
SMRY
A tool to get summaries and get past paywalls
Stars: 1220
SMRY.ai is a Next.js application that bypasses paywalls and generates AI-powered summaries by fetching content from multiple sources simultaneously. It provides a distraction-free reader with summary builder, cleans articles, offers multi-source fetching, built-in AI summaries in 14 languages, rich debug context, soft paywall access, smart extraction using Diffbot's AI, multi-source parallel fetching, type-safe error handling, dual caching strategy, intelligent source routing, content parsing pipeline, multilingual summaries, and more. The tool aims to make referencing reporting easier, provide original articles alongside summaries, and offer concise summaries in various languages.
README:
SMRY.ai is a Next.js application that bypasses paywalls and generates AI-powered summaries by fetching content from multiple sources simultaneously. It is the spiritual successor to 12ft: type http://smry.ai/ in front of any article URL and you'll land on a distraction-free reader with the summary builder already loaded.
- Paywalls make it hard to reference reporting, even when articles are already public on social media.
- Researchers, journalists, and readers still need the original article, not just an LLM hallucination.
- Summaries should live next to the cleaned article, not in a separate chat window.
- A single extraction service often fails, so we hit multiple sources at once and cache whatever works.
-
Prepend the prefix: Add
smry.ai/before any article URL (e.g.smry.ai/example.com/2026/any-article) to jump straight into SMRY. - Paste a link on the homepage: smry.ai will fetch it, clean it, and let you generate summaries.
- Use the bookmarklet: Drag the provided bookmarklet to your bookmarks bar; click it on any page to wrap it in SMRY.
-
Call the proxy route directly:
https://your-domain.com/proxy?url=https://example.com/articleworks for deep linking and integrations.
- Clean reader that strips overlays, ads, and archive UI.
- Multi-source fetching (direct, proxy, wayback) so at least one source usually succeeds.
- Built-in AI summaries in 14 languages with caching and rate limiting.
- Rich debug context for every fetch so you can see what worked and why.
-
Soft Paywall Access: Fetches article content from three sources in parallel:
- Direct (smry-fast): Fetches and parses content directly using Mozilla Readability (server-side)
- Proxy (smry-slow): Uses Diffbot API for intelligent article extraction from original URLs (server-side)
- Wayback Machine: Uses Diffbot API to extract clean content from archived pages (server-side)
Note: Hard paywalls (Bloomberg, Barron's, etc.) cannot be accessed. See /hard-paywalls for details.
-
AI Summaries: Generates concise summaries in 8 languages using OpenRouter (openai/gpt-oss-20b:free)
-
Smart Extraction: Uses Diffbot's AI-powered extraction for direct and archived content
Uses TanStack Query to fetch from all sources simultaneously, displaying whichever responds first. Each source is independently cached.
Server-side sources (Direct, Wayback):
// These hit the /api/article endpoint
const serverQueries = useQueries({
queries: SERVER_SOURCES.map((source) => ({
queryKey: ["article", source, url],
queryFn: () => articleAPI.getArticle(url, source),
}))
});Uses neverthrow's Result types for error handling instead of try-catch, making errors type-safe:
// Returns Result<DiffbotArticle, AppError> instead of throwing
export function fetchArticleWithDiffbot(url: string, source: string): ResultAsync<DiffbotArticle, AppError>Nine distinct error types (NetworkError, RateLimitError, TimeoutError, etc.) with user-friendly messages.
Enhanced Error Context: All errors now include debug context showing:
- What extraction methods were attempted
- Why each method failed or succeeded
- Content length at each step
- Complete extraction timeline
This makes debugging extraction failures much easier.
- Server-side: Upstash Redis for persistent caching across requests
- Client-side: TanStack Query for instant UI updates (1min stale time, 5min GC)
Articles are cached by source:url key. When fetching, if a longer version exists in cache, it's preserved.
Different sources require different extraction strategies:
Direct & Wayback → Diffbot API with Multi-Layer Fallbacks
// Diffbot extracts structured article data with fallback chain:
// 1. Diffbot API extraction
// 2. Mozilla Readability on returned DOM
// 3. Multiple Diffbot fields (html, text, media)
// 4. Wayback-specific original URL extraction
const diffbotResult = await fetchArticleWithDiffbot(urlWithSource, source);This multi-layered approach maximizes content extraction success across diverse article formats and site structures.
