Awesome-LLM-RAG-Application
the resources about the application based on LLM with RAG pattern
Stars: 1545
Awesome-LLM-RAG-Application is a repository that provides resources and information about applications based on Large Language Models (LLM) with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pattern. It includes a survey paper, GitHub repo, and guides on advanced RAG techniques. The repository covers various aspects of RAG, including academic papers, evaluation benchmarks, downstream tasks, tools, and technologies. It also explores different frameworks, preprocessing tools, routing mechanisms, evaluation frameworks, embeddings, security guardrails, prompting tools, SQL enhancements, LLM deployment, observability tools, and more. The repository aims to offer comprehensive knowledge on RAG for readers interested in exploring and implementing LLM-based systems and products.
README:
Awesome LLM RAG Application is a curated list of application resources based on LLM with RAG pattern. (latest update: 2025-08-27)
论文顺序由近及远
-
2025.08.19 基于大模型的Deep Search智能体综述
-
2025.08.18 Deep Research: 自治型研究智能体综述
-
2025.08.13 Open Deep Research的优化和演进
-
2025.07.03 从网页搜索到智能体特性的深度研究功能:通过推理智能体优化搜索
-
2025.06.22 Deep Research Agents 总结
-
《Deep Research Agents: A Systematic Examination And Roadmap》
详情
-
2025.06.14 Deep Research 总结
https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.18096
-
2025.02.04 Agentic RAG 总结
-
《Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation: A Survey on Agentic RAG》
详情
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.09136
- 核心原理与机制:阐释Agentic RAG的基础概念及核心Agentic机制,包括反思(reflection)、规划(planning)、工具调用(tool use) 与多智能体协作(multi-agent collaboration)。
- 系统分类框架:构建Agentic RAG的详细分类体系,涵盖单智能体(single-agent)、多智能体(multi-agent)、层次化(hierarchical)、纠错型(corrective)、自适应(adaptive) 及图结构驱动(graph-based RAG) 等不同架构。
- 横向对比分析:系统比较传统RAG、Agentic RAG与智能体文档工作流(ADW) 的优劣势及适用场景。
- 落地应用案例:探索Agentic RAG在医疗诊断、个性化教育、金融风控、法律合规等行业的实际应用。
- 挑战与发展趋势:探讨该领域面临的系统可扩展性、AI伦理规范、多模态融合、人机协同模式等关键问题及未来方向。
-
-
2024.12.23 RAG中的查询优化技术总结
-
2024.10.23 RAG技术演进的回顾总结
-
2024.09.23 综述RAG数据利用方案
-
2024.08.15 综述GraphRAG方案
-
《Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation: A Survey》
详情
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.08921
- 系统性地回顾了Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation (GraphRAG) 的现状和发展方向。
-
-
2024.07.18 综述RAG用于NLP自然语言处理
-
2024.05.13 综述RAG的评估
-
2024.05.10 综述RAG与LLM的结合范式
-
2024.04.30 综述检索增强语言模型(RALMs)
-
《RAG and RAU: A Survey on Retrieval-Augmented Language Model in Natural Language Processing》
详情
全面综述检索增强语言模型(RALMs),包括检索增强生成(RAG)和检索增强理解(RAU),并探讨其在自然语言处理(NLP)中的应用和发展,不仅关注RAG,还涵盖了RAU,详细描述了检索器和语言模型的不同交互模式,并提供了RALMs的工作时间表和应用总结。
-
-
2024.04.17 综述面向检索的核心技术
-
《A Survey on Retrieval-Augmented Text Generation for Large Language Models》
详情
地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.10981 主要回顾当前RAG在各个阶段的核心技术。例如,对于检索,分成了基本检索策略:线性工作流程,适用于简单任务;迭代检索策略:多次检索,逐步优化结果;递归检索策略:处理层次化或分层信息,适用于复杂查询;条件检索策略:根据特定条件或规则进行检索;以及自适应检索策略:动态调整检索策略以优化结果。
-
-
2024.02.29 面向AIGC生成做全面综述
-
2023.11.18 首个全面RAG综述
-
2023.03.20 多模态RAG综述
详情
https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.10868 探讨了通过检索多模态知识来增强生成模型的方法,特别是如何利用图像、代码、结构化知识、音频和视频等多模态信息来提升大型语言模型(LLMs)的生成能力。
-
2022.02.02近三年首个综述
- 大语言模型的检索增强生成 (RAG) 方法
- Advaned RAG Techniques: an Illustrated Overview
- 高级RAG应用构建指南和总结
- Patterns for Building LLM-based Systems & Products
- RAG大全
-
Open RAG Base
- Open RAG Base 是一个基于公开资料收集整理汇总的RAG知识库。它基于Notion构建,是目前最全面RAG的资料汇总仓库。目的是为读者提提供前沿和全面的RAG知识,提供多维度的分析汇总,涵盖RAG的方方面,包括:学术论文、前沿阅读资料、RAG评估与基准、下游任务与数据集、工具与技术栈
- 一个繁体的RAG资料集
- 关于RAG技术的综合合集RAG_Techniques
- DeepSearch 与 DeepResearch 的设计和实现
- Microsoft-Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) in Azure AI Search
- azure openai design patterns- RAG
- IBM-What is retrieval-augmented generation-IBM
- Amazon-Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
- Nvidia-What Is Retrieval-Augmented Generation?
- Meta-Retrieval Augmented Generation: Streamlining the creation of intelligent natural language processing models
- Cohere-Introducing Chat with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
- Pinecone-Retrieval Augmented Generation
- Milvus-Build AI Apps with Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
- Knowledge Retrieval Takes Center Stage
- Disadvantages of RAG
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) or Fine-tuning — Which Is the Best Tool to Boost Your LLM Application?
- 提示工程、RAGs 与微调的对比
- RAG vs Finetuning — Which Is the Best Tool to Boost Your LLM Application?
