
moly
Moly: A Desktop + Cloud AI LLM GUI app in pure Rust
Stars: 336
Moly is an AI LLM client written in Rust, showcasing the capabilities of the Makepad UI toolkit and Project Robius, a framework for multi-platform application development in Rust. It is currently in beta, allowing users to build and run Moly on macOS, Linux, and Windows. The tool provides packaging support for different platforms, such as `.app`, `.dmg`, `.deb`, AppImage, pacman, and `.exe` (NSIS). Users can easily set up WasmEdge using `moly-runner` and leverage `cargo` commands to build and run Moly. Additionally, Moly offers pre-built releases for download and supports packaging for distribution on Linux, Windows, and macOS.
README:
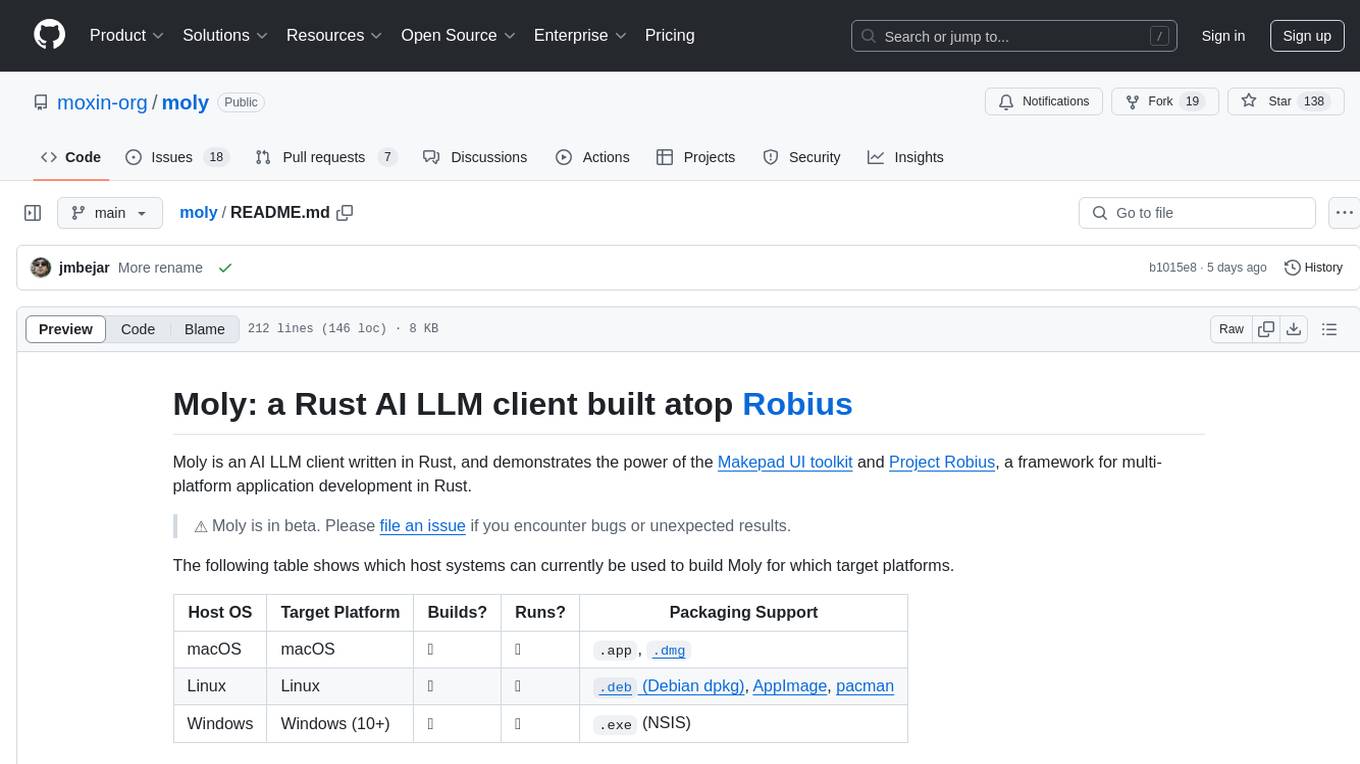
Moly: a Rust AI LLM client built atop Robius
Moly is an AI LLM client written in Rust, that demonstrates the power of the Makepad UI toolkit and Project Robius, a framework for multi-platform application development in Rust.
