
pai-opencode
PAI 2.4 (Personal AI Infrastructure) ported to OpenCode - Community contribution
Stars: 67
PAI-OpenCode is a complete port of Daniel Miessler's Personal AI Infrastructure (PAI) to OpenCode, an open-source, provider-agnostic AI coding assistant. It brings modular capabilities, dynamic multi-agent orchestration, session history, and lifecycle automation to personalize AI assistants for users. With support for 75+ AI providers, PAI-OpenCode offers dynamic per-task model routing, full PAI infrastructure, real-time session sharing, and multiple client options. The tool optimizes cost and quality with a 3-tier model strategy and a 3-tier research system, allowing users to switch presets for different routing strategies. PAI-OpenCode's architecture preserves PAI's design while adapting to OpenCode, documented through Architecture Decision Records (ADRs).
README:
Personal AI Infrastructure for OpenCode — Bring Daniel Miessler's renowned PAI scaffolding to any AI provider.
v1.3 Release — Multi-Provider Agent System with Dynamic Tier Routing. Every agent scales to the right model for the task. Choose your preset:
zen-paid,openrouter, orlocal-ollama. See CHANGELOG.md.
PAI-OpenCode is the complete port of Daniel Miessler's Personal AI Infrastructure (PAI) to OpenCode — an open-source, provider-agnostic AI coding assistant.
PAI is a scaffolding system that makes AI assistants work better for you. It's not about which model you use — it's about the infrastructure around it:
- Skills — Modular capabilities (code review, security testing, research, design)
- Agents — Dynamic multi-agent orchestration
- Memory — Session history, project context, learning loops
- Plugins — Lifecycle automation (session init, security validation, observability)
OpenCode is an open-source alternative to Claude Code that supports 75+ AI providers — from Anthropic and OpenAI to Google, AWS Bedrock, Ollama, and beyond.
PAI-OpenCode = The best of both worlds.
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| PAI was built for Claude Code (Anthropic only) | PAI-OpenCode works with any AI provider |
| Vendor lock-in limits your options | Switch providers freely while keeping your infrastructure |
| One model fits all wastes money or quality | Each agent scales to the right model per task — cheap for simple work, powerful for complex reasoning |
| Generic AI assistants don't know your workflow | PAI's skills, memory, and plugins personalize to your needs |
| One-shot interactions lose context | PAI's memory system builds knowledge over time |
The scaffolding is more important than the model. PAI-OpenCode gives you:
✅ Dynamic per-task model routing — the orchestrator selects the right model and provider for each task, automatically ✅ Provider freedom (Claude, GPT-4, Gemini, Kimi, Ollama, etc.) ✅ Full PAI infrastructure (skills, agents, memory, plugins) ✅ Real-time session sharing (OpenCode feature) ✅ Terminal + Desktop + Web clients ✅ Community-driven, open-source foundation
Note: Dynamic per-task model routing is built by the PAI-OpenCode agent system on top of OpenCode's multi-provider support. Other AI coding tools either lock you to one provider (Claude Code, Copilot) or let you switch manually (Cursor, Aider) — but none route different models to the same agent automatically based on task complexity.
# 1. Clone PAI-OpenCode
git clone https://github.com/Steffen025/pai-opencode.git
cd pai-opencode
# 2. Run the Installation Wizard
bun run .opencode/PAIOpenCodeWizard.ts
# 3. Start OpenCode
opencodeAlready using OpenCode? If you have an existing
~/.opencodedirectory, see Existing OpenCode Users in the Installation Guide for symlink setup.
The wizard will ask you to:
-
Choose your preset —
zen-paid(recommended),openrouter(provider diversity), orlocal-ollama(fully offline) - Configure research agents (optional)
- Set your name and timezone
- Name your AI assistant
Takes ~2 minutes and creates all necessary configuration files.
After running the wizard, start OpenCode and paste this prompt for full personalization:
Let's do the onboarding. Guide me through setting up my personal context -
my name, my goals, my values, and how I want you to behave. Create the TELOS
and identity files that make this AI mine.
This 10-15 minute interactive session will configure your complete TELOS framework:
| What Gets Created | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Mission & Goals | Your life purposes and specific objectives |
| Challenges & Strategies | What's blocking you and how to overcome it |
| Values & Beliefs | Core principles that guide decisions |
| Narratives | Your key talking points and messages |
| Tech Preferences | Languages, frameworks, tools you prefer |
Why TELOS matters: PAI becomes exponentially more useful when it knows your context. Generic AI gives generic advice. PAI with TELOS gives you-specific guidance.
