
gptel-aibo
An AI Writing Assistant for Emacs
Stars: 51

gptel-aibo is an AI writing assistant system built on top of gptel. It helps users create and manage content in Emacs, including code, documentation, and novels. Users can interact with the Language Model (LLM) to receive suggestions and apply them easily. The tool provides features like sending requests, applying suggestions, and completing content at the current position based on context. Users can customize settings and face settings for a better user experience. gptel-aibo aims to enhance productivity and efficiency in content creation and management within Emacs environment.
README:
gptel-aibo is an AI writing assistant system built on top of
gptel .
It helps you create and manage content in Emacs, including code, documentation,
and even novels. As you talk to the LLM, it automatically sends the content (or
a portion of it) that you're currently working on, allowing you to refer to
elements like "this function," "this class," "this file," etc. It also defines
an action set and its format with the LLM, so once a response is received, you
can easily apply the suggestions with a single command (
gptel-aibo-apply-last-suggestions, bound to C-c !).
The term aibo, meaning partner, is currently ambiguous—it could refer to gptel’s partner, or the user’s.
This package requires gptel and access to any LLM through it. See its README for details on setting up your LLM environment.
Since this package is developed based on the Doom Emacs gptel package, it uses
a very recent version of gptel. If you're not using Doom Emacs, it's recommended
to install gptel using straight.el or the built-in package-vc-install.
In your packages.el, add this line:
(package! gptel-aibo :recipe (:host github :repo "dolmens/gptel-aibo"))Note: In the gptel-aibo interface, it overrides the flycheck keybinding
C-c ! (you generally won't need to use flycheck in the gptel-aibo
interface, especially with the shortcut key). Therefore, if you want to
configure further using use-package!, make sure gptel-aibo is loaded after
flycheck.
(use-package! gptel-aibo
:after (gptel flycheck))Alternatively, define a different keybinding:
(use-package! gptel-aibo
:after (gptel)
:config
(define-key gptel-aibo-mode-map
(kbd "C-c /") #'gptel-aibo-apply-last-suggestions))With the gptel-aibo interactive command, you can open or switch to an existing
gptel-aibo console, which is a markdown page with the gptel-aibo minor
mode enabled, an extension of gptel-mode.
To get started, open your file, move the cursor to the section you're working
on, or even start from a project-related buffer, such as the compilation buffer,
and then switch to the gptel-aibo console. There, you can talk to the LLM
and receive suggestions. Use gptel-aibo-send to send your request, which is
bound to C-c RET, just like the send command in gptel-mode.
Once a response is received, you can apply it using the command
gptel-aibo-apply-last-suggestions (bound to C-c !), or continue the
conversation with more detailed instructions.
There is also a custom variable, gptel-aibo-auto-apply. When set, gptel-aibo
will automatically apply the LLM’s response to your project after receiving it.
This makes gptel-aibo function like the aider’s no-auto-commits. Use it carefully!
gptel-aibo also provides a minor mode gptel-aibo-complete-mode and an
interactive command gptel-aibo-complete-at-point, which can insert relevant
content at the current position based on the context. For example, after
writing a function comment, you can use this single command to generate the
corresponding code. Use TAB or Enter to accept, and other keys to discard.
You can globally enable gptel-aibo-complete-mode, which has no side effects
and only works when you invoke it. You can also add it to specific mode hooks if
that suits your workflow. In the minor mode, gptel-aibo-complete-at-point is
bound to C-c C-c i. It’s a bit long, but less likely to upset someone by
taking away their favorite key. You can also bind your own key, for example:
- Doom Emacs
(use-package! gptel-aibo
:after (gptel)
:config
(define-key gptel-aibo-complete-mode-map
(kbd "C-c i") #'gptel-aibo-complete-at-point)
(add-hook 'prog-mode-hook #'gptel-aibo-complete-mode))NOTE: Tasks like refactoring, which involve multiple files, require you to
set gptel-aibo-max-buffer-count to a larger value, such as 5. In the long run,
this inconvenience will be eliminated through a more automated approach, like
tool calling.
