aibolit
A Static Analyzer for Java Powered by Machine Learning: Identifies Anti-Patterns Begging for Refactoring
Stars: 87
Aibolit is a machine learning-based static analyzer for Java that helps identify patterns contributing to Cyclomatic Complexity in Java source code. It provides recommendations for fixing identified issues and allows users to suppress certain patterns. Aibolit can analyze individual Java files or entire folders of Java source code. Users can customize the output format and exclude specific files from analysis. The tool also supports training custom models for analyzing Java code. Aibolit is designed to help developers improve code quality and maintainability by identifying and addressing potential issues in Java code.
README:
Learn how Aibolit works in our White Paper.
First, you install it (you must have Python 3.11+ and Pip installed):
pip3 install aibolit~=1.3.0To analyze your Java sources, located at src/java (for example), run:
aibolit check --filenames src/java/File.java src/java/AnotherFile.javaor
aibolit recommend --filenames src/java/File.java src/java/AnotherFile.javaAlso, you can set a folder with Java files:
aibolit recommend --folder src/javaIt will run recommendation function for the model (model is located in
aibolit/binary_files/model.pkl).
The model finds a pattern which contribution is the largest to the
Cyclomatic Complexity.
If anything is found, you will see all recommendations for the mentioned
patterns.
You can see the list of all patterns in
Patterns.md.
The output of recommendation will be redirected to the stdout.
If the program has the 0 exit code, it means that all analyzed files do
not have any issues.
If the program has the 1 exit code, it means that at least 1 analyzed file
has an issue.
If the program has the 2 exit code, it means that program crash occurred.
You can suppress certain patterns (comma separated value) and they will be ignored. They won't be included into the report, also their importance will be set to 0.
aibolit recommend --folder src/java --suppress=P12,P13You can change the format, using the --format parameter. The default value
is --format=compact.
aibolit recommend --folder src/java --format=compact --fullIt will output sorted patterns by importance in descending order and grouped by a pattern name:
Show all patterns
Configuration.java score: 127.67642529949538
Configuration.java[3840]: Var in the middle (P21: 30.95612931128819 1/4)
Configuration.java[3844]: Var in the middle (P21: 30.95612931128819 1/4)
Configuration.java[3848]: Var in the middle (P21: 30.95612931128819 1/4)
Configuration.java[2411]: Null Assignment (P28: 10.76 2/4)
Configuration.java[826]: Many primary constructors (P9: 10.76 3/4)
Configuration.java[840]: Many primary constructors (P9: 10.76 3/4)
Configuration.java[829]: Partial synchronized (P14: 0.228 4/4)
Configuration.java[841]: Partial synchronized (P14: 0.228 4/4)
Configuration.java[865]: Partial synchronized (P14: 0.228 4/4)
Configuration.java[2586]: Partial synchronized (P14: 0.228 4/4)
Configuration.java[3230]: Partial synchronized (P14: 0.228 4/4)
Configuration.java[3261]: Partial synchronized (P14: 0.228 4/4)
Configuration.java[3727]: Partial synchronized (P14: 0.228 4/4)
Configuration.java[3956]: Partial synchronized (P14: 0.228 4/4)
ErrorExample.java: error when calculating patterns: Can't count P1 metric:
Total score: 127.67642529949538
(P21: 30.95612931128819 1/4) means the following:
30.95612931128819 is the score of this pattern
1 is the position of this pattern in the total list of patterns
found in the file 4 is the total number of found patterns
You can use format=long. In this case all results will be sorted by a
line number:
Show all patterns
Configuration.java: some issues found
Configuration.java score: 127.67642529949538
Configuration.java[826]: Many primary constructors (P9: 10.76 3/4)
Configuration.java[829]: Partial synchronized (P14: 0.228 4/4)