Modular, reusable capabilities invoked by name:
- CORE — Identity, preferences, auto-loaded at session start
- Art — Excalidraw-style visual diagrams
- Browser — Code-first browser automation
- Security — Pentesting, secret scanning
- Research — Cost-aware multi-provider research system (see below)
Dynamic multi-agent composition with intelligent tier routing — every agent scales up or down based on task complexity:
| Agent | Default | Scales Down To | Scales Up To |
|---|---|---|---|
| Algorithm | Claude Opus 4.6 | — | — |
| Architect | Kimi K2.5 | GLM 4.7 (quick review) | Claude Opus 4.6 (complex architecture) |
| Engineer | Kimi K2.5 | GLM 4.7 (batch edits) | Claude Sonnet 4.5 (complex debugging) |
| DeepResearcher | GLM 4.7 | MiniMax (quick lookup) | Kimi K2.5 (deep analysis) |
| GeminiResearcher | Gemini 3 Flash | — | Gemini 3 Pro (deep research) |
| PerplexityResearcher | Sonar | — | Sonar Deep Research |
| GrokResearcher | Grok 4.1 Fast | — | Grok 4.1 (full analysis) |
| CodexResearcher | GPT-5.1 Codex Mini | — | GPT-5.2 Codex |
| Writer | Gemini 3 Flash | MiniMax (quick drafts) | Claude Sonnet 4.5 (premium copy) |
| Pentester | Kimi K2.5 | GLM 4.7 (quick scan) | Claude Sonnet 4.5 (deep audit) |
| Intern | MiniMax M2.1 | — | — |
| Explore | MiniMax M2.1 | — | — |
| QATester | GLM 4.7 | — | — |
| Designer | Kimi K2.5 | GLM 4.7 | Claude Sonnet 4.5 |
| Artist | Kimi K2.5 | GLM 4.7 | Claude Sonnet 4.5 |
| General | GLM 4.7 | MiniMax | Kimi K2.5 |
The orchestrator decides per task which model tier to use. You always pay exactly what the task requires.
Persistent context across sessions:
- Session transcripts (
.opencode/MEMORY/SESSIONS/) - Project documentation (
.opencode/MEMORY/projects/) - Learning loops (
.opencode/MEMORY/LEARNINGS/)
TypeScript lifecycle plugins with comprehensive coverage:
- Context injection at session start
- Security validation before commands
- Voice notifications (ElevenLabs + Google TTS + macOS say)
- Implicit sentiment detection from user messages
- Tab state updates for Kitty terminal
- ISC tracking and response capture
- Rating capture and learning loops
- Observability (real-time event streaming and monitoring)
Use any AI provider:
- Anthropic (Claude)
- OpenAI (GPT-4)
- Google (Gemini)
- AWS Bedrock
- Groq, Mistral, Ollama, and more...
PAI-OpenCode offers three presets — each gives you access to 75+ providers with different routing strategies:
| Preset | Best For | Providers | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
zen-paid (Recommended) |
Production use, privacy-conscious | 75+ providers via Zen AI Gateway | ~$1-75/1M tokens depending on tier |
openrouter |
Provider diversity, experimental models | OpenRouter routing to 100+ models | Varies by model |
local-ollama |
Full privacy, offline operation | Local Ollama instance | FREE (your hardware) |
The key insight is dynamic multi-provider routing within a single session. Unlike tools locked to one provider, PAI-OpenCode can:
- Route the orchestrator to Anthropic (Opus 4.6) for complex decisions
- Route research agents to Zen (GLM 4.7, Kimi K2.5) for cost-effective search
- Route real-time queries to Perplexity (Sonar) for breaking news
- All in the same task, automatically
This is what PAI on OpenCode can do that PAI on Claude Code cannot — Claude Code is locked to Anthropic only.
Easy to customize later via ADVANCED-SETUP.md
# Re-run the wizard to change preset
bun run .opencode/PAIOpenCodeWizard.tsEach agent uses a 3-tier model strategy — the orchestrator selects the right tier based on task complexity:
| Tier | Purpose | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Quick | Fast, cheap tasks | Batch edits, simple replacements, file search |
| Standard | Most work | Feature implementation, research, bug fixes |
| Advanced | Complex reasoning | Edge cases, architecture decisions, debugging |
The same agent uses different models depending on the task:
| Task | Agent | Tier | Model | Why |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch rename files | Engineer | quick |
GLM 4.7 | Simple mechanical work |
| Implement auth middleware | Engineer | standard |
Kimi K2.5 | Real coding task |
| Debug race condition | Engineer | advanced |
Claude Sonnet 4.5 | Complex reasoning needed |
| Quick web lookup | DeepResearcher | quick |
MiniMax | Simple fact check |
| Strategic market analysis | DeepResearcher | standard |
GLM 4.7 | Multi-step research |
| Deep technical investigation | DeepResearcher | advanced |
Kimi K2.5 | Large context, complex synthesis |
The orchestrator automatically selects the tier via the model_tier parameter in Task tool calls. You pay for exactly what the task requires — no more, no less.
Note: Model tier routing is configured in
opencode.json. The orchestrator makes the decision per task based on complexity assessment.
