
ai-edge-quantizer
AI Edge Quantizer: flexible post training quantization for LiteRT models.
Stars: 66
AI Edge Quantizer is a tool designed for advanced developers to quantize converted LiteRT models. It aims to optimize performance on resource-demanding models by providing quantization recipes for edge device deployment. The tool supports dynamic quantization, weight-only quantization, and static quantization methods, allowing users to customize the quantization process for different hardware deployments. Users can specify quantization recipes to apply to source models, resulting in quantized LiteRT models ready for deployment. The tool also includes advanced features such as selective quantization and mixed precision schemes for fine-tuning quantization recipes.
README:
A quantizer for advanced developers to quantize converted LiteRT models. It aims to facilitate advanced users to strive for optimal performance on resource demanding models (e.g., GenAI models).
| Build Type | Status |
|---|---|
| Unit Tests (Linux) | |
| Nightly Release | |
| Nightly Colab |
Nightly PyPi package:
pip install ai-edge-quantizer-nightlyThe quantizer requires two inputs:
- An unquantized source LiteRT model (with FP32 data type in the FlatBuffer format with
.tfliteextension) - A quantization recipe (details below)
and outputs a quantized LiteRT model that's ready for deployment on edge devices.
In a nutshell, the quantizer works according to the following steps:
- Instantiate a
Quantizerclass. This is the entry point to the quantizer's functionalities that the user accesses. - Load a desired quantization recipe (details in subsection).
- Quantize (and save) the model. This is where most of the quantizer's internal logic works.
qt = quantizer.Quantizer("path/to/input/tflite")
qt.load_quantization_recipe(recipe.dynamic_wi8_afp32())
qt.quantize().export_model("/path/to/output/tflite")Please see the getting started colab for the simplest quick start guide on those 3 steps, and the selective quantization colab with more details on advanced features.
Please refer to the LiteRT documentation for ways to generate LiteRT models from Jax, PyTorch and TensorFlow. The input source model should be an FP32 (unquantized) model in the FlatBuffer format with .tflite extension.
The user needs to specify a quantization recipe using AI Edge Quantizer's API to apply to the source model. The quantization recipe encodes all information on how a model is to be quantized, such as number of bits, data type, symmetry, scope name, etc.
Essentially, a quantization recipe is defined as a collection of commands of the following type:
“Apply Quantization Algorithm X on Operator Y under Scope Z with ConfigN”.
For example:
"Uniformly quantize the FullyConnected op under scope 'dense1/' with INT8 symmetric with Dynamic Quantization".
All the unspecified ops will be kept as FP32 (unquantized). The scope of an operator in TFLite is defined as the output tensor name of the op, which preserves the hierarchical model information from the source model (e.g., scope in TF). The best way to obtain scope name is by visualizing the model with Model Explorer.
Currently, there are three ways to quantize an operator:
-
dynamic quantization (recommended): weights are quantized while activations remain in a float format and are not processed by AI Edge Quantizer (AEQ). The runtime kernel handles the on-the-fly quantization of these activations, as identified by
compute_precision=integerandexplicit_dequantize=False.- Pros: reduced model size and memory usage. Latency improvement due to integer computation. No sample data requirement (calibration).
- Cons: on-the-fly quantization of activation tensors can affect model quality. Not supported in all hardware (e.g., some GPU and NPU).
-
weight only quantization: only model weights are quantized, not activations. The actual operation (op) computation remains in float. The quantized weight is explicitly dequantized before being fed into the op, by inserting a dequantize op between the quantized weight and the consuming op. To enable this,
compute_precisionwill be set tofloatandexplicit_dequantizetoTrue.- Pros: reduced model size and memory usage. No sample data requirement (calibration). Usually has the best model quality.
- Cons: no latency benefit (may be worse) due to float computation with explicit dequantization.
-
static quantization: both weights and activations are quantized. This requires a calibration phase to estimate quantization parameters of runtime tensors (activations).
- Pros: reduced model size, memory usage, and latency.
- Cons: requires sample data for calibration. Imposing static quantization parameters (derived from calibration) on runtime tensors can compromise quality.
Generally, we recommend dynamic quantization for CPU/GPU deployment and static quantization for NPU deployment.
