symbolicai
A neurosymbolic perspective on LLMs
Stars: 1666
SymbolicAI is a neuro-symbolic framework that combines classical Python programming with the differentiable, programmable nature of Large Language Models (LLMs). It allows for easy extensibility and customization, enabling users to write their own engines, host local engines, or interface with tools like web search and image generation. The framework introduces two key concepts: 'primitives' and 'contracts'. Primitives include syntactic and semantic Symbol objects, while contracts bring Design by Contract principles to LLMs, ensuring correctness in code design. SymbolicAI also features a configuration management system with priority-based loading for settings. The tool supports various engines for text, speech, and image processing, along with search engine access. Users can install SymbolicAI via pip and set up optional features and dependencies as needed.
README:
SymbolicAI is a neuro-symbolic framework, combining classical Python programming with the differentiable, programmable nature of LLMs in a way that actually feels natural in Python. It's built to not stand in the way of your ambitions. It's easily extensible and customizable to your needs by virtue of its modular design. It's quite easy to write your own engine, host locally an engine of your choice, or interface with tools like web search or image generation. To keep things concise in this README, we'll introduce two key concepts that define SymbolicAI: primitives and contracts.
❗️NOTE❗️ The framework's name is intended to credit the foundational work of Allen Newell and Herbert Simon that inspired this project.
At the core of SymbolicAI are Symbol objects—each one comes with a set of tiny, composable operations that feel like native Python.
from symai import SymbolSymbol comes in two flavours:
- Syntactic – behaves like a normal Python value (string, list, int ‐ whatever you passed in).
- Semantic – is wired to the neuro-symbolic engine and therefore understands meaning and context.
Why is syntactic the default?
Because Python operators (==, ~, &, …) are overloaded in symai.
If we would immediately fire the engine for every bitshift or comparison, code would be slow and could produce surprising side-effects.
Starting syntactic keeps things safe and fast; you opt-in to semantics only where you need them.
-
At creation time
S = Symbol("Cats are adorable", semantic=True) # already semantic print("feline" in S) # => True
-
On demand with the
.semprojection – the twin.synflips you back:S = Symbol("Cats are adorable") # default = syntactic print("feline" in S.sem) # => True print("feline" in S) # => False
-
Invoking dot-notation operations—such as
.map()or any other semantic function—automatically switches the symbol to semantic mode:S = Symbol(['apple', 'banana', 'cherry', 'cat', 'dog']) print(S.map('convert all fruits to vegetables')) # => ['carrot', 'broccoli', 'spinach', 'cat', 'dog']
Because the projections return the same underlying object with just a different behavioural coat, you can weave complex chains of syntactic and semantic operations on a single symbol. Think of them as your building blocks for semantic reasoning. Right now, we support a wide range of primitives; check out the docs here, but here's a quick snack:
| Primitive/Operator | Category | Syntactic | Semantic | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
== |
Comparison | ✓ | ✓ | Tests for equality. Syntactic: literal match. Semantic: fuzzy/conceptual equivalence (e.g. 'Hi' == 'Hello'). |
+ |
Arithmetic | ✓ | ✓ | Syntactic: numeric/string/list addition. Semantic: meaningful composition, blending, or conceptual merge. |
& |
Logical/Bitwise | ✓ | ✓ | Syntactic: bitwise/logical AND. Semantic: logical conjunction, inference, e.g., context merge. |
symbol[index] = value |
Iteration | ✓ | ✓ | Set item or slice. |
.startswith(prefix) |
String Helper | ✓ | ✓ | Check if a string starts with given prefix (in both modes). |
.choice(cases, default) |
Pattern Matching | ✓ | Select best match from provided cases. | |
.foreach(condition, apply) |
Execution Control | ✓ | Apply action to each element. | |
.cluster(**clustering_kwargs?) |
Data Clustering | ✓ | Cluster data into groups semantically. (uses sklearn's DBSCAN) | |
.similarity(other, metric?, normalize?) |
Embedding | ✓ | Compute similarity between embeddings. | |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
They say LLMs hallucinate—but your code can't afford to. That's why SymbolicAI brings Design by Contract principles into the world of LLMs. Instead of relying solely on post-hoc testing, contracts help build correctness directly into your design, everything packed into a decorator that will operate on your defined data models and validation constraints:
from symai import Expression
from symai.strategy import contract
from symai.models import LLMDataModel # Compatible with Pydantic's BaseModel
from pydantic import Field, field_validator
# ▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
# Data models ▬
# – clear structure + rich Field descriptions power ▬
# validation, automatic prompt templating & remedies ▬
# ▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
class DataModel(LLMDataModel):
some_field: some_type = Field(description="very descriptive field", and_other_supported_options_here="...")