- A Survey on In-context Learning
-
- RAGFlow:基于OCR和文档解析的下一代 RAG 引擎。在文档解析上做了增强,2024年4月1日开源,在数据处理上支持文档结构、图片、表格的深度解析,支持可控分片,可对查询进行深入分析识别关键信息,在检索上提供多路找回/重排能力,界面提供友好的引用参考查看功能。
-
- 融合了 Backend as Service 和 LLMOps 的理念,涵盖了构建生成式 AI 原生应用所需的核心技术栈,包括一个内置 RAG 引擎。使用 Dify,你可以基于任何模型自部署类似 Assistants API 和 GPTs 的能力。
-
- 您的第二大脑,利用 GenerativeAI 的力量成为您的私人助理!但增强了人工智能功能。
- Quivr
-
详情
- GraphRAG 是一种基于图的检索增强方法,由微软开发并开源。 它通过结合LLM和图机器学习的技术,从非结构化的文本中提取结构化的数据,构建知识图谱,以支持问答、摘要等多种应用场景。
- 微软GraphRAG框架演进之路及带来的一些思考
-
详情
- 微软Graph的简化版本,将社区、社区宅摘要这些环节做了去除,这种去除是好的,不会太重,对于知识更新也更快;
-
详情
一个开源的、基于 RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) 的文档问答工具,支持多用户登录、本地和云端 LLM 及 Embedding 模型、图表多模态文档解析和问答、混合检索带文档预览的高级引用功能、持复杂推理方法,如问题分解、基于 agent 的推理(如 ReAct、ReWOO)等。
-
- 致力于支持任意格式文件或数据库的本地知识库问答系统,可断网安装使用。任何格式的本地文件都可以往里扔,即可获得准确、快速、靠谱的问答体验。目前已支持格式: PDF,Word(doc/docx),PPT,Markdown,Eml,TXT,图片(jpg,png等),网页链接
-
- 这是向量数据库weaviate开源的一款RAG应用,旨在为开箱即用的检索增强生成 (RAG) 提供端到端、简化且用户友好的界面。只需几个简单的步骤,即可在本地或通过 OpenAI、Cohere 和 HuggingFace 等 LLM 提供商轻松探索数据集并提取见解。
-
- 允许您针对内部文档提出自然语言问题,并获得由源材料中的引用和参考文献支持的可靠答案,以便您始终可以信任您得到的结果。您可以连接到许多常用工具,例如 Slack、GitHub、Confluence 等。
-
- Cognita 在底层使用了Langchain/Llamaindex,并对代码进行了结构化组织,其中每个 RAG 组件都是模块化的、API 驱动的、易于扩展的。Cognita 可在本地设置中轻松使用,同时还能为您提供无代码用户界面支持的生产就绪环境。Cognita 默认还支持增量索引。
-
详情
一款低代码构建多Agent大模型应用的开发工具,协助开发者用极低的成本构建复杂的AI应用,并可以持续的迭代优化效果。使用LazyLLM搭建RAG应用非常便捷和灵活,可以任意字定义多路检索和召回策略。除此之外,LazyLLM的AI应用构建流程是原型搭建 -> 数据回流 -> 迭代优化,用户可以先基于LazyLLM快速搭建RAG应用的,再结合场景任务数据进行bad-case分析,然后对应用中的关键环节进行算法迭代和模型微调,进而逐步提升整个RAG应用的效果。
-
- GPT-RAG提供了一个强大的架构,专为RAG模式的企业级部署量身定制。它确保了扎实的回应,并建立在零信任安全和负责任的人工智能基础上,确保可用性、可扩展性和可审计性。非常适合正在从探索和PoC阶段过渡到全面生产和MVP的组织。
-
详情
该库提供了用于摄取和预处理图像和文本文档(如 PDF、HTML、WORD 文档等)的开源组件。 unstructured的使用场景围绕着简化和优化LLM数据处理工作流程, unstructured模块化功能和连接器形成了一个有内聚性的系统,简化了数据摄取和预处理,使其能够适应不同的平台,并有效地将非结构化数据转换为结构化输出。
-
- 对文档进行分块是一项具有挑战性的任务,它支撑着任何 RAG 系统。高质量的结果对于人工智能应用的成功至关重要,但大多数开源库处理复杂文档的能力都受到限制。
- Open Parse 旨在通过提供灵活、易于使用的库来填补这一空白,该库能够直观地识别文档布局并有效地对其进行分块。
-
- 使用 LLMs 从文件和文档中提取数据的库。 extract_thinker 在文件和 LLMs 之间提供 ORM 风格的交互,从而实现灵活且强大的文档提取工作流程。
-
- OmniParser 是一个统一的框架,无缝地结合了三个基本的 OCR 任务:文本识别、关键信息提取和表格识别。
-
- 给定一个 HTML 文档,提取并清理主体文本和标题。
-
- Neural Optical Understanding for Academic Documents.这是学术文档 PDF 解析器,它能理解 LaTeX 数学和表格。但对中文支持不好,需要单独微调。
-
- Pix2Struct 是一种预训练的图像到文本模型,专为纯视觉语言理解而设计。
-
- Indexify 是一个开源引擎,用于使用可重复使用的提取器进行嵌入、转换和特征提取,为非结构化数据(视频、音频、图像和文档)快速构建数据流水线。当;流水线生成嵌入或结构化数据时,Indexify 会自动更新向量数据库、结构化数据库 (Postgres)。
-
- MegaParse 是一个强大且通用的解析器,可以轻松处理各种类型的文档,包括文本、PDF、PowerPoint 演示文稿、Word 文档等。它旨在在解析过程中尽可能减少信息丢失。
- 解析内容包括: ✅ Tables ✅ TOC ✅ Headers ✅ Footers ✅ Images
-
- Ragas是一个用于评估RAG应用的框架,包括忠诚度(Faithfulness)、答案相关度(Answer Relevance)、上下文精确度(Context Precision)、上下文相关度(Context Relevancy)、上下文召回(Context Recall)
-
- 一个简单易用的开源LLM评估框架,适用于LLM应用程序。它与 Pytest 类似,但专门用于单元测试 LLM 应用程序。 DeepEval 使用 LLMs 以及在您的计算机上本地运行的各种其他 NLP 模型,根据幻觉、答案相关性、RAGAS 等指标来评估性能。
-
- TruLens 提供了一套用于开发和监控神经网络的工具,包括大型语言模型。这包括使用 TruLens-Eval 评估基于 LLMs 和 LLM 的应用程序的工具以及使用 TruLens-Explain 进行深度学习可解释性的工具。 TruLens-Eval 和 TruLens-Explain 位于单独的软件包中,可以独立使用。
-
- 用于评估和改进生成式人工智能应用的开源统一平台。提供了20多项预配置检查(涵盖语言、代码、嵌入用例)评分,对失败案例进行根本原因分析,并就如何解决这些问题提出见解。
- 比如prompt注入、越狱检测、整通对话的用户满意度等
-
- 一个用于 RAG 开发和实验跟踪的平台,用于评估检索增强生成 (RAG) 应用程序响应质量的指标。
-
BCEmbedding
- 网易有道开发的双语和跨语种语义表征算法模型库,其中包含 EmbeddingModel和 RerankerModel两类基础模型。EmbeddingModel专门用于生成语义向量,在语义搜索和问答中起着关键作用,而 RerankerModel擅长优化语义搜索结果和语义相关顺序精排。
-
BGE-Embedding
- 北京智源人工智能研究院开源的embeeding通用向量模型,使用retromae 对模型进行预训练,再用对比学习在大规模成对数据上训练模型。
-
bge-reranker-large
- 北京智源人工智能研究院开源,交叉编码器将对查询和答案实时计算相关性分数,这比向量模型(即双编码器)更准确,但比向量模型更耗时。 因此,它可以用来对嵌入模型返回的前k个文档重新排序
-
gte-base-zh
- GTE text embedding GTE中文通用文本表示模型 通义实验室提供
-
详情
- Crawl4AI是一个开源的、用于为AI而生的智能、快速且灵活的网络爬虫工具。它针对大语言模型(LLM)、AI Agent和数据流水线提供了优秀的爬取性能,通过高速、精确和易部署的特点来赋能开发者。
- 为LLM量身打造的Markdown生成功能。
- 提供6倍于常规爬虫的超快速爬取能力。
- 支持会话管理、代理和自定义钩子,实现灵活的浏览器控制。
- 采用高级算法进行高效抽取,减少对昂贵模型的依赖。
- 完全开源无API密钥,支持Docker和云端集成。
-
详情
Firecrawl 是一个强大的 API 服务,可以从任何网站抓取数据并转换为干净的 Markdown 或结构化数据。它具有高级的抓取、爬取和数据提取功能,可以帮助您的 AI 应用程序获取干净的数据。
主要功能点
- 抓取: 抓取网页内容并以 LLM 就绪格式(Markdown、结构化数据、截图、HTML)返回
- 爬取: 抓取网页上的所有 URL 并以 LLM 就绪格式返回内容
- 映射: 输入一个网站,获取该网站的所有 URL - 速度极快 强大的功能: 支持 LLM 就绪格式、代理、反机器人机制、动态内容(JS 渲染)、输出解析、编排等
- 可定制性: 排除标签、在身份验证墙后爬取、最大爬取深度等
-
- 它将任何 URL 转换为LLM 友好的输入,
-
- JoySafety 是一个开源的大模型安全框架。该框架在京东内部广泛应用,覆盖AI导购、物流客服、销售助手、医疗问诊、商家工作台、法务咨询、安全问答等场景,支持日均亿级调用、95%+攻击拦截率,致力于为企业提供一套成熟、可靠、免费的大模型安全防护方案。
-
详情
NeMo Guardrails 是一个开源工具包,用于为基于 LLM 的对话应用程序轻松添加可编程的保护轨。Guardrails(简称 "轨")是控制大型语言模型输出的特定方式,例如不谈论政治、以特定方式响应特定用户请求、遵循预定义对话路径、使用特定语言风格、提取结构化数据等。
-
详情
- Guardrails 是一个 Python 框架,通过执行两个关键功能来帮助构建可靠的人工智能应用程序:
- Guardrails 在应用程序中运行输入/输出防护装置,以检测、量化和减轻特定类型风险的存在。要查看全套风险,请访问 Guardrails Hub。
- Guardrails 可帮助您从 LLMs 生成结构化数据。对输入和输出进行检测
-
详情
- LLM Guard 是一款旨在增强大型语言模型 (LLMs) 安全性的综合工具。
- 输入(Anonymize 匿名化、BanCode 禁止代码、BanCompetitors 禁止竞争对手、BanSubstrings 禁止子串、BanTopics 禁止话题、PromptInjection 提示词注射 、Toxicity 毒性等)
- 输出(代码、anCompetitors 禁止竞争对手、Deanonymize 去匿名化、JSON、LanguageSame 语言相同、MaliciousURLs 恶意URL、NoRefusal 不可拒绝、FactualConsistency 事实一致性、URLReachability URL可达性等)
- 各个检测功能是利用了huggingface上的各种开源模型
-
-
RefChecker
- RefChecker 提供了一个标准化的评估框架来识别大型语言模型输出中存在的微妙幻觉。
-
vigil-llm
- Vigil是一个Python库和REST API,可以根据一组扫描器评估大型语言模型提示和响应,以检测提示注入、越狱和其他潜在威胁。该存储库还提供了必要的检测特征(签名)和数据集,支持用户自行部署和使用。 该应用程序目前处于 alpha 状态,应被视为实验/用于研究目的。
-
- DSPy 是一款功能强大的框架。它可以用来自动优化大型语言模型(LLM)的提示词和响应。还能让我们的 LLM 应用即使在 OpenAI/Gemini/Claude版本升级也能正常使用。无论你有多少数据,它都能帮助你优化模型,获得更高的准确度和性能。通过选择合适的优化器,并根据具体需求进行调优,你可以在各种任务中获得出色的结果。
-
- GenAI 应用程序的自动提示工程助手 YiVal 是一款最先进的工具,旨在简化 GenAI 应用程序提示和循环中任何配置的调整过程。有了 YiVal,手动调整已成为过去。这种以数据驱动和以评估为中心的方法可确保最佳提示、精确的 RAG 配置和微调的模型参数。使用 YiVal 使您的应用程序能够轻松实现增强的结果、减少延迟并最大限度地降低推理成本!