For Direct & Wayback (via Diffbot):
- Send URL to Diffbot API
- Receive structured article data (title, HTML, text, siteName)
-
Fallback chain if extraction incomplete:
- Try Mozilla Readability on Diffbot's returned DOM
- For Wayback: Try extracting original URL and re-parsing
- Attempt multiple Diffbot article fields
- Track extraction steps in debug context
- Cache the parsed result
Each article fetch now includes detailed debug context that tracks:
- All extraction attempts and their outcomes
- Fallback strategies that were tried
- Content length at each step
- Timestamps for performance analysis
- Error details for troubleshooting
Debug context is preserved through errors and displayed in the UI for debugging.
Language-specific prompts for 14 languages (en, es, fr, de, zh, ja, pt, ru, hi, it, ko, ar, nl, tr). Each language gets its own cache key:
summary:en:https://example.com
summary:es:https://example.com
Rate limited to 20 summaries per IP per day, 6 per minute.
- Next.js 16 (App Router) with React Server Components
- TanStack Query for client-side data fetching and caching
- Zod for runtime type validation
- neverthrow for Result-based error handling
- Upstash Redis for caching
- OpenRouter for AI summaries (unified access to 300+ models)
- Diffbot API for AI-powered article extraction (direct & wayback sources)
- Mozilla Readability for fallback content extraction
- Logo.dev API for company logos (client-side)
- Radix UI + Tailwind CSS for UI
app/
├── api/
│ ├── article/route.ts # Fetches & parses articles from sources
│ └── summary/route.ts # Generates AI summaries with rate limiting
├── proxy/page.tsx # Main article display page
└── page.tsx # Landing page
lib/
├── api/
│ ├── diffbot.ts # Diffbot API with multi-layer fallback extraction
│ └── client.ts # Type-safe API client
├── errors/
│ ├── types.ts # Type-safe error definitions (9 types)
│ ├── safe-error.ts # Safe error utilities
│ └── index.ts # Barrel export
├── logger.ts # Pino structured logging
└── hooks/
└── use-articles.ts # TanStack Query hook for parallel fetching
components/
├── arrow-tabs.tsx # Tab interface for switching sources
├── article-content.tsx # Renders parsed article with summary form
├── summary-form.tsx # AI summary generation UI
└── proxy-content.tsx # Main content wrapper
types/
└── api.ts # Zod schemas for all API requests/responses
User enters URL
↓
ProxyContent component
↓
useArticles() hook - fires 3 parallel requests
↓
API route /api/article?url=...&source=...
↓
Route to appropriate fetcher:
- Direct/Wayback → fetchArticleWithDiffbot() with multi-layer fallback
↓
Cache in Upstash Redis (if longer than existing)
↓
Return to client
↓
Display first successful response
User clicks "Generate Summary"
↓
POST /api/summary with content + language
↓
Check cache by language:url key
↓
If miss: OpenRouter openai/gpt-oss-20b:free with language-specific prompt
↓
Cache result
↓
Return summary
All variables are required. The app will fail to start if any are missing.
# Auth - https://clerk.com
CLERK_SECRET_KEY=
NEXT_PUBLIC_CLERK_PUBLISHABLE_KEY=
# AI/API
OPENROUTER_API_KEY= # https://openrouter.ai/settings/keys
DIFFBOT_API_KEY= # https://diffbot.com
# Cache - https://console.upstash.com
UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_URL=
UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_TOKEN=
# Analytics - ClickHouse (use docker-compose for local dev)
CLICKHOUSE_URL=http://localhost:8123
CLICKHOUSE_USER=default
CLICKHOUSE_PASSWORD=
CLICKHOUSE_DATABASE=smry_analytics
# Alerting - https://resend.com
RESEND_API_KEY=
ALERT_EMAIL=
# Server config
CORS_ORIGIN=http://localhost:3000
NEXT_PUBLIC_URL=http://localhost:3000- Install dependencies:
pnpm install-
Set up environment variables:
- Copy
.env.exampleto.env.local - Get API keys from: Clerk, OpenRouter, Diffbot, Upstash, Resend
- Run
docker-compose up -d clickhousefor local analytics
- Copy
-
Run development server:
pnpm dev- Build for production:
pnpm build
pnpm starthttp://smry.ai/https://example.com/article
Type that directly into the address bar (or edit the existing URL) and SMRY will load the cleaned article plus summary controls immediately. This works on smry.ai or any self-hosted deployment.
https://your-domain.com
Open the homepage, paste the article URL into the input, and we’ll route you to the proxy page with all sources firing in parallel.
