
PrefixQuant
An algorithm for static activation quantization of LLMs
Stars: 105
PrefixQuant is an official PyTorch implementation for static quantization that outperforms dynamic quantization in Large Language Models (LLMs) by utilizing prefixed outliers. The tool provides functionalities for quantization, inference, and visualization of activation distributions. Users can fine-tune quantization settings and evaluate pre-quantized models for tasks like PIQA, ARC, Hellaswag, and Winogrande. The approach aims to improve performance and efficiency in LLMs through innovative quantization techniques.
README:
Official PyTorch implement for PrefixQuant:Static Quantization Beats Dynamic through Prefixed Outliers in LLMs.
[2025/1] Support the learnable activation cliping for dynamic quantization.
[2024/10] We release PrefixQuant, the first work to let static activation quantization outperforms dynamic ones in LLM. We only open the fake quantization code now, and the inference kernels will be released later.
conda create -n prefixquant python==3.9
conda activate prefixquant
pip install -r requirements.txt
We provide an example command to quantized Llama-3-8B without fine-tuning:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python main.py \
--model_path path/to/llama-3-8B \
--model_name Llama-3-8b \
--output_dir ./log/llama-3-8b-w4a4kv4 \
--wbits 4 \
--input_bits 4 \
--input_mode static \
--v_bits 4 \
--k_bits 4 \
--kv_group_size 128 \
--kv_mode static \
--mse_init \
--pre_rotate \
--down_online_had \
--qk_online_had \
--set_prefixed_tokens \
--eval_ppl \
--eval_tasks piqa,arc_easy,arc_challenge,hellaswag,winogrande \
--save_quant_dir ./pre_quantized_models/llama-3-8b-w4a4kv4
You can find the detailed fine-tuning setting in the paper. There are some useful information as follows:
- For dynamic quantization, you should add
--activation_clippingto enhance the perfomance. - You can add
--epochs 20to introduce fine-tuning for W4A4KV4 quantization, and--epochs 10for W4A8KV4 quantization. - For Llama-3-70B(-Instruct) models, you should change the default learning rate to
--quant_lr 2e-5 --weight_lr 2e-6. - For Llama-2-70B, you should set
--loss_type skip_msefor the training stability.
We provide an example command to evaluate the quantize models:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python eval.py \
--quant_model ./pre_quantized_models/llama-3-8b-w4a4kv4 \
--eval_ppl \
--eval_tasks piqa,arc_easy,arc_challenge,hellaswag,winogrande
We provide an example command to visualize token-wsie maximum values for linear inputs:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python plot_activation.py \
--model_path path/to/llama-2-7b \
--model_name llama-2-7b \
--plot_linear_input
You can add --pre_rotate --down_online_had --qk_online_had to apply hadamard rotation, and add --set_prefixed_tokens to set the proposed prefixed tokens in our paper.
Additionally, you can also change --plot_linear_input to other plotting choices, details are as follows:
-
--plot_linear_output: plot token-wsie maximum values for linear outputs (such as Q/K/V). -
--plot_outlier_token_position: count the token index of outlier tokens. -
--plot_outlier_token: count the token content of outlier tokens -
--plot_layer_wise_outlier_token_number: plot layer-wise outlier token number -
--plot_layer_input_3d: plot the 3D image of layer inputs. -
--plot_block_output_3d: plot the 3D image of block outputs.
More examples can be found in ./examples/plot.sh.
If you use our PrefixQuant approach in your research, please cite our paper:
@article{prefixquant,
title={PrefixQuant: Static Quantization Beats Dynamic through Prefixed Outliers in LLMs},
author={Chen, Mengzhao and Liu, Yi and Wang, Jiahao and Bin, Yi and Shao, Wenqi and Luo, Ping},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.05265},
year={2024}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for PrefixQuant
Similar Open Source Tools

PrefixQuant
PrefixQuant is an official PyTorch implementation for static quantization that outperforms dynamic quantization in Large Language Models (LLMs) by utilizing prefixed outliers. The tool provides functionalities for quantization, inference, and visualization of activation distributions. Users can fine-tune quantization settings and evaluate pre-quantized models for tasks like PIQA, ARC, Hellaswag, and Winogrande. The approach aims to improve performance and efficiency in LLMs through innovative quantization techniques.