-
- Vanna 是一个MIT许可的开源Python RAG(检索增强生成)框架,用于SQL生成和相关功能。
- Vanna 的工作过程分为两个简单步骤 - 在您的数据上训练 RAG“模型”,然后提出问题,这些问题将返回 SQL 查询。训练的数据主要是一些 DDL schema、业务说明文档以及示例sql等,所谓训练主要是将这些数据embedding化,用于向量检索。
-
- 由前阿里巴巴成员创建并开源,一个智能和多功能的通用SQL客户端和报表工具,集成了ChatGPT功能,,14.3k
-
- 一个可以将自然语言转换为SQL查询的工具,4.1k
-
- 使用AI驱动的数据管理平台,帮助用户将自然语言查询转换为SQL。,3.2k
-
- 一个高效的自然语言到SQL转换工具,支持多种数据库。,1.4k
-
- 由腾讯音乐开源,高性能的SQL生成工具,支持复杂查询的自动生成。1.6k
- vllm
- OpenLLM
-
RAGxplorer
- RAGxplorer 是一种交互式 Streamlit 工具,通过将文档块和的查询问句展示为embedding向量空间中可的视化内容来支持检索增强生成 (RAG) 应用程序的构建。
-
Rule-Based-Retrieval
- rule-based-retrieval是一个 Python 包,使您能够创建和管理具有高级筛选功能的检索增强生成 (RAG) 应用程序。它与用于文本生成的 OpenAI 和用于高效矢量数据库管理的 Pinecone 无缝集成。
-
instructor
- 借助大模型从一段文本中提取为结构化数据的库
-
RAGLAB
- RAGLAB是一个模块化、面向研究的开源框架,用于检索增强型生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation, RAG)算法。它提供了6种现有RAG算法的复制,以及一个全面的评估系统,包括10个基准数据集,使得RAG算法之间的公平比较和新算法、数据集和评估指标的高效开发成为可能。
-
https://github.com/khoj-ai/khoj
-
https://github.com/ItzCrazyKns/Perplexica
- scira: https://github.com/zaidmukaddam/scira
-
详情
网页搜索:使用 Tavily 的 API 搜索网页。 特定 URL 搜索:从特定 URL 获取信息。 天气:使用 OpenWeather 的 API 获取任何位置的当前天气。 编程:使用 E2B 的 API 运行多种语言的代码片段。 地图:使用 Google Maps API、Mapbox API 和 TripAdvisor API 获取任何地点的位置。 YouTube 搜索:搜索 YouTube 视频并获取时间戳和字幕。 学术搜索:搜索学术论文。 X 帖子搜索:搜索 X.com 上的帖子。 航班跟踪:使用 AviationStack 的 API 跟踪航班。 热门电影和电视节目:获取热门电影和电视节目的信息。 电影或电视节目搜索:获取任何电影或电视节目的信息。
-
https://github.com/nashsu/FreeAskInternet
-
https://github.com/miurla/morphic
-
https://github.com/leptonai/search_with_lepton
- AZure-search-openai-demo:https://github.com/Azure-Samples/azure-search-openai-demo
-
https://github.com/InternLM/MindSearch
-
https://github.com/nilsherzig/LLocalSearch
- llm-answer-engine:https://github.com/developersdigest/llm-answer-engine
-
https://github.com/rashadphz/farfalle
- Gerev:https://github.com/GerevAI/gerev
- Gemini-Search:https://github.com/ammaarreshi/Gemini-Search
- 一个基于 Google 的 Gemini 2.0 Flash 模型和 Google 搜索的 Perplexity 风格的搜索引擎。它提供 AI 驱动的问答功能,可以实时获取网络资源并提供引用。
-
https://github.com/Nutlope/turboseek
-
https://github.com/memfreeme/memfree
-
https://github.com/supermemoryai/opensearch-ai
-
https://github.com/yokingma/search_with_ai
- OpenPerPlex:https://github.com/YassKhazzan/openperplex_backend_os
- search4all:https://github.com/fatwang2/search4all
-
https://github.com/QmiAI/Qmedia?tab=readme-ov-file
-
https://github.com/luyu0279/BrainyAI
-
https://github.com/OcularEngineering/ocular
-
https://github.com/jjleng/sensei
-
https://github.com/shadowfax92/Fyin
-
https://github.com/YassKhazzan/openperplex_front
-
https://github.com/Alibaba-NLP/DeepResearch
-
https://github.com/jina-ai/node-DeepResearch
-
https://github.com/bytedance/deer-flow
-
https://github.com/dzhng/deep-research
-
https://github.com/langchain-ai/open_deep_research
-
https://github.com/langchain-ai/local-deep-researcher
-
https://github.com/firecrawl/firesearch
-
Kimi Chat
- 支持发送网页链接和上传文件进行回答
-
GPTs
- 支持上传文档进行类似RAG应用
-
百川知识库
- 1.新建知识库后得到知识库 ID;
- 2.上传文件,获取文件 ID;
- 3.通过文件 ID 与知识库 ID 进行知识库文件关联,知识库中可以关联多个文档。
- 4.调用对话接口时通过 knowledge_base 字段传入知识库 ID 列表,大模型使用检索到的知识信息回答问题。
-
COZE
- 应用编辑平台,旨在开发下一代人工智能聊天机器人。无论您是否有编程经验,该平台都可以让您快速创建各种类型的聊天机器人并将其部署在不同的社交平台和消息应用程序上。
-
Devv-ai
- 最懂程序员的新一代 AI 搜索引擎,底层采用了RAG的大模型应用模式,LLM模型为其微调的模型。
- Qcon 句子互动 高原 Agentic RAG 的现在与未来
- Qcon 尹一峰-RAG 基本范式的选择与系统设计
- Qcon 夏源-在医疗健康领域,企业大模型RAG优化实践
- Qcon 费跃 阿里云-构建企业级 RAG 系统的创新实践
- AIConf 阿里云客户服务领域Agent在业务提效上的思考与创新实践_姜剑(飞樰)
- 新加坡科研局 黄佳-大模型+数据资产变现,RAG 驱动企业智能化实践案例
- 枫清科技 王传阳 - QCon北京2025-复杂场景下的 RAG 架构演进:跨模态知识联邦与统一语义推理实践
- BISHENG AI Conf 覃睿-DeepResearch如何在企业内落地
- AIConf QAnything:大模型驱动下的知识库问答体系革新与实践
