MM-RLHF
The Next Step Forward in Multimodal LLM Alignment
Stars: 116

MM-RLHF is a comprehensive project for aligning Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) with human preferences. It includes a high-quality MLLM alignment dataset, a Critique-Based MLLM reward model, a novel alignment algorithm MM-DPO, and benchmarks for reward models and multimodal safety. The dataset covers image understanding, video understanding, and safety-related tasks with model-generated responses and human-annotated scores. The reward model generates critiques of candidate texts before assigning scores for enhanced interpretability. MM-DPO is an alignment algorithm that achieves performance gains with simple adjustments to the DPO framework. The project enables consistent performance improvements across 10 dimensions and 27 benchmarks for open-source MLLMs.
README:
[📖 arXiv Paper] [📊 MM-RLHF Data] [📝 Homepage]
[🏆 Reward Model] [🔮 MM-RewardBench] [🔮 MM-SafetyBench] [📈 Evaluation Suite]
[2025/03/04] 🔥 MM-RLHF is now available on model scope.
[2025/02/27] 🔥 MM-RLHF is now fully supported by swift. Simply process your data using scripts/convert_to_swift.py and execute the scripts/swift.sh command to get started.
[2025/02/10] 🔥 We are proud to open-source MM-RLHF, a comprehensive project for aligning Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) with human preferences. This release includes:
- A high-quality MLLM alignment dataset (120K samples, created by over 50 experts over two months, including ratings and manual annotations across eight dimensions.).
- A strong Critique-Based MLLM reward model which is trained on human annotations, achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on public benchmarks.
- A novel alignment algorithm MM-DPO, effectively integrates reward signals to improve the data efficiency of DPO training..
- Two new benchmarks designed for the reward model and multimodal safety, addressing gaps in existing benchmarks in these areas..
Our dataset and algorithms enable consistent performance improvements across 10 dimensions and 27 benchmarks for open-source MLLMs.
1. MM-RLHF Dataset (data.jsonl in MM-RLHF Data)
- 20k instructions covering image understanding, video understanding, and safety-related tasks.
- Each instruction includes 3-5 model-generated responses, along with human-annotated scores, rankings, and fine-grained textual feedback.
-
80k comparison pairs derived from ranked samples for each instruction, suitable for RLHF training.

- We release the MM-RLHF-Reward-7B, a Critique-Based Reward Model that generates critiques of candidate texts before assigning scores, offering enhanced interpretability and more informative feedback.
- Includes the training algorithm for the reward model, enabling researchers to reproduce and extend our work.
- Complete training code for MM-DPO, a novel alignment algorithm that achieves significant performance gains with simple adjustments to the DPO framework.
- MM-RLHF-RewardBench: Evaluates the quality of reward models.
- MM-RLHF-SafetyBench: Focuses on MLLM safety, including tasks like adversarial attacks, red teaming, jailbreaking, and harmful content detection.
git clone https://github.com/yfzhang114/MM-RLHF
cd MM-RLHFInstall the inference package:
conda create -n llava python=3.10 -y
conda activate llava
pip install --upgrade pip # Enable PEP 660 support.
pip install -e .
pip install -e ".[train]"
pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolationDownload 📊 MM-RLHF Data, unzip the image and video datasets, and the final structure should look like this:
MM-RLHF
-- | long
-- | mcq
-- | safety
-- | short
-- | data.jsonl
-- | dpo_pairs.jsonl
Here, data.jsonl contains all labeled information, and dpo_pairs.jsonl contains pairs of different ranks used for subsequent DPO and reward model training. The other folders contain the image and video frames.
Specify the model to learn the critic and provide the reward's loss weight, such as critic_rewards_weight and float_rewards_weight.
sh scripts/train/critic_reward_7b.shStep 1: Precompute Logits with Reference Model
To save GPU memory during DPO training, precompute logits using the reference model. Specify DATA_PATH and OUTPUT_DATA_PATH in the script.
sh scripts/train/generate_ref_logits.shThe output file will add elements like "reference_chosen_logp" and "reference_rejected_logp" to the data.
Step 2: Run DPO Algorithm with Precomputed Logits
sh scripts/train/dpo_ov7b.shFor alignment models, the evaluation code is available in the mmrlhf-eval repository. This code provides various evaluation tasks that test the alignment capabilities of your model across multiple benchmarks. These benchmarks include standard tests for model robustness, safety, and hallucination handling in multimodal contexts.
For reward models, we offer the MM-RLHF-RewardBench (available on Hugging Face at MM-RLHF-RewardBench) for detailed evaluation. To perform the evaluation, download the required images and the mm_reward_bench.jsonl file from the repository and place them in the appropriate directories. Then, follow these steps:
-
Download the dataset and necessary files:
- Ensure the repository contains the image data and the
mm_reward_bench.jsonlfile in the designated folder (path_to_data/).