- generate a docstring for this function
- make the comment conform to Doxygen style
- generate the code for this function based on the comments (better done with
gptel-aibo-complete-at-point) - refactor this function and reorganize its logic
- reformat this function, as some lines are too long
- extract the common parts of functions A and B into a new function
- change the coding style from snake_case to camelCase (or vice versa)
-
gptel-aibo-max-buffer-sizeThe size limit for the buffers that is automatically sent to the LLM.
If the working buffer (the buffer you are currently working on) exceeds this size, only a fragment of content around the cursor (typically a function or class) will be sent.
For other buffers in the same project: if their size exceeds this limit and they have an outline available, only the outline will be sent. Otherwise, their content will not be sent.
The default value is 16000.
-
gptel-aibo-max-buffer-countThe maximum number of buffers within the same project as your working buffer that are automatically sent to the LLM.
The default value is 2.
-
gptel-aibo-default-modeFunctions similarly to
gptel-default-mode; when set, it takes precedence over the latter. -
gptel-aibo-prompt-prefix-alistFunctions similarly to
gptel-default-mode; when set, it takes precedence over the latter.
-
gptel-aibo-op-displayCurrently, the
<OP>marker is displayed as the character 🏹 in the gptel-aibo console. If you prefer a different symbol, you can define another one, choose different characters for different operations, or even disable it entirely. -
gptel-aibo-op-faceThis setting controls the face for OP action names, such as
MODIFY,CREATE, andDELETE. You can customize it, or even set different faces for different actions.For more details, check out
gptel-aibo-face.el.
To make the gptel-aibo console look a bit fancier, I copied the following markdown configuration from this Reddit post beautify_markdown_on_emacs. Thanks to the original author!
If you like it, you can add it to your configuration file.
(after! markdown-mode
(custom-set-faces!
'(markdown-header-delimiter-face :foreground "#616161" :height 0.9)
'(markdown-header-face-1 :height 1.8 :foreground "#A3BE8C" :weight extra-bold :inherit markdown-header-face)
'(markdown-header-face-2 :height 1.4 :foreground "#EBCB8B" :weight extra-bold :inherit markdown-header-face)
'(markdown-header-face-3 :height 1.2 :foreground "#D08770" :weight extra-bold :inherit markdown-header-face)
'(markdown-header-face-4 :height 1.15 :foreground "#BF616A" :weight bold :inherit markdown-header-face)
'(markdown-header-face-5 :height 1.1 :foreground "#b48ead" :weight bold :inherit markdown-header-face)
'(markdown-header-face-6 :height 1.05 :foreground "#5e81ac" :weight semi-bold :inherit markdown-header-face)))- The file path and content of the current working buffer, as well as buffers from the same project, may be sent to the LLM.
- There are three actions defined in
gptel-aibo: modification, creation, and deletion. These actions are only allowed if the target is under the project root of the current working buffer. If a buffer is not part of a project, only modifications to itself can be executed. - Modifications and creations are saved immediately after they are applied, with an additional confirmation required for deletion. While some changes can be reverted using Emacs’ undo system, it’s best to place your project under version control to enhance safety and recoverability.
- To align with MELPA naming conventions, the initial draft prefix
gptaihas been changed to the officialgptel-aibo.
- interactive command
gptai→gptel-aibo -
gptai-apply-last-suggestions→gptel-aibo-apply-last-suggestions -
gptai-mode-map→gptel-aibo-mode-map -
gptai-complete-at-point→gptel-aibo-complete-at-point -
gptai-complete-mode-map→gptel-aibo-complete-mode-map
- The variable
gptai--max-buffer-sizehas been renamed togptel-aibo-max-buffer-size. - The variable
gptai--max-project-buffer-sizehas been removed. Both the working buffer and the project buffers are now controlled bygptel-aibo-max-buffer-size. - The variable
gptai--max-project-buffer-counthas been renamed togptel-aibo-max-buffer-count.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for gptel-aibo
Similar Open Source Tools

gptel-aibo
gptel-aibo is an AI writing assistant system built on top of gptel. It helps users create and manage content in Emacs, including code, documentation, and novels. Users can interact with the Language Model (LLM) to receive suggestions and apply them easily. The tool provides features like sending requests, applying suggestions, and completing content at the current position based on context. Users can customize settings and face settings for a better user experience. gptel-aibo aims to enhance productivity and efficiency in content creation and management within Emacs environment.

