
airllm
AirLLM 70B inference with single 4GB GPU
Stars: 5909
AirLLM is a tool that optimizes inference memory usage, enabling large language models to run on low-end GPUs without quantization, distillation, or pruning. It supports models like Llama3.1 on 8GB VRAM. The tool offers model compression for up to 3x inference speedup with minimal accuracy loss. Users can specify compression levels, profiling modes, and other configurations when initializing models. AirLLM also supports prefetching and disk space management. It provides examples and notebooks for easy implementation and usage.
README:
Quickstart | Configurations | MacOS | Example notebooks | FAQ
AirLLM optimizes inference memory usage, allowing 70B large language models to run inference on a single 4GB GPU card without quantization, distillation and pruning. And you can run 405B Llama3.1 on 8GB vram now.
[2024/08/20] v2.11.0: Support Qwen2.5
[2024/08/18] v2.10.1 Support CPU inference. Support non sharded models. Thanks @NavodPeiris for the great work!
[2024/07/30] Support Llama3.1 405B (example notebook). Support 8bit/4bit quantization.
[2024/04/20] AirLLM supports Llama3 natively already. Run Llama3 70B on 4GB single GPU.
[2023/12/25] v2.8.2: Support MacOS running 70B large language models.
[2023/12/20] v2.7: Support AirLLMMixtral.
[2023/12/20] v2.6: Added AutoModel, automatically detect model type, no need to provide model class to initialize model.
[2023/12/18] v2.5: added prefetching to overlap the model loading and compute. 10% speed improvement.
[2023/12/03] added support of ChatGLM, QWen, Baichuan, Mistral, InternLM!
[2023/12/02] added support for safetensors. Now support all top 10 models in open llm leaderboard.
[2023/12/01] airllm 2.0. Support compressions: 3x run time speed up!
[2023/11/20] airllm Initial version!
- Quick start
- Model Compression
- Configurations
- Run on MacOS
- Example notebooks
- Supported Models
- Acknowledgement
- FAQ
First, install the airllm pip package.
pip install airllmThen, initialize AirLLMLlama2, pass in the huggingface repo ID of the model being used, or the local path, and inference can be performed similar to a regular transformer model.
(You can also specify the path to save the splitted layered model through layer_shards_saving_path when init AirLLMLlama2.
from airllm import AutoModel
MAX_LENGTH = 128
# could use hugging face model repo id:
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("garage-bAInd/Platypus2-70B-instruct")
# or use model's local path...
#model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("/home/ubuntu/.cache/huggingface/hub/models--garage-bAInd--Platypus2-70B-instruct/snapshots/b585e74bcaae02e52665d9ac6d23f4d0dbc81a0f")
input_text = [
'What is the capital of United States?',
#'I like',
]
input_tokens = model.tokenizer(input_text,
return_tensors="pt",
return_attention_mask=False,
truncation=True,
max_length=MAX_LENGTH,
padding=False)
generation_output = model.generate(
input_tokens['input_ids'].cuda(),
max_new_tokens=20,
use_cache=True,
return_dict_in_generate=True)
output = model.tokenizer.decode(generation_output.sequences[0])
print(output)Note: During inference, the original model will first be decomposed and saved layer-wise. Please ensure there is sufficient disk space in the huggingface cache directory.
We just added model compression based on block-wise quantization-based model compression. Which can further speed up the inference speed for up to 3x , with almost ignorable accuracy loss! (see more performance evaluation and why we use block-wise quantization in this paper)
- Step 1. make sure you have bitsandbytes installed by
pip install -U bitsandbytes - Step 2. make sure airllm verion later than 2.0.0:
pip install -U airllm - Step 3. when initialize the model, passing the argument compression ('4bit' or '8bit'):
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("garage-bAInd/Platypus2-70B-instruct",
compression='4bit' # specify '8bit' for 8-bit block-wise quantization
)Quantization normally needs to quantize both weights and activations to really speed things up. Which makes it harder to maintain accuracy and avoid the impact of outliers in all kinds of inputs.
While in our case the bottleneck is mainly at the disk loading, we only need to make the model loading size smaller. So, we get to only quantize the weights' part, which is easier to ensure the accuracy.
