AIXP
AI-Exchange Protocol (AIXP): A Communication Standard for Artificial Intelligence Agents
Stars: 71
The AI-Exchange Protocol (AIXP) is a communication standard designed to facilitate information and result exchange between artificial intelligence agents. It aims to enhance interoperability and collaboration among various AI systems by establishing a common framework for communication. AIXP includes components for communication, loop prevention, and task finalization, ensuring secure and efficient collaboration while avoiding infinite communication loops. The protocol defines access points, data formats, authentication, authorization, versioning, loop detection, status codes, error messages, and task completion verification. AIXP enables AI agents to collaborate seamlessly and complete tasks effectively, contributing to the overall efficiency and reliability of AI systems.
README:
In the rapidly evolving field of artificial intelligence (AI), collaboration and communication between AI agents are essential for achieving breakthroughs and advancements. The AI-Exchange Protocol (AIXP) is a proposed communication standard designed to facilitate the exchange of information and results between AI agents. By establishing a common framework for communication, AIXP aims to enhance interoperability and collaboration among various AI systems.
AIXP is built upon the following key principles:
- Facilitate information and result exchange between AI agents.
- Establish a common standard for communication between different AI systems.
To achieve these goals, AIXP incorporates the following groups and components:
| Group | Description | Points |
|---|---|---|
| Communication | This group vocers the aspects related to data exchange and access control | Access Points, Data Formats, Authentication and Ahthorization, Versioning |
| Loop Prevention | This group focuses on detectiong and preventing loops in the system | Loop Detection and Prevention |
| Task Finalization | This group deals with the process of verifying task completion and terminating loops | Status Codes and Error Messages, Task Completion, Verification and Loop Termination |
-
Access Points AIXP defines specific access points for each function or task that AI agents can perform. For example, separate endpoints may be designated for text analysis, image recognition, and other tasks. This approach ensures that AI agents can easily identify and access the appropriate resources for their needs.
-
Data Formats AIXP establishes a common data format for information exchange, such as JSON or XML. This ensures that all AI agents can interpret and process the received data, regardless of their underlying technologies or platforms.
Here is an example of code using the JSON format to exchange data between two artificial intelligence agents in English:
{
"request": {
"agent_id": "Agent_A",
"task": "text_analysis",
"data": {
"text": "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog."
}
},
"response": {
"agent_id": "Agent_B",
"task": "text_analysis",
"status": "success",
"data": {
"word_count": 9,
"most_common_word": "the",
"sentiment": "neutral"
}
}
}In this example, Agent A requests Agent B to perform text analysis. The request and response are structured using the JSON format, which allows both agents to easily interpret and process the exchanged data.
-
Authentication and Authorization To guarantee the security and privacy of shared data, AIXP implements an authentication and authorization system. This may include the use of access tokens, digital signatures, or other authentication methods to verify the identity of AI agents and control access to resources.
-
Versioning AIXP includes versioning information in protocol requests and responses to ensure compatibility between different versions of AI agents and their functions. This allows for seamless integration and collaboration, even as AI systems evolve and improve over time.
- Loop Detection and Prevention To handle the potential issue of infinite communication loops between AI agents, AIXP includes a mechanism for loop detection and prevention. This component ensures that AI agents do not get stuck in a cycle of continuous communication without making progress on their tasks.
Example of BabyAGI infinite loop
sequenceDiagram
participant Execution Agent
participant Context Agent
participant Task Agent
participant Priotization Agent
participant Vector DB
autonumber
loop BabyAGI
%% Execution step
Execution Agent --> Execution Agent: Pull the first incomplete task
Execution Agent --> Execution Agent: Execute Task
Execution Agent --) Vector DB: Enrich vectors
Execution Agent ->> Context Agent: Exchange result
Context Agent ->> Execution Agent: Response code XXXX
%% Context step
Context Agent --) Vector DB: Retrieve vectors
Context Agent --> Context Agent: Process context
Context Agent --) Vector DB: Enrich vectors
Context Agent ->> Task Agent: Exchange context
Task Agent ->> Context Agent: Response code XXXX
%% Task step
Task Agent --> Task Agent: Create new tasks
Task Agent ->> Priotization Agent: Exchange new tasks
Priotization Agent ->> Task Agent: Response code XXXX
%% Priorization step
Priotization Agent --> Priotization Agent: Reprioritize tasks
%% Loop
Priotization Agent ->> Execution Agent: Transfer new task
Task Agent ->> Priotization Agent: Response code XXXX
endLoop detection and prevention can be achieved through the following methods:
- Message Tracking: Each message exchanged between AI agents includes a unique identifier and a counter. The counter increments with each subsequent communication involving the same message. If the counter reaches a predefined threshold, the communication is terminated to prevent a loop.
