
iree-amd-aie
IREE plugin repository for the AMD AIE accelerator
Stars: 106
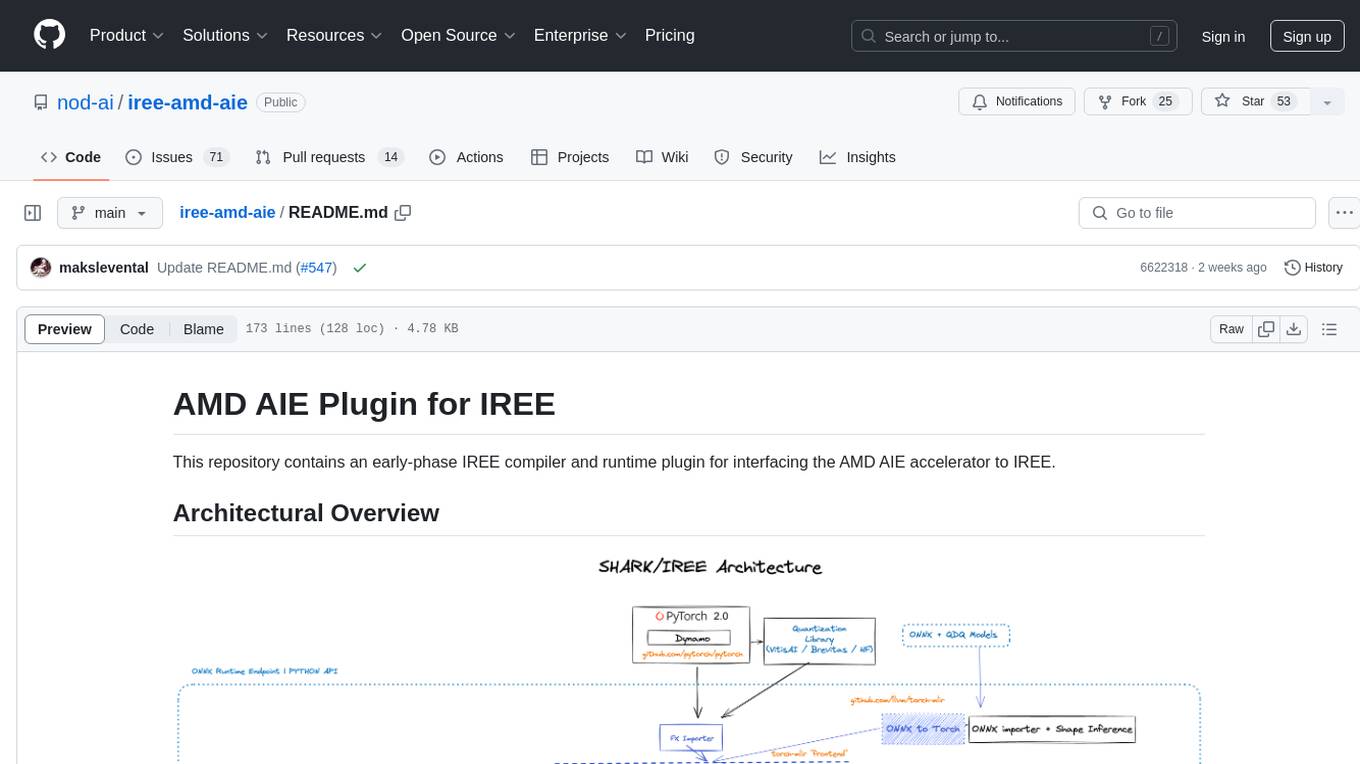
This repository contains an early-phase IREE compiler and runtime plugin for interfacing the AMD AIE accelerator to IREE. It provides architectural overview, developer setup instructions, building guidelines, and runtime driver setup details. The repository focuses on enabling the integration of the AMD AIE accelerator with IREE, offering developers the tools and resources needed to build and run applications leveraging this technology.
README:
This repository contains an early-phase IREE compiler and runtime plugin for targeting AMD NPUs with IREE.
Strong recommendation: check the CI scripts @ .github/workflows - they do a fresh checkout and build on every commit and are written to be read by a non-CI expert.