- Ensure the repository contains the image data and the
-
Run the reward model evaluation: This step involves evaluating the reward model against the dataset by running the following command:
python llava/eval/eval_mm_reward_bench.py --model-path your_reward_model --question-file path_to_data/mm_reward_bench.jsonl --answers-file your_answer_file
-
Calculate performance metrics: After generating the answer file, you can calculate the performance of your reward model by running the following command:
python llava/eval/cal_performance_mmreward_bench.py --input_file your_answer_file
If you find it useful for your research and applications, please cite related papers/blogs using this BibTeX:
@article{zhang2025mm,
title={MM-RLHF: The Next Step Forward in Multimodal LLM Alignment},
author={Zhang, Yi-Fan and Yu, Tao and Tian, Haochen and Fu, Chaoyou and Li, Peiyan and Zeng, Jianshu and Xie, Wulin and Shi, Yang and Zhang, Huanyu and Wu, Junkang and others},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.10391},
year={2025}
}- MME-RealWorld: Could Your Multimodal LLM Challenge High-Resolution Real-World Scenarios that are Difficult for Humans?
- MME-Survey: A Comprehensive Survey on Evaluation of Multimodal LLMs
- Beyond LLaVA-HD: Diving into High-Resolution Large Multimodal Models
- VITA-1.5: Towards GPT-4o Level Real-Time Vision and Speech Interaction
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for MM-RLHF
Similar Open Source Tools

MM-RLHF
MM-RLHF is a comprehensive project for aligning Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) with human preferences. It includes a high-quality MLLM alignment dataset, a Critique-Based MLLM reward model, a novel alignment algorithm MM-DPO, and benchmarks for reward models and multimodal safety. The dataset covers image understanding, video understanding, and safety-related tasks with model-generated responses and human-annotated scores. The reward model generates critiques of candidate texts before assigning scores for enhanced interpretability. MM-DPO is an alignment algorithm that achieves performance gains with simple adjustments to the DPO framework. The project enables consistent performance improvements across 10 dimensions and 27 benchmarks for open-source MLLMs.
llms-interview-questions
This repository contains a comprehensive collection of 63 must-know Large Language Models (LLMs) interview questions. It covers topics such as the architecture of LLMs, transformer models, attention mechanisms, training processes, encoder-decoder frameworks, differences between LLMs and traditional statistical language models, handling context and long-term dependencies, transformers for parallelization, applications of LLMs, sentiment analysis, language translation, conversation AI, chatbots, and more. The readme provides detailed explanations, code examples, and insights into utilizing LLMs for various tasks.
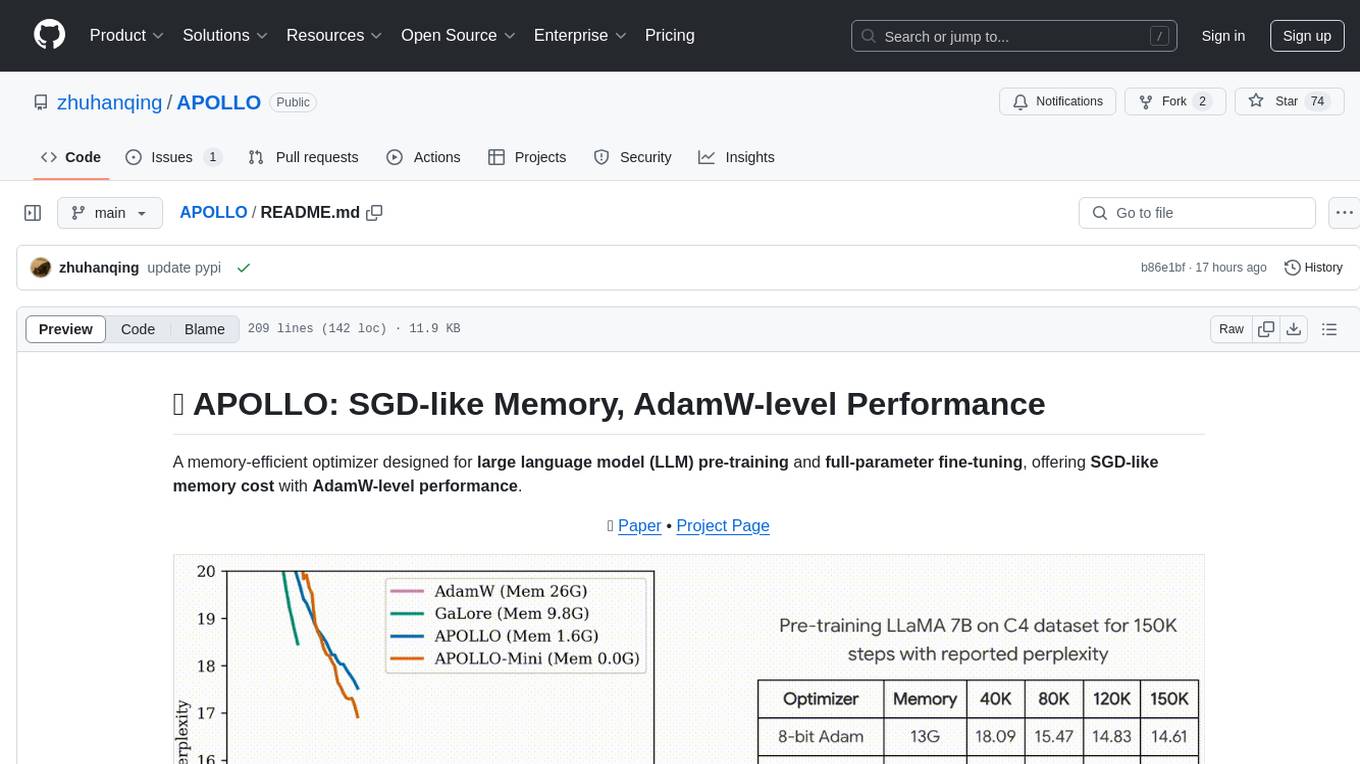
APOLLO
APOLLO is a memory-efficient optimizer designed for large language model (LLM) pre-training and full-parameter fine-tuning. It offers SGD-like memory cost with AdamW-level performance. The optimizer integrates low-rank approximation and optimizer state redundancy reduction to achieve significant memory savings while maintaining or surpassing the performance of Adam(W). Key contributions include structured learning rate updates for LLM training, approximated channel-wise gradient scaling in a low-rank auxiliary space, and minimal-rank tensor-wise gradient scaling. APOLLO aims to optimize memory efficiency during training large language models.