When initialize the model, we support the following configurations:
- compression: supported options: 4bit, 8bit for 4-bit or 8-bit block-wise quantization, or by default None for no compression
- profiling_mode: supported options: True to output time consumptions or by default False
- layer_shards_saving_path: optionally another path to save the splitted model
- hf_token: huggingface token can be provided here if downloading gated models like: meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf
- prefetching: prefetching to overlap the model loading and compute. By default, turned on. For now, only AirLLMLlama2 supports this.
- delete_original: if you don't have too much disk space, you can set delete_original to true to delete the original downloaded hugging face model, only keep the transformed one to save half of the disk space.
Just install airllm and run the code the same as on linux. See more in Quick Start.
- make sure you installed mlx and torch
- you probably need to install python native see more here
- only Apple silicon is supported
Example [python notebook] (https://github.com/lyogavin/airllm/blob/main/air_llm/examples/run_on_macos.ipynb)
Example colabs here:
- ChatGLM:
from airllm import AutoModel
MAX_LENGTH = 128
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("THUDM/chatglm3-6b-base")
input_text = ['What is the capital of China?',]
input_tokens = model.tokenizer(input_text,
return_tensors="pt",
return_attention_mask=False,
truncation=True,
max_length=MAX_LENGTH,
padding=True)
generation_output = model.generate(
input_tokens['input_ids'].cuda(),
max_new_tokens=5,
use_cache= True,
return_dict_in_generate=True)
model.tokenizer.decode(generation_output.sequences[0])- QWen:
from airllm import AutoModel
MAX_LENGTH = 128
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen-7B")
input_text = ['What is the capital of China?',]
input_tokens = model.tokenizer(input_text,
return_tensors="pt",
return_attention_mask=False,
truncation=True,
max_length=MAX_LENGTH)
generation_output = model.generate(
input_tokens['input_ids'].cuda(),
max_new_tokens=5,
use_cache=True,
return_dict_in_generate=True)
model.tokenizer.decode(generation_output.sequences[0])- Baichuan, InternLM, Mistral, etc:
from airllm import AutoModel
MAX_LENGTH = 128
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("baichuan-inc/Baichuan2-7B-Base")
#model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("internlm/internlm-20b")
#model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.1")
input_text = ['What is the capital of China?',]
input_tokens = model.tokenizer(input_text,
return_tensors="pt",
return_attention_mask=False,
truncation=True,
max_length=MAX_LENGTH)
generation_output = model.generate(
input_tokens['input_ids'].cuda(),
max_new_tokens=5,
use_cache=True,
return_dict_in_generate=True)
model.tokenizer.decode(generation_output.sequences[0])To request other model support: here
A lot of the code are based on SimJeg's great work in the Kaggle exam competition. Big shoutout to SimJeg:
GitHub account @SimJeg, the code on Kaggle, the associated discussion.
safetensors_rust.SafetensorError: Error while deserializing header: MetadataIncompleteBuffer
If you run into this error, most possible cause is you run out of disk space. The process of splitting model is very disk-consuming. See this. You may need to extend your disk space, clear huggingface .cache and rerun.
Most likely you are loading QWen or ChatGLM model with Llama2 class. Try the following:
For QWen model:
from airllm import AutoModel #<----- instead of AirLLMLlama2
AutoModel.from_pretrained(...)For ChatGLM model:
from airllm import AutoModel #<----- instead of AirLLMLlama2
AutoModel.from_pretrained(...)Some models are gated models, needs huggingface api token. You can provide hf_token:
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf", #hf_token='HF_API_TOKEN')Some model's tokenizer doesn't have padding token, so you can set a padding token or simply turn the padding config off:
input_tokens = model.tokenizer(input_text,
return_tensors="pt",
return_attention_mask=False,
truncation=True,
max_length=MAX_LENGTH,
padding=False #<----------- turn off padding
)If you find AirLLM useful in your research and wish to cite it, please use the following BibTex entry:
@software{airllm2023,
author = {Gavin Li},
title = {AirLLM: scaling large language models on low-end commodity computers},
url = {https://github.com/lyogavin/airllm/},
version = {0.0},
year = {2023},
}
Welcomed contributions, ideas and discussions!