Create a browser bookmark with this URL:
javascript:(function(){window.location='https://your-domain.com/'+window.location.href})()Drag it to your bookmarks bar. Clicking it on any page reloads the article inside SMRY with summaries ready.
https://your-domain.com/proxy?url=https://example.com/article
Use this when you want to share or embed a direct link to the cleaned reader.
The Diffbot integration uses a sophisticated fallback chain to maximize extraction success:
- Primary: Diffbot API - AI-powered article extraction
- Fallback 1: Mozilla Readability - Applied to Diffbot's returned DOM for complex layouts
- Fallback 2: Multiple Diffbot fields - Tries html, text, and media fields
- Fallback 3: Wayback re-extraction - For archived pages, extracts original URL and re-parses
Each step is tracked in debug context, making it easy to understand what worked and what didn't. This approach handles challenging cases like:
- Google Blogger sites with complex DOM structures
- Paywalled content with dynamic loading
- Archive.org pages with wrapped content
- Sites with heavy JavaScript rendering
- Direct (smry-fast): Fast direct fetch with Readability parsing, works for most sites
- Proxy (smry-slow): Diffbot AI-powered extraction bypasses most paywalls and anti-bot measures
- Wayback + Diffbot: Extracts clean content from archived pages, removing archive.org UI clutter
By fetching all three in parallel and displaying any that succeed, the app maximizes success rate.
Diffbot's API is specifically trained to extract article content from HTML, removing navigation, ads, and other clutter. This works excellently for:
- Direct URLs: Bypasses many paywall implementations
- Wayback archives: Removes archive.org's UI wrapper and metadata
Fallback Strategy: If Diffbot's extraction is incomplete, the system automatically tries:
- Mozilla Readability on the returned DOM for better extraction
- Multiple Diffbot fields (html, text, media) to find the best content
- Wayback-specific logic to extract and re-parse original URLs
This multi-layered approach maximizes content extraction success, especially for complex sites like Google Blogger or pages with dynamic layouts.
Articles are cached with the article itself as the value, not just metadata. When a new fetch completes, it compares text length to the cached version and keeps the longer one. This prevents losing content if a source returns a partial article.
All API routes validate inputs with Zod schemas at runtime. This catches invalid data before it reaches application logic. The schemas are shared between client and server, ensuring consistency.
Using neverthrow's Result types instead of exceptions means errors are handled explicitly. Each error type has a user-friendly message, so users get helpful feedback instead of generic errors.
Uses Pino for production-ready logging:
- Development: Pretty-printed, colorized output for easy debugging
- Production: Structured JSON logs for parsing and monitoring
-
Contextual: Each module has its own logger context (e.g.,
api:article,lib:fetch) - Levels: debug, info, warn, error with appropriate defaults
See LOGGING.md for detailed documentation and integration with log aggregation services like Axiom, Logtail, or Datadog.
Contributions are very welcome! Areas where help is especially appreciated:
- [ ] Support for more content sources (Archive.is, Google Cache, etc.)
- [ ] Better soft paywall handling for news sites
- [ ] Browser extension for easier access
- [ ] PDF export functionality
- [ ] Better mobile UI/UX
- [ ] Streaming AI summaries for real-time generation
- [ ] Webhook support for asynchronous processing
- [ ] Support for video/podcast content
- [ ] OCR for image-based paywalls
- [x] Upstash Redis for caching (self-hosted compatible)
- [ ] Dark mode
- [ ] Reading time estimate
- [ ] Text-to-speech integration
- [ ] Customizable fonts and layouts
- [ ] Save/bookmark functionality
- [ ] Unit tests for core functions
- [ ] Integration tests for API routes
- [ ] E2E tests for critical paths
How to contribute:
- Fork the repository
- Create a feature branch
- Make your changes with clear commit messages
- Add tests if applicable
- Submit a pull request
For major changes, open an issue first to discuss the approach.