We include commonly used recipes in recipe.py. This is demonstrated in the getting started colab example. Advanced users can build their own recipe through the quantizer API.
Please refer to the LiteRT deployment documentation for ways to deploy a quantized LiteRT model.
There are many ways the user can configure and customize the quantization recipe beyond using a template in recipe.py. For example, the user can configure the recipe to achieve these features:
- Selective quantization (exclude selected ops from being quantized)
- Flexible mixed scheme quantization (mixture of different precision, compute precision, scope, op, config, etc)
- 4-bit weight quantization
The selective quantization colab shows some of these more advanced features.
For specifics of the recipe schema, please refer to the OpQuantizationRecipe in [recipe_manager.py].
For advanced usage involving mixed quantization, the following API may be useful:
- Use
Quantizer:load_quantization_recipe()in quantizer.py to load a custom recipe. - Use
Quantizer:update_quantization_recipe()in quantizer.py to extend or override specific parts of the recipe.
The table below outlines the allowed configurations for available recipes.
| Config | DYNAMIC_WI8_AFP32 | DYNAMIC_WI4_AFP32 | STATIC_WI8_AI16 | STATIC_WI4_AI16 | STATIC_WI8_AI8 | STATIC_WI4_AI8 | WEIGHTONLY_WI8_AFP32 | WEIGHTONLY_WI4_AFP32 | |
| activation | num_bits | None | None | 16 | 16 | 8 | 8 | None | None |
| symmetric | None | None | TRUE | TRUE | [TRUE, FALSE] | [TRUE, FALSE] | None | None | |
| granularity | None | None | TENSORWISE | TENSORWISE | TENSORWISE | TENSORWISE | None | None | |
| dtype | None | None | INT | INT | INT | INT | None | None | |
| weight | num_bits | 8 | 4 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 4 |
| symmetric | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | [TRUE, FALSE] | [TRUE, FALSE] | |
| granularity | [CHANNELWISE, TENSORWISE] | [CHANNELWISE, TENSORWISE] | [CHANNELWISE, TENSORWISE] | [CHANNELWISE, TENSORWISE] | [CHANNELWISE, TENSORWISE] | [CHANNELWISE, TENSORWISE] | [CHANNELWISE, TENSORWISE] | [CHANNELWISE, TENSORWISE] | |
| dtype | INT | INT | INT | INT | INT | INT | INT | INT | |
| explicit_dequantize | FALSE | FALSE | FALSE | FALSE | FALSE | FALSE | TRUE | TRUE | |
| compute_precision | INTEGER | INTEGER | INTEGER | INTEGER | INTEGER | INTEGER | FLOAT | FLOAT |
Operators Supporting Quantization
| Config | DYNAMIC_WI8_AFP32 | DYNAMIC_WI4_AFP32 | STATIC_WI8_AI16 | STATIC_WI4_AI16 | STATIC_WI8_AI8 | STATIC_WI4_AI8 | WEIGHTONLY_WI8_AFP32 | WEIGHTONLY_WI4_AFP32 |
| FULLY_CONNECTED | ✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
| CONV_2D | ✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
||
| BATCH_MATMUL | ✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
||||
| EMBEDDING_LOOKUP | ✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
||
| DEPTHWISE_CONV_2D | ✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
||||
| AVERAGE_POOL_2D | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| RESHAPE | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| SOFTMAX | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| TANH | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| TRANSPOSE | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| GELU | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| ADD | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| CONV_2D_TRANSPOSE | ✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|||||
| SUB | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| MUL | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| MEAN | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| RSQRT | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| CONCATENATION | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| STRIDED_SLICE | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| SPLIT | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| LOGISTIC | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| SLICE | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| SELECT | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| SELECT_V2 | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| SUM | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| PAD | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| PADV2 | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| SQUARED_DIFFERENCE | ✓ |
|||||||
| MAX_POOL_2D | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| RESIZE_BILINEAR | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| GATHER_ND | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| PACK | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| UNPACK | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| DIV | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| SQRT | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| GATHER | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| HARD_SWISH | ✓ |
|||||||
| MAXIMUM | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| REDUCE_MIN | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| EQUAL | ✓ |
✓ |
||||||
| NOT_EQUAL | ✓ |
✓ |
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for ai-edge-quantizer
Similar Open Source Tools

ai-edge-quantizer
AI Edge Quantizer is a tool designed for advanced developers to quantize converted LiteRT models. It aims to optimize performance on resource-demanding models by providing quantization recipes for edge device deployment. The tool supports dynamic quantization, weight-only quantization, and static quantization methods, allowing users to customize the quantization process for different hardware deployments. Users can specify quantization recipes to apply to source models, resulting in quantized LiteRT models ready for deployment. The tool also includes advanced features such as selective quantization and mixed precision schemes for fine-tuning quantization recipes.
