
MMOS
Mix of Minimal Optimal Sets (MMOS) of dataset has two advantages for two aspects, higher performance and lower construction costs on math reasoning.
Stars: 61
MMOS (Mix of Minimal Optimal Sets) is a dataset designed for math reasoning tasks, offering higher performance and lower construction costs. It includes various models and data subsets for tasks like arithmetic reasoning and math word problem solving. The dataset is used to identify minimal optimal sets through reasoning paths and statistical analysis, with a focus on QA-pairs generated from open-source datasets. MMOS also provides an auto problem generator for testing model robustness and scripts for training and inference.
README:
| ArXiv | Models | Data | Code |
- [2024/6/22] Revised the article and added attempts on automatic theorem proving tasks. Codes are in MMOS-F2F.
- [2024/3/30] Update result on MMOS-Code 34B and MMOS-LLEMMA 34B Notice the vllm and transformers version.
- [2024/3/8] 🔥🔥🔥Models MMOS-DeepSeekMath 7B show nice performence with self-consistency and k=50 !!
- [2024/2/28] 🔥 Models MMOS-DeepSeekMath 7B show nice performence and released at MMOS-DeepSeekMath 7B !!
- [2024/2/27] 🔥 Models MMOS-LLEMMA 7B show nice performence and released at MMOS-LLEMMA 7B !!
- [2024/2/27] 🔥 Models MMOS-CODE 13B and MMOS-CODE 34B released at MMOS-CODE 13B and MMOS-CODE 34B !!
- [2024/2/27] 🔥 Models MMOS-CODE 7B released at MMOS-CODE 7B !!
- [2024/2/26] 🔥🔥🔥 Dataset MMOS released at 😊 HuggingFace !!
- [2024/2/23] 🔥🔥🔥Arxiv released at An Empirical Study of Data Ability Boundary in LLMs' Math Reasoning ~
Mix of Minimal Optimal Sets (MMOS) of dataset has two advantages for two aspects, higher performance and lower construction costs on math reasoning.
