joinly
Make your meetings accessible to AI Agents
Stars: 433

joinly.ai is a connector middleware designed to enable AI agents to actively participate in video calls, providing essential meeting tools for AI agents to perform tasks and interact in real time. It supports live interaction, conversational flow, cross-platform compatibility, bring-your-own-LLM, and choose-your-preferred-TTS/STT services. The tool is 100% open-source, self-hosted, and privacy-first, aiming to make meetings accessible to AI agents by joining and participating in video calls.
README:
joinly.ai is a connector middleware designed to enable AI agents to join and actively participate in video calls. Through its MCP server, joinly.ai provides essential meeting tools and resources that can equip any AI agent with the skills to perform tasks and interact with you in real time during your meetings.
Want to dive right in? Jump to the Quickstart! Want to know more? Visit our website!
[!IMPORTANT]
Don't want the hustle of setting everything up? Try our cloud first! ☁️🚀
- Live Interaction: Lets your agents execute tasks and respond in real-time by voice or chat within your meetings
- Conversational flow: Built-in logic that ensures natural conversations by handling interruptions and multi-speaker interactions
- Cross-platform: Join Google Meet, Zoom, and Microsoft Teams (or any available over the browser)
- Bring-your-own-LLM: Works with all LLM providers (also locally with Ollama)
- Choose-your-preferred-TTS/STT: Modular design supports multiple services - Whisper/Deepgram for STT and Kokoro/ElevenLabs/Deepgram for TTS (and more to come...)
- 100% open-source, self-hosted and privacy-first 🚀
In this demo video, joinly answers the question 'What is Joinly?' by accessing the latest news from the web. It then creates an issue in a GitHub demo repository.
In this demo video, we connect joinly to our notion via MCP and let it edit the content of a page content live in the meeting.
Any ideas what we should build next? Write us! 🚀
Run joinly via Docker with a basic conversational agent client.
[!IMPORTANT] Prerequisites: Docker installation
Create a new folder joinly or clone this repository (not mandatory for the following steps). In this directory, create a new .env file with a valid API key for the LLM provider you want to use, e.g. OpenAI:
[!TIP] You can find the OpenAI API key here
# .env
# for OpenAI LLM
# change key and model to your desired one
JOINLY_LLM_MODEL=gpt-4o
JOINLY_LLM_PROVIDER=openai
OPENAI_API_KEY=your-openai-api-key[!NOTE] See .env.example for complete configuration options including Anthropic (Claude) and Ollama setups. Replace the placeholder values with your actual API keys and adjust the model name as needed. Delete the placeholder values of the providers you don't use.
Pull the Docker image (~2.3GB since it packages browser and models):
docker pull ghcr.io/joinly-ai/joinly:latestLaunch your meeting in Zoom, Google Meet or Teams and let joinly join the meeting using the meeting link as <MeetingURL>. Then, run the following command from the folder where you created the .env file:
docker run --env-file .env ghcr.io/joinly-ai/joinly:latest --client <MeetingURL>🔴 Having trouble getting started? Let's figure it out together on our discord!
In Quickstart, we ran the Docker Container directly as a client using --client. But we can also run it as a server and connect to it from outside the container, which allows us to connect other MCP servers. Here, we run an external client using the joinly-client package and connect it to the joinly MCP server.
[!IMPORTANT] Prerequisites: do the Quickstart (except the last command), install uv, and open two terminals
Start the joinly server in the first terminal (note, we are not using --client here and forward port 8000):
docker run -p 8000:8000 ghcr.io/joinly-ai/joinly:latestWhile the server is running, start the example client implementation in the second terminal window to connect to it and join a meeting:
uvx joinly-client --env-file .env <MeetingUrl>Add the tools of any MCP server to the agent by providing a JSON configuration. The configuration file can contain multiple entries under "mcpServers" which will all be available as tools in the meeting (see fastmcp client docs for config syntax):
{
"mcpServers": {
"localServer": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "[email protected]"]
},
"remoteServer": {
"url": "http://mcp.example.com",
"auth": "oauth"
}
}
}Add for example a Tavily config for web searching, then run the client using the config file, here named config.json:
uvx joinly-client --env-file .env --mcp-config config.json <MeetingUrl>Configurations can be given via env variables and/or command line args. Here is a list of common configuration options, which can be used when starting the docker container:
docker run --env-file .env -p 8000:8000 ghcr.io/joinly-ai/joinly:latest <MyOptionArgs>Alternatively, you can pass --name, --lang, and provider settings as command line arguments using joinly-client, which will override settings of the server:
uvx joinly-client <MyOptionArgs> <MeetingUrl>In general, the docker image provides an MCP server which is started by default. But to quickly get started, we also include a client implementation that can be used via --client. Note, in this case no server is started and no other client can connect to it.
