
emigo
Agentic AI Development in Emacs
Stars: 91
Emigo is an AI-powered development tool for Emacs that integrates large language models to interact with projects, read files, write code, execute commands, and more. It acts as an agentic AI assistant, leveraging tool use to enhance development workflows within Emacs. Emigo is actively developed, offering features like agentic tool use, Emacs integration, flexible LLM support, and context-aware interactions. Users can install Emigo with Python dependencies and configure it within Emacs for seamless integration. The tool's core strength lies in its agentic tool use, where the AI analyzes requests, selects appropriate tools, executes actions, and provides feedback, enabling users to accomplish complex tasks efficiently.
README:
Emigo brings AI-powered development to Emacs, integrating large language models directly into your workflow. Inspired by the capabilities of tools like Aider and Cline, and building upon the foundation of Aidermacs, Emigo acts as an agentic AI assistant. It leverages tool use to interact with your project, read files, write code, execute commands, and more, all within Emacs.
Emigo is under active development. Expect frequent updates, potential breaking changes, and evolving features. Contributions and feedback are highly welcome!
- Agentic Tool Use: Emigo doesn't just generate text; it uses tools to interact with your environment based on the LLM's reasoning.
- Emacs Integration: Designed to feel native within Emacs, leveraging familiar interfaces and workflows.
- Flexible LLM Support: Connects to various LLM providers through LiteLLM, allowing you to choose the model that best suits your needs.
- Context-Aware Interactions: Manages chat history and project context for coherent sessions.
-
Prerequisites:
- Emacs 28 or higher.
- Python 3.x.
-
Install Python Dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
-
Install with straight.el: Add to your Emacs config:
(use-package emigo :straight (:host github :repo "MatthewZMD/emigo") :config (emigo-enable) ;; Starts the background process automatically :custom ;; Example using OpenRouter with Claude 3.7 Sonnet (emigo-model "openrouter/anthropic/claude-3.7-sonnet") (emigo-base-url "https://openrouter.ai/api/v1") ;; Securely load your API key (replace with your preferred method) (emigo-api-key (emigo-read-file-content "~/.config/openrouter/key.txt"))) ;; With the current limitations, I do not recommend using a thinking model ;; by default to save tokens ;; --- Other LLM Examples (adjust model, base_url, api_key) --- ;; Anthropic: ;; (setq emigo-model "claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620") ;; (setq emigo-base-url nil) ; Uses default Anthropic endpoint ;; (setq emigo-api-key (getenv "ANTHROPIC_API_KEY")) ;; OpenAI: ;; (setq emigo-model "gpt-4o") ;; (setq emigo-base-url nil) ; Uses default OpenAI endpoint ;; (setq emigo-api-key (getenv "OPENAI_API_KEY")) ; Or use emigo-read-file-content
-
Start Emigo: Navigate to your project directory (or any directory you want to work in) and run
M-x emigo. - Enter Prompt: You'll be prompted for your request in the minibuffer.
- Interact: Emigo will open a dedicated buffer. The AI will respond, potentially using tools. You might be asked for approval for certain actions (like running commands or writing files).
-
Add Files to Context: Mention files in your prompt using the
@symbol (e.g.,Refactor the function in @src/utils.py). Emigo will automatically add mentioned files to the context if they exist within the project. -
Manage Context:
-
C-c C-l(emigo-list-context-files): List files currently included in the chat context. -
C-c C-f(emigo-remove-file-from-context): Remove a file from the context.
-
Emigo manages sessions based on the directory where you invoke M-x emigo. If invoked within a Git repository, the repository root is typically used as the session path. Use C-u M-x emigo to force the session path to be the current default-directory.
The core of Emigo's power lies in its agentic tool use. Instead of just providing code suggestions, the LLM analyzes your request and decides which actions (tools) are necessary to accomplish the task.
- LLM Reasoning: Based on your prompt and the current context, the LLM determines the next step.
-
Tool Selection: It chooses an appropriate tool, such as
read_file,write_to_file,replace_in_file,execute_command,list_files,list_repomap, orask_followup_question. - Tool Execution: Emigo executes the chosen tool, potentially asking for your approval for sensitive operations.