llmfit
llmfit is a terminal tool designed to optimize LLM models for your system's RAM, CPU, and GPU. It detects your hardware, scores models based on quality, speed, fit, and context, and recommends models that will run well on your machine. It supports multi-GPU setups, MoE architectures, dynamic quantization selection, and speed estimation. The tool provides an interactive TUI and a classic CLI mode for ease of use. It includes a database of 94 models from 30 providers sourced from the HuggingFace API, with memory requirements computed from parameter counts across a quantization hierarchy. llmfit uses multi-dimensional scoring to rank models and estimates speed based on backend-specific constants. It also offers dynamic quantization selection to fit models to available memory efficiently.
airllm
AirLLM is a tool that optimizes inference memory usage, enabling large language models to run on low-end GPUs without quantization, distillation, or pruning. It supports models like Llama3.1 on 8GB VRAM. The tool offers model compression for up to 3x inference speedup with minimal accuracy loss. Users can specify compression levels, profiling modes, and other configurations when initializing models. AirLLM also supports prefetching and disk space management. It provides examples and notebooks for easy implementation and usage.
FLAME
FLAME is a lightweight and efficient deep learning framework designed for edge devices. It provides a simple and user-friendly interface for developing and deploying deep learning models on resource-constrained devices. With FLAME, users can easily build and optimize neural networks for tasks such as image classification, object detection, and natural language processing. The framework supports various neural network architectures and optimization techniques, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in the field of edge computing.
checkpoint-engine
Checkpoint-engine is a middleware tool designed for updating model weights in LLM inference engines efficiently. It provides implementations for both Broadcast and P2P weight update methods, orchestrating the transfer process and controlling the inference engine through ZeroMQ socket. The tool optimizes weight broadcast by arranging data transfer into stages and organizing transfers into a pipeline for performance. It supports flexible installation options and is tested with various models and device setups. Checkpoint-engine also allows reusing weights from existing instances and provides a patch for FP8 quantization in vLLM.
Fast-dLLM
Fast-DLLM is a diffusion-based Large Language Model (LLM) inference acceleration framework that supports efficient inference for models like Dream and LLaDA. It offers fast inference support, multiple optimization strategies, code generation, evaluation capabilities, and an interactive chat interface. Key features include Key-Value Cache for Block-Wise Decoding, Confidence-Aware Parallel Decoding, and overall performance improvements. The project structure includes directories for Dream and LLaDA model-related code, with installation and usage instructions provided for using the LLaDA and Dream models.
AI_Spectrum
AI_Spectrum is a versatile machine learning library that provides a wide range of tools and algorithms for building and deploying AI models. It offers a user-friendly interface for data preprocessing, model training, and evaluation. With AI_Spectrum, users can easily experiment with different machine learning techniques and optimize their models for various tasks. The library is designed to be flexible and scalable, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced data scientists.
openvino
OpenVINO™ is an open-source toolkit for optimizing and deploying AI inference. It provides a common API to deliver inference solutions on various platforms, including CPU, GPU, NPU, and heterogeneous devices. OpenVINO™ supports pre-trained models from Open Model Zoo and popular frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and ONNX. Key components of OpenVINO™ include the OpenVINO™ Runtime, plugins for different hardware devices, frontends for reading models from native framework formats, and the OpenVINO Model Converter (OVC) for adjusting models for optimal execution on target devices.
ml-retreat
ML-Retreat is a comprehensive machine learning library designed to simplify and streamline the process of building and deploying machine learning models. It provides a wide range of tools and utilities for data preprocessing, model training, evaluation, and deployment. With ML-Retreat, users can easily experiment with different algorithms, hyperparameters, and feature engineering techniques to optimize their models. The library is built with a focus on scalability, performance, and ease of use, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced machine learning practitioners.