# Start directly as client; default is as server, to which an external client can connect
--client <MeetingUrl>
# Change participant name (default: joinly)
--name "AI Assistant"
# Change language of TTS/STT (default: en)
# Note, availability depends on the TTS/STT provider
--lang de
# Change host & port of the joinly MCP server
--host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000# Kokoro (local) TTS (default)
--tts kokoro
--tts-arg voice=<VoiceName> # optionally, set different voice
# ElevenLabs TTS, include ELEVENLABS_API_KEY in .env
--tts elevenlabs
--tts-arg voice_id=<VoiceID> # optionally, set different voice
# Deepgram TTS, include DEEPGRAM_API_KEY in .env
--tts deepgram
--tts-arg model_name=<ModelName> # optionally, set different model (voice)# Whisper (local) STT (default)
--stt whisper
--stt-arg model_name=<ModelName> # optionally, set different model (default: base), for GPU support see below
# Deepgram STT, include DEEPGRAM_API_KEY in .env
--stt deepgram
--stt-arg model_name=<ModelName> # optionally, set different model# Start browser with a VNC server for debugging;
# forward the port and connect to it using a VNC client
--vnc-server --vnc-server-port 5900
# Logging
-v # or -vv, -vvv
# Help
--helpWe provide a Docker image with CUDA GPU support for running the transcription and TTS models on a GPU. To use it, you need to have the NVIDIA Container Toolkit installed and CUDA >= 12.6. Then pull the CUDA-enabled image:
docker pull ghcr.io/joinly-ai/joinly:latest-cudaRun as client or server with the same commands as above, but use the joinly:{version}-cuda image and set --gpus all:
# Run as server
docker run --gpus all --env-file .env -p 8000:8000 ghcr.io/joinly-ai/joinly:latest-cuda -v
# Run as client
docker run --gpus all --env-file .env ghcr.io/joinly-ai/joinly:latest-cuda -v --client <MeetingURL>By default, the joinly image uses the Whisper model base for transcription, since it still runs reasonably fast on CPU. For cuda, it automatically defaults to distil-large-v3 for significantly better transcription quality. You can change the model by setting --stt-arg model_name=<model_name> (e.g., --stt-arg model_name=large-v3). However, only the respective default models are packaged in the docker image, so it will start to download the model weights on container start.
You can also write your own agent and connect it to our joinly MCP server. See the code examples for the joinly-client package or the client_example.py if you want a starting point that doesn't depend on our framework.
The joinly MCP server provides following tools and resources:
-
join_meeting- Join meeting with URL, participant name, and optional passcode -
leave_meeting- Leave the current meeting -
speak_text- Speak text using TTS (requirestextparameter) -
send_chat_message- Send chat message (requiresmessageparameter) -
mute_yourself- Mute microphone -
unmute_yourself- Unmute microphone -
get_chat_history- Get current meeting chat history in JSON format -
get_participants- Get current meeting participants in JSON format -
get_transcript- Get current meeting transcript in JSON format, optionally filtered by minutes -
get_video_snapshot- Get an image from the current meeting, e.g., view a current screenshare
-
transcript://live- Live meeting transcript in JSON format, including timestamps and speaker information. Subscribable for real-time updates when new utterances are added.
For development we recommend using the development container, which installs all necessary dependencies. To get started, install the DevContainer Extension for Visual Studio Code, open the repository and choose Reopen in Container.