- Result Feedback: The result of the tool execution (e.g., file content, command output, error message) is fed back into the conversation history.
- Iteration: The LLM uses this new information to decide the next step, continuing the cycle until the task is complete or requires further input.
This iterative process allows Emigo to tackle more complex tasks that involve multiple steps and interactions with your project files and system. The LLM uses an XML format to specify the tool and its parameters.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for emigo
Similar Open Source Tools

emigo
Emigo is an AI-powered development tool for Emacs that integrates large language models to interact with projects, read files, write code, execute commands, and more. It acts as an agentic AI assistant, leveraging tool use to enhance development workflows within Emacs. Emigo is actively developed, offering features like agentic tool use, Emacs integration, flexible LLM support, and context-aware interactions. Users can install Emigo with Python dependencies and configure it within Emacs for seamless integration. The tool's core strength lies in its agentic tool use, where the AI analyzes requests, selects appropriate tools, executes actions, and provides feedback, enabling users to accomplish complex tasks efficiently.
architext
Architext is a Python library designed for Large Language Model (LLM) applications, focusing on Context Engineering. It provides tools to construct and reorganize input context for LLMs dynamically. The library aims to elevate context construction from ad-hoc to systematic engineering, enabling precise manipulation of context content for AI Agents.

maiar-ai
MAIAR is a composable, plugin-based AI agent framework designed to abstract data ingestion, decision-making, and action execution into modular plugins. It enables developers to define triggers and actions as standalone plugins, while the core runtime handles decision-making dynamically. This framework offers extensibility, composability, and model-driven behavior, allowing seamless addition of new functionality. MAIAR's architecture is influenced by Unix pipes, ensuring highly composable plugins, dynamic execution pipelines, and transparent debugging. It remains declarative and extensible, allowing developers to build complex AI workflows without rigid architectures.
deep-research
Deep Research is a lightning-fast tool that uses powerful AI models to generate comprehensive research reports in just a few minutes. It leverages advanced 'Thinking' and 'Task' models, combined with an internet connection, to provide fast and insightful analysis on various topics. The tool ensures privacy by processing and storing all data locally. It supports multi-platform deployment, offers support for various large language models, web search functionality, knowledge graph generation, research history preservation, local and server API support, PWA technology, multi-key payload support, multi-language support, and is built with modern technologies like Next.js and Shadcn UI. Deep Research is open-source under the MIT License.
arbigent
Arbigent (Arbiter-Agent) is an AI agent testing framework designed to make AI agent testing practical for modern applications. It addresses challenges faced by traditional UI testing frameworks and AI agents by breaking down complex tasks into smaller, dependent scenarios. The framework is customizable for various AI providers, operating systems, and form factors, empowering users with extensive customization capabilities. Arbigent offers an intuitive UI for scenario creation and a powerful code interface for seamless test execution. It supports multiple form factors, optimizes UI for AI interaction, and is cost-effective by utilizing models like GPT-4o mini. With a flexible code interface and open-source nature, Arbigent aims to revolutionize AI agent testing in modern applications.
langmanus
LangManus is a community-driven AI automation framework that combines language models with specialized tools for tasks like web search, crawling, and Python code execution. It implements a hierarchical multi-agent system with agents like Coordinator, Planner, Supervisor, Researcher, Coder, Browser, and Reporter. The framework supports LLM integration, search and retrieval tools, Python integration, workflow management, and visualization. LangManus aims to give back to the open-source community and welcomes contributions in various forms.
tinystruct
Tinystruct is a simple Java framework designed for easy development with better performance. It offers a modern approach with features like CLI and web integration, built-in lightweight HTTP server, minimal configuration philosophy, annotation-based routing, and performance-first architecture. Developers can focus on real business logic without dealing with unnecessary complexities, making it transparent, predictable, and extensible.