⚠️ Moly is in early development. Please file an issue if you encounter bugs or unexpected results.
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/bc50f75d-c82a-49c4-8faa-363afff198a1
Want to try Moly without building it from source? You can download the latest stable pre-built releases of Moly.
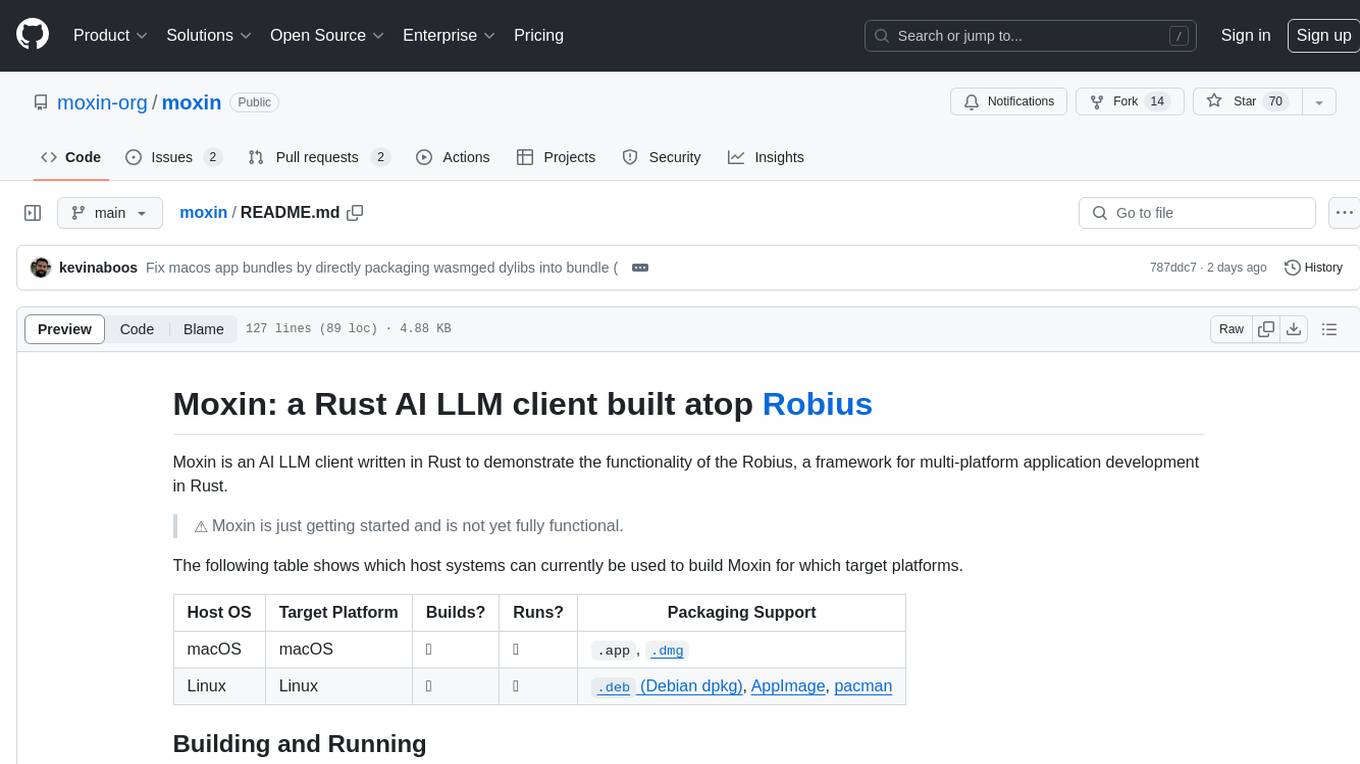
The following table shows which host systems can currently be used to build Moly for which target platforms.