| Model | Size | GSM8K | SVAMP | ASDiv | MATH | Size | GSM8K | SVAMP | ASDiv | MATH | Size | GSM8K | SVAMP | ASDiv | MATH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WizardMath | 7B | 54.9 | 57.3 | 59.1 | 10.7 | 13B | 63.9 | 64.3 | 65.8 | 14.0 | 34B | - | - | - | - |
| MAMMOTH | 7B | 53.6 | 67.7 | 31.5 | - | 13B | 62.0 | 72.4 | - | 34.2 | 34B | - | - | - | - |
| MetaMath | 7B | 66.5 | - | - | 19.8 | 13B | 72.3 | - | - | 22.4 | 34B | - | - | - | - |
| MathCoder-L | 7B | 64.2 | 71.5 | - | 23.3 | 13B | 72.6 | 76.9 | - | 29.9 | 34B | - | - | - | - |
| MathCoder-CL | 7B | 67.8 | 70.7 | - | 30.2 | 13B | 74.1 | 78.0 | - | 35.9 | 34B | - | - | - | - |
| TORA | 7B | 68.8 | 68.2 | 73.9 | 40.1 | 13B | 72.7 | 72.9 | 77.2 | 43.0 | 34B | - | - | - | - |
| TORA-CODE | 7B | 72.6 | 70.4 | 78.7 | 44.6 | 13B | 75.8 | 75.7 | 81.4 | 48.1 | 34B | 80.7 | 80.5 | 84.2 | 50.8 |
| MMOS | 7B | 69.9 | 73.4 | 76.8 | 40.2 | 13B | 74.8 | 77.0 | 80.0 | 43.2 | 34B | - | - | - | - |
| MMOS-CODE | 7B | 73.9 | 76.4 | 78.6 | 44.3 | 13B | 77.1 | 77.5 | 81.9 | 48.1 | 34B | 81.7 | 81.9 | 82.8 | 48.8 |
| MMOS-MinCODE | 7B | 70.3 | 72.5 | 76.7 | 44.6 | 13B | - | - | - | - | 34B | - | - | - | - |
| MMOS-LLEMMA | 7B | 76.5 | 77.7 | 81.4 | 48.8 | 13B | - | - | - | - | 34B | 82.8 | 81.8 | 84.8 | 51.3 |
| MMOS-DeepSeekMath | 7B | 80.5 | 79.3 | 87.6 | 55.0 | 13B | - | - | - | - | 34B | - | - | - | - |
| MMOS-DeepSeekMath(SC,k=50) | 7B | 87.2 | - | - | 63.7 | 13B | - | - | - | - | 34B | - | - | - | - |
git clone https://github.com/cyzhh/MMOS.git
cd MMOS
conda create -n MMOS python=3.10
conda activate MMOS
pip install -r requirements.txt
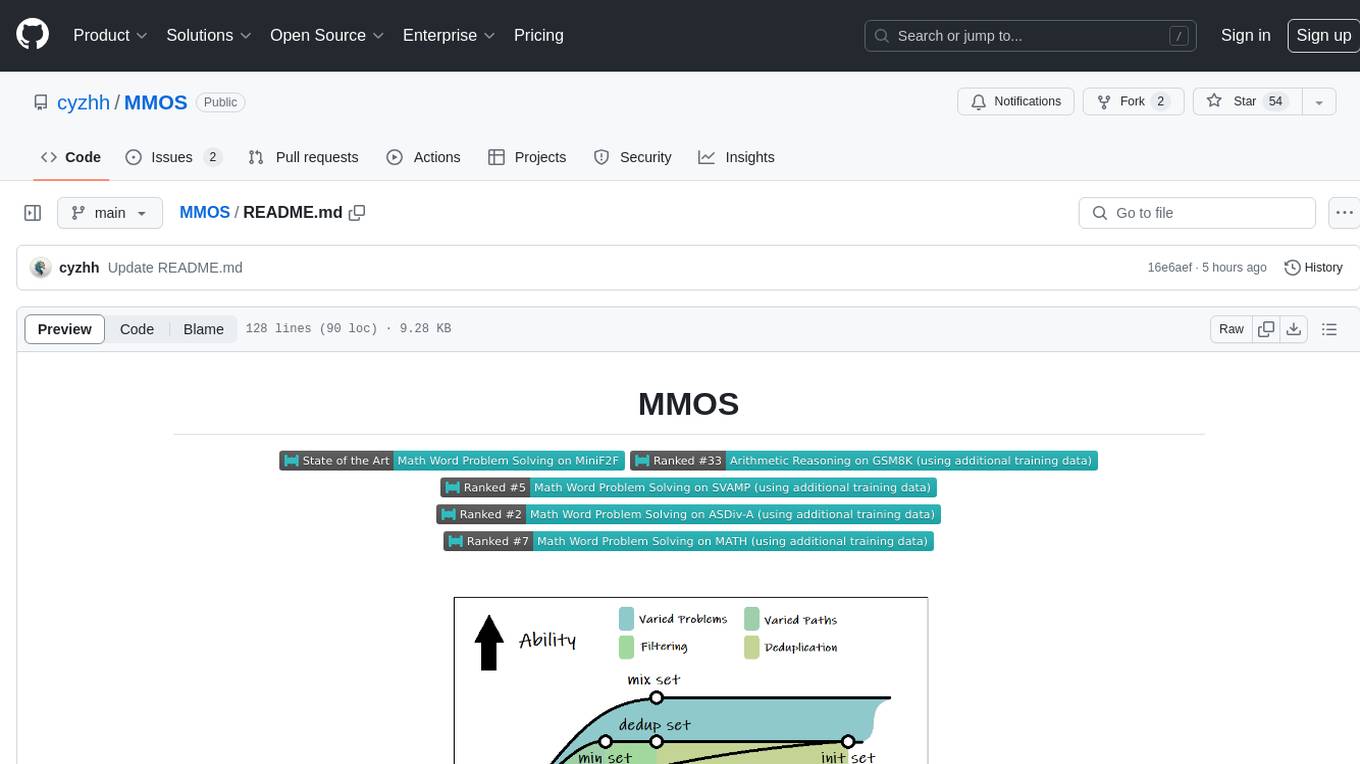
To identify the minimal optimal set, we follow these steps:
- Sample a sufficient number of correct reasoning paths to form initial set.