OpenAdapt
OpenAdapt is an open-source software adapter between Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) and traditional desktop and web Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs). It aims to automate repetitive GUI workflows by leveraging the power of LMMs. OpenAdapt records user input and screenshots, converts them into tokenized format, and generates synthetic input via transformer model completions. It also analyzes recordings to generate task trees and replay synthetic input to complete tasks. OpenAdapt is model agnostic and generates prompts automatically by learning from human demonstration, ensuring that agents are grounded in existing processes and mitigating hallucinations. It works with all types of desktop GUIs, including virtualized and web, and is open source under the MIT license.
RepoAgent
RepoAgent is an LLM-powered framework designed for repository-level code documentation generation. It automates the process of detecting changes in Git repositories, analyzing code structure through AST, identifying inter-object relationships, replacing Markdown content, and executing multi-threaded operations. The tool aims to assist developers in understanding and maintaining codebases by providing comprehensive documentation, ultimately improving efficiency and saving time.
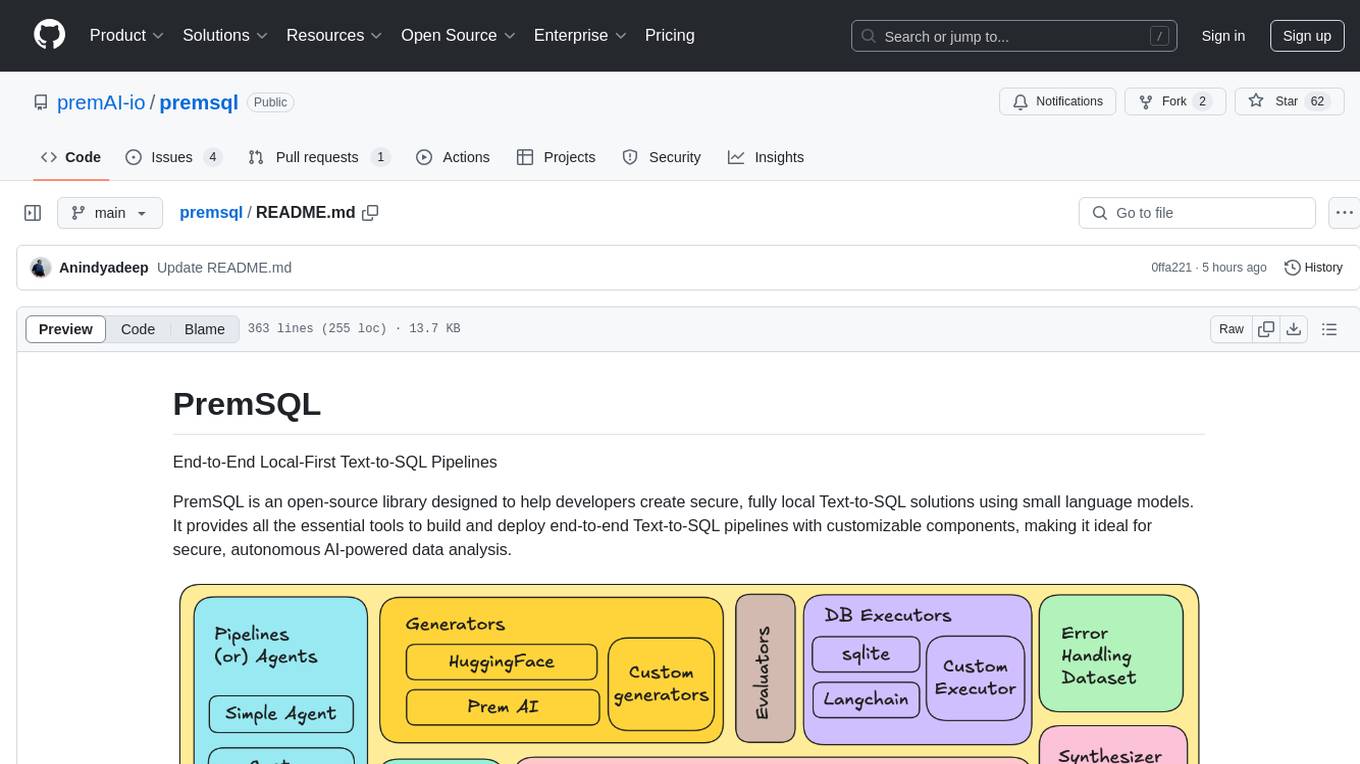
premsql
PremSQL is an open-source library designed to help developers create secure, fully local Text-to-SQL solutions using small language models. It provides essential tools for building and deploying end-to-end Text-to-SQL pipelines with customizable components, ideal for secure, autonomous AI-powered data analysis. The library offers features like Local-First approach, Customizable Datasets, Robust Executors and Evaluators, Advanced Generators, Error Handling and Self-Correction, Fine-Tuning Support, and End-to-End Pipelines. Users can fine-tune models, generate SQL queries from natural language inputs, handle errors, and evaluate model performance against predefined metrics. PremSQL is extendible for customization and private data usage.

