
ai-containers
This repository contains Dockerfiles, scripts, yaml files, Helm charts, etc. used to scale out AI containers with versions of TensorFlow and PyTorch that have been optimized for Intel platforms. Scaling is done with python, Docker, kubernetes, kubeflow, cnvrg.io, Helm, and other container orchestration frameworks for use in the cloud and on-premise
Stars: 52
This repository contains Dockerfiles, scripts, yaml files, Helm charts, etc. used to scale out AI containers with versions of TensorFlow and PyTorch optimized for Intel platforms. Scaling is done with python, Docker, kubernetes, kubeflow, cnvrg.io, Helm, and other container orchestration frameworks for use in the cloud and on-premise.
README:
This repository contains Dockerfiles, scripts, yaml files, Helm charts, etc. used to scale out AI containers with versions of TensorFlow and PyTorch that have been optimized for Intel platforms. Scaling is done with python, Docker, kubernetes, kubeflow, cnvrg.io, Helm, and other container orchestration frameworks for use in the cloud and on-premise.
Define your project's registry and repository each time you use the project:
# REGISTRY/REPO:TAG
export REGISTRY=<registry_name>
export REPO=<repo_name>
docker login $REGISTRY
# Verify your access permissions
docker pull $REGISTRY/$REPO:latestThe maintainers of AI Containers use Azure to store containers, but an open source container registry like harbor is preferred.
[!WARNING] You can optionally skip this step and use some placeholder values, however some container groups depend on other images and will pull from a registry that you have not defined and result in an error.
You'll need to install Docker Engine on your development system. Note that while Docker Engine is free to use, Docker Desktop may require you to purchase a license. See the Docker Engine Server installation instructions for details.
Ensure you have Docker Compose installed on your machine. If you don't have this tool installed, consult the official Docker Compose installation documentation.
DOCKER_CONFIG=${DOCKER_CONFIG:-$HOME/.docker}
mkdir -p $DOCKER_CONFIG/cli-plugins
curl -SL https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/v2.26.1/docker-compose-linux-x86_64 -o $DOCKER_CONFIG/cli-plugins/docker-compose
chmod +x $DOCKER_CONFIG/cli-plugins/docker-compose
docker compose version[!CAUTION] Docker compose
v2.25.0is the minimum required version for some container groups.
Select your framework of choice (TensorFlow*, PyTorch*, Classical ML) and run the docker compose commands:
cd <framework>
docker compose up --buildTo configure these containers, simply append the relevant environment variable to the docker compose command based on the build arguments in the compose file. For example:
# I want to build ipex-base with Intel® Distribution for Python
cd pytorch
PACKAGE_OPTION=idp docker compose up --build ipex-base[!NOTE] If you didn't specify
REGISTRYorREPO, you also need to add theidpservice to the list to build the dependent python image.
To test the containers, use the Test Runner Framework:
# I want to test ipex-base with Intel® Distribution for Python
# 1. build the container in the above section
# 2. push it to a relevant registry
PACKAGE_OPTION=idp docker compose push ipex-base
cd ..
# 3. install the test runner python requirements
pip install -r test-runner/requirements.txt
# 4. Run the test file
PACKAGE_OPTION=idp python test-runner/test_runner.py -f pytorch/tests/tests.yaml[!TIP] To test a container built by GitHub Actions CI/CD, find the
run numberassociated with the workflow run and set theGITHUB_RUN_NUMBERenvironment variable during execution to pull the desired image.
Install Helm
This assumes you've setup kubectl and have a KUBECONFIG.
curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3 && \
chmod 700 get_helm.sh && \
./get_helm.shcd workflows/charts
# Select a Chart and check its README for a list of customization options and other steps required.
helm install <name> \
--namespace=<namespace> \
--set <key>=<value> \
<chart-folder>Install Chart Testing.
pip install -r workflows/charts/dev-requirements.txt
brew install chart-testingUtilize the ct CLI to run helm lint, helm install, and helm test.
ct lint-and-install --namespace=<namespace> --config .github/ct.yaml --charts workflow/charts/<chart>- See the Docker Troubleshooting Article.