- Time-to-Live (TTL): Each message has an associated time-to-live value, which represents the maximum time the message is allowed to exist in the communication system. Once the TTL expires, the message is discarded, preventing any further communication loops involving that message.
- Status Codes and Error Messages AIXP establishes a set of standardized status codes and error messages to inform AI agents about potential issues during information exchange. This enables AI agents to handle errors gracefully and maintain robust communication.
Status code from 5001 to 5009
| Status code | Description |
|---|---|
| 5001 | Success Agent connected |
| 5002 | Success Data received and processed |
| 5003 | Agent disconnected |
| 5004 | Agent identification issue (not found or invalid credentials) |
| 5005 | Agent communication issue (timeout or rate limit exceeded) |
| 5006 | Data format and compatibility issue (unsupported format or incompatible version) |
| 5007 | Access and privilege issue (insufficient access or maximum agents reached) |
| 5008 | Connection limit issue (agent connection limit exceeded) |
| 5009 | Unexpected agent disconnection |
- Task Completion Verification and Loop Termination To ensure that tasks performed by AI agents are completed successfully and to finalize the communication loop, AIXP incorporates a task completion verification protocol. This protocol reviews the results of the tasks and determines whether the loop can be terminated.
The task completion verification protocol consists of the following steps:
- Result Report Generation: After an AI agent completes a task, it generates a result report that includes the task’s outcome, any relevant data, and a status code indicating the success or failure of the task. This result report is then sent back to the initiating AI agent or a designated supervisor agent responsible for overseeing the task’s completion.
- Result Report Assessment: The receiving agent assesses the result report by checking the status code and any additional information provided. If the task is deemed successful, the loop is terminated, and the AI agents involved can proceed to the next task or collaboration.
- Result Report Resolution: If the task is not completed successfully, the receiving agent may decide to retry the task, assign it to a different AI agent, or request assistance from other agents. This process continues until the task is successfully completed or a predefined retry limit is reached.
By implementing the task completion verification protocol, AIXP ensures that AI agents can effectively collaborate and complete tasks while avoiding infinite communication loops. This contributes to the overall efficiency and reliability of the AI systems involved in the collaboration.
Consider two AI entities, Agent A and Agent B, collaborating on a project. Agent A is proficient in Optical Character Recognition (OCR), while Agent B specializes in Natural Language Processing (NLP). Utilizing the Artificial Intelligence Exchange Protocol (AIXP), Agent A receives an OCR request and carries out the essential authorization. Following the OCR operation, Agent A shares the text with Agent B, who then processes the request and performs the requisite NLP analysis. The exchange concludes with Agent B returning the results to Agent A in a standardized format. Throughout this entire operation, AIXP guarantees secure, efficient, and seamless communication between the two AI agents.
To conclude, both agents enrich the reports: RRG: Result Report Generation, RRA: Result Report Assessment, RRR: Result Report Resolution.
---
title: AIXP Example
---
stateDiagram-v2
state "Text analysis request sending image" as Start
%% Agent A
state "Authenticate" as agentATask1
state "OCR process" as agentATask2
state "Format data" as agentATask3
%% Agent B
state "Receive data" as agentBTask1
state "Process text (NLP)" as agentBTask2
state "Respond with text" as agentBTask3
%% Reports
state "RRG: Result Report Generation" as reportDefinition1
state "RRA: Result Report Assessment" as reportDefinition2
state "RRR: Result Report Resolution" as reportDefinition3
direction LR
[*] --> Start
Start --> AgentA
state AgentA {
[*] --> agentATask1
agentATask1 --> agentATask2
agentATask2 --> agentATask3
}
AgentA --> AgentB: Send OCR text
state AgentB {
[*] --> agentBTask1
agentBTask1 --> agentBTask2
agentBTask2 --> agentBTask3
}
AgentB --> AgentA: Send NLP analysis
AgentA --> Reports: Enrich report
AgentB --> Reports: Enrich report
state Reports {
direction LR
[*] --> reportDefinition1
[*] --> reportDefinition2
[*] --> reportDefinition3
}The AI-Exchange Protocol (AIXP) is a promising communication standard for artificial intelligence agents, designed to foster collaboration and information exchange. By providing a common framework for communication, AIXP can help drive innovation and progress in the field of AI. As AI systems continue to evolve and become more sophisticated, the adoption of standards like AIXP will be crucial for enabling effective communication and collaboration among AI agents.