patchwork
PatchWork is an open-source framework designed for automating development tasks using large language models. It enables users to automate workflows such as PR reviews, bug fixing, security patching, and more through a self-hosted CLI agent and preferred LLMs. The framework consists of reusable atomic actions called Steps, customizable LLM prompts known as Prompt Templates, and LLM-assisted automations called Patchflows. Users can run Patchflows locally in their CLI/IDE or as part of CI/CD pipelines. PatchWork offers predefined patchflows like AutoFix, PRReview, GenerateREADME, DependencyUpgrade, and ResolveIssue, with the flexibility to create custom patchflows. Prompt templates are used to pass queries to LLMs and can be customized. Contributions to new patchflows, steps, and the core framework are encouraged, with chat assistants available to aid in the process. The roadmap includes expanding the patchflow library, introducing a debugger and validation module, supporting large-scale code embeddings, parallelization, fine-tuned models, and an open-source GUI. PatchWork is licensed under AGPL-3.0 terms, while custom patchflows and steps can be shared using the Apache-2.0 licensed patchwork template repository.
RainbowGPT
RainbowGPT is a versatile tool that offers a range of functionalities, including Stock Analysis for financial decision-making, MySQL Management for database navigation, and integration of AI technologies like GPT-4 and ChatGlm3. It provides a user-friendly interface suitable for all skill levels, ensuring seamless information flow and continuous expansion of emerging technologies. The tool enhances adaptability, creativity, and insight, making it a valuable asset for various projects and tasks.
atropos
Atropos is a robust and scalable framework for Reinforcement Learning Environments with Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides a flexible platform to accelerate LLM-based RL research across diverse interactive settings. Atropos supports multi-turn and asynchronous RL interactions, integrates with various inference APIs, offers a standardized training interface for experimenting with different RL algorithms, and allows for easy scalability by launching more environment instances. The framework manages diverse environment types concurrently for heterogeneous, multi-modal training.
RA.Aid
RA.Aid is an AI software development agent powered by `aider` and advanced reasoning models like `o1`. It combines `aider`'s code editing capabilities with LangChain's agent-based task execution framework to provide an intelligent assistant for research, planning, and implementation of multi-step development tasks. It handles complex programming tasks by breaking them down into manageable steps, running shell commands automatically, and leveraging expert reasoning models like OpenAI's o1. RA.Aid is designed for everyday software development, offering features such as multi-step task planning, automated command execution, and the ability to handle complex programming tasks beyond single-shot code edits.

sieves
sieves is a library for zero- and few-shot NLP tasks with structured generation, enabling rapid prototyping of NLP applications without the need for training. It simplifies NLP prototyping by bundling capabilities into a single library, providing zero- and few-shot model support, a unified interface for structured generation, built-in tasks for common NLP operations, easy extendability, document-based pipeline architecture, caching to prevent redundant model calls, and more. The tool draws inspiration from spaCy and spacy-llm, offering features like immediate inference, observable pipelines, integrated tools for document parsing and text chunking, ready-to-use tasks such as classification, summarization, translation, and more, persistence for saving and loading pipelines, distillation for specialized model creation, and caching to optimize performance.
restai
RestAI is an AIaaS (AI as a Service) platform that allows users to create and consume AI agents (projects) using a simple REST API. It supports various types of agents, including RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation), RAGSQL (RAG for SQL), inference, vision, and router. RestAI features automatic VRAM management, support for any public LLM supported by LlamaIndex or any local LLM supported by Ollama, a user-friendly API with Swagger documentation, and a frontend for easy access. It also provides evaluation capabilities for RAG agents using deepeval.