If you find it useful, please ⭐ or buy me a coffee! 🙏
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for airllm
Similar Open Source Tools

airllm
AirLLM is a tool that optimizes inference memory usage, enabling large language models to run on low-end GPUs without quantization, distillation, or pruning. It supports models like Llama3.1 on 8GB VRAM. The tool offers model compression for up to 3x inference speedup with minimal accuracy loss. Users can specify compression levels, profiling modes, and other configurations when initializing models. AirLLM also supports prefetching and disk space management. It provides examples and notebooks for easy implementation and usage.
llmfit
llmfit is a terminal tool designed to optimize LLM models for your system's RAM, CPU, and GPU. It detects your hardware, scores models based on quality, speed, fit, and context, and recommends models that will run well on your machine. It supports multi-GPU setups, MoE architectures, dynamic quantization selection, and speed estimation. The tool provides an interactive TUI and a classic CLI mode for ease of use. It includes a database of 94 models from 30 providers sourced from the HuggingFace API, with memory requirements computed from parameter counts across a quantization hierarchy. llmfit uses multi-dimensional scoring to rank models and estimates speed based on backend-specific constants. It also offers dynamic quantization selection to fit models to available memory efficiently.
Fast-dLLM
Fast-DLLM is a diffusion-based Large Language Model (LLM) inference acceleration framework that supports efficient inference for models like Dream and LLaDA. It offers fast inference support, multiple optimization strategies, code generation, evaluation capabilities, and an interactive chat interface. Key features include Key-Value Cache for Block-Wise Decoding, Confidence-Aware Parallel Decoding, and overall performance improvements. The project structure includes directories for Dream and LLaDA model-related code, with installation and usage instructions provided for using the LLaDA and Dream models.
ai-inference
AI Inference is a Python library that provides tools for deploying and running machine learning models in production environments. It simplifies the process of integrating AI models into applications by offering a high-level API for inference tasks. With AI Inference, developers can easily load pre-trained models, perform inference on new data, and deploy models as RESTful APIs. The library supports various deep learning frameworks such as TensorFlow and PyTorch, making it versatile for a wide range of AI applications.
BentoVLLM
BentoVLLM is an example project demonstrating how to serve and deploy open-source Large Language Models using vLLM, a high-throughput and memory-efficient inference engine. It provides a basis for advanced code customization, such as custom models, inference logic, or vLLM options. The project allows for simple LLM hosting with OpenAI compatible endpoints without the need to write any code. Users can interact with the server using Swagger UI or other methods, and the service can be deployed to BentoCloud for better management and scalability. Additionally, the repository includes integration examples for different LLM models and tools.
AI_Spectrum
AI_Spectrum is a versatile machine learning library that provides a wide range of tools and algorithms for building and deploying AI models. It offers a user-friendly interface for data preprocessing, model training, and evaluation. With AI_Spectrum, users can easily experiment with different machine learning techniques and optimize their models for various tasks. The library is designed to be flexible and scalable, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced data scientists.
MemOS
MemOS is an operating system for Large Language Models (LLMs) that enhances them with long-term memory capabilities. It allows LLMs to store, retrieve, and manage information, enabling more context-aware, consistent, and personalized interactions. MemOS provides Memory-Augmented Generation (MAG) with a unified API for memory operations, a Modular Memory Architecture (MemCube) for easy integration and management of different memory types, and multiple memory types including Textual Memory, Activation Memory, and Parametric Memory. It is extensible, allowing users to customize memory modules, data sources, and LLM integrations. MemOS demonstrates significant improvements over baseline memory solutions in multiple reasoning tasks, with a notable improvement in temporal reasoning accuracy compared to the OpenAI baseline.
distributed-llama
Distributed Llama is a tool that allows you to run large language models (LLMs) on weak devices or make powerful devices even more powerful by distributing the workload and dividing the RAM usage. It uses TCP sockets to synchronize the state of the neural network, and you can easily configure your AI cluster by using a home router. Distributed Llama supports models such as Llama 2 (7B, 13B, 70B) chat and non-chat versions, Llama 3, and Grok-1 (314B).