LayerSkip
LayerSkip is an implementation enabling early exit inference and self-speculative decoding. It provides a code base for running models trained using the LayerSkip recipe, offering speedup through self-speculative decoding. The tool integrates with Hugging Face transformers and provides checkpoints for various LLMs. Users can generate tokens, benchmark on datasets, evaluate tasks, and sweep over hyperparameters to optimize inference speed. The tool also includes correctness verification scripts and Docker setup instructions. Additionally, other implementations like gpt-fast and Native HuggingFace are available. Training implementation is a work-in-progress, and contributions are welcome under the CC BY-NC license.
PDEBench
PDEBench provides a diverse and comprehensive set of benchmarks for scientific machine learning, including challenging and realistic physical problems. The repository consists of code for generating datasets, uploading and downloading datasets, training and evaluating machine learning models as baselines. It features a wide range of PDEs, realistic and difficult problems, ready-to-use datasets with various conditions and parameters. PDEBench aims for extensibility and invites participation from the SciML community to improve and extend the benchmark.
alignment-attribution-code
This repository provides an original implementation of Assessing the Brittleness of Safety Alignment via Pruning and Low-Rank Modifications. It includes tools for neuron-level pruning, pruning based on set difference, Wanda/SNIP score dumping, rank-level pruning, and rank removal with orthogonal projection. Users can specify parameters like prune method, datasets, sparsity ratio, model, and save location to evaluate and modify neural networks for safety alignment.
mirage
Mirage Persistent Kernel (MPK) is a compiler and runtime system that automatically transforms LLM inference into a single megakernel—a fused GPU kernel that performs all necessary computation and communication within a single kernel launch. This end-to-end GPU fusion approach reduces LLM inference latency by 1.2× to 6.7×, all while requiring minimal developer effort.
mergekit
Mergekit is a toolkit for merging pre-trained language models. It uses an out-of-core approach to perform unreasonably elaborate merges in resource-constrained situations. Merges can be run entirely on CPU or accelerated with as little as 8 GB of VRAM. Many merging algorithms are supported, with more coming as they catch my attention.
ice-score
ICE-Score is a tool designed to instruct large language models to evaluate code. It provides a minimum viable product (MVP) for evaluating generated code snippets using inputs such as problem, output, task, aspect, and model. Users can also evaluate with reference code and enable zero-shot chain-of-thought evaluation. The tool is built on codegen-metrics and code-bert-score repositories and includes datasets like CoNaLa and HumanEval. ICE-Score has been accepted to EACL 2024.
datadreamer
DataDreamer is an advanced toolkit designed to facilitate the development of edge AI models by enabling synthetic data generation, knowledge extraction from pre-trained models, and creation of efficient and potent models. It eliminates the need for extensive datasets by generating synthetic datasets, leverages latent knowledge from pre-trained models, and focuses on creating compact models suitable for integration into any device and performance for specialized tasks. The toolkit offers features like prompt generation, image generation, dataset annotation, and tools for training small-scale neural networks for edge deployment. It provides hardware requirements, usage instructions, available models, and limitations to consider while using the library.
probsem
ProbSem is a repository that provides a framework to leverage large language models (LLMs) for assigning context-conditional probability distributions over queried strings. It supports OpenAI engines and HuggingFace CausalLM models, and is flexible for research applications in linguistics, cognitive science, program synthesis, and NLP. Users can define prompts, contexts, and queries to derive probability distributions over possible completions, enabling tasks like cloze completion, multiple-choice QA, semantic parsing, and code completion. The repository offers CLI and API interfaces for evaluation, with options to customize models, normalize scores, and adjust temperature for probability distributions.