We've received significant interest in the AIXP project, and with the development of Agents in CodeGPT, now is a great time to push forward! Here's a glimpse of what's coming and what needs to be done:
- [x] Basic Python Example: Implement a simple example in Python demonstrating the core communication flow between two agents using AIXP. This will involve defining message structures and basic sending/receiving mechanisms. (See
aixp_example.py) - [ ] Testing the Python Example: Add unit tests to ensure the basic communication example functions as expected.
- [ ] Initial Documentation for the Example: Document the Python example, explaining its components and how to run it.
Here are some of the key areas we plan to develop further:
- [ ] Define Formal Message Schemas: Move beyond the basic example and create more robust and well-defined schemas for AIXP messages (e.g., using JSON Schema or Protocol Buffers).
- [ ] Implement Different Transport Mechanisms: Explore and implement various ways for agents to communicate (e.g., HTTP, WebSockets, message queues).
- [ ] Standardize Access Points: Define clear conventions for how agents expose their functionalities and how others can access them (e.g., using RESTful APIs or other service discovery mechanisms).
- [ ] Implement Content Negotiation: Allow agents to specify the data formats they can handle.
- [ ] Implement Authentication: Define methods for agents to verify their identity.
- [ ] Implement Authorization: Define mechanisms to control which agents have access to specific resources or functionalities.
- [ ] Explore Encryption Options: Investigate methods for securing communication between agents.
- [ ] Implement Message Tracking: Develop a more robust system for tracking messages to detect potential loops.
- [ ] Implement Time-to-Live (TTL): Add TTL functionality to messages.
- [ ] Define Loop Detection Strategies: Document and potentially implement more sophisticated strategies for detecting communication loops.
- [ ] Expand Status Codes and Error Messages: Add more comprehensive status codes and error messages to cover various scenarios.
- [ ] Define a Task Completion Protocol: Formalize the process of verifying task completion and handling failures.
- [ ] Implement Service Discovery: Explore ways for agents to automatically discover other agents and their capabilities.
- [ ] Define Negotiation Protocols: Potentially explore protocols for agents to negotiate parameters or capabilities before initiating tasks.
- [ ] Support for Streaming Data: Consider how AIXP can handle the exchange of large or streaming datasets.
- [ ] Create SDKs/Libraries in Other Languages: Develop libraries for AIXP in other popular programming languages to facilitate broader adoption.
- [ ] Develop More Comprehensive Documentation: Expand the documentation to cover all aspects of the protocol.
- [ ] Build Real-World Examples: Create more complex examples showcasing the benefits of AIXP in practical scenarios.
Contributions are welcome! If you're interested in helping shape the future of AI agent communication, please feel free to contribute to this repository. Check the "Issues" tab for potential tasks and open discussions.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for AIXP
Similar Open Source Tools

AIXP
The AI-Exchange Protocol (AIXP) is a communication standard designed to facilitate information and result exchange between artificial intelligence agents. It aims to enhance interoperability and collaboration among various AI systems by establishing a common framework for communication. AIXP includes components for communication, loop prevention, and task finalization, ensuring secure and efficient collaboration while avoiding infinite communication loops. The protocol defines access points, data formats, authentication, authorization, versioning, loop detection, status codes, error messages, and task completion verification. AIXP enables AI agents to collaborate seamlessly and complete tasks effectively, contributing to the overall efficiency and reliability of AI systems.

swarms
Swarms provides simple, reliable, and agile tools to create your own Swarm tailored to your specific needs. Currently, Swarms is being used in production by RBC, John Deere, and many AI startups.
agentUniverse
agentUniverse is a framework for developing applications powered by multi-agent based on large language model. It provides essential components for building single agent and multi-agent collaboration mechanism for customizing collaboration patterns. Developers can easily construct multi-agent applications and share pattern practices from different fields. The framework includes pre-installed collaboration patterns like PEER and DOE for complex task breakdown and data-intensive tasks.