- Implement a deduplication algorithm to obtain its deduplicated subset.
- Conduct a statistical analysis on the upper limit of reasoning paths per question k with the subset data amount N.
- Perform SFT on several subsets to analyze the impact of removing duplicates and keeping varied reasoning paths.
We use ToRA series to generate QA-pairs from open source dataset GSM8K, MATH, TAL-SCQ. The QA-pairs are processed by our deduplication algorithm, resulting in the dataset MMOS. The total number of QA-pairs is 135K.
The DATA, which we publish at 😊 HuggingFace, need to be placed under the relative path, ./train_data/MMOS/.
If you are interested in our work, we will publish details about the data processing aspects after the paper is published.
Following scripts/generate.sh:
- Prepare your sampling results.
- Combine the results.
- Extract the true cases.
- Dedup the cases.
- (Filter) and rerank.
You can generate a data set for testing the numerical robustness of model performance by executing the following script command:
bash scripts/generate.sh
bash scripts/attack.sh
bash scripts/rerank.sh
Due to resource constraints, we performed supervised fine-tuning on CodeLLaMA 7B, CodeLLaMA 13B and CodeLLaMA 34B using our dataset on A100 40G GPUs. To reproduce our work from CodeLLaMA 7B/13B, you can train according to the following instruction. You can also train the 34B model through DDP script instructions.
bash scripts/train_single.sh codellama 7b
bash scripts/train.sh codellama 34b
bash scripts/infer.sh
If you find this repository helpful, please consider citing our paper:
@misc{chen2024empirical,
title={An Empirical Study of Data Ability Boundary in LLMs' Math Reasoning},
author={Zui Chen and Yezeng Chen and Jiaqi Han and Zhijie Huang and Ji Qi and Yi Zhou},
year={2024},
eprint={2403.00799},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for MMOS
Similar Open Source Tools

MMOS
MMOS (Mix of Minimal Optimal Sets) is a dataset designed for math reasoning tasks, offering higher performance and lower construction costs. It includes various models and data subsets for tasks like arithmetic reasoning and math word problem solving. The dataset is used to identify minimal optimal sets through reasoning paths and statistical analysis, with a focus on QA-pairs generated from open-source datasets. MMOS also provides an auto problem generator for testing model robustness and scripts for training and inference.
DataFlow
DataFlow is a data preparation and training system designed to parse, generate, process, and evaluate high-quality data from noisy sources, improving the performance of large language models in specific domains. It constructs diverse operators and pipelines, validated to enhance domain-oriented LLM's performance in fields like healthcare, finance, and law. DataFlow also features an intelligent DataFlow-agent capable of dynamically assembling new pipelines by recombining existing operators on demand.
TRACE
TRACE is a temporal grounding video model that utilizes causal event modeling to capture videos' inherent structure. It presents a task-interleaved video LLM model tailored for sequential encoding/decoding of timestamps, salient scores, and textual captions. The project includes various model checkpoints for different stages and fine-tuning on specific datasets. It provides evaluation codes for different tasks like VTG, MVBench, and VideoMME. The repository also offers annotation files and links to raw videos preparation projects. Users can train the model on different tasks and evaluate the performance based on metrics like CIDER, METEOR, SODA_c, F1, mAP, Hit@1, etc. TRACE has been enhanced with trace-retrieval and trace-uni models, showing improved performance on dense video captioning and general video understanding tasks.

MOSS-TTS
MOSS-TTS Family is an open-source speech and sound generation model family designed for high-fidelity, high-expressiveness, and complex real-world scenarios. It includes five production-ready models: MOSS-TTS, MOSS-TTSD, MOSS-VoiceGenerator, MOSS-TTS-Realtime, and MOSS-SoundEffect, each serving specific purposes in speech generation, dialogue, voice design, real-time interactions, and sound effect generation. The models offer features like long-speech generation, fine-grained control over phonemes and duration, multilingual synthesis, voice cloning, and real-time voice agents.