Either
# ssh
git clone --recursive [email protected]:nod-ai/iree-amd-aie.git
# https
git clone --recursive https://github.com/nod-ai/iree-amd-aie.git
or, if you want a faster checkout,
git \
-c submodule."third_party/torch-mlir".update=none \
-c submodule."third_party/stablehlo".update=none \
-c submodule."third_party/XRT".update=none \
clone \
--recursive \
--shallow-submodules \
[email protected]:nod-ai/iree-amd-aie.git # https://github.com/nod-ai/iree-amd-aie.git
The above avoids cloning entire repo histories for submodules, and skips a few, currently, unused, submodules that are nested in IREE.
Checkout xdna-driver, using commit 2daf25f:
git clone [email protected]:amd/xdna-driver.git
cd <root-of-source-tree>
# get code for submodules
git checkout 2daf25f
git submodule update --init --recursive
Remove any previously installed drivers, if applicable.
packages=$(dpkg -l | awk '/^ii/ && $2 ~ /^xrt/ { print $2 }')
sudo apt-get remove -y $packages
cd <root-of-source-tree>
rm xrt/build/Release/*.deb
rm build/Release/*.deb
Follow the instructions to build and install the driver module: xdna-driver.
You will need at least Peano/llvm-aie to be installed in your system to run e2e examples as it's needed for compiling AIE core code. For best performance (but slower compilation times), you will also need Chess.
To install llvm-aie in the current working directory:
bash <path-to-iree-amd-aie>/build_tools/download_peano.sh
Now, you should see a directory named llvm-aie in your current working directory.
After building IREE, you can then run e2e tests by passing --peano_dir=<path-to-llvm-aie> to tests, see Testing.
For best performance and to run all tests, you can install Chess in the following way:
- Install Vitis™ AIE Essentials from Ryzen AI Software 1.3 Early Accesss.
tar -xzvf ryzen_ai_1.3.1-ea-lnx64-20250116.tgz cd ryzen_ai_1.3.1-ea-lnx64-20250116 mkdir vitis_aie_essentials mv vitis_aie_essentials*.whl vitis_aie_essentials cd vitis_aie_essentials unzip vitis_aie_essentials*.whl
- Set up an AI Engine license.
- Get a local license for AI Engine tools from https://www.xilinx.com/getlicense.
- Copy your license file (Xilinx.lic) to your preferred location, e.g.
/opt/Xilinx.lic.
After building IREE, you can then run e2e tests by passing --vitis_dir=<path-to-vitis-aie-essentials> to tests, see Testing. Note however that you need to export the path to the AI Engine license for successful compilation:
export XILINXD_LICENSE_FILE=<path-to-Xilinx.lic>
cd iree-amd-aie
cmake \
-B <WHERE_YOU_WOULD_LIKE_TO_BUILD> \
-S third_party/iree \
-DIREE_CMAKE_PLUGIN_PATHS=$PWD \
-DIREE_BUILD_PYTHON_BINDINGS=ON \
-DIREE_INPUT_STABLEHLO=OFF \
-DIREE_INPUT_TORCH=OFF \
-DIREE_INPUT_TOSA=OFF \
-DIREE_HAL_DRIVER_DEFAULTS=OFF \
-DIREE_TARGET_BACKEND_DEFAULTS=OFF \
-DIREE_TARGET_BACKEND_LLVM_CPU=ON \
-DIREE_BUILD_TESTS=ON \
-DIREE_EXTERNAL_HAL_DRIVERS=xrt-lite \
-DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=<WHERE_YOU_WOULD_LIKE_TO_INSTALL>
cmake --build <WHERE_YOU_WOULD_LIKE_TO_BUILD>
The bare minimum configure command for IREE with the amd-aie plugin
cmake \
-B <WHERE_YOU_WOULD_LIKE_TO_BUILD> \
-S <IREE_REPO_SRC_DIR> \
-DIREE_CMAKE_PLUGIN_PATHS=<IREE_AMD_AIE_REPO_SRC_DIR> \
-DIREE_BUILD_PYTHON_BINDINGS=ON
Very likely, you will want to use ccache and lld (or some other modern linker like mold)
-DCMAKE_C_COMPILER_LAUNCHER=ccache \
-DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_LAUNCHER=ccache \
-DCMAKE_EXE_LINKER_FLAGS="-fuse-ld=lld" \
-DCMAKE_SHARED_LINKER_FLAGS="-fuse-ld=lld"
If you don't plan on using any of IREE's frontends or backends/targets (e.g., you're doing work on this code base itself),
you can opt-out of everything (except the llvm-cpu backend) with
-DIREE_INPUT_STABLEHLO=OFF \
-DIREE_INPUT_TORCH=OFF \
-DIREE_INPUT_TOSA=OFF \
-DIREE_HAL_DRIVER_DEFAULTS=OFF \
-DIREE_TARGET_BACKEND_DEFAULTS=OFF \
-DIREE_TARGET_BACKEND_LLVM_CPU=ON
With the above you can also skip cloning the stablehlo and torch-mlir submodules/repos but in this case you will need to add
-DIREE_ERROR_ON_MISSING_SUBMODULES=OFF
If you're "bringing your own LLVM", i.e., you have a prebuilt/compiled distribution of LLVM you'd like to use, you can add
-DIREE_BUILD_BUNDLED_LLVM=OFF
In this case you will need lit somewhere in your environment and you will need to add to CMake -DLLVM_EXTERNAL_LIT=<SOMEWHERE>
(e.g., pip install lit; SOMEWHERE=$(which lit)).