| Host OS | Target Platform | Builds? | Runs? | Packaging Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| macOS | macOS | ✅ | ✅ |
.app, .dmg
|
| Linux | Linux | ✅ | ✅ |
.deb (Debian dpkg), AppImage, pacman
|
| Windows | Windows (10+) | ✅ | ✅ |
.exe (NSIS) |
| Any | Web | ✅ | ✅ | N/A |
| Any | Android | ✅ | ✅ | TODO |
| macOS | iOS | ✅ | ✅ | TODO |
The Moly app supports different types of AI providers:
-
OpenAI-compatible AI providers: configured through the Providers Dashboard.
- Support for other clients will be added to MolyKit. To create your own custom clients, checkout the MolyKit documentation.
- If you want to contribute providers, or extend the list of supported models for a given provider, see instructions here
- Moly Server: a local LLM backend that allows exploring, downloading and running OSS LLMs locally. For usage and installation see instructions here
- MoFa Servers: MoFa is a framework for building AI agents. Using MoFa, AI agents can be constructed via templates, and then exposed via a Dora server that is OpenAI-compatible. MoFa servers can be added to the application through the Providers Dashboard. See instructions here.
Moly Server is a local HTTP server which provides capabilities for searching, downloading, and running local LLMs over an OpenAI-compatible API. While not required in order to use Moly, it can be run alongside the main Moly application for an integrated, local experience.
To get started, simply download and extract the latest version for your platform from the server releases page and run the executable in a command line from inside the directory.
Alternatively, to compile it from source, follow the setup guide and then run:
cd moly-server/
cargo run -p moly-server-
Obtain the source code for this repository:
git clone https://github.com/moxin-org/moly.git- Run
cargo run --release[!IMPORTANT] If your CPU does not support AVX512, then you should append the
--noavxoption onto the above command. To build Moly on Linux, you must install the following dependencies:openssl,clang/libclang,binfmt,Xcursor/X11,asound/pulse. On a Debian-like Linux distro (e.g., Ubuntu), run the following:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install libssl-dev pkg-config llvm clang libclang-dev binfmt-support libxcursor-dev libx11-dev libasound2-dev libpulse-devThen use cargo to build and run Moly:
cd moly
cargo run --release- Install Rust and cargo-makepad.
- Obtain the source code for this repository:
git clone https://github.com/moxin-org/moly.git- Run and serve the Moly app:
cargo makepad wasm --bindgen run -p moly --release[!NOTE] If you want to deploy it, it's recommended to optimize for size building it like this:
cargo makepad wasm --strip --brotli --bindgen build -p moly --profile=small
Note: we already have pre-built releases of Moly available for download.
Install cargo-packager:
rustup update stable ## Rust version 1.79 or higher is required
cargo +stable install --force --locked cargo-packagerFor posterity, these instructions have been tested on cargo-packager version 0.10.1, which requires Rust v1.79.
On a Debian-based Linux distribution (e.g., Ubuntu), you can generate a .deb Debian package, an AppImage, and a pacman installation package.
[!IMPORTANT] You can only generate a
.debDebian package on a Debian-based Linux distribution, asdpkgis needed.
[!NOTE] The
pacmanpackage has not yet been tested.
Ensure you are in the root moly directory, and then you can use cargo packager to generate all three package types at once:
cargo packager --release --verbose ## --verbose is optionalTo install the Moly app from the .debpackage on a Debian-based Linux distribution (e.g., Ubuntu), run:
cd dist/
sudo apt install ./moly_*.deb ## Replace * with version/arch. The leading "./" part is requiredWe recommend using apt install to install the .deb file instead of dpkg -i, because apt will auto-install all of Moly's required dependencies, whereas dpkg will require you to install them manually.