- Verify that Docker Engine Post-Install Steps are completed.
- When facing socket error check the group membership of the user and ensure they are part of the
dockergroup. - After changing any docker files or configs, restart the docker service
sudo systemctl restart docker. - Enable Docker Desktop for WSL 2.
- If you are trying to access a container UI from the browser, make sure you have port forwarded and reconnect.
- If your environment requires a proxy to access the internet, export your development system's proxy settings to the docker environment:
export DOCKER_BUILD_ARGS="--build-arg ftp_proxy=${ftp_proxy} \
--build-arg FTP_PROXY=${FTP_PROXY} --build-arg http_proxy=${http_proxy} \
--build-arg HTTP_PROXY=${HTTP_PROXY} --build-arg https_proxy=${https_proxy} \
--build-arg HTTPS_PROXY=${HTTPS_PROXY} --build-arg no_proxy=${no_proxy} \
--build-arg NO_PROXY=${NO_PROXY} --build-arg socks_proxy=${socks_proxy} \
--build-arg SOCKS_PROXY=${SOCKS_PROXY}"export DOCKER_RUN_ENVS="-e ftp_proxy=${ftp_proxy} \
-e FTP_PROXY=${FTP_PROXY} -e http_proxy=${http_proxy} \
-e HTTP_PROXY=${HTTP_PROXY} -e https_proxy=${https_proxy} \
-e HTTPS_PROXY=${HTTPS_PROXY} -e no_proxy=${no_proxy} \
-e NO_PROXY=${NO_PROXY} -e socks_proxy=${socks_proxy} \
-e SOCKS_PROXY=${SOCKS_PROXY}"docker build $DOCKER_BUILD_ARGS -t my:tag .
docker run $DOCKER_RUN_ENVS --rm -it my:tagThe Intel AI MLOps team tracks bugs and enhancement requests using GitHub issues. Before submitting a suggestion or bug report, search the existing GitHub issues to see if your issue has already been reported.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for ai-containers
Similar Open Source Tools

ai-containers
This repository contains Dockerfiles, scripts, yaml files, Helm charts, etc. used to scale out AI containers with versions of TensorFlow and PyTorch optimized for Intel platforms. Scaling is done with python, Docker, kubernetes, kubeflow, cnvrg.io, Helm, and other container orchestration frameworks for use in the cloud and on-premise.
frontend
Nuclia frontend apps and libraries repository contains various frontend applications and libraries for the Nuclia platform. It includes components such as Dashboard, Widget, SDK, Sistema (design system), NucliaDB admin, CI/CD Deployment, and Maintenance page. The repository provides detailed instructions on installation, dependencies, and usage of these components for both Nuclia employees and external developers. It also covers deployment processes for different components and tools like ArgoCD for monitoring deployments and logs. The repository aims to facilitate the development, testing, and deployment of frontend applications within the Nuclia ecosystem.
jupyter-quant
Jupyter Quant is a dockerized environment tailored for quantitative research, equipped with essential tools like statsmodels, pymc, arch, py_vollib, zipline-reloaded, PyPortfolioOpt, numpy, pandas, sci-py, scikit-learn, yellowbricks, shap, optuna, and more. It provides Interactive Broker connectivity via ib_async and includes major Python packages for statistical and time series analysis. The image is optimized for size, includes jedi language server, jupyterlab-lsp, and common command line utilities. Users can install new packages with sudo, leverage apt cache, and bring their own dot files and SSH keys. The tool is designed for ephemeral containers, ensuring data persistence and flexibility for quantitative analysis tasks.