Configuration.java[840]: Many primary constructors (P9: 10.76 3/4)
Configuration.java[841]: Partial synchronized (P14: 0.228 4/4)
Configuration.java[865]: Partial synchronized (P14: 0.228 4/4)
Configuration.java[2411]: Null Assignment (P28: 10.76 2/4)
Configuration.java[2586]: Partial synchronized (P14: 0.228 4/4)
Configuration.java[3230]: Partial synchronized (P14: 0.228 4/4)
Configuration.java[3261]: Partial synchronized (P14: 0.228 4/4)
Configuration.java[3727]: Partial synchronized (P14: 0.228 4/4)
Configuration.java[3840]: Var in the middle (P21: 30.95612931128819 1/4)
Configuration.java[3844]: Var in the middle (P21: 30.95612931128819 1/4)
Configuration.java[3848]: Var in the middle (P21: 30.95612931128819 1/4)
Configuration.java[3956]: Partial synchronized (P14: 0.228 4/4)
ErrorExample.java: error when calculating patterns: Can't count P1 metric:
MavenSlice.java: your code is perfect in aibolit's opinion
Total score: 127.67642529949538
You can also choose xml format. It will have the same format as compact
mode, but xml will be created:
<report>
<score>127.67642529949538</score>
<!--Show all patterns-->
<files>
<file>
<path>Configuration.java</path>
<summary>Some issues found</summary>
<score>127.67642529949538</score>
<patterns>
<pattern code="P13">
<details>Null check</details>
<lines>
<number>294</number>
<number>391</number>
</lines>
<score>30.95612931128819</score>
<order>1/4</order>
</pattern>
<pattern code="P12">
<details>Non final attribute</details>
<lines>
<number>235</number>
</lines>
<score>10.76</score>
<order>2/4</order>
</pattern>
<pattern code="P21">
<details>Var in the middle</details>
<lines>
<number>235</number>
</lines>
<score>2.056</score>
<order>3/4</order>
</pattern>
<pattern code="P28">
<details>Null Assignment</details>
<lines>
<number>2411</number>
</lines>
<score>0.228</score>
<order>4/4</order>
</pattern>
</patterns>
</file>
<file>
<path>ErrorExample.java</path>
<summary>Error when calculating patterns: Can't count P1 metric:</summary>
</file>
<file>
<path>MavenSlice.java</path>
<summary>Your code is perfect in aibolit's opinion</summary>
</file>
</files>
</report>The score is the relative importance of the pattern (there is no range for it). The larger score is, the most important pattern is. E.g., if you have several patterns, first you need to fix the pattern with the score 5.45:
SampleTests.java[43]: Non final attribute (P12: 5.45 1/10)
SampleTests.java[44]: Non final attribute (P12: 5.45 1/10)
SampleTests.java[80]: Var in the middle (P21: 3.71 2/10)
SampleTests.java[121]: Var in the middle (P21: 3.71 2/10)
SampleTests.java[122]: Var declaration distance for 5 lines (P20_5: 2.13 3/10)
SampleTests.java[41]: Non final class (P24: 1.95 4/10)
SampleTests.java[59]: Force Type Casting (P5: 1.45 5/10)
SampleTests.java[122]: Var declaration distance for 7 lines (P20_7: 1.07 6/10)
SampleTests.java[122]: Var declaration distance for 11 lines (P20_11: 0.78 7/10)
SampleTests.java[51]: Protected Method (P30: 0.60 8/10)
SampleTests.java[52]: Super Method (P18: 0.35 9/10)
SampleTests.java[100]: Partial synchronized (P14: 0.08 10/10)
SampleTests.java[106]: Partial synchronized (P14: 0.08 10/10)
SampleTests.java[113]: Partial synchronized (P14: 0.08 10/10)
The score per class is the sum of all patterns scores.
SampleTests.java score: 17.54698560768407
The total score is an average among all java files in a project (folder you've set to analyze)
Total average score: 4.0801854775508914
If you have 2 scores of different projects, the worst project is that one which has the highest score.
Model is automatically installed with aibolit package, but you can also try your own model
aibolit recommend --folder src/java --model /mnt/d/some_folder/model.pklYou can get full report with --full command, then all patterns will be
included to the output:
aibolit recommend --folder src/java --fullYou can exclude files with --exclude command.