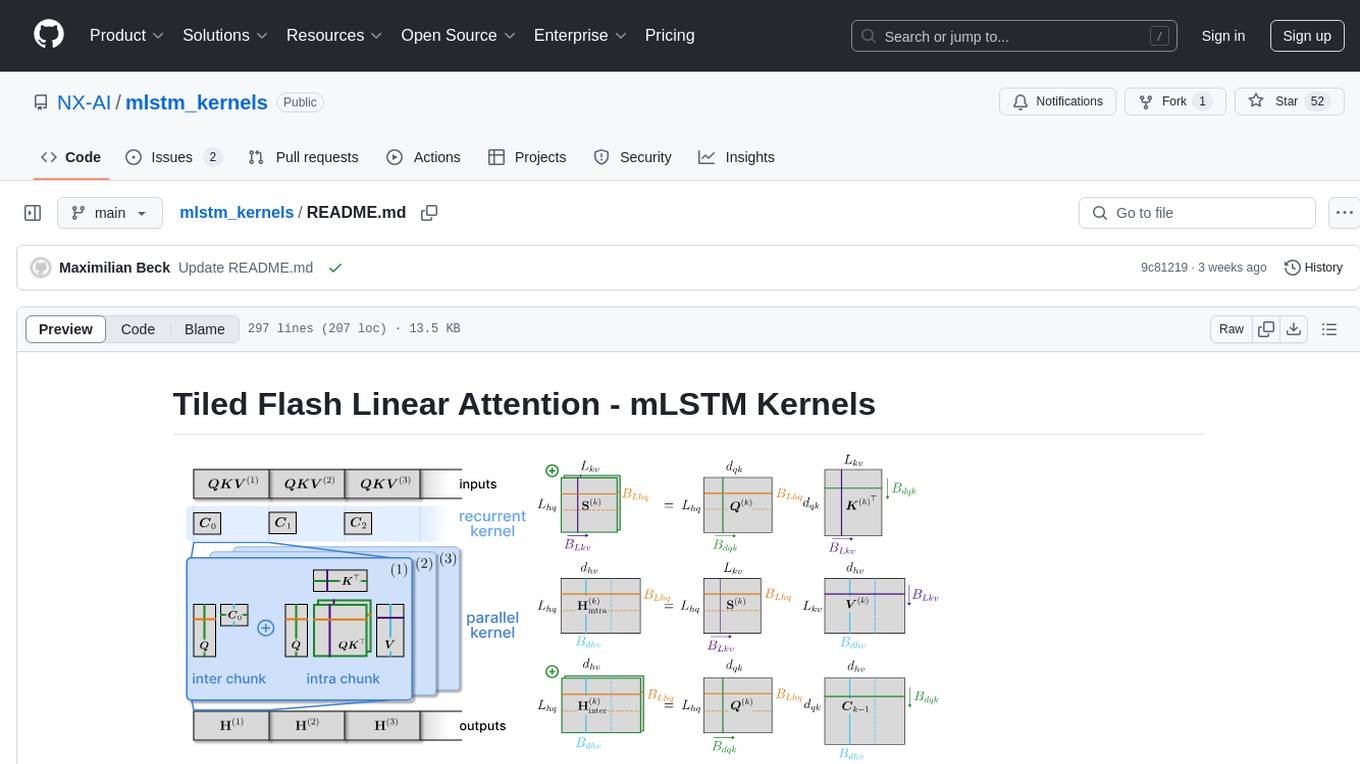
mlstm_kernels
This repository provides fast and efficient mLSTM training and inference Triton kernels built on Tiled Flash Linear Attention (TFLA). It includes implementations in JAX, PyTorch, and Triton, with chunkwise, parallel, and recurrent kernels for mLSTM. The repository also contains a benchmark library for runtime benchmarks and full mLSTM Huggingface models.
topicGPT
TopicGPT is a repository containing scripts and prompts for the paper 'TopicGPT: Topic Modeling by Prompting Large Language Models' (NAACL'24). The 'topicgpt_python' package offers functions to generate high-level and specific topics, refine topics, assign topics to input text, and correct generated topics. It supports various APIs like OpenAI, VertexAI, Azure, Gemini, and vLLM for inference. Users can prepare data in JSONL format, run the pipeline using provided scripts, and evaluate topic alignment with ground-truth labels.
verifiers
Verifiers is a library of modular components for creating RL environments and training LLM agents. It includes an async GRPO implementation built around the `transformers` Trainer, is supported by `prime-rl` for large-scale FSDP training, and can easily be integrated into any RL framework which exposes an OpenAI-compatible inference client. The library provides tools for creating and evaluating RL environments, training LLM agents, and leveraging OpenAI-compatible models for various tasks. Verifiers aims to be a reliable toolkit for building on top of, minimizing fork proliferation in the RL infrastructure ecosystem.
kvpress
This repository implements multiple key-value cache pruning methods and benchmarks using transformers, aiming to simplify the development of new methods for researchers and developers in the field of long-context language models. It provides a set of 'presses' that compress the cache during the pre-filling phase, with each press having a compression ratio attribute. The repository includes various training-free presses, special presses, and supports KV cache quantization. Users can contribute new presses and evaluate the performance of different presses on long-context datasets.