PAI-OpenCode includes a 3-tier research system that optimizes for both quality and cost:
| Tier | Workflow | Agents | Cost | Trigger |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quick (DEFAULT) | QuickResearch |
1 agent | $0 FREE | "research X" |
| Standard | StandardResearch |
3 (Claude + Gemini + Perplexity) | ~$0.01 | "standard research" |
| Extensive | ExtensiveResearch |
4-5 providers | ~$0.10-0.50 | "extensive research" |
Quick Research is FREE — Uses free tier or cached results. No API keys needed for basic queries.
Standard Research adds multi-perspective coverage with Gemini and Perplexity for ~$0.01 per query.
Extensive Research requires explicit confirmation before running (cost gate) to prevent unexpected charges.
| Agent | Model | Specialty | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
DeepResearcher |
Configured in opencode.json
|
Academic depth, scholarly synthesis | Free/Paid |
GeminiResearcher |
Gemini 2.5 Flash | Multi-perspective analysis | ~$0.002 |
GrokResearcher |
xAI Grok 4.1 Fast | Contrarian, social media, X access | ~$0.01 |
PerplexityResearcher |
Perplexity Sonar | Real-time news, breaking events | ~$0.01 |
CodexResearcher |
GPT-4.1 / GPT-5.1 | Technical, TypeScript-focused | ~$0.03 |
Option 1: Wizard — The installation wizard asks about research configuration during setup.
Option 2: CLI — Add research agents anytime:
bun run .opencode/tools/switch-provider.ts --add-researchersRequired API keys (add to ~/.opencode/.env):
| Key | For | Where to get |
|---|---|---|
GOOGLE_API_KEY |
GeminiResearcher | https://aistudio.google.com/apikey |
XAI_API_KEY |
GrokResearcher | https://console.x.ai/ |
PERPLEXITY_API_KEY |
PerplexityResearcher | https://perplexity.ai/settings/api |
OPENROUTER_API_KEY |
CodexResearcher | https://openrouter.ai/keys |
Missing a key? No problem — that researcher falls back to your primary provider.
PAI-OpenCode's design is documented through Architecture Decision Records (ADRs)—formal documents explaining why we made specific choices during the port from Claude Code to OpenCode.
| ADR | Decision | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| ADR-001 | Hooks → Plugins | OpenCode uses in-process plugins, not subprocess hooks |
| ADR-002 |
.claude/ → .opencode/
|
Platform directory convention |
| ADR-003 | Skills System Unchanged | Preserves upstream PAI compatibility |
| ADR-004 | File-Based Logging | Prevents TUI corruption from console.log |
| ADR-005 | Dual Config Files | PAI settings.json + OpenCode opencode.json |
| ADR-006 | Security Patterns Preserved | Critical security validation unchanged |
| ADR-007 | Memory Structure Preserved | File-based MEMORY/ system unchanged |
Key Principles:
- Preserve PAI's design where possible
- Adapt to OpenCode where necessary
- Document every change in ADRs
| Document | Description |
|---|---|
| CHANGELOG.md | Version history and release notes |
| docs/WHAT-IS-PAI.md | PAI fundamentals explained |
| docs/OPENCODE-FEATURES.md | OpenCode unique features |
| docs/PLUGIN-SYSTEM.md | Plugin architecture (14 handlers) |
| docs/PAI-ADAPTATIONS.md | Changes from PAI 2.5 |
| docs/MIGRATION.md | Migration from Claude Code PAI |
| ROADMAP.md | Version roadmap |
| CONTRIBUTING.md | Contribution guidelines |
For Contributors:
| Document | Description |
|---|---|
| PAI-to-OpenCode Mapping | How to correctly import PAI components |
Upstream Resources:
- Daniel Miessler's PAI — Original PAI documentation
- OpenCode Documentation — OpenCode official docs
PAI-OpenCode stands on the shoulders of giants:
The original PAI vision and architecture. Daniel's work on personalized AI scaffolding is foundational to this project. 🔗 github.com/danielmiessler/Personal_AI_Infrastructure
The open-source, provider-agnostic runtime that makes PAI-OpenCode possible. 🔗 github.com/anomalyco/opencode 🔗 docs.opencode.ai
MIT License — see LICENSE for details.
PAI-OpenCode is an independent port. Original PAI by Daniel Miessler, OpenCode by Anomaly.
git clone https://github.com/Steffen025/pai-opencode.git
cd pai-opencode && bun run .opencode/PAIOpenCodeWizard.ts && opencodeWelcome to Personal AI Infrastructure, your way.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for pai-opencode
Similar Open Source Tools

pai-opencode
PAI-OpenCode is a complete port of Daniel Miessler's Personal AI Infrastructure (PAI) to OpenCode, an open-source, provider-agnostic AI coding assistant. It brings modular capabilities, dynamic multi-agent orchestration, session history, and lifecycle automation to personalize AI assistants for users. With support for 75+ AI providers, PAI-OpenCode offers dynamic per-task model routing, full PAI infrastructure, real-time session sharing, and multiple client options. The tool optimizes cost and quality with a 3-tier model strategy and a 3-tier research system, allowing users to switch presets for different routing strategies. PAI-OpenCode's architecture preserves PAI's design while adapting to OpenCode, documented through Architecture Decision Records (ADRs).