@field_validator('some_field')
def validate_some_field(cls, v):
# Custom basic validation logic can be added here too besides pre/post
valid_opts = ['A', 'B', 'C']
if v not in valid_opts:
raise ValueError(f'Must be one of {valid_opts}, got "{v}".')
return v
# ▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
# The contracted expression class ▬
# ▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
@contract(
# ── Remedies ─────────────────────────────────────────── #
pre_remedy=True, # Try to fix bad inputs automatically
post_remedy=True, # Try to fix bad LLM outputs automatically
accumulate_errors=True, # Feed history of errors to each retry
verbose=True, # Nicely displays progress in terminal
remedy_retry_params=dict(tries=3, delay=0.4, max_delay=4.0,
jitter=0.15, backoff=1.8, graceful=False),
)
class Agent(Expression):
#
# High-level behaviour:
# *. `prompt` – a *static* description of what the LLM must do (mandatory)
# 1. `pre` – sanity-check inputs (optional)
# 2. `act` – mutate state (optional)
# 3. LLM – generate expected answer (handled by SymbolicAI engine)
# 4. `post` – ensure answer meets semantic rules (optional)
# 5. `forward` (mandatory)
# • if contract succeeded → return type validated LLM object
# • else → graceful fallback answer
# ...Because we don't want to bloat this README file with long Python snippets, learn more about contracts here and here.
To get started with SymbolicAI, you can install it using pip:
pip install symbolicaiAlternatively, clone the repository and set up a Python virtual environment using uv:
git clone [email protected]:ExtensityAI/symbolicai.git
cd symbolicai
uv sync --python x.xx
source ./.venv/bin/activateRunning symconfig will now use this Python environment.
SymbolicAI uses multiple engines to process text, speech and images. We also include search engine access to retrieve information from the web. To use all of them, you will need to also install the following dependencies and assign the API keys to the respective engines. E.g.:
pip install "symbolicai[hf]",
pip install "symbolicai[llamacpp]",
pip install "symbolicai[bitsandbytes]",
pip install "symbolicai[wolframalpha]",
pip install "symbolicai[whisper]",
pip install "symbolicai[scrape]",
pip install "symbolicai[serpapi]",
pip install "symbolicai[services]",
pip install "symbolicai[solver]"Or, install all optional dependencies at once:
pip install "symbolicai[all]"To install dependencies exactly as locked in the provided lock file:
uv sync --frozenTo install optional extras via uv:
uv sync --extra all # all optional extras
uv sync --extra scrape # only scrape❗️NOTE❗️Please note that some of these optional dependencies may require additional installation steps. Additionally, some are only experimentally supported now and may not work as expected. If a feature is extremely important to you, please consider contributing to the project or reaching out to us.