cortex
Cortex is a tool that simplifies and accelerates the process of creating applications utilizing modern AI models like chatGPT and GPT-4. It provides a structured interface (GraphQL or REST) to a prompt execution environment, enabling complex augmented prompting and abstracting away model connection complexities like input chunking, rate limiting, output formatting, caching, and error handling. Cortex offers a solution to challenges faced when using AI models, providing a simple package for interacting with NL AI models.
mystic
The `mystic` framework provides a collection of optimization algorithms and tools that allow the user to robustly solve hard optimization problems. It offers fine-grained power to monitor and steer optimizations during the fit processes. Optimizers can advance one iteration or run to completion, with customizable stop conditions. `mystic` optimizers share a common interface for easy swapping without writing new code. The framework supports parameter constraints, including soft and hard constraints, and provides tools for scientific machine learning, uncertainty quantification, adaptive sampling, nonlinear interpolation, and artificial intelligence. `mystic` is actively developed and welcomes user feedback and contributions.
paxml
Pax is a framework to configure and run machine learning experiments on top of Jax.
For similar tasks

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.
promptfoo
Promptfoo is a tool for testing and evaluating LLM output quality. With promptfoo, you can build reliable prompts, models, and RAGs with benchmarks specific to your use-case, speed up evaluations with caching, concurrency, and live reloading, score outputs automatically by defining metrics, use as a CLI, library, or in CI/CD, and use OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure, Google, HuggingFace, open-source models like Llama, or integrate custom API providers for any LLM API.
vespa
Vespa is a platform that performs operations such as selecting a subset of data in a large corpus, evaluating machine-learned models over the selected data, organizing and aggregating it, and returning it, typically in less than 100 milliseconds, all while the data corpus is continuously changing. It has been in development for many years and is used on a number of large internet services and apps which serve hundreds of thousands of queries from Vespa per second.
python-aiplatform
The Vertex AI SDK for Python is a library that provides a convenient way to use the Vertex AI API. It offers a high-level interface for creating and managing Vertex AI resources, such as datasets, models, and endpoints. The SDK also provides support for training and deploying custom models, as well as using AutoML models. With the Vertex AI SDK for Python, you can quickly and easily build and deploy machine learning models on Vertex AI.
ScandEval
ScandEval is a framework for evaluating pretrained language models on mono- or multilingual language tasks. It provides a unified interface for benchmarking models on a variety of tasks, including sentiment analysis, question answering, and machine translation. ScandEval is designed to be easy to use and extensible, making it a valuable tool for researchers and practitioners alike.
opencompass
OpenCompass is a one-stop platform for large model evaluation, aiming to provide a fair, open, and reproducible benchmark for large model evaluation. Its main features include: * Comprehensive support for models and datasets: Pre-support for 20+ HuggingFace and API models, a model evaluation scheme of 70+ datasets with about 400,000 questions, comprehensively evaluating the capabilities of the models in five dimensions. * Efficient distributed evaluation: One line command to implement task division and distributed evaluation, completing the full evaluation of billion-scale models in just a few hours. * Diversified evaluation paradigms: Support for zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought evaluations, combined with standard or dialogue-type prompt templates, to easily stimulate the maximum performance of various models. * Modular design with high extensibility: Want to add new models or datasets, customize an advanced task division strategy, or even support a new cluster management system? Everything about OpenCompass can be easily expanded! * Experiment management and reporting mechanism: Use config files to fully record each experiment, and support real-time reporting of results.
flower
Flower is a framework for building federated learning systems. It is designed to be customizable, extensible, framework-agnostic, and understandable. Flower can be used with any machine learning framework, for example, PyTorch, TensorFlow, Hugging Face Transformers, PyTorch Lightning, scikit-learn, JAX, TFLite, MONAI, fastai, MLX, XGBoost, Pandas for federated analytics, or even raw NumPy for users who enjoy computing gradients by hand.
thinc
Thinc is a lightweight deep learning library that offers an elegant, type-checked, functional-programming API for composing models, with support for layers defined in other frameworks such as PyTorch, TensorFlow and MXNet. You can use Thinc as an interface layer, a standalone toolkit or a flexible way to develop new models.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.