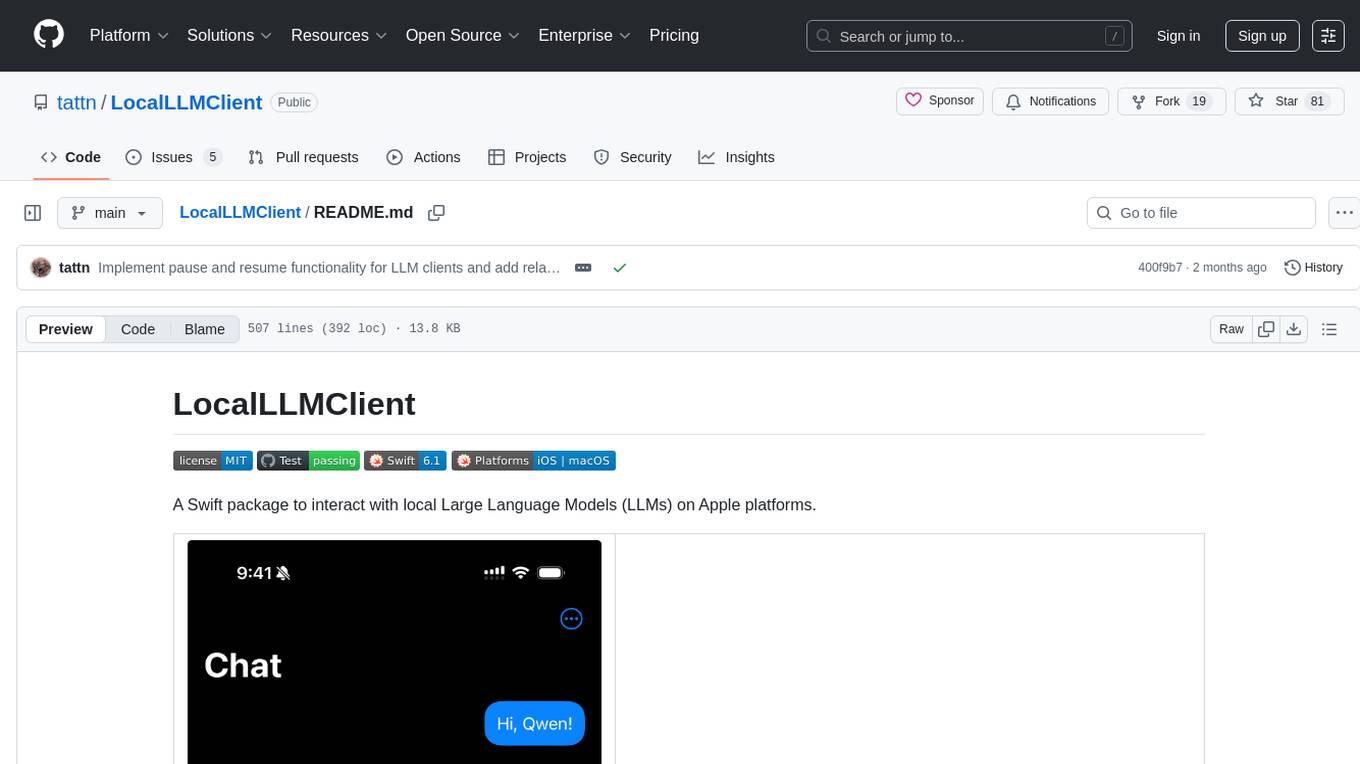
LocalLLMClient
LocalLLMClient is a Swift package designed to interact with local Large Language Models (LLMs) on Apple platforms. It supports GGUF, MLX models, and the FoundationModels framework, providing streaming API, multimodal capabilities, and tool calling functionalities. Users can easily integrate this tool to work with various models for text generation and processing. The package also includes advanced features for low-level API control and multimodal image processing. LocalLLMClient is experimental and subject to API changes, offering support for iOS, macOS, and Linux platforms.