- Qconf 董振兴-明略科技多模态数据驱动的RAG增强实践.pdf
- 纷享销客AIAgent平台落地实践
- 快手 从被动服务到主动任务,Agentic AI 在 B 端商业化的应用探索
- B站大模型×领域RAG:打造高效、智能化的用户服务体验 PPT
- 哈啰出行从Copilot到Agent模式的探索-贾立 PPT
- 51Talk-AI+Agent+-+在业务增长中的落地实践 PPT
- 万科物业科技 PPT
- 京东商家助手 PPT
- 58同城-灵犀大模型PPT
- 阿⾥云AI搜索RAG⼤模型优化实践PPT
- 向量化与文档解析技术加速大模型RAG应用落地PPT
- RAG应用在得物开放平台的智能答疑的探索
- 用户案例|Milvus向量引擎在携程酒店搜索中的应用场景和探索
- OpenAI 如何优化 LLM 的效果
- What We Learned from a Year of Building with LLMs 系列
- 构建企业级AI助手的经验教训
-
RAG最佳实践《Searching for Best Practices in Retrieval-Augmented Generation》
-
- Seven Failure Points When Engineering a Retrieval Augmented Generation System
-
Is ChatGPT Good at Search? Investigating Large Language Models as Re-Ranking Agents
-
Zero-Shot Listwise Document Reranking with a Large Language Model
- 两种重新排序方法:逐点重新排名、列表重新排名。
- 逐点重新排名是给定文档列表,我们将查询+每个文档单独提供给 LLM 并要求它产生相关性分数。
- 列表重新排名是给定文档列表,我们同时向 LLM 提供查询 + 文档列表,并要求它按相关性对文档进行重新排序。
- 建议对 RAG 检索到的文档按列表重新排序,列表重排优于逐点重排。
-
Self-RAG: Learning to Retrieve, Generate, and Critique through Self-Reflection
这里列出了一些重要的研究论文,它们揭示了 RAG 领域的关键洞察和最新进展。
洞见 参考来源 发布日期 提出一种名为纠正检索增强生成(CRAG, Corrective Retrieval Augmented Generation)的方法,旨在提升 RAG 系统生成内容的稳定性和准确性。其核心在于增加一个能够自我修正的组件至检索器中,并优化检索文档的使用,以促进更优质的内容生成。此外,引入了一种检索评估机制,用于评价针对特定查询检索到的文档的整体品质。通过网络搜索和知识的优化利用,能够有效提升文档自我修正和利用的效率。 纠正检索增强生成 2024年1月 RAPTOR 模型通过递归方式嵌入、聚类并总结文本信息,自底向上构建出层次化的总结树。在使用时,该模型能够从这棵树中检索信息,实现对长文档在不同抽象层面上信息的综合利用。 RAPTOR:递归抽象处理用于树组织检索 2024年1月 开发了一个通用框架,通过大语言模型(LLM)与检索器之间的多步骤互动,有效处理多标签分类难题。 在上下文中学习用于极端多标签分类 2024年1月 研究表明,通过提取高资源语言中语义相似的提示,可以显著提升多语言预训练语言模型在多种任务上的零样本学习能力。 从分类到生成:洞察跨语言检索增强的 ICL 2023年11月 针对 RAGs 模型在处理噪声较多、不相关文档以及未知情境时的稳健性进行了改善,通过为检索文档生成序列化阅读笔记,深入评估其与提问的相关性,并整合信息以构建最终答案。 链式笔记:增强检索增强语言模型的鲁棒性 2023年11月 通过去除可能不会对答案生成贡献关键信息的标记,优化了检索增强阅读模型的处理流程,实现了高达 62.2% 的运行时间缩减,同时保持性能仅降低了2%。 通过标记消除优化检索增强阅读器模型 通过对小型语言模型 (LM) 进行指令式微调,我们开发了一个独立的验证器,以验证知识增强语言模型 (knowledge-augmented LMs) 的输出及其知识准确性。这种方法特别有助于解决模型在面对特定查询时未能检索相关知识,或在生成文本中未能准确反映检索到的知识的情况。 知识增强语言模型验证 2023年10月 我们设立了一个基准测试,以分析不同大型语言模型 (LLMs) 在检索增强生成 (RAG) 所需的四项核心能力——噪声容忍、排除不相关信息、信息融合和对反事实情境的适应性——的表现。 大型语言模型在检索增强生成中的基准测试 2023年10月 介绍了一种自我反思的检索增强生成 (Self-RAG) 框架,旨在通过检索和自我反思来提升语言模型的质量和事实性。该框架利用语言模型动态检索信息,并通过反思标记来生成和评估检索到的内容及其自生成内容。 自我反思检索增强生成: 通过自我反思学习检索、生成及自我批判 2023年10月 通过生成增强检索 (GAR) 和检索增强生成 (RAG) 的迭代改善,提高了零样本信息检索的能力。该过程中的改写-检索阶段有效提升了召回率,而重排阶段则显著提高了精度。 零样本信息检索中的GAR与RAG相结合的新范式 2023年10月 通过使用基于 43B GPT 模型的预训练和从 1.2 万亿 Token 中检索信息,我们预训练了一个 48B 的检索模型。进一步通过指令式微调,该模型在多种零样本任务上相比经过指令式微调的 GPT 模型显示出显著的性能提升。 InstructRetro: 检索增强预训练后的指令式微调 2023年10月 通过两步精细调整,我们为大型语言模型增加了检索功能:一步是优化预训练的语言模型以更有效利用检索到的信息,另一步则是改进检索器以返回更符合语言模型偏好的相关结果。这种分阶段的微调方法,在要求知识利用和上下文感知的任务中,显著提升了性能。 检索增强的双重指令微调 (RA-DIT) 2023年10月 介绍了一种提升 RAGs 在面对不相关内容时鲁棒性的方法。该方法通过在训练期间混合使用相关与不相关的上下文,自动产生数据以微调语言模型,从而有效利用检索到的文段。 让基于检索增强的语言模型对无关上下文更加鲁棒 2023年10月 研究表明,采用简单检索增强技术的 4K 上下文窗口的大语言模型在生成过程中,其表现与通过位置插值对长上下文任务进行微调的 16K 上下文窗口的大语言模型相媲美。 当检索遇上长上下文的大语言模型 2023年10月 在上下文融合前将检索文档压缩为文本摘要,既降低了计算成本,也减轻了模型从长文档中识别关键信息的难度。 RECOMP: 用压缩和选择性增强提升检索增强语言模型 2023年10月 提出了一个迭代式的检索与生成协同工作框架,它结合了参数化和非参数化知识,通过检索与生成的互动来寻找正确的推理路径。这一框架特别适合需要多步推理的任务,能够显著提高大语言模型的推理能力。 检索与生成的协同作用加强了大语言模型的推理能力 2023年10月 提出“澄清树”框架,该框架通过少样本提示并借助外部知识,为含糊问题递归构建一个消歧树。然后利用这棵树产生详细的答案。 利用检索增强大语言模型回答含糊问题的“澄清树”方法 2023年10月 介绍了一种使大语言模型能够参考其之前遇到的问题,并在面对新问题时动态调用外部资源的方法。 借助自我知识的大语言模型检索增强策略 2023年10月 提供了一组评估指标,用于从多个维度(如检索系统识别相关及集中上下文段落的能力、大语言模型忠实利用这些段落的能力,以及生成内容本身的质量)评价不同方面,而无需依赖人工注释的真实数据。 RAGAS: 对检索增强生成进行自动化评估的指标体系 2023年9月 提出了一种创新方法——生成后阅读(GenRead),它让大型语言模型先根据提问生成相关文档,再从这些文档中提取答案。 生成而非检索:大型语言模型作为强大的上下文生成器 2023年9月 展示了在 RAG 系统中如何使用特定排名器(比如 DiversityRanker 和 LostInTheMiddleRanker)来挑选信息,从而更好地利用大型语言模型的上下文窗口。 