backend.ai-webui
Backend.AI Web UI is a user-friendly web and app interface designed to make AI accessible for end-users, DevOps, and SysAdmins. It provides features for session management, inference service management, pipeline management, storage management, node management, statistics, configurations, license checking, plugins, help & manuals, kernel management, user management, keypair management, manager settings, proxy mode support, service information, and integration with the Backend.AI Web Server. The tool supports various devices, offers a built-in websocket proxy feature, and allows for versatile usage across different platforms. Users can easily manage resources, run environment-supported apps, access a web-based terminal, use Visual Studio Code editor, manage experiments, set up autoscaling, manage pipelines, handle storage, monitor nodes, view statistics, configure settings, and more.
steel-browser
Steel is an open-source browser API designed for AI agents and applications, simplifying the process of building live web agents and browser automation tools. It serves as a core building block for a production-ready, containerized browser sandbox with features like stealth capabilities, text-to-markdown session management, UI for session viewing/debugging, and full browser control through popular automation frameworks. Steel allows users to control, run, and manage a production-ready browser environment via a REST API, offering features such as full browser control, session management, proxy support, extension support, debugging tools, anti-detection mechanisms, resource management, and various browser tools. It aims to streamline complex browsing tasks programmatically, enabling users to focus on their AI applications while Steel handles the underlying complexity.
trieve
Trieve is an advanced relevance API for hybrid search, recommendations, and RAG. It offers a range of features including self-hosting, semantic dense vector search, typo tolerant full-text/neural search, sub-sentence highlighting, recommendations, convenient RAG API routes, the ability to bring your own models, hybrid search with cross-encoder re-ranking, recency biasing, tunable popularity-based ranking, filtering, duplicate detection, and grouping. Trieve is designed to be flexible and customizable, allowing users to tailor it to their specific needs. It is also easy to use, with a simple API and well-documented features.
jupyter-quant
Jupyter Quant is a dockerized environment tailored for quantitative research, equipped with essential tools like statsmodels, pymc, arch, py_vollib, zipline-reloaded, PyPortfolioOpt, numpy, pandas, sci-py, scikit-learn, yellowbricks, shap, optuna, ib_insync, Cython, Numba, bottleneck, numexpr, jedi language server, jupyterlab-lsp, black, isort, and more. It does not include conda/mamba and relies on pip for package installation. The image is optimized for size, includes common command line utilities, supports apt cache, and allows for the installation of additional packages. It is designed for ephemeral containers, ensuring data persistence, and offers volumes for data, configuration, and notebooks. Common tasks include setting up the server, managing configurations, setting passwords, listing installed packages, passing parameters to jupyter-lab, running commands in the container, building wheels outside the container, installing dotfiles and SSH keys, and creating SSH tunnels.
langstream
LangStream is a tool for natural language processing tasks, providing a CLI for easy installation and usage. Users can try sample applications like Chat Completions and create their own applications using the developer documentation. It supports running on Kubernetes for production-ready deployment, with support for various Kubernetes distributions and external components like Apache Kafka or Apache Pulsar cluster. Users can deploy LangStream locally using minikube and manage the cluster with mini-langstream. Development requirements include Docker, Java 17, Git, Python 3.11+, and PIP, with the option to test local code changes using mini-langstream.
browser
Lightpanda Browser is an open-source headless browser designed for fast web automation, AI agents, LLM training, scraping, and testing. It features ultra-low memory footprint, exceptionally fast execution, and compatibility with Playwright and Puppeteer through CDP. Built for performance, Lightpanda offers Javascript execution, support for Web APIs, and is optimized for minimal memory usage. It is a modern solution for web scraping and automation tasks, providing a lightweight alternative to traditional browsers like Chrome.
elyra
Elyra is a set of AI-centric extensions to JupyterLab Notebooks that includes features like Visual Pipeline Editor, running notebooks/scripts as batch jobs, reusable code snippets, hybrid runtime support, script editors with execution capabilities, debugger, version control using Git, and more. It provides a comprehensive environment for data scientists and AI practitioners to develop, test, and deploy machine learning models and workflows efficiently.