MIT License - see LICENSE file for details
- 12ft.io - Original inspiration
- archive.is - Archive service
- Diffbot - Article extraction API
Issues and feature requests: GitHub Issues
Built with Next.js 16, TanStack Query, and OpenRouter.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for SMRY
Similar Open Source Tools

SMRY
SMRY.ai is a Next.js application that bypasses paywalls and generates AI-powered summaries by fetching content from multiple sources simultaneously. It provides a distraction-free reader with summary builder, cleans articles, offers multi-source fetching, built-in AI summaries in 14 languages, rich debug context, soft paywall access, smart extraction using Diffbot's AI, multi-source parallel fetching, type-safe error handling, dual caching strategy, intelligent source routing, content parsing pipeline, multilingual summaries, and more. The tool aims to make referencing reporting easier, provide original articles alongside summaries, and offer concise summaries in various languages.

probe
Probe is an AI-friendly, fully local, semantic code search tool designed to power the next generation of AI coding assistants. It combines the speed of ripgrep with the code-aware parsing of tree-sitter to deliver precise results with complete code blocks, making it perfect for large codebases and AI-driven development workflows. Probe is fully local, keeping code on the user's machine without relying on external APIs. It supports multiple languages, offers various search options, and can be used in CLI mode, MCP server mode, AI chat mode, and web interface. The tool is designed to be flexible, fast, and accurate, providing developers and AI models with full context and relevant code blocks for efficient code exploration and understanding.

Mira
Mira is an agentic AI library designed for automating company research by gathering information from various sources like company websites, LinkedIn profiles, and Google Search. It utilizes a multi-agent architecture to collect and merge data points into a structured profile with confidence scores and clear source attribution. The core library is framework-agnostic and can be integrated into applications, pipelines, or custom workflows. Mira offers features such as real-time progress events, confidence scoring, company criteria matching, and built-in services for data gathering. The tool is suitable for users looking to streamline company research processes and enhance data collection efficiency.
DeepSeekAI
DeepSeekAI is a browser extension plugin that allows users to interact with AI by selecting text on web pages and invoking the DeepSeek large model to provide AI responses. The extension enhances browsing experience by enabling users to get summaries or answers for selected text directly on the webpage. It features context text selection, API key integration, draggable and resizable window, AI streaming replies, Markdown rendering, one-click copy, re-answer option, code copy functionality, language switching, and multi-turn dialogue support. Users can install the extension from Chrome Web Store or Edge Add-ons, or manually clone the repository, install dependencies, and build the extension. Configuration involves entering the DeepSeek API key in the extension popup window to start using the AI-driven responses.
better-chatbot
Better Chatbot is an open-source AI chatbot designed for individuals and teams, inspired by various AI models. It integrates major LLMs, offers powerful tools like MCP protocol and data visualization, supports automation with custom agents and visual workflows, enables collaboration by sharing configurations, provides a voice assistant feature, and ensures an intuitive user experience. The platform is built with Vercel AI SDK and Next.js, combining leading AI services into one platform for enhanced chatbot capabilities.
chatnio
Chat Nio is a next-generation AIGC one-stop business solution that combines the advantages of frontend-oriented lightweight deployment projects with powerful API distribution systems. It offers rich model support, beautiful UI design, complete Markdown support, multi-theme support, internationalization support, text-to-image support, powerful conversation sync, model market & preset system, rich file parsing, full model internet search, Progressive Web App (PWA) support, comprehensive backend management, multiple billing methods, innovative model caching, and additional features. The project aims to address limitations in conversation synchronization, billing, file parsing, conversation URL sharing, channel management, and API call support found in existing AIGC commercial sites, while also providing a user-friendly interface design and C-end features.
g4f.dev
G4f.dev is the official documentation hub for GPT4Free, a free and convenient AI tool with endpoints that can be integrated directly into apps, scripts, and web browsers. The documentation provides clear overviews, quick examples, and deeper insights into the major features of GPT4Free, including text and image generation. Users can choose between Python and JavaScript for installation and setup, and can access various API endpoints, providers, models, and client options for different tasks.
payload-ai
The Payload AI Plugin is an advanced extension that integrates modern AI capabilities into your Payload CMS, streamlining content creation and management. It offers features like text generation, voice and image generation, field-level prompt customization, prompt editor, document analyzer, fact checking, automated content workflows, internationalization support, editor AI suggestions, and AI chat support. Users can personalize and configure the plugin by setting environment variables. The plugin is actively developed and tested with Payload version v3.2.1, with regular updates expected.