For similar tasks
aichat
Aichat is an AI-powered CLI chat and copilot tool that seamlessly integrates with over 10 leading AI platforms, providing a powerful combination of chat-based interaction, context-aware conversations, and AI-assisted shell capabilities, all within a customizable and user-friendly environment.
wingman-ai
Wingman AI allows you to use your voice to talk to various AI providers and LLMs, process your conversations, and ultimately trigger actions such as pressing buttons or reading answers. Our _Wingmen_ are like characters and your interface to this world, and you can easily control their behavior and characteristics, even if you're not a developer. AI is complex and it scares people. It's also **not just ChatGPT**. We want to make it as easy as possible for you to get started. That's what _Wingman AI_ is all about. It's a **framework** that allows you to build your own Wingmen and use them in your games and programs. The idea is simple, but the possibilities are endless. For example, you could: * **Role play** with an AI while playing for more immersion. Have air traffic control (ATC) in _Star Citizen_ or _Flight Simulator_. Talk to Shadowheart in Baldur's Gate 3 and have her respond in her own (cloned) voice. * Get live data such as trade information, build guides, or wiki content and have it read to you in-game by a _character_ and voice you control. * Execute keystrokes in games/applications and create complex macros. Trigger them in natural conversations with **no need for exact phrases.** The AI understands the context of your dialog and is quite _smart_ in recognizing your intent. Say _"It's raining! I can't see a thing!"_ and have it trigger a command you simply named _WipeVisors_. * Automate tasks on your computer * improve accessibility * ... and much more
letmedoit
LetMeDoIt AI is a virtual assistant designed to revolutionize the way you work. It goes beyond being a mere chatbot by offering a unique and powerful capability - the ability to execute commands and perform computing tasks on your behalf. With LetMeDoIt AI, you can access OpenAI ChatGPT-4, Google Gemini Pro, and Microsoft AutoGen, local LLMs, all in one place, to enhance your productivity.
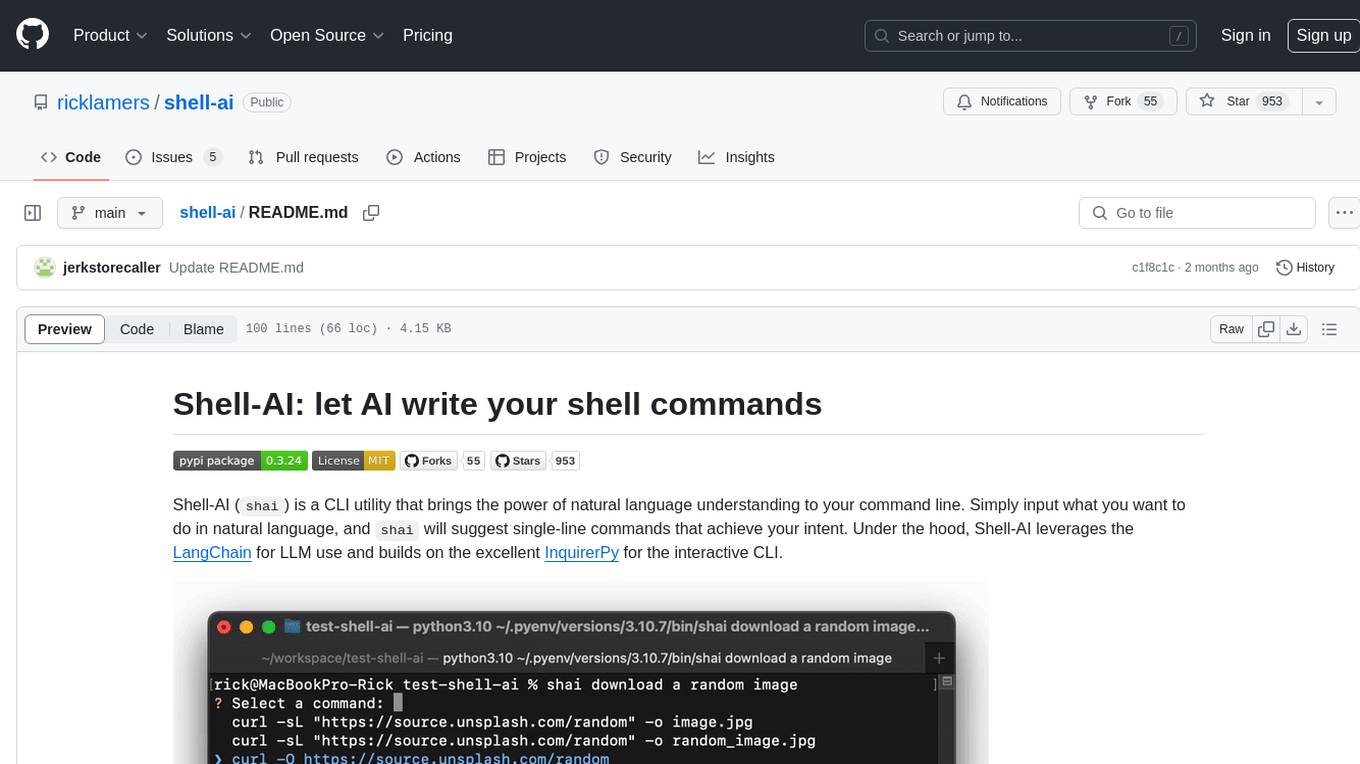
shell-ai
Shell-AI (`shai`) is a CLI utility that enables users to input commands in natural language and receive single-line command suggestions. It leverages natural language understanding and interactive CLI tools to enhance command line interactions. Users can describe tasks in plain English and receive corresponding command suggestions, making it easier to execute commands efficiently. Shell-AI supports cross-platform usage and is compatible with Azure OpenAI deployments, offering a user-friendly and efficient way to interact with the command line.