提升 Haystack 中 RAG 系统的能力:DiversityRanker 和 LostInTheMiddleRanker 的引入 2023年8月 描述了如何将大型语言模型与不同的知识库结合,以便于知识的检索和储存。通过编程思维的提示来生成知识库的搜索代码,此外,还能够根据用户的需要,将知识储存在个性化的知识库中。 KnowledGPT: 利用知识库检索和存储功能增强大型语言模型 2023年8月 提出一种模型,通过结合检索增强掩码语言建模和前缀语言建模,引入上下文融合学习,以此提高少样本学习的效果,使模型能够在不增加训练负担的情况下使用更多上下文示例。 RAVEN: 借助检索增强编解码器语言模型实现的上下文学习 2023年8月 RaLLe 是一款开源工具,专门用于开发、评估和提升针对知识密集型任务的 RAG 系统的性能。 RaLLe: 针对检索增强大型语言模型的开发和评估框架 2023年8月 研究发现,当相关信息的位置发生变化时,大型语言模型的性能会明显受影响,这揭示了大型语言模型在处理长篇上下文信息时的局限性。 中途迷失:大型语言模型处理长篇上下文的方式 2023年7月 通过迭代的方式,模型能够将检索和生成过程相互协同。模型的输出不仅展示了完成任务所需的内容,还为检索更多相关知识提供了丰富的上下文,从而在下一轮迭代中帮助产生更优的结果。 通过迭代检索-生成协同增强检索增强的大语言模型 2023年5月 介绍了一种新的视角,即在文本生成过程中,系统能够主动决定何时以及检索什么信息。接着,提出了一种名为FLARE的方法,通过预测下一句话来预见未来的内容,利用此内容作为关键词检索相关文档,并在发现不确定的表达时重新生成句子。 主动检索增强生成 2023年5月 提出了一个能够通用应用于各种大语言模型的检索插件,即使在模型未知或不能共同微调的情况下也能提升模型性能。 适应增强型检索器改善大语言模型的泛化作为通用插件 2023年5月 通过两种创新的预训练方法,提高了对结构化数据的密集检索效果。首先,通过对结构化数据和非结构化数据之间的关联进行预训练来提升模型的结构感知能力;其次,通过实现遮蔽实体预测来更好地捕捉结构语义。 结构感知的语言模型预训练改善结构化数据上的密集检索 2023年5月 该框架能够动态地融合来自不同领域的多样化信息源,以提高大语言模型的事实准确性。通过一个自适应的查询生成器,根据不同知识源定制查询,确保信息的准确性逐步得到修正,避免错误信息的累积和传播。 知识链:通过动态知识适应异质来源来基础大语言模型 2023年5月 此框架通过首先检索知识图谱中的相关子图,并通过调整检索到的子图的词嵌入来确保事实的一致性,然后利用对比学习确保生成的对话与知识图谱高度一致,为生成与上下文相关且基于知识的对话提供了新方法。 用于知识基础对话生成的知识图谱增强大语言模型 2023年5月 通过采用小型语言模型作为可训练重写器,以适应黑盒式大语言模型(LLM)的需求。重写器通过强化学习(RL)根据 LLM 的反馈进行训练,从而构建了一个名为“重写-检索-阅读”的新框架,专注于查询优化。 为检索增强的大语言模型重写查询 2023年5月 利用检索增强生成器迭代创建无限记忆池,并通过记忆选择器挑选出适合下一轮生成的记忆。此方法允许模型利用自身产出的记忆,称为“自我记忆”,以提升内容生成质量。 自我提升:带有自我记忆的检索增强文本生成 2023年5月 通过为大语言模型(LLM)装配知识引导模块,让它们在不改变内部参数的情况下,获取相关知识。这一策略显著提高了模型在需要丰富知识的领域任务(如事实知识增加7.9%,表格知识增加11.9%,医学知识增加3.0%,多模态知识增加8.1%)的表现。 用参数知识引导增强大语言模型 2023年5月 为大语言模型(LLM)引入了一个通用的读写记忆单元,允许它们根据任务需要从文本中提取、存储并回忆知识。 RET-LLM:朝向大语言模型的通用读写记忆 2023年5月 通过使用任务不可知检索器,构建了一个共享静态索引,有效选出候选证据。随后,设计了一个基于提示的重排机制,根据任务的特定相关性重新排序最相关的证据,为读者提供精准信息。 针对非知识密集型任务的提示引导检索增强 2023年5月 提出了UPRISE(通用提示检索以改善零样本评估),通过调整一个轻量级且多功能的检索器,它能自动为给定零样本任务的输入检索出最合适的提示,以此来改善评估效果。 UPRISE:改进零样本评估的通用提示检索 2023年3月 结合了 SLMs 作为过滤器和 LLMs 作为重排器的优势,提出了一个适应性的“过滤-再重排”范式,有效提升了难样本的信息提取与重排效果。 大语言模型不是一个理想的少样本信息提取器,但它在重排难样本方面表现出色! 2023年3月 零样本学习指导一款能够遵循指令的大语言模型,创建一个虚拟文档来抓住重要的联系模式。接着,一个名为Contriever的工具会将这份文档转化成嵌入向量,利用这个向量在大数据集的嵌入空间中找到相似文档的聚集地,通过向量的相似度来检索真实文档。 无需相关标签的精确零样本密集检索 2022年12月 提出了一个名为展示-搜索-预测(DSP)的新框架,通过这个框架可以编写高级程序,这些程序能够先展示流程,然后搜索相关信息,并基于这些信息做出预测。它能够将复杂问题分解成小的、更易于解决的步骤。 通过检索和语言模型组合,为复杂的自然语言处理任务提供解决方案 2022年12月 采用了一种新的多步骤问答策略,通过在思维链条的每一步中穿插检索信息,使用检索到的信息来丰富和改善思维链条。这种方法显著提升了解决知识密集型多步问题的效果。 结合思维链条推理和信息检索解决复杂多步骤问题 2022年12月 研究发现,增加检索环节可以有效减轻对已有训练信息的依赖,使得RAG变成一个有效捕捉信息长尾的策略。 大语言模型在学习长尾知识方面的挑战 2022年11月 通过抽样方式,从大语言模型的记忆中提取相关信息段落,进而生成最终答案。 通过回忆增强语言模型的能力 2022年10月 将大语言模型用作少量示例的查询生成器,根据这些生成的数据构建针对特定任务的检索系统。 Promptagator: 基于少量示例实现密集检索 2022年9月 介绍了Atlas,这是一个经过预训练的检索增强型语言模型,它能够通过极少数的示例学习掌握知识密集任务。 Atlas: 借助检索增强型语言模型进行少样本学习 2022年8月 通过从训练数据中进行智能检索,实现了在多个自然语言生成和理解任务上的性能提升。 重新认识训练数据的价值:通过训练数据检索的简单有效方法 2022年3月 通过在连续的数据存储条目之间建立指针关联,并将这些条目分组成不同的状态,我们近似模拟了数据存储搜索过程。这种方法创造了一个加权有限自动机,在推理时能够在不降低模型预测准确性(困惑度)的情况下,节约高达 83% 的查找最近邻居的计算量。 通过自动机增强检索的神经符号语言建模 2022 年 1 月 通过将自回归语言模型与从大规模文本库中检索的文档块相结合,基于这些文档与前文 Token 的局部相似性,我们实现了模型的显著改进。该策略利用了一个庞大的数据库(2 万亿 Token),大大增强了语言模型的能力。 通过从数万亿 Token 中检索来改善语言模型 2021 年 12 月 我们采用了一种创新的零样本任务处理方法,通过为检索增强生成模型引入严格的负样本和强化训练流程,提升了密集段落检索的效果,用于零样本槽填充任务。 用于零样本槽填充的鲁棒检索增强生成 2021 年 8 月 介绍了 RAG 模型,这是一种结合了预训练的 seq2seq 模型(作为参数记忆)和基于密集向量索引的 Wikipedia(作为非参数记忆)的模型。此模型通过预训练的神经网络检索器访问信息,比较了两种 RAG 设计:一种是在生成过程中始终依赖相同检索的段落,另一种则是每个 Token 都使用不同的段落。 用于知识密集型 NLP 任务的检索增强生成 2020 年 5 月 展示了一种仅通过密集表示实现信息检索的方法,该方法通过简单的双编码框架从少量问题和文本段落中学习嵌入。这种方法为开放域问答提供了一种高效的密集段落检索方案。 用于开放域问答的密集段落检索 2020 年 4 月 - Weaviate What is Agentic RAG
- Traditional RAG vs. Agentic RAG—Why AI Agents Need Dynamic Knowledge to Get Smarter
- What is agentic RAG?