AirCasting
AirCasting is a platform for gathering, visualizing, and sharing environmental data. It aims to provide a central hub for environmental data, making it easier for people to access and use this information to make informed decisions about their environment.
Oxen
Oxen is a data version control library, written in Rust. It's designed to be fast, reliable, and easy to use. Oxen can be used in a variety of ways, from a simple command line tool to a remote server to sync to, to integrations into other ecosystems such as python.
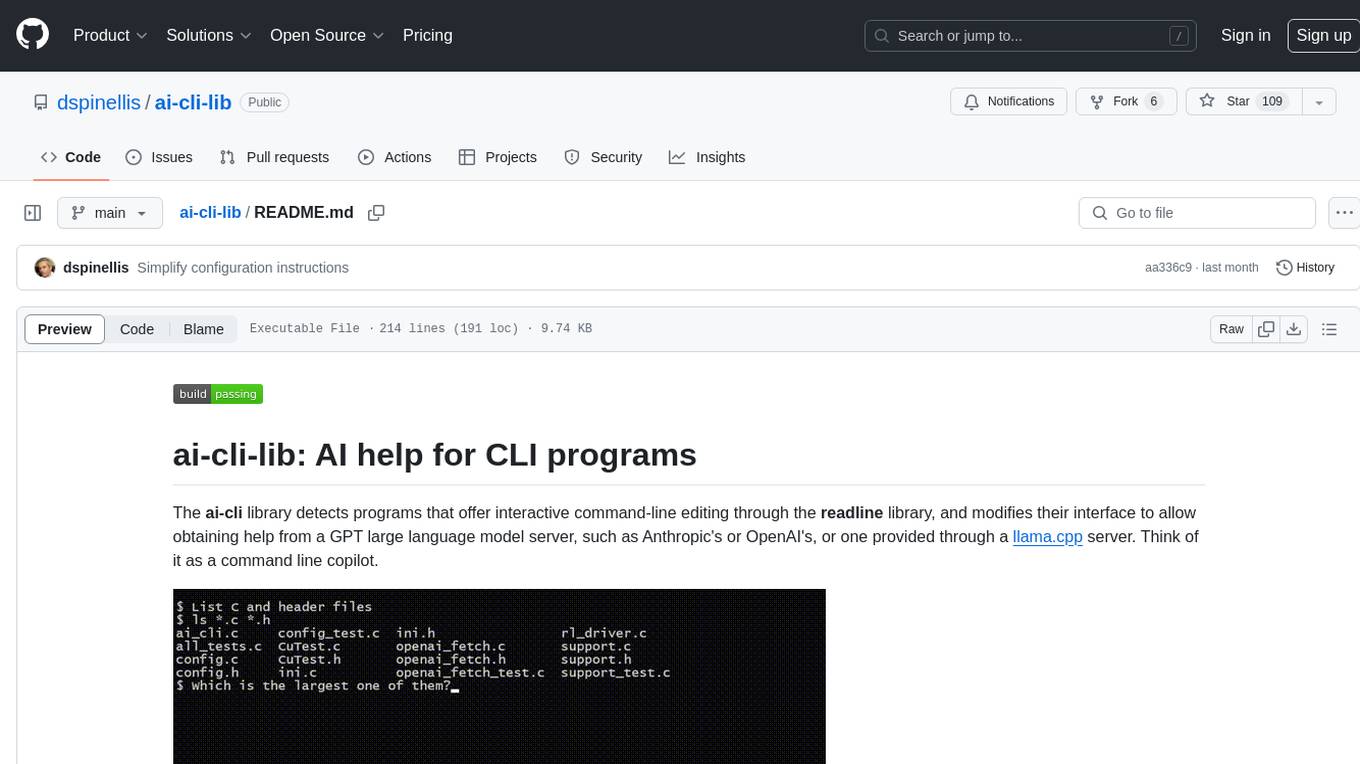
ai-cli-lib
The ai-cli-lib is a library designed to enhance interactive command-line editing programs by integrating with GPT large language model servers. It allows users to obtain AI help from servers like Anthropic's or OpenAI's, or a llama.cpp server. The library acts as a command line copilot, providing natural language prompts and responses to enhance user experience and productivity. It supports various platforms such as Debian GNU/Linux, macOS, and Cygwin, and requires specific packages for installation and operation. Users can configure the library to activate during shell startup and interact with command-line programs like bash, mysql, psql, gdb, sqlite3, and bc. Additionally, the library provides options for configuring API keys, setting up llama.cpp servers, and ensuring data privacy by managing context settings.