SymbolicAI now features a configuration management system with priority-based loading. The configuration system looks for settings in three different locations, in order of priority:
-
Debug Mode (Current Working Directory)
- Highest priority
- Only applies to
symai.config.json - Useful for development and testing
-
Environment-Specific Config (Python Environment)
- Second priority
- Located in
{python_env}/.symai/ - Ideal for project-specific settings
-
Global Config (Home Directory)
- Lowest priority
- Located in
~/.symai/ - Default fallback for all settings
The system manages three main configuration files:
-
symai.config.json: Main SymbolicAI configuration -
symsh.config.json: Shell configuration -
symserver.config.json: Server configuration
Before using the symai, we recommend inspecting your current configuration setup using the command below. It will start the initial packages caching and initializing the symbolicai configuration files.
symconfig
# UserWarning: No configuration file found for the environment. A new configuration file has been created at <full-path>/.symai/symai.config.json. Please configure your environment.You then must edit the symai.config.json file. A neurosymbolic engine is required to use the symai package. Read more about how to use a neuro-symbolic engine here.
This command will show:
- All configuration locations
- Active configuration paths
- Current settings (with sensitive data truncated)
my_project/ # Debug mode (highest priority)
└── symai.config.json # Only this file is checked in debug mode
{python_env}/.symai/ # Environment config (second priority)
├── symai.config.json
├── symsh.config.json
└── symserver.config.json
~/.symai/ # Global config (lowest priority)
├── symai.config.json
├── symsh.config.json
└── symserver.config.jsonIf a configuration file exists in multiple locations, the system will use the highest-priority version. If the environment-specific configuration is missing or invalid, the system will automatically fall back to the global configuration in the home directory.
- Use the global config (
~/.symai/) for your default settings - Use environment-specific configs for project-specific settings
- Use debug mode (current directory) for development and testing
- Run
symconfigto inspect your current configuration setup
You can specify engine properties in a symai.config.json file in your project path. This will replace the environment variables.
Example of a configuration file with all engines enabled:
{
"NEUROSYMBOLIC_ENGINE_API_KEY": "<OPENAI_API_KEY>",
"NEUROSYMBOLIC_ENGINE_MODEL": "gpt-4o",
"SYMBOLIC_ENGINE_API_KEY": "<WOLFRAMALPHA_API_KEY>",
"SYMBOLIC_ENGINE": "wolframalpha",
"EMBEDDING_ENGINE_API_KEY": "<OPENAI_API_KEY>",
"EMBEDDING_ENGINE_MODEL": "text-embedding-3-small",
"SEARCH_ENGINE_API_KEY": "<PERPLEXITY_API_KEY>",
"SEARCH_ENGINE_MODEL": "sonar",
"TEXT_TO_SPEECH_ENGINE_API_KEY": "<OPENAI_API_KEY>",
"TEXT_TO_SPEECH_ENGINE_MODEL": "tts-1",
"INDEXING_ENGINE_API_KEY": "<PINECONE_API_KEY>",
"INDEXING_ENGINE_ENVIRONMENT": "us-west1-gcp",
"DRAWING_ENGINE_API_KEY": "<OPENAI_API_KEY>",
"DRAWING_ENGINE_MODEL": "dall-e-3",
"VISION_ENGINE_MODEL": "openai/clip-vit-base-patch32",
"OCR_ENGINE_API_KEY": "<APILAYER_API_KEY>",
"SPEECH_TO_TEXT_ENGINE_MODEL": "turbo",
"SPEECH_TO_TEXT_API_KEY": ""
}With these steps completed, you should be ready to start using SymbolicAI in your projects.
❗️NOTE❗️By default, the user warnings are enabled. To disable them, export
SYMAI_WARNINGS=0in your environment variables.
Some examples of running tests locally:
# Run all tests
pytest tests
# Run mandatory tests
pytest -m mandatoryBe sure to have your configuration set up correctly before running the tests. You can also run the tests with coverage to see how much of the code is covered by tests:
pytest --cov=symbolicai testsNow, there are tools like DeepWiki that provide better documentation than we could ever write, and we don’t want to compete with that; we'll correct it where it's plain wrong. Please go read SymbolicAI's DeepWiki page. There's a lot of interesting stuff in there. Last but not least, check out our paper that describes the framework in detail. If you like watching videos, we have a series of tutorials that you can find here.