- Agentic RAG: How It Works, Use Cases, Comparison With RAG
- RAG, AI Agents, and Agentic RAG: An In-Depth Review and Comparative Analysis
- Agentic RAG: How It Works, and How to Evaluate RAG agents
- Agentic RAG vs. Traditional RAG: The Future of AI Decision-Making
- Top 20+ Agentic RAG Frameworks in 2025
- RAG vs Agentic RAG: The Evolution of Smarter, More Dynamic AI Systems
- Agentic RAG Systems: Integration of Retrieval and Generation in AI Architectures
- Building an agentic RAG pipeline
- From Good to Great: How Pre-processing Documents Supercharges AI’s Output
- Advanced RAG 02: Unveiling PDF Parsing
- Advanced RAG 07: Exploring RAG for Tables
- 5 Levels Of Text Splitting
- Advanced RAG series: Indexing
- Advanced RAG 06: Exploring Query Rewriting
- Advanced RAG 11: Query Classification and Refinement
- Advanced RAG Series:Routing and Query Construction
- Query Transformations
- Query Construction
-
Foundations of Vector Retrieval
- 这本200多页的专题论文提供了向量检索文献中主要算法里程碑的总结,目的是作为新老研究者可以独立参考的资料。
- Improving Retrieval Performance in RAG Pipelines with Hybrid Search
- Multi-Vector Retriever for RAG on tables, text, and images
- Relevance and ranking in vector search
- Boosting RAG: Picking the Best Embedding & Reranker models
- Azure Cognitive Search: Outperforming vector search with hybrid retrieval and ranking capabilities
- Optimizing Retrieval Augmentation with Dynamic Top-K Tuning for Efficient Question Answering
- Building Production-Ready LLM Apps with LlamaIndex: Document Metadata for Higher Accuracy Retrieval
- dvanced RAG Series: Retrieval
-
How to Cut RAG Costs by 80% Using Prompt Compression
- 第一种压缩方法是 AutoCompressors。它的工作原理是将长文本汇总为短向量表示,称为汇总向量。然后,这些压缩的摘要向量充当模型的软提示。
- LangChain Contextual Compression
-
Bridging the rift in Retrieval Augmented Generation
- 不是直接微调检索器和语言模型等效果不佳的基础模块,而是引入了第三个参与者——位于现有组件之间的中间桥接模块。涉及技术包括排序、压缩、上下文框架、条件推理脚手架、互动询问等 (可参考后续论文)
- Evaluating RAG Applications with RAGAs
- Best Practices for LLM Evaluation of RAG Applications
- Advanced RAG 03: Using RAGAs + LlamaIndex for RAG evaluation
- Exploring End-to-End Evaluation of RAG Pipelines
- Evaluating Multi-Modal Retrieval-Augmented Generation
- RAG Evaluation
-
Evaluation - LlamaIndex
- 评估-LlamaIndex
-
Pinecone的RAG评测
- 不同数据规模下不同模型的RAG忠实度效果
- 不同模型下使用RAG与不是用RAG(仅依靠内部知识)的忠实度效果
- 不同模型下结合内部和外部知识后的RAG忠实度效果
- 不同模型下的RAG的答案相关度效果
- zilliz:Optimizing RAG Applications: A Guide to Methodologies, Metrics, and Evaluation Tools for Enhanced Reliability
- Advanced RAG Series: Generation and Evaluation
- 短课程 Building and Evaluating Advanced RAG Applications
- Retrieval Augmented Generation for Production with LangChain & LlamaIndex
- A Survey of Techniques for Maximizing LLM Performance
- How do domain-specific chatbots work? An overview of retrieval augmented generation (RAG)
- nvidia:Augmenting LLMs Using Retrieval Augmented Generation
- How to Choose a Vector Database
-
大语言模型
- 大模型技术的中文参考资料,由中国人民大学师生联手打造,由赵鑫教授和文继荣教授领衔。书籍注重为大模型技术的入门读者提供讲解,力图展现一个整体的大模型技术框架和路线图。本书适用于具有深度学习基础的高年级本科生以及低年级研究生使用,可以作为一本入门级的技术书籍。
- 下载地址: http://aibox.ruc.edu.cn/docs//2024-04/da308db79a5d4c5697da99e012d46c76.pdf
- 大模型基础
-
《大规模语言模型:从理论到实践》
- 本书围绕大语言模型构建的四个主要阶段:预训练、有监督微调、奖励建模和强化学习,详细介绍各阶段使用的算法、数据、难点以及实践经验。
- 下载地址: https://intro-llm.github.io/chapter/LLM-TAP.pdf
-
中文大模型相关汇总
- 包括数据、微调、推理、评估、体验、RAG、Agent、搜索、书籍和课程等方面的资源:
- Large Language Model (LLM) Disruption of Chatbots
- Gen AI: why does simple Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) not work for insurance?
- End-to-End LLMOps Platform
-
RefChecker
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Awesome-LLM-RAG-Application
Similar Open Source Tools

Awesome-LLM-RAG-Application
Awesome-LLM-RAG-Application is a repository that provides resources and information about applications based on Large Language Models (LLM) with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pattern. It includes a survey paper, GitHub repo, and guides on advanced RAG techniques. The repository covers various aspects of RAG, including academic papers, evaluation benchmarks, downstream tasks, tools, and technologies. It also explores different frameworks, preprocessing tools, routing mechanisms, evaluation frameworks, embeddings, security guardrails, prompting tools, SQL enhancements, LLM deployment, observability tools, and more. The repository aims to offer comprehensive knowledge on RAG for readers interested in exploring and implementing LLM-based systems and products.
LLMOne
LLMOne is an open-source, lightweight enterprise-level platform for deploying and serving large language models. It aims to address pain points in traditional large model private deployment such as long cycles, complex configurations, performance challenges, and high operational costs. LLMOne simplifies the deployment process with highly automated workflows and optimized runtime environments, ensuring enterprise-level performance and stability. It caters to developers, manufacturers, and users of large language models, providing features like rapid deployment, professional inference performance, broad compatibility with AI hardware, flexible model and application management, visual operational monitoring, and an open application ecosystem.