AReaL
AReaL (Ant Reasoning RL) is an open-source reinforcement learning system developed at the RL Lab, Ant Research. It is designed for training Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) in a fully open and inclusive manner. AReaL provides reproducible experiments for 1.5B and 7B LRMs, showcasing its scalability and performance across diverse computational budgets. The system follows an iterative training process to enhance model performance, with a focus on mathematical reasoning tasks. AReaL is equipped to adapt to different computational resource settings, enabling users to easily configure and launch training trials. Future plans include support for advanced models, optimizations for distributed training, and exploring research topics to enhance LRMs' reasoning capabilities.

motia
Motia is an AI agent framework designed for software engineers to create, test, and deploy production-ready AI agents quickly. It provides a code-first approach, allowing developers to write agent logic in familiar languages and visualize execution in real-time. With Motia, developers can focus on business logic rather than infrastructure, offering zero infrastructure headaches, multi-language support, composable steps, built-in observability, instant APIs, and full control over AI logic. Ideal for building sophisticated agents and intelligent automations, Motia's event-driven architecture and modular steps enable the creation of GenAI-powered workflows, decision-making systems, and data processing pipelines.
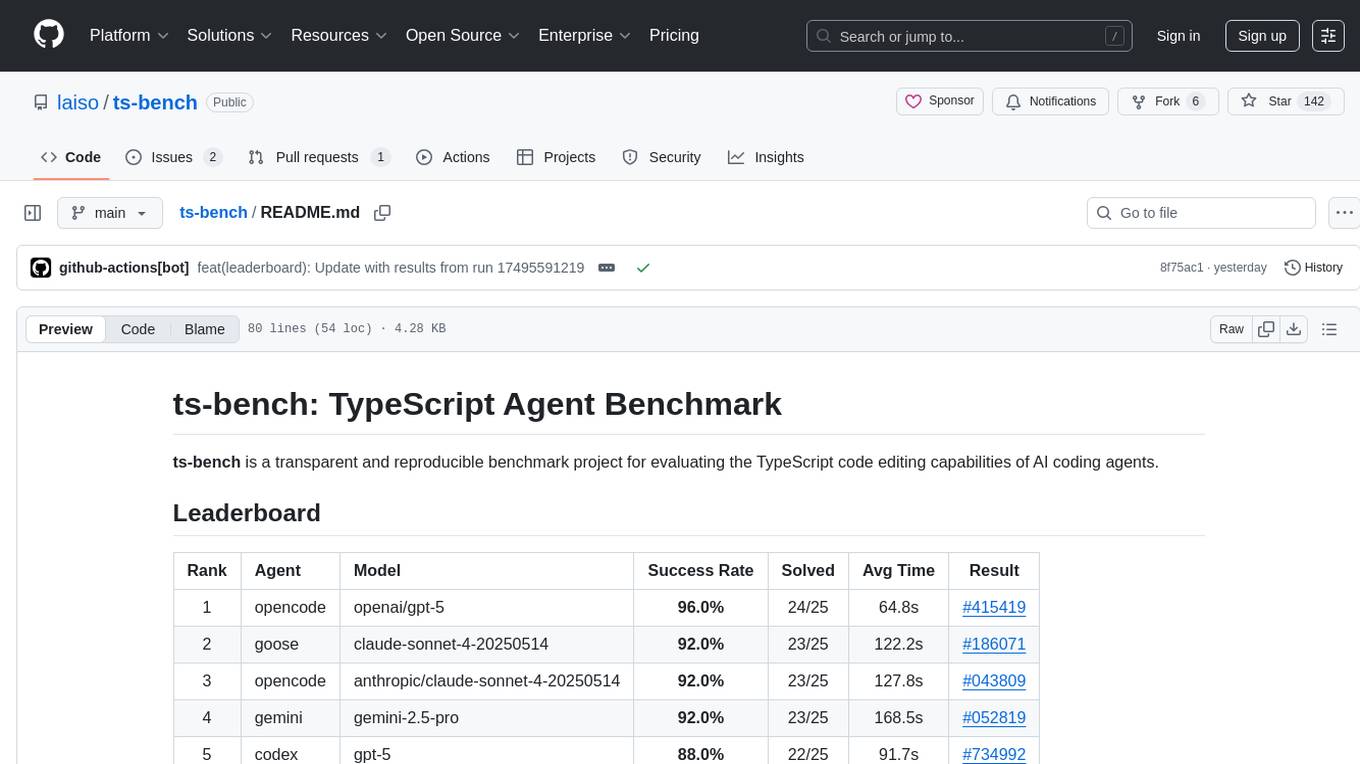
ts-bench
TS-Bench is a performance benchmarking tool for TypeScript projects. It provides detailed insights into the performance of TypeScript code, helping developers optimize their projects. With TS-Bench, users can measure and compare the execution time of different code snippets, functions, or modules. The tool offers a user-friendly interface for running benchmarks and analyzing the results. TS-Bench is a valuable asset for developers looking to enhance the performance of their TypeScript applications.