You to set glob patterns to ignore:
aibolit recommend --folder src/java \
--exclude=**/*Test*.java --exclude=**/*Impl*.javaIf you need help, run
aibolit recommend --helpTrain command does the following:
- Calculates patterns and metrics
- Creates a dataset
- Trains model and save it
Train works only with cloned git repository.
- Clone aibolit repository
- Go to
cloned_aibolit_path - Run
pip install . - Set env variable
export HOME_AIBOLIT=cloned_aibolit_path(example for Linux). - Set env variable
TARGET_FOLDERif you need to save all dataset files to another directory. - You have to specify train and test dataset: set the
HOME_TRAIN_DATASETenvironment variable for train dataset and theHOME_TEST_DATASETenvironment variable for test dataset.
Usually, these files are in scripts/target/08 directory after dataset
collection (if you have not skipped it).
But you can use your own datasets.
Please notice, that if you set TARGET_FOLDER, your dataset files will be
in TARGET_FOLDER/target.
That is why it is necessary to
set HOME_TRAIN_DATASET=TARGET_FOLDER\target\08\08-train.csv,
HOME_TEST_DATASET =TARGET_FOLDER\target\08\08-test.csv
7. If you need to set up own directory where model will be saved, set up also
SAVE_MODEL_FOLDER environment variable.
Otherwise model will be saved into
cloned_aibolit_path/aibolit/binary_files/model.pkl
8. If you need to set up own folder with Java files, use --java_folder parameter, the default value will be scripts/target/01 of aibolit cloned
repo
Or you can use our docker image (link will be soon here)
Run train pipeline:
aibolit train --java_folder=src/java [--max_classes=100] [--dataset_file]If you need to save the dataset with all calculated metrics to a different
directory, you need to use dataset_file parameter
aibolit train --java_folder=src/java --dataset_file /mnt/d/new_dir/dataset.csvYou can skip dataset collection with skip_collect_dataset parameter. In
this case
the model will be trained with predefined dataset (see 5 point):
aibolit train --java_folder=src/java --skip_collect_datasetFirst, you need to install:
Install the following packages if you don't have them:
apt-get install ruby-dev libz-dev libxml2This project does not include a virtual environment by default. If you're using one (e.g., .venv, venv), update the .xcop file to exclude it:
--exclude=.venv/**After forking and editing the repo, verify the build is clean by running:
makeTo build white paper:
cd wp
latexmk -c && latexmk -pdf wp.texIf everything is fine, submit a pull request.
Using Docker recommendation pipeline
docker run --rm -it \
-v <absolute_path_to_folder_with_classes>:/in \
-v <absolute_path_to_out_dir>:/out \
cqfn/aibolit-imageFor Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for aibolit
Similar Open Source Tools

aibolit
Aibolit is a machine learning-based static analyzer for Java that helps identify patterns contributing to Cyclomatic Complexity in Java source code. It provides recommendations for fixing identified issues and allows users to suppress certain patterns. Aibolit can analyze individual Java files or entire folders of Java source code. Users can customize the output format and exclude specific files from analysis. The tool also supports training custom models for analyzing Java code. Aibolit is designed to help developers improve code quality and maintainability by identifying and addressing potential issues in Java code.

fastfit
FastFit is a Python package designed for fast and accurate few-shot classification, especially for scenarios with many semantically similar classes. It utilizes a novel approach integrating batch contrastive learning and token-level similarity score, significantly improving multi-class classification performance in speed and accuracy across various datasets. FastFit provides a convenient command-line tool for training text classification models with customizable parameters. It offers a 3-20x improvement in training speed, completing training in just a few seconds. Users can also train models with Python scripts and perform inference using pretrained models for text classification tasks.
