
raycast_api_proxy
This is a simple Raycast AI API proxy.
Stars: 317
The Raycast AI Proxy is a tool that acts as a proxy for the Raycast AI application, allowing users to utilize the application without subscribing. It intercepts and forwards Raycast requests to various AI APIs, then reformats the responses for Raycast. The tool supports multiple AI providers and allows for custom model configurations. Users can generate self-signed certificates, add them to the system keychain, and modify DNS settings to redirect requests to the proxy. The tool is designed to work with providers like OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Google, and more, enabling tasks such as AI chat completions, translations, and image generation.
README:
This is a simple Raycast AI API proxy. It allows you to use the Raycast AI application without subscribing. The proxy converts requests from Raycast into a format to send to AI model providers (e.g., OpenAI), and then converts the responses back into Raycast’s format.
This project uses a man-in-the-middle approach to intercept and forward Raycast requests to various AI APIs, then returns the responses after reformatting them for Raycast. It primarily maps:
-
GET /api/v1/me: Modifies the flag indicating user support for AI. -
POST /api/v1/translations: Translation interface. -
POST /api/v1/ai/chat_completions: Common AI interface. -
GET /api/v1/ai/models: AI model list interface.
- Modify DNS or
/etc/hoststo pointbackend.raycast.comto this proxy instead of the official server. - The proxy receives the HTTPS requests from Raycast.
- A self-signed certificate is used to decrypt and forward these requests to the configured AI endpoints (e.g., OpenAI, Anthropic).
- The responses are re-encrypted and returned to Raycast.
Because Raycast and its API communicate via HTTPS, you need to trust the self-signed certificate for this interception to work. More details on man-in-the-middle proxies can be found at mitmproxy documentation.
Environment variables are becoming deprecated. Now you can define multiple models in config.yml, allowing providers to coexist:
models:
- provider_name: "openai"
api_type: "openai"
params:
api_key: "sk-xxxx"
allow_model_patterns:
- "gpt-\\d+"
- provider_name: "azure openai"
api_type: "openai"
params:
api_key: "xxxxxx"
base_url: "https://your-resource.openai.azure.com"
# ...
- provider_name: "google"
api_type: "gemini"
params:
api_key: "xxxxxx"
- provider_name: "anthropic"
api_type: "anthropic"
params:
api_key: "sk-ant-xxx"
- provider_name: "deepseek"
api_type: "openai" # openai-compatible
params:
api_key: "sk-deepseek-xxx"
default_model: "gpt-4"Each provider entry specifies the provider name, API type, and parameters.
-
provider_name: The provider name. used for identification. -
api_type: The API type. For example,openai,gemini, oranthropic. -
params:base_url,api_key, and other parameters required by the provider.
Supported providers: you can combine multiple models, Common options include:
| Provider | Model | Test Status | Image Generation |
|---|---|---|---|
openai |
from api | Tested | Supported |
azure openai |
Same as above | Tested | Supported |
google |
from api | Tested | Not supported |
anthropic |
claude-3-sonnet, claude-3-opus, claude-3-5-opus | Tested | Not supported |
deepseek |
from api | Tested | Not supported |
ollama |
from api | Tested | Not Supported |
Refer to the config.yml.example file for more details.
Only OpenAI API supports image generation.
pip3 install mitmproxy
python -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/yufeikang/raycast_api_proxy/main/scripts/cert_gen.py)" --domain backend.raycast.com --out ./certOr
Clone this repository and run:
pdm run cert_genOpen the CA certificate in the cert folder and add it to the system keychain and trust it.
This is mandatory, as the Raycast AI proxy uses a self-signed certificate, and it must be trusted to work correctly.
Note:
When using on macOS with Apple Silicon, if you encounter application hanging issues when manually adding the CA certificate to the "Keychain Access", you can use the following command in the terminal as an alternative:
sudo security add-trusted-cert -d -p ssl -p basic -k /Library/Keychains/System.keychain ~/.mitmproxy/mitmproxy-ca-cert.pem127.0.0.1 backend.raycast.com
::1 backend.raycast.com
The purpose of this modification is to redirect backend.raycast.com to the local machine, rather than the real backend.raycast.com. You can also add this record in your DNS server.