deepfabric
DeepFabric is a CLI tool and SDK designed for researchers and developers to generate high-quality synthetic datasets at scale using large language models. It leverages a graph and tree-based architecture to create diverse and domain-specific datasets while minimizing redundancy. The tool supports generating Chain of Thought datasets for step-by-step reasoning tasks and offers multi-provider support for using different language models. DeepFabric also allows for automatic dataset upload to Hugging Face Hub and uses YAML configuration files for flexibility in dataset generation.
sktime
sktime is a Python library for time series analysis that provides a unified interface for various time series learning tasks such as classification, regression, clustering, annotation, and forecasting. It offers time series algorithms and tools compatible with scikit-learn for building, tuning, and validating time series models. sktime aims to enhance the interoperability and usability of the time series analysis ecosystem by empowering users to apply algorithms across different tasks and providing interfaces to related libraries like scikit-learn, statsmodels, tsfresh, PyOD, and fbprophet.
UniCoT
Uni-CoT is a unified reasoning framework that extends Chain-of-Thought (CoT) principles to the multimodal domain, enabling Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to perform interpretable, step-by-step reasoning across both text and vision. It decomposes complex multimodal tasks into structured, manageable steps that can be executed sequentially or in parallel, allowing for more scalable and systematic reasoning.
ai-dev-kit
The AI Dev Kit is a comprehensive toolkit designed to enhance AI-driven development on Databricks. It provides trusted sources for AI coding assistants like Claude Code and Cursor to build faster and smarter on Databricks. The kit includes features such as Spark Declarative Pipelines, Databricks Jobs, AI/BI Dashboards, Unity Catalog, Genie Spaces, Knowledge Assistants, MLflow Experiments, Model Serving, Databricks Apps, and more. Users can choose from different adventures like installing the kit, using the visual builder app, teaching AI assistants Databricks patterns, executing Databricks actions, or building custom integrations with the core library. The kit also includes components like databricks-tools-core, databricks-mcp-server, databricks-skills, databricks-builder-app, and ai-dev-project.
axonhub
AxonHub is an all-in-one AI development platform that serves as an AI gateway allowing users to switch between model providers without changing any code. It provides features like vendor lock-in prevention, integration simplification, observability enhancement, and cost control. Users can access any model using any SDK with zero code changes. The platform offers full request tracing, enterprise RBAC, smart load balancing, and real-time cost tracking. AxonHub supports multiple databases, provides a unified API gateway, and offers flexible model management and API key creation for authentication. It also integrates with various AI coding tools and SDKs for seamless usage.

EasyEdit
EasyEdit is a Python package for edit Large Language Models (LLM) like `GPT-J`, `Llama`, `GPT-NEO`, `GPT2`, `T5`(support models from **1B** to **65B**), the objective of which is to alter the behavior of LLMs efficiently within a specific domain without negatively impacting performance across other inputs. It is designed to be easy to use and easy to extend.
spark-nlp
Spark NLP is a state-of-the-art Natural Language Processing library built on top of Apache Spark. It provides simple, performant, and accurate NLP annotations for machine learning pipelines that scale easily in a distributed environment. Spark NLP comes with 36000+ pretrained pipelines and models in more than 200+ languages. It offers tasks such as Tokenization, Word Segmentation, Part-of-Speech Tagging, Named Entity Recognition, Dependency Parsing, Spell Checking, Text Classification, Sentiment Analysis, Token Classification, Machine Translation, Summarization, Question Answering, Table Question Answering, Text Generation, Image Classification, Image to Text (captioning), Automatic Speech Recognition, Zero-Shot Learning, and many more NLP tasks. Spark NLP is the only open-source NLP library in production that offers state-of-the-art transformers such as BERT, CamemBERT, ALBERT, ELECTRA, XLNet, DistilBERT, RoBERTa, DeBERTa, XLM-RoBERTa, Longformer, ELMO, Universal Sentence Encoder, Llama-2, M2M100, BART, Instructor, E5, Google T5, MarianMT, OpenAI GPT2, Vision Transformers (ViT), OpenAI Whisper, and many more not only to Python and R, but also to JVM ecosystem (Java, Scala, and Kotlin) at scale by extending Apache Spark natively.