CursorLens
Cursor Lens is an open-source tool that acts as a proxy between Cursor and various AI providers, logging interactions and providing detailed analytics to help developers optimize their use of AI in their coding workflow. It supports multiple AI providers, captures and logs all requests, provides visual analytics on AI usage, allows users to set up and switch between different AI configurations, offers real-time monitoring of AI interactions, tracks token usage, estimates costs based on token usage and model pricing. Built with Next.js, React, PostgreSQL, Prisma ORM, Vercel AI SDK, Tailwind CSS, and shadcn/ui components.
swift-chat
SwiftChat is a fast and responsive AI chat application developed with React Native and powered by Amazon Bedrock. It offers real-time streaming conversations, AI image generation, multimodal support, conversation history management, and cross-platform compatibility across Android, iOS, and macOS. The app supports multiple AI models like Amazon Bedrock, Ollama, DeepSeek, and OpenAI, and features a customizable system prompt assistant. With a minimalist design philosophy and robust privacy protection, SwiftChat delivers a seamless chat experience with various features like rich Markdown support, comprehensive multimodal analysis, creative image suite, and quick access tools. The app prioritizes speed in launch, request, render, and storage, ensuring a fast and efficient user experience. SwiftChat also emphasizes app privacy and security by encrypting API key storage, minimal permission requirements, local-only data storage, and a privacy-first approach.

mcp-pointer
MCP Pointer is a local tool that combines an MCP Server with a Chrome Extension to allow users to visually select DOM elements in the browser and make textual context available to agentic coding tools like Claude Code. It bridges between the browser and AI tools via the Model Context Protocol, enabling real-time communication and compatibility with various AI tools. The tool extracts detailed information about selected elements, including text content, CSS properties, React component detection, and more, making it a valuable asset for developers working with AI-powered web development.

TranslateBookWithLLM
TranslateBookWithLLM is a Python application designed for large-scale text translation, such as entire books (.EPUB), subtitle files (.SRT), and plain text. It leverages local LLMs via the Ollama API or Gemini API. The tool offers both a web interface for ease of use and a command-line interface for advanced users. It supports multiple format translations, provides a user-friendly browser-based interface, CLI support for automation, multiple LLM providers including local Ollama models and Google Gemini API, and Docker support for easy deployment.
vearch
Vearch is a cloud-native distributed vector database designed for efficient similarity search of embedding vectors in AI applications. It supports hybrid search with vector search and scalar filtering, offers fast vector retrieval from millions of objects in milliseconds, and ensures scalability and reliability through replication and elastic scaling out. Users can deploy Vearch cluster on Kubernetes, add charts from the repository or locally, start with Docker-compose, or compile from source code. The tool includes components like Master for schema management, Router for RESTful API, and PartitionServer for hosting document partitions with raft-based replication. Vearch can be used for building visual search systems for indexing images and offers a Python SDK for easy installation and usage. The tool is suitable for AI developers and researchers looking for efficient vector search capabilities in their applications.
pyspur
PySpur is a graph-based editor designed for LLM (Large Language Models) workflows. It offers modular building blocks, node-level debugging, and performance evaluation. The tool is easy to hack, supports JSON configs for workflow graphs, and is lightweight with minimal dependencies. Users can quickly set up PySpur by cloning the repository, creating a .env file, starting docker services, and accessing the portal. PySpur can also work with local models served using Ollama, with steps provided for configuration. The roadmap includes features like canvas, async/batch execution, support for Ollama, new nodes, pipeline optimization, templates, code compilation, multimodal support, and more.

chunkhound
ChunkHound is a modern tool for transforming your codebase into a searchable knowledge base for AI assistants. It utilizes semantic search via the cAST algorithm and regex search, integrating with AI assistants through the Model Context Protocol (MCP). With features like cAST Algorithm, Multi-Hop Semantic Search, Regex search, and support for 22 languages, ChunkHound offers a local-first approach to code analysis and discovery. It provides intelligent code discovery, universal language support, and real-time indexing capabilities, making it a powerful tool for developers looking to enhance their coding experience.