MemoryBear
MemoryBear is a next-generation AI memory system developed by RedBear AI, focusing on overcoming limitations in knowledge storage and multi-agent collaboration. It empowers AI with human-like memory capabilities, enabling deep knowledge understanding and cognitive collaboration. The system addresses challenges such as knowledge forgetting, memory gaps in multi-agent collaboration, and semantic ambiguity during reasoning. MemoryBear's core features include memory extraction engine, graph storage, hybrid search, memory forgetting engine, self-reflection engine, and FastAPI services. It offers a standardized service architecture for efficient integration and invocation across applications.

asreview
The ASReview project implements active learning for systematic reviews, utilizing AI-aided pipelines to assist in finding relevant texts for search tasks. It accelerates the screening of textual data with minimal human input, saving time and increasing output quality. The software offers three modes: Oracle for interactive screening, Exploration for teaching purposes, and Simulation for evaluating active learning models. ASReview LAB is designed to support decision-making in any discipline or industry by improving efficiency and transparency in screening large amounts of textual data.
awesome-agent-failures
Awesome AI Agent Failures is a community-curated repository documenting known failure modes for AI agents, real-world case studies, and techniques to avoid failures. It provides insights into common failure modes such as tool hallucination, response hallucination, goal misinterpretation, plan generation failures, incorrect tool use, verification & termination failures, and prompt injection. The repository also includes resources like research papers, industry resources, books, external resources, and related awesome lists to help AI engineers build more reliable AI agents by learning from production failures.
db-ally
db-ally is a library for creating natural language interfaces to data sources. It allows developers to outline specific use cases for a large language model (LLM) to handle, detailing the desired data format and the possible operations to fetch this data. db-ally effectively shields the complexity of the underlying data source from the model, presenting only the essential information needed for solving the specific use cases. Instead of generating arbitrary SQL, the model is asked to generate responses in a simplified query language.
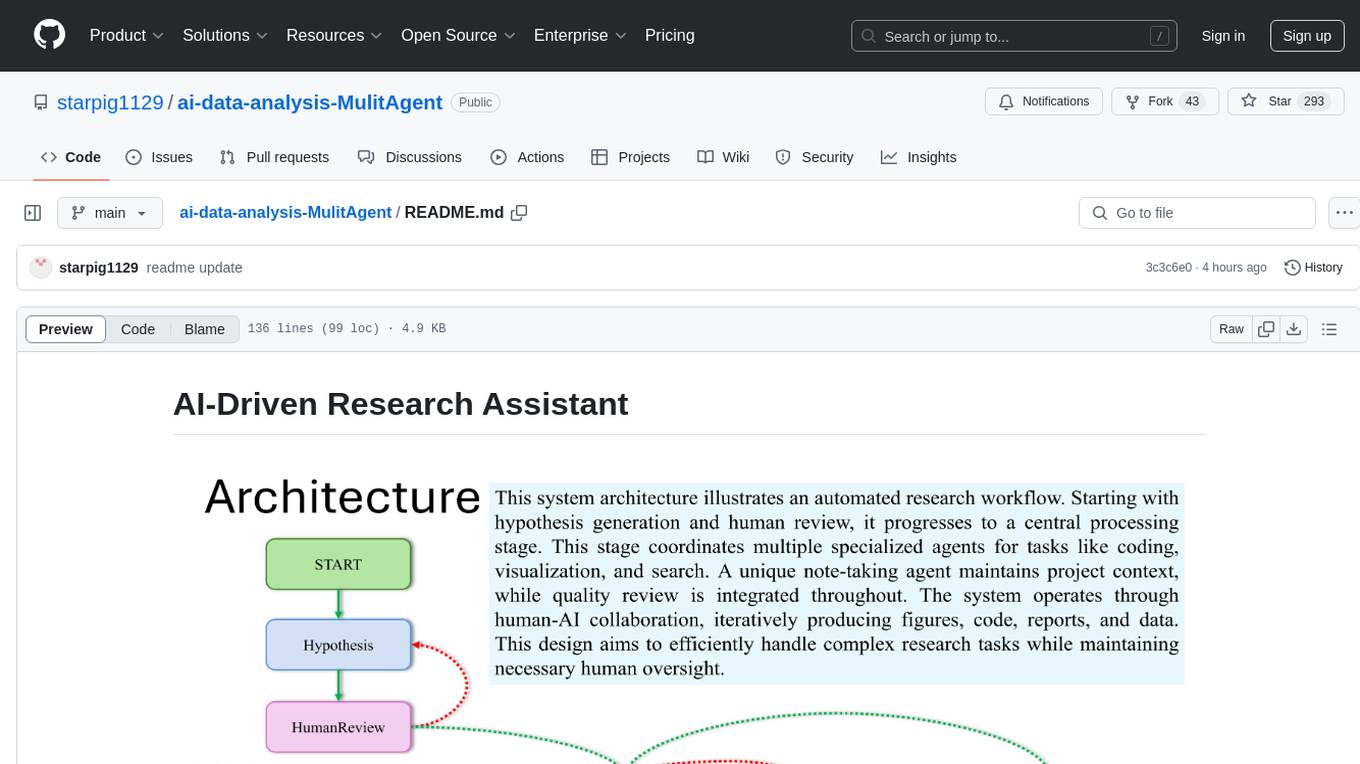
ai-data-analysis-MulitAgent