qserve
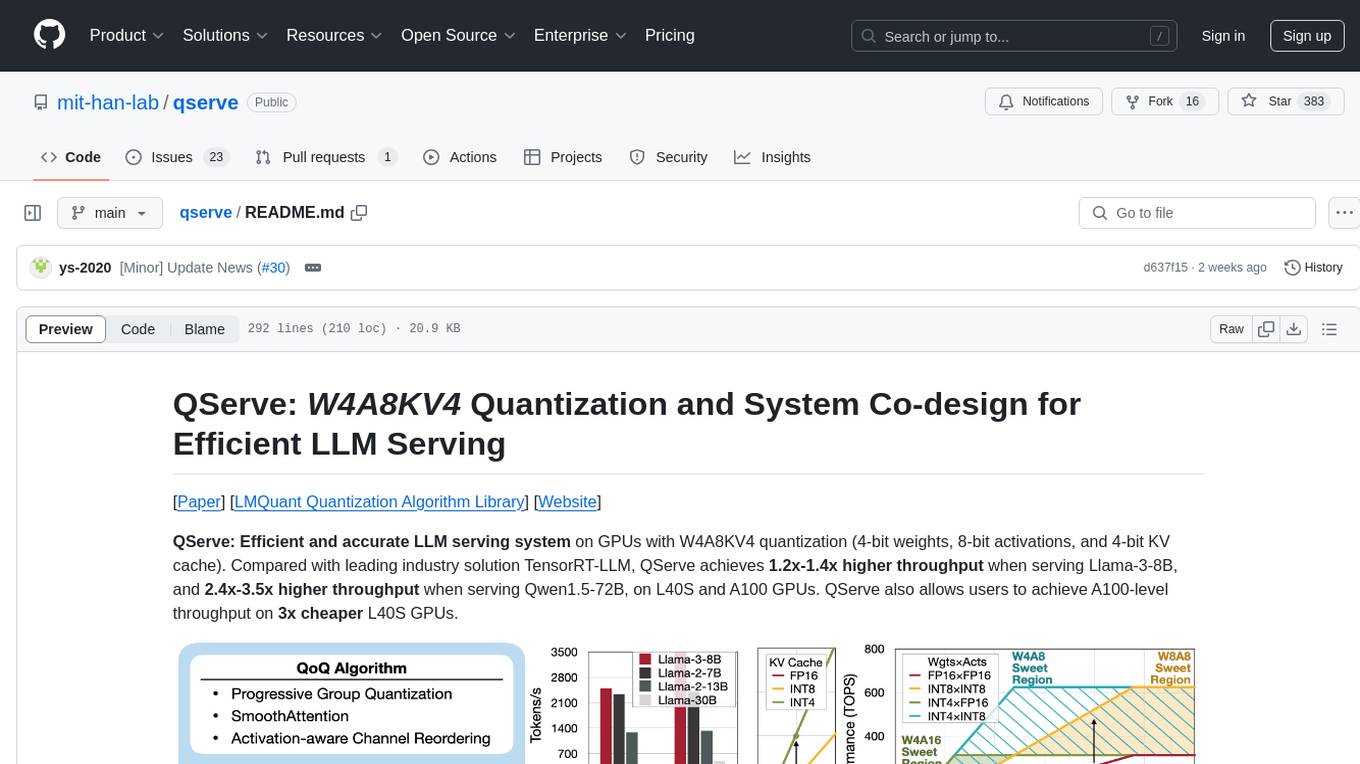
QServe is a serving system designed for efficient and accurate Large Language Models (LLM) on GPUs with W4A8KV4 quantization. It achieves higher throughput compared to leading industry solutions, allowing users to achieve A100-level throughput on cheaper L40S GPUs. The system introduces the QoQ quantization algorithm with 4-bit weight, 8-bit activation, and 4-bit KV cache, addressing runtime overhead challenges. QServe improves serving throughput for various LLM models by implementing compute-aware weight reordering, register-level parallelism, and fused attention memory-bound techniques.
azure-agentic-infraops
Agentic InfraOps is a multi-agent orchestration system for Azure infrastructure development that transforms how you build Azure infrastructure with AI agents. It provides a structured 7-step workflow that coordinates specialized AI agents through a complete infrastructure development cycle: Requirements → Architecture → Design → Plan → Code → Deploy → Documentation. The system enforces Azure Well-Architected Framework (WAF) alignment and Azure Verified Modules (AVM) at every phase, combining the speed of AI coding with best practices in cloud engineering.
Botright
Botright is a tool designed for browser automation that focuses on stealth and captcha solving. It uses a real Chromium-based browser for enhanced stealth and offers features like browser fingerprinting and AI-powered captcha solving. The tool is suitable for developers looking to automate browser tasks while maintaining anonymity and bypassing captchas. Botright is available in async mode and can be easily integrated with existing Playwright code. It provides solutions for various captchas such as hCaptcha, reCaptcha, and GeeTest, with high success rates. Additionally, Botright offers browser stealth techniques and supports different browser functionalities for seamless automation.