VibeSurf
VibeSurf is an open-source AI agentic browser that combines workflow automation with intelligent AI agents, offering faster, cheaper, and smarter browser automation. It allows users to create revolutionary browser workflows, run multiple AI agents in parallel, perform intelligent AI automation tasks, maintain privacy with local LLM support, and seamlessly integrate as a Chrome extension. Users can save on token costs, achieve efficiency gains, and enjoy deterministic workflows for consistent and accurate results. VibeSurf also provides a Docker image for easy deployment and offers pre-built workflow templates for common tasks.
For similar tasks

SMRY
SMRY.ai is a Next.js application that bypasses paywalls and generates AI-powered summaries by fetching content from multiple sources simultaneously. It provides a distraction-free reader with summary builder, cleans articles, offers multi-source fetching, built-in AI summaries in 14 languages, rich debug context, soft paywall access, smart extraction using Diffbot's AI, multi-source parallel fetching, type-safe error handling, dual caching strategy, intelligent source routing, content parsing pipeline, multilingual summaries, and more. The tool aims to make referencing reporting easier, provide original articles alongside summaries, and offer concise summaries in various languages.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.
zep
Zep is a long-term memory service for AI Assistant apps. With Zep, you can provide AI assistants with the ability to recall past conversations, no matter how distant, while also reducing hallucinations, latency, and cost. Zep persists and recalls chat histories, and automatically generates summaries and other artifacts from these chat histories. It also embeds messages and summaries, enabling you to search Zep for relevant context from past conversations. Zep does all of this asyncronously, ensuring these operations don't impact your user's chat experience. Data is persisted to database, allowing you to scale out when growth demands. Zep also provides a simple, easy to use abstraction for document vector search called Document Collections. This is designed to complement Zep's core memory features, but is not designed to be a general purpose vector database. Zep allows you to be more intentional about constructing your prompt: 1. automatically adding a few recent messages, with the number customized for your app; 2. a summary of recent conversations prior to the messages above; 3. and/or contextually relevant summaries or messages surfaced from the entire chat session. 4. and/or relevant Business data from Zep Document Collections.

ontogpt