llmxcpg
LLMxCPG is a framework for vulnerability detection using Code Property Graphs (CPG) and Large Language Models (LLM). It involves a two-phase process: Slice Construction where an LLM generates queries for a CPG to extract a code slice, and Vulnerability Detection where another LLM classifies the code slice as vulnerable or safe. The repository includes implementations of baseline models, information on datasets, scripts for running models, prompt templates, query generation examples, and configurations for fine-tuning models.
octocode-mcp
Octocode is a methodology and platform that empowers AI assistants with the skills of a Senior Staff Engineer. It transforms how AI interacts with code by moving from 'guessing' based on training data to 'knowing' based on deep, evidence-based research. The ecosystem includes the Manifest for Research Driven Development, the MCP Server for code interaction, Agent Skills for extending AI capabilities, a CLI for managing agent capabilities, and comprehensive documentation covering installation, core concepts, tutorials, and reference materials.
DriveLM
DriveLM is a multimodal AI model that enables autonomous driving by combining computer vision and natural language processing. It is designed to understand and respond to complex driving scenarios using visual and textual information. DriveLM can perform various tasks related to driving, such as object detection, lane keeping, and decision-making. It is trained on a massive dataset of images and text, which allows it to learn the relationships between visual cues and driving actions. DriveLM is a powerful tool that can help to improve the safety and efficiency of autonomous vehicles.
veScale
veScale is a PyTorch Native LLM Training Framework. It provides a set of tools and components to facilitate the training of large language models (LLMs) using PyTorch. veScale includes features such as 4D parallelism, fast checkpointing, and a CUDA event monitor. It is designed to be scalable and efficient, and it can be used to train LLMs on a variety of hardware platforms.
llamafarm
LlamaFarm is a comprehensive AI framework that empowers users to build powerful AI applications locally, with full control over costs and deployment options. It provides modular components for RAG systems, vector databases, model management, prompt engineering, and fine-tuning. Users can create differentiated AI products without needing extensive ML expertise, using simple CLI commands and YAML configs. The framework supports local-first development, production-ready components, strategy-based configuration, and deployment anywhere from laptops to the cloud.
VisioFirm
VisioFirm is an open-source, AI-powered image annotation tool designed to accelerate labeling for computer vision tasks like classification, object detection, oriented bounding boxes (OBB), segmentation and video annotation. Built for speed and simplicity, it leverages state-of-the-art models for semi-automated pre-annotations, allowing you to focus on refining rather than starting from scratch. Whether you're preparing datasets for YOLO, SAM, or custom models, VisioFirm streamlines your workflow with an intuitive web interface and powerful backend. Perfect for researchers, data scientists, and ML engineers handling large image datasets—get high-quality annotations in minutes, not hours!