MaixPy
MaixPy is a Python SDK that enables users to easily create AI vision projects on edge devices. It provides a user-friendly API for accessing NPU, making it suitable for AI Algorithm Engineers, STEM teachers, Makers, Engineers, Students, Enterprises, and Contestants. The tool supports Python programming, MaixVision Workstation, AI vision, video streaming, voice recognition, and peripheral usage. It also offers an online AI training platform called MaixHub. MaixPy is designed for new hardware platforms like MaixCAM, offering improved performance and features compared to older versions. The ecosystem includes hardware, software, tools, documentation, and a cloud platform.
sf-skills
sf-skills is a collection of reusable skills for Agentic Salesforce Development, enabling AI-powered code generation, validation, testing, debugging, and deployment. It includes skills for development, quality, foundation, integration, AI & automation, DevOps & tooling. The installation process is newbie-friendly and includes an installer script for various CLIs. The skills are compatible with platforms like Claude Code, OpenCode, Codex, Gemini, Amp, Droid, Cursor, and Agentforce Vibes. The repository is community-driven and aims to strengthen the Salesforce ecosystem.
For similar tasks
ai-codereviewer
AI Code Reviewer is a GitHub Action that utilizes OpenAI's GPT-4 API to provide intelligent feedback and suggestions on pull requests. It helps enhance code quality and streamline the code review process by offering insightful comments and filtering out specified files. The tool is easy to set up and integrate into GitHub workflows.
100x-LLM
This repository contains code snippets and examples from the 100x Applied AI cohort lectures. It includes implementations of LLM Workflows, RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation), Agentic Patterns, Chat Completions with various providers, Function Calling, and more. The repository structure consists of core components like LLM Workflows, RAG Implementations, Agentic Patterns, Chat Completions, Function Calling, Hugging Face Integration, and additional components for various agent implementations, presentation generation, Notion API integration, FastAPI-based endpoints, authentication implementations, and LangChain usage examples.

pai-opencode
PAI-OpenCode is a complete port of Daniel Miessler's Personal AI Infrastructure (PAI) to OpenCode, an open-source, provider-agnostic AI coding assistant. It brings modular capabilities, dynamic multi-agent orchestration, session history, and lifecycle automation to personalize AI assistants for users. With support for 75+ AI providers, PAI-OpenCode offers dynamic per-task model routing, full PAI infrastructure, real-time session sharing, and multiple client options. The tool optimizes cost and quality with a 3-tier model strategy and a 3-tier research system, allowing users to switch presets for different routing strategies. PAI-OpenCode's architecture preserves PAI's design while adapting to OpenCode, documented through Architecture Decision Records (ADRs).

choco-builder
ChocoBuilder (aka Chocolate Factory) is an open-source LLM application development framework designed to help you easily create powerful software development SDLC + LLM generation assistants. It provides modules for integration into JVM projects, usage with RAGScript, and local deployment examples. ChocoBuilder follows a Domain Driven Problem-Solving design philosophy with key concepts like ProblemClarifier, ProblemAnalyzer, SolutionDesigner, SolutionReviewer, and SolutionExecutor. It offers use cases for desktop/IDE, server, and Android applications, with examples for frontend design, semantic code search, testcase generation, and code interpretation.
evolving-agents
A toolkit for agent autonomy, evolution, and governance enabling agents to learn from experience, collaborate, communicate, and build new tools within governance guardrails. It focuses on autonomous evolution, agent self-discovery, governance firmware, self-building systems, and agent-centric architecture. The toolkit leverages existing frameworks to enable agent autonomy and self-governance, moving towards truly autonomous AI systems.
plandex
Plandex is an open source, terminal-based AI coding engine designed for complex tasks. It uses long-running agents to break up large tasks into smaller subtasks, helping users work through backlogs, navigate unfamiliar technologies, and save time on repetitive tasks. Plandex supports various AI models, including OpenAI, Anthropic Claude, Google Gemini, and more. It allows users to manage context efficiently in the terminal, experiment with different approaches using branches, and review changes before applying them. The tool is platform-independent and runs from a single binary with no dependencies.