AirspeedVelocity.jl
AirspeedVelocity.jl is a tool designed to simplify benchmarking of Julia packages over their lifetime. It provides a CLI to generate benchmarks, compare commits/tags/branches, plot benchmarks, and run benchmark comparisons for every submitted PR as a GitHub action. The tool freezes the benchmark script at a specific revision to prevent old history from affecting benchmarks. Users can configure options using CLI flags and visualize benchmark results. AirspeedVelocity.jl can be used to benchmark any Julia package and offers features like generating tables and plots of benchmark results. It also supports custom benchmarks and can be integrated into GitHub actions for automated benchmarking of PRs.

wllama
Wllama is a WebAssembly binding for llama.cpp, a high-performance and lightweight language model library. It enables you to run inference directly on the browser without the need for a backend or GPU. Wllama provides both high-level and low-level APIs, allowing you to perform various tasks such as completions, embeddings, tokenization, and more. It also supports model splitting, enabling you to load large models in parallel for faster download. With its Typescript support and pre-built npm package, Wllama is easy to integrate into your React Typescript projects.

siftrank
siftrank is an implementation of the Sift Rank document ranking algorithm that uses Large Language Models (LLMs) to efficiently find the most relevant items in any dataset based on a given prompt. It addresses issues like non-determinism, limited context, output constraints, and scoring subjectivity encountered when using LLMs directly. siftrank allows users to rank anything without fine-tuning or domain-specific models, running in seconds and costing pennies. It supports JSON input, Go template syntax for customization, and various advanced options for configuration and optimization.
chromem-go
chromem-go is an embeddable vector database for Go with a Chroma-like interface and zero third-party dependencies. It enables retrieval augmented generation (RAG) and similar embeddings-based features in Go apps without the need for a separate database. The focus is on simplicity and performance for common use cases, allowing querying of documents with minimal memory allocations. The project is in beta and may introduce breaking changes before v1.0.0.
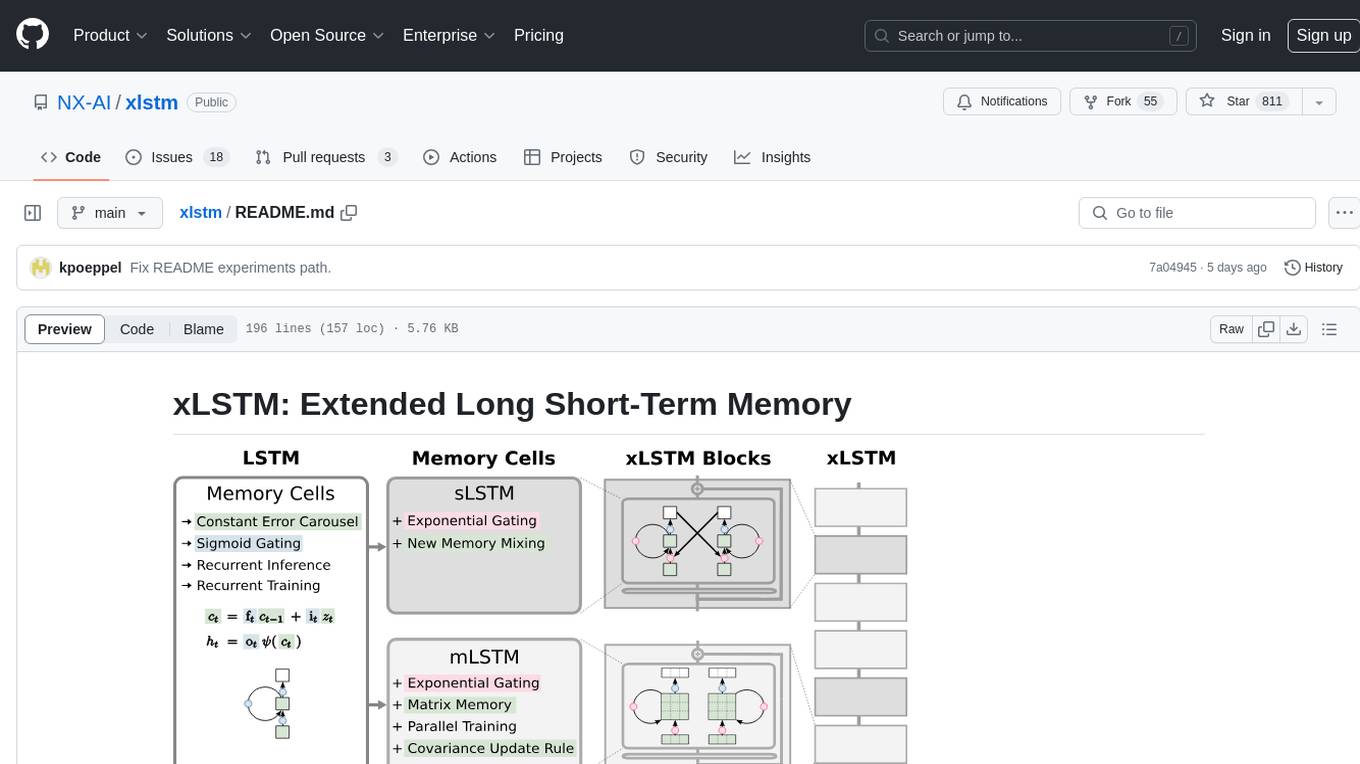
xlstm
xLSTM is a new Recurrent Neural Network architecture based on ideas of the original LSTM. Through Exponential Gating with appropriate normalization and stabilization techniques and a new Matrix Memory it overcomes the limitations of the original LSTM and shows promising performance on Language Modeling when compared to Transformers or State Space Models. The package is based on PyTorch and was tested for versions >=1.8. For the CUDA version of xLSTM, you need Compute Capability >= 8.0. The xLSTM tool provides two main components: xLSTMBlockStack for non-language applications or integrating in other architectures, and xLSTMLMModel for language modeling or other token-based applications.
consult-llm-mcp