Alternatively, you can add this record to your DNS server. The ultimate goal is to make backend.raycast.com point to the address where this project is deployed. The 127.0.0.1 can be
replaced with your deployment address. If you deploy this project in the cloud or in your local network, you can point this address to your deployment address.
docker run --name raycast \
-e OPENAI_API_KEY=$OPENAI_API_KEY \
-p 443:443 \
--dns 1.1.1.1 \
-v $PWD/cert/:/data/cert \
-e CERT_FILE=/data/cert/backend.raycast.com.cert.pem \
-e CERT_KEY=/data/cert/backend.raycast.com.key.pem \
-e LOG_LEVEL=INFO \
-d \
ghcr.io/yufeikang/raycast_api_proxy:mainYou can also deploy this service in the cloud or your local network, as long as your Raycast can access this address.
Then, restart Raycast, and you should be able to use it.
Refer to How to switch between OpenAI and Azure OpenAI endpoints with Python.
Simply modify the corresponding environment variables.
docker run --name raycast \
-e OPENAI_API_KEY=$OPENAI_API_KEY \
-e OPENAI_BASE_URL=https://your-resource.openai.azure.com \
-e OPENAI_API_VERSION=2023-05-15 \
-e OPENAI_API_TYPE=azure \
-e AZURE_DEPLOYMENT_ID=your-deployment-id \
-p 443:443 \
--dns 1.1.1.1 \
-v $PWD/cert/:/data/cert \
-e CERT_FILE=/data/cert/backend.raycast.com.cert.pem \
-e CERT_KEY=/data/cert/backend.raycast.com.key.pem \
-e LOG_LEVEL=INFO \
-d \
ghcr.io/yufeikang/raycast_api_proxy:mainCan be used together with the OpenAI API by setting the corresponding environment variables.
Obtain your Google API Key and export it as GOOGLE_API_KEY.
# git clone this repo and cd to it
docker build -t raycast .
docker run --name raycast \
-e GOOGLE_API_KEY=$GOOGLE_API_KEY \
-p 443:443 \
--dns 1.1.1.1 \
-v $PWD/cert/:/data/cert \
-e CERT_FILE=/data/cert/backend.raycast.com.cert.pem \
-e CERT_KEY=/data/cert/backend.raycast.com.key.pem \
-e LOG_LEVEL=INFO \
-d \
raycast:latest- Clone this repository
- Install dependencies using
pdm install - Create environment variables
export OPENAI_API_KEY=<your openai api key>
- Generate self-signed certificate using
./scripts/cert_gen.py --domain backend.raycast.com --out ./cert - Start the service using
python ./app/main.py
Since you might have modified the local DNS, developing locally might lead to DNS loops. To avoid this, use Docker during local development and start the development environment by specifying the DNS.
Reference:
sh ./local_docker.shYou can refer to the custom_mapping.yml.example file in the project directory to customize the modifications to some interface responses.
"api/v1/me/trial_status":
get:
response:
body:
# json path replace
"$.trial_limits.commands_limit": 30For example, the above configuration will replace $.trial_limits.commands_limit in the response body of the GET api/v1/me/trial_status interface with 30. The
$.trial_limits.commands_limit is a JSON path.
Currently, only response body replacements are supported.
If you want to allow multiple users to share this service or you deploy the service on the public internet, you need to restrict which users can access the service. You can use the
ALLOWED_USERS environment variable to restrict which users can access the service.
ALLOWED_USERS="[email protected],[email protected]"The email addresses are the Raycast user email addresses, separated by commas.
-
DNS Designation Due to the presence of GFW (Great Firewall of China), if you use this in mainland China, you might need to designate a domestic DNS server. Otherwise, domain names might not resolve correctly. For instance:
--dns 223.5.5.5. -
DNS Not Taking Effect Sometimes on macOS, modifying the
/etc/hostsfile does not take effect immediately. There’s no known solution to this yet. Sometimes restarting Raycast helps, or modifying the/etc/hostsfile again might work.