@software{Dinu_SymbolicAI_2022,
author = {Dinu, Marius-Constantin},
editor = {Leoveanu-Condrei, Claudiu},
title = {{SymbolicAI: A Neuro-Symbolic Perspective on Large Language Models (LLMs)}},
url = {https://github.com/ExtensityAI/symbolicai},
month = {11},
year = {2022}
}This project is licensed under the BSD-3-Clause License.
If you appreciate this project, please leave a star ⭐️ and share it with friends and colleagues. To support the ongoing development of this project even further, consider donating. Thank you!
We are also seeking contributors or investors to help grow and support this project. If you are interested, please reach out to us.
Feel free to contact us with any questions about this project via email, through our website, or find us on Discord:
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for symbolicai
Similar Open Source Tools

symbolicai
SymbolicAI is a neuro-symbolic framework that combines classical Python programming with the differentiable, programmable nature of Large Language Models (LLMs). It allows for easy extensibility and customization, enabling users to write their own engines, host local engines, or interface with tools like web search and image generation. The framework introduces two key concepts: 'primitives' and 'contracts'. Primitives include syntactic and semantic Symbol objects, while contracts bring Design by Contract principles to LLMs, ensuring correctness in code design. SymbolicAI also features a configuration management system with priority-based loading for settings. The tool supports various engines for text, speech, and image processing, along with search engine access. Users can install SymbolicAI via pip and set up optional features and dependencies as needed.
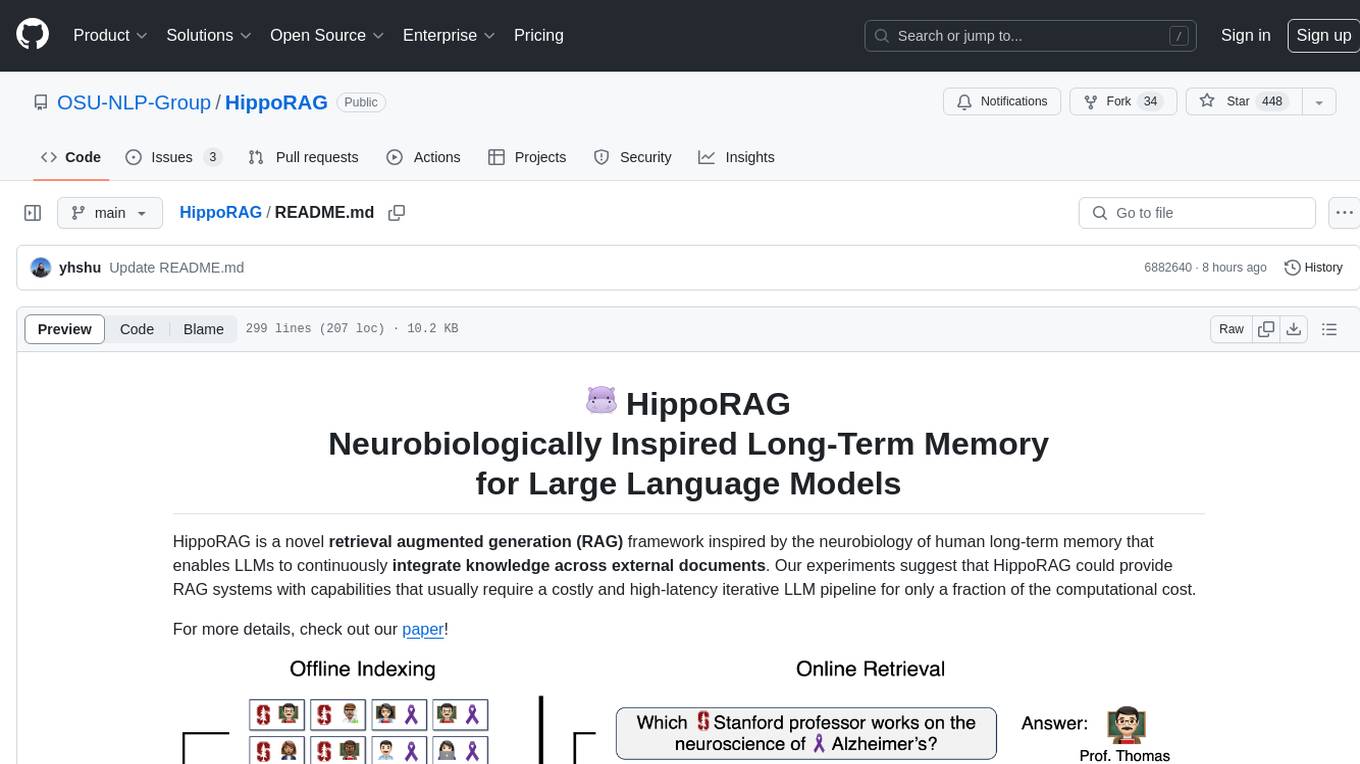
HippoRAG