reader
Reader is a tool that converts any URL to an LLM-friendly input with a simple prefix `https://r.jina.ai/`. It improves the output for your agent and RAG systems at no cost. Reader supports image reading, captioning all images at the specified URL and adding `Image [idx]: [caption]` as an alt tag. This enables downstream LLMs to interact with the images in reasoning, summarizing, etc. Reader offers a streaming mode, useful when the standard mode provides an incomplete result. In streaming mode, Reader waits a bit longer until the page is fully rendered, providing more complete information. Reader also supports a JSON mode, which contains three fields: `url`, `title`, and `content`. Reader is backed by Jina AI and licensed under Apache-2.0.
kwaak
Kwaak is a tool that allows users to run a team of autonomous AI agents locally from their own machine. It enables users to write code, improve test coverage, update documentation, and enhance code quality while focusing on building innovative projects. Kwaak is designed to run multiple agents in parallel, interact with codebases, answer questions about code, find examples, write and execute code, create pull requests, and more. It is free and open-source, allowing users to bring their own API keys or models via Ollama. Kwaak is part of the bosun.ai project, aiming to be a platform for autonomous code improvement.
easy-llama
easy-llama is a Python tool designed to make text generation using on-device large language models (LLMs) as easy as possible. It provides an abstraction layer over llama-cpp-python, simplifying the process of utilizing language models. The tool offers features such as automatic context length adjustment, terminal-based interactive chat, programmatic multi-turn interaction, support for various prompt formats, message-based context length handling, retrieval of likely next tokens, and compatibility with multiple models supported by llama-cpp-python. The upcoming version 0.2.0 will remove the llama-cpp-python dependency for improved efficiency and maintainability.
ComfyUI-mnemic-nodes
ComfyUI-mnemic-nodes is a repository hosting a collection of nodes developed for ComfyUI, providing useful components to enhance project functionality. The nodes include features like returning file paths, saving text files, downloading images from URLs, tokenizing text, cleaning strings, querying Groq language models, generating negative prompts, and more. Some nodes are experimental and marked with a 'Caution' label. Installation instructions and setup details are provided for each node, along with examples and presets for different tasks.
sage
Sage is a tool that allows users to chat with any codebase, providing a chat interface for code understanding and integration. It simplifies the process of learning how a codebase works by offering heavily documented answers sourced directly from the code. Users can set up Sage locally or on the cloud with minimal effort. The tool is designed to be easily customizable, allowing users to swap components of the pipeline and improve the algorithms powering code understanding and generation.
abliteration
Abliteration is a tool that allows users to create abliterated models using transformers quickly and easily. It is not a tool for uncensorship, but rather for making models that will not explicitly refuse users. Users can clone the repository, install dependencies, and make abliterations using the provided commands. The tool supports adjusting parameters for stubborn models and offers various options for customization. Abliteration can be used for creating modified models for specific tasks or topics.
web-codegen-scorer
Web Codegen Scorer is a tool designed to evaluate the quality of web code generated by Large Language Models (LLMs). It allows users to make evidence-based decisions related to AI-generated code by iterating on system prompts, comparing code quality from different models, and monitoring code quality over time. The tool focuses specifically on web code and offers various features such as configuring evaluations, specifying system instructions, using built-in checks for code quality, automatically repairing issues, and viewing results with an intuitive report viewer UI.
paper-qa
PaperQA is a minimal package for question and answering from PDFs or text files, providing very good answers with in-text citations. It uses OpenAI Embeddings to embed and search documents, and includes a process of embedding docs, queries, searching for top passages, creating summaries, using an LLM to re-score and select relevant summaries, putting summaries into prompt, and generating answers. The tool can be used to answer specific questions related to scientific research by leveraging citations and relevant passages from documents.
web-llm
WebLLM is a modular and customizable javascript package that directly brings language model chats directly onto web browsers with hardware acceleration. Everything runs inside the browser with no server support and is accelerated with WebGPU. WebLLM is fully compatible with OpenAI API. That is, you can use the same OpenAI API on any open source models locally, with functionalities including json-mode, function-calling, streaming, etc. We can bring a lot of fun opportunities to build AI assistants for everyone and enable privacy while enjoying GPU acceleration.