Consult LLM MCP is an MCP server that enables users to consult powerful AI models like GPT-5.2, Gemini 3.0 Pro, and DeepSeek Reasoner for complex problem-solving. It supports multi-turn conversations, direct queries with optional file context, git changes inclusion for code review, comprehensive logging with cost estimation, and various CLI modes for Gemini and Codex. The tool is designed to simplify the process of querying AI models for assistance in resolving coding issues and improving code quality.
minja
Minja is a minimalistic C++ Jinja templating engine designed specifically for integration with C++ LLM projects, such as llama.cpp or gemma.cpp. It is not a general-purpose tool but focuses on providing a limited set of filters, tests, and language features tailored for chat templates. The library is header-only, requires C++17, and depends only on nlohmann::json. Minja aims to keep the codebase small, easy to understand, and offers decent performance compared to Python. Users should be cautious when using Minja due to potential security risks, and it is not intended for producing HTML or JavaScript output.
python-aiplatform
The Vertex AI SDK for Python is a library that provides a convenient way to use the Vertex AI API. It offers a high-level interface for creating and managing Vertex AI resources, such as datasets, models, and endpoints. The SDK also provides support for training and deploying custom models, as well as using AutoML models. With the Vertex AI SDK for Python, you can quickly and easily build and deploy machine learning models on Vertex AI.
magika
Magika is a novel AI-powered file type detection tool that relies on deep learning to provide accurate detection. It employs a custom, highly optimized model to enable precise file identification within milliseconds. Trained on a dataset of ~100M samples across 200+ content types, achieving an average ~99% accuracy. Used at scale by Google to improve user safety by routing files to security scanners. Available as a command line tool in Rust, Python API, and bindings for Rust, JavaScript/TypeScript, and GoLang.

simple-openai
Simple-OpenAI is a Java library that provides a simple way to interact with the OpenAI API. It offers consistent interfaces for various OpenAI services like Audio, Chat Completion, Image Generation, and more. The library uses CleverClient for HTTP communication, Jackson for JSON parsing, and Lombok to reduce boilerplate code. It supports asynchronous requests and provides methods for synchronous calls as well. Users can easily create objects to communicate with the OpenAI API and perform tasks like text-to-speech, transcription, image generation, and chat completions.
openai
An open-source client package that allows developers to easily integrate the power of OpenAI's state-of-the-art AI models into their Dart/Flutter applications. The library provides simple and intuitive methods for making requests to OpenAI's various APIs, including the GPT-3 language model, DALL-E image generation, and more. It is designed to be lightweight and easy to use, enabling developers to focus on building their applications without worrying about the complexities of dealing with HTTP requests. Note that this is an unofficial library as OpenAI does not have an official Dart library.