See Bringing your own LLVM below for more information on using prebuilt/compiled distributions of LLVM.
Lit tests (i.e., compiler tests) specific to AIE can be run with something like
cd <WHERE_YOU_WOULD_LIKE_TO_BUILD>
ctest -R amd-aie --output-on-failure -j 10
(the -j 10 runs 10 tests in parallel)
Other tests, which run on device, are in the build_tools subdirectory.
See build_tools/ci/run_all_runtime_tests.sh for an example script that shows how to run all the runtime tests.
When using a pre-built distribution of LLVM, getting the right/matching build, that works with IREE, is tough (besides the commit hash, there are various flags to set).
To enable adventurous users to avail themselves of -DIREE_BUILD_BUNDLED_LLVM=OFF we cache/store/save the LLVM distribution for every successful CI run.
These can then be downloaded by checking the artifacts section of any recent CI run's Summary page:
You can turn on HAL API tracing by adding to CMake:
-DIREE_ENABLE_RUNTIME_TRACING=ON
-DIREE_TRACING_PROVIDER=console
// optional but recommended
-DIREE_TRACING_CONSOLE_FLUSH=1
This will you show you all the HAL APIs that have IREE_TRACE_ZONE_BEGIN ... IREE_TRACE_ZONE_END that are hit during a run/execution (of, e.g., iree-run-module).
You can turn on VM tracing by adding to CMake:
-DIREE_VM_EXECUTION_TRACING_ENABLE=1
-DIREE_VM_EXECUTION_TRACING_FORCE_ENABLE=1
// optional
-DIREE_VM_EXECUTION_TRACING_SRC_LOC_ENABLE=1
This will show you all of the VM dispatches that actually occur during a run/execution.
Note, this is roughly equivalent to passing --compile-to=vm to iree-compile.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for iree-amd-aie
Similar Open Source Tools

iree-amd-aie
This repository contains an early-phase IREE compiler and runtime plugin for interfacing the AMD AIE accelerator to IREE. It provides architectural overview, developer setup instructions, building guidelines, and runtime driver setup details. The repository focuses on enabling the integration of the AMD AIE accelerator with IREE, offering developers the tools and resources needed to build and run applications leveraging this technology.
vibe
Vibe Design System is a collection of packages for React.js development, providing components, styles, and guidelines to streamline the development process and enhance user experience. It includes a Core component library, Icons library, Testing utilities, Codemods, and more. The system also features an MCP server for intelligent assistance with component APIs, usage examples, icons, and best practices. Vibe 2 is no longer actively maintained, with users encouraged to upgrade to Vibe 3 for the latest improvements and ongoing support.
arcade-ai
Arcade AI is a developer-focused tooling and API platform designed to enhance the capabilities of LLM applications and agents. It simplifies the process of connecting agentic applications with user data and services, allowing developers to concentrate on building their applications. The platform offers prebuilt toolkits for interacting with various services, supports multiple authentication providers, and provides access to different language models. Users can also create custom toolkits and evaluate their tools using Arcade AI. Contributions are welcome, and self-hosting is possible with the provided documentation.