- [ ] Support web search
- [ ] Support more AI models
- [ ] Improve project structure
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for raycast_api_proxy
Similar Open Source Tools

raycast_api_proxy
The Raycast AI Proxy is a tool that acts as a proxy for the Raycast AI application, allowing users to utilize the application without subscribing. It intercepts and forwards Raycast requests to various AI APIs, then reformats the responses for Raycast. The tool supports multiple AI providers and allows for custom model configurations. Users can generate self-signed certificates, add them to the system keychain, and modify DNS settings to redirect requests to the proxy. The tool is designed to work with providers like OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Google, and more, enabling tasks such as AI chat completions, translations, and image generation.
chatgpt-cli
ChatGPT CLI provides a powerful command-line interface for seamless interaction with ChatGPT models via OpenAI and Azure. It features streaming capabilities, extensive configuration options, and supports various modes like streaming, query, and interactive mode. Users can manage thread-based context, sliding window history, and provide custom context from any source. The CLI also offers model and thread listing, advanced configuration options, and supports GPT-4, GPT-3.5-turbo, and Perplexity's models. Installation is available via Homebrew or direct download, and users can configure settings through default values, a config.yaml file, or environment variables.
agenticSeek
AgenticSeek is a voice-enabled AI assistant powered by DeepSeek R1 agents, offering a fully local alternative to cloud-based AI services. It allows users to interact with their filesystem, code in multiple languages, and perform various tasks autonomously. The tool is equipped with memory to remember user preferences and past conversations, and it can divide tasks among multiple agents for efficient execution. AgenticSeek prioritizes privacy by running entirely on the user's hardware without sending data to the cloud.
clickclickclick
ClickClickClick is a framework designed to enable autonomous Android and computer use using various LLM models, both locally and remotely. It supports tasks such as drafting emails, opening browsers, and starting games, with current support for local models via Ollama, Gemini, and GPT 4o. The tool is highly experimental and evolving, with the best results achieved using specific model combinations. Users need prerequisites like `adb` installation and USB debugging enabled on Android phones. The tool can be installed via cloning the repository, setting up a virtual environment, and installing dependencies. It can be used as a CLI tool or script, allowing users to configure planner and finder models for different tasks. Additionally, it can be used as an API to execute tasks based on provided prompts, platform, and models.
mLoRA
mLoRA (Multi-LoRA Fine-Tune) is an open-source framework for efficient fine-tuning of multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) using LoRA and its variants. It allows concurrent fine-tuning of multiple LoRA adapters with a shared base model, efficient pipeline parallelism algorithm, support for various LoRA variant algorithms, and reinforcement learning preference alignment algorithms. mLoRA helps save computational and memory resources when training multiple adapters simultaneously, achieving high performance on consumer hardware.
lexido
Lexido is an innovative assistant for the Linux command line, designed to boost your productivity and efficiency. Powered by Gemini Pro 1.0 and utilizing the free API, Lexido offers smart suggestions for commands based on your prompts and importantly your current environment. Whether you're installing software, managing files, or configuring system settings, Lexido streamlines the process, making it faster and more intuitive.
hash
HASH is a self-building, open-source database which grows, structures and checks itself. With it, we're creating a platform for decision-making, which helps you integrate, understand and use data in a variety of different ways.
runpod-worker-comfy
runpod-worker-comfy is a serverless API tool that allows users to run any ComfyUI workflow to generate an image. Users can provide input images as base64-encoded strings, and the generated image can be returned as a base64-encoded string or uploaded to AWS S3. The tool is built on Ubuntu + NVIDIA CUDA and provides features like built-in checkpoints and VAE models. Users can configure environment variables to upload images to AWS S3 and interact with the RunPod API to generate images. The tool also supports local testing and deployment to Docker hub using Github Actions.
chat-ui
A chat interface using open source models, eg OpenAssistant or Llama. It is a SvelteKit app and it powers the HuggingChat app on hf.co/chat.
fish-ai
fish-ai is a tool that adds AI functionality to Fish shell. It can be integrated with various AI providers like OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Google, Hugging Face, Mistral, or a self-hosted LLM. Users can transform comments into commands, autocomplete commands, and suggest fixes. The tool allows customization through configuration files and supports switching between contexts. Data privacy is maintained by redacting sensitive information before submission to the AI models. Development features include debug logging, testing, and creating releases.
loz
Loz is a command-line tool that integrates AI capabilities with Unix tools, enabling users to execute system commands and utilize Unix pipes. It supports multiple LLM services like OpenAI API, Microsoft Copilot, and Ollama. Users can run Linux commands based on natural language prompts, enhance Git commit formatting, and interact with the tool in safe mode. Loz can process input from other command-line tools through Unix pipes and automatically generate Git commit messages. It provides features like chat history access, configurable LLM settings, and contribution opportunities.