LightRAG
LightRAG is a PyTorch library designed for building and optimizing Retriever-Agent-Generator (RAG) pipelines. It follows principles of simplicity, quality, and optimization, offering developers maximum customizability with minimal abstraction. The library includes components for model interaction, output parsing, and structured data generation. LightRAG facilitates tasks like providing explanations and examples for concepts through a question-answering pipeline.
For similar tasks

aibolit
Aibolit is a machine learning-based static analyzer for Java that helps identify patterns contributing to Cyclomatic Complexity in Java source code. It provides recommendations for fixing identified issues and allows users to suppress certain patterns. Aibolit can analyze individual Java files or entire folders of Java source code. Users can customize the output format and exclude specific files from analysis. The tool also supports training custom models for analyzing Java code. Aibolit is designed to help developers improve code quality and maintainability by identifying and addressing potential issues in Java code.
code-review-gpt
Code Review GPT uses Large Language Models to review code in your CI/CD pipeline. It helps streamline the code review process by providing feedback on code that may have issues or areas for improvement. It should pick up on common issues such as exposed secrets, slow or inefficient code, and unreadable code. It can also be run locally in your command line to review staged files. Code Review GPT is in alpha and should be used for fun only. It may provide useful feedback but please check any suggestions thoroughly.
digma
Digma is a Continuous Feedback platform that provides code-level insights related to performance, errors, and usage during development. It empowers developers to own their code all the way to production, improving code quality and preventing critical issues. Digma integrates with OpenTelemetry traces and metrics to generate insights in the IDE, helping developers analyze code scalability, bottlenecks, errors, and usage patterns.
ai-codereviewer
AI Code Reviewer is a GitHub Action that utilizes OpenAI's GPT-4 API to provide intelligent feedback and suggestions on pull requests. It helps enhance code quality and streamline the code review process by offering insightful comments and filtering out specified files. The tool is easy to set up and integrate into GitHub workflows.
sourcery
Sourcery is an automated code reviewer tool that provides instant feedback on pull requests, helping to speed up the code review process, improve code quality, and accelerate development velocity. It offers high-level feedback, line-by-line suggestions, and aims to mimic the type of code review one would expect from a colleague. Sourcery can also be used as an IDE coding assistant to understand existing code, add unit tests, optimize code, and improve code quality with instant suggestions. It is free for public repos/open source projects and offers a 14-day trial for private repos.
RTL-Coder
RTL-Coder is a tool designed to outperform GPT-3.5 in RTL code generation by providing a fully open-source dataset and a lightweight solution. It targets Verilog code generation and offers an automated flow to generate a large labeled dataset with over 27,000 diverse Verilog design problems and answers. The tool addresses the data availability challenge in IC design-related tasks and can be used for various applications beyond LLMs. The tool includes four RTL code generation models available on the HuggingFace platform, each with specific features and performance characteristics. Additionally, RTL-Coder introduces a new LLM training scheme based on code quality feedback to further enhance model performance and reduce GPU memory consumption.