To run the AppImage bundle, simply set the file as executable and then run it:
cd dist/
chmod +x moly_*.AppImage ## Replace * with version/arch
./moly_*.AppImage ## Replace * with version/archThis can only be run on an actual Windows machine, due to platform restrictions.
First, install the necessary build tools if you haven't already (e.g., Visual Studio Build Tools, LLVM as mentioned in some setups).
Ensure you are in the root moly directory, and then you can use cargo packager to generate a setup.exe file using NSIS:
cargo packager --release --formats nsis --verbose ## --verbose is optionalAfter the command completes, you should see a Windows installer called moly_*_x64-setup.exe (replace * with version) in the dist/ directory.
Double-click that file to install Moly on your machine, and then run it as you would a regular application.
This can only be run on an actual macOS machine, due to platform restrictions.
Ensure you are in the root moly directory, and then you can use cargo packager to generate an .app bundle and a .dmg disk image:
cargo packager --release --verbose ## --verbose is optional[!IMPORTANT] You will see a .dmg window pop up — please leave it alone, it will auto-close once the packaging procedure has completed.
[!TIP] If you receive the following error:
ERROR cargo_packager::cli: Error running create-dmg script: File exists (os error 17)then open Finder and unmount any Moly-related disk images, then try the above
cargo packagercommand again.
[!TIP] If you receive an error like so:
Creating disk image... hdiutil: create failed - Operation not permitted could not access /Volumes/Moly/Moly.app - Operation not permittedthen you need to grant "App Management" permissions to the app in which you ran the
cargo packagercommand, e.g., Terminal, Visual Studio Code, etc. To do this, openSystem Preferences→Privacy & Security→App Management, and then click the toggle switch next to the relevant app to enable that permission. Then, try the abovecargo packagercommand again.
After the command completes, you should see both the Moly.app and the .dmg in the dist/ directory.
You can immediately double-click the Moly.app bundle to run it, or you can double-click the .dmg file to install.
Note that the
.dmgis what should be distributed for installation on other machines, not the.app.
If you'd like to modify the .dmg background, here is the Google Drawings file used to generate the MacOS .dmg background image.
MoFa is a software framework for building AI agents. Moly supports connecting to MoFa servers to interact with AI agents in the same way it does with local or remote LLMs.
To run Moly with a local MoFa server, you can follow these steps:
https://github.com/dora-rs/dora?tab=readme-ov-file#installation
Requires python ^3.10
git clone https://github.com/moxin-org/mofa.gitInstall the required Python libraries, and mainly, the mofa library itself
cd python && pip install -r requirements.txt && pip install -e .
pip install dora-rsNavigate to the folder of the Dora node that implements the http server
cd examples/moly_clientRun MoFa with
dora up
dora build dataflow.yml
dora start dataflow.yml
If there's any error when doing dora start, you can restart dora
dora destroy && dora upAt this point the server should be up You can verify it with a request for chat completion:
curl http://localhost:8000/v1/chat/completions \
-v -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "moly-chat",
"messages": [
{ "role": "system", "content": "Use positive language and offer helpful solutions to their problems." },
{ "role": "user", "content": "What is the currency used in Spain?" }
],
"temperature": 0.7,
"stream": true
}'This should return a JSON response with the completion.
Go to the Providers Dashboard and enable the MoFa entry (or add new ones if needed)
One of the easiest ways to contribute to Moly is by extending the list of predefined supported providers and their models.
- Add the provider information to supported_providers.json.
-
name: The name to display in the UI -
url: The full API endpoint for this provider, including versioning, e.g. "https://api.openai.com/v1" -
provider_type: The type of API format that the provider uses, e.g. the"provider_type": "OpenAI"will use theOpenAIClientfrom MolyKit. In Moly, the mapping between supported provider types and MolyKit clients can be found in src/chat/chat_screen.rs (if you were to add a custom MolyKit client and default supported provider, you would need to extend the mapping here). -
supported_models: A list of model ids to be used as the whitelist of allowed/supported models in Moly for this provider.