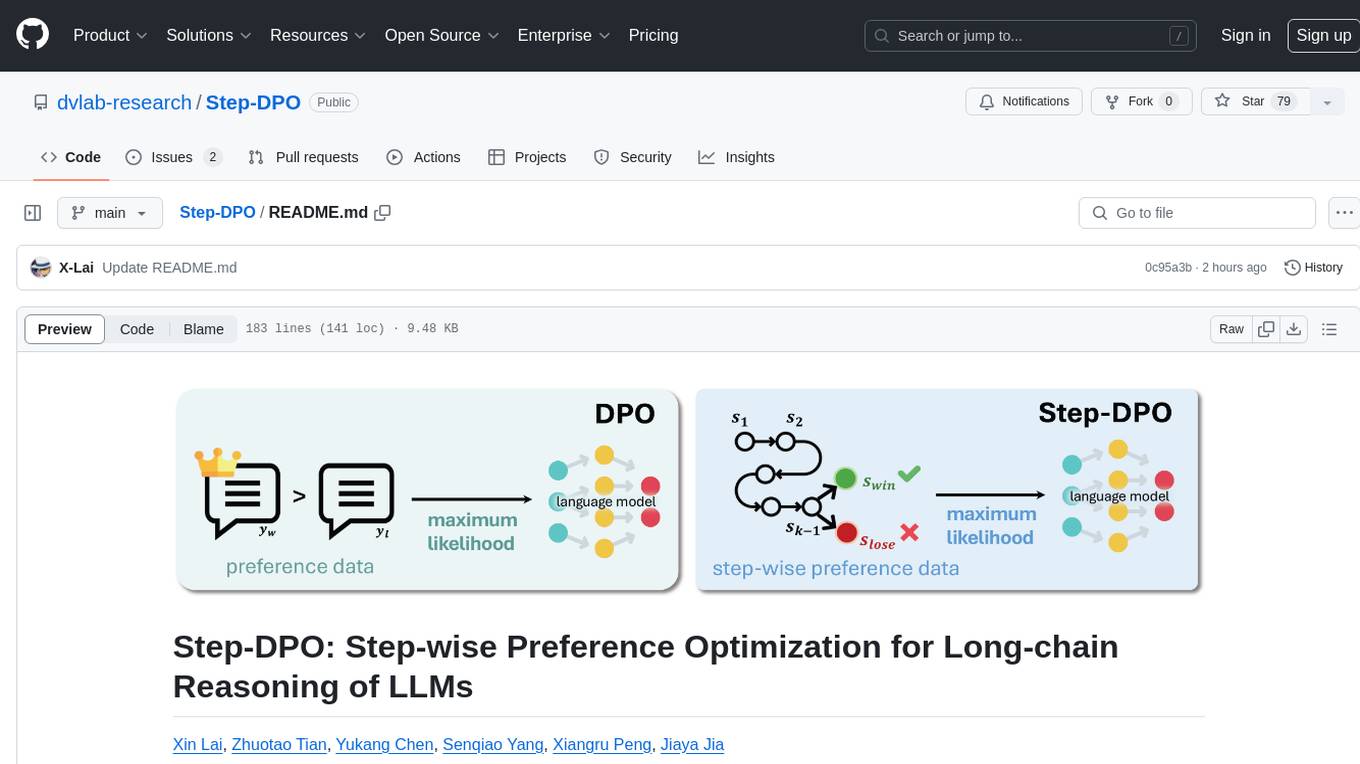
Step-DPO
Step-DPO is a method for enhancing long-chain reasoning ability of LLMs with a data construction pipeline creating a high-quality dataset. It significantly improves performance on math and GSM8K tasks with minimal data and training steps. The tool fine-tunes pre-trained models like Qwen2-7B-Instruct with Step-DPO, achieving superior results compared to other models. It provides scripts for training, evaluation, and deployment, along with examples and acknowledgements.