edge-ai-libraries
The Edge AI Libraries project is a collection of libraries, microservices, and tools for Edge application development. It includes sample applications showcasing generic AI use cases. Key components include Anomalib, Dataset Management Framework, Deep Learning Streamer, ECAT EnableKit, EtherCAT Masterstack, FLANN, OpenVINO toolkit, Audio Analyzer, ORB Extractor, PCL, PLCopen Servo, Real-time Data Agent, RTmotion, Audio Intelligence, Deep Learning Streamer Pipeline Server, Document Ingestion, Model Registry, Multimodal Embedding Serving, Time Series Analytics, Vector Retriever, Visual-Data Preparation, VLM Inference Serving, Intel Geti, Intel SceneScape, Visual Pipeline and Platform Evaluation Tool, Chat Question and Answer, Document Summarization, PLCopen Benchmark, PLCopen Databus, Video Search and Summarization, Isolation Forest Classifier, Random Forest Microservices. Visit sub-directories for instructions and guides.
Automodel
Automodel is a Python library for automating the process of building and evaluating machine learning models. It provides a set of tools and utilities to streamline the model development workflow, from data preprocessing to model selection and evaluation. With Automodel, users can easily experiment with different algorithms, hyperparameters, and feature engineering techniques to find the best model for their dataset. The library is designed to be user-friendly and customizable, allowing users to define their own pipelines and workflows. Automodel is suitable for data scientists, machine learning engineers, and anyone looking to quickly build and test machine learning models without the need for manual intervention.
ktransformers
KTransformers is a flexible Python-centric framework designed to enhance the user's experience with advanced kernel optimizations and placement/parallelism strategies for Transformers. It provides a Transformers-compatible interface, RESTful APIs compliant with OpenAI and Ollama, and a simplified ChatGPT-like web UI. The framework aims to serve as a platform for experimenting with innovative LLM inference optimizations, focusing on local deployments constrained by limited resources and supporting heterogeneous computing opportunities like GPU/CPU offloading of quantized models.
speculators
Speculators is a unified library for building, training, and storing speculative decoding algorithms for large language model (LLM) inference. It speeds up LLM inference by using a smaller, faster draft model (the speculator) to propose tokens, which are then verified by the larger base model, reducing latency without compromising output quality. Trained models can seamlessly run in vLLM, enabling the deployment of speculative decoding in production-grade inference servers.
BentoVLLM
BentoVLLM is an example project demonstrating how to serve and deploy open-source Large Language Models using vLLM, a high-throughput and memory-efficient inference engine. It provides a basis for advanced code customization, such as custom models, inference logic, or vLLM options. The project allows for simple LLM hosting with OpenAI compatible endpoints without the need to write any code. Users can interact with the server using Swagger UI or other methods, and the service can be deployed to BentoCloud for better management and scalability. Additionally, the repository includes integration examples for different LLM models and tools.
lemonai
LemonAI is a versatile machine learning library designed to simplify the process of building and deploying AI models. It provides a wide range of tools and algorithms for data preprocessing, model training, and evaluation. With LemonAI, users can easily experiment with different machine learning techniques and optimize their models for various tasks. The library is well-documented and beginner-friendly, making it suitable for both novice and experienced data scientists. LemonAI aims to streamline the development of AI applications and empower users to create innovative solutions using state-of-the-art machine learning methods.
RustGPT
A complete Large Language Model implementation in pure Rust with no external ML frameworks. Demonstrates building a transformer-based language model from scratch, including pre-training, instruction tuning, interactive chat mode, full backpropagation, and modular architecture. Model learns basic world knowledge and conversational patterns. Features custom tokenization, greedy decoding, gradient clipping, modular layer system, and comprehensive test coverage. Ideal for understanding modern LLMs and key ML concepts. Dependencies include ndarray for matrix operations and rand for random number generation. Contributions welcome for model persistence, performance optimizations, better sampling, evaluation metrics, advanced architectures, training improvements, data handling, and model analysis. Follows standard Rust conventions and encourages contributions at beginner, intermediate, and advanced levels.