-
Add a new icon for the provider under /resources/images/providers (in PNG format), using the same name as the provider you registered in the previous step.
-
Update the providers view, importing the new image and referencing the import:
- At the top of the live_design!{} block, add your import, e.g.:
ICON_GEMINI = dep("crate://self/resources/images/providers/gemini.png")- Add the icon to the list of provider_icons:
provider_icons: [
...
(ICON_GEMINI), // Add this line to reference the imported file.
]For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for moly
Similar Open Source Tools

moly
Moly is an AI LLM client written in Rust, showcasing the capabilities of the Makepad UI toolkit and Project Robius, a framework for multi-platform application development in Rust. It is currently in beta, allowing users to build and run Moly on macOS, Linux, and Windows. The tool provides packaging support for different platforms, such as `.app`, `.dmg`, `.deb`, AppImage, pacman, and `.exe` (NSIS). Users can easily set up WasmEdge using `moly-runner` and leverage `cargo` commands to build and run Moly. Additionally, Moly offers pre-built releases for download and supports packaging for distribution on Linux, Windows, and macOS.
WindowsAgentArena
Windows Agent Arena (WAA) is a scalable Windows AI agent platform designed for testing and benchmarking multi-modal, desktop AI agents. It provides researchers and developers with a reproducible and realistic Windows OS environment for AI research, enabling testing of agentic AI workflows across various tasks. WAA supports deploying agents at scale using Azure ML cloud infrastructure, allowing parallel running of multiple agents and delivering quick benchmark results for hundreds of tasks in minutes.
ai-starter-kit
SambaNova AI Starter Kits is a collection of open-source examples and guides designed to facilitate the deployment of AI-driven use cases for developers and enterprises. The kits cover various categories such as Data Ingestion & Preparation, Model Development & Optimization, Intelligent Information Retrieval, and Advanced AI Capabilities. Users can obtain a free API key using SambaNova Cloud or deploy models using SambaStudio. Most examples are written in Python but can be applied to any programming language. The kits provide resources for tasks like text extraction, fine-tuning embeddings, prompt engineering, question-answering, image search, post-call analysis, and more.
ComfyUI