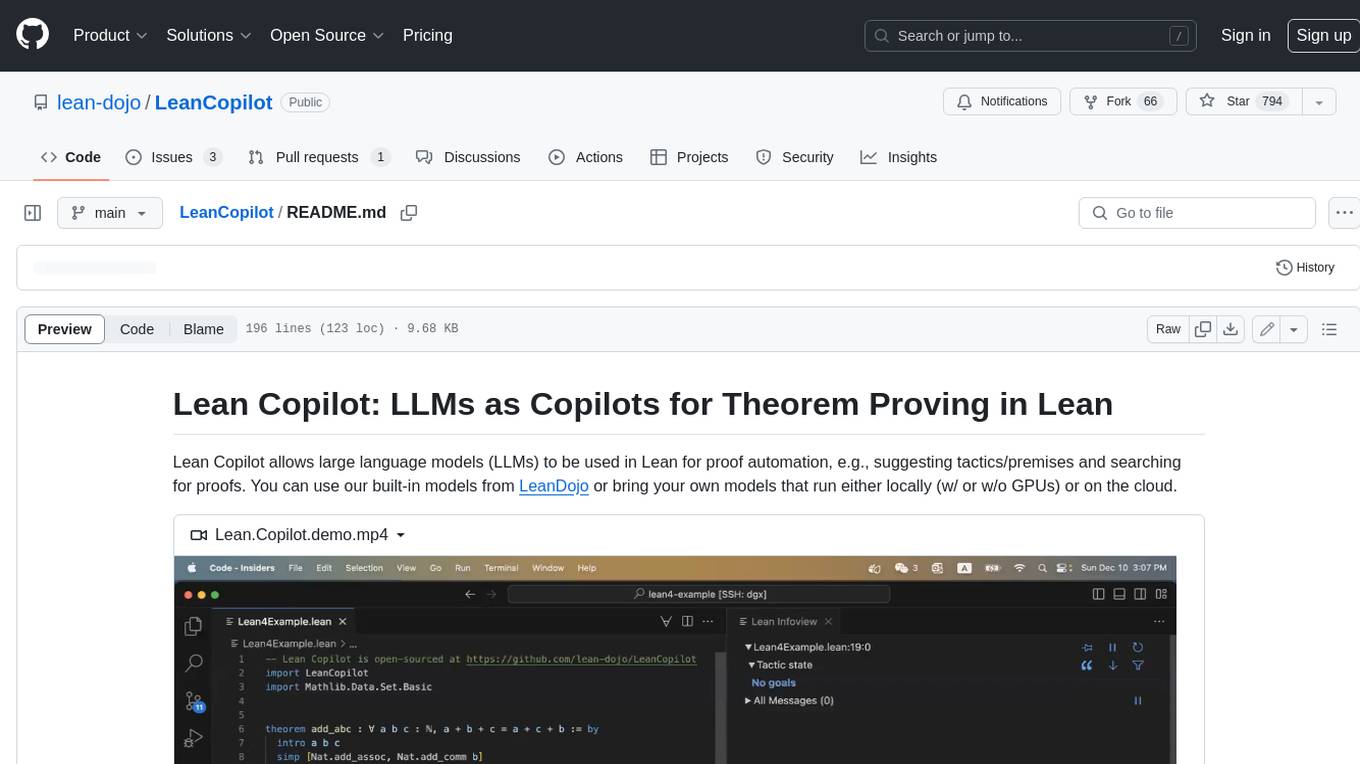
LeanCopilot
Lean Copilot is a tool that enables the use of large language models (LLMs) in Lean for proof automation. It provides features such as suggesting tactics/premises, searching for proofs, and running inference of LLMs. Users can utilize built-in models from LeanDojo or bring their own models to run locally or on the cloud. The tool supports platforms like Linux, macOS, and Windows WSL, with optional CUDA and cuDNN for GPU acceleration. Advanced users can customize behavior using Tactic APIs and Model APIs. Lean Copilot also allows users to bring their own models through ExternalGenerator or ExternalEncoder. The tool comes with caveats such as occasional crashes and issues with premise selection and proof search. Users can get in touch through GitHub Discussions for questions, bug reports, feature requests, and suggestions. The tool is designed to enhance theorem proving in Lean using LLMs.