trieve
Trieve is an advanced relevance API for hybrid search, recommendations, and RAG. It offers a range of features including self-hosting, semantic dense vector search, typo tolerant full-text/neural search, sub-sentence highlighting, recommendations, convenient RAG API routes, the ability to bring your own models, hybrid search with cross-encoder re-ranking, recency biasing, tunable popularity-based ranking, filtering, duplicate detection, and grouping. Trieve is designed to be flexible and customizable, allowing users to tailor it to their specific needs. It is also easy to use, with a simple API and well-documented features.
mcpdoc
The MCP LLMS-TXT Documentation Server is an open-source server that provides developers full control over tools used by applications like Cursor, Windsurf, and Claude Code/Desktop. It allows users to create a user-defined list of `llms.txt` files and use a `fetch_docs` tool to read URLs within these files, enabling auditing of tool calls and context returned. The server supports various applications and provides a way to connect to them, configure rules, and test tool calls for tasks related to documentation retrieval and processing.
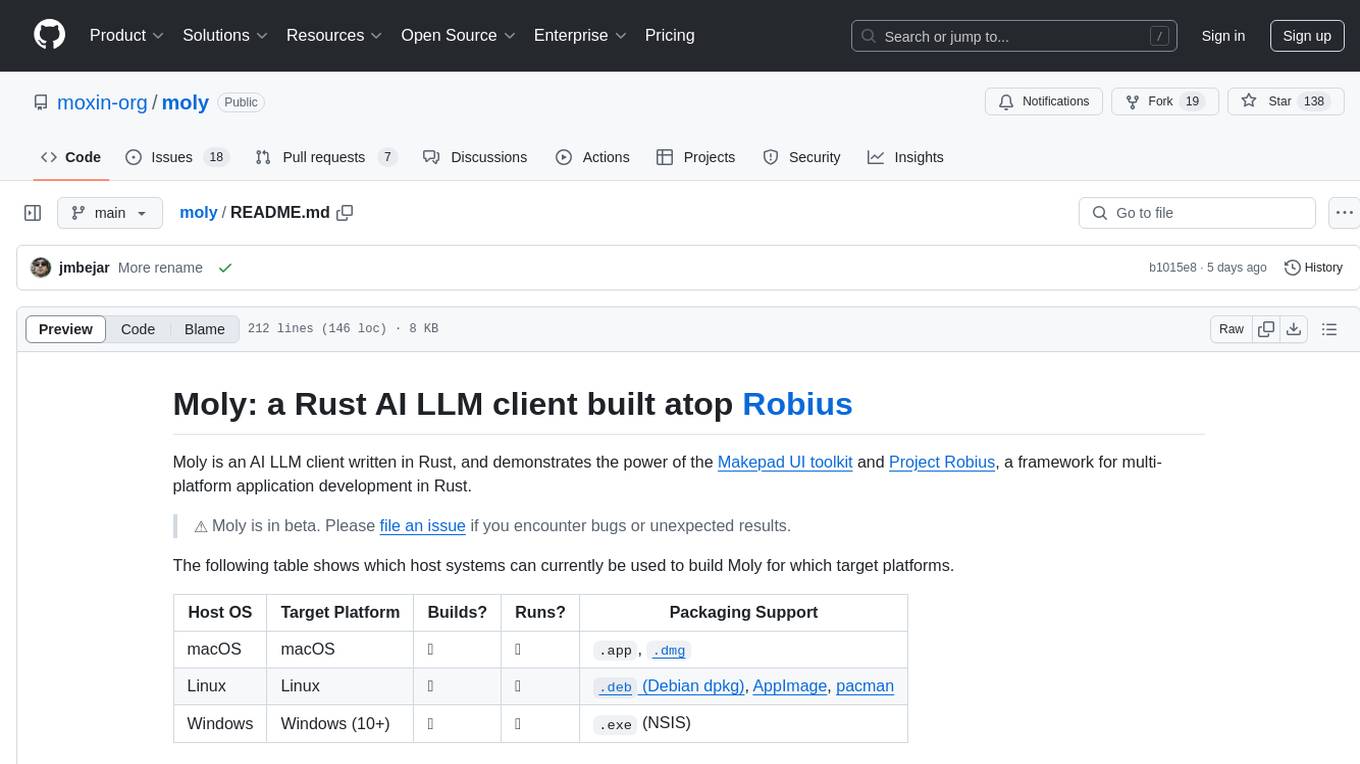
moly
Moly is an AI LLM client written in Rust, showcasing the capabilities of the Makepad UI toolkit and Project Robius, a framework for multi-platform application development in Rust. It is currently in beta, allowing users to build and run Moly on macOS, Linux, and Windows. The tool provides packaging support for different platforms, such as `.app`, `.dmg`, `.deb`, AppImage, pacman, and `.exe` (NSIS). Users can easily set up WasmEdge using `moly-runner` and leverage `cargo` commands to build and run Moly. Additionally, Moly offers pre-built releases for download and supports packaging for distribution on Linux, Windows, and macOS.