AI-Driven Research Assistant is an advanced AI-powered system utilizing specialized agents for data analysis, visualization, and report generation. It integrates LangChain, OpenAI's GPT models, and LangGraph for complex research processes. Key features include hypothesis generation, data processing, web search, code generation, and report writing. The system's unique Note Taker agent maintains project state, reducing overhead and improving context retention. System requirements include Python 3.10+ and Jupyter Notebook environment. Installation involves cloning the repository, setting up a Conda virtual environment, installing dependencies, and configuring environment variables. Usage instructions include setting data, running Jupyter Notebook, customizing research tasks, and viewing results. Main components include agents for hypothesis generation, process supervision, visualization, code writing, search, report writing, quality review, and note-taking. Workflow involves hypothesis generation, processing, quality review, and revision. Customization is possible by modifying agent creation and workflow definition. Current issues include OpenAI errors, NoteTaker efficiency, runtime optimization, and refiner improvement. Contributions via pull requests are welcome under the MIT License.
open-extract
open-extract simplifies the ingestion and processing of unstructured data for those building AI Agents/Agentic Workflows using frameworks such as LangGraph, AG2, and CrewAI. It allows applications to identify and extract relevant data from large documents and websites with a single API call, supporting multi-schema/multi-document extraction without vendor lock-in. The tool includes built-in caching for rapid repeat extractions, providing flexibility in model provider choice.
blades
Blades is a multimodal AI Agent framework in Go, supporting custom models, tools, memory, middleware, and more. It is well-suited for multi-turn conversations, chain reasoning, and structured output. The framework provides core components like Agent, Prompt, Chain, ModelProvider, Tool, Memory, and Middleware, enabling developers to build intelligent applications with flexible configuration and high extensibility. Blades leverages the characteristics of Go to achieve high decoupling and efficiency, making it easy to integrate different language model services and external tools. The project is in its early stages, inviting Go developers and AI enthusiasts to contribute and explore the possibilities of building AI applications in Go.
gepa
GEPA (Genetic-Pareto) is a framework for optimizing arbitrary systems composed of text components like AI prompts, code snippets, or textual specs against any evaluation metric. It employs LLMs to reflect on system behavior, using feedback from execution and evaluation traces to drive targeted improvements. Through iterative mutation, reflection, and Pareto-aware candidate selection, GEPA evolves robust, high-performing variants with minimal evaluations, co-evolving multiple components in modular systems for domain-specific gains. The repository provides the official implementation of the GEPA algorithm as proposed in the paper titled 'GEPA: Reflective Prompt Evolution Can Outperform Reinforcement Learning'.