The installation can take some time, since it downloads all packages as well as models for Whisper/Kokoro and the Chromium browser. At the end, it automatically invokes the download_assets.py script. If you see errors like Missing kokoro-v1.0.onnx, run this script manually using:
uv run scripts/download_assets.pyWe'd love to see what you are using it for or building with it. Showcase your work on our discord
Meeting
- [x] Meeting chat access
- [ ] Camera in video call with status updates
- [ ] Enable screen share during video conferences
- [ ] Participant metadata and joining/leaving
- [ ] Improve browser agent capabilities
Conversation
- [x] Speaker attribute for transcription
- [ ] Improve client memory: reduce token usage, allow persistence across meetings events
- [ ] Improve End-of-Utterance/turn-taking detection
- [ ] Human approval mechanism from inside the meeting
Integrations
- [ ] Showcase how to add agents using the A2A protocol
- [ ] Add more provider integrations (STT, TTS)
- [ ] Integrate meeting platform SDKs
- [ ] Add alternative open-source meeting provider
- [ ] Add support for Speech2Speech models
Contributions are always welcome! Feel free to open issues for bugs or submit a feature request. We'll do our best to review all contributions promptly and help merge your changes.
Please check our Roadmap and don't hesitate to reach out to us!
This project is licensed under the MIT License ‒ see the LICENSE file for details.
If you have questions or feedback, or if you would like to chat with the maintainers or other community members, please use the following links:
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for joinly
Similar Open Source Tools

joinly
joinly.ai is a connector middleware designed to enable AI agents to actively participate in video calls, providing essential meeting tools for AI agents to perform tasks and interact in real time. It supports live interaction, conversational flow, cross-platform compatibility, bring-your-own-LLM, and choose-your-preferred-TTS/STT services. The tool is 100% open-source, self-hosted, and privacy-first, aiming to make meetings accessible to AI agents by joining and participating in video calls.
kwaak
Kwaak is a tool that allows users to run a team of autonomous AI agents locally from their own machine. It enables users to write code, improve test coverage, update documentation, and enhance code quality while focusing on building innovative projects. Kwaak is designed to run multiple agents in parallel, interact with codebases, answer questions about code, find examples, write and execute code, create pull requests, and more. It is free and open-source, allowing users to bring their own API keys or models via Ollama. Kwaak is part of the bosun.ai project, aiming to be a platform for autonomous code improvement.
agenticSeek
AgenticSeek is a voice-enabled AI assistant powered by DeepSeek R1 agents, offering a fully local alternative to cloud-based AI services. It allows users to interact with their filesystem, code in multiple languages, and perform various tasks autonomously. The tool is equipped with memory to remember user preferences and past conversations, and it can divide tasks among multiple agents for efficient execution. AgenticSeek prioritizes privacy by running entirely on the user's hardware without sending data to the cloud.
bedrock-claude-chat
This repository is a sample chatbot using the Anthropic company's LLM Claude, one of the foundational models provided by Amazon Bedrock for generative AI. It allows users to have basic conversations with the chatbot, personalize it with their own instructions and external knowledge, and analyze usage for each user/bot on the administrator dashboard. The chatbot supports various languages, including English, Japanese, Korean, Chinese, French, German, and Spanish. Deployment is straightforward and can be done via the command line or by using AWS CDK. The architecture is built on AWS managed services, eliminating the need for infrastructure management and ensuring scalability, reliability, and security.

AutoAgent
AutoAgent is a fully-automated and zero-code framework that enables users to create and deploy LLM agents through natural language alone. It is a top performer on the GAIA Benchmark, equipped with a native self-managing vector database, and allows for easy creation of tools, agents, and workflows without any coding. AutoAgent seamlessly integrates with a wide range of LLMs and supports both function-calling and ReAct interaction modes. It is designed to be dynamic, extensible, customized, and lightweight, serving as a personal AI assistant.
lexido
Lexido is an innovative assistant for the Linux command line, designed to boost your productivity and efficiency. Powered by Gemini Pro 1.0 and utilizing the free API, Lexido offers smart suggestions for commands based on your prompts and importantly your current environment. Whether you're installing software, managing files, or configuring system settings, Lexido streamlines the process, making it faster and more intuitive.
mobile-use
Mobile-use is an open-source AI agent that controls Android or IOS devices using natural language. It understands commands to perform tasks like sending messages and navigating apps. Features include natural language control, UI-aware automation, data scraping, and extensibility. Users can automate their mobile experience by setting up environment variables, customizing LLM configurations, and launching the tool via Docker or manually for development. The tool supports physical Android phones, Android simulators, and iOS simulators. Contributions are welcome, and the project is licensed under MIT.