HippoRAG is a novel retrieval augmented generation (RAG) framework inspired by the neurobiology of human long-term memory that enables Large Language Models (LLMs) to continuously integrate knowledge across external documents. It provides RAG systems with capabilities that usually require a costly and high-latency iterative LLM pipeline for only a fraction of the computational cost. The tool facilitates setting up retrieval corpus, indexing, and retrieval processes for LLMs, offering flexibility in choosing different online LLM APIs or offline LLM deployments through LangChain integration. Users can run retrieval on pre-defined queries or integrate directly with the HippoRAG API. The tool also supports reproducibility of experiments and provides data, baselines, and hyperparameter tuning scripts for research purposes.
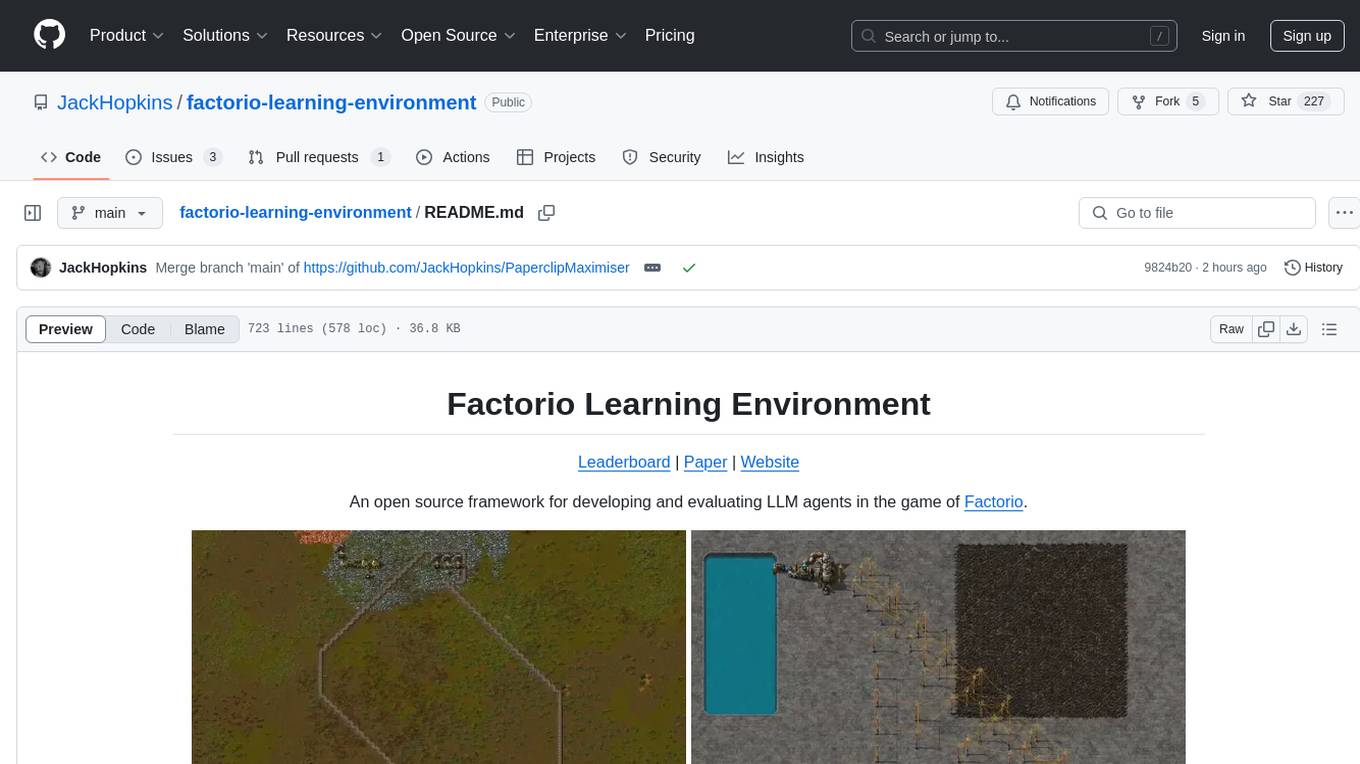
factorio-learning-environment
Factorio Learning Environment is an open source framework designed for developing and evaluating LLM agents in the game of Factorio. It provides two settings: Lab-play with structured tasks and Open-play for building large factories. Results show limitations in spatial reasoning and automation strategies. Agents interact with the environment through code synthesis, observation, action, and feedback. Tools are provided for game actions and state representation. Agents operate in episodes with observation, planning, and action execution. Tasks specify agent goals and are implemented in JSON files. The project structure includes directories for agents, environment, cluster, data, docs, eval, and more. A database is used for checkpointing agent steps. Benchmarks show performance metrics for different configurations.
SwiftAI