EnvScaler
EnvScaler is an automated, scalable framework that creates tool-interactive environments for training LLM agents. It consists of SkelBuilder for environment description mining and quality inspection, ScenGenerator for synthesizing multiple environment scenarios, and modules for supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning. The tool provides data, models, and evaluation guides for users to build, generate scenarios, collect training data, train models, and evaluate performance. Users can interact with environments, build environments from scratch, and improve LLMs' task-solving abilities in complex environments.
kserve
KServe provides a Kubernetes Custom Resource Definition for serving predictive and generative machine learning (ML) models. It encapsulates the complexity of autoscaling, networking, health checking, and server configuration to bring cutting edge serving features like GPU Autoscaling, Scale to Zero, and Canary Rollouts to ML deployments. KServe enables a simple, pluggable, and complete story for Production ML Serving including prediction, pre-processing, post-processing, and explainability. It is a standard, cloud agnostic Model Inference Platform for serving predictive and generative AI models on Kubernetes, built for highly scalable use cases.
holisticai
Holistic AI is an open-source library dedicated to assessing and improving the trustworthiness of AI systems. It focuses on measuring and mitigating bias, explainability, robustness, security, and efficacy in AI models. The tool provides comprehensive metrics, mitigation techniques, a user-friendly interface, and visualization tools to enhance AI system trustworthiness. It offers documentation, tutorials, and detailed installation instructions for easy integration into existing workflows.
eureka-framework
The Eureka Framework is an open-source toolkit that leverages advanced Artificial Intelligence and Decentralized Science principles to revolutionize scientific discovery. It enables researchers, developers, and decentralized organizations to explore scientific papers, conduct AI-driven experiments, monetize research contributions, provide token-gated access to AI agents, and customize AI agents for specific research domains. The framework also offers features like a RESTful API, robust scheduler for task automation, and webhooks for real-time notifications, empowering users to automate research tasks, enhance productivity, and foster a committed research community.
rllm
rLLM (relationLLM) is a Pytorch library for Relational Table Learning (RTL) with LLMs. It breaks down state-of-the-art GNNs, LLMs, and TNNs as standardized modules and facilitates novel model building in a 'combine, align, and co-train' way using these modules. The library is LLM-friendly, processes various graphs as multiple tables linked by foreign keys, introduces new relational table datasets, and is supported by students and teachers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University and Tsinghua University.
joliGEN
JoliGEN is an integrated framework for training custom generative AI image-to-image models. It implements GAN, Diffusion, and Consistency models for various image translation tasks, including domain and style adaptation with conservation of semantics. The tool is designed for real-world applications such as Controlled Image Generation, Augmented Reality, Dataset Smart Augmentation, and Synthetic to Real transforms. JoliGEN allows for fast and stable training with a REST API server for simplified deployment. It offers a wide range of options and parameters with detailed documentation available for models, dataset formats, and data augmentation.
For similar tasks

MM-RLHF
MM-RLHF is a comprehensive project for aligning Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) with human preferences. It includes a high-quality MLLM alignment dataset, a Critique-Based MLLM reward model, a novel alignment algorithm MM-DPO, and benchmarks for reward models and multimodal safety. The dataset covers image understanding, video understanding, and safety-related tasks with model-generated responses and human-annotated scores. The reward model generates critiques of candidate texts before assigning scores for enhanced interpretability. MM-DPO is an alignment algorithm that achieves performance gains with simple adjustments to the DPO framework. The project enables consistent performance improvements across 10 dimensions and 27 benchmarks for open-source MLLMs.
CritiqueLLM
CritiqueLLM is an official implementation of a model designed for generating informative critiques to evaluate large language model generation. It includes functionalities for data collection, referenced pointwise grading, referenced pairwise comparison, reference-free pairwise comparison, reference-free pointwise grading, inference for pointwise grading and pairwise comparison, and evaluation of the generated results. The model aims to provide a comprehensive framework for evaluating the performance of large language models based on human ratings and comparisons.
Vision-LLM-Alignment
Vision-LLM-Alignment is a repository focused on implementing alignment training for visual large language models (LLMs), including SFT training, reward model training, and PPO/DPO training. It supports various model architectures and provides datasets for training. The repository also offers benchmark results and installation instructions for users.
foundations-of-gen-ai
This repository contains code for the O'Reilly Live Online Training for 'Transformer Architectures for Generative AI'. The course provides a deep understanding of transformer architectures and their impact on natural language processing (NLP) and vision tasks. Participants learn to harness transformers to tackle problems in text, image, and multimodal AI through theory and practical exercises.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.