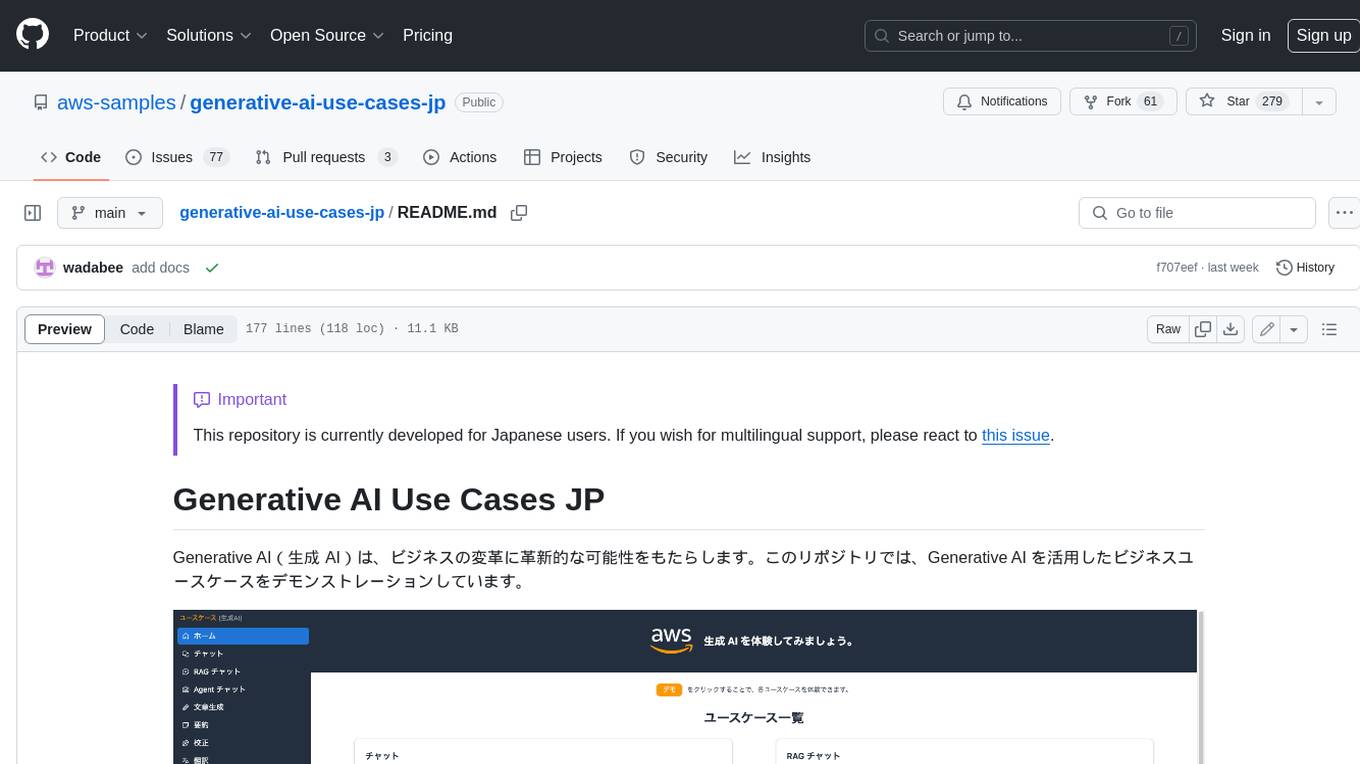
generative-ai-use-cases-jp
Generative AI (生成 AI) brings revolutionary potential to transform businesses. This repository demonstrates business use cases leveraging Generative AI.
cia
CIA is a powerful open-source tool designed for data analysis and visualization. It provides a user-friendly interface for processing large datasets and generating insightful reports. With CIA, users can easily explore data, perform statistical analysis, and create interactive visualizations to communicate findings effectively. Whether you are a data scientist, analyst, or researcher, CIA offers a comprehensive set of features to streamline your data analysis workflow and uncover valuable insights.
LLMs-from-scratch-CN
This repository is a Chinese translation of the GitHub project 'LLMs-from-scratch', including detailed markdown notes and related Jupyter code. The translation process aims to maintain the accuracy of the original content while optimizing the language and expression to better suit Chinese learners' reading habits. The repository features detailed Chinese annotations for all Jupyter code, aiding users in practical implementation. It also provides various supplementary materials to expand knowledge. The project focuses on building Large Language Models (LLMs) from scratch, covering fundamental constructions like Transformer architecture, sequence modeling, and delving into deep learning models such as GPT and BERT. Each part of the project includes detailed code implementations and learning resources to help users construct LLMs from scratch and master their core technologies.

agenta
Agenta is an open-source LLM developer platform for prompt engineering, evaluation, human feedback, and deployment of complex LLM applications. It provides tools for prompt engineering and management, evaluation, human annotation, and deployment, all without imposing any restrictions on your choice of framework, library, or model. Agenta allows developers and product teams to collaborate in building production-grade LLM-powered applications in less time.
happy-llm
Happy-LLM is a systematic learning tutorial for Large Language Models (LLM) that covers NLP research methods, LLM architecture, training process, and practical applications. It aims to help readers understand the principles and training processes of large language models. The tutorial delves into Transformer architecture, attention mechanisms, pre-training language models, building LLMs, training processes, and practical applications like RAG and Agent technologies. It is suitable for students, researchers, and LLM enthusiasts with programming experience, Python knowledge, and familiarity with deep learning and NLP concepts. The tutorial encourages hands-on practice and participation in LLM projects and competitions to deepen understanding and contribute to the open-source LLM community.
HaE
HaE is a framework project in the field of network security (data security) that combines artificial intelligence (AI) large models to achieve highlighting and information extraction of HTTP messages (including WebSocket). It aims to reduce testing time, focus on valuable and meaningful messages, and improve vulnerability discovery efficiency. The project provides a clear and visual interface design, simple interface interaction, and centralized data panel for querying and extracting information. It also features built-in color upgrade algorithm, one-click export/import of data, and integration of AI large models API for optimized data processing.
CVPR2024-Papers-with-Code-Demo
This repository contains a collection of papers and code for the CVPR 2024 conference. The papers cover a wide range of topics in computer vision, including object detection, image segmentation, image generation, and video analysis. The code provides implementations of the algorithms described in the papers, making it easy for researchers and practitioners to reproduce the results and build upon the work of others. The repository is maintained by a team of researchers at the University of California, Berkeley.
awesome-ai-efficiency
Awesome AI Efficiency is a curated list of resources dedicated to enhancing efficiency in AI systems. The repository covers various topics essential for optimizing AI models and processes, aiming to make AI faster, cheaper, smaller, and greener. It includes topics like quantization, pruning, caching, distillation, factorization, compilation, parameter-efficient fine-tuning, speculative decoding, hardware optimization, training techniques, inference optimization, sustainability strategies, and scalability approaches.
Code-Review-GPT-Gitlab
A project that utilizes large models to help with Code Review on Gitlab, aimed at improving development efficiency. The project is customized for Gitlab and is developing a Multi-Agent plugin for collaborative review. It integrates various large models for code security issues and stays updated with the latest Code Review trends. The project architecture is designed to be powerful, flexible, and efficient, with easy integration of different models and high customization for developers.

omnia
Omnia is a deployment tool designed to turn servers with RPM-based Linux images into functioning Slurm/Kubernetes clusters. It provides an Ansible playbook-based deployment for Slurm and Kubernetes on servers running an RPM-based Linux OS. The tool simplifies the process of setting up and managing clusters, making it easier for users to deploy and maintain their infrastructure.
FaceAISDK_Android
FaceAI SDK is an on-device offline face detection, recognition, liveness detection, anti-spoofing, and 1:N/M:N face search SDK. It enables quick integration to achieve on-device face recognition, face search, and other functions. The SDK performs all functions offline on the device without the need for internet connection, ensuring privacy and security. It supports various actions for liveness detection, custom camera management, and clear imaging even in challenging lighting conditions.
99AI
99AI is a commercializable AI web application based on NineAI 2.4.2 (no authorization, no backdoors, no piracy, integrated front-end and back-end integration packages, supports Docker rapid deployment). The uncompiled source code is temporarily closed. Compared with the stable version, the development version is faster.
nndeploy
nndeploy is a tool that allows you to quickly build your visual AI workflow without the need for frontend technology. It provides ready-to-use algorithm nodes for non-AI programmers, including large language models, Stable Diffusion, object detection, image segmentation, etc. The workflow can be exported as a JSON configuration file, supporting Python/C++ API for direct loading and running, deployment on cloud servers, desktops, mobile devices, edge devices, and more. The framework includes mainstream high-performance inference engines and deep optimization strategies to help you transform your workflow into enterprise-level production applications.