ComfyUI is a powerful and modular visual AI engine and application that allows users to design and execute advanced stable diffusion pipelines using a graph/nodes/flowchart based interface. It provides a user-friendly environment for creating complex Stable Diffusion workflows without the need for coding. ComfyUI supports various models for image editing, video processing, audio manipulation, 3D modeling, and more. It offers features like smart memory management, support for different GPU types, loading and saving workflows as JSON files, and offline functionality. Users can also use API nodes to access paid models from external providers through the online Comfy API.
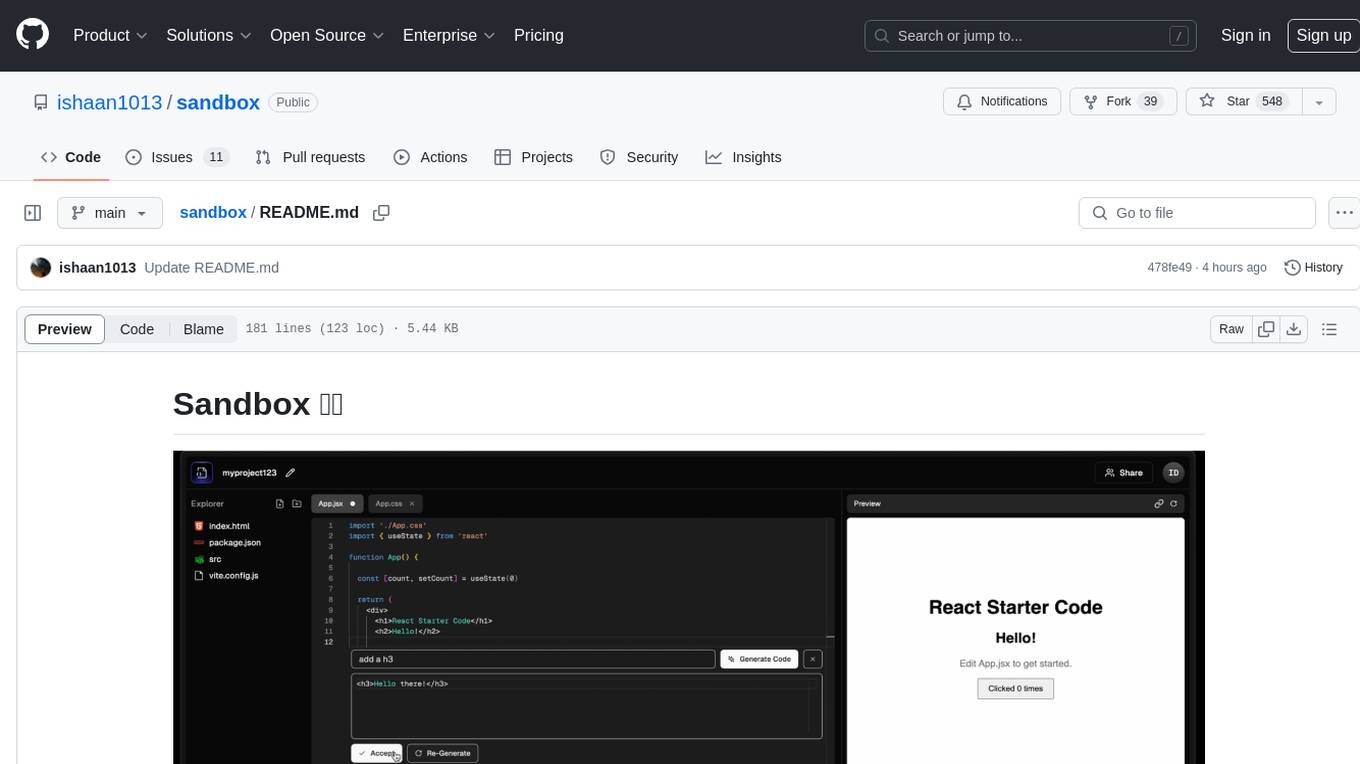
sandbox
Sandbox is an open-source cloud-based code editing environment with custom AI code autocompletion and real-time collaboration. It consists of a frontend built with Next.js, TailwindCSS, Shadcn UI, Clerk, Monaco, and Liveblocks, and a backend with Express, Socket.io, Cloudflare Workers, D1 database, R2 storage, Workers AI, and Drizzle ORM. The backend includes microservices for database, storage, and AI functionalities. Users can run the project locally by setting up environment variables and deploying the containers. Contributions are welcome following the commit convention and structure provided in the repository.
log10
Log10 is a one-line Python integration to manage your LLM data. It helps you log both closed and open-source LLM calls, compare and identify the best models and prompts, store feedback for fine-tuning, collect performance metrics such as latency and usage, and perform analytics and monitor compliance for LLM powered applications. Log10 offers various integration methods, including a python LLM library wrapper, the Log10 LLM abstraction, and callbacks, to facilitate its use in both existing production environments and new projects. Pick the one that works best for you. Log10 also provides a copilot that can help you with suggestions on how to optimize your prompt, and a feedback feature that allows you to add feedback to your completions. Additionally, Log10 provides prompt provenance, session tracking and call stack functionality to help debug prompt chains. With Log10, you can use your data and feedback from users to fine-tune custom models with RLHF, and build and deploy more reliable, accurate and efficient self-hosted models. Log10 also supports collaboration, allowing you to create flexible groups to share and collaborate over all of the above features.
vim-ollama
The 'vim-ollama' plugin for Vim adds Copilot-like code completion support using Ollama as a backend, enabling intelligent AI-based code completion and integrated chat support for code reviews. It does not rely on cloud services, preserving user privacy. The plugin communicates with Ollama via Python scripts for code completion and interactive chat, supporting Vim only. Users can configure LLM models for code completion tasks and interactive conversations, with detailed installation and usage instructions provided in the README.