SwiftAI is a modern, type-safe Swift library for building AI-powered apps. It provides a unified API that works seamlessly across different AI models, including Apple's on-device models and cloud-based services like OpenAI. With features like model agnosticism, structured output, agent tool loop, conversations, extensibility, and Swift-native design, SwiftAI offers a powerful toolset for developers to integrate AI capabilities into their applications. The library supports easy installation via Swift Package Manager and offers detailed guidance on getting started, structured responses, tool use, model switching, conversations, and advanced constraints. SwiftAI aims to simplify AI integration by providing a type-safe and versatile solution for various AI tasks.
marvin
Marvin is a lightweight AI toolkit for building natural language interfaces that are reliable, scalable, and easy to trust. Each of Marvin's tools is simple and self-documenting, using AI to solve common but complex challenges like entity extraction, classification, and generating synthetic data. Each tool is independent and incrementally adoptable, so you can use them on their own or in combination with any other library. Marvin is also multi-modal, supporting both image and audio generation as well using images as inputs for extraction and classification. Marvin is for developers who care more about _using_ AI than _building_ AI, and we are focused on creating an exceptional developer experience. Marvin users should feel empowered to bring tightly-scoped "AI magic" into any traditional software project with just a few extra lines of code. Marvin aims to merge the best practices for building dependable, observable software with the best practices for building with generative AI into a single, easy-to-use library. It's a serious tool, but we hope you have fun with it. Marvin is open-source, free to use, and made with 💙 by the team at Prefect.