fabric
Fabric is an open-source framework for augmenting humans using AI. It provides a structured approach to breaking down problems into individual components and applying AI to them one at a time. Fabric includes a collection of pre-defined Patterns (prompts) that can be used for a variety of tasks, such as extracting the most interesting parts of YouTube videos and podcasts, writing essays, summarizing academic papers, creating AI art prompts, and more. Users can also create their own custom Patterns. Fabric is designed to be easy to use, with a command-line interface and a variety of helper apps. It is also extensible, allowing users to integrate it with their own AI applications and infrastructure.

1backend
1Backend is a flexible and scalable platform designed for running AI models on private servers and handling high-concurrency workloads. It provides a ChatGPT-like interface for users and a network-accessible API for machines, serving as a general-purpose backend framework. The platform offers on-premise ChatGPT alternatives, a microservices-first web framework, out-of-the-box services like file uploads and user management, infrastructure simplification acting as a container orchestrator, reverse proxy, multi-database support with its own ORM, and AI integration with platforms like LlamaCpp and StableDiffusion.
allms
allms is a versatile and powerful library designed to streamline the process of querying Large Language Models (LLMs). Developed by Allegro engineers, it simplifies working with LLM applications by providing a user-friendly interface, asynchronous querying, automatic retrying mechanism, error handling, and output parsing. It supports various LLM families hosted on different platforms like OpenAI, Google, Azure, and GCP. The library offers features for configuring endpoint credentials, batch querying with symbolic variables, and forcing structured output format. It also provides documentation, quickstart guides, and instructions for local development, testing, updating documentation, and making new releases.
tonic_validate
Tonic Validate is a framework for the evaluation of LLM outputs, such as Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) pipelines. Validate makes it easy to evaluate, track, and monitor your LLM and RAG applications. Validate allows you to evaluate your LLM outputs through the use of our provided metrics which measure everything from answer correctness to LLM hallucination. Additionally, Validate has an optional UI to visualize your evaluation results for easy tracking and monitoring.
hash
HASH is a self-building, open-source database which grows, structures and checks itself. With it, we're creating a platform for decision-making, which helps you integrate, understand and use data in a variety of different ways.
For similar tasks

gptel-aibo
gptel-aibo is an AI writing assistant system built on top of gptel. It helps users create and manage content in Emacs, including code, documentation, and novels. Users can interact with the Language Model (LLM) to receive suggestions and apply them easily. The tool provides features like sending requests, applying suggestions, and completing content at the current position based on context. Users can customize settings and face settings for a better user experience. gptel-aibo aims to enhance productivity and efficiency in content creation and management within Emacs environment.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

onnxruntime-genai
ONNX Runtime Generative AI is a library that provides the generative AI loop for ONNX models, including inference with ONNX Runtime, logits processing, search and sampling, and KV cache management. Users can call a high level `generate()` method, or run each iteration of the model in a loop. It supports greedy/beam search and TopP, TopK sampling to generate token sequences, has built in logits processing like repetition penalties, and allows for easy custom scoring.

mistral.rs
Mistral.rs is a fast LLM inference platform written in Rust. We support inference on a variety of devices, quantization, and easy-to-use application with an Open-AI API compatible HTTP server and Python bindings.
generative-ai-python
The Google AI Python SDK is the easiest way for Python developers to build with the Gemini API. The Gemini API gives you access to Gemini models created by Google DeepMind. Gemini models are built from the ground up to be multimodal, so you can reason seamlessly across text, images, and code.
jetson-generative-ai-playground
This repo hosts tutorial documentation for running generative AI models on NVIDIA Jetson devices. The documentation is auto-generated and hosted on GitHub Pages using their CI/CD feature to automatically generate/update the HTML documentation site upon new commits.
chat-ui
A chat interface using open source models, eg OpenAssistant or Llama. It is a SvelteKit app and it powers the HuggingChat app on hf.co/chat.