Controllable-RAG-Agent
This repository contains a sophisticated deterministic graph-based solution for answering complex questions using a controllable autonomous agent. The solution is designed to ensure that answers are solely based on the provided data, avoiding hallucinations. It involves various steps such as PDF loading, text preprocessing, summarization, database creation, encoding, and utilizing large language models. The algorithm follows a detailed workflow involving planning, retrieval, answering, replanning, content distillation, and performance evaluation. Heuristics and techniques implemented focus on content encoding, anonymizing questions, task breakdown, content distillation, chain of thought answering, verification, and model performance evaluation.
agents
Agents 2.0 is a framework for training language agents using symbolic learning, inspired by connectionist learning for neural nets. It implements main components of connectionist learning like back-propagation and gradient-based weight update in the context of agent training using language-based loss, gradients, and weights. The framework supports optimizing multi-agent systems and allows multiple agents to take actions in one node.

nesa
Nesa is a tool that allows users to run on-prem AI for a fraction of the cost through a blind API. It provides blind privacy, zero latency on protected inference, wide model coverage, cost savings compared to cloud and on-prem AI, RAG support, and ChatGPT compatibility. Nesa achieves blind AI through Equivariant Encryption (EE), a new security technology that provides complete inference encryption with no additional latency. EE allows users to perform inference on neural networks without exposing the underlying data, preserving data privacy and security.
For similar tasks
phospho
Phospho is a text analytics platform for LLM apps. It helps you detect issues and extract insights from text messages of your users or your app. You can gather user feedback, measure success, and iterate on your app to create the best conversational experience for your users.
OpenFactVerification
Loki is an open-source tool designed to automate the process of verifying the factuality of information. It provides a comprehensive pipeline for dissecting long texts into individual claims, assessing their worthiness for verification, generating queries for evidence search, crawling for evidence, and ultimately verifying the claims. This tool is especially useful for journalists, researchers, and anyone interested in the factuality of information.
open-parse
Open Parse is a Python library for visually discerning document layouts and chunking them effectively. It is designed to fill the gap in open-source libraries for handling complex documents. Unlike text splitting, which converts a file to raw text and slices it up, Open Parse visually analyzes documents for superior LLM input. It also supports basic markdown for parsing headings, bold, and italics, and has high-precision table support, extracting tables into clean Markdown formats with accuracy that surpasses traditional tools. Open Parse is extensible, allowing users to easily implement their own post-processing steps. It is also intuitive, with great editor support and completion everywhere, making it easy to use and learn.
spaCy
spaCy is an industrial-strength Natural Language Processing (NLP) library in Python and Cython. It incorporates the latest research and is designed for real-world applications. The library offers pretrained pipelines supporting 70+ languages, with advanced neural network models for tasks such as tagging, parsing, named entity recognition, and text classification. It also facilitates multi-task learning with pretrained transformers like BERT, along with a production-ready training system and streamlined model packaging, deployment, and workflow management. spaCy is commercial open-source software released under the MIT license.
NanoLLM
NanoLLM is a tool designed for optimized local inference for Large Language Models (LLMs) using HuggingFace-like APIs. It supports quantization, vision/language models, multimodal agents, speech, vector DB, and RAG. The tool aims to provide efficient and effective processing for LLMs on local devices, enhancing performance and usability for various AI applications.

ontogpt
OntoGPT is a Python package for extracting structured information from text using large language models, instruction prompts, and ontology-based grounding. It provides a command line interface and a minimal web app for easy usage. The tool has been evaluated on test data and is used in related projects like TALISMAN for gene set analysis. OntoGPT enables users to extract information from text by specifying relevant terms and provides the extracted objects as output.

lima
LIMA is a multilingual linguistic analyzer developed by the CEA LIST, LASTI laboratory. It is Free Software available under the MIT license. LIMA has state-of-the-art performance for more than 60 languages using deep learning modules. It also includes a powerful rules-based mechanism called ModEx for extracting information in new domains without annotated data.
liboai
liboai is a simple C++17 library for the OpenAI API, providing developers with access to OpenAI endpoints through a collection of methods and classes. It serves as a spiritual port of OpenAI's Python library, 'openai', with similar structure and features. The library supports various functionalities such as ChatGPT, Audio, Azure, Functions, Image DALL·E, Models, Completions, Edit, Embeddings, Files, Fine-tunes, Moderation, and Asynchronous Support. Users can easily integrate the library into their C++ projects to interact with OpenAI services.