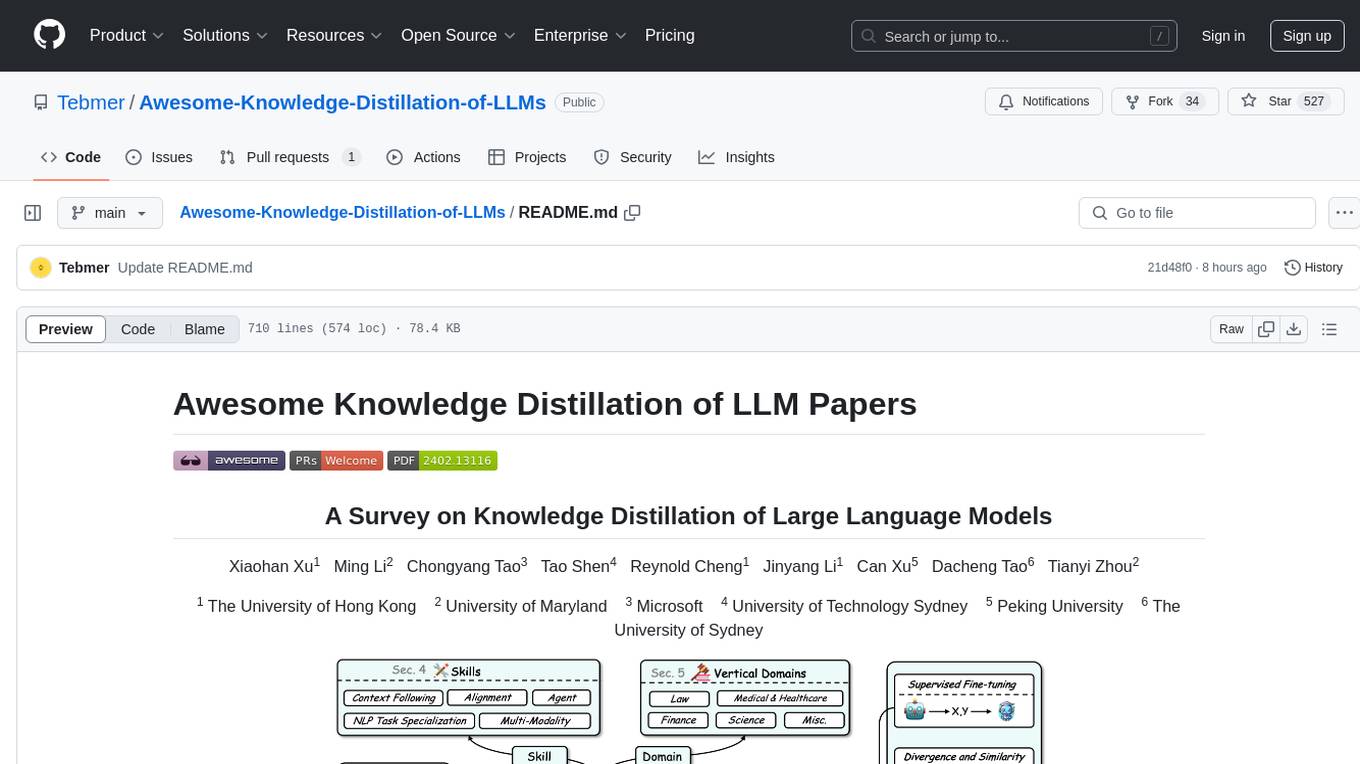
Awesome-Knowledge-Distillation-of-LLMs
A collection of papers related to knowledge distillation of large language models (LLMs). The repository focuses on techniques to transfer advanced capabilities from proprietary LLMs to smaller models, compress open-source LLMs, and refine their performance. It covers various aspects of knowledge distillation, including algorithms, skill distillation, verticalization distillation in fields like law, medical & healthcare, finance, science, and miscellaneous domains. The repository provides a comprehensive overview of the research in the area of knowledge distillation of LLMs.