MetaGPT
MetaGPT is a multi-agent framework that enables GPT to work in a software company, collaborating to tackle more complex tasks. It assigns different roles to GPTs to form a collaborative entity for complex tasks. MetaGPT takes a one-line requirement as input and outputs user stories, competitive analysis, requirements, data structures, APIs, documents, etc. Internally, MetaGPT includes product managers, architects, project managers, and engineers. It provides the entire process of a software company along with carefully orchestrated SOPs. MetaGPT's core philosophy is "Code = SOP(Team)", materializing SOP and applying it to teams composed of LLMs.
For similar jobs

sourcegraph
Sourcegraph is a code search and navigation tool that helps developers read, write, and fix code in large, complex codebases. It provides features such as code search across all repositories and branches, code intelligence for navigation and refactoring, and the ability to fix and refactor code across multiple repositories at once.
pr-agent
PR-Agent is a tool that helps to efficiently review and handle pull requests by providing AI feedbacks and suggestions. It supports various commands such as generating PR descriptions, providing code suggestions, answering questions about the PR, and updating the CHANGELOG.md file. PR-Agent can be used via CLI, GitHub Action, GitHub App, Docker, and supports multiple git providers and models. It emphasizes real-life practical usage, with each tool having a single GPT-4 call for quick and affordable responses. The PR Compression strategy enables effective handling of both short and long PRs, while the JSON prompting strategy allows for modular and customizable tools. PR-Agent Pro, the hosted version by CodiumAI, provides additional benefits such as full management, improved privacy, priority support, and extra features.
code-review-gpt
Code Review GPT uses Large Language Models to review code in your CI/CD pipeline. It helps streamline the code review process by providing feedback on code that may have issues or areas for improvement. It should pick up on common issues such as exposed secrets, slow or inefficient code, and unreadable code. It can also be run locally in your command line to review staged files. Code Review GPT is in alpha and should be used for fun only. It may provide useful feedback but please check any suggestions thoroughly.
DevoxxGenieIDEAPlugin