OntoGPT is a Python package for extracting structured information from text using large language models, instruction prompts, and ontology-based grounding. It provides a command line interface and a minimal web app for easy usage. The tool has been evaluated on test data and is used in related projects like TALISMAN for gene set analysis. OntoGPT enables users to extract information from text by specifying relevant terms and provides the extracted objects as output.
mslearn-ai-language
This repository contains lab files for Azure AI Language modules. It provides hands-on exercises and resources for learning about various AI language technologies on the Azure platform. The labs cover topics such as natural language processing, text analytics, language understanding, and more. By following the exercises in this repository, users can gain practical experience in implementing AI language solutions using Azure services.
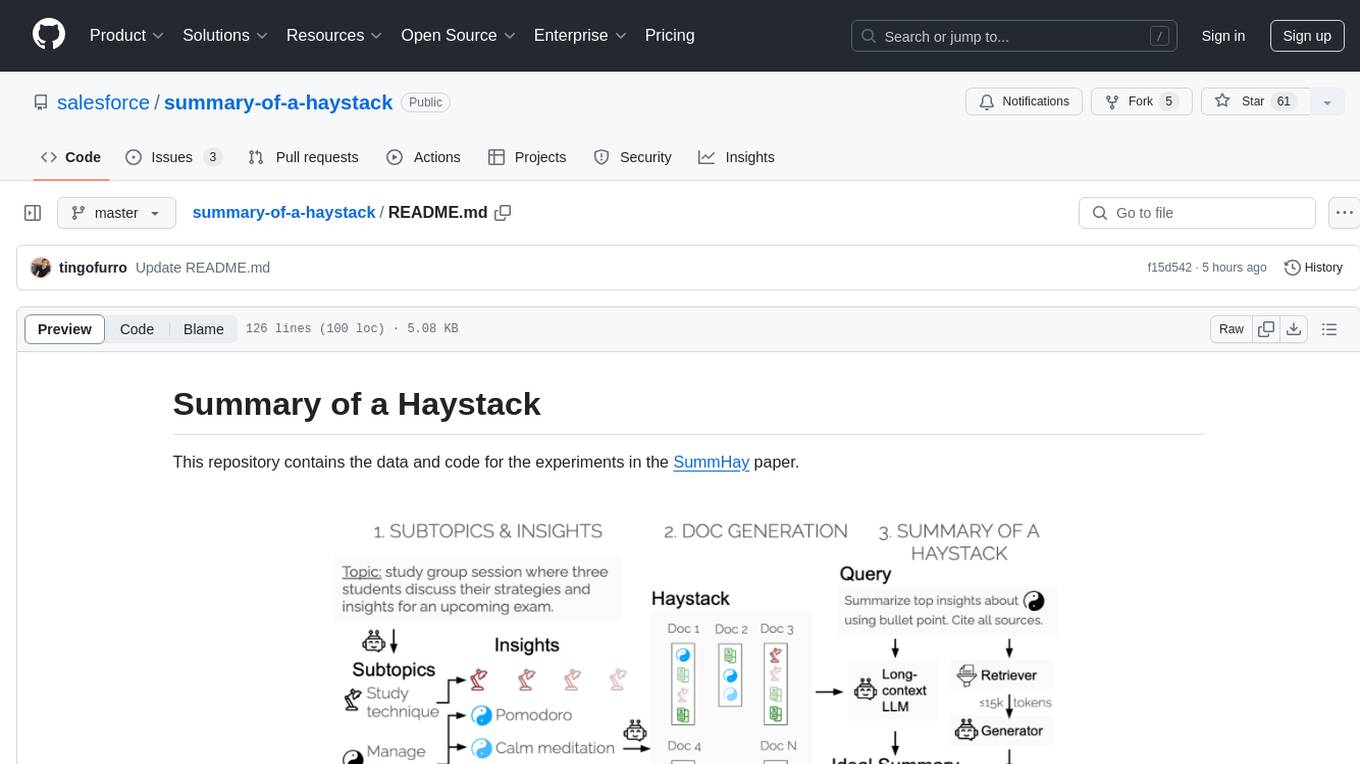
summary-of-a-haystack
This repository contains data and code for the experiments in the SummHay paper. It includes publicly released Haystacks in conversational and news domains, along with scripts for running the pipeline, visualizing results, and benchmarking automatic evaluation. The data structure includes topics, subtopics, insights, queries, retrievers, summaries, evaluation summaries, and documents. The pipeline involves scripts for retriever scores, summaries, and evaluation scores using GPT-4o. Visualization scripts are provided for compiling and visualizing results. The repository also includes annotated samples for benchmarking and citation information for the SummHay paper.
llm-book
The 'llm-book' repository is dedicated to the introduction of large-scale language models, focusing on natural language processing tasks. The code is designed to run on Google Colaboratory and utilizes datasets and models available on the Hugging Face Hub. Note that as of July 28, 2023, there are issues with the MARC-ja dataset links, but an alternative notebook using the WRIME Japanese sentiment analysis dataset has been added. The repository covers various chapters on topics such as Transformers, fine-tuning language models, entity recognition, summarization, document embedding, question answering, and more.
Controllable-RAG-Agent
This repository contains a sophisticated deterministic graph-based solution for answering complex questions using a controllable autonomous agent. The solution is designed to ensure that answers are solely based on the provided data, avoiding hallucinations. It involves various steps such as PDF loading, text preprocessing, summarization, database creation, encoding, and utilizing large language models. The algorithm follows a detailed workflow involving planning, retrieval, answering, replanning, content distillation, and performance evaluation. Heuristics and techniques implemented focus on content encoding, anonymizing questions, task breakdown, content distillation, chain of thought answering, verification, and model performance evaluation.