For similar tasks

ai-edge-quantizer
AI Edge Quantizer is a tool designed for advanced developers to quantize converted LiteRT models. It aims to optimize performance on resource-demanding models by providing quantization recipes for edge device deployment. The tool supports dynamic quantization, weight-only quantization, and static quantization methods, allowing users to customize the quantization process for different hardware deployments. Users can specify quantization recipes to apply to source models, resulting in quantized LiteRT models ready for deployment. The tool also includes advanced features such as selective quantization and mixed precision schemes for fine-tuning quantization recipes.
neural-compressor
Intel® Neural Compressor is an open-source Python library that supports popular model compression techniques such as quantization, pruning (sparsity), distillation, and neural architecture search on mainstream frameworks such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, ONNX Runtime, and MXNet. It provides key features, typical examples, and open collaborations, including support for a wide range of Intel hardware, validation of popular LLMs, and collaboration with cloud marketplaces, software platforms, and open AI ecosystems.
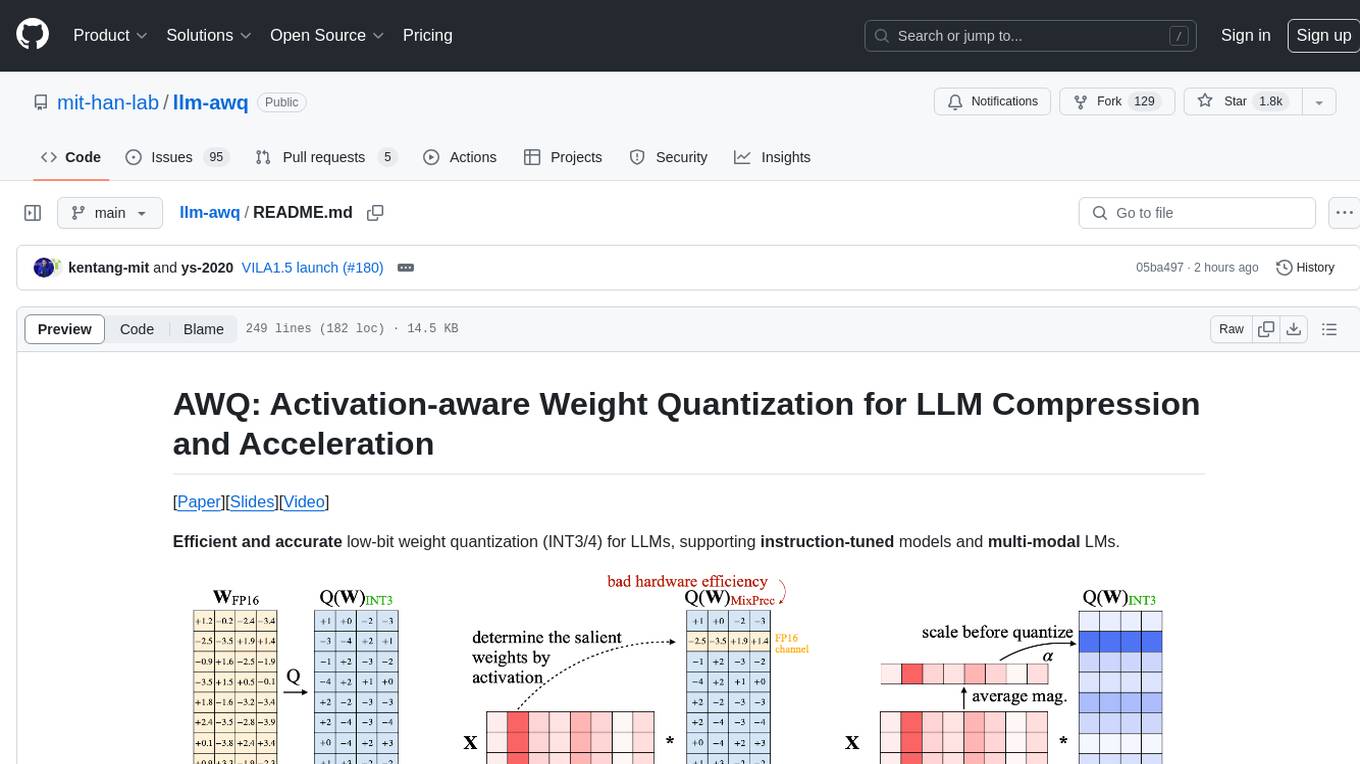
llm-awq
AWQ (Activation-aware Weight Quantization) is a tool designed for efficient and accurate low-bit weight quantization (INT3/4) for Large Language Models (LLMs). It supports instruction-tuned models and multi-modal LMs, providing features such as AWQ search for accurate quantization, pre-computed AWQ model zoo for various LLMs, memory-efficient 4-bit linear in PyTorch, and efficient CUDA kernel implementation for fast inference. The tool enables users to run large models on resource-constrained edge platforms, delivering more efficient responses with LLM/VLM chatbots through 4-bit inference.