InternVL
InternVL scales up the ViT to _**6B parameters**_ and aligns it with LLM. It is a vision-language foundation model that can perform various tasks, including: **Visual Perception** - Linear-Probe Image Classification - Semantic Segmentation - Zero-Shot Image Classification - Multilingual Zero-Shot Image Classification - Zero-Shot Video Classification **Cross-Modal Retrieval** - English Zero-Shot Image-Text Retrieval - Chinese Zero-Shot Image-Text Retrieval - Multilingual Zero-Shot Image-Text Retrieval on XTD **Multimodal Dialogue** - Zero-Shot Image Captioning - Multimodal Benchmarks with Frozen LLM - Multimodal Benchmarks with Trainable LLM - Tiny LVLM InternVL has been shown to achieve state-of-the-art results on a variety of benchmarks. For example, on the MMMU image classification benchmark, InternVL achieves a top-1 accuracy of 51.6%, which is higher than GPT-4V and Gemini Pro. On the DocVQA question answering benchmark, InternVL achieves a score of 82.2%, which is also higher than GPT-4V and Gemini Pro. InternVL is open-sourced and available on Hugging Face. It can be used for a variety of applications, including image classification, object detection, semantic segmentation, image captioning, and question answering.
Awesome-Interpretability-in-Large-Language-Models
This repository is a collection of resources focused on interpretability in large language models (LLMs). It aims to help beginners get started in the area and keep researchers updated on the latest progress. It includes libraries, blogs, tutorials, forums, tools, programs, papers, and more related to interpretability in LLMs.

CogVLM2
CogVLM2 is a new generation of open source models that offer significant improvements in benchmarks such as TextVQA and DocVQA. It supports 8K content length, image resolution up to 1344 * 1344, and both Chinese and English languages. The project provides basic calling methods, fine-tuning examples, and OpenAI API format calling examples to help developers quickly get started with the model.
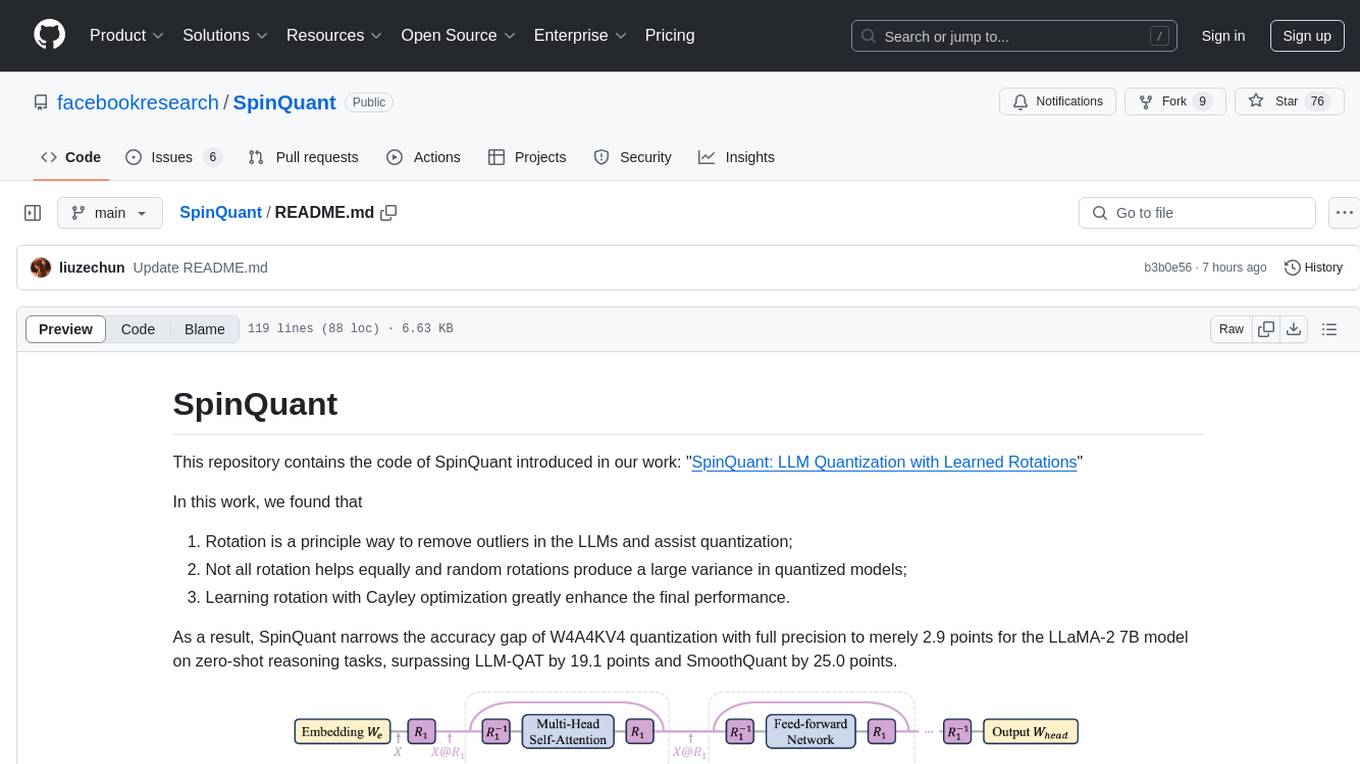
SpinQuant
SpinQuant is a tool designed for LLM quantization with learned rotations. It focuses on optimizing rotation matrices to enhance the performance of quantized models, narrowing the accuracy gap to full precision models. The tool implements rotation optimization and PTQ evaluation with optimized rotation, providing arguments for model name, batch sizes, quantization bits, and rotation options. SpinQuant is based on the findings that rotation helps in removing outliers and improving quantization, with specific enhancements achieved through learning rotation with Cayley optimization.
LlamaV-o1