AIRAVAT
AIRAVAT is a multifunctional Android Remote Access Tool (RAT) with a GUI-based Web Panel that does not require port forwarding. It allows users to access various features on the victim's device, such as reading files, downloading media, retrieving system information, managing applications, SMS, call logs, contacts, notifications, keylogging, admin permissions, phishing, audio recording, music playback, device control (vibration, torch light, wallpaper), executing shell commands, clipboard text retrieval, URL launching, and background operation. The tool requires a Firebase account and tools like ApkEasy Tool or ApkTool M for building. Users can set up Firebase, host the web panel, modify Instagram.apk for RAT functionality, and connect the victim's device to the web panel. The tool is intended for educational purposes only, and users are solely responsible for its use.
chatflow
Chatflow is a tool that provides a chat interface for users to interact with systems using natural language. The engine understands user intent and executes commands for tasks, allowing easy navigation of complex websites/products. This approach enhances user experience, reduces training costs, and boosts productivity.
Wave-executor
Wave Executor is an innovative Windows executor developed by SPDM Team and CodeX engineers, featuring cutting-edge technologies like AI, built-in script hub, HDWID spoofing, and enhanced scripting capabilities. It offers a 100% stealth mode Byfron bypass, advanced features like decompiler and save instance functionality, and a commercial edition with ad-free experience and direct download link. Wave Premium provides multi-instance, multi-inject, and 100% UNC support, making it a cost-effective option for executing scripts in popular Roblox games.
agent-zero
Agent Zero is a personal and organic AI framework designed to be dynamic, organically growing, and learning as you use it. It is fully transparent, readable, comprehensible, customizable, and interactive. The framework uses the computer as a tool to accomplish tasks, with no single-purpose tools pre-programmed. It emphasizes multi-agent cooperation, complete customization, and extensibility. Communication is key in this framework, allowing users to give proper system prompts and instructions to achieve desired outcomes. Agent Zero is capable of dangerous actions and should be run in an isolated environment. The framework is prompt-based, highly customizable, and requires a specific environment to run effectively.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.