deepflow
DeepFlow is an open-source project that provides deep observability for complex cloud-native and AI applications. It offers Zero Code data collection with eBPF for metrics, distributed tracing, request logs, and function profiling. DeepFlow is integrated with SmartEncoding to achieve Full Stack correlation and efficient access to all observability data. With DeepFlow, cloud-native and AI applications automatically gain deep observability, removing the burden of developers continually instrumenting code and providing monitoring and diagnostic capabilities covering everything from code to infrastructure for DevOps/SRE teams.
Memento
Memento is a lightweight and user-friendly version control tool designed for small to medium-sized projects. It provides a simple and intuitive interface for managing project versions and collaborating with team members. With Memento, users can easily track changes, revert to previous versions, and merge different branches. The tool is suitable for developers, designers, content creators, and other professionals who need a streamlined version control solution. Memento simplifies the process of managing project history and ensures that team members are always working on the latest version of the project.
jadx-ai-mcp
JADX-AI-MCP is a plugin for the JADX decompiler that integrates with Model Context Protocol (MCP) to provide live reverse engineering support with LLMs like Claude. It allows for quick analysis, vulnerability detection, and AI code modification, all in real time. The tool combines JADX-AI-MCP and JADX MCP SERVER to analyze Android APKs effortlessly. It offers various prompts for code understanding, vulnerability detection, reverse engineering helpers, static analysis, AI code modification, and documentation. The tool is part of the Zin MCP Suite and aims to connect all android reverse engineering and APK modification tools with a single MCP server for easy reverse engineering of APK files.
ramalama
The Ramalama project simplifies working with AI by utilizing OCI containers. It automatically detects GPU support, pulls necessary software in a container, and runs AI models. Users can list, pull, run, and serve models easily. The tool aims to support various GPUs and platforms in the future, making AI setup hassle-free.

SpecForge
SpecForge is a powerful tool for generating API specifications from code. It helps developers to easily create and maintain accurate API documentation by extracting information directly from the codebase. With SpecForge, users can streamline the process of documenting APIs, ensuring consistency and reducing manual effort. The tool supports various programming languages and frameworks, making it versatile and adaptable to different development environments. By automating the generation of API specifications, SpecForge enhances collaboration between developers and stakeholders, improving overall project efficiency and quality.
tools