LlamaV-o1 is a Large Multimodal Model designed for spontaneous reasoning tasks. It outperforms various existing models on multimodal reasoning benchmarks. The project includes a Step-by-Step Visual Reasoning Benchmark, a novel evaluation metric, and a combined Multi-Step Curriculum Learning and Beam Search Approach. The model achieves superior performance in complex multi-step visual reasoning tasks in terms of accuracy and efficiency.
Awesome-Tabular-LLMs
This repository is a collection of papers on Tabular Large Language Models (LLMs) specialized for processing tabular data. It includes surveys, models, and applications related to table understanding tasks such as Table Question Answering, Table-to-Text, Text-to-SQL, and more. The repository categorizes the papers based on key ideas and provides insights into the advancements in using LLMs for processing diverse tables and fulfilling various tabular tasks based on natural language instructions.
VoiceBench
VoiceBench is a repository containing code and data for benchmarking LLM-Based Voice Assistants. It includes a leaderboard with rankings of various voice assistant models based on different evaluation metrics. The repository provides setup instructions, datasets, evaluation procedures, and a curated list of awesome voice assistants. Users can submit new voice assistant results through the issue tracker for updates on the ranking list.
speechless
Speechless.AI is committed to integrating the superior language processing and deep reasoning capabilities of large language models into practical business applications. By enhancing the model's language understanding, knowledge accumulation, and text creation abilities, and introducing long-term memory, external tool integration, and local deployment, our aim is to establish an intelligent collaborative partner that can independently interact, continuously evolve, and closely align with various business scenarios.
Awesome-LLMs-for-Video-Understanding
Awesome-LLMs-for-Video-Understanding is a repository dedicated to exploring Video Understanding with Large Language Models. It provides a comprehensive survey of the field, covering models, pretraining, instruction tuning, and hybrid methods. The repository also includes information on tasks, datasets, and benchmarks related to video understanding. Contributors are encouraged to add new papers, projects, and materials to enhance the repository.
FlipAttack
FlipAttack is a jailbreak attack tool designed to exploit black-box Language Model Models (LLMs) by manipulating text inputs. It leverages insights into LLMs' autoregressive nature to construct noise on the left side of the input text, deceiving the model and enabling harmful behaviors. The tool offers four flipping modes to guide LLMs in denoising and executing malicious prompts effectively. FlipAttack is characterized by its universality, stealthiness, and simplicity, allowing users to compromise black-box LLMs with just one query. Experimental results demonstrate its high success rates against various LLMs, including GPT-4o and guardrail models.