desktop
ComfyUI Desktop is a packaged desktop application that allows users to easily use ComfyUI with bundled features like ComfyUI source code, ComfyUI-Manager, and uv. It automatically installs necessary Python dependencies and updates with stable releases. The app comes with Electron, Chromium binaries, and node modules. Users can store ComfyUI files in a specified location and manage model paths. The tool requires Python 3.12+ and Visual Studio with Desktop C++ workload for Windows. It uses nvm to manage node versions and yarn as the package manager. Users can install ComfyUI and dependencies using comfy-cli, download uv, and build/launch the code. Troubleshooting steps include rebuilding modules and installing missing libraries. The tool supports debugging in VSCode and provides utility scripts for cleanup. Crash reports can be sent to help debug issues, but no personal data is included.
llm-foundry
LLM Foundry is a codebase for training, finetuning, evaluating, and deploying LLMs for inference with Composer and the MosaicML platform. It is designed to be easy-to-use, efficient _and_ flexible, enabling rapid experimentation with the latest techniques. You'll find in this repo: * `llmfoundry/` - source code for models, datasets, callbacks, utilities, etc. * `scripts/` - scripts to run LLM workloads * `data_prep/` - convert text data from original sources to StreamingDataset format * `train/` - train or finetune HuggingFace and MPT models from 125M - 70B parameters * `train/benchmarking` - profile training throughput and MFU * `inference/` - convert models to HuggingFace or ONNX format, and generate responses * `inference/benchmarking` - profile inference latency and throughput * `eval/` - evaluate LLMs on academic (or custom) in-context-learning tasks * `mcli/` - launch any of these workloads using MCLI and the MosaicML platform * `TUTORIAL.md` - a deeper dive into the repo, example workflows, and FAQs
LLM-Engineers-Handbook
The LLM Engineer's Handbook is an official repository containing a comprehensive guide on creating an end-to-end LLM-based system using best practices. It covers data collection & generation, LLM training pipeline, a simple RAG system, production-ready AWS deployment, comprehensive monitoring, and testing and evaluation framework. The repository includes detailed instructions on setting up local and cloud dependencies, project structure, installation steps, infrastructure setup, pipelines for data processing, training, and inference, as well as QA, tests, and running the project end-to-end.
iffy
Iffy is a tool for intelligent content moderation at scale, allowing users to keep unwanted content off their platform without the need to manage a team of moderators. It provides features such as a Moderation Dashboard to view and manage all moderation activity, User Lifecycle to automatically suspend users with flagged content, Appeals Management for efficient handling of user appeals, and Powerful Rules & Presets to create custom moderation rules. Users can choose between the managed Iffy Cloud or the free self-hosted Iffy Community version, each offering different features and setup requirements.
garak
Garak is a free tool that checks if a Large Language Model (LLM) can be made to fail in a way that is undesirable. It probes for hallucination, data leakage, prompt injection, misinformation, toxicity generation, jailbreaks, and many other weaknesses. Garak's a free tool. We love developing it and are always interested in adding functionality to support applications.
btp-genai-starter-kit
This repository provides a quick way for users of the SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) to learn how to use generative AI with BTP services. It guides users through setting up the necessary infrastructure, deploying AI models, and running genAI experiments on SAP BTP. The repository includes scripts, examples, and instructions to help users get started with generative AI on the SAP BTP platform.
opencharacter
OpenCharacter is an open-source tool that allows users to create and run characters locally with local models or use the hosted version. The stack includes Next.js for frontend, TailwindCSS for styling, Drizzle ORM for database access, NextAuth for authentication, Cloudflare D1 for serverless databases, Cloudflare Pages for hosting, and ShadcnUI as the component library. Users can integrate OpenCharacter with OpenRouter by configuring the OpenRouter API key. The tool is fully scalable, composable, and cost-effective, with powerful tools like Wrangler for database management and migrations. No environment variables are needed, making it easy to use and deploy.