Fabric
Fabric is an open-source framework designed to augment humans using AI by organizing prompts by real-world tasks. It addresses the integration problem of AI by creating and organizing prompts for various tasks. Users can create, collect, and organize AI solutions in a single place for use in their favorite tools. Fabric also serves as a command-line interface for those focused on the terminal. It offers a wide range of features and capabilities, including support for multiple AI providers, internationalization, speech-to-text, AI reasoning, model management, web search, text-to-speech, desktop notifications, and more. The project aims to help humans flourish by leveraging AI technology to solve human problems and enhance creativity.
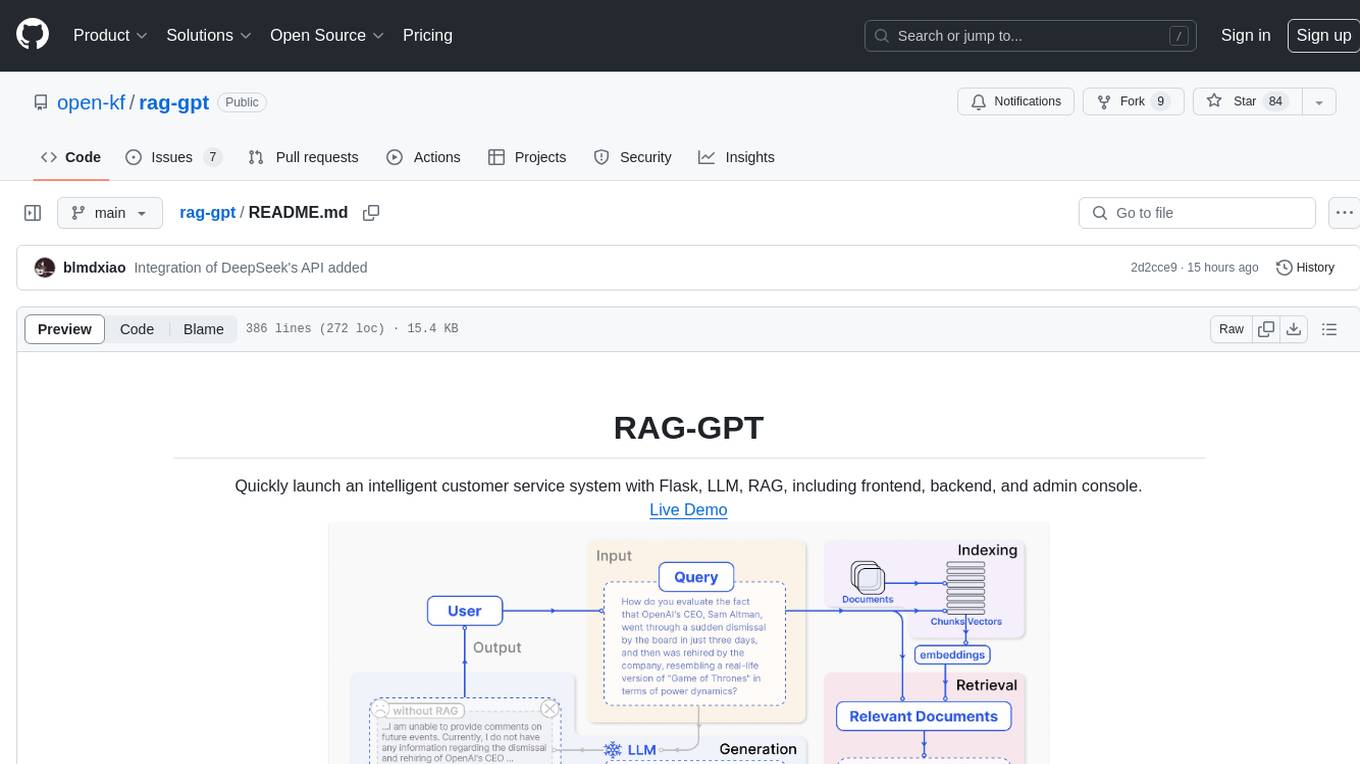
rag-gpt
RAG-GPT is a tool that allows users to quickly launch an intelligent customer service system with Flask, LLM, and RAG. It includes frontend, backend, and admin console components. The tool supports cloud-based and local LLMs, enables deployment of conversational service robots in minutes, integrates diverse knowledge bases, offers flexible configuration options, and features an attractive user interface.