For similar tasks

MMOS
MMOS (Mix of Minimal Optimal Sets) is a dataset designed for math reasoning tasks, offering higher performance and lower construction costs. It includes various models and data subsets for tasks like arithmetic reasoning and math word problem solving. The dataset is used to identify minimal optimal sets through reasoning paths and statistical analysis, with a focus on QA-pairs generated from open-source datasets. MMOS also provides an auto problem generator for testing model robustness and scripts for training and inference.
AI-TOD
AI-TOD is a dataset for tiny object detection in aerial images, containing 700,621 object instances across 28,036 images. Objects in AI-TOD are smaller with a mean size of 12.8 pixels compared to other aerial image datasets. To use AI-TOD, download xView training set and AI-TOD_wo_xview, then generate the complete dataset using the provided synthesis tool. The dataset is publicly available for academic and research purposes under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
LLMFarm
LLMFarm is an iOS and MacOS app designed to work with large language models (LLM). It allows users to load different LLMs with specific parameters, test the performance of various LLMs on iOS and macOS, and identify the most suitable model for their projects. The tool is based on ggml and llama.cpp by Georgi Gerganov and incorporates sources from rwkv.cpp by saharNooby, Mia by byroneverson, and LlamaChat by alexrozanski. LLMFarm features support for MacOS (13+) and iOS (16+), various inferences and sampling methods, Metal compatibility (not supported on Intel Mac), model setting templates, LoRA adapters support, LoRA finetune support, LoRA export as model support, and more. It also offers a range of inferences including LLaMA, GPTNeoX, Replit, GPT2, Starcoder, RWKV, Falcon, MPT, Bloom, and others. Additionally, it supports multimodal models like LLaVA, Obsidian, and MobileVLM. Users can customize inference options through JSON files and access supported models for download.
abliterator
abliterator.py is a simple Python library/structure designed to ablate features in large language models (LLMs) supported by TransformerLens. It provides capabilities to enter temporary contexts, cache activations with N samples, calculate refusal directions, and includes tokenizer utilities. The library aims to streamline the process of experimenting with ablation direction turns by encapsulating useful logic and minimizing code complexity. While currently basic and lacking comprehensive documentation, the library serves well for personal workflows and aims to expand beyond feature ablation to augmentation and additional features over time with community support.
Korean-SAT-LLM-Leaderboard
The Korean SAT LLM Leaderboard is a benchmarking project that allows users to test their fine-tuned Korean language models on a 10-year dataset of the Korean College Scholastic Ability Test (CSAT). The project provides a platform to compare human academic ability with the performance of large language models (LLMs) on various question types to assess reading comprehension, critical thinking, and sentence interpretation skills. It aims to share benchmark data, utilize a reliable evaluation dataset curated by the Korea Institute for Curriculum and Evaluation, provide annual updates to prevent data leakage, and promote open-source LLM advancement for achieving top-tier performance on the Korean CSAT.

LMeterX
LMeterX is a professional large language model performance testing platform that supports model inference services based on large model inference frameworks and cloud services. It provides an intuitive Web interface for creating and managing test tasks, monitoring testing processes, and obtaining detailed performance analysis reports to support model deployment and optimization.

ai-on-gke
This repository contains assets related to AI/ML workloads on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). Run optimized AI/ML workloads with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) platform orchestration capabilities. A robust AI/ML platform considers the following layers: Infrastructure orchestration that support GPUs and TPUs for training and serving workloads at scale Flexible integration with distributed computing and data processing frameworks Support for multiple teams on the same infrastructure to maximize utilization of resources

ray
Ray is a unified framework for scaling AI and Python applications. It consists of a core distributed runtime and a set of AI libraries for simplifying ML compute, including Data, Train, Tune, RLlib, and Serve. Ray runs on any machine, cluster, cloud provider, and Kubernetes, and features a growing ecosystem of community integrations. With Ray, you can seamlessly scale the same code from a laptop to a cluster, making it easy to meet the compute-intensive demands of modern ML workloads.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.





