproducibility.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.
LocalAI
LocalAI is a free and open-source OpenAI alternative that acts as a drop-in replacement REST API compatible with OpenAI (Elevenlabs, Anthropic, etc.) API specifications for local AI inferencing. It allows users to run LLMs, generate images, audio, and more locally or on-premises with consumer-grade hardware, supporting multiple model families and not requiring a GPU. LocalAI offers features such as text generation with GPTs, text-to-audio, audio-to-text transcription, image generation with stable diffusion, OpenAI functions, embeddings generation for vector databases, constrained grammars, downloading models directly from Huggingface, and a Vision API. It provides a detailed step-by-step introduction in its Getting Started guide and supports community integrations such as custom containers, WebUIs, model galleries, and various bots for Discord, Slack, and Telegram. LocalAI also offers resources like an LLM fine-tuning guide, instructions for local building and Kubernetes installation, projects integrating LocalAI, and a how-tos section curated by the community. It encourages users to cite the repository when utilizing it in downstream projects and acknowledges the contributions of various software from the community.

AiTreasureBox
AiTreasureBox is a versatile AI tool that provides a collection of pre-trained models and algorithms for various machine learning tasks. It simplifies the process of implementing AI solutions by offering ready-to-use components that can be easily integrated into projects. With AiTreasureBox, users can quickly prototype and deploy AI applications without the need for extensive knowledge in machine learning or deep learning. The tool covers a wide range of tasks such as image classification, text generation, sentiment analysis, object detection, and more. It is designed to be user-friendly and accessible to both beginners and experienced developers, making AI development more efficient and accessible to a wider audience.

glide
Glide is a cloud-native LLM gateway that provides a unified REST API for accessing various large language models (LLMs) from different providers. It handles LLMOps tasks such as model failover, caching, key management, and more, making it easy to integrate LLMs into applications. Glide supports popular LLM providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI, AWS Bedrock (Titan), Cohere, Google Gemini, OctoML, and Ollama. It offers high availability, performance, and observability, and provides SDKs for Python and NodeJS to simplify integration.

jupyter-ai
Jupyter AI connects generative AI with Jupyter notebooks. It provides a user-friendly and powerful way to explore generative AI models in notebooks and improve your productivity in JupyterLab and the Jupyter Notebook. Specifically, Jupyter AI offers: * An `%%ai` magic that turns the Jupyter notebook into a reproducible generative AI playground. This works anywhere the IPython kernel runs (JupyterLab, Jupyter Notebook, Google Colab, Kaggle, VSCode, etc.). * A native chat UI in JupyterLab that enables you to work with generative AI as a conversational assistant. * Support for a wide range of generative model providers, including AI21, Anthropic, AWS, Cohere, Gemini, Hugging Face, NVIDIA, and OpenAI. * Local model support through GPT4All, enabling use of generative AI models on consumer grade machines with ease and privacy.

langchain_dart
LangChain.dart is a Dart port of the popular LangChain Python framework created by Harrison Chase. LangChain provides a set of ready-to-use components for working with language models and a standard interface for chaining them together to formulate more advanced use cases (e.g. chatbots, Q&A with RAG, agents, summarization, extraction, etc.). The components can be grouped into a few core modules: * **Model I/O:** LangChain offers a unified API for interacting with various LLM providers (e.g. OpenAI, Google, Mistral, Ollama, etc.), allowing developers to switch between them with ease. Additionally, it provides tools for managing model inputs (prompt templates and example selectors) and parsing the resulting model outputs (output parsers). * **Retrieval:** assists in loading user data (via document loaders), transforming it (with text splitters), extracting its meaning (using embedding models), storing (in vector stores) and retrieving it (through retrievers) so that it can be used to ground the model's responses (i.e. Retrieval-Augmented Generation or RAG). * **Agents:** "bots" that leverage LLMs to make informed decisions about which available tools (such as web search, calculators, database lookup, etc.) to use to accomplish the designated task. The different components can be composed together using the LangChain Expression Language (LCEL).

infinity
Infinity is an AI-native database designed for LLM applications, providing incredibly fast full-text and vector search capabilities. It supports a wide range of data types, including vectors, full-text, and structured data, and offers a fused search feature that combines multiple embeddings and full text. Infinity is easy to use, with an intuitive Python API and a single-binary architecture that simplifies deployment. It achieves high performance, with 0.1 milliseconds query latency on million-scale vector datasets and up to 15K QPS.
For similar jobs

promptflow
**Prompt flow** is a suite of development tools designed to streamline the end-to-end development cycle of LLM-based AI applications, from ideation, prototyping, testing, evaluation to production deployment and monitoring. It makes prompt engineering much easier and enables you to build LLM apps with production quality.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.