aimeos-laravel
Aimeos Laravel is a professional, full-featured, and ultra-fast Laravel ecommerce package that can be easily integrated into existing Laravel applications. It offers a wide range of features including multi-vendor, multi-channel, and multi-warehouse support, fast performance, support for various product types, subscriptions with recurring payments, multiple payment gateways, full RTL support, flexible pricing options, admin backend, REST and GraphQL APIs, modular structure, SEO optimization, multi-language support, AI-based text translation, mobile optimization, and high-quality source code. The package is highly configurable and extensible, making it suitable for e-commerce SaaS solutions, marketplaces, and online shops with millions of vendors.

langserve
LangServe helps developers deploy `LangChain` runnables and chains as a REST API. This library is integrated with FastAPI and uses pydantic for data validation. In addition, it provides a client that can be used to call into runnables deployed on a server. A JavaScript client is available in LangChain.js.
lollms_legacy
Lord of Large Language Models (LoLLMs) Server is a text generation server based on large language models. It provides a Flask-based API for generating text using various pre-trained language models. This server is designed to be easy to install and use, allowing developers to integrate powerful text generation capabilities into their applications. The tool supports multiple personalities for generating text with different styles and tones, real-time text generation with WebSocket-based communication, RESTful API for listing personalities and adding new personalities, easy integration with various applications and frameworks, sending files to personalities, running on multiple nodes to provide a generation service to many outputs at once, and keeping data local even in the remote version.

shellChatGPT
ShellChatGPT is a shell wrapper for OpenAI's ChatGPT, DALL-E, Whisper, and TTS, featuring integration with LocalAI, Ollama, Gemini, Mistral, Groq, and GitHub Models. It provides text and chat completions, vision, reasoning, and audio models, voice-in and voice-out chatting mode, text editor interface, markdown rendering support, session management, instruction prompt manager, integration with various service providers, command line completion, file picker dialogs, color scheme personalization, stdin and text file input support, and compatibility with Linux, FreeBSD, MacOS, and Termux for a responsive experience.