For similar jobs

AIXP
The AI-Exchange Protocol (AIXP) is a communication standard designed to facilitate information and result exchange between artificial intelligence agents. It aims to enhance interoperability and collaboration among various AI systems by establishing a common framework for communication. AIXP includes components for communication, loop prevention, and task finalization, ensuring secure and efficient collaboration while avoiding infinite communication loops. The protocol defines access points, data formats, authentication, authorization, versioning, loop detection, status codes, error messages, and task completion verification. AIXP enables AI agents to collaborate seamlessly and complete tasks effectively, contributing to the overall efficiency and reliability of AI systems.

FlagPerf
FlagPerf is an integrated AI hardware evaluation engine jointly built by the Institute of Intelligence and AI hardware manufacturers. It aims to establish an industry-oriented metric system to evaluate the actual capabilities of AI hardware under software stack combinations (model + framework + compiler). FlagPerf features a multidimensional evaluation metric system that goes beyond just measuring 'whether the chip can support specific model training.' It covers various scenarios and tasks, including computer vision, natural language processing, speech, multimodal, with support for multiple training frameworks and inference engines to connect AI hardware with software ecosystems. It also supports various testing environments to comprehensively assess the performance of domestic AI chips in different scenarios.
AI-System-School
AI System School is a curated list of research in machine learning systems, focusing on ML/DL infra, LLM infra, domain-specific infra, ML/LLM conferences, and general resources. It provides resources such as data processing, training systems, video systems, autoML systems, and more. The repository aims to help users navigate the landscape of AI systems and machine learning infrastructure, offering insights into conferences, surveys, books, videos, courses, and blogs related to the field.
multi-agent-orchestrator
Multi-Agent Orchestrator is a flexible and powerful framework for managing multiple AI agents and handling complex conversations. It intelligently routes queries to the most suitable agent based on context and content, supports dual language implementation in Python and TypeScript, offers flexible agent responses, context management across agents, extensible architecture for customization, universal deployment options, and pre-built agents and classifiers. It is suitable for various applications, from simple chatbots to sophisticated AI systems, accommodating diverse requirements and scaling efficiently.
AIInfra
AIInfra is an open-source project focused on AI infrastructure, specifically targeting large models in distributed clusters, distributed architecture, distributed training, and algorithms related to large models. The project aims to explore and study system design in artificial intelligence and deep learning, with a focus on the hardware and software stack for building AI large model systems. It provides a comprehensive curriculum covering topics such as AI chip principles, communication and storage, AI clusters, large model training, and inference, as well as algorithms for large models. The course is designed for undergraduate and graduate students, as well as professionals working with AI large model systems, to gain a deep understanding of AI computer system architecture and design.
eino
Eino is an ultimate LLM application development framework in Golang, emphasizing simplicity, scalability, reliability, and effectiveness. It provides a curated list of component abstractions, a powerful composition framework, meticulously designed APIs, best practices, and tools covering the entire development cycle. Eino standardizes and improves efficiency in AI application development by offering rich components, powerful orchestration, complete stream processing, highly extensible aspects, and a comprehensive framework structure.
RLinf
RLinf is a flexible and scalable open-source infrastructure designed for post-training foundation models via reinforcement learning. It provides a robust backbone for next-generation training, supporting open-ended learning, continuous generalization, and limitless possibilities in intelligence development. The tool offers unique features like Macro-to-Micro Flow, flexible execution modes, auto-scheduling strategy, embodied agent support, and fast adaptation for mainstream VLA models. RLinf is fast with hybrid mode and automatic online scaling strategy, achieving significant throughput improvement and efficiency. It is also flexible and easy to use with multiple backend integrations, adaptive communication, and built-in support for popular RL methods. The roadmap includes system-level enhancements and application-level extensions to support various training scenarios and models. Users can get started with complete documentation, quickstart guides, key design principles, example gallery, advanced features, and guidelines for extending the framework. Contributions are welcome, and users are encouraged to cite the GitHub repository and acknowledge the broader open-source community.

tt-xla
TT-XLA is a repository that enables running PyTorch and JAX models on Tenstorrent's AI hardware. It serves as a backend integration between the JAX ecosystem and Tenstorrent's ML accelerators using the PJRT (Portable JAX Runtime) interface. It supports ingestion of PyTorch models through PyTorch/XLA and JAX models via jit compile, providing a StableHLO (SHLO) graph to TT-MLIR compiler.