openai_trtllm
OpenAI-compatible API for TensorRT-LLM and NVIDIA Triton Inference Server, which allows you to integrate with langchain

joinly
joinly.ai is a connector middleware designed to enable AI agents to actively participate in video calls, providing essential meeting tools for AI agents to perform tasks and interact in real time. It supports live interaction, conversational flow, cross-platform compatibility, bring-your-own-LLM, and choose-your-preferred-TTS/STT services. The tool is 100% open-source, self-hosted, and privacy-first, aiming to make meetings accessible to AI agents by joining and participating in video calls.
For similar tasks

raycast_api_proxy
The Raycast AI Proxy is a tool that acts as a proxy for the Raycast AI application, allowing users to utilize the application without subscribing. It intercepts and forwards Raycast requests to various AI APIs, then reformats the responses for Raycast. The tool supports multiple AI providers and allows for custom model configurations. Users can generate self-signed certificates, add them to the system keychain, and modify DNS settings to redirect requests to the proxy. The tool is designed to work with providers like OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Google, and more, enabling tasks such as AI chat completions, translations, and image generation.

lollms-webui
LoLLMs WebUI (Lord of Large Language Multimodal Systems: One tool to rule them all) is a user-friendly interface to access and utilize various LLM (Large Language Models) and other AI models for a wide range of tasks. With over 500 AI expert conditionings across diverse domains and more than 2500 fine tuned models over multiple domains, LoLLMs WebUI provides an immediate resource for any problem, from car repair to coding assistance, legal matters, medical diagnosis, entertainment, and more. The easy-to-use UI with light and dark mode options, integration with GitHub repository, support for different personalities, and features like thumb up/down rating, copy, edit, and remove messages, local database storage, search, export, and delete multiple discussions, make LoLLMs WebUI a powerful and versatile tool.
daily-poetry-image
Daily Chinese ancient poetry and AI-generated images powered by Bing DALL-E-3. GitHub Action triggers the process automatically. Poetry is provided by Today's Poem API. The website is built with Astro.
InvokeAI
InvokeAI is a leading creative engine built to empower professionals and enthusiasts alike. Generate and create stunning visual media using the latest AI-driven technologies. InvokeAI offers an industry leading Web Interface, interactive Command Line Interface, and also serves as the foundation for multiple commercial products.
LocalAI
LocalAI is a free and open-source OpenAI alternative that acts as a drop-in replacement REST API compatible with OpenAI (Elevenlabs, Anthropic, etc.) API specifications for local AI inferencing. It allows users to run LLMs, generate images, audio, and more locally or on-premises with consumer-grade hardware, supporting multiple model families and not requiring a GPU. LocalAI offers features such as text generation with GPTs, text-to-audio, audio-to-text transcription, image generation with stable diffusion, OpenAI functions, embeddings generation for vector databases, constrained grammars, downloading models directly from Huggingface, and a Vision API. It provides a detailed step-by-step introduction in its Getting Started guide and supports community integrations such as custom containers, WebUIs, model galleries, and various bots for Discord, Slack, and Telegram. LocalAI also offers resources like an LLM fine-tuning guide, instructions for local building and Kubernetes installation, projects integrating LocalAI, and a how-tos section curated by the community. It encourages users to cite the repository when utilizing it in downstream projects and acknowledges the contributions of various software from the community.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.
StableSwarmUI
StableSwarmUI is a modular Stable Diffusion web user interface that emphasizes making power tools easily accessible, high performance, and extensible. It is designed to be a one-stop-shop for all things Stable Diffusion, providing a wide range of features and capabilities to enhance the user experience.
civitai
Civitai is a platform where people can share their stable diffusion models (textual inversions, hypernetworks, aesthetic gradients, VAEs, and any other crazy stuff people do to customize their AI generations), collaborate with others to improve them, and learn from each other's work. The platform allows users to create an account, upload their models, and browse models that have been shared by others. Users can also leave comments and feedback on each other's models to facilitate collaboration and knowledge sharing.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.