Strands Agents Tools is a community-driven project that provides a powerful set of tools for your agents to use. It bridges the gap between large language models and practical applications by offering ready-to-use tools for file operations, system execution, API interactions, mathematical operations, and more. The tools cover a wide range of functionalities including file operations, shell integration, memory storage, web infrastructure, HTTP client, Slack client, Python execution, mathematical tools, AWS integration, image and video processing, audio output, environment management, task scheduling, advanced reasoning, swarm intelligence, dynamic MCP client, parallel tool execution, browser automation, diagram creation, RSS feed management, and computer automation.
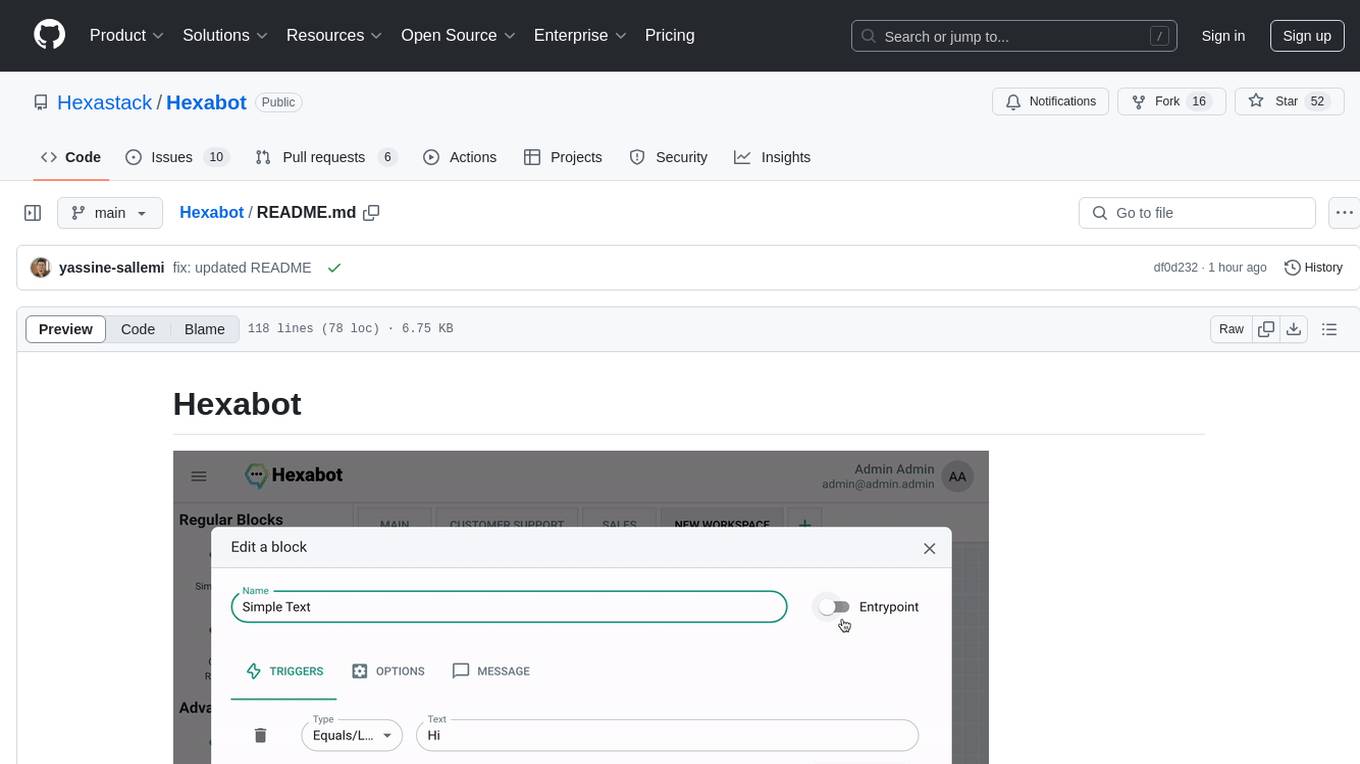
Hexabot
Hexabot Community Edition is an open-source chatbot solution designed for flexibility and customization, offering powerful text-to-action capabilities. It allows users to create and manage AI-powered, multi-channel, and multilingual chatbots with ease. The platform features an analytics dashboard, multi-channel support, visual editor, plugin system, NLP/NLU management, multi-lingual support, CMS integration, user roles & permissions, contextual data, subscribers & labels, and inbox & handover functionalities. The directory structure includes frontend, API, widget, NLU, and docker components. Prerequisites for running Hexabot include Docker and Node.js. The installation process involves cloning the repository, setting up the environment, and running the application. Users can access the UI admin panel and live chat widget for interaction. Various commands are available for managing the Docker services. Detailed documentation and contribution guidelines are provided for users interested in contributing to the project.
ai-manus
AI Manus is a general-purpose AI Agent system that supports running various tools and operations in a sandbox environment. It offers deployment with minimal dependencies, supports multiple tools like Terminal, Browser, File, Web Search, and messaging tools, allocates separate sandboxes for tasks, manages session history, supports stopping and interrupting conversations, file upload and download, and is multilingual. The system also provides user login and authentication. The project primarily relies on Docker for development and deployment, with model capability requirements and recommended Deepseek and GPT models.
docs
This repository contains the documentation for the Strands Agents SDK, a simple yet powerful framework for building and running AI agents. The documentation is built using MkDocs and provides guides, examples, and API references. The official documentation is available online at: https://strandsagents.com.
mcp-fundamentals
The mcp-fundamentals repository is a collection of fundamental concepts and examples related to microservices, cloud computing, and DevOps. It covers topics such as containerization, orchestration, CI/CD pipelines, and infrastructure as code. The repository provides hands-on exercises and code samples to help users understand and apply these concepts in real-world scenarios. Whether you are a beginner looking to learn the basics or an experienced professional seeking to refresh your knowledge, mcp-fundamentals has something for everyone.