MegaDetector
MegaDetector is an AI model that identifies animals, people, and vehicles in camera trap images (which also makes it useful for eliminating blank images). This model is trained on several million images from a variety of ecosystems. MegaDetector is just one of many tools that aims to make conservation biologists more efficient with AI. If you want to learn about other ways to use AI to accelerate camera trap workflows, check out our of the field, affectionately titled "Everything I know about machine learning and camera traps".

leapfrogai
LeapfrogAI is a self-hosted AI platform designed to be deployed in air-gapped resource-constrained environments. It brings sophisticated AI solutions to these environments by hosting all the necessary components of an AI stack, including vector databases, model backends, API, and UI. LeapfrogAI's API closely matches that of OpenAI, allowing tools built for OpenAI/ChatGPT to function seamlessly with a LeapfrogAI backend. It provides several backends for various use cases, including llama-cpp-python, whisper, text-embeddings, and vllm. LeapfrogAI leverages Chainguard's apko to harden base python images, ensuring the latest supported Python versions are used by the other components of the stack. The LeapfrogAI SDK provides a standard set of protobuffs and python utilities for implementing backends and gRPC. LeapfrogAI offers UI options for common use-cases like chat, summarization, and transcription. It can be deployed and run locally via UDS and Kubernetes, built out using Zarf packages. LeapfrogAI is supported by a community of users and contributors, including Defense Unicorns, Beast Code, Chainguard, Exovera, Hypergiant, Pulze, SOSi, United States Navy, United States Air Force, and United States Space Force.

llava-docker
This Docker image for LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant) provides a convenient way to run LLaVA locally or on RunPod. LLaVA is a powerful AI tool that combines natural language processing and computer vision capabilities. With this Docker image, you can easily access LLaVA's functionalities for various tasks, including image captioning, visual question answering, text summarization, and more. The image comes pre-installed with LLaVA v1.2.0, Torch 2.1.2, xformers 0.0.23.post1, and other necessary dependencies. You can customize the model used by setting the MODEL environment variable. The image also includes a Jupyter Lab environment for interactive development and exploration. Overall, this Docker image offers a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for leveraging LLaVA's capabilities.

carrot
The 'carrot' repository on GitHub provides a list of free and user-friendly ChatGPT mirror sites for easy access. The repository includes sponsored sites offering various GPT models and services. Users can find and share sites, report errors, and access stable and recommended sites for ChatGPT usage. The repository also includes a detailed list of ChatGPT sites, their features, and accessibility options, making it a valuable resource for ChatGPT users seeking free and unlimited GPT services.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.

AI-YinMei
AI-YinMei is an AI virtual anchor Vtuber development tool (N card version). It supports fastgpt knowledge base chat dialogue, a complete set of solutions for LLM large language models: [fastgpt] + [one-api] + [Xinference], supports docking bilibili live broadcast barrage reply and entering live broadcast welcome speech, supports Microsoft edge-tts speech synthesis, supports Bert-VITS2 speech synthesis, supports GPT-SoVITS speech synthesis, supports expression control Vtuber Studio, supports painting stable-diffusion-webui output OBS live broadcast room, supports painting picture pornography public-NSFW-y-distinguish, supports search and image search service duckduckgo (requires magic Internet access), supports image search service Baidu image search (no magic Internet access), supports AI reply chat box [html plug-in], supports AI singing Auto-Convert-Music, supports playlist [html plug-in], supports dancing function, supports expression video playback, supports head touching action, supports gift smashing action, supports singing automatic start dancing function, chat and singing automatic cycle swing action, supports multi scene switching, background music switching, day and night automatic switching scene, supports open singing and painting, let AI automatically judge the content.