AwesomeLLM4APR
Awesome LLM for APR is a repository dedicated to exploring the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in Automated Program Repair (APR). It provides a comprehensive collection of research papers, tools, and resources related to using LLMs for various scenarios such as repairing semantic bugs, security vulnerabilities, syntax errors, programming problems, static warnings, self-debugging, type errors, web UI tests, smart contracts, hardware bugs, performance bugs, API misuses, crash bugs, test case repairs, formal proofs, GitHub issues, code reviews, motion planners, human studies, and patch correctness assessments. The repository serves as a valuable reference for researchers and practitioners interested in leveraging LLMs for automated program repair.
monacopilot
Monacopilot is a powerful and customizable AI auto-completion plugin for the Monaco Editor. It supports multiple AI providers such as Anthropic, OpenAI, Groq, and Google, providing real-time code completions with an efficient caching system. The plugin offers context-aware suggestions, customizable completion behavior, and framework agnostic features. Users can also customize the model support and trigger completions manually. Monacopilot is designed to enhance coding productivity by providing accurate and contextually appropriate completions in daily spoken language.
For similar jobs

sourcegraph
Sourcegraph is a code search and navigation tool that helps developers read, write, and fix code in large, complex codebases. It provides features such as code search across all repositories and branches, code intelligence for navigation and refactoring, and the ability to fix and refactor code across multiple repositories at once.
pr-agent
PR-Agent is a tool that helps to efficiently review and handle pull requests by providing AI feedbacks and suggestions. It supports various commands such as generating PR descriptions, providing code suggestions, answering questions about the PR, and updating the CHANGELOG.md file. PR-Agent can be used via CLI, GitHub Action, GitHub App, Docker, and supports multiple git providers and models. It emphasizes real-life practical usage, with each tool having a single GPT-4 call for quick and affordable responses. The PR Compression strategy enables effective handling of both short and long PRs, while the JSON prompting strategy allows for modular and customizable tools. PR-Agent Pro, the hosted version by CodiumAI, provides additional benefits such as full management, improved privacy, priority support, and extra features.

code-review-gpt
Code Review GPT uses Large Language Models to review code in your CI/CD pipeline. It helps streamline the code review process by providing feedback on code that may have issues or areas for improvement. It should pick up on common issues such as exposed secrets, slow or inefficient code, and unreadable code. It can also be run locally in your command line to review staged files. Code Review GPT is in alpha and should be used for fun only. It may provide useful feedback but please check any suggestions thoroughly.