middleware
Middleware is an open-source engineering management tool that helps engineering leaders measure and analyze team effectiveness using DORA metrics. It integrates with CI/CD tools, automates DORA metric collection and analysis, visualizes key performance indicators, provides customizable reports and dashboards, and integrates with project management platforms. Users can set up Middleware using Docker or manually, generate encryption keys, set up backend and web servers, and access the application to view DORA metrics. The tool calculates DORA metrics using GitHub data, including Deployment Frequency, Lead Time for Changes, Mean Time to Restore, and Change Failure Rate. Middleware aims to provide DORA metrics to users based on their Git data, simplifying the process of tracking software delivery performance and operational efficiency.
mcpd
mcpd is a tool developed by Mozilla AI to declaratively manage Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers, enabling consistent interface for defining and running tools across different environments. It bridges the gap between local development and enterprise deployment by providing secure secrets management, declarative configuration, and seamless environment promotion. mcpd simplifies the developer experience by offering zero-config tool setup, language-agnostic tooling, version-controlled configuration files, enterprise-ready secrets management, and smooth transition from local to production environments.
desktop
ComfyUI Desktop is a packaged desktop application that allows users to easily use ComfyUI with bundled features like ComfyUI source code, ComfyUI-Manager, and uv. It automatically installs necessary Python dependencies and updates with stable releases. The app comes with Electron, Chromium binaries, and node modules. Users can store ComfyUI files in a specified location and manage model paths. The tool requires Python 3.12+ and Visual