For similar jobs
book
Podwise is an AI knowledge management app designed specifically for podcast listeners. With the Podwise platform, you only need to follow your favorite podcasts, such as "Hardcore Hackers". When a program is released, Podwise will use AI to transcribe, extract, summarize, and analyze the podcast content, helping you to break down the hard-core podcast knowledge. At the same time, it is connected to platforms such as Notion, Obsidian, Logseq, and Readwise, embedded in your knowledge management workflow, and integrated with content from other channels including news, newsletters, and blogs, helping you to improve your second brain 🧠.
extractor
Extractor is an AI-powered data extraction library for Laravel that leverages OpenAI's capabilities to effortlessly extract structured data from various sources, including images, PDFs, and emails. It features a convenient wrapper around OpenAI Chat and Completion endpoints, supports multiple input formats, includes a flexible Field Extractor for arbitrary data extraction, and integrates with Textract for OCR functionality. Extractor utilizes JSON Mode from the latest GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 models, providing accurate and efficient data extraction.
Scrapegraph-ai
ScrapeGraphAI is a Python library that uses Large Language Models (LLMs) and direct graph logic to create web scraping pipelines for websites, documents, and XML files. It allows users to extract specific information from web pages by providing a prompt describing the desired data. ScrapeGraphAI supports various LLMs, including Ollama, OpenAI, Gemini, and Docker, enabling users to choose the most suitable model for their needs. The library provides a user-friendly interface through its `SmartScraper` class, which simplifies the process of building and executing scraping pipelines. ScrapeGraphAI is open-source and available on GitHub, with extensive documentation and examples to guide users. It is particularly useful for researchers and data scientists who need to extract structured data from web pages for analysis and exploration.
databerry
Chaindesk is a no-code platform that allows users to easily set up a semantic search system for personal data without technical knowledge. It supports loading data from various sources such as raw text, web pages, files (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, PDF, Markdown, Plain Text), and upcoming support for web sites, Notion, and Airtable. The platform offers a user-friendly interface for managing datastores, querying data via a secure API endpoint, and auto-generating ChatGPT Plugins for each datastore. Chaindesk utilizes a Vector Database (Qdrant), Openai's text-embedding-ada-002 for embeddings, and has a chunk size of 1024 tokens. The technology stack includes Next.js, Joy UI, LangchainJS, PostgreSQL, Prisma, and Qdrant, inspired by the ChatGPT Retrieval Plugin.

auto-news
Auto-News is an automatic news aggregator tool that utilizes Large Language Models (LLM) to pull information from various sources such as Tweets, RSS feeds, YouTube videos, web articles, Reddit, and journal notes. The tool aims to help users efficiently read and filter content based on personal interests, providing a unified reading experience and organizing information effectively. It features feed aggregation with summarization, transcript generation for videos and articles, noise reduction, task organization, and deep dive topic exploration. The tool supports multiple LLM backends, offers weekly top-k aggregations, and can be deployed on Linux/MacOS using docker-compose or Kubernetes.
SemanticFinder
SemanticFinder is a frontend-only live semantic search tool that calculates embeddings and cosine similarity client-side using transformers.js and SOTA embedding models from Huggingface. It allows users to search through large texts like books with pre-indexed examples, customize search parameters, and offers data privacy by keeping input text in the browser. The tool can be used for basic search tasks, analyzing texts for recurring themes, and has potential integrations with various applications like wikis, chat apps, and personal history search. It also provides options for building browser extensions and future ideas for further enhancements and integrations.
1filellm
1filellm is a command-line data aggregation tool designed for LLM ingestion. It aggregates and preprocesses data from various sources into a single text file, facilitating the creation of information-dense prompts for large language models. The tool supports automatic source type detection, handling of multiple file formats, web crawling functionality, integration with Sci-Hub for research paper downloads, text preprocessing, and token count reporting. Users can input local files, directories, GitHub repositories, pull requests, issues, ArXiv papers, YouTube transcripts, web pages, Sci-Hub papers via DOI or PMID. The tool provides uncompressed and compressed text outputs, with the uncompressed text automatically copied to the clipboard for easy pasting into LLMs.
Agently-Daily-News-Collector
Agently Daily News Collector is an open-source project showcasing a workflow powered by the Agent ly AI application development framework. It allows users to generate news collections on various topics by inputting the field topic. The AI agents automatically perform the necessary tasks to generate a high-quality news collection saved in a markdown file. Users can edit settings in the YAML file, install Python and required packages, input their topic idea, and wait for the news collection to be generated. The process involves tasks like outlining, searching, summarizing, and preparing column data. The project dependencies include Agently AI Development Framework, duckduckgo-search, BeautifulSoup4, and PyYAM.