For similar tasks
dify
Dify is an open-source LLM app development platform that combines AI workflow, RAG pipeline, agent capabilities, model management, observability features, and more. It allows users to quickly go from prototype to production. Key features include: 1. Workflow: Build and test powerful AI workflows on a visual canvas. 2. Comprehensive model support: Seamless integration with hundreds of proprietary / open-source LLMs from dozens of inference providers and self-hosted solutions. 3. Prompt IDE: Intuitive interface for crafting prompts, comparing model performance, and adding additional features. 4. RAG Pipeline: Extensive RAG capabilities that cover everything from document ingestion to retrieval. 5. Agent capabilities: Define agents based on LLM Function Calling or ReAct, and add pre-built or custom tools. 6. LLMOps: Monitor and analyze application logs and performance over time. 7. Backend-as-a-Service: All of Dify's offerings come with corresponding APIs for easy integration into your own business logic.
intro-to-intelligent-apps
This repository introduces and helps organizations get started with building AI Apps and incorporating Large Language Models (LLMs) into them. The workshop covers topics such as prompt engineering, AI orchestration, and deploying AI apps. Participants will learn how to use Azure OpenAI, Langchain/ Semantic Kernel, Qdrant, and Azure AI Search to build intelligent applications.
runhouse
Runhouse is a tool that allows you to build, run, and deploy production-quality AI apps and workflows on your own compute. It provides simple, powerful APIs for the full lifecycle of AI development, from research to evaluation to production to updates to scaling to management, and across any infra. By automatically packaging your apps into scalable, secure, and observable services, Runhouse can also turn otherwise redundant AI activities into common reusable components across your team or company, which improves cost, velocity, and reproducibility.

Awesome-LLM-RAG-Application
Awesome-LLM-RAG-Application is a repository that provides resources and information about applications based on Large Language Models (LLM) with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pattern. It includes a survey paper, GitHub repo, and guides on advanced RAG techniques. The repository covers various aspects of RAG, including academic papers, evaluation benchmarks, downstream tasks, tools, and technologies. It also explores different frameworks, preprocessing tools, routing mechanisms, evaluation frameworks, embeddings, security guardrails, prompting tools, SQL enhancements, LLM deployment, observability tools, and more. The repository aims to offer comprehensive knowledge on RAG for readers interested in exploring and implementing LLM-based systems and products.
sdfx
SDFX is the ultimate no-code platform for building and sharing AI apps with beautiful UI. It enables the creation of user-friendly interfaces for complex workflows by combining Comfy workflow with a UI. The tool is designed to merge the benefits of form-based UI and graph-node based UI, allowing users to create intricate graphs with a high-level UI overlay. SDFX is fully compatible with ComfyUI, abstracting the need for installing ComfyUI. It offers features like animated graph navigation, node bookmarks, UI debugger, custom nodes manager, app and template export, image and mask editor, and more. The tool compiles as a native app or web app, making it easy to maintain and add new features.
Build-Modern-AI-Apps
This repository serves as a hub for Microsoft Official Build & Modernize AI Applications reference solutions and content. It provides access to projects demonstrating how to build Generative AI applications using Azure services like Azure OpenAI, Azure Container Apps, Azure Kubernetes, and Azure Cosmos DB. The solutions include Vector Search & AI Assistant, Real-Time Payment and Transaction Processing, and Medical Claims Processing. Additionally, there are workshops like the Intelligent App Workshop for Microsoft Copilot Stack, focusing on infusing intelligence into traditional software systems using foundation models and design thinking.
RAG_Hack
RAGHack is a hackathon focused on building AI applications using the power of RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation). RAG combines large language models with search engine knowledge to provide contextually relevant answers. Participants can learn to build RAG apps on Azure AI using various languages and retrievers, explore frameworks like LangChain and Semantic Kernel, and leverage technologies such as agents and vision models. The hackathon features live streams, hack submissions, and prizes for innovative projects.
generative-ai-with-javascript
The 'Generative AI with JavaScript' repository is a comprehensive resource hub for JavaScript developers interested in delving into the world of Generative AI. It provides code samples, tutorials, and resources from a video series, offering best practices and tips to enhance AI skills. The repository covers the basics of generative AI, guides on building AI applications using JavaScript, from local development to deployment on Azure, and scaling AI models. It is a living repository with continuous updates, making it a valuable resource for both beginners and experienced developers looking to explore AI with JavaScript.
For similar jobs

Awesome-LLM-RAG-Application
Awesome-LLM-RAG-Application is a repository that provides resources and information about applications based on Large Language Models (LLM) with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pattern. It includes a survey paper, GitHub repo, and guides on advanced RAG techniques. The repository covers various aspects of RAG, including academic papers, evaluation benchmarks, downstream tasks, tools, and technologies. It also explores different frameworks, preprocessing tools, routing mechanisms, evaluation frameworks, embeddings, security guardrails, prompting tools, SQL enhancements, LLM deployment, observability tools, and more. The repository aims to offer comprehensive knowledge on RAG for readers interested in exploring and implementing LLM-based systems and products.
ChatGPT-On-CS
ChatGPT-On-CS is an intelligent chatbot tool based on large models, supporting various platforms like WeChat, Taobao, Bilibili, Douyin, Weibo, and more. It can handle text, voice, and image inputs, access external resources through plugins, and customize enterprise AI applications based on proprietary knowledge bases. Users can set custom replies, utilize ChatGPT interface for intelligent responses, send images and binary files, and create personalized chatbots using knowledge base files. The tool also features platform-specific plugin systems for accessing external resources and supports enterprise AI applications customization.
call-gpt
Call GPT is a voice application that utilizes Deepgram for Speech to Text, elevenlabs for Text to Speech, and OpenAI for GPT prompt completion. It allows users to chat with ChatGPT on the phone, providing better transcription, understanding, and speaking capabilities than traditional IVR systems. The app returns responses with low latency, allows user interruptions, maintains chat history, and enables GPT to call external tools. It coordinates data flow between Deepgram, OpenAI, ElevenLabs, and Twilio Media Streams, enhancing voice interactions.
awesome-LLM-resourses
A comprehensive repository of resources for Chinese large language models (LLMs), including data processing tools, fine-tuning frameworks, inference libraries, evaluation platforms, RAG engines, agent frameworks, books, courses, tutorials, and tips. The repository covers a wide range of tools and resources for working with LLMs, from data labeling and processing to model fine-tuning, inference, evaluation, and application development. It also includes resources for learning about LLMs through books, courses, and tutorials, as well as insights and strategies from building with LLMs.
tappas
Hailo TAPPAS is a set of full application examples that implement pipeline elements and pre-trained AI tasks. It demonstrates Hailo's system integration scenarios on predefined systems, aiming to accelerate time to market, simplify integration with Hailo's runtime SW stack, and provide a starting point for customers to fine-tune their applications. The tool supports both Hailo-15 and Hailo-8, offering various example applications optimized for different common hosts. TAPPAS includes pipelines for single network, two network, and multi-stream processing, as well as high-resolution processing via tiling. It also provides example use case pipelines like License Plate Recognition and Multi-Person Multi-Camera Tracking. The tool is regularly updated with new features, bug fixes, and platform support.
cloudflare-rag
This repository provides a fullstack example of building a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) app with Cloudflare. It utilizes Cloudflare Workers, Pages, D1, KV, R2, AI Gateway, and Workers AI. The app features streaming interactions to the UI, hybrid RAG with Full-Text Search and Vector Search, switchable providers using AI Gateway, per-IP rate limiting with Cloudflare's KV, OCR within Cloudflare Worker, and Smart Placement for workload optimization. The development setup requires Node, pnpm, and wrangler CLI, along with setting up necessary primitives and API keys. Deployment involves setting up secrets and deploying the app to Cloudflare Pages. The project implements a Hybrid Search RAG approach combining Full Text Search against D1 and Hybrid Search with embeddings against Vectorize to enhance context for the LLM.
pixeltable
Pixeltable is a Python library designed for ML Engineers and Data Scientists to focus on exploration, modeling, and app development without the need to handle data plumbing. It provides a declarative interface for working with text, images, embeddings, and video, enabling users to store, transform, index, and iterate on data within a single table interface. Pixeltable is persistent, acting as a database unlike in-memory Python libraries such as Pandas. It offers features like data storage and versioning, combined data and model lineage, indexing, orchestration of multimodal workloads, incremental updates, and automatic production-ready code generation. The tool emphasizes transparency, reproducibility, cost-saving through incremental data changes, and seamless integration with existing Python code and libraries.
wave-apps
Wave Apps is a directory of sample applications built on H2O Wave, allowing users to build AI apps faster. The apps cover various use cases such as explainable hotel ratings, human-in-the-loop credit risk assessment, mitigating churn risk, online shopping recommendations, and sales forecasting EDA. Users can download, modify, and integrate these sample apps into their own projects to learn about app development and AI model deployment.