distill
Distill is a reliability layer for LLM context that provides deterministic deduplication to remove redundancy before reaching the model. It aims to reduce redundant data, lower costs, provide faster responses, and offer more efficient and deterministic results. The tool works by deduplicating, compressing, summarizing, and caching context to ensure reliable outputs. It offers various installation methods, including binary download, Go install, Docker usage, and building from source. Distill can be used for tasks like deduplicating chunks, connecting to vector databases, integrating with AI assistants, analyzing files for duplicates, syncing vectors to Pinecone, querying from the command line, and managing configuration files. The tool supports self-hosting via Docker, Docker Compose, building from source, Fly.io deployment, Render deployment, and Railway integration. Distill also provides monitoring capabilities with Prometheus-compatible metrics, Grafana dashboard, and OpenTelemetry tracing.
osaurus
Osaurus is a versatile open-source tool designed for data scientists and machine learning engineers. It provides a wide range of functionalities for data preprocessing, feature engineering, model training, and evaluation. With Osaurus, users can easily clean and transform raw data, extract relevant features, build and tune machine learning models, and analyze model performance. The tool supports various machine learning algorithms and techniques, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced practitioners in the field. Osaurus is actively maintained and updated to incorporate the latest advancements in the machine learning domain, ensuring users have access to state-of-the-art tools and methodologies for their projects.
pdr_ai_v2
pdr_ai_v2 is a Python library for implementing machine learning algorithms and models. It provides a wide range of tools and functionalities for data preprocessing, model training, evaluation, and deployment. The library is designed to be user-friendly and efficient, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced data scientists. With pdr_ai_v2, users can easily build and deploy machine learning models for various applications, such as classification, regression, clustering, and more.
data-juicer
Data-Juicer is a one-stop data processing system to make data higher-quality, juicier, and more digestible for LLMs. It is a systematic & reusable library of 80+ core OPs, 20+ reusable config recipes, and 20+ feature-rich dedicated toolkits, designed to function independently of specific LLM datasets and processing pipelines. Data-Juicer allows detailed data analyses with an automated report generation feature for a deeper understanding of your dataset. Coupled with multi-dimension automatic evaluation capabilities, it supports a timely feedback loop at multiple stages in the LLM development process. Data-Juicer offers tens of pre-built data processing recipes for pre-training, fine-tuning, en, zh, and more scenarios. It provides a speedy data processing pipeline requiring less memory and CPU usage, optimized for maximum productivity. Data-Juicer is flexible & extensible, accommodating most types of data formats and allowing flexible combinations of OPs. It is designed for simplicity, with comprehensive documentation, easy start guides and demo configs, and intuitive configuration with simple adding/removing OPs from existing configs.
checkpoint-engine
Checkpoint-engine is a middleware tool designed for updating model weights in LLM inference engines efficiently. It provides implementations for both Broadcast and P2P weight update methods, orchestrating the transfer process and controlling the inference engine through ZeroMQ socket. The tool optimizes weight broadcast by arranging data transfer into stages and organizing transfers into a pipeline for performance. It supports flexible installation options and is tested with various models and device setups. Checkpoint-engine also allows reusing weights from existing instances and provides a patch for FP8 quantization in vLLM.
edge-ai-libraries
The Edge AI Libraries project is a collection of libraries, microservices, and tools for Edge application development. It includes sample applications showcasing generic AI use cases. Key components include Anomalib, Dataset Management Framework, Deep Learning Streamer, ECAT EnableKit, EtherCAT Masterstack, FLANN, OpenVINO toolkit, Audio Analyzer, ORB Extractor, PCL, PLCopen Servo, Real-time Data Agent, RTmotion, Audio Intelligence, Deep Learning Streamer Pipeline Server, Document Ingestion, Model Registry, Multimodal Embedding Serving, Time Series Analytics, Vector Retriever, Visual-Data Preparation, VLM Inference Serving, Intel Geti, Intel SceneScape, Visual Pipeline and Platform Evaluation Tool, Chat Question and Answer, Document Summarization, PLCopen Benchmark, PLCopen Databus, Video Search and Summarization, Isolation Forest Classifier, Random Forest Microservices. Visit sub-directories for instructions and guides.

deeppowers
Deeppowers is a powerful Python library for deep learning applications. It provides a wide range of tools and utilities to simplify the process of building and training deep neural networks. With Deeppowers, users can easily create complex neural network architectures, perform efficient training and optimization, and deploy models for various tasks. The library is designed to be user-friendly and flexible, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced deep learning practitioners.