PrefixQuant
PrefixQuant is an official PyTorch implementation for static quantization that outperforms dynamic quantization in Large Language Models (LLMs) by utilizing prefixed outliers. The tool provides functionalities for quantization, inference, and visualization of activation distributions. Users can fine-tune quantization settings and evaluate pre-quantized models for tasks like PIQA, ARC, Hellaswag, and Winogrande. The approach aims to improve performance and efficiency in LLMs through innovative quantization techniques.
ck
Collective Mind (CM) is a collection of portable, extensible, technology-agnostic and ready-to-use automation recipes with a human-friendly interface (aka CM scripts) to unify and automate all the manual steps required to compose, run, benchmark and optimize complex ML/AI applications on any platform with any software and hardware: see online catalog and source code. CM scripts require Python 3.7+ with minimal dependencies and are continuously extended by the community and MLCommons members to run natively on Ubuntu, MacOS, Windows, RHEL, Debian, Amazon Linux and any other operating system, in a cloud or inside automatically generated containers while keeping backward compatibility - please don't hesitate to report encountered issues here and contact us via public Discord Server to help this collaborative engineering effort! CM scripts were originally developed based on the following requirements from the MLCommons members to help them automatically compose and optimize complex MLPerf benchmarks, applications and systems across diverse and continuously changing models, data sets, software and hardware from Nvidia, Intel, AMD, Google, Qualcomm, Amazon and other vendors: * must work out of the box with the default options and without the need to edit some paths, environment variables and configuration files; * must be non-intrusive, easy to debug and must reuse existing user scripts and automation tools (such as cmake, make, ML workflows, python poetry and containers) rather than substituting them; * must have a very simple and human-friendly command line with a Python API and minimal dependencies; * must require minimal or zero learning curve by using plain Python, native scripts, environment variables and simple JSON/YAML descriptions instead of inventing new workflow languages; * must have the same interface to run all automations natively, in a cloud or inside containers. CM scripts were successfully validated by MLCommons to modularize MLPerf inference benchmarks and help the community automate more than 95% of all performance and power submissions in the v3.1 round across more than 120 system configurations (models, frameworks, hardware) while reducing development and maintenance costs.
aimet
AIMET is a library that provides advanced model quantization and compression techniques for trained neural network models. It provides features that have been proven to improve run-time performance of deep learning neural network models with lower compute and memory requirements and minimal impact to task accuracy. AIMET is designed to work with PyTorch, TensorFlow and ONNX models. We also host the AIMET Model Zoo - a collection of popular neural network models optimized for 8-bit inference. We also provide recipes for users to quantize floating point models using AIMET.
byteir
The ByteIR Project is a ByteDance model compilation solution. ByteIR includes compiler, runtime, and frontends, and provides an end-to-end model compilation solution. Although all ByteIR components (compiler/runtime/frontends) are together to provide an end-to-end solution, and all under the same umbrella of this repository, each component technically can perform independently. The name, ByteIR, comes from a legacy purpose internally. The ByteIR project is NOT an IR spec definition project. Instead, in most scenarios, ByteIR directly uses several upstream MLIR dialects and Google Mhlo. Most of ByteIR compiler passes are compatible with the selected upstream MLIR dialects and Google Mhlo.
hqq
HQQ is a fast and accurate model quantizer that skips the need for calibration data. It's super simple to implement (just a few lines of code for the optimizer). It can crunch through quantizing the Llama2-70B model in only 4 minutes! 🚀
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.