fastapi
智元 Fast API is a one-stop API management system that unifies various LLM APIs in terms of format, standards, and management, achieving the ultimate in functionality, performance, and user experience. It supports various models from companies like OpenAI, Azure, Baidu, Keda Xunfei, Alibaba Cloud, Zhifu AI, Google, DeepSeek, 360 Brain, and Midjourney. The project provides user and admin portals for preview, supports cluster deployment, multi-site deployment, and cross-zone deployment. It also offers Docker deployment, a public API site for registration, and screenshots of the admin and user portals. The API interface is similar to OpenAI's interface, and the project is open source with repositories for API, web, admin, and SDK on GitHub and Gitee.
koog
Koog is a Kotlin-based framework for building and running AI agents entirely in idiomatic Kotlin. It allows users to create agents that interact with tools, handle complex workflows, and communicate with users. Key features include pure Kotlin implementation, MCP integration, embedding capabilities, custom tool creation, ready-to-use components, intelligent history compression, powerful streaming API, persistent agent memory, comprehensive tracing, flexible graph workflows, modular feature system, scalable architecture, and multiplatform support.

crystal
Crystal is an Electron desktop application that allows users to run, inspect, and test multiple Claude Code instances simultaneously using git worktrees. It provides features such as parallel sessions, git worktree isolation, session persistence, git integration, change tracking, notifications, and the ability to run scripts. Crystal simplifies the workflow by creating isolated sessions, iterating with Claude Code, reviewing diff changes, and squashing commits for a clean history. It is a tool designed for collaborative AI notebook editing and testing.
For similar tasks
python-tutorial-notebooks
This repository contains Jupyter-based tutorials for NLP, ML, AI in Python for classes in Computational Linguistics, Natural Language Processing (NLP), Machine Learning (ML), and Artificial Intelligence (AI) at Indiana University.
open-parse
Open Parse is a Python library for visually discerning document layouts and chunking them effectively. It is designed to fill the gap in open-source libraries for handling complex documents. Unlike text splitting, which converts a file to raw text and slices it up, Open Parse visually analyzes documents for superior LLM input. It also supports basic markdown for parsing headings, bold, and italics, and has high-precision table support, extracting tables into clean Markdown formats with accuracy that surpasses traditional tools. Open Parse is extensible, allowing users to easily implement their own post-processing steps. It is also intuitive, with great editor support and completion everywhere, making it easy to use and learn.
MoonshotAI-Cookbook
The MoonshotAI-Cookbook provides example code and guides for accomplishing common tasks with the MoonshotAI API. To run these examples, you'll need an MoonshotAI account and associated API key. Most code examples are written in Python, though the concepts can be applied in any language.
AHU-AI-Repository
This repository is dedicated to the learning and exchange of resources for the School of Artificial Intelligence at Anhui University. Notes will be published on this website first: https://www.aoaoaoao.cn and will be synchronized to the repository regularly. You can also contact me at [email protected].
modern_ai_for_beginners
This repository provides a comprehensive guide to modern AI for beginners, covering both theoretical foundations and practical implementation. It emphasizes the importance of understanding both the mathematical principles and the code implementation of AI models. The repository includes resources on PyTorch, deep learning fundamentals, mathematical foundations, transformer-based LLMs, diffusion models, software engineering, and full-stack development. It also features tutorials on natural language processing with transformers, reinforcement learning, and practical deep learning for coders.
Building-AI-Applications-with-ChatGPT-APIs
This repository is for the book 'Building AI Applications with ChatGPT APIs' published by Packt. It provides code examples and instructions for mastering ChatGPT, Whisper, and DALL-E APIs through building innovative AI projects. Readers will learn to develop AI applications using ChatGPT APIs, integrate them with frameworks like Flask and Django, create AI-generated art with DALL-E APIs, and optimize ChatGPT models through fine-tuning.
examples
This repository contains a collection of sample applications and Jupyter Notebooks for hands-on experience with Pinecone vector databases and common AI patterns, tools, and algorithms. It includes production-ready examples for review and support, as well as learning-optimized examples for exploring AI techniques and building applications. Users can contribute, provide feedback, and collaborate to improve the resource.
lingoose
LinGoose is a modular Go framework designed for building AI/LLM applications. It offers the flexibility to import only the necessary modules, abstracts features for customization, and provides a comprehensive solution for developing AI/LLM applications from scratch. The framework simplifies the process of creating intelligent applications by allowing users to choose preferred implementations or create their own. LinGoose empowers developers to leverage its capabilities to streamline the development of cutting-edge AI and LLM projects.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.