HuixiangDou
HuixiangDou is a **group chat** assistant based on LLM (Large Language Model). Advantages: 1. Design a two-stage pipeline of rejection and response to cope with group chat scenario, answer user questions without message flooding, see arxiv2401.08772 2. Low cost, requiring only 1.5GB memory and no need for training 3. Offers a complete suite of Web, Android, and pipeline source code, which is industrial-grade and commercially viable Check out the scenes in which HuixiangDou are running and join WeChat Group to try AI assistant inside. If this helps you, please give it a star ⭐
gfm-rag
The GFM-RAG is a graph foundation model-powered pipeline that combines graph neural networks to reason over knowledge graphs and retrieve relevant documents for question answering. It features a knowledge graph index, efficiency in multi-hop reasoning, generalizability to unseen datasets, transferability for fine-tuning, compatibility with agent-based frameworks, and interpretability of reasoning paths. The tool can be used for conducting retrieval and question answering tasks using pre-trained models or fine-tuning on custom datasets.

VITA
VITA is an open-source interactive omni multimodal Large Language Model (LLM) capable of processing video, image, text, and audio inputs simultaneously. It stands out with features like Omni Multimodal Understanding, Non-awakening Interaction, and Audio Interrupt Interaction. VITA can respond to user queries without a wake-up word, track and filter external queries in real-time, and handle various query inputs effectively. The model utilizes state tokens and a duplex scheme to enhance the multimodal interactive experience.

langserve
LangServe helps developers deploy `LangChain` runnables and chains as a REST API. This library is integrated with FastAPI and uses pydantic for data validation. In addition, it provides a client that can be used to call into runnables deployed on a server. A JavaScript client is available in LangChain.js.
python-tgpt
Python-tgpt is a Python package that enables seamless interaction with over 45 free LLM providers without requiring an API key. It also provides image generation capabilities. The name _python-tgpt_ draws inspiration from its parent project tgpt, which operates on Golang. Through this Python adaptation, users can effortlessly engage with a number of free LLMs available, fostering a smoother AI interaction experience.
repomix
Repomix is a powerful tool that packs your entire repository into a single, AI-friendly file. It is designed to format your codebase for easy understanding by AI tools like Large Language Models (LLMs), Claude, ChatGPT, and Gemini. Repomix offers features such as AI optimization, token counting, simplicity in usage, customization options, Git awareness, and security-focused checks using Secretlint. It allows users to pack their entire repository or specific directories/files using glob patterns, and even supports processing remote Git repositories. The tool generates output in plain text, XML, or Markdown formats, with options for including/excluding files, removing comments, and performing security checks. Repomix also provides a global configuration option, custom instructions for AI context, and a security check feature to detect sensitive information in files.

obsei
Obsei is an open-source, low-code, AI powered automation tool that consists of an Observer to collect unstructured data from various sources, an Analyzer to analyze the collected data with various AI tasks, and an Informer to send analyzed data to various destinations. The tool is suitable for scheduled jobs or serverless applications as all Observers can store their state in databases. Obsei is still in alpha stage, so caution is advised when using it in production. The tool can be used for social listening, alerting/notification, automatic customer issue creation, extraction of deeper insights from feedbacks, market research, dataset creation for various AI tasks, and more based on creativity.
ultracontext
UltraContext is a context API for AI agents that simplifies controlling what agents see by allowing users to replace messages, compact or offload context, replay decisions, and roll back mistakes with a single API call. It provides versioned context out of the box with full history and zero complexity. The tool aims to address the issue of context rot in large language models by providing a simple API with automatic versioning, time-travel capabilities, schema-free data storage, framework-agnostic compatibility, and fast performance. UltraContext is designed to streamline the process of managing context for AI agents, enabling users to focus on solving interesting problems rather than spending time gluing context together.
quantalogic
QuantaLogic is a ReAct framework for building advanced AI agents that seamlessly integrates large language models with a robust tool system. It aims to bridge the gap between advanced AI models and practical implementation in business processes by enabling agents to understand, reason about, and execute complex tasks through natural language interaction. The framework includes features such as ReAct Framework, Universal LLM Support, Secure Tool System, Real-time Monitoring, Memory Management, and Enterprise Ready components.