Studio with Desktop C++ workload for Windows. It uses nvm to manage node versions and yarn as the package manager. Users can install ComfyUI and dependencies using comfy-cli, download uv, and build/launch the code. Troubleshooting steps include rebuilding modules and installing missing libraries. The tool supports debugging in VSCode and provides utility scripts for cleanup. Crash reports can be sent to help debug issues, but no personal data is included.
For similar tasks
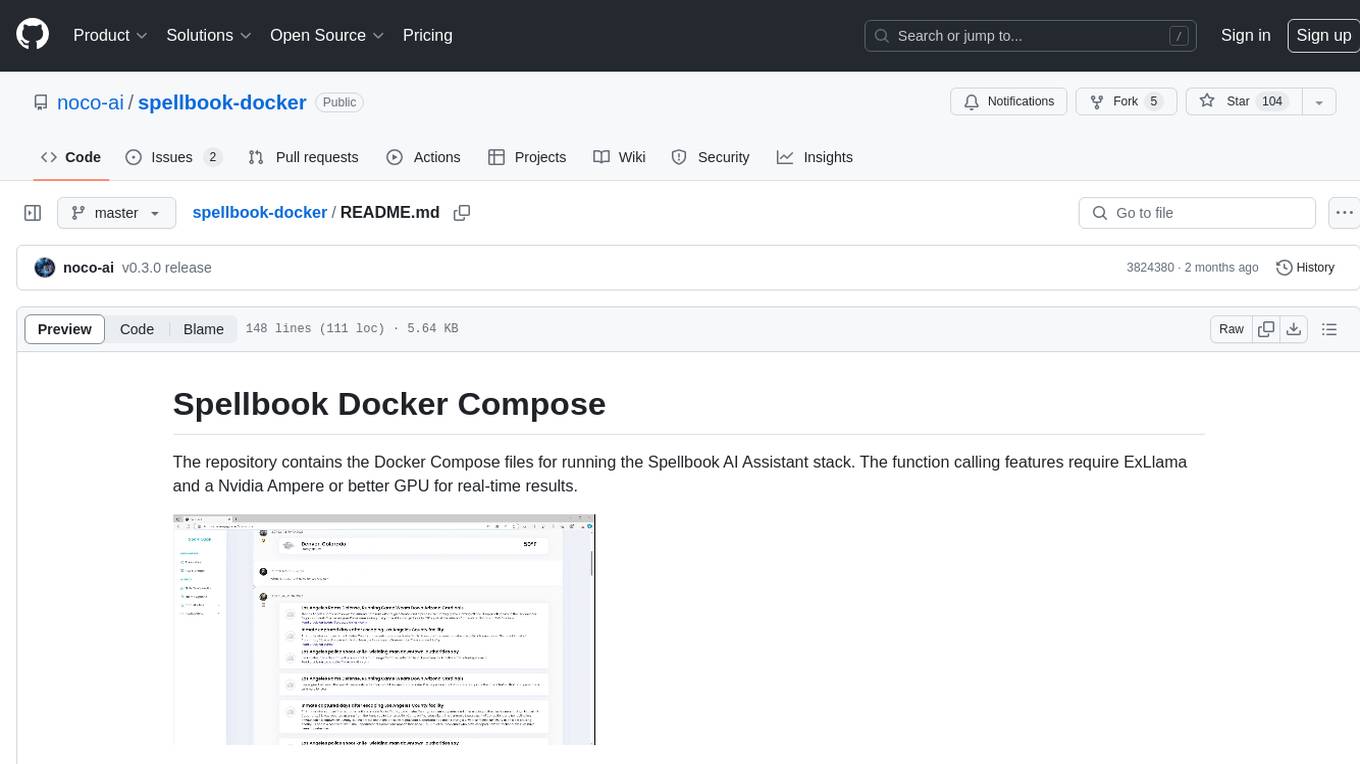
spellbook-docker
The Spellbook Docker Compose repository contains the Docker Compose files for running the Spellbook AI Assistant stack. It requires ExLlama and a Nvidia Ampere or better GPU for real-time results. The repository provides instructions for installing Docker, building and starting containers with or without GPU, additional workers, Nvidia driver installation, port forwarding, and fresh installation steps. Users can follow the detailed guidelines to set up the Spellbook framework on Ubuntu 22, enabling them to run the UI, middleware, and additional workers for resource access.

ai-containers
This repository contains Dockerfiles, scripts, yaml files, Helm charts, etc. used to scale out AI containers with versions of TensorFlow and PyTorch optimized for Intel platforms. Scaling is done with python, Docker, kubernetes, kubeflow, cnvrg.io, Helm, and other container orchestration frameworks for use in the cloud and on-premise.
fastllm
A collection of LLM services you can self host via docker or modal labs to support your applications development. The goal is to provide docker containers or modal labs deployments of common patterns when using LLMs and endpoints to integrate easily with existing codebases using the openai api. It supports GPT4all's embedding api, JSONFormer api for chat completion, Cross Encoders based on sentence transformers, and provides documentation using MkDocs.