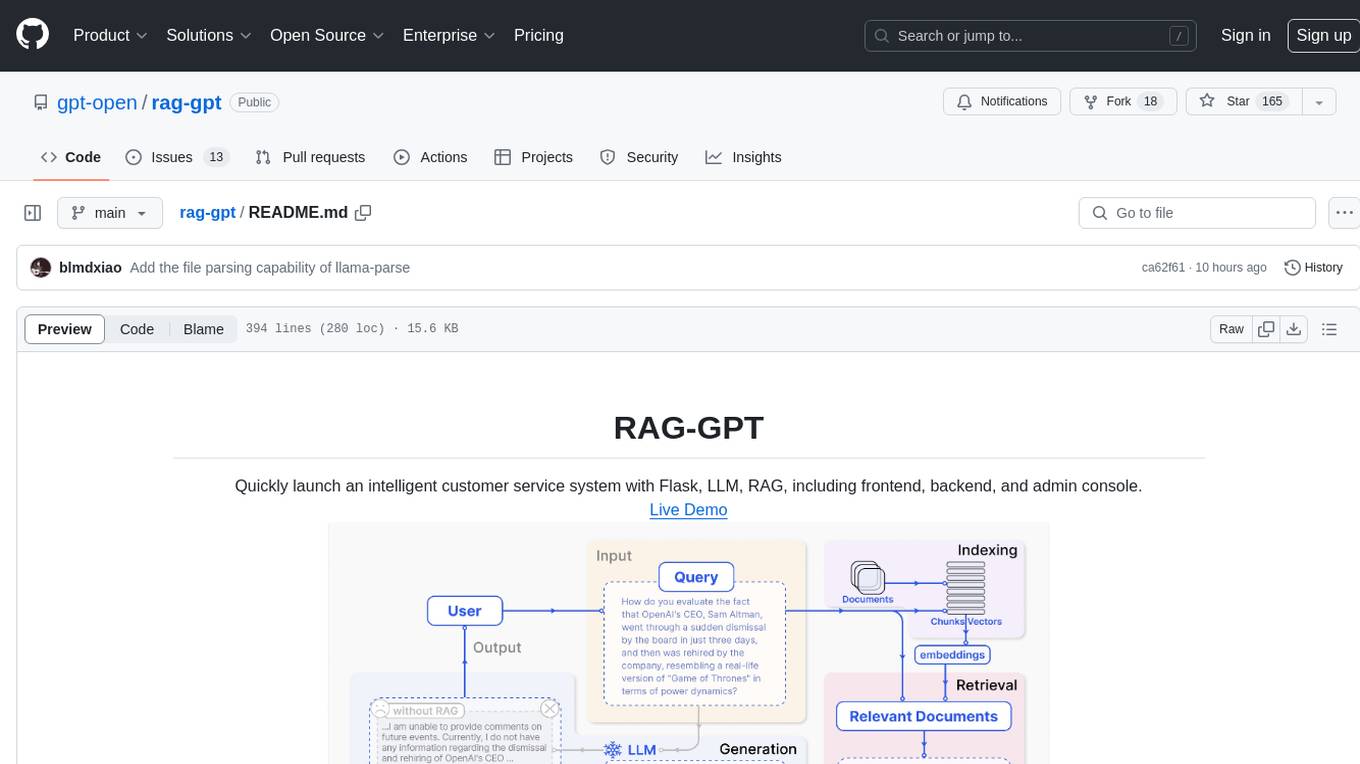
rag-gpt
RAG-GPT is a tool that allows users to quickly launch an intelligent customer service system with Flask, LLM, and RAG. It includes frontend, backend, and admin console components. The tool supports cloud-based and local LLMs, offers quick setup for conversational service robots, integrates diverse knowledge bases, provides flexible configuration options, and features an attractive user interface.
slack-bot
The Slack Bot is a tool designed to enhance the workflow of development teams by integrating with Jenkins, GitHub, GitLab, and Jira. It allows for custom commands, macros, crons, and project-specific commands to be implemented easily. Users can interact with the bot through Slack messages, execute commands, and monitor job progress. The bot supports features like starting and monitoring Jenkins jobs, tracking pull requests, querying Jira information, creating buttons for interactions, generating images with DALL-E, playing quiz games, checking weather, defining custom commands, and more. Configuration is managed via YAML files, allowing users to set up credentials for external services, define custom commands, schedule cron jobs, and configure VCS systems like Bitbucket for automated branch lookup in Jenkins triggers.
steel-browser
Steel is an open-source browser API designed for AI agents and applications, simplifying the process of building live web agents and browser automation tools. It serves as a core building block for a production-ready, containerized browser sandbox with features like stealth capabilities, text-to-markdown session management, UI for session viewing/debugging, and full browser control through popular automation frameworks. Steel allows users to control, run, and manage a production-ready browser environment via a REST API, offering features such as full browser control, session management, proxy support, extension support, debugging tools, anti-detection mechanisms, resource management, and various browser tools. It aims to streamline complex browsing tasks programmatically, enabling users to focus on their AI applications while Steel handles the underlying complexity.