DevoxxGenieIDEAPlugin
Devoxx Genie is a Java-based IntelliJ IDEA plugin that integrates with local and cloud-based LLM providers to aid in reviewing, testing, and explaining project code. It supports features like code highlighting, chat conversations, and adding files/code snippets to context. Users can modify REST endpoints and LLM parameters in settings, including support for cloud-based LLMs. The plugin requires IntelliJ version 2023.3.4 and JDK 17. Building and publishing the plugin is done using Gradle tasks. Users can select an LLM provider, choose code, and use commands like review, explain, or generate unit tests for code analysis.
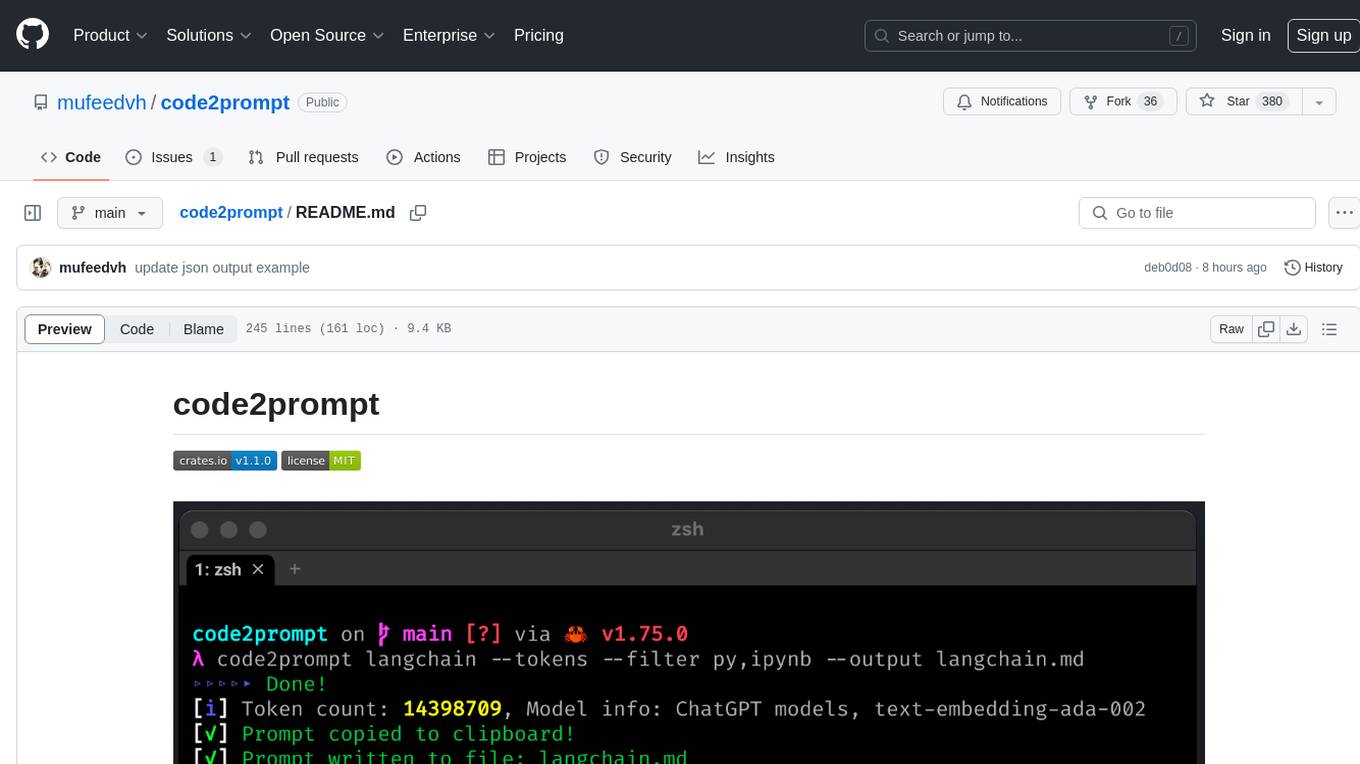
code2prompt
code2prompt is a command-line tool that converts your codebase into a single LLM prompt with a source tree, prompt templating, and token counting. It automates generating LLM prompts from codebases of any size, customizing prompt generation with Handlebars templates, respecting .gitignore, filtering and excluding files using glob patterns, displaying token count, including Git diff output, copying prompt to clipboard, saving prompt to an output file, excluding files and folders, adding line numbers to source code blocks, and more. It helps streamline the process of creating LLM prompts for code analysis, generation, and other tasks.

ai-codereviewer
AI Code Reviewer is a GitHub Action that utilizes OpenAI's GPT-4 API to provide intelligent feedback and suggestions on pull requests. It helps enhance code quality and streamline the code review process by offering insightful comments and filtering out specified files. The tool is easy to set up and integrate into GitHub workflows.
github-pr-summary
github-pr-summary is a bot designed to summarize GitHub Pull Requests, helping open source contributors make faster decisions. It automatically summarizes commits and changed files in PRs, triggered by new commits or a magic trigger phrase. Users can deploy their own code review bot in 3 steps: create a bot from their GitHub repo, configure it to review PRs, and connect to GitHub for access to the target repo. The bot runs on flows.network using Rust and WasmEdge Runtimes. It utilizes ChatGPT/4 to review and summarize PR content, posting the result back as a comment on the PR. The bot can be used on multiple repos by creating new flows and importing the source code repo, specifying the target repo using flow config. Users can also change the magic phrase to trigger a review from a PR comment.
fittencode.nvim
Fitten Code AI Programming Assistant for Neovim provides fast completion using AI, asynchronous I/O, and support for various actions like document code, edit code, explain code, find bugs, generate unit test, implement features, optimize code, refactor code, start chat, and more. It offers features like accepting suggestions with Tab, accepting line with Ctrl + Down, accepting word with Ctrl + Right, undoing accepted text, automatic scrolling, and multiple HTTP/REST backends. It can run as a coc.nvim source or nvim-cmp source.