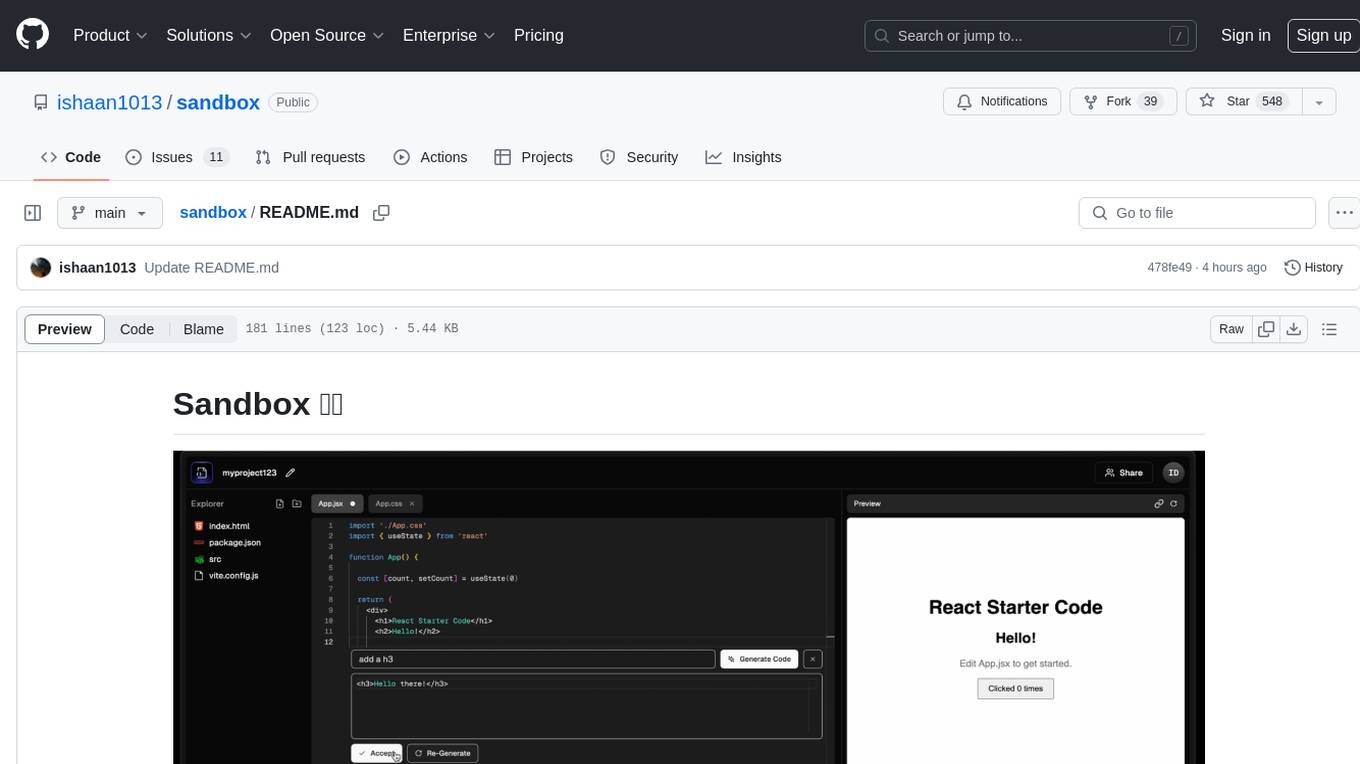
sandbox
Sandbox is an open-source cloud-based code editing environment with custom AI code autocompletion and real-time collaboration. It consists of a frontend built with Next.js, TailwindCSS, Shadcn UI, Clerk, Monaco, and Liveblocks, and a backend with Express, Socket.io, Cloudflare Workers, D1 database, R2 storage, Workers AI, and Drizzle ORM. The backend includes microservices for database, storage, and AI functionalities. Users can run the project locally by setting up environment variables and deploying the containers. Contributions are welcome following the commit convention and structure provided in the repository.
openorch
OpenOrch is a daemon that transforms servers into a powerful development environment, running AI models, containers, and microservices. It serves as a blend of Kubernetes and a language-agnostic backend framework for building applications on fixed-resource setups. Users can deploy AI models and build microservices, managing applications while retaining control over infrastructure and data.
airo
Airo is a tool designed to simplify the process of deploying containers to self-hosted servers. It allows users to focus on building their products without the complexity of Kubernetes or CI/CD pipelines. With Airo, users can easily build and push Docker images, deploy instantly with a single command, update configurations securely using SSH, and set up HTTPS and reverse proxy automatically using Caddy.