For similar tasks
AGiXT
AGiXT is a dynamic Artificial Intelligence Automation Platform engineered to orchestrate efficient AI instruction management and task execution across a multitude of providers. Our solution infuses adaptive memory handling with a broad spectrum of commands to enhance AI's understanding and responsiveness, leading to improved task completion. The platform's smart features, like Smart Instruct and Smart Chat, seamlessly integrate web search, planning strategies, and conversation continuity, transforming the interaction between users and AI. By leveraging a powerful plugin system that includes web browsing and command execution, AGiXT stands as a versatile bridge between AI models and users. With an expanding roster of AI providers, code evaluation capabilities, comprehensive chain management, and platform interoperability, AGiXT is consistently evolving to drive a multitude of applications, affirming its place at the forefront of AI technology.
aiexe
aiexe is a cutting-edge command-line interface (CLI) and graphical user interface (GUI) tool that integrates powerful AI capabilities directly into your terminal or desktop. It is designed for developers, tech enthusiasts, and anyone interested in AI-powered automation. aiexe provides an easy-to-use yet robust platform for executing complex tasks with just a few commands. Users can harness the power of various AI models from OpenAI, Anthropic, Ollama, Gemini, and GROQ to boost productivity and enhance decision-making processes.
claude.vim
Claude.vim is a Vim plugin that integrates Claude, an AI pair programmer, into your Vim workflow. It allows you to chat with Claude about what to build or how to debug problems, and Claude offers opinions, proposes modifications, or even writes code. The plugin provides a chat/instruction-centric interface optimized for human collaboration, with killer features like access to chat history and vimdiff interface. It can refactor code, modify or extend selected pieces of code, execute complex tasks by reading documentation, cloning git repositories, and more. Note that it is early alpha software and expected to rapidly evolve.
mistreevous
Mistreevous is a library written in TypeScript for Node and browsers, used to declaratively define, build, and execute behaviour trees for creating complex AI. It allows defining trees with JSON or a minimal DSL, providing in-browser editor and visualizer. The tool offers methods for tree state, stepping, resetting, and getting node details, along with various composite, decorator, leaf nodes, callbacks, guards, and global functions/subtrees. Version history includes updates for node types, callbacks, global functions, and TypeScript conversion.

project_alice
Alice is an agentic workflow framework that integrates task execution and intelligent chat capabilities. It provides a flexible environment for creating, managing, and deploying AI agents for various purposes, leveraging a microservices architecture with MongoDB for data persistence. The framework consists of components like APIs, agents, tasks, and chats that interact to produce outputs through files, messages, task results, and URL references. Users can create, test, and deploy agentic solutions in a human-language framework, making it easy to engage with by both users and agents. The tool offers an open-source option, user management, flexible model deployment, and programmatic access to tasks and chats.
flock
Flock is a workflow-based low-code platform that enables rapid development of chatbots, RAG applications, and coordination of multi-agent teams. It offers a flexible, low-code solution for orchestrating collaborative agents, supporting various node types for specific tasks, such as input processing, text generation, knowledge retrieval, tool execution, intent recognition, answer generation, and more. Flock integrates LangChain and LangGraph to provide offline operation capabilities and supports future nodes like Conditional Branch, File Upload, and Parameter Extraction for creating complex workflows. Inspired by StreetLamb, Lobe-chat, Dify, and fastgpt projects, Flock introduces new features and directions while leveraging open-source models and multi-tenancy support.
RoboMatrix
RoboMatrix is a skill-centric hierarchical framework for scalable robot task planning and execution in an open-world environment. It provides a structured approach to robot task execution using a combination of hardware components, environment configuration, installation procedures, and data collection methods. The framework is developed using the ROS2 framework on Ubuntu and supports robots from DJI's RoboMaster series. Users can follow the provided installation guidance to set up RoboMatrix and utilize it for various tasks such as data collection, task execution, and dataset construction. The framework also includes a supervised fine-tuning dataset and aims to optimize communication and release additional components in the future.
agentscript
AgentScript is an open-source framework for building AI agents that think in code. It prompts a language model to generate JavaScript code, which is then executed in a dedicated runtime with resumability, state persistence, and interactivity. The framework allows for abstract task execution without needing to know all the data beforehand, making it flexible and efficient. AgentScript supports tools, deterministic functions, and LLM-enabled functions, enabling dynamic data processing and decision-making. It also provides state management and human-in-the-loop capabilities, allowing for pausing, serialization, and resumption of execution.