playword
PlayWord is a tool designed to supercharge web test automation experience with AI. It provides core features such as enabling browser operations and validations using natural language inputs, as well as monitoring interface to record and dry-run test steps. PlayWord supports multiple AI services including Anthropic, Google, and OpenAI, allowing users to select the appropriate provider based on their requirements. The tool also offers features like assertion handling, frame handling, custom variables, test recordings, and an Observer module to track user interactions on web pages. With PlayWord, users can interact with web pages using natural language commands, reducing the need to worry about element locators and providing AI-powered adaptation to UI changes.
suno-api
Suno AI API is an open-source project that allows developers to integrate the music generation capabilities of Suno.ai into their own applications. The API provides a simple and convenient way to generate music, lyrics, and other audio content using Suno.ai's powerful AI models. With Suno AI API, developers can easily add music generation functionality to their apps, websites, and other projects.
For similar tasks
phospho
Phospho is a text analytics platform for LLM apps. It helps you detect issues and extract insights from text messages of your users or your app. You can gather user feedback, measure success, and iterate on your app to create the best conversational experience for your users.
OpenFactVerification
Loki is an open-source tool designed to automate the process of verifying the factuality of information. It provides a comprehensive pipeline for dissecting long texts into individual claims, assessing their worthiness for verification, generating queries for evidence search, crawling for evidence, and ultimately verifying the claims. This tool is especially useful for journalists, researchers, and anyone interested in the factuality of information.
open-parse
Open Parse is a Python library for visually discerning document layouts and chunking them effectively. It is designed to fill the gap in open-source libraries for handling complex documents. Unlike text splitting, which converts a file to raw text and slices it up, Open Parse visually analyzes documents for superior LLM input. It also supports basic markdown for parsing headings, bold, and italics, and has high-precision table support, extracting tables into clean Markdown formats with accuracy that surpasses traditional tools. Open Parse is extensible, allowing users to easily implement their own post-processing steps. It is also intuitive, with great editor support and completion everywhere, making it easy to use and learn.
spaCy
spaCy is an industrial-strength Natural Language Processing (NLP) library in Python and Cython. It incorporates the latest research and is designed for real-world applications. The library offers pretrained pipelines supporting 70+ languages, with advanced neural network models for tasks such as tagging, parsing, named entity recognition, and text classification. It also facilitates multi-task learning with pretrained transformers like BERT, along with a production-ready training system and streamlined model packaging, deployment, and workflow management. spaCy is commercial open-source software released under the MIT license.
NanoLLM
NanoLLM is a tool designed for optimized local inference for Large Language Models (LLMs) using HuggingFace-like APIs. It supports quantization, vision/language models, multimodal agents, speech, vector DB, and RAG. The tool aims to provide efficient and effective processing for LLMs on local devices, enhancing performance and usability for various AI applications.

ontogpt
OntoGPT is a Python package for extracting structured information from text using large language models, instruction prompts, and ontology-based grounding. It provides a command line interface and a minimal web app for easy usage. The tool has been evaluated on test data and is used in related projects like TALISMAN for gene set analysis. OntoGPT enables users to extract information from text by specifying relevant terms and provides the extracted objects as output.

lima
LIMA is a multilingual linguistic analyzer developed by the CEA LIST, LASTI laboratory. It is Free Software available under the MIT license. LIMA has state-of-the-art performance for more than 60 languages using deep learning modules. It also includes a powerful rules-based mechanism called ModEx for extracting information in new domains without annotated data.
liboai
liboai is a simple C++17 library for the OpenAI API, providing developers with access to OpenAI endpoints through a collection of methods and classes. It serves as a spiritual port of OpenAI's Python library, 'openai', with similar structure and features. The library supports various functionalities such as ChatGPT, Audio, Azure, Functions, Image DALL·E, Models, Completions, Edit, Embeddings, Files, Fine-tunes, Moderation, and Asynchronous Support. Users can easily integrate the library into their C++ projects to interact with OpenAI services.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.