RooFlow
RooFlow is a VS Code extension that enhances AI-assisted development by providing persistent project context and optimized mode interactions. It reduces token consumption and streamlines workflow by integrating Architect, Code, Test, Debug, and Ask modes. The tool simplifies setup, offers real-time updates, and provides clearer instructions through YAML-based rule files. It includes components like Memory Bank, System Prompts, VS Code Integration, and Real-time Updates. Users can install RooFlow by downloading specific files, placing them in the project structure, and running an insert-variables script. They can then start a chat, select a mode, interact with Roo, and use the 'Update Memory Bank' command for synchronization. The Memory Bank structure includes files for active context, decision log, product context, progress tracking, and system patterns. RooFlow features persistent context, real-time updates, mode collaboration, and reduced token consumption.
emigo
Emigo is an AI-powered development tool for Emacs that integrates large language models to interact with projects, read files, write code, execute commands, and more. It acts as an agentic AI assistant, leveraging tool use to enhance development workflows within Emacs. Emigo is actively developed, offering features like agentic tool use, Emacs integration, flexible LLM support, and context-aware interactions. Users can install Emigo with Python dependencies and configure it within Emacs for seamless integration. The tool's core strength lies in its agentic tool use, where the AI analyzes requests, selects appropriate tools, executes actions, and provides feedback, enabling users to accomplish complex tasks efficiently.
For similar jobs

promptflow
**Prompt flow** is a suite of development tools designed to streamline the end-to-end development cycle of LLM-based AI applications, from ideation, prototyping, testing, evaluation to production deployment and monitoring. It makes prompt engineering much easier and enables you to build LLM apps with production quality.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.

MegaDetector
MegaDetector is an AI model that identifies animals, people, and vehicles in camera trap images (which also makes it useful for eliminating blank images). This model is trained on several million images from a variety of ecosystems. MegaDetector is just one of many tools that aims to make conservation biologists more efficient with AI. If you want to learn about other ways to use AI to accelerate camera trap workflows, check out our of the field, affectionately titled "Everything I know about machine learning and camera traps".

leapfrogai
LeapfrogAI is a self-hosted AI platform designed to be deployed in air-gapped resource-constrained environments. It brings sophisticated AI solutions to these environments by hosting all the necessary components of an AI stack, including vector databases, model backends, API, and UI. LeapfrogAI's API closely matches that of OpenAI, allowing tools built for OpenAI/ChatGPT to function seamlessly with a LeapfrogAI backend. It provides several backends for various use cases, including llama-cpp-python, whisper, text-embeddings, and vllm. LeapfrogAI leverages Chainguard's apko to harden base python images, ensuring the latest supported Python versions are used by the other components of the stack. The LeapfrogAI SDK provides a standard set of protobuffs and python utilities for implementing backends and gRPC. LeapfrogAI offers UI options for common use-cases like chat, summarization, and transcription. It can be deployed and run locally via UDS and Kubernetes, built out using Zarf packages. LeapfrogAI is supported by a community of users and contributors, including Defense Unicorns, Beast Code, Chainguard, Exovera, Hypergiant, Pulze, SOSi, United States Navy, United States Air Force, and United States Space Force.

llava-docker
This Docker image for LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant) provides a convenient way to run LLaVA locally or on RunPod. LLaVA is a powerful AI tool that combines natural language processing and computer vision capabilities. With this Docker image, you can easily access LLaVA's functionalities for various tasks, including image captioning, visual question answering, text summarization, and more. The image comes pre-installed with LLaVA v1.2.0, Torch 2.1.2, xformers 0.0.23.post1, and other necessary dependencies. You can customize the model used by setting the MODEL environment variable. The image also includes a Jupyter Lab environment for interactive development and exploration. Overall, this Docker image offers a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for leveraging LLaVA's capabilities.

carrot
The 'carrot' repository on GitHub provides a list of free and user-friendly ChatGPT mirror sites for easy access. The repository includes sponsored sites offering various GPT models and services. Users can find and share sites, report errors, and access stable and recommended sites for ChatGPT usage. The repository also includes a detailed list of ChatGPT sites, their features, and accessibility options, making it a valuable resource for ChatGPT users seeking free and unlimited GPT services.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.

AI-YinMei
AI-YinMei is an AI virtual anchor Vtuber development tool (N card version). It supports fastgpt knowledge base chat dialogue, a complete set of solutions for LLM large language models: [fastgpt] + [one-api] + [Xinference], supports docking bilibili live broadcast barrage reply and entering live broadcast welcome speech, supports Microsoft edge-tts speech synthesis, supports Bert-VITS2 speech synthesis, supports GPT-SoVITS speech synthesis, supports expression control Vtuber Studio, supports painting stable-diffusion-webui output OBS live broadcast room, supports painting picture pornography public-NSFW-y-distinguish, supports search and image search service duckduckgo (requires magic Internet access), supports image search service Baidu image search (no magic Internet access), supports AI reply chat box [html plug-in], supports AI singing Auto-Convert-Music, supports playlist [html plug-in], supports dancing function, supports expression video playback, supports head touching action, supports gift smashing action, supports singing automatic start dancing function, chat and singing automatic cycle swing action, supports multi scene switching, background music switching, day and night automatic switching scene, supports open singing and painting, let AI automatically judge the content.