For similar jobs
TPI-LLM
TPI-LLM (Tensor Parallelism Inference for Large Language Models) is a system designed to bring LLM functions to low-resource edge devices, addressing privacy concerns by enabling LLM inference on edge devices with limited resources. It leverages multiple edge devices for inference through tensor parallelism and a sliding window memory scheduler to minimize memory usage. TPI-LLM demonstrates significant improvements in TTFT and token latency compared to other models, and plans to support infinitely large models with low token latency in the future.
KAI-Scheduler
KAI Scheduler is a robust, efficient, and scalable Kubernetes scheduler optimized for GPU resource allocation in AI and machine learning workloads. It supports batch scheduling, bin packing, spread scheduling, workload priority, hierarchical queues, resource distribution, fairness policies, workload consolidation, elastic workloads, dynamic resource allocation, GPU sharing, and works in both cloud and on-premise environments.

ai-containers
This repository contains Dockerfiles, scripts, yaml files, Helm charts, etc. used to scale out AI containers with versions of TensorFlow and PyTorch optimized for Intel platforms. Scaling is done with python, Docker, kubernetes, kubeflow, cnvrg.io, Helm, and other container orchestration frameworks for use in the cloud and on-premise.
azure-agentic-infraops
Agentic InfraOps is a multi-agent orchestration system for Azure infrastructure development that transforms how you build Azure infrastructure with AI agents. It provides a structured 7-step workflow that coordinates specialized AI agents through a complete infrastructure development cycle: Requirements → Architecture → Design → Plan → Code → Deploy → Documentation. The system enforces Azure Well-Architected Framework (WAF) alignment and Azure Verified Modules (AVM) at every phase, combining the speed of AI coding with best practices in cloud engineering.

AirGo
AirGo is a front and rear end separation, multi user, multi protocol proxy service management system, simple and easy to use. It supports vless, vmess, shadowsocks, and hysteria2.
mosec
Mosec is a high-performance and flexible model serving framework for building ML model-enabled backend and microservices. It bridges the gap between any machine learning models you just trained and the efficient online service API. * **Highly performant** : web layer and task coordination built with Rust 🦀, which offers blazing speed in addition to efficient CPU utilization powered by async I/O * **Ease of use** : user interface purely in Python 🐍, by which users can serve their models in an ML framework-agnostic manner using the same code as they do for offline testing * **Dynamic batching** : aggregate requests from different users for batched inference and distribute results back * **Pipelined stages** : spawn multiple processes for pipelined stages to handle CPU/GPU/IO mixed workloads * **Cloud friendly** : designed to run in the cloud, with the model warmup, graceful shutdown, and Prometheus monitoring metrics, easily managed by Kubernetes or any container orchestration systems * **Do one thing well** : focus on the online serving part, users can pay attention to the model optimization and business logic
llm-code-interpreter
The 'llm-code-interpreter' repository is a deprecated plugin that provides a code interpreter on steroids for ChatGPT by E2B. It gives ChatGPT access to a sandboxed cloud environment with capabilities like running any code, accessing Linux OS, installing programs, using filesystem, running processes, and accessing the internet. The plugin exposes commands to run shell commands, read files, and write files, enabling various possibilities such as running different languages, installing programs, starting servers, deploying websites, and more. It is powered by the E2B API and is designed for agents to freely experiment within a sandboxed environment.

pezzo
Pezzo is a fully cloud-native and open-source LLMOps platform that allows users to observe and monitor AI operations, troubleshoot issues, save costs and latency, collaborate, manage prompts, and deliver AI changes instantly. It supports various clients for prompt management, observability, and caching. Users can run the full Pezzo stack locally using Docker Compose, with prerequisites including Node.js 18+, Docker, and a GraphQL Language Feature Support VSCode Extension. Contributions are welcome, and the source code is available under the Apache 2.0 License.