HuggingFaceGuidedTourForMac
HuggingFaceGuidedTourForMac is a guided tour on how to install optimized pytorch and optionally Apple's new MLX, JAX, and TensorFlow on Apple Silicon Macs. The repository provides steps to install homebrew, pytorch with MPS support, MLX, JAX, TensorFlow, and Jupyter lab. It also includes instructions on running large language models using HuggingFace transformers. The repository aims to help users set up their Macs for deep learning experiments with optimized performance.
moxin
Moxin is an AI LLM client written in Rust to demonstrate the functionality of the Robius framework for multi-platform application development. It is currently in early stages of development and not fully functional. The tool supports building and running on macOS and Linux systems, with packaging options available for distribution. Users can install the required WasmEdge WASM runtime and dependencies to build and run Moxin. Packaging for distribution includes generating `.deb` Debian packages, AppImage, and pacman installation packages for Linux, as well as `.app` bundles and `.dmg` disk images for macOS. The macOS app is not signed, leading to a warning on installation, which can be resolved by removing the quarantine attribute from the installed app.
For similar tasks
python-tutorial-notebooks
This repository contains Jupyter-based tutorials for NLP, ML, AI in Python for classes in Computational Linguistics, Natural Language Processing (NLP), Machine Learning (ML), and Artificial Intelligence (AI) at Indiana University.
open-parse
Open Parse is a Python library for visually discerning document layouts and chunking them effectively. It is designed to fill the gap in open-source libraries for handling complex documents. Unlike text splitting, which converts a file to raw text and slices it up, Open Parse visually analyzes documents for superior LLM input. It also supports basic markdown for parsing headings, bold, and italics, and has high-precision table support, extracting tables into clean Markdown formats with accuracy that surpasses traditional tools. Open Parse is extensible, allowing users to easily implement their own post-processing steps. It is also intuitive, with great editor support and completion everywhere, making it easy to use and learn.
MoonshotAI-Cookbook
The MoonshotAI-Cookbook provides example code and guides for accomplishing common tasks with the MoonshotAI API. To run these examples, you'll need an MoonshotAI account and associated API key. Most code examples are written in Python, though the concepts can be applied in any language.
AHU-AI-Repository
This repository is dedicated to the learning and exchange of resources for the School of Artificial Intelligence at Anhui University. Notes will be published on this website first: https://www.aoaoaoao.cn and will be synchronized to the repository regularly. You can also contact me at [email protected].
modern_ai_for_beginners
This repository provides a comprehensive guide to modern AI for beginners, covering both theoretical foundations and practical implementation. It emphasizes the importance of understanding both the mathematical principles and the code implementation of AI models. The repository includes resources on PyTorch, deep learning fundamentals, mathematical foundations, transformer-based LLMs, diffusion models, software engineering, and full-stack development. It also features tutorials on natural language processing with transformers, reinforcement learning, and practical deep learning for coders.
Building-AI-Applications-with-ChatGPT-APIs
This repository is for the book 'Building AI Applications with ChatGPT APIs' published by Packt. It provides code examples and instructions for mastering ChatGPT, Whisper, and DALL-E APIs through building innovative AI projects. Readers will learn to develop AI applications using ChatGPT APIs, integrate them with frameworks like Flask and Django, create AI-generated art with DALL-E APIs, and optimize ChatGPT models through fine-tuning.
examples
This repository contains a collection of sample applications and Jupyter Notebooks for hands-on experience with Pinecone vector databases and common AI patterns, tools, and algorithms. It includes production-ready examples for review and support, as well as learning-optimized examples for exploring AI techniques and building applications. Users can contribute, provide feedback, and collaborate to improve the resource.
lingoose
LinGoose is a modular Go framework designed for building AI/LLM applications. It offers the flexibility to import only the necessary modules, abstracts features for customization, and provides a comprehensive solution for developing AI/LLM applications from scratch. The framework simplifies the process of creating intelligent applications by allowing users to choose preferred implementations or create their own. LinGoose empowers developers to leverage its capabilities to streamline the development of cutting-edge AI and LLM projects.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.