For similar jobs

promptflow
**Prompt flow** is a suite of development tools designed to streamline the end-to-end development cycle of LLM-based AI applications, from ideation, prototyping, testing, evaluation to production deployment and monitoring. It makes prompt engineering much easier and enables you to build LLM apps with production quality.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.

MegaDetector
MegaDetector is an AI model that identifies animals, people, and vehicles in camera trap images (which also makes it useful for eliminating blank images). This model is trained on several million images from a variety of ecosystems. MegaDetector is just one of many tools that aims to make conservation biologists more efficient with AI. If you want to learn about other ways to use AI to accelerate camera trap workflows, check out our of the field, affectionately titled "Everything I know about machine learning and camera traps".

leapfrogai
LeapfrogAI is a self-hosted AI platform designed to be deployed in air-gapped resource-constrained environments. It brings sophisticated AI solutions to these environments by hosting all the necessary components of an AI stack, including vector databases, model backends, API, and UI. LeapfrogAI's API closely matches that of OpenAI, allowing tools built for OpenAI/ChatGPT to function seamlessly with a LeapfrogAI backend. It provides several backends for various use cases, including llama-cpp-python, whisper, text-embeddings, and vllm. LeapfrogAI leverages Chainguard's apko to harden base python images, ensuring the latest supported Python versions are used by the other components of the stack. The LeapfrogAI SDK provides a standard set of protobuffs and python utilities for implementing backends and gRPC. LeapfrogAI offers UI options for common use-cases like chat, summarization, and transcription. It can be deployed and run locally via UDS and Kubernetes, built out using Zarf packages. LeapfrogAI is supported by a community of users and contributors, including Defense Unicorns, Beast Code, Chainguard, Exovera, Hypergiant, Pulze, SOSi, United States Navy, United States Air Force, and United States Space Force.

llava-docker
This Docker image for LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant) provides a convenient way to run LLaVA locally or on RunPod. LLaVA is a powerful AI tool that combines natural language processing and computer vision capabilities. With this Docker image, you can easily access LLaVA's functionalities for various tasks, including image captioning, visual question answering, text summarization, and more. The image comes pre-installed with LLaVA v1.2.0, Torch 2.1.2, xformers 0.0.23.post1, and other necessary dependencies. You can customize the model used by setting the MODEL environment variable. The image also includes a Jupyter Lab environment for interactive development and exploration. Overall, this Docker image offers a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for leveraging LLaVA's capabilities.

carrot
The 'carrot' repository on GitHub provides a list of free and user-friendly ChatGPT mirror sites for easy access. The repository includes sponsored sites offering various GPT models and services. Users can find and share sites, report errors, and access stable and recommended sites for ChatGPT usage. The repository also includes a detailed list of ChatGPT sites, their features, and accessibility options, making it a valuable resource for ChatGPT users seeking free and unlimited GPT services.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.

AI-YinMei
AI-YinMei is an AI virtual anchor Vtuber development tool (N card version). It supports fastgpt knowledge base chat dialogue, a complete set of solutions for LLM large language models: [fastgpt] + [one-api] + [Xinference], supports docking bilibili live broadcast barrage reply and entering live broadcast welcome speech, supports Microsoft edge-tts speech synthesis, supports Bert-VITS2 speech synthesis, supports GPT-SoVITS speech synthesis, supports expression control Vtuber Studio, supports painting stable-diffusion-webui output OBS live broadcast room, supports painting picture pornography public-NSFW-y-distinguish, supports search and image search service duckduckgo (requires magic Internet access), supports image search service Baidu image search (no magic Internet access), supports AI reply chat box [html plug-in], supports AI singing Auto-Convert-Music, supports playlist [html plug-in], supports dancing function, supports expression video playback, supports head touching action, supports gift smashing action, supports singing automatic start dancing function, chat and singing automatic cycle swing action, supports multi scene switching, background music switching, day and night automatic switching scene, supports open singing and painting, let AI automatically judge the content.