For similar tasks

airllm
AirLLM is a tool that optimizes inference memory usage, enabling large language models to run on low-end GPUs without quantization, distillation, or pruning. It supports models like Llama3.1 on 8GB VRAM. The tool offers model compression for up to 3x inference speedup with minimal accuracy loss. Users can specify compression levels, profiling modes, and other configurations when initializing models. AirLLM also supports prefetching and disk space management. It provides examples and notebooks for easy implementation and usage.
flutter_gemma
Flutter Gemma is a family of lightweight, state-of-the art open models that bring the power of Google's Gemma language models directly to Flutter applications. It allows for local execution on user devices, supports both iOS and Android platforms, and offers LoRA support for tailored AI behavior. The tool provides a simple interface for integrating Gemma models into Flutter projects, enabling advanced AI capabilities without relying on external servers. Users can easily download pre-trained Gemma models, fine-tune them for specific use cases, and customize behavior using LoRA weights. The tool supports model and LoRA weight management, model initialization, response generation, and chat scenarios, with considerations for model size, LoRA weights, and production app deployment.

djl
Deep Java Library (DJL) is an open-source, high-level, engine-agnostic Java framework for deep learning. It is designed to be easy to get started with and simple to use for Java developers. DJL provides a native Java development experience and allows users to integrate machine learning and deep learning models with their Java applications. The framework is deep learning engine agnostic, enabling users to switch engines at any point for optimal performance. DJL's ergonomic API interface guides users with best practices to accomplish deep learning tasks, such as running inference and training neural networks.
caikit
Caikit is an AI toolkit that enables users to manage models through a set of developer friendly APIs. It provides a consistent format for creating and using AI models against a wide variety of data domains and tasks.
agents
The LiveKit Agent Framework is designed for building real-time, programmable participants that run on servers. Easily tap into LiveKit WebRTC sessions and process or generate audio, video, and data streams. The framework includes plugins for common workflows, such as voice activity detection and speech-to-text. Agents integrates seamlessly with LiveKit server, offloading job queuing and scheduling responsibilities to it. This eliminates the need for additional queuing infrastructure. Agent code developed on your local machine can scale to support thousands of concurrent sessions when deployed to a server in production.
llm-finetuning
llm-finetuning is a repository that provides a serverless twist to the popular axolotl fine-tuning library using Modal's serverless infrastructure. It allows users to quickly fine-tune any LLM model with state-of-the-art optimizations like Deepspeed ZeRO, LoRA adapters, Flash attention, and Gradient checkpointing. The repository simplifies the fine-tuning process by not exposing all CLI arguments, instead allowing users to specify options in a config file. It supports efficient training and scaling across multiple GPUs, making it suitable for production-ready fine-tuning jobs.
LeanCopilot
Lean Copilot is a tool that enables the use of large language models (LLMs) in Lean for proof automation. It provides features such as suggesting tactics/premises, searching for proofs, and running inference of LLMs. Users can utilize built-in models from LeanDojo or bring their own models to run locally or on the cloud. The tool supports platforms like Linux, macOS, and Windows WSL, with optional CUDA and cuDNN for GPU acceleration. Advanced users can customize behavior using Tactic APIs and Model APIs. Lean Copilot also allows users to bring their own models through ExternalGenerator or ExternalEncoder. The tool comes with caveats such as occasional crashes and issues with premise selection and proof search. Users can get in touch through GitHub Discussions for questions, bug reports, feature requests, and suggestions. The tool is designed to enhance theorem proving in Lean using LLMs.
awesome-local-llms
The 'awesome-local-llms' repository is a curated list of open-source tools for local Large Language Model (LLM) inference, covering both proprietary and open weights LLMs. The repository categorizes these tools into LLM inference backend engines, LLM front end UIs, and all-in-one desktop applications. It collects GitHub repository metrics as proxies for popularity and active maintenance. Contributions are encouraged, and users can suggest additional open-source repositories through the Issues section or by running a provided script to update the README and make a pull request. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive resource for exploring and utilizing local LLM tools.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.