Devoxx Genie is a Java-based IntelliJ IDEA plugin that integrates with local and cloud-based LLM providers to aid in reviewing, testing, and explaining project code. It supports features like code highlighting, chat conversations, and adding files/code snippets to context. Users can modify REST endpoints and LLM parameters in settings, including support for cloud-based LLMs. The plugin requires IntelliJ version 2023.3.4 and JDK 17. Building and publishing the plugin is done using Gradle tasks. Users can select an LLM provider, choose code, and use commands like review, explain, or generate unit tests for code analysis.
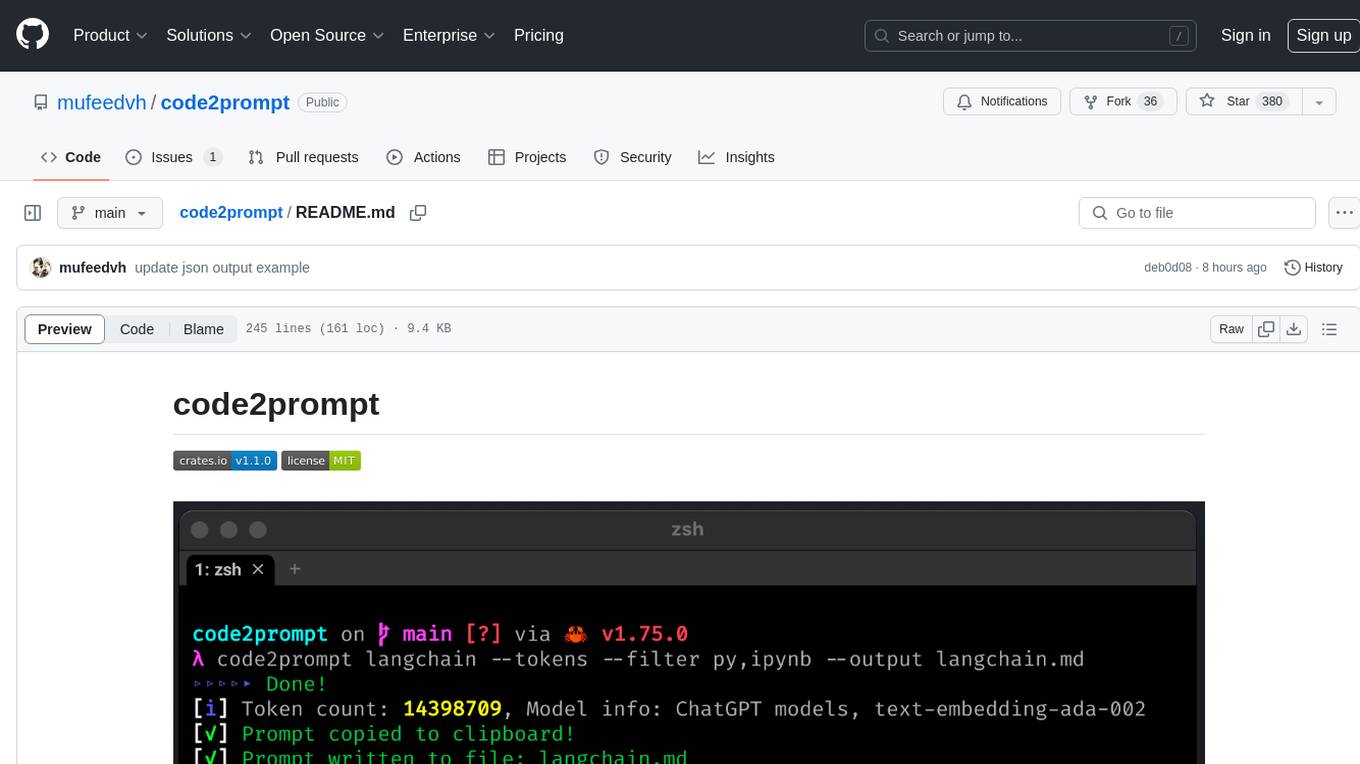
code2prompt
code2prompt is a command-line tool that converts your codebase into a single LLM prompt with a source tree, prompt templating, and token counting. It automates generating LLM prompts from codebases of any size, customizing prompt generation with Handlebars templates, respecting .gitignore, filtering and excluding files using glob patterns, displaying token count, including Git diff output, copying prompt to clipboard, saving prompt to an output file, excluding files and folders, adding line numbers to source code blocks, and more. It helps streamline the process of creating LLM prompts for code analysis, generation, and other tasks.
ai-codereviewer
AI Code Reviewer is a GitHub Action that utilizes OpenAI's GPT-4 API to provide intelligent feedback and suggestions on pull requests. It helps enhance code quality and streamline the code review process by offering insightful comments and filtering out specified files. The tool is easy to set up and integrate into GitHub workflows.
github-pr-summary
github-pr-summary is a bot designed to summarize GitHub Pull Requests, helping open source contributors make faster decisions. It automatically summarizes commits and changed files in PRs, triggered by new commits or a magic trigger phrase. Users can deploy their own code review bot in 3 steps: create a bot from their GitHub repo, configure it to review PRs, and connect to GitHub for access to the target repo. The bot runs on flows.network using Rust and WasmEdge Runtimes. It utilizes ChatGPT/4 to review and summarize PR content, posting the result back as a comment on the PR. The bot can be used on multiple repos by creating new flows and importing the source code repo, specifying the target repo using flow config. Users can also change the magic phrase to trigger a review from a PR comment.
fittencode.nvim
Fitten Code AI Programming Assistant for Neovim provides fast completion using AI, asynchronous I/O, and support for various actions like document code, edit code, explain code, find bugs, generate unit test, implement features, optimize code, refactor code, start chat, and more. It offers features like accepting suggestions with Tab, accepting line with Ctrl + Down, accepting word with Ctrl + Right, undoing accepted text, automatic scrolling, and multiple HTTP/REST backends. It can run as a coc.